Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for COVID 2019-Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Comparison between First and Second Waves (Stage 2)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
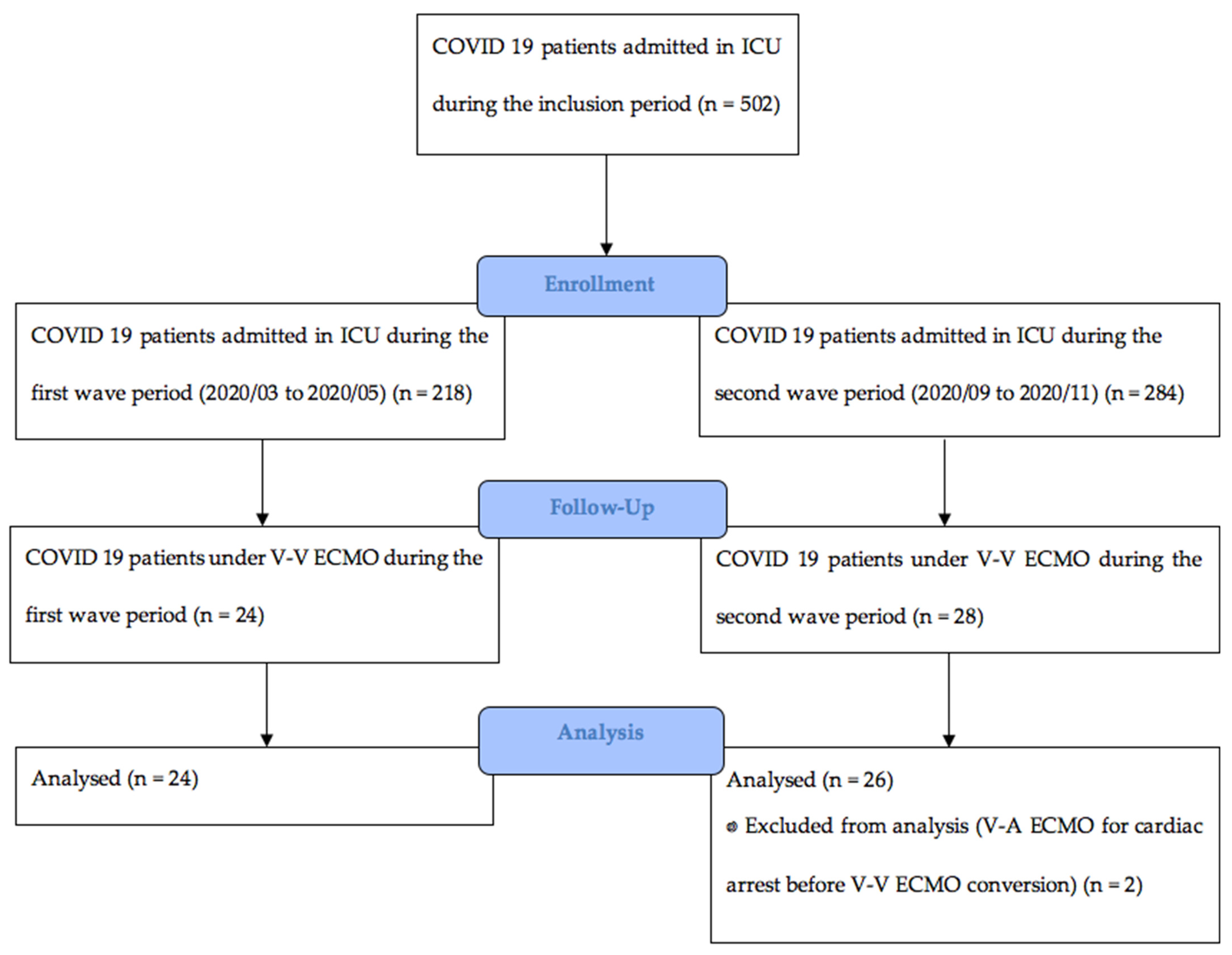
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Data Collection and Outcome Measures
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Serafim, R.B.; Póvoa, P.; Souza-Dantas, V.; Kalil, A.C.; Salluh, J.I.F. Clinical Course and Outcomes of Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19 Infection: A Systematic Review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camporota, L.; Vasques, F.; Sanderson, B.; Barrett, N.A.; Gattinoni, L. Identification of Pathophysiological Patterns for Triage and Respiratory Support in COVID-19. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 752–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esnault, P.; Cardinale, M.; Hraiech, S.; Goutorbe, P.; Baumstrack, K.; Prud’homme, E.; Bordes, J.; Forel, J.-M.; Meaudre, E.; Papazian, L.; et al. High Respiratory Drive and Excessive Respiratory Efforts Predict Relapse of Respiratory Failure in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 202, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobin, M.J.; Laghi, F.; Jubran, A. Caution about Early Intubation and Mechanical Ventilation in COVID-19. Ann. Intensive Care 2020, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, M.J.; Laghi, F.; Jubran, A. P-SILI is not Justification for Intubation of COVID-19 Patients. Ann. Intensive Care 2020, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhazzani, W.; Møller, M.H.; Arabi, Y.M.; Loeb, M.; Gong, M.N.; Fan, E.; Oczkowski, S.; Levy, M.M.; Derde, L.; Dzierba, A.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: Guidelines on the Management of Critically Ill Adults with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 854–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cook, T.M.; El-Boghdadly, K.; McGuire, B.; McNarry, A.F.; Patel, A.; Higgs, A. Consensus Guidelines for Managing the Airway in Patients with COVID-19: Guidelines from the Difficult Airway Society, the Association of Anaesthetists the Intensive Care Society, the Faculty of Intensive Care Medicine and the Royal College of Anaesthetists. Anaesthesia 2020, 75, 785–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissman, D.N.; de Perio, M.A.; Radonovich, L.J. COVID-19 and Risks Posed to Personnel during Endotracheal Intubation. JAMA 2020, 323, 2027–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewster, D.J.; Chrimes, N.; Do, T.B.; Fraser, K.; Groombridge, C.J.; Higgs, A.; Humar, M.J.; Leeuwenburg, T.J.; McGloughlin, S.; Newman, F.G.; et al. Consensus Statement: Safe Airway Society Principles of Airway Management and Tracheal Intubation Specific to the COVID-19 Adult Patient Group. Med. J. Aust. 2020, 212, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, J.C.-H.; Ho, L.T.; Cheng, J.V.; Cham, E.Y.K.; Lam, K.N. Staff Safety during Emergency Airway Management for COVID-19 in Hong Kong. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, J.J.; Gattinoni, L. Management of COVID-19 Respiratory Distress. JAMA 2020, 323, 2329–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wax, R.S.; Christian, M.D. Practical Recommendations for Critical Care and Anesthesiology Teams Caring for Novel Coronavirus (2019-NCoV) Patients. Can. J. Anaesth. J. Can. Anesth. 2020, 67, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Battaglini, D.; Robba, C.; Ball, L.; Silva, P.L.; Cruz, F.F.; Pelosi, P.; Rocco, P.R.M. Noninvasive Respiratory Support and Patient Self-Inflicted Lung Injury in COVID-19: A Narrative Review. Br. J. Anaesth. 2021, 127, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 693–704. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasselli, G.; Cattaneo, E.; Florio, G.; Ippolito, M.; Zanella, A.; Cortegiani, A.; Huang, J.; Pesenti, A.; Einav, S. Mechanical Ventilation Parameters in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: A Scoping Review. Crit. Care. 2021, 25, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasselli, G.; Tonetti, T.; Protti, A.; Langer, T.; Girardis, M.; Bellani, G.; Laffey, J.; Carrafiello, G.; Carsana, L.; Rizzuto, C.; et al. Pathophysiology of COVID-19-Associated Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Multicentre Prospective Observational Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Hajage, D.; Demoule, A.; Pham, T.; Combes, A.; Dres, M.; Lebbah, S.; Kimmoun, A.; Mercat, A.; Beduneau, G.; et al. Clinical Characteristics and Day-90 Outcomes of 4244 Critically Ill Adults with COVID-19: A Prospective Cohort Study. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contou, D.; Fraissé, M.; Pajot, O.; Tirolien, J.-A.; Mentec, H.; Plantefève, G. Comparison between First and Second Wave among Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients Admitted to a French ICU: No Prognostic Improvement during the Second Wave? Crit. Care 2021, 25, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badulak, J.; Antonini, M.V.; Stead, C.M.; Shekerdemian, L.; Raman, L.; Paden, M.L.; Agerstrand, C.; Bartlett, R.H.; Barrett, N.; Combes, A.; et al. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for COVID-19: Updated 2021 Guidelines from the Extracorporeal Life Support Organization. ASAIO J. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs 2021, 67, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaro, R.P.; MacLaren, G.; Boonstra, P.S.; Iwashyna, T.J.; Slutsky, A.S.; Fan, E.; Bartlett, R.H.; Tonna, J.E.; Hyslop, R.; Fanning, J.J.; et al. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Support in COVID-19: An International Cohort Study of the Extracorporeal Life Support Organization Registry. Lancet 2020, 396, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLaren, G.; Combes, A.; Brodie, D. What’s New in ECMO for COVID-19? Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekar, K.; Badulak, J.; Peek, G.; Boeken, U.; Dalton, H.J.; Arora, L.; Zakhary, B.; Ramanathan, K.; Starr, J.; Akkanti, B.; et al. Extracorporeal Life Support Organization Coronavirus Disease 2019 Interim Guidelines: A Consensus Document from an International Group of Interdisciplinary Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Providers. ASAIO J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, E.; Song, J.; Deane, A.M.; Plummer, M.P. Global Impact of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection Requiring Admission to the ICU: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Chest 2021, 159, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broman, L.M.; Eksborg, S.; Coco, V.L.; De Piero, M.E.; Belohlavek, J.; Lorusso, R. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for COVID-19 during First and Second Waves. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, E80–E81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ARDS Definition Task Force; Ranieri, V.M.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Thompson, B.T.; Ferguson, N.D.; Caldwell, E.; Fan, E.; Camporota, L.; Slutsky, A.S. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: The Berlin Definition. JAMA 2012, 307, 2526–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combes, A.; Hajage, D.; Capellier, G.; Demoule, A.; Lavoué, S.; Guervilly, C.; Da Silva, D.; Zafrani, L.; Tirot, P.; Veber, B.; et al. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1965–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, M.B.P.; Meade, M.O.; Slutsky, A.S.; Brochard, L.; Costa, E.L.V.; Schoenfeld, D.A.; Stewart, T.E.; Briel, M.; Talmor, D.; Mercat, A.; et al. Driving Pressure and Survival in the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Available online: https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMsa1410639 (accessed on 16 August 2021).
- Gattinoni, L.; Tonetti, T.; Cressoni, M.; Cadringher, P.; Herrmann, P.; Moerer, O.; Protti, A.; Gotti, M.; Chiurazzi, C.; Carlesso, E.; et al. Ventilator-Related Causes of Lung Injury: The Mechanical Power. Intensive Care Med. 2016, 42, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiumello, D.; Gotti, M.; Guanziroli, M.; Formenti, P.; Umbrello, M.; Pasticci, I.; Mistraletti, G.; Busana, M. Bedside Calculation of Mechanical Power during Volume- and Pressure-Controlled Mechanical Ventilation. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, J.R.; Lemeshow, S.; Saulnier, F. A New Simplified Acute Physiology Score (SAPS II) Based on a European/North American Multicenter Study. JAMA 1993, 270, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.L.; Moreno, R.; Takala, J.; Willatts, S.; De Mendonça, A.; Bruining, H.; Reinhart, C.K.; Suter, P.M.; Thijs, L.G. The SOFA (Sepsis-Related Organ Failure Assessment) Score to Describe Organ Dysfunction/Failure. On Behalf of the Working Group on Sepsis-Related Problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med. 1996, 22, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Bailey, M.; Sheldrake, J.; Hodgson, C.; Aubron, C.; Rycus, P.T.; Scheinkestel, C.; Cooper, D.J.; Brodie, D.; Pellegrino, V.; et al. Predicting Survival after Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Severe Acute Respiratory Failure. The Respiratory Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Survival Prediction (RESP) Score. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 1374–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, R.A.; Graf, J.; Zambrano, J.M.; Ruiz, C.; Espinoza, J.A.; Bravo, S.I.; Salazar, P.A.; Bahamondes, J.C.; Castillo, L.B.; Gajardo, A.I.J.; et al. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for COVID-19–Associated Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Chile: A Nationwide Incidence and Cohort Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 204, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebreton, G.; Schmidt, M.; Ponnaiah, M.; Folliguet, T.; Para, M.; Guihaire, J.; Lansac, E.; Sage, E.; Cholley, B.; Mégarbane, B.; et al. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Network Organisation and Clinical Outcomes during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Greater Paris, France: A Multicentre Cohort Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Hajage, D.; Lebreton, G.; Monsel, A.; Voiriot, G.; Levy, D.; Baron, E.; Beurton, A.; Chommeloux, J.; Meng, P.; et al. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Associated with COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorusso, R.; Combes, A.; Coco, V.L.; De Piero, M.E.; Belohlavek, J.; Euro ECMO COVID-19 Working Group; Euro-ELSO Steering Committee. ECMO for COVID-19 Patients in Europe and Israel. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, K.; Shekar, K.; Ling, R.R.; Barbaro, R.P.; Wong, S.N.; Tan, C.S.; Rochwerg, B.; Fernando, S.M.; Takeda, S.; MacLaren, G.; et al. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagiannidis, C.; Strassmann, S.; Merten, M.; Bein, T.; Windisch, W.; Meybohm, P.; Weber-Carstens, S. High In-Hospital Mortality in COVID Patients Receiving ECMO in Germany–A Critical Analysis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 204, 991–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supady, A.; Taccone, F.S.; Lepper, P.M.; Ziegeler, S.; Staudacher, D.L.; COVEC-Study Group. Survival after Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Severe COVID-19 ARDS: Results from an International Multicenter Registry. Crit. Care. 2021, 25, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recovery Collaborative Group. Lopinavir-Ritonavir in Patients Admitted to Hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): A Randomised, Controlled, Open-Label, Platform Trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recovery Collaborative Group; Horby, P.; Mafham, M.; Linsell, L.; Bell, J.L.; Staplin, N.; Emberson, J.R.; Wiselka, M.; Ustianowski, A.; Elmahi, E.; et al. Effect of Hydroxychloroquine in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2030–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigel, J.H.; Tomashek, K.M.; Dodd, L.E.; Mehta, A.K.; Zingman, B.S.; Kalil, A.C.; Hohmann, E.; Chu, H.Y.; Luetkemeyer, A.; Kline, S.; et al. Remdesivir for the Treatment of COVID-19-Final Report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1813–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, B.; Tan, T.T.; Leo, Y.S. The Place for Remdesivir in COVID-19 Treatment. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 20–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repurposed Antiviral Drugs for COVID-19—Interim WHO Solidarity Trial Results. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 384, 497–511. [CrossRef]
- Gorman, E.; Connolly, B.; Couper, K.; Perkins, G.D.; McAuley, D.F. Non-Invasive Respiratory Support Strategies in COVID-19. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.B.; June, C.H. Cytokine Release Syndrome in Severe COVID-19. Science 2020, 368, 473–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambermont, B.; Rousseau, A.-F.; Seidel, L.; Thys, M.; Cavalleri, J.; Delanaye, P.; Chase, J.G.; Gillet, P.; Misset, B. Outcome Improvement Between the First Two Waves of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic in a Single Tertiary-Care Hospital in Belgium. Crit. Care Explor. 2021, 3, e0438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics at ECMO Initiation | All Patients (=50) | First Wave (=24) | Second Wave (=26) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 61 (53–66) | 58 (49–63) | 63 (59–67) | 0.017 |
| Male | 46 (92) | 21 (87.5) | 25 (96.2) | 0.34 |
| BMI (kg/m²) | 31 (28–36) | 33 (29–38) | 30 (27–35) | 0.158 |
| SAPSII | 58 (34–67) | 60 (42–69) | 42 (32–67) | 0.079 |
| SOFA | 10 (8–12) | 11 (9–12) | 9 (8–11) | 0.027 |
| RESP | −3 (−6,−1) | −2 (−4,−1) | −5 (−6.3,−1) | 0.063 |
| No Comorbidities | 9 (18) | 6 (25) | 3 (11.5) | 0.216 |
| HTA | 27 (54) | 11 (46) | 16 (61.5) | 0.266 |
| Diabetes | 18 (36) | 9 (37.5) | 9 (34.6) | 0.832 |
| Dyslipidemia | 20 (40) | 7 (29.2) | 13 (50) | 0.133 |
| Obesity (BMI > 30) | 29 (58) | 16 (66.7) | 13 (50) | 0.233 |
| Malignancy | 1 (2) | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 0.48 |
| Other immunocompromised condition | 6 (12) | 2 (8.3) | 4 (15.4) | 0.669 |
| Time from first symptoms to ECMO (days) | 16 (14–26) | 15 (11–16) | 19 (16–26) | 0.004 |
| Time from first symptoms to ICU (days) | 7 (5–9) | 7 (5–9) | 6 (4–9) | 0.33 |
| Time from ICU admission to ECMO (days) | 12 (6–15) | 7.5 (5–12) | 14 (11–20) | <0.001 |
| Time from ICU admission to intubation (days) | 1 (0–6) | 0 (0–1) | 5,5 (1–9) | <0.001 |
| Pre-ECMO Characteristics | All Patients (=50) | First Wave (=24) | Second Wave (=26) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Respiratory Support | ||||
| FIO2 | 100 (100–100) | 100 (100–100) | 100 (88–100) | 0.082 |
| Vt (mL) | 420 (380–460) | 425 (393–480) | 410 (380–440) | 0.08 |
| Vt IBW (mL/kg) | 6.1 (5.7–6.6) | 6.5 (5.7–7) | 6 (5.3–6.2) | 0.009 |
| RR (bpm) | 30 (26–31) | 30 (26–30) | 30 (30–32) | 0.159 |
| Ppeak (cmH2O) | 40 (36–45) | 43 (38–47) | 38 (35–42) | 0.068 |
| Pplat (cmH2O) | 30 (28–32) | 30 (27–32) | 31 (30–32) | 0.402 |
| PEEP (cmH2O) | 12 (7.5–15) | 14 (12–16) | 10 (5–14) | <0.001 |
| Driving Pressure (cmH2O) | 17 (14–22) | 15 (12–17) | 21 (17–24) | <0.001 |
| Static Compliance (mL/cm H2O) | 25 (18–29) | 29 (25–37) | 20 (16–26) | <0.001 |
| Mechanical Power (J/min) | 35 (30–47) | 43 (34–52) | 32 (28–39) | 0.004 |
| Adjuvant treatment | ||||
| Prone Positioning (PP) | 48 (96) | 24 (100) | 24 (92) | 0.491 |
| Number of PP before ECMO | 3 (2–5) | 3 (2–5) | 3 (2–5) | 0.979 |
| Neuromuscular Blockade | 50 (100) | 24 (100) | 26 (100) | 1 |
| Inhaled nitric oxide | 44 (88) | 21 (87.5) | 23 (88.5) | 1 |
| Almitrine | 29 (58) | 11 (45.8) | 18 (69) | 0.094 |
| COVID-19 therapies | ||||
| Glucocorticoids | 30 (60) | 4 (16.7) | 26 (100) | <0.001 |
| Antiviral | 14 (28) | 11 (45.8) | 3 (11.5) | 0.007 |
| Complications pre-ECMO | ||||
| Renal replacement therapy | 8 (16) | 5 (21) | 3 (11.5) | 0.456 |
| Pulmonary embolism | 15 (30) | 7 (29) | 8 (31) | 0.902 |
| Pneumothorax | 5 (10) | 0 (0) | 5 (19.2) | 0.051 |
| Documented bacterial co-infection | 21 (42) | 5 (21) | 16 (61.5) | 0.004 |
| Day 1 Characteristics | Parameters | All Patients (=50) | First Wave Group (=24) | Second Wave Group (=26) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECMO parameters | FmO2 (%) α | 100 (80–100) | 100 (80–100) | 95 (79–100) | 0.648 |
| RPM β | 3600 (3300–4033) | 3500 (3200–4065) | 3600 (3375–4025) | 0.705 | |
| ECMO blood flow (L/min) γ | 5.5 (5–6) | 5.9 (5.5–6.1) | 5.1 (4.8–5.5) | 0.025 | |
| Sweep gaz flow (L/min) δ | 5 (4.3–6) | 6 (4–6) | 5 (4.4–6.3) | 0.336 | |
| Ventilation parameters | FiO2 (%) φ | 50 (40–50) | 50 (40–60) | 50 (40–60) | 0.674 |
| Vt (mL) χ | 250 (180–295) | 280 (240–300) | 230 (180–250) | 0.197 | |
| Vt IBW (mL/kg) ε | 3.6 (2.7–4.3) | 4 (3.5–4.8) | 3.4 (2.4–3.9) | 0.223 | |
| RR (cpm) † | 17 (13–20) | 16 (14–20) | 17 (12–21) | 0.82 | |
| Pplat (cmH2O) # | 24 (20–26) | 25 (22–27) | 23 (20–25) | 0.034 | |
| PEEP (cmH2O) ‡ | 12 (10–14) | 14 (10–16) | 10 (10–12) | 0.007 | |
| Driving Pressure (cmH2O) ¶ | 12 (10–14) | 11 (10–15) | 12 (10–14) | 0.376 | |
| Compliance RS (mL/cm H2O) ¥ | 21 (14–30) | 23 (17–31) | 19 (12–26) | 0.273 | |
| Mechanical Power (J/min) ¤ | 9.4 (6.6–15) | 12 (9–17) | 7.4 (4.4–10) | 0.01 | |
| Biological parameters | pH | 7.4 (7.3–7.5) | 7.4 (7.3–7.5) | 7.4 (7.3–7.5) | 0.836 |
| PaO2 (mmHg) | 75 (65–85) | 76 (67–87) | 73 (65–84) | 0.299 | |
| PaCO2 (mmHg) | 47 (42–55) | 44 (40–50) | 52 (44–59) | 0.016 | |
| Bicarbonates (mmol/L) | 30 (26–34) | 28 (24–32) | 30 (27–35) | 0.089 | |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 8.7 (7.9–9.8) | 8.5 (8–9.7) | 8.7 (7.6–10) | 0.841 | |
| Platelets (109/L) | 234 (162–301) | 245 (178–326) | 202 (156–267) | 0.163 | |
| Fibrinogen (g/L) | 7.1 (5.4–8.2) | 7.9 (6.6–8.7) | 6.1 (4.6–7.6) | 0.002 | |
| aPTT (ratio) | 1.5 (1.2–1.8) | 1.5 (1.2–1.8) | 1.5 (1.2–1.7) | 0.662 | |
| CRP (mg/L) d | 148 (92–252) | 178 (104–329) | 107 (79–176) | 0.025 | |
| PCT (ng/mL) e | 1 (0.3–3.2) | 2.3 (0.6–4.8) | 0.48 (0.2–1.8) | 0.048 |
| Outcomes and Complications under ECMO | All Patients (=50) | First Wave (=24) | Second Wave (=26) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcomes | ||||
| Lenght of stay ICU (days) | 33 (20–60) | 25 (17–42) | 35 (26–71) | 0.055 |
| Lenght of stay Hospital (days) | 33 (21–64) | 26 (19–53) | 40 (26–97) | 0.021 |
| Length of Catecholamines (days) | 14 (7–17) | 8 (6–16) | 15 (9–27) | 0.049 |
| Length of RRT (days) | 0 (0–10) | 5 (0–13) | 0 (0–6.3) | 0.045 |
| Length of Mechanical ventilation (days) | 23 (16–45) | 21 (15–38) | 29 (19–61) | 0.097 |
| ECMO weaning | 20 (40) | 11 (46) | 9 (35) | 0.419 |
| ECMO duration (days) | 12 (7–16) | 11 (6–13) | 14 (8.8–25) | 0.013 |
| Tracheotomy | 16 (32) | 6 (25) | 10 (38) | 0.308 |
| Hospital mortality | 31 (62) | 14 (58) | 17 (65) | 0.608 |
| Complications | ||||
| Ischemic stroke | 2 (4) | 2 (8.3) | 0 (0) | 0.225 |
| Hemorrhagic stroke | 6 (12) | 4 (16.6) | 2 (7.7) | 0.409 |
| RRT | 22 (44) | 15 (62.5) | 7 (26.9) | 0.011 |
| Hemorrhagic—Site canulation | 32 (64) | 12 (50) | 20 (76.9) | 0.048 |
| Hemorrhagic—Other | 33 (66) | 14 (58.3) | 19 (73.1) | 0.272 |
| Thrombotic | 8 (16) | 5 (20.8) | 3 (11.5) | 0.456 |
| Circuit change | 20 (40) | 8 (33.3) | 12 (46.2) | 0.355 |
| Massive Hemolysis | 11 (22.9) | 8 (33.3) | 3 (12.5) | 0.086 |
| Cardiac arrest | 3 (6) | 2 (8.3) | 1 (3.8) | 0.602 |
| Pneumothorax | 7 (14) | 3 (12.5) | 4 (15.4) | 1 |
| Antibiotic-treated blood stream infection | 30 (60) | 11 (45.8) | 19 (73) | 0.049 |
| Antibiotic-treated VAP | 33 (66) | 15 (62.5) | 18 (69.2) | 0.616 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dognon, N.; Gaudet, A.; Parmentier-Decrucq, E.; Normandin, S.; Vincentelli, A.; Moussa, M.; Poissy, J.; Duburcq, T.; Lille Intensive Care COVID-19 Group. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for COVID 2019-Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Comparison between First and Second Waves (Stage 2). J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4839. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214839
Dognon N, Gaudet A, Parmentier-Decrucq E, Normandin S, Vincentelli A, Moussa M, Poissy J, Duburcq T, Lille Intensive Care COVID-19 Group. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for COVID 2019-Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Comparison between First and Second Waves (Stage 2). Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(21):4839. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214839
Chicago/Turabian StyleDognon, Nicolas, Alexandre Gaudet, Erika Parmentier-Decrucq, Sylvain Normandin, André Vincentelli, Mouhamed Moussa, Julien Poissy, Thibault Duburcq, and Lille Intensive Care COVID-19 Group. 2021. "Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for COVID 2019-Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Comparison between First and Second Waves (Stage 2)" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 21: 4839. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214839
APA StyleDognon, N., Gaudet, A., Parmentier-Decrucq, E., Normandin, S., Vincentelli, A., Moussa, M., Poissy, J., Duburcq, T., & Lille Intensive Care COVID-19 Group. (2021). Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for COVID 2019-Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Comparison between First and Second Waves (Stage 2). Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(21), 4839. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214839







