Identifying Patient-Reported Outcome Measures (PROMs) for Routine Surveillance of Physical and Emotional Symptoms in Head and Neck Cancer Populations: A Systematic Review
Abstract
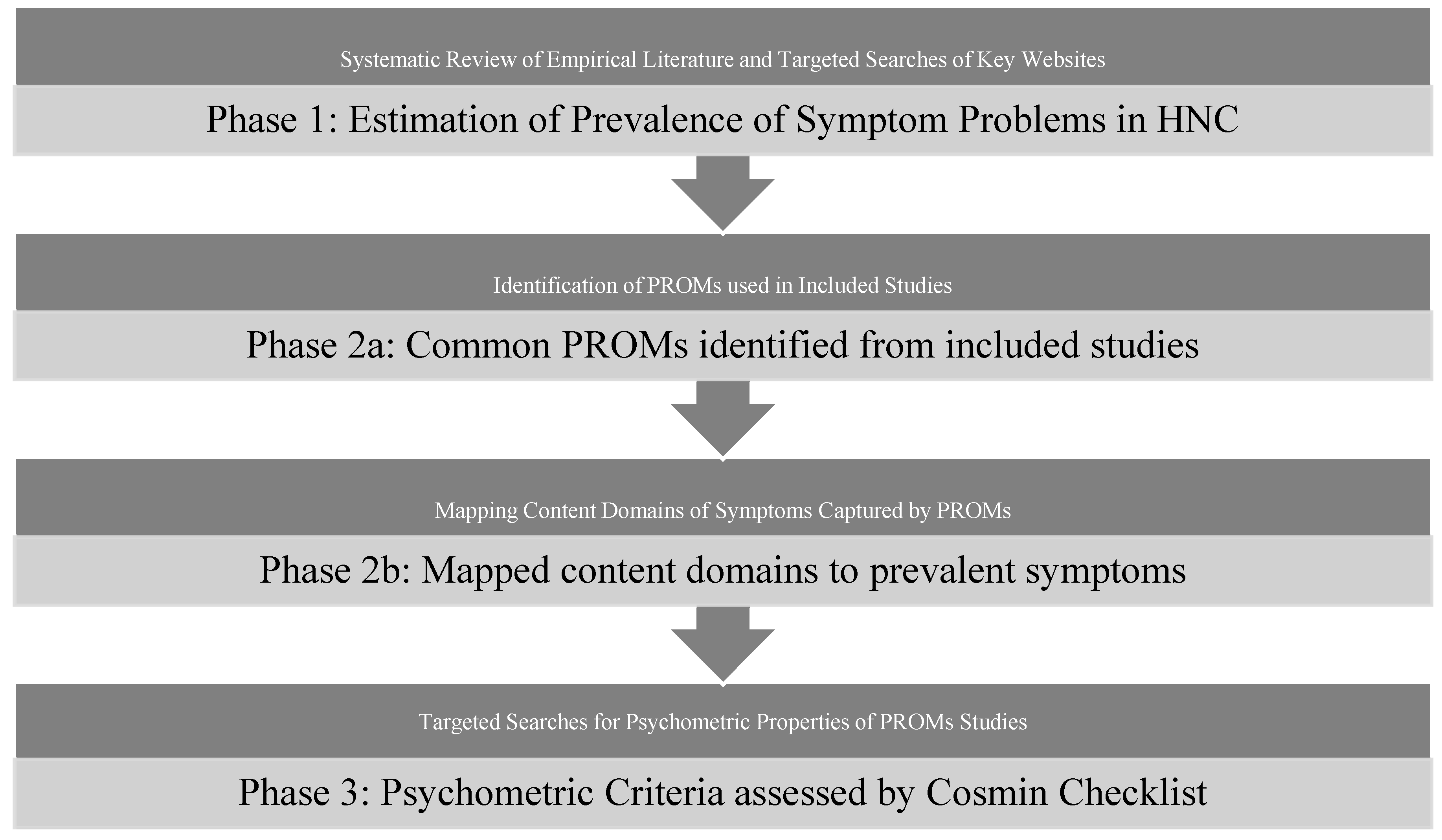
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Selection of Studies
2.3. Data Extraction and Assessment
2.4. Content Analysis of the PROMs
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Included Studies
3.2. Emotional Distress and Psychosocial Symptoms
3.2.1. Depression
3.2.2. Sadness
3.2.3. Anxiety
3.2.4. Emotional Distress
3.2.5. Other Emotional Symptoms
3.2.6. Satisfaction with Appearance
3.2.7. Avoidance of Social Interactions
3.2.8. Substance Abuse Problems
3.2.9. Delirium
3.3. Physical Symptoms
3.3.1. Eating and Nutritional Status
Dysphagia
Xerostomia/Saliva Function
Trismus
Difficulty Chewing and Dental Problems
Dysgeusia
Changes in Appetite
Weight Change and Malnutrition
Oral Mucositis
3.3.2. Communication
Voice and Speech Impairment
Hearing Loss
3.3.3. Pain
3.3.4. Dyspnea and Cough
3.4. Functional Well-Being
3.4.1. Activities of Daily Living
Difficulties with Activities of Daily Living
Sexual Function
3.4.2. Fatigue and Energy
Fatigue
Decreased Alertness/Drowsiness
Sleep Quality
3.5. Characteristics of Outcome Measurement Instruments
3.6. Psychometric Comparison of the Instruments
3.6.1. Reliability
3.6.2. Construct Validity (Convergent Validity, Known-Groups Validity)
3.6.3. Criterion Validity (Concurrent Validity)
3.6.4. Responsiveness
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| No. | Term |
|---|---|
| 1 | *“Head and Neck Neoplasms”/ |
| 2 | (“head and neck” adj2 cancer$).tw. |
| 3 | Exp *Esophageal Neoplasms/ |
| 4 | Exp *Facial Neoplasms/ |
| 5 | Exp *mouth neoplasms/ |
| 6 | exp *Otorhinolaryngologic Neoplasms/ |
| 7 | exp *Tracheal Neoplasms/ |
| 8 | ((?esophageal or pharyn* or laryn* or hypophary* or oropharyn* or nasopharyn* or trachael or oral or mouth or tongue or nose or ear) adj2 cancer$).mp |
| 9 | Or/1–8 |
| 10 | exp *”signs and symptoms”/ |
| 11 | symptom$.ti |
| 12 | *”Quality of Life”/ |
| 13 | Nutrition Disorders/ |
| 14 | (eating adj1 (difficult? or disorder?)).ti,ab. |
| 15 | exp Body Weight/ |
| 16 | salivary gland diseases/or sialadenitis/or xerostomia/ |
| 17 | exp Taste Disorders/ |
| 18 | Mucositis/ |
| 19 | Deglutition Disorders/ |
| 20 | “dry mouth”.ti,ab. |
| 21 | Stomatitis/ |
| 22 | exp Tooth Diseases/ |
| 23 | exp Voice Disorders/ |
| 24 | Speech Disorders/ |
| 25 | (voice or speech or taste or sialedenitis or xerostomia or dysphagia or stomatitis or mucositis or deglutition or swallowing).ti,ab. |
| 26 | Sleep Disorders/ |
| 27 | “Sleep Initiation and Maintenance Disorders”/ |
| 28 | Fatigue/ |
| 29 | fatigue.ti,ab. |
| 30 | Muscle Weakness/ |
| 31 | Trismus/ |
| 32 | (trismus or spasm$).ti,ab. |
| 33 | exp Nausea/ |
| 34 | Anxiety/ |
| 35 | Depression/ |
| 36 | Anger/ |
| 37 | Depressive Disorder/ |
| 38 | (anxiety or anger or depression).ti,ab. |
| 39 | Body Image/ |
| 40 | exp self concept/ |
| 41 | (“body image” or “self-esteem”).ti,ab. |
| 42 | spirituality/ |
| 43 | “well being”.tw. |
| 44 | exp Social Adjustment/ |
| 45 | exp Interpersonal Relations/ |
| 46 | Stress, Psychological/ |
| 47 | ((emotional or instrumental or social or Information) adj1 support$).ti,ab. |
| 48 | exp Adaptation, Psychological/ |
| 49 | coping.ti,ab. |
| 50 | Or/10-49 |
| 51 | 9 and 50 |
| 52 | *incidence/ |
| 53 | *Prevalence/ |
| 54 | exp Registries/sn [Statistics & Numerical Data] |
| 55 | (incidence or prevalence).ti,ab. |
| 56 | Survivors/sn [Statistics & Numerical Data] |
| 57 | Cross-sectional.tw |
| 58 | Cross-sectional studies/ |
| 59 | (observational adj1 (study or studies)).tw |
| 60 | OR/52-59 |
| 61 | 51 and 60 |
| 62 | Limit 61 to (English language and yr = 2004-Current”) |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, N.; Fedewa, S.; Chen, A.Y. Epidemiology and Demographics of the Head and Neck Cancer Population. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 30, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Cancer Institute. Head and Neck Cancers. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/types/head-and-neck/head-neck-fact-sheet#what-are-cancers-of-the-head-and-neck (accessed on 26 August 2021).
- Nilsen, M.L.; Mady, L.J.; Hodges, J.; Wasserman-Wincko, T.; Johnson, J.T. Burden of treatment: Reported outcomes in a head and neck cancer survivorship clinic. Laryngoscope 2019, 129, E437–E444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubrak, C.; Martin, L.; Gramlich, L.; Scrimger, R.; Jha, N.; Debenham, B.; Chua, N.; Walker, J.; Baracos, V.E. Prevalence and prognostic significance of malnutrition in patients with cancers of the head and neck. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennie, C.; Stoddart, K.M.; Hubbard, G. A new normal: Reconciling change in appearance and function for men with head and neck cancer. Cancer Nurs. Pract. 2018, 17, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hinte, G.; Wetzels, J.-W.G.H.; Merkx, M.A.W.; De Haan, A.F.J.; Koole, R.; Speksnijder, C.M. Factors influencing neck and shoulder function after oral oncology treatment: A five-year prospective cohort study in 113 patients. Support. Care Cancer 2018, 27, 2553–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howren, M.B.; Christensen, A.J.; Karnell, L.H.; Funk, G.F. Psychological factors associated with head and neck cancer treatment and survivorship: Evidence and opportunities for behavioral medicine. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2013, 81, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvert, M.; Kyte, D.; Price, G.; Valderas, J.M.; Hjollund, N.H. Maximising the impact of patient reported outcome assessment for patients and society. BMJ 2019, 364, k5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hughes, S.E.; Rapport, F.L.; Boisvert, I.; McMahon, C.M.; Hutchings, H.A. Patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) for assessing perceived listening effort in hearing loss: Protocol for a systematic review. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e014995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pusic, A.; Liu, J.; Chen, C.M.; Cano, S.; Davidge, K.; Klassen, A.; Branski, R.; Patel, S.; Kraus, D.; Cordeiro, P.G. A systematic review of patient-reported outcome measures in head and neck cancer surgery. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2007, 136, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojo, B.; Genden, E.M.; Teng, M.S.; Milbury, K.; Misiukiewicz, K.J.; Badr, H. A systematic review of head and neck cancer quality of life assessment instruments. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 923–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ringash, J.; Bezjak, A. A structured review of quality of life instruments for head and neck cancer patients. Head Neck 2001, 23, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Deeks, J.J. Chapter 7: Selecting studies and collecting data. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Scientific Research: Wuhan, China, 2011; pp. 33–65. [Google Scholar]
- Macefield, R.C.; Jacobs, M.; Korfage, I.J.; Nicklin, J.; Whistance, R.N.; Brookes, S.T.; Sprangers, M.A.G.; Blazeby, J.M.; Whistance, R.N.; Sprangers, M.A.G. Developing core outcomes sets: Methods for identifying and including patient-reported outcomes (PROs). Trials 2014, 15, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, A.M.; Jennelle, R.L.; Grady, V.; Tovar, A.; Bowen, K.; Simonin, P.; Tracy, J.; McCrudden, D.; Stella, J.R.; Vijayakumar, S. Prospective Study of Psychosocial Distress Among Patients Undergoing Radiotherapy for Head and Neck Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2009, 73, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neilson, K.; Pollard, A.; Boonzaier, A.; Corry, J.; Castle, D.; Smith, D.; Trauer, T.; Couper, J. A longitudinal study of distress (depression and anxiety) up to 18 months after radiotherapy for head and neck cancer. Psycho-Oncology 2012, 22, 1843–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veer, V.; Kia, S.; Papesch, M. Anxiety and depression in head and neck out-patients. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2010, 124, 774–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.S.; Tian, J. Prevalence of anxiety and depression and their risk factors in Chinese cancer patients. Support. Care Cancer 2014, 22, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, S.; Danker, H.; Dietz, A.; Kienast, U.; Pabst, F.; Meister, E.F.; Oeken, J.; Thiele, A.; Schwarz, R. Sexual Problems After Total or Partial Laryngectomy. Laryngoscope 2008, 118, 2218–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šiupšinskienė, N.; Vaitkus, S.; Grėbliauskaitė, M.; Engelmanaitė, L.; Šumskienė, J. Quality of life and voice in patients treated for early laryngeal cancer. Medical 2008, 44, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, C.; Paleri, V.; Downs, C.; Shah, R. Deterioration in quality of life and depressive symptoms during radiation therapy for head and neck cancer. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2007, 136, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, L.J.; Rock, K.; Xu, W.; Chan, B.; Waldron, J.; Lu, L.; Ezzat, S.; Pothier, D.; Bernstein, L.; So, N.; et al. Long-Term Late Toxicity, Quality of Life, and Emotional Distress in Patients With Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Treated With Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 102, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.-Y.; Chen, S.-C.; Chen, W.-C.; Huang, B.-S.; Lin, C.-Y. Postradiation trismus and its impact on quality of life in patients with head and neck cancer. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2015, 119, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Deno, M.; Myers, M.; Asakage, T.; Takahashi, K.; Saito, K.; Mori, Y.; Saito, H.; Ichikawa, Y.; Yamamoto-Mitani, N.; et al. Anxiety and depression in patients after surgery for head and neck cancer in Japan. Palliat. Support. Care 2015, 14, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnell, L.H.; Funk, G.F.; Christensen, A.J.; Rosenthal, E.L.; Magnuson, J.S. Persistent posttreatment depressive symptoms in patients with head and neck cancer. Head Neck 2006, 28, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutkowska, M.; Gerber, H.; Nowak, R.; Piatkowski, J. Depression in patients with oral or facial malignancy. Arch. Med. Sci. Arch. Med. Sci. 2007, 3, 392–395. [Google Scholar]
- Paula, J.M.D.; Sonobe, H.M.; Nicolussi, A.C.; Zago, M.M.F.; Sawada, N.O. Symptoms of depression in patients with cancer of the head and neck undergoing radiotherapy treatment: A prospective study. Rev. Lat. Am. Enfermagem. 2012, 20, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duffy, S.A.; Ronis, D.L.; Valenstein, M.; Fowler, K.E.; Lambert, M.T.; Bishop, C.; Terrell, J.E. Depressive Symptoms, Smoking, Drinking, and Quality of Life Among Head and Neck Cancer Patients. J. Psychosom. Res. 2007, 48, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, S.M.; Hawkins, D.K.; Murphy, B.A. Caregiver-Reported Neuropsychiatric Symptoms in Patients Undergoing Treatment for Head and Neck Cancer. Cancer Nurs. 2014, 37, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katz, M.R.; Kopek, N.; Waldron, J.; Devins, G.M.; Tomlinson, G. Screening for depression in head and neck cancer. Psycho-Oncology 2004, 13, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.M.; Daly, M.E.; Vazquez, E.; Courquin, J.; Luu, Q.; Donald, P.J.; Farwell, D.G. Depression Among Long-term Survivors of Head and Neck Cancer Treated With Radiation Therapy. JAMA Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2013, 139, 885–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassanein, K.A.-A.M.; Musgrove, B.T.; Bradbury, E. Psychological outcome of patients following treatment of oral cancer and its relation with functional status and coping mechanisms. J. Cranio-Maxillof. Surg. 2005, 33, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lango, M.N.; Egleston, B.; Fang, C.; Burtness, B.; Galloway, T.; Liu, J.; Mehra, R.; Ebersole, B.; Moran, K.; Ridge, J.A. Baseline health perceptions, dysphagia, and survival in patients with head and neck cancer. Cancer 2013, 120, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gosak, M.; Gradišar, K.; Kozjek, N.R.; Strojan, P. Psychological distress and nutritional status in head and neck cancer patients: A pilot study. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 277, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henry, M.; Fuehrmann, F.; Hier, M.; Zeitouni, A.; Kost, K.; Richardson, K.; Mlynarek, A.; Black, M.; Macdonald, C.; Chartier, G.; et al. Contextual and historical factors for increased levels of anxiety and depression in patients with head and neck cancer: A prospective longitudinal study. Head Neck 2019, 41, 2538–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokker, M.E.; Offerman, M.P.J.; Van Der Velden, L.-A.; De Boer, M.F.; Pruyn, J.F.A.; Teunissen, S.C.C.M. Symptoms of patients with incurable head and neck cancer: Prevalence and impact on daily functioning. Head Neck 2012, 35, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, G.B.; Mendoza, T.R.; Fuller, C.D.; Gning, I.; Frank, S.J.; Beadle, B.M.; Hanna, E.; Lu, C.; Cleeland, C.S.; Rosenthal, D. High symptom burden prior to radiation therapy for head and neck cancer: A patient-reported outcomes study. Head Neck 2012, 35, 1490–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, A.A.; Timmons, A.; Molcho, M.; Pearce, A.; Gallagher, P.; Butow, P.; O’Sullivan, E.; Gooberman-Hill, R.; O’Neill, C.; Sharp, L. Quality of life in urban and rural settings: A study of head and neck cancer survivors. Oral Oncol. 2014, 50, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, E.Y.; Mendoza, T.R.; Rosenthal, D.I.; Gunn, G.B.; Sehra, P.; Yücel, E.; Cleeland, C.S. The symptom burden of treatment-naive patients with head and neck cancer. Cancer 2015, 121, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, W.; Chan, C.W.; Fan, Y.; Leung, D.Y.; Xia, W.; He, Y.; Tang, L. Symptom clusters in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma during radiotherapy. Eur. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2017, 28, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biazevic, M.G.; Antunes, J.L.F.; Togni, J.; de Andrade, F.P.; de Carvalho, M.B.; Wünsch-Filho, V. Immediate Impact of Primary Surgery on Health-Related Quality of Life of Hospitalized Patients With Oral and Oropharyngeal Cancer. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 66, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenewein, J.; Zwahlen, R.A.; Zwahlen, D.; Drabe, N.; Moergeli, H.; Büchi, S. Quality of life and dyadic adjustment in oral cancer patients and their female partners. Eur. J. Cancer Care 2008, 17, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwahlen, R.A.; Dannemann, C.; Grätz, K.W.; Studer, G.; Zwahlen, D.; Moergeli, H.; Drabe, N.; Büchi, S.; Jenewein, J. Quality of Life and Psychiatric Morbidity in Patients Successfully Treated for Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Cancer and Their Wives. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 66, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, M.L.; Sandow, P.; Werning, J.W.; Brenneman, L.; Psoter, W.J. The Head and Neck Cancer Patient Concern Inventory©: Patient Concerns’ Prevalence, Dental Concerns’ Impact, and Relationships of Concerns with Quality of Life Measures. J. Prosthodont. Off. J. Am. Coll. 2017, 26, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almonacid, C.I.F.; Ramos, A.J.; Rodríguez-Borrego, M.-A. Level of anxiety versus self-care in the preoperative and postoperative periods of total laryngectomy patients 1. Rev. Latino-Am. Enferm. 2016, 24, e2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haisfield-Wolfe, M.E.; McGuire, D.B.; Soeken, K.; Geiger-Brown, J.; De Forge, B.R. Prevalence and correlates of depression among patients with head and neck cancer: A systematic review of implications for research. Oncol. Nurs. Forum 2009, 36, E104–E125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maher, N.G.; Britton, B.; Hoffman, G.R. Early Screening in Patients With Head and Neck Cancer Identified High Levels of Pain and Distress. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 71, 1458–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchmann, L.; Conlee, J.; Hunt, J.; Agarwal, J.; White, S. Psychosocial distress is prevalent in head and neck cancer patients. Laryngoscope 2013, 123, 1424–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, M.; Cunningham, M.; Lang, H.; Swartzman, S.; Philp, J.; Taylor, L.; Thomson, J. Distress, concerns and unmet needs in survivors of head and neck cancer: A cross-sectional survey. Eur. J. Cancer Care 2015, 24, 748–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, V.; Noronha, V.; Joshi, A.; Deodhar, J.; Goswami, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Ramaswamy, A.; Dhumal, S.; M.V., C.; Karpe, A.; et al. Distress Management in Patients With Head and Neck Cancer Before Start of Palliative Chemotherapy: A Practical Approach. J. Glob. Oncol. 2018, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.-E. Changes of satisfaction with appearance and working status for head and neck tumour patients. J. Clin. Nurs. 2008, 17, 1930–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingeret, M.C.; Yuan, Y.; Urbauer, D.; Weston, J.; Nipomnick, S.; Weber, R. The nature and extent of body image concerns among surgically treated patients with head and neck cancer. Psycho-Oncology 2012, 21, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graboyes, E.M.; Hill, E.G.; Marsh, C.H.; Maurer, S.; Day, T.A.; Sterba, K.R. Body Image Disturbance in Surgically Treated Head and Neck Cancer Patients: A Prospective Cohort Pilot Study. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2019, 161, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, R.C.; Rose, S.S.; Chisholm, E.J.; Bisase, B.; Amen, F.; Nutting, C.M.; Clarke, P.M.; Kerawala, C.J.; Rhys-Evans, P.H.; Harrington, K.; et al. Evaluation of speech outcomes using English version of the Speech Handicap Index in a cohort of head and neck cancer patients. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Peris, P.; Parón, L.; Velasco, C.; de la Cuerda, C.; Camblor, M.; Bretón, I.; Herencia, H.; Verdaguer, J.; Navarro, C.; Clavé, P. Long-term prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia in head and neck cancer patients: Impact on quality of life. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 26, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, H.T.; Schrøder, S.A.; Bonding, P. Unilateral Deafness after Acoustic Neuroma Surgery: Subjective Hearing Handicap and the Effect of the Bone-Anchored Hearing Aid. Otol. Neurotol. 2006, 27, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haisfield-Wolfe, M.E.; McGuire, D.B.; Soeken, K.; Geiger-Brown, J.; De Forge, B.; Suntharalingam, M. Prevalence and correlates of symptoms and uncertainty in illness among head and neck cancer patients receiving definitive radiation with or without chemotherapy. Support. Care Cancer 2012, 20, 1885–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, S.M.; Dietrich, M.S.; Shuster, J.L., Jr.; Murphy, B.A. Delirium in patients with head and neck cancer in the outpatient treatment setting. Support. Care Cancer 2011, 20, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager-Wittenaar, H.; Dijkstra, P.U.; Vissink, A.; van der Laan, B.; Van Oort, R.P.; Roodenburg, J.L.N. Critical weight loss in head and neck cancer—prevalence and risk factors at diagnosis: An explorative study. Support. Care Cancer 2007, 15, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maurer, J.; Hipp, M.; Schäfer, C.; Kölbl, O. Dysphagia. Impact on quality of life after radio(chemo)therapy of head and neck cancer. Strahlenther. Onkol. Organ Dtsch. Rontgenges. 2011, 187, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, M.G.A.V.D.; Rütten, H.; Rasmussen-Conrad, E.L.; Knuijt, S.; Takes, R.P.; Van Herpen, C.M.L.; Wanten, G.J.A.; Kaanders, J.H.A.M.; Merkx, M.A.W. Nutritional status, food intake, and dysphagia in long-term survivors with head and neck cancer treated with chemoradiotherapy: A cross-sectional study. Head Neck 2013, 36, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuydam, A.; Lowe, D.; Brown, J.; Vaughan, E.; Rogers, S.N. Predictors of speech and swallowing function following primary surgery for oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2005, 30, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, D.O.; Weymuller, J.E.A.; Parvathaneni, U.; Merati, A.L.; Yueh, B. Dysphagia, Stricture, and Pneumonia in Head and Neck Cancer Patients: Does Treatment Modality Matter? Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2010, 119, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazi, R.; Johnson, C.; Prasad, V.; De Cordova, J.; Venkitaraman, R.; Nutting, C.M.; Clarke, P.; Evans, P.R.; Harrington, K. Quality of life outcome measures following partial glossectomy: Assessment using the UW-QOL scale. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2008, 4, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez-Cunqueiro, M.-M.; Schramm, A.; Schoen, R.; Seoane-Leston, J.; Otero-Cepeda, X.-L.; Bormann, K.-H.; Kokemueller, H.; Metzger, M.; Diz-Dios, P.; Gellrich, N.-C. Speech and Swallowing Impairment After Treatment for Oral and Oropharyngeal Cancer. Arch. Otolaryngol.—Head Neck Surg. 2008, 134, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ku, P.K.; Yuen, E.H.; Cheung, D.M.; Chan, B.Y.; Ahuja, A.; Leung, S.F.; Tong, M.C.; Van Hasselt, A. Early Swallowing Problems in a Cohort of Patients With Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Symptomatology and Videofluoroscopic Findings. Laryngoscope 2007, 117, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, J.; Wilson, J. The clinical value of dysphagia preassessment in the management of head and neck cancer patients. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2011, 19, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaukar, D.A.; Walvekar, R.R.; Das, A.K.; Deshpande, M.S.; Pai, P.S.; Chaturvedi, P.; Kakade, A.; D’Cruz, A.K. Quality of life in head and neck cancer survivors: A cross-sectional survey. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2009, 30, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thom, B.; Vincent, A.; Plourde, G.; Nabil Rizk, M.D.; Rusch, V.W.; Manjit Bains MB, B.S. Patterns of Symptoms Following Surgery for Esophageal Cancer. Oncol. Nurs. Forum 2013, 40, E101–E107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, S.; Cassell, O.; Corbridge, R.; Goodacre, T.; Cox, G. Quality of life following resection, free flap reconstruction and postoperative external beam radiotherapy for squamous cell carcinoma of the base of tongue1. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2004, 29, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alterio, D.; Gerardi, M.A.; Cella, L.; Spoto, R.; Zurlo, V.; Sabbatini, A.; Fodor, C.I.; D’Avino, V.; Conson, M.; Valoriani, F.; et al. Radiation-induced acute dysphagia: Prospective observational study on 42 head and neck cancer patients. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2017, 193, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arribas, L.; Hurtós, L.; Taberna, M.; Peiró, I.; Vilajosana, E.; Lozano, A.; Vazquez, S.; Mesia, R.; Virgili, N. Nutritional changes in patients with locally advanced head and neck cancer during treatment. Oral Oncol. 2017, 71, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, S.; Akin, M.; Çoban, Y.; Yildirim, C.; Uzel, O. Acute toxicity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with IMRT/VMAT. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 1897–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezdirec, M.; Strojan, P.; Boltezar, I.H. Swallowing disorders after treatment for head and neck cancer. Radiol. Oncol. 2019, 53, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rinkel, R.; Leeuw, I.M.V.-D.; Doornaert, P.; Buter, J.; De Bree, R.; Langendijk, J.A.; Aaronson, N.K.; Leemans, C.R. Prevalence of swallowing and speech problems in daily life after chemoradiation for head and neck cancer based on cut-off scores of the patient-reported outcome measures SWAL-QOL and SHI. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2015, 273, 1849–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahl, A.; Oinam, A.S.; Kaur, S.; Verma, R.; Elangovan, A.; Bhandari, S.; Bakshi, J.; Panda, N.; Ghoshal, S. Evaluation of Acute Toxicity and Early Clinical Outcome in Head and Neck Cancers Treated With Conventional Radiotherapy and Simultaneous Integrated Boost Arc Radiotherapy. World J. Oncol. 2017, 8, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, T.-L.; Chien, C.-Y.; Tsai, W.-L.; Liao, K.-C.; Chou, S.-Y.; Lin, H.-C.; Luo, S.D.; Lee, T.-F.; Lee, C.-H.; Fang, F.-M. Long-term late toxicities and quality of life for survivors of nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with intensity-modulated radiotherapy versus non-intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Head Neck 2015, 38, E1026–E1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroney, L.B.; Helios, J.; Ward, E.C.; Crombie, J.; Wockner, L.F.; Burns, C.L.; Spurgin, A.-L.; Blake, C.; Kenny, L.; Hughes, B.G. Patterns of dysphagia and acute toxicities in patients with head and neck cancer undergoing helical IMRT±concurrent chemotherapy. Oral Oncol. 2017, 64, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moroney, L.B.; Helios, J.; Ward, E.; Crombie, J.; Pelecanos, A.; Burns, C.; Spurgin, A.-L.; Blake, C.; Kenny, L.; Chua, B.; et al. Helical intensity-modulated radiotherapy with concurrent chemotherapy for oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma: A prospective investigation of acute swallowing and toxicity patterns. Head Neck 2018, 40, 1955–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzumder, S.; Srikantia, N.; Udayashankar, A.H.; Kainthaje, P.B.; Sebastian, M.G.J. Burden of acute toxicities in head-and-neck radiation therapy: A single-institutional experience. South Asian J. Cancer 2019, 8, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, G.M.; Portas, J.; López, R.V.M.; Côrrea, D.F.; Arantes, L.M.P.B.; Carvalho, A.L. Study of Dysphagia in Patients with Advanced Oropharyngeal Cancer Subjected to an Organ Preservation Protocol Based on Concomitant Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2019, 20, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huh, G.; Ahn, S.-H.; Suk, J.-G.; Lee, M.; Kim, W.S.; Kwon, S.K.; Ock, C.-Y.; Keam, B.; Heo, D.S.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Severe late dysphagia after multimodal treatment of stage III/IV laryngeal and hypopharyngeal cancer. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 50, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutcheson, K.A.; Warneke, C.L.; Yao, C.M.K.L.; Zaveri, J.; Elgohari, B.; Goepfert, R.; Hessel, A.C.; Kupferman, M.E.; Lai, S.Y.; Fuller, C.D.; et al. Dysphagia After Primary Transoral Robotic Surgery With Neck Dissection vs Nonsurgical Therapy in Patients With Low- to Intermediate-Risk Oropharyngeal Cancer. JAMA Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2019, 145, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jellema, A.P.; Slotman, B.; Doornaert, P.; Leemans, C.R.; Langendijk, J.A. Impact of Radiation-Induced Xerostomia on Quality of Life After Primary Radiotherapy Among Patients With Head and Neck Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2007, 69, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamstra, J.I.; Jager-Wittenaar, H.; Dijkstra, P.U.; Huisman, P.M.; Van Oort, R.P.; van der Laan, B.; Roodenburg, J.L.N. Oral symptoms and functional outcome related to oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Support. Care Cancer 2010, 19, 1327–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Möller, P.; Perrier, M.; Ozsahin, M.; Monnier, P. A prospective study of salivary gland function in patients undergoing radiotherapy for squamous cell carcinoma of the oropharynx. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2004, 97, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Tang, L.-L.; Mao, Y.-P.; Zhou, G.-Q.; Qi, Z.-Y.; Liu, L.-Z.; Lin, A.-H.; Liu, M.-Z.; Ma, J.; Sun, Y. Clinical Outcomes of Volume-Modulated Arc Therapy in 205 Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: An Analysis of Survival and Treatment Toxicities. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, R.C.; Qazali, A.; Zaveri, J.; Chambers, M.S.; Gunn, G.B.; Fuller, C.D.; Lai, S.Y.; Mott, F.E.; Hutcheson, K.A. Self-reported oral morbidities in long-term oropharyngeal cancer survivors: A cross-sectional survey of 906 survivors. Oral Oncol. 2018, 84, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, S.N.; Arshad, O.; Kwok, J.; Tran, E.; Howard, A.F.; Serrano, I.; Goddard, K.; Fuchsia Howard, A.; Serrano, I. Documentation and incidence of late effects and screening recommendations for adolescent and young adult head and neck cancer survivors treated with radiotherapy. Support. Care Cancer Off. J. Multinatl. Assoc. Support. Care Cancer 2019, 27, 2609–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.; Slevin, N.; Musgrove, B.; Swindell, R.; Molassiotis, A. Prediction of post-treatment trismus in head and neck cancer patients. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 50, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauli, N.; Johnson, J.; Finizia, C.; Andréll, P. The incidence of trismus and long-term impact on health-related quality of life in patients with head and neck cancer. Acta Oncol. 2012, 52, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindblom, U.; Gärskog, O.; Kjellén, E.; Laurell, G.; Jäghagen, E.L.; Wahlberg, P.; Zackrisson, B.; Nilsson, P. Radiation-induced trismus in the ARTSCAN head and neck trial. Acta Oncol. 2014, 53, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Astradsson, T.; Laurell, G.; Ahlberg, A.; Nikolaidis, P.; Johansson, H.; Ehrsson, Y.T. Trismus in patients with head and neck cancer and 5-year overall survival. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2018, 138, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kadam, S.A.; Nagaraja, S.; Selvaraj, K.; Ahmed, I.; Javarappa, R. Trismus in head and neck cancer patients treated by telecobalt and effect of early rehabilitation measures. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2016, 12, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owosho, A.A.; Ramalho, L.; Rosenberg, H.I.; Yom, S.K.; Drill, E.; Riedel, E.; Tsai, C.J.; Lee, N.Y.; Huryn, J.M.; Estilo, C.L. Objective assessment of trismus in oral and oropharyngeal cancer patients treated with intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT). J. Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surg. Off. Publ. Eur. Assoc. Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surg. 2016, 44, 1408–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steiner, F.; Evans, J.; Marsh, R.; Rigby, P.; James, S.; Sutherland, K.; Wickens, R.; Nedev, N.; Kelly, B.; Tan, S. Mouth opening and trismus in patients undergoing curative treatment for head and neck cancer. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 44, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Geer, S.J.; Kamstra, J.I.; Roodenburg, J.L.; van Leeuwen, M.; Reintsema, H.; Langendijk, J.A.; Dijkstra, P.U. Predictors for trismus in patients receiving radiotherapy. Acta Oncol. 2016, 55, 1318–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baharvand, M.; ShoalehSaadi, N.; Barakian, R.; Moghaddam, E.J. Taste alteration and impact on quality of life after head and neck radiotherapy. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2012, 42, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, L. Taste dysfunction in head and neck cancer survivors. Oncol. Nurs. Forum 2012, 40, E4–E13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Lu, Q.; Jin, S.; Zhang, L.; Cui, H.; Li, H. Relationship between subjective taste alteration and weight loss in head and neck cancer patients treated with radiotherapy: A longitudinal study. Eur. J. Oncol. Nurs. Off. J. Eur. Oncol. Nurs. Soc. 2018, 37, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuano, G.; Gentile, P.C.; Bianciardi, F.; Tosti, M.; Palladino, A.; Di Palma, M. Prevalence and influence of malnutrition on quality of life and performance status in patients with locally advanced head and neck cancer before treatment. Support. Care Cancer 2009, 18, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager-Wittenaar, H.; Dijkstra, P.U.; Vissink, A.; Van Oort, R.P.; van der Laan, B.; Roodenburg, J.L.N. Malnutrition in patients treated for oral or oropharyngeal cancer—prevalence and relationship with oral symptoms: An explorative study. Support. Care Cancer 2011, 19, 1675–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jager-Wittenaar, H.; Dijkstra, P.U.; Dijkstra, G.; Bijzet, J.; Langendijk, J.A.; van der Laan, B.; Roodenburg, J.L. High prevalence of cachexia in newly diagnosed head and neck cancer patients: An exploratory study. Nutrition 2017, 35, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orell-Kotikangas, H.; Österlund, P.; Mäkitie, O.; Saarilahti, K.; Ravasco, P.; Schwab, U.; Mäkitie, A.A. Cachexia at diagnosis is associated with poor survival in head and neck cancer patients. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2017, 137, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemsen, A.C.; Hoeben, A.; Lalisang, R.I.; Van Helvoort, A.; Wesseling, F.W.; Hoebers, F.; Baijens, L.W.; Schols, A.M. Disease-induced and treatment-induced alterations in body composition in locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cachex-Sarcopenia Muscle 2020, 11, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishimura, N.; Nakano, K.; Ueda, K.; Kodaira, M.; Yamada, S.; Mishima, Y.; Yokoyama, M.; Terui, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Hatake, K. Prospective evaluation of incidence and severity of oral mucositis induced by conventional chemotherapy in solid tumors and malignant lymphomas. Support. Care Cancer 2011, 20, 2053–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elting, L.S.; Keefe, D.M.; Sonis, S.T.; Garden, A.; Spijkervet, F.K.L.; Barasch, A.; Tishler, R.B.; Canty, T.P.; Kudrimoti, M.K.; Vera-Llonch, M.; et al. Patient-reported measurements of oral mucositis in head and neck cancer patients treated with radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy. Cancer 2008, 113, 2704–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshikawa, H.; Kishino, T.; Mori, T.; Indo, K.; Inamoto, R.; Akiyama, K.; Miyashita, T.; Mori, N. Clinical outcomes of nedaplatin and S-1 treatment with concurrent radiotherapy in advanced head and neck cancer. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2014, 135, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, I.F.; Firmino, R.T.; Meira, H.C.; Vasconcelos, B.C.D.E.; Noronha, V.R.A.D.S.; Santos, V.R. Radiation-induced Oral Mucositis in Brazilian Patients: Prevalence and Associated Factors. In Vivo 2019, 33, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luitel, A.; Rimal, J.; Maharjan, I.K.; Regmee, P. Assessment of Oral Mucositis among Patients Undergoing Radiotherapy for Head and Neck Cancer: An Audit. Kathmandu Univ. Med. J. 2019, 17, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Nemati, S.; Saedi, H.S.; Gerami, H.; Soltanipour, S.; Habibi, A.F.; Mirhosseyni, M.; Montazeri, S. Frequency of chemoradiotherapy-induced mucositis and related risk factors in patients with the head-and-neck cancers: A survey in the North of Iran. Dent. Res. J. 2019, 16, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.L.; Kaur, H.; Rishi, K.S. Self Reported Oral Pain and Dysfunctions Associated with Radiation Induced Oral Mucositis among Head and Neck Cancer Patients-A Prospective Observational Study. Indian J. Public Health Res. Dev. 2019, 10, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.; Jones, T.; Tandon, S.; Carding, P.; Lowe, D.; Rogers, S.N. Speech and voice outcomes in oropharyngeal cancer and evaluation of the University of Washington Quality of Life speech domain. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2009, 34, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piai, V.; Prins, J.B.; Leeuw, I.M.V.-D.; Leemans, C.R.; Terhaard, C.H.J.; Langendijk, J.A.; De Jong, R.J.B.; Smit, J.H.; Takes, R.P.; Kessels, R.P.C. Assessment of Neurocognitive Impairment and Speech Functioning Before Head and Neck Cancer Treatment. JAMA Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2019, 145, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schultz, C.; Goffi-Gomez, M.V.S.; Liberman, P.H.P.; Pellizzon, A.C.D.A.; Carvalho, A.L. Hearing Loss and Complaint in Patients With Head and Neck Cancer Treated With Radiotherapy. Arch. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2010, 136, 1065–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liberman, P.H.P.; Schultz, C.; Gomez, M.V.S.G.; Carvalho, A.L.; Pellizzon, A.C.A.; Testa, J.R.; Feher, O.; Kowalski, L.P. Auditory Effects After Organ Preservation Protocol for Laryngeal/Hypopharyngeal Carcinomas. Arch. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2004, 130, 1265–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, P.N.; Chatterjee, A.; Choudhary, A.H.; Sareen, R. Prevalence, Etiology, and Management of Neuropathic Pain in an Indian Cancer Hospital. J. Pain Palliat. Care Pharmacother. 2009, 23, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.E.; Yen JT, C.; Parker, G.; Chapman, S.; Kandikattu, S.; Barbachano, Y. Prevalence of pain in head and neck cancer out-patients. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2010, 124, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignon, T.; Fernandez, L.; Ayasso, S.; Durand, M.-A.; Badinand, D.; Cowen, D. Impact of radiation oncology practice on pain: A cross-sectional survey. Int. J. Radiation. Oncol. Biol. Physi. 2004, 60, 1204–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, J.B.; Wilkie, D.J.; Fischer, D.J.; Kim, Y.-O.; Villines, D. Neuropathic and nociceptive pain in head and neck cancer patients receiving radiation therapy. Head Neck Oncol. 2009, 1, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cramer, J.D.; Johnson, J.T.; Nilsen, M.L. Pain in Head and Neck Cancer Survivors: Prevalence, Predictors, and Quality-of-Life Impact. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2018, 159, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff-Burchfield, E.; Dietrich, M.S.; Ridner, S.; Murphy, B.A. Late systemic symptoms in head and neck cancer survivors. Support. Care Cancer 2019, 27, 2893–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benito, J.; Holsinger, F.C.; Martin, A.P.; Garcia, D.; Weinstein, G.S.; Laccourreye, O. Aspiration after supracricoid partial laryngectomy: Incidence, risk factors, management, and outcomes. Head Neck 2010, 33, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.A.; Carding, P.; Patterson, J. Dysphagia after Nonsurgical head and neck cancer treatment:Patients’ Perspectives. otolaryngology–head and. neck surgery. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2011, 145, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, W.; Haight, J.; Poon, I.; Enepekides, D.; Higgins, K.M. Sleep apnea in patients with oral cavity and oropharyngeal cancer after surgery and chemoradiation therapy. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2010, 143, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossi, P.; Di Pede, P.; Guglielmo, M.; Granata, R.; Alfieri, S.; Iacovelli, N.A.; Orlandi, E.; Guzzo, M.; Bianchi, R.; Ferella, L.; et al. Prevalence of Fatigue in Head and Neck Cancer Survivors. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2019, 128, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huyett, P.; Kim, S.; Johnson, J.T.; Soose, R.J. Obstructive sleep apnea in the irradiated head and neck cancer patient. Laryngoscope 2017, 127, 2673–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Otomaru, T.; Taniguchi, H. Sleep quality in long-term survivors of head and neck cancer: Preliminary findings. Support. Care Cancer: Off. J. Multinatl. Assoc. Support. Care Cancer. 2017, 25, 3741–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riis, C.L.; Bechmann, T.; Jensen, P.T.; Coulter, A.; Steffensen, K.D. Are patient-reported outcomes useful in post-treatment follow-up care for women with early breast cancer? A scoping review. Patient Relat. Outcome Meas. 2019, 10, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, M.C.F.; Lo, P.S.Y.; Wong, K.H.; Yeung, R.M.W.; Van Hasselt, C.A.; Eremenco, S.; Cella, D. Development and validation of the functional assessment of cancer therapy nasopharyngeal cancer subscale. Head Neck 2009, 31, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, C.; Schuller, D.E. A functional status scale for measuring quality of life outcomes in head and neck cancer patients. Cancer Nurs. 1995, 18, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.K.F.; Leung, S.F.; Thompson, D.R.; Tai, J.W.M.; Liang, R.H.S.; Kan, A.S.T.; Ying, F.W.O.; Yeung, R.M.W. New measure of health-related quality of life for patients with oropharyngeal mucositis. Cancer 2007, 109, 2590–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.K.F.; Leung, S.F.; Liang, R.H.S.; Tai, J.W.M.; Yeung, R.M.W.; Thompson, D.R. A patient-reported outcome instrument to assess the impact of oropharyngeal mucositis on health-related quality of life: A longitudinal psychometric evaluation. Support. Care Cancer 2008, 17, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, D.I.; Mendoza, T.R.; Chambers, M.S.; Asper, J.A.; Gning, I.; Kies, M.S.; Weber, R.S.; Lewin, J.; Garden, A.; Ang, K.K.; et al. Measuring head and neck cancer symptom burden: The development and validation of the M. D. Anderson symptom inventory, head and neck module. Head Neck 2007, 29, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, D.I.; Mendoza, T.R.; Chambers, M.S.; Burkett, V.S.; Garden, A.; Hessell, A.C.; Lewin, J.; Ang, K.K.; Kies, M.S.; Gning, I.; et al. The M. D. Anderson Symptom Inventory–Head and Neck Module, a Patient-Reported Outcome Instrument, Accurately Predicts the Severity of Radiation-Induced Mucositis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2008, 72, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, H.A.; Hershock, D.; Machtay, M.; Chalian, A.A.; Weber, R.S.; Weinstein, G.S.; Schumacher, K.; Kligerman, M.M.; Berlin, J.A.; Rosenthal, D. Preliminary Investigation of Symptom Distress in the Head and Neck Patient Population: Validation of a Measurement Instrumen. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 29, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terwee, C.B.; Mokkink, L.B.; Knol, D.L.; Ostelo, R.; Bouter, L.; De Vet, H.C.W. Rating the methodological quality in systematic reviews of studies on measurement properties: A scoring system for the COSMIN checklist. Qual. Life Res. 2011, 21, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shunmugasundaram, C.; Rutherford, C.; Butow, P.N.; Sundaresan, P.; Dhillon, H.M. What are the optimal measures to identify anxiety and depression in people diagnosed with head and neck cancer (HNC): A systematic review. J. Patient-Rep. Outcomes 2020, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottomley, A.; Reijneveld, J.C.; Koller, M.; Flechtner, H.; Tomaszewski, K.A.; Greimel, E.; Ganz, P.A.; Ringash, J.; O’Connor, D.; Kluetz, P.G.; et al. Current state of quality of life and patient-reported outcomes research. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Symptom | Cancer Type | Treatment | Measure and Cut-Off Score | Number of Studies | Range of Prevalence | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Treatment | Treatment | Post-Treatment | Overall/ NS * | References | |||||
| Depression | Oral cavity, larynx, Oropharynx, salivary gland, nasal cavity, thyroid, nasopharynx, unknown primary, paranasal sinus | Surgery ± RT ± chemo | SADS (RDC criteria), BDI, HADS-D, UWQOL-mood, NPI-Q, GDS-SF, PHQ-8 | 22 | 7.5–84% | 7–75% | 2–78% | 46% | [4,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36] |
| Sadness | Oropharynx, oral cavity, larynx, nasopharynx, skin, hypopharynx, skull base, thyroid, nasal cavity/sinus, salivary gland | RT ± chemo ± surgery or treatment-naive patients | MDASI-HN, Pal-C, FACT-HN, Not specified | 5 | 8–27% | 82% | 19–57% | [37,38,39,40,41] | |
| Anxiety | Oropharynx, thyroid, oral cavity, larynx, parotid gland, paranasal sinus, nasopharynx salivary gland (not specified) | RT ± chemo ± surgery or treatment-naive patients | HADS-A, UWQOL, GAD-2, Pal-SI, NPI-Q, PCI, Not specified, | 20 | 20–72% | 34.5% | 1–97.5% | 12–29% | [4,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,25,30,33,35,36,37,42,43,44,45,46] |
| Worry | Oral cavity, sinus, oropharynx, larynx, pharynx, salivary gland, nasal fossa | Surgery ± RT ± chemo | MSAS, Pal-C, NPI-Q | 3 | 38–62% | 30–57% | 33–52% | 61% | [30,37,47] |
| Distress | Oropharynx, oral cavity, larynx, salivary gland, nasopharynx, sinus, hypopharynx, skin, thyroid, skull base, nasal cavity, neck, | RT ± chemo ± surgery or treatment-naive patients | MDASI-HN, DT | 7 | 14–51% | 86% | 33–35% | 44.5% | [38,40,41,48,49,50,51] |
| Satisfaction with Appearance | Oral cavity, skin, mid-face, larynx, oropharynx, hypopharynx, nasopharynx, unknown (not specified) | Surgery ± chemo or ±RT | MBSRQ, BASS, BIS, PCI | 4 | 11% | 25–27% | 73–75% | 89% | [45,52,53,54] |
| Avoidance of Social Interactions | Oral cavity, oropharynx, skin, cancer of the mid-face, maxilla cancer, others | Surgery ± RT ± chemo | Speech Handicap Index BIS | 3 | - | - | 16–62% | - | [53,55,56] |
| Symptom | Cancer Type | Treatment | Measure and Cut-Off Score | Number of Studies | Range of Prevalence | References | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Treatment | Treatment | Post-Treatment | Overall/ NS * | ||||||
| Eating And Weight Changes | |||||||||
| Dysphagia | Oral cavity, larynx, oropharynx, thyroid hypopharynx, skin, nasopharynx, sinus pharynx, nasal fossa salivary gland, nasal cavity, primary maxillary, unknown | Surgery ± RT ± chemo Or not specified | SWAL-QOL, MDADI, MDASI-HN, PCI, PG-SGA, EAT-10, Pal-C, CTCAE, UW-QOL, MSAS-SF, QLQ H&N-35, FACT-HN, FEES, Not specified, medical record, chest X-ray | 35 | 12–75% | 38–100% | 0–100% | 28–80% | [4,5,37,38,39,41,42,45,56,58,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84] |
| Xerostomia | Oral cavity, naso/oropharynx, skin, hypopharynx, larynx, salivary glands, thyroid, nasal cavity/sinus, unknown, skull base | Surgery ± RT ± chemo or not specified | PCI, UW-QOL, EORTC QLQ-C30/H&N-35, FACT-HN, PG-SGA, MFIQ, CTCAE, MSAS, study-specific questionnaire | 23 | 4–18% | 71–97.5% | 0–100% | 36–80% | [5,38,39,40,41,42,45,58,65,67,69,71,73,77,78,79,80,85,86,87,88,89,90] |
| Trismus | Oral, oropharynx, larynx, neck, ear hypo/nasopharynx, salivary/parotid gland, thyroid, sinus salivary gland, unknown | RT ± chemo ± surgery or treatment-naive | MIO, EORTC H&N35, EORTC QLQ-C30, MFIQ, PCI, CTCAE | 14 | 3–41% | - | 12–57% | 4–19% | [24,45,69,77,86,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98] |
| Difficulty chewing | Oropharynx, oral cavity, nasal cavity/sinus, salivary gland hypo/nasopharynx, larynx, thyroid, skin, unknown | RT ± chemo ± surgery (prior tx not described) | UW-QOL MDASI-HN, PCI, CTCAE | 5 | 12–44% | 98.5% | 91% | 30% | [38,41,42,45,71] |
| Dysgeusia/ Taste | Oropharynx, oral cavity, naso/hypopharynx, larynx, thyroid, salivary gland, nasal cavity/sinus, skin, maxilla/mandible parotid unknown | RT ± chemo ± surgery (prior tx not described) | MSAS, UW-QOL, MDASI-HN, pipette droplet, EORTC QLQ H&N35, PCI, PG-SGA, STA | 15 | 3–21.5% | 38–97% | 1–100% | 27–76% | [5,38,41,42,45,58,71,73,77,79,80,90,99,100,101] |
| Dental problems | Oropharynx, skin, oral cavity, larynx, salivary gland naso/hypopharynx, nasal cavity/sinus, thyroid, unknown | RT ± chemo ± surgery | EORTC QLQ-C30, MDASI-HN, PCI, PG-SGA | 6 | 13–27% | 82% | 14–42% | 19% | [5,38,41,45,69,89] |
| Malnutrition/weight loss | Oropharynx, oral cavity, esophageal naso/hypopharynx, larynx, maxillary sinus, submandibular gland unknown | Chemo ± surgery ± RT or none Not specified | BMI, albumin, weight loss, MSAS, MSAS-SF, PCI, PG-SGA, FFMI, WLG, hand grip | 16 | 8.5–42% | 43–91% | 3–95% | 17% | [5,34,35,45,56,58,60,62,70,73,81,102,103,104,105,106] |
| Lack of appetite | Oropharynx, oral cavity, skull base salivary gland, skin, hypo/nasopharynx, larynx, thyroid, nasal cavity/sinus, maxilla, others unknown | RT ± chemo ± surgery treatment-naive | MSAS, EORTC QLQ-C30, NPI-Q, MDASI-HN, PCI, PG-SGA, CTCAE | 10 | 5–24% | 33–95% | 20.0–48.0% | 22–96% | [5,30,38,40,41,45,58,69,73,81] |
| Oral mucositis | Oral cavity, larynx oropharynx, hypo/nasopharynx, Not specified others | RT ± chemo ± surgery | CTCAE, OMDQ PG-SGA, WHO grading, not specified | 15 | 44–68% | 7–100% | 2–85% | 42–83% | [73,74,77,78,79,80,81,88,107,108,109,110,111,112,113] |
| Communication | |||||||||
| Voice/speech | Oropharynx, oral cavity, maxillary naso/hypopharynx, larynx, thyroid, salivary gland, nasal cavity/sinus, skin unknown | RT ± chemo ± surgery Not specified | UW-QOL, VHI, MDASI-HN, FACT-HN, PCI DÖSAK, SHI V-RQOL, GRBAS | 14 | 3–55% | 9–85% | 20–91% | 16–64% | [21,38,39,41,42,45,55,63,65,66,71,76,114,115] |
| Hearing loss | Larynx, naso/hypopharynx, parotid, oral cancer, unknown | RT + chemo, surgery, surgery + RT | PCI, CTCAE not specified | 4 | - | - | 2–72% | 18% | [45,78,116,117] |
| Pain | |||||||||
| Pain | Oropharynx, oral cavity, thyroid, nasopharynx, larynx, esophageal hypopharynx, salivary gland, nasal cavity/sinus, skin visceral, parotid, neck SCC unknown skull base | RT ± chemo ± surgery Not described treatment-naive patients | NRS, Pal-C, MDASI-HN, MSAS, VAS, UW-QOL, PCI, UMCG H&N CST, EORTC H&N35, PG-SGA, VHNSS, Self-report pain, EQ5D-3L CTCAE, not specified | 22 | 9–50% | 62–89% | 31–91% | 20–54% | [5,21,34,37,38,40,41,42,45,48,58,60,70,77,81,93,118,119,120,121,122,123] |
| Other Physical Symptoms | |||||||||
| Dyspnea | Oropharynx, oral cavity, larynx, hypo/nasopharynx, thyroid/trachea, salivary gland, nasal cavity/sinus, skin | RT ± chemo ± surgery | Pal-C, MDASI-HN | 3 | 3–12% | 68% | - | 21% | [37,38,41] |
| Cough | Esophageal oral cavity, oropharynx, hypo/nasopharynx, larynx, maxilla | RT ± chemo ± surgery | EORTC QLQ-C30 MSAS-SF, Pearson’s scale | 3 | 32% | - | 10.5–52% | - | [69,70,124] |
| Cancer Type | Treatment | Measure and Cut-Off Score | Number of Studies | Range of Prevalence | References | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Treatment | Treatment | Post-Treatment | Overall/ NS * | ||||||
| Activities of Daily Living | |||||||||
| Activities of daily living | Oral cavity, oropharynx, larynx, naso/hypopharynx, unknown | NR | EQ-5D-3L | 1 | 2–14% | - | - | - | [34] |
| Sexual function | Larynx, hypo/pharynx oral cancer, salivary glands | Surgery ± RT or NR | EORTC QLQ-H&N35, FACT-HN | 2 | - | - | 42% | 32–42% | [20,39] |
| Fatigue and Energy | |||||||||
| Fatigue | Oropharynx, oral cavity, hypo/nasopharynx, larynx, pharynx, thyroid, salivary gland, nasal cavity/sinus, skin maxilla unknown skull base | Surgery ± RT ± chemo Not reported | MSAS, Pal-C, MDASI-HN, EORTC QLQ-C30, ESS, MSAS-SF FACT-HN, PCI, BFI, VHNSS, CTCAE | 14 | 14–58% | 71–95% | 7–85% | 7–81% | [23,37,38,39,40,41,45,58,69,70,77,123,126,127] |
| Drowsiness/ decreased alertness | Oropharynx, oral cavity, larynx, skin hypo/nasopharynx, thyroid, salivary gland, nasal cavity/sinus, skull base | RT ± chemo ± surgery or treatment-naïve | MDASI-HN, NPI-Q | 4 | 8–22% | 91% | 70% | - | [30,38,40,41] |
| Sleeping problems | Oropharynx, oral cavity, larynx, hypo/nasopharynx, thyroid, salivary gland, nasal cavity/sinus, skin, skull base, esophageal unknown, not described | Surgery ± RT ± chemo or treatment-naïve | Pal-SI, MDASI-HN, MSAS-SF, RDI, PCI, AHI, PSQI, VHNSS, CTCAE | 11 | 16–41% | 94.5% | 40–100% | 0–29% | [37,38,40,41,45,70,77,123,126,128,129] |
| PROMS Domain | Symptoms | FACT-NP | FSH&N-SR | HNRT-Q | MDASI-HN | OMQOL | QLQ-Rathmell | QOL-Thyroid | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disease Specific | |||||||||
| Physical well-being | Eating and weight changes | Swallowing problems (e.g., swallowing different type of food, painfulness, stressfulness, etc.) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | - |
| Saliva/dry mouth/drooling (xerostomia) | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | - | ||
| Cough/chocking when swallowing | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | ||
| Trismus | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | ||
| Mucus/phlegm | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | ||
| Appetite/eating/taste(chewing, teeth/dentures/gum problem, taste/smell, eating speed, ability of eating, use of nutritional supplements/stomach tube, change in diet and quantity of food intake) | 3 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 7 | 3 | 1 | ||
| Weight change | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Communication | Voice change | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Communication/talking/speaking | 1 | 1 | - | - | 5 | 1 | - | ||
| hearing loss | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Appearance | Noticeable change (e.g., disfigurement) | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | 2 | 1 | |
| Ulceration/erythema (oral, cheek) | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | ||
| Skin symptoms | - | - | 2 | 1 | - | - | 1 | ||
| Pain | Pain | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 1 | |
| Fatigue and energy | Sleep issue (drowsy, sleep quality) | 1 | - | 1 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 | |
| Fatigue | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | ||
| Breathing | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | ||
| Other physical symptoms | Feeling sick | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | |
| Nausea/upset stomach/vomiting | 1 | - | 2 | 1 | - | 2 | - | ||
| Loss of vision | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Shoulder/upper body mobility/stiffness | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Constipation | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | 1 | ||
| Swelling in mouth | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | ||
| Memory problem | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | 1 | ||
| Tolerance to cold or heat | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | ||
| Swelling/fluid retention | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | ||
| Menstrual changes or fertility | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | ||
| Nasal outcomes (sneezing, runny nose, nasal discharge) | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Motor skills/coordination | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | ||
| Throat discomfort | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | ||
| Generic | |||||||||
| Quality of life (general)/rate overall quality of life | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 | ||
| Overall health | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | ||
| Functional well-being | Physical function (ability to work, daily activities, ability to walk, drive, concentrate, to engage in recreational activities) | 2 | - | 2 | 3 | - | 1 | 9 | |
| Enjoyment of food (includes ability to eat favorite food) | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | ||
| Enjoyment of life | 1 | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | ||
| Enjoyment of things for fun | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Income loss/financial burden | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | ||
| Sexual enjoyment | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | ||
| Psychological/emotional well-being | Psychological distress (distress, bothered, upset, unhappy with symptoms, appearance, treatment, uncertainty etc.) | 3 | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | 8 | |
| Life satisfaction | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 | ||
| Emotional function | 7 | 1 | 2 | 1 | - | 1 | 12 | ||
| Spiritual life | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | ||
| Social well-being | Social function | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| Acceptance of illness by family | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Family communication about illness | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Support from family/friends | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | ||
| Instruments | Internal Consistency | Test–Retest Reliability | Measurement Error | Content Validity | Construct Validity | Criterion Validity | Responsiveness | Interpret-Ability | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Convergent Validity | Known Groups Validity | Concurrent Validity | |||||||
| FACT-NP [131] | X | X | X | X | |||||
| FSH&N-SR [132] | X | X | X | X | |||||
| OMQOL [134] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| MDASI-H&N [135,136] | X | X | X | ||||||
| HNRT-Q [137] | X | ||||||||
| QOL-Rathmell | There were no validation studies for these instruments | ||||||||
| QOL-Thyroid | |||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Oliveira Faria, S.; Hurwitz, G.; Kim, J.; Liberty, J.; Orchard, K.; Liu, G.; Barbera, L.; Howell, D. Identifying Patient-Reported Outcome Measures (PROMs) for Routine Surveillance of Physical and Emotional Symptoms in Head and Neck Cancer Populations: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4162. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184162
de Oliveira Faria S, Hurwitz G, Kim J, Liberty J, Orchard K, Liu G, Barbera L, Howell D. Identifying Patient-Reported Outcome Measures (PROMs) for Routine Surveillance of Physical and Emotional Symptoms in Head and Neck Cancer Populations: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(18):4162. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184162
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Oliveira Faria, Sheilla, Gillian Hurwitz, Jaemin Kim, Jacqueline Liberty, Kimberly Orchard, Geoffrey Liu, Lisa Barbera, and Doris Howell. 2021. "Identifying Patient-Reported Outcome Measures (PROMs) for Routine Surveillance of Physical and Emotional Symptoms in Head and Neck Cancer Populations: A Systematic Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 18: 4162. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184162
APA Stylede Oliveira Faria, S., Hurwitz, G., Kim, J., Liberty, J., Orchard, K., Liu, G., Barbera, L., & Howell, D. (2021). Identifying Patient-Reported Outcome Measures (PROMs) for Routine Surveillance of Physical and Emotional Symptoms in Head and Neck Cancer Populations: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(18), 4162. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184162






