Shaft Fractures in Patients Requiring Primary or Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty Can Be Successfully Treated with Long-Stemmed Implants without Additional Fixation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
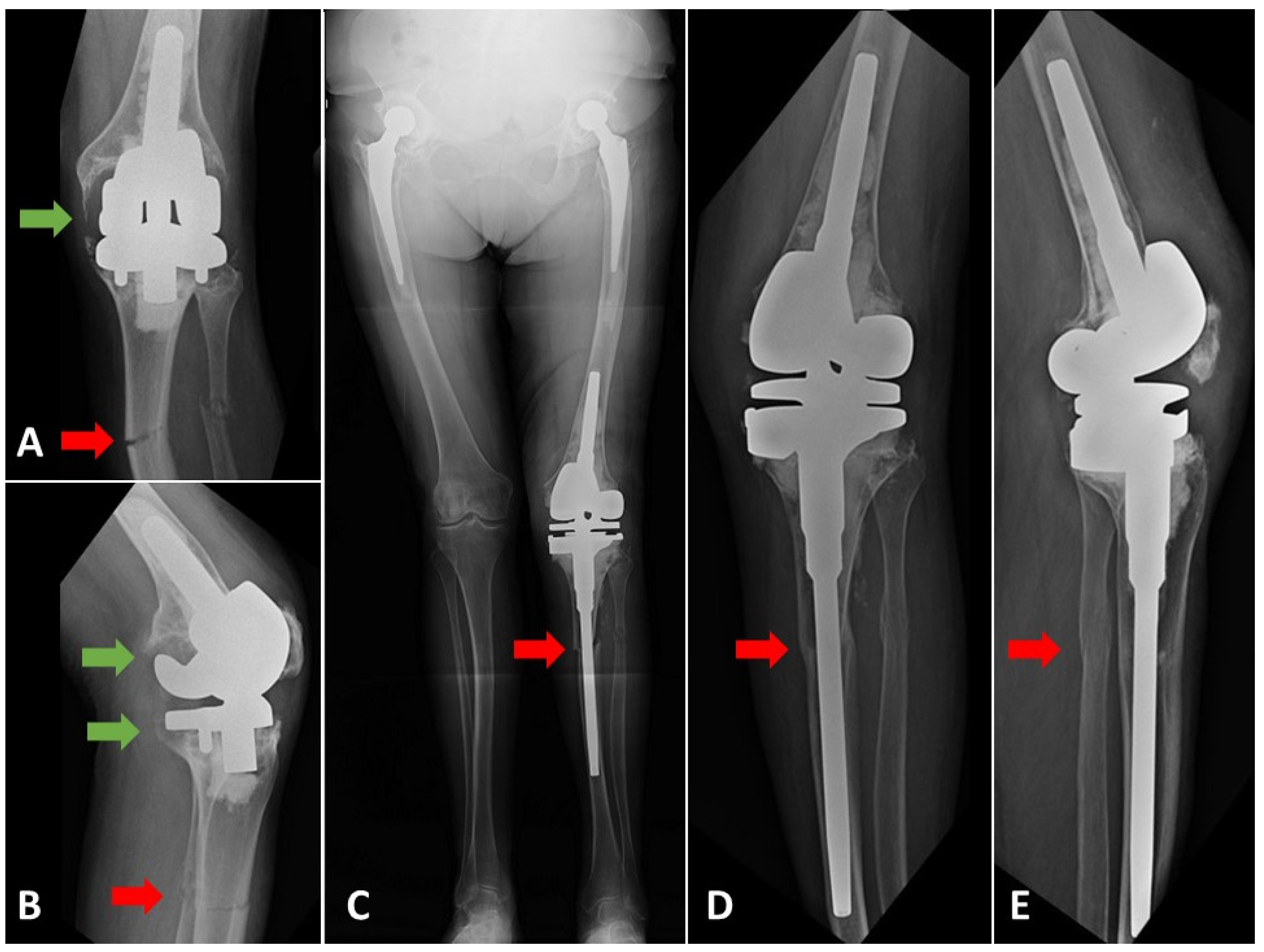
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yoo, J.D.; Kim, N.K. Periprosthetic fractures following total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg. Relat. Res. 2015, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehouse, M.R.; Mehendale, S. Periprosthetic fractures around the knee: Current concepts and advances in management. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2014, 7, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alden, K.J.; Duncan, W.H.; Trousdale, R.T.; Pagnano, M.W.; Haidukewych, G.J. Intraoperative fracture during primary total knee arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canton, G.; Ratti, C.; Fattori, R.; Hoxhaj, B.; Murena, L. Periprosthetic knee fractures. A review of epidemiology, risk factors, diagnosis, management and outcome. Acta Biomed. 2017, 88, 118–128. [Google Scholar]
- Meek, R.M.; Norwood, T.; Smith, R.; Brenkel, I.J.; Howie, C.R. The risk of peri-prosthetic fracture after primary and revision total hip and knee replacement. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2011, 93, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyk, P.R.T.; Watts, E.; Backstein, D. Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty for the Management of Periprosthetic Fractures. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2017, 25, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, A.; Dong, R.J.; Shah, R.; Li, C. Management of periprosthetic fractures of knee arthroplasty with revision surgery. J. Orthop. 2020, 22, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, S.S.; Bechtold, D.; Sassoon, A. Periprosthetic fractures of the distal femur after total knee arthroplasty: Plate versus nail fixation. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2017, 103, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, R.S.; Patel, J.N.; Liporace, F.A. Nail and Plate Combination Fixation for Periprosthetic and Interprosthetic Fractures. J. Orthop. Trauma 2019, 33 (Suppl. 6), S18–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebraheim, N.A.; Carroll, T.; Bonaventura, B.; Moral, M.Z.; Jabaly, Y.G.; Liu, J. Challenge of managing distal femur fractures with long-stemmed total knee implants. Orthop. Surg. 2014, 6, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radke, S.; Radke, J. Total knee arthroplasty in combination with a one-stage tibial osteotomy: A technique for correction of a gonarthrosis with a severe (>15 degrees) tibial extra-articular deformity. J. Arthroplast. 2002, 17, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzelecki, D.; Dudek, P.; Kowalczewski, J.; Marczak, D. Złamanie okołoprotezowe dalszego końca kości udowej po całkowitej alloplastyce stawu kolanowego—Opis przypadku. Chir. Narządów Ruchu Ortop. Pol. 2016, 81, 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Parratte, S.; Ollivier, M.; Argenson, J.N. Primary total knee arthroplasty for acute fracture around the knee. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2018, 104, S71–S80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Chang, M.J.; Kang, S.-B.; Chang, C.B.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, S.A.; Mok, S.J. Management and clinical outcomes of periprosthetic fractures after total knee arthroplasty with a stem extension. Medicine 2019, 98, e16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzelecki, D.; Szneider, J.; Marczak, D.; Kowalczewski, J. Total knee arthroplasty with simultaneous tibial shaft osteotomy in patient with multiple hereditary osteochondromas and multiaxial limb deformity—A case report. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2020, 21, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Koch, P.; Nazarian, S.; Schatzker, J. The Comprehensive Classification of Fractures of Long Bones; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rorabeck, C.H.; Taylor, J.W. Classification of periprosthetic fractures complicating total knee arthroplasty. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 1999, 30, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, N.A.; Stuart, M.J.; Hanssen, A.D. Periprosthetic fractures of the tibia associated with total knee arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1997, 345, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrales, L.A.; Morshed, S.; Bhandari, M.; Miclau, T. Variability in the assessment of fracture-healing in orthopaedic trauma studies. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2008, 90, 1862–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insall, J.N.; Dorr, L.D.; Scott, R.D.; Scott, W.N. Rationale of the Knee Society clinical rating system. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1989, 248, 13–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boureau, F.; Benad, K.; Putman, S.; Dereudre, G.; Kern, G.; Chantelot, C. Does primary total knee arthroplasty for acute knee joint fracture maintain autonomy in the elderly? A retrospective study of 21 cases. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2015, 101, 947–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marczak, D.; Synder, M.; Sibiński, M.; Okoń, T.; Kowalczewski, J. One-stage total knee arthroplasty with pre-existing fracture deformity: Post-fracture total knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2014, 29, 2104–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeney, J.A. Periprosthetic total knee arthroplasty fractures: Revision arthroplasty technique. J. Knee Surg. 2013, 26, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannu, T.S.; Villa, J.M.; Cohen, E.M.; Hayda, R.A.; Higuera, C.A.; Deren, M.E. Periprosthetic Tibial Fractures After Total Knee Arthroplasty: Early and Long-Term Clinical Outcomes. J. Arthroplast. 2021, 36, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, C.; Zaharia, B.; Galliot, F.; Parot, J.; Houfani, F.; Mayer, J.; Mainard, D. Management and results in periprosthetic tibial fracture after total knee arthroplasty: Two-center 15-case retrospective series at 2 years’ follow-up. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2020, 106, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begue, T.; Tricoire, J.-L.; Veillard, D.; Ingels, A.; Thomazeau, H. Periprosthetic fractures around total hip and knee arthroplasty. Therapeutic algorithm for periprosthetic fractures after total knee arthroplasties. Rev. Chir. Orthop. Reparatrice Appar. Mot. 2006, 92 (Suppl. 5), 2S90–2S96. [Google Scholar]
- Quinzi, D.A.; Childs, S.; Lipof, J.; Soin, S.; Ricciardi, B.F. The Treatment of Periprosthetic Distal Femoral Fractures after Total Knee Replacement: A Critical Analysis Review. JBJS Rev. 2020, 8, e2000003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gausden, E.B.; Lim, P.K.; Rabonivich, A.; Shaath, M.K.; Mitchell, P.M.; Hartline, B.; Achor, T.S.; Warner, S.J. Outcomes of periprosthetic distal femur fractures following total knee arthroplasty: Intramedullary nailing versus plating. Injury 2021, 52, 1875–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondalia, V.; Choi, D.H.; Lee, S.C.; Nam, C.H.; Hwang, B.H.; Ahn, H.S.; Ong, A.C.; Park, H.Y.; Jung, K.A. Periprosthetic supracondylar femoral fractures following total knee arthroplasty: Clinical comparison and related complications of the femur plate system and retrograde-inserted supracondylar nail. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 2014, 15, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darrith, B.; Bohl, D.; Karadsheh, M.S.; Sporer, S.M.; Berger, R.A.; Levine, B.R. Periprosthetic Fractures of the Distal Femur: Is Open Reduction and Internal Fixation or Distal Femoral Replacement Superior? J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, 1402–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.-J.; Liu, Y.-J.; Chen, B.-J.; Wang, J.; Niu, C.-L.; Feng, E.-H.; Mai, X.-J.; Huang, Y.-M. Failure of Less-Invasive Stabilization System (LISS) plating for periprosthetic distal femur fractures: Three case reports. Medicine 2020, 99, e19195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohm, E.R.; Tufescu, T.V.; Marsh, J.P. The operative management of osteoporotic fractures of the knee: To fix or replace? J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2012, 94, 1160–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parratte, S.; Bonnevialle, P.; Pietu, G.; Saragaglia, D.; Cherrier, B.; Lafosse, J. Primary total knee arthroplasty in the management of epiphyseal fracture around the knee. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2011, 97 (Suppl. 6), S87–S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, N.; Takai, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Fujiwara, H.; Ohshima, Y.; Hirasawa, Y. Primary total knee arthroplasty for supracondylar/condylar femoral fracture in osteoarthritic knees. J. Arthroplast. 2001, 16, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marczak, D.; Marczak, D.; Kowalczewski, J.; Czubak, J.; Okoń, T.; Synder, M. Short and mid term results of revision total knee arthroplasty with Global Modular Replacement System. Indian J. Orthop. 2017, 51, 324–329. [Google Scholar]
- Tampere, T.; Ollivier, M.; Jacquet, C.; Fabre-Aubrespy, M.; Parratte, S. Knee arthroplasty for acute fractures around the knee. EFORT Open Rev. 2020, 5, 713–723.37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wui, N.B.; Anuar, M.A.A.; Wahid, A.M.A. Short-Term Outcome of Early Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty for Fractures Around the Knee in the Elderly Population: The Experience of a Secondary Healthcare Centre in Malaysia. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 27, 64–71. [Google Scholar]





| Periprosthetic Fractures (n = 12) | Fractures with Knee OA (n = 13) | |
|---|---|---|
| Constrained condylar knee(CCK) | ||
| Triathlon TS (Stryker, Mahwah, NJ, USA) | 5 | 7 |
| PFC Sigma TC3 (DePuy Synthes, Raynham, MA, USA) | 1 | 2 |
| Vanguard 360 (Zimmer Biomet, Warsaw, IN, USA) | 1 | - |
| Scorpio TS (Stryker, Mahwah, NJ, USA) | - | 1 |
| Constrained rotating-hinge(RH) | ||
| MRH (Stryker, Mahwah, NJ, USA) | 5 | 3 |
| Periprosthetic Fractures | Fractures with Knee OA | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. | 12 | 13 | - |
| Gender (M/F) | 1/11 | 1/12 | 0.95 * |
| Age (years) | 74.2 (±7.4) | 69.9 (±8.9) | 0.12 ** |
| Prosthesis type | 0.32 * | ||
| semi-constrained (CCK) | 7 | 10 | |
| constrained (RH) | 5 | 3 | |
| Fracture level (shaft) | 0.07 * | ||
| middle 1/3 femur | 2 | 0 | |
| distal 1/3 femur | 5 | 4 | |
| proximal 1/3 tibia | 3 | 9 | |
| middle 1/3 tibia | 2 | 0 | |
| Type of fracture | 0.06 * | ||
| acute fracture | 6 | 2 | |
| pseudarthrosis | 6 | 11 | |
| Bone union rate | 0.61 * | ||
| total | 11 | 11 | |
| partial | 1 | 1 | |
| non-union | 0 | 1 | |
| Hardware in situ before TKA | 0.89 * | ||
| Yes | 4 | 4 | |
| No | 8 | 9 | |
| Concomitant diseases | |||
| Rheumatoid arthritis | 2 | 1 | 0.59 * |
| Diabetes | 1 | 2 | 0.59 * |
| Stem length (above or below the fracture level) (mm) | |||
| Femur | 109.3 (±31.1) | 123.7 (±55.2) | 0.6 ** |
| Tibia | 124.6 (±24.2) | 125.5 (±22.9) | 0.94 ** |
| Stem diameter (% of filling the medullary canal in the narrowest point) | |||
| Femur | 95.5 (±4.4) | 85 (±14.4) | 0.1 ** |
| Tibia | 93.7 (±10.1) | 90 (±8.4) | 0.46 ** |
| KSS (clinical) | 73.1 (±13.3) | 84.1 (±11) | 0.03 ** |
| KSS (functional) | 59.2 (±18.8) | 76.2 (±20.6) | 0.04 ** |
| ROM (mean, range) | |||
| Extension | 0° | 0.77° (±2.8°) From 0° to −10° | 0.35 ** |
| Flexion | 96.7° (±26°) From 25° to 120° | 93.6° (±26.3°) From 30° to 120° | 0.85 ** |
| Complications | |||
| Surgical site infection | 2 | 1 | 0.59 * |
| Arthrofibrosis | 1 | 1 | 0.95 * |
| Delayed union | 1 | 2 | 0.59 * |
| Non-union | 1 | 0 | 0.33 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grzelecki, D.; Marczak, D.; Kwolek, K.; Dudek, P.; Tyrakowski, M.; Olewnik, Ł.; Czubak-Wrzosek, M.; Kowalczewski, J. Shaft Fractures in Patients Requiring Primary or Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty Can Be Successfully Treated with Long-Stemmed Implants without Additional Fixation. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4926. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214926
Grzelecki D, Marczak D, Kwolek K, Dudek P, Tyrakowski M, Olewnik Ł, Czubak-Wrzosek M, Kowalczewski J. Shaft Fractures in Patients Requiring Primary or Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty Can Be Successfully Treated with Long-Stemmed Implants without Additional Fixation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(21):4926. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214926
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrzelecki, Dariusz, Dariusz Marczak, Kamil Kwolek, Piotr Dudek, Marcin Tyrakowski, Łukasz Olewnik, Maria Czubak-Wrzosek, and Jacek Kowalczewski. 2021. "Shaft Fractures in Patients Requiring Primary or Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty Can Be Successfully Treated with Long-Stemmed Implants without Additional Fixation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 21: 4926. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214926
APA StyleGrzelecki, D., Marczak, D., Kwolek, K., Dudek, P., Tyrakowski, M., Olewnik, Ł., Czubak-Wrzosek, M., & Kowalczewski, J. (2021). Shaft Fractures in Patients Requiring Primary or Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty Can Be Successfully Treated with Long-Stemmed Implants without Additional Fixation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(21), 4926. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214926






