Metabolic Effects of Gastrectomy and Duodenal Bypass in Early Gastric Cancer Patients with T2DM: A Prospective Single-Center Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
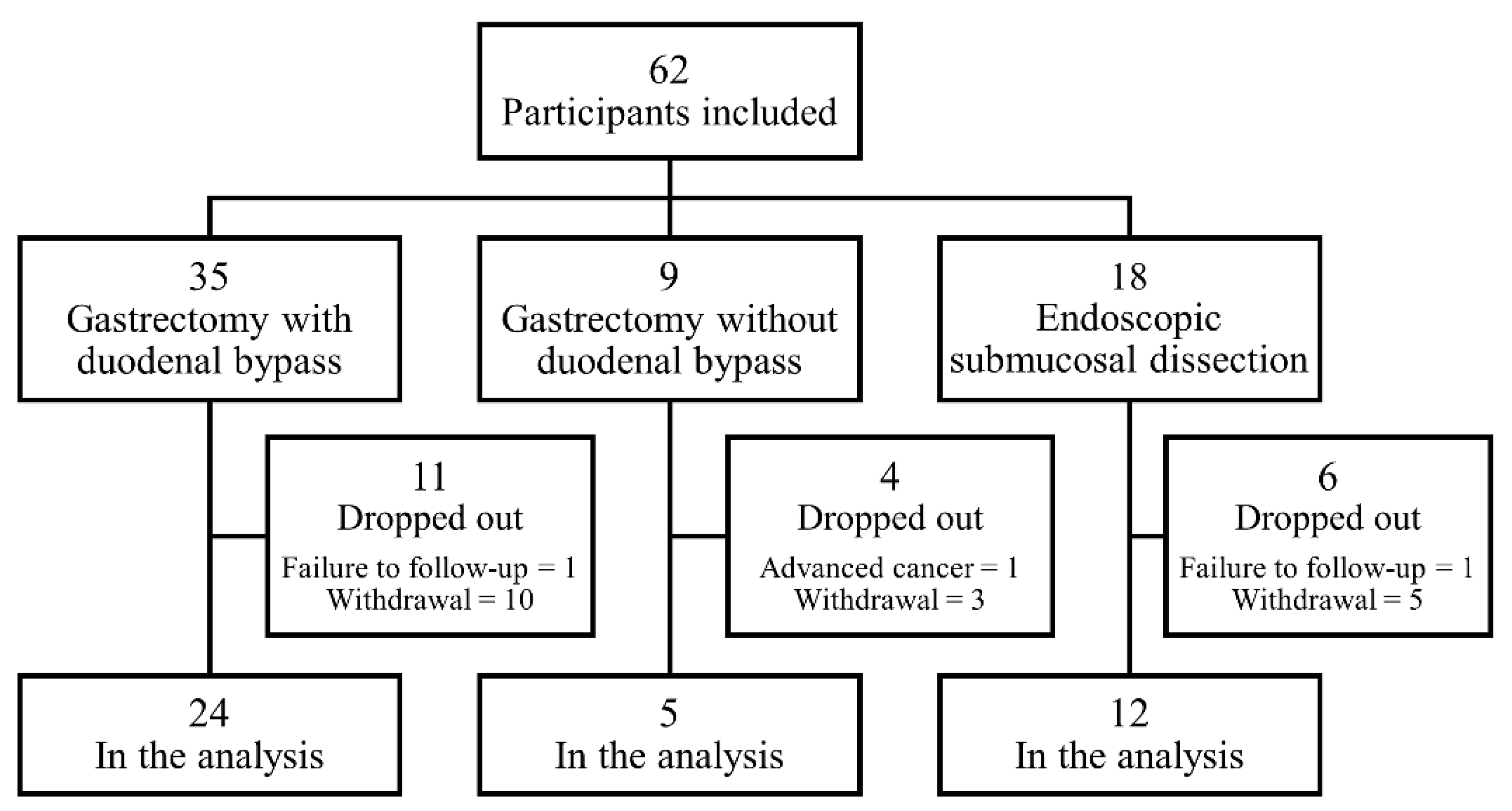
2.1. Study Subjects and Protocols
2.2. Identification and Management Protocols for T2DM
2.3. Metabolic Hormones and Adipokines Measurement
2.4. Glycemic Control Status Assessment
2.5. Long-Term Outcomes
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Assessment of Effect Modification
3. Results
3.1. Patient Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Glycemic Control Status at the 1-Year Visit
3.3. Changes in Metabolic Parameters after Gastrectomy
3.4. Changes in Metabolic Hormones and Adipokines after Gastrectomy
3.5. Factors Influencing the Metabolic Effects of Gastrectomy with Duodenal Bypass
3.6. Long-Term Outcomes
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hong, S.; Won, Y.J.; Park, Y.R.; Jung, K.W.; Kong, H.J.; Lee, E.S. Cancer statistics in korea: Incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2017. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 52, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jun, J.K.; Choi, K.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Suh, M.; Park, B.; Song, S.H.; Jung, K.W.; Lee, C.W.; Choi, I.J.; Park, E.C.; et al. Effectiveness of the korean national cancer screening program in reducing gastric cancer mortality. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1319–1328.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, B.K.; Noone, A.M.; Mariotto, A.B.; Simard, E.P.; Boscoe, F.P.; Henley, S.J.; Jemal, A.; Cho, H.; Anderson, R.N.; Kohler, B.A.; et al. Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975–2010, featuring prevalence of comorbidity and impact on survival among persons with lung, colorectal, breast, or prostate cancer. Cancer 2014, 120, 1290–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gelder, T.; Mulhern, B.; Schoormans, D.; Husson, O.; Lourenço, R.D.A. Assessing health-related quality of life in cancer survivors: Factors impacting on eortc qlu-c10d-derived utility values. Qual. Life Res. 2020, 29, 1483–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfati, D.; Gurney, J.; Lim, B.T.; Bagheri, N.; Simpson, A.; Koea, J.; Dennett, E. Identifying important comorbidity among cancer populations using administrative data: Prevalence and impact on survival. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 12, e47–e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, N.H.; Shaw, J.E.; Karuranga, S.; Huang, Y.; Fernandes, J.D.d.R.; Ohlrogge, A.W.; Malanda, B. Idf diabetes atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 138, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.H.; Son, J.W.; Kang, S.; Kim, W.J.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, H.S.; Seo, M.; Shin, H.J.; Lee, S.S.; Jeong, S.J.; et al. Diabetes fact sheets in korea, 2020: An appraisal of current status. Diabetes Metab. J. 2021, 45, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwangbo, Y.; Kang, D.; Kang, M.; Kim, S.; Lee, E.K.; Kim, Y.A.; Chang, Y.J.; Choi, K.S.; Jung, S.Y.; Woo, S.M.; et al. Incidence of diabetes after cancer development: A korean national cohort study. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.M.; Son, K.Y.; Eom, C.S.; Durrance, D.; Park, S.M. Pre-existing diabetes mellitus increases the risk of gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guideline Committee of the Korean Gastric Cancer Association (KGCA); Development Working Group and Review Panel. Korean practice guideline for gastric cancer 2018: An evidence-based, multi-disciplinary approach. J. Gastric Cancer 2019, 19, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikramuddin, S.; Korner, J.; Lee, W.J.; Connett, J.E.; Inabnet, W.B.; Billington, C.J.; Thomas, A.J.; Leslie, D.B.; Chong, K.; Jeffery, R.W.; et al. Roux-en-y gastric bypass vs. intensive medical management for the control of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia: The diabetes surgery study randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2013, 309, 2240–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, P.R.; Kashyap, S.R.; Wolski, K.; Brethauer, S.A.; Kirwan, J.P.; Pothier, C.E.; Thomas, S.; Abood, B.; Nissen, S.E.; Bhatt, D.L. Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy in obese patients with diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schauer, P.R.; Bhatt, D.L.; Kirwan, J.P.; Wolski, K.; Brethauer, S.A.; Navaneethan, S.D.; Aminian, A.; Pothier, C.E.; Kim, E.S.; Nissen, S.E.; et al. Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy for diabetes-3-year outcomes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2002–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, Y.Y.; Noh, S.H.; An, J.Y. A randomized controlled trial of roux-en-y gastrojejunostomy vs. Gastroduodenostomy with respect to the improvement of type 2 diabetes mellitus after distal gastrectomy in gastric cancer patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.H.; Huh, Y.J.; Park, S.; Park, Y.S.; Park, D.J.; Kwon, J.W.; Lee, J.H.; Heo, Y.S.; Choi, S.H. Multicenter results of long-limb bypass reconstruction after gastrectomy in patients with gastric cancer and type ii diabetes. Asian J. Surg. 2020, 43, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Cheong, J.H.; Hyung, W.J.; Choi, S.H.; Noh, S.H. Outcome after gastrectomy in gastric cancer patients with type 2 diabetes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.K.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Kwak, M.H.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, I.J.; Cho, S.J.; Kim, Y.W.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, C.G.; et al. Improvement of diabetes and hypertension after gastrectomy: A nationwide cohort study. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes—2011. Diabetes Care 2011, 34 (Suppl. 1), S11–S61. [Google Scholar]
- Khorgami, Z.; Shoar, S.; Saber, A.A.; Howard, C.A.; Danaei, G.; Sclabas, G.M. Outcomes of bariatric surgery versus medical management for type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Nam, S.J.; Choi, H.S.; Kim, K.O.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, J.W.; Sohn, W.; Yoon, J.H.; Jung, S.H.; Hyun, Y.S.; et al. Comparative efficacy of bariatric surgery in the treatment of morbid obesity and diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 2180–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, B.; Truong, K.; Spitler, H.; Zhang, L.; Tong, X.; Chen, L. The long-term effects of bariatric surgery on type 2 diabetes remission, microvascular and macrovascular complications, and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Surg. 2017, 27, 2724–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Gao, K.; Zhao, Q.; Xu, X. Long-term outcomes of macrovascular diseases and metabolic indicators of bariatric surgery for severe obesity type 2 diabetes patients with a meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billeter, A.T.; Scheurlen, K.M.; Probst, P.; Eichel, S.; Nickel, F.; Kopf, S.; Fischer, L.; Diener, M.K.; Nawroth, P.P.; Müller-Stich, B.P. Meta-analysis of metabolic surgery versus medical treatment for microvascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Br. J. Surg. 2018, 105, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, D.E.; Cohen, R.V. Bariatric/metabolic surgery to treat type 2 diabetes in patients with a bmi < 35 kg/m2. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rubio-Almanza, M.; Hervás-Marín, D.; Cámara-Gómez, R.; Caudet-Esteban, J.; Merino-Torres, J.F. Does metabolic surgery lead to diabetes remission in patients with bmi < 30 kg/m2?: A meta-analysis. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 1105–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Li, P.; Li, W.; Sun, X.; Yu, Z.; Li, R.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, S. The effect of bariatric surgery on asian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and body mass index < 30 kg/m2: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 2492–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.W.; Zhang, D.Y.; Liu, X.M.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, F.T. Comparison of different gastric bypass procedures in gastric carcinoma patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 18427–18431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.Y.; Faintuch, J.; Yagi, O.K.; Yamaguchi, C.M.; Faintuch, J.J.; Cecconello, I. Does roux-en-y gastrectomy for gastric cancer influence glucose homeostasis in lean patients? Surg. Endosc. 2013, 27, 2829–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askarpour, M.; Alizadeh, S.; Hadi, A.; Symonds, M.E.; Miraghajani, M.; Sheikhi, A.; Ghaedi, E. Effect of bariatric surgery on the circulating level of adiponectin, chemerin, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, leptin, resistin, and visfatin: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Horm. Metab. Res. 2020, 52, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelesidis, T.; Kelesidis, I.; Chou, S.; Mantzoros, C.S. Narrative review: The role of leptin in human physiology: Emerging clinical applications. Ann. Intern. Med. 2010, 152, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsiki, N.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Banach, M. Leptin, cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1176–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simonds, S.E.; Pryor, J.T.; Ravussin, E.; Greenway, F.L.; Dileone, R.; Allen, A.M.; Bassi, J.; Elmquist, J.K.; Keogh, J.M.; Henning, E.; et al. Leptin mediates the increase in blood pressure associated with obesity. Cell 2014, 159, 1404–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boutari, C.; Perakakis, N.; Mantzoros, C.S. Association of adipokines with development and progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 33, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, R.B. Cytokine and cytokine-like inflammation markers, endothelial dysfunction, and imbalanced coagulation in development of diabetes and its complications. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 3171–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, R.G.; Motazedian, P.; Ramirez, F.D.; Simard, T.; Di Santo, P.; Visintini, S.; Faraz, M.A.; Labinaz, A.; Jung, Y.; Hibbert, B. Association between plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and cardiovascular events: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Thromb. J. 2018, 16, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cabrera, L.O.; Trindade, E.N.; Leite, C.; Abegg, E.H.; Trindade, M.R.M. Preoperative level of leptin can be a predictor of glycemic control for patients with diabetes undergoing bariatric surgery. Obes. Surg. 2020, 30, 4829–4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Baseline Characteristics | Total (n = 41) | Gastrectomy with Duodenal Bypass (n = 24) | Gastrectomy without Duodenal Bypass (n = 5) | Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (n = 12) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 62.4 ± 8.4 | 61.6 ± 9.0 | 63.8 ± 10.9 | 63.3 ± 6.3 | 0.800 |
| Female sex | 8 (19.5%) | 4 (16.7%) | 3 (60.0%) | 1 (8.3%) | 0.054 |
| DM duration (years) | 6.8 ± 6.1 | 6.1 ± 5.7 | 6.2 ± 3.9 | 8.6 ± 7.5 | 0.489 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.5 ± 3.1 | 24.1 ± 2.6 | 21.9 ± 1.7 * | 26.1 ± 3.6 | 0.022 |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.3 ± 1.6 | 7.5 ± 1.8 | 6.8 ± 1.5 | 7.1 ± 0.9 | 0.579 |
| Fasting glucose (mg/dL) | 132.5 ± 43.7 | 141.2 ± 53.3 | 120.8 ± 18.8 | 120.2 ± 22.3 | 0.332 |
| Postprandial 2-hour glucose (mg/dL) | 292.4 ± 97.8 | 301.2 ± 105.2 | 318.8 ± 140.5 | 262.9 ± 52.5 | 0.474 |
| HOMA-IR | 1.7 (1.1–3.8) | 2.5 (1.2–3.8) | 1.0 (0.9–1.5) | 1.7 (1.3–4.3) | 0.169 |
| Fasting | |||||
| Ghrelin (pg/mL) | 501.8 (242.1–935.8) | 460.6 (234.7–968.5) | 941.5 (152.5–1457.0) | 520.5 (372.5–873.8) | 0.937 |
| GIP (pg/mL) | 211.3 (123.1–261.5) | 235.4 (170.6–295.9) | 211.2 (118.6–224.7) | 144.7 (113.7–204.7) | 0.097 |
| GLP-1 (pg/mL) | 191.8 (102.9–259.5) | 222.5 (134.3–261.8) | 129.8 (93.4–538.9) | 186.6 (72.9–232.4) | 0.657 |
| Glucagon (pg/mL) | 124.0 (75.7–258.4) | 144.2 (78.7–263.3) | 84.8 (79.6–385.3) | 85.1 (69.6–121.4) | 0.182 |
| Leptin (ng/mL) | 2.1 (1.1–3.9) | 2.1 (1.1–4.0) | 1.2 (0.7–5.8) | 2.4 (0.9–3.0) | 0.932 |
| PAI-1 (ng/mL) | 47.6 (37.5–72.6) | 43.5 (35.8–66.9) | 35.2 (28.6–71.7) | 53.8 (47.6–149.0) | 0.036 |
| Resistin (ng/mL) | 5.4 (3.0–8.8) | 5.1 (2.6–8.0) | 5.1 (3.5–10.6) | 5.9 (3.2–9.5) | 0.570 |
| Visfatin (ng/mL) | 2.7 (1.1–5.8) | 2.7 (0.8–4.6) | 4.1 (1.5–9.4) | 2.3 (1.3–6.8) | 0.406 |
| Postprandial 2 h | |||||
| Ghrelin (pg/mL) | 444.3 (278.3–774.5) | 370.7 (273.3–751.5) | 693.9 (123.3–1173.3) | 505.2 (374.4–779.3) | 0.789 |
| GIP (pg/mL) | 355.1 (299.8–474.2) | 367.4 (297.0–551.3) | 427.3 (368.6–496.8) | 314.6 (260.0–445.4) | 0.418 |
| GLP-1 (pg/mL) | 222.3 (127.5–276.9) | 229.4 (147.2–291.8) | 206.6 (162.1–530.3) | 205.6 (85.5–266.6) | 0.624 |
| Glucagon (pg/mL) | 127.2 (74.8–245.3) | 172.7 (83.8–251.3) | 110.1 (82.8–382.7) | 91.2 (70.8–139.0) | 0.453 |
| Leptin (ng/mL) | 1.8 (0.9–3.3) | 1.7 (0.9–3.4) | 1.1 (0.7–5.4) | 1.8 (0.9–2.6) | 0.972 |
| PAI-1 (ng/mL) | 45.1 (33.7–69.0) | 47.5 (31.1–66.1) | 33.7 (25.6–37.1) * | 61.0 (43.2–222.9) | 0.016 |
| Resistin (ng/mL) | 4.5 (2.5–6.5) | 4.9 (2.7–6.0) | 3.9 (2.5–5.8) | 3.8 (2.4–9.4) | 0.867 |
| Visfatin (ng/mL) | 2.0 (1.0–5.8) | 1.9 (0.9–5.2) | 2.1 (1.6–4.4) | 2.2 (0.9–9.7) | 0.762 |
| Variables | Univariable Model | Full Multivariable Model | Final Multivariable Model 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Type of the intervention | ||||||
| ESD | 1 | Reference | 1 | Reference | 1 | Reference |
| Gastrectomy with duodenal bypass | 7.93 (1.81–34.70) | 0.006 | 11.94 (2.03–70.26) | 0.006 | 8.68 (1.81–41.63) | 0.007 |
| Gastrectomy without duodenal bypass | 4.27 (0.55–33.37) | 0.166 | 12.02 (0.74–193.91) | 0.080 | 10.60 (1.10–102.35) | 0.041 |
| Age (years) | 0.98 (0.92–1.06) | 0.658 | 0.99 (0.90–1.09) | 0.890 | ||
| Female sex | 2.05 (0.44–9.54) | 0.359 | 1.98 (0.24–16.18) | 0.525 | ||
| DM duration (years) | 0.92 (0.84–1.02) | 0.119 | 0.97 (0.85–1.11) | 0.658 | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 1.06 (0.87–1.29) | 0.557 | 1.15 (0.87–1.53) | 0.323 | ||
| HbA1c (%) | 0.90 (0.62–1.30) | 0.562 | 0.79 (0.48–1.31) | 0.362 | ||
| HOMA-IR | 1.65 (1.07–2.54) | 0.024 | 1.96 (1.08–3.55) | 0.027 | 1.88 (1.16–3.07) | 0.011 |
| Metabolic Parameters | Groups | Difference from the Control Group 1 | Change from the Baseline 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-Month Visit | 1-Year Visit | ||||||
| Estimates | p-Value | Mean ± SD | p-Value | Mean ± SD | p-Value | ||
| HbA1c (%) | ESD | 0 | Ref | −0.3 ± 1.2 | 0.885 | −0.1 ± 1.5 | >0.999 |
| Group 1 | −0.5 | 0.028 | −1.1 ± 1.6 | 0.007 | −0.9 ± 1.7 | 0.045 | |
| Group 2 | −0.5 | 0.184 | −0.5 ± 1.1 | 0.640 | 0.0 ± 1.3 | >0.999 | |
| Fasting glucose (mg/dL) | ESD | 0 | Ref | 17.4 ± 27.1 | 0.095 | 23.8 ± 27.4 | 0.024 |
| Group 1 | −11.1 | 0.328 | −12.2 ± 71.8 | 0.831 | 0.2 ± 54.5 | >0.999 | |
| Group 2 | −0.6 | 0.971 | 19.2 ± 33.2 | 0.532 | 9.0 ± 21.6 | 0.808 | |
| Postprandial 2 h glucose (mg/dL) | ESD | 0 | Ref | −17.2 ± 49.4 | 0.551 | 13.6 ± 50.2 | 0.828 |
| Group 1 | −97.9 | <0.001 | −151.1 ± 103.8 | <0.001 | −99.0 ± 109.0 | 0.001 | |
| Group 2 | −67.8 | 0.044 | −121.4 ± 123.5 | 0.186 | −117.0 ± 113.2 | 0.261 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | ESD | 0 | Ref | −0.2 ± 1.3 | >0.999 | −0.4 ± 1.9 | 0.983 |
| Group 1 | −2.1 | <0.001 | −2.2 ± 1.8 | <0.001 | −1.6 ± 1.9 | 0.002 | |
| Group 2 | −2.3 | 0.001 | −2.0 ± 0.4 | 0.001 | −1.5 ± 0.8 | 0.062 | |
| Log(HOMA-IR) | ESD | 0 | Ref | 0.00 ± 0.31 | >0.999 | 0.01 ± 0.30 | >0.999 |
| Group 1 | −0.21 | 0.019 | −0.21 ± 0.44 | 0.064 | −0.28 ± 0.58 | 0.067 | |
| Group 2 | −0.31 | 0.036 | −0.10 ± 0.41 | >0.999 | 0.01 ± 0.11 | >0.999 | |
| Metabolic Parameters | Subgroups by Preoperative Fasting Leptin | Subgroups by Preoperative Postprandial Leptin | Subgroups by Preoperative Fasting PAI-1 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High (≥2.1 ng/mL) | Low (<2.1 ng/mL) | p for Interaction 1 | High (≥1.8 ng/mL) | Low (<1.8 ng/mL) | p for Interaction 1 | High (≥47.6 ng/mL) | Low (<47.6 ng/mL) | p for Interaction 1 | |||||||
| Effects | p-Value | Effects | p-Value | Effects | p-Value | Effects | p-Value | Effects | p-Value | Effects | p-Value | ||||
| HbA1c (%) | −0.6 | 0.016 | −0.4 | 0.342 | 0.182 | −0.6 | 0.011 | −0.5 | 0.229 | 0.290 | −0.3 | 0.505 | −1.1 | 0.009 | 0.510 |
| Fasting glucose (mg/dL) | −22.3 | 0.068 | 6.9 | 0.718 | 0.255 | −20.2 | 0.065 | 2.6 | 0.896 | 0.381 | −7.9 | 0.641 | −6.5 | 0.741 | 0.574 |
| Postprandial 2-h glucose (mg/dL) | −127.1 | <0.001 | −72.3 | 0.050 | 0.017 | −133.5 | <0.001 | −72.4 | 0.046 | 0.017 | −80.5 | 0.005 | −100.3 | 0.002 | 0.375 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | −3.1 | <0.001 | −1.2 | 0.090 | 0.018 | −3.0 | <0.001 | −1.2 | 0.075 | 0.010 | −1.7 | 0.004 | −3.4 | <0.001 | 0.147 |
| Log(HOMA-IR) | −0.9 | 0.001 | −0.1 | 0.743 | 0.223 | −0.9 | 0.002 | −0.1 | 0.696 | 0.224 | −0.3 | 0.322 | −0.9 | 0.015 | 0.266 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.K.; Lee, E.K.; Lee, Y.J.; Eom, B.W.; Yoon, H.M.; Kim, Y.-I.; Cho, S.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, C.G.; Kong, S.-Y.; et al. Metabolic Effects of Gastrectomy and Duodenal Bypass in Early Gastric Cancer Patients with T2DM: A Prospective Single-Center Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4008. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10174008
Lee YK, Lee EK, Lee YJ, Eom BW, Yoon HM, Kim Y-I, Cho SJ, Lee JY, Kim CG, Kong S-Y, et al. Metabolic Effects of Gastrectomy and Duodenal Bypass in Early Gastric Cancer Patients with T2DM: A Prospective Single-Center Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(17):4008. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10174008
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Young Ki, Eun Kyung Lee, You Jin Lee, Bang Wool Eom, Hong Man Yoon, Young-Il Kim, Soo Jeong Cho, Jong Yeul Lee, Chan Gyoo Kim, Sun-Young Kong, and et al. 2021. "Metabolic Effects of Gastrectomy and Duodenal Bypass in Early Gastric Cancer Patients with T2DM: A Prospective Single-Center Cohort Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 17: 4008. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10174008
APA StyleLee, Y. K., Lee, E. K., Lee, Y. J., Eom, B. W., Yoon, H. M., Kim, Y.-I., Cho, S. J., Lee, J. Y., Kim, C. G., Kong, S.-Y., Yoo, M. K., Hwangbo, Y., Kim, Y.-W., Choi, I. J., Kim, H. J., Kwak, M. H., & Ryu, K. W. (2021). Metabolic Effects of Gastrectomy and Duodenal Bypass in Early Gastric Cancer Patients with T2DM: A Prospective Single-Center Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(17), 4008. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10174008






