Abstract
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) is a rare thrombotic microangiopathy characterized by microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, severe thrombocytopenia, and ischemic end organ injury due to microvascular platelet-rich thrombi. TTP results from a severe deficiency of the specific von Willebrand factor (VWF)-cleaving protease, ADAMTS13 (a disintegrin and metalloprotease with thrombospondin type 1 repeats, member 13). ADAMTS13 deficiency is most commonly acquired due to anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibodies. It can also be inherited in the congenital form as a result of biallelic mutations in the ADAMTS13 gene. In adults, the condition is most often immune-mediated (iTTP) whereas congenital TTP (cTTP) is often detected in childhood or during pregnancy. iTTP occurs more often in women and is potentially lethal without prompt recognition and treatment. Front-line therapy includes daily plasma exchange with fresh frozen plasma replacement and immunosuppression with corticosteroids. Immunosuppression targeting ADAMTS13 autoantibodies with the humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab is frequently added to the initial therapy. If available, anti-VWF therapy with caplacizumab is also added to the front-line setting. While it is hypothesized that refractory TTP will be less common in the era of caplacizumab, in relapsed or refractory cases cyclosporine A, N-acetylcysteine, bortezomib, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, or splenectomy can be considered. Novel agents, such as recombinant ADAMTS13, are also currently under investigation and show promise for the treatment of TTP. Long-term follow-up after the acute episode is critical to monitor for relapse and to diagnose and manage chronic sequelae of this disease.
Keywords:
thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura; TTP; ADAMTS13; treatment; diagnosis; follow-up; review; caplacizumab 1. Introduction
1.1. History of Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
In 1924, Dr. Eli Moschcowitz described a previously healthy 16-year-old girl who became acutely ill with fever, weakness, focal neurological symptoms, and severe thrombocytopenia. Ultimately, she became comatose and died after one week. Autopsy revealed widely disseminated thrombi in the terminal arterioles and capillaries of various organs but the underlying etiology of this mysterious illness was unknown [1,2]. This poorly understood condition was named thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) by Singer in 1947 [3]. Two decades later, Amorosi and Ultmann introduced the classic diagnostic pentad of TTP consisting of fever, thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia, renal injury, and neurological manifestations. Their case series and review of the literature also highlighted the >90% mortality rate of this devastating condition [4]. Shortly thereafter, case reports detailing the successful treatment of congenital TTP (cTTP) patients with infusions of plasma led to the conclusion that a deficiency of an unknown plasma factor contributed to the disease [5,6]. In 1982, Moake et al. first identified “unusually large” von Willebrand factor (VWF) multimers in the plasma of four chronic relapsing TTP patients—similar to the large multimers synthesized and secreted by human endothelial cells in culture. They hypothesized that these hyperadhesive ultralarge VWF (ULVWF) multimers were due to a suspected deficiency of a VWF depolymerase present in normal plasma [7]. Their hypothesis was reinforced when a highly effective therapy for TTP, plasma exchange, was described in 1991. The treatment of immune-mediated TTP (iTTP) was revolutionized and the mortality rate was improved from >90% to 10–20% with prompt therapy [8]. Five years later, a novel metalloprotease which specifically cleaved ULVWF was purified from human plasma [9,10]. A severe deficiency of this protease was noted in TTP patients, both through acquired autoantibodies and through an inherited deficiency [11,12]. In 2001, this was subsequently identified as ADAMTS13 (a disintegrin and metalloprotease with thrombospondin type 1 motifs, member 13), the only known function of which is to cleave VWF [13,14,15,16,17]. As of 2020, the improved molecular understanding of TTP along with study of survivors have allowed for marked advancements in diagnosis [18], treatment [19,20,21,22], and the long-term management [23,24,25] of these patients.
1.2. Definitions and Terminology
Thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) is a broad term which has both pathologic (occlusive microvascular or macrovascular disease commonly with intraluminal thrombus formation) and clinical (microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (MAHA) with thrombocytopenia) definitions [26,27]. The different entities presenting with TMA findings have historically been difficult to distinguish from one another, but elucidating the pathophysiology of TTP has allowed for more accurate differentiation. As a result, standard definitions and terminology have been adopted [27,28].
TTP is characterized by MAHA with severe thrombocytopenia and variable organ ischemia, most commonly neurologic, cardiac, or renal [3,4,23,29]. The diagnosis is confirmed by a severe deficiency (<10%) of ADAMTS13 activity [11,12,27]. TTP is further divided into two categories based on the mechanism of ADAMTS13 deficiency: congenital (inherited) vs. immune-mediated (acquired). Congenital TTP, also known as Upshaw–Schulman syndrome or hereditary TTP, is defined by a persistent severe deficiency (<10%) in ADAMTS13 caused by biallelic pathogenic mutations in the ADAMTS13 gene [27]. Immune-mediated TTP, sometimes referred to as acquired TTP, is caused by ADAMTS13 deficiency mediated by autoantibodies [12,27]. iTTP is further subdivided into primary iTTP, when there is no obvious associated disorder, and secondary iTTP, when an associated condition can be identified [27].
2. Epidemiology
iTTP typically presents in adulthood, accounting for 90% of cases [29]. The annual incidence is 1.5–6 cases per million per year in adults [29,30,31,32]. Discrepancies in annual incidence rate are likely due to demographic factors in the country of origin. In France and Germany, which are predominantly Caucasian, the incidence is ~1.5 cases per million per year [29,32]. The annual incidence in the U.S. is 2.99 cases per million per year, possibly a result of the higher proportion of African Americans, who have an approximately eightfold-increased incidence rate of TTP [31,33]. In a regional UK registry, the incidence rate was found to be six per million, though this could represent an overestimation as TTP was diagnosed clinically and did not rely on ADAMTS13 measurement in all cases [30].
Childhood-onset iTTP is considerably less common, comprising approximately 10% of all cases [34]. There is a scarcity of data regarding the incidence and prevalence of child and adolescent onset iTTP. The French National TMA Registry estimates the yearly incidence of childhood-onset iTTP to be 0.2 new cases per million with a prevalence of 1 case per million as of December 2015 [34]. This is consistent with the childhood iTTP incidence rate found in the Oklahoma (U.S.) registry of 0.1 cases per million [31].
Women are two to three times more likely to develop iTTP, which is consistent across registries globally [29,30,31,32,34,35,36,37]. ADAMTS13 deficiency is caused by an acquired autoimmune mechanism for the vast majority of TTP cases.
An inherited deficiency of ADAMTS13 due to mutations in the ADAMTS13 gene occurs in approximately 3–5% of patients with TTP [29,30,31,36]. The exact prevalence of cTTP is uncertain, though some experts estimate this to be 0.5–2 cases per million; further investigation is needed [38]. cTTP often presents in childhood prior to 10 years of age [39,40,41,42] but large registries have reported that 10% of cases occur after the age of 40 [40,41,42]. cTTP accounts for a significant proportion of TTP cases in children and obstetrical TTP patients, consisting of 33% and 34% of all cases in those cohorts respectively [29,34].
3. Pathophysiology
3.1. Role of ADAMTS13 and VWF in TTP
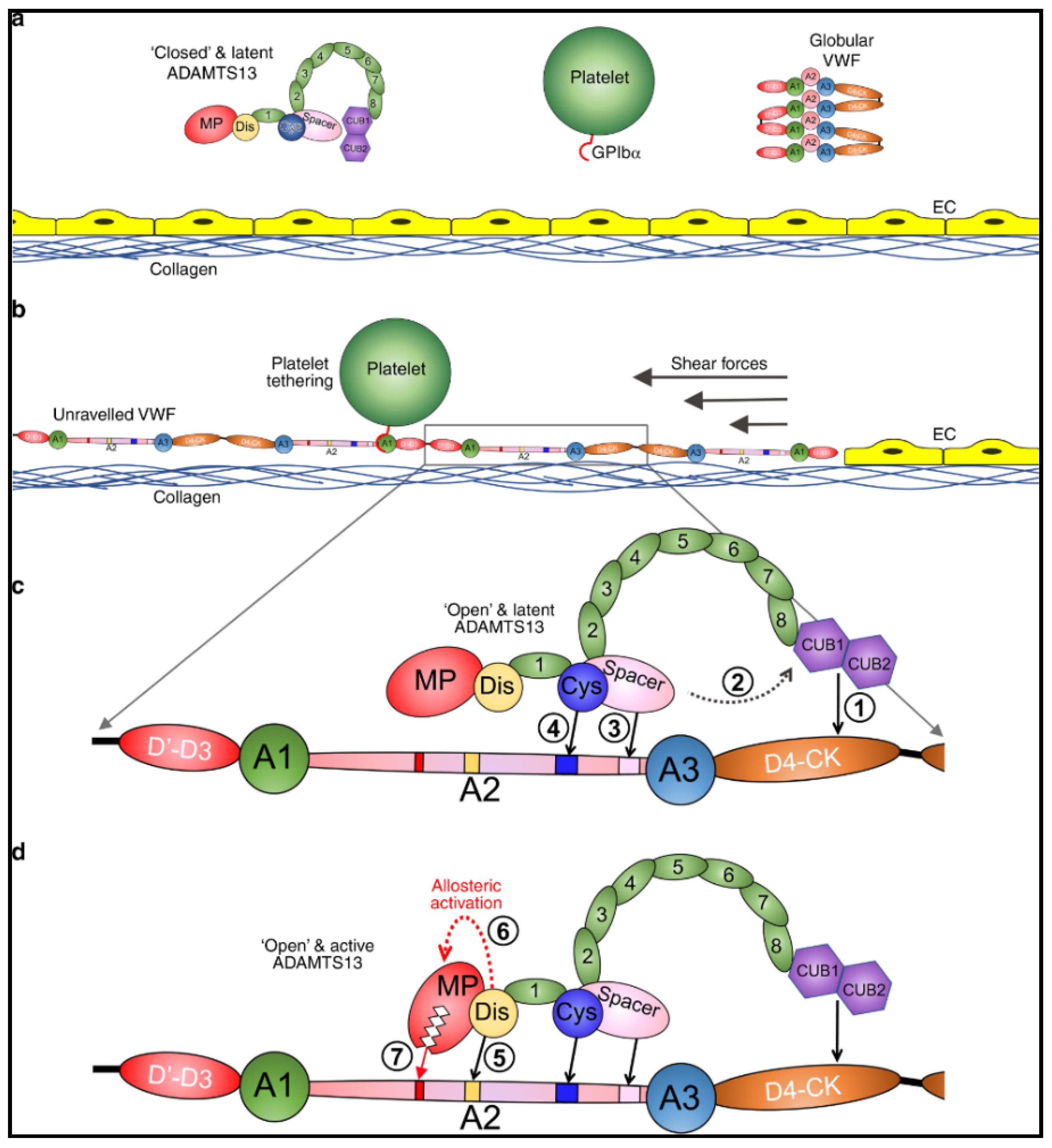
ADAMTS13 is a critically important enzyme, synthesized in hepatic stellate cells [43,44], whose only known function is to regulate VWF multimers [9,10]. In physiologic conditions, ADAMTS13 is in a latent, closed conformation and VWF, secreted by platelets and endothelial cells, is in a globular state (Figure 1a) [45,46]. Proteolytic activity of ADAMTS13 on VWF is dependent on the conformational change of both proteins [45,46,47,48,49,50]. Under shear forces VWF unravels and exposes its A1 domain allowing for interaction with platelets through the GpIb/IX/V complex (Figure 1b) [51,52,53]. In this unraveled state, the A2 domain of VWF is elongated and exposes the ADAMTS13 binding sites [48,50] and the cleavage site Tyr1605-Met1606 [9,10]. Initial interaction of CUB1-2 domains with VWF D4-CK domains allosterically activates ADAMTS13, inducing an open conformation (Figure 1c) [47,49]. Sequential exosite interactions and binding of the disintegrin-like domain of ADAMTS13 to VWF induces further allosteric activation of the metalloprotease domain which results in proteolysis (Figure 1d) [54]. When severe ADAMTS13 deficiency (<10%) is present, ULVWF multimers can accumulate leading to unregulated platelet adhesion and aggregation, resulting in TTP with disseminated microthrombi and organ ischemia [4,7,26].
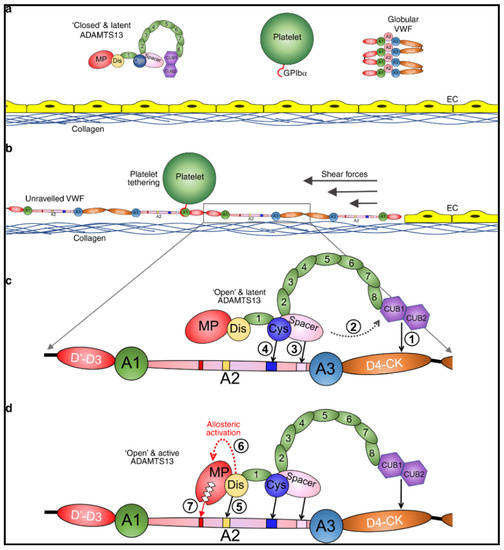
Figure 1.
Mode of action of ADAMTS13. (a) Under normal circumstances, multimeric von Willebrand factor (VWF) circulates in the plasma in a globular conformation, in which its A1 domains are concealed, and so does not interact with platelets. ADAMTS13 circulates in a “closed” conformation stabilized through the interaction of the C-terminal CUB domains with the central Spacer domain. The MP domain of ADAMTS13 also has a latent conformation in which the active site cleft is occluded by the Ca2+-binding loop. This prevents ADAMTS13 from proteolyzing off-target substrates and confers resistance to plasma inhibitors. (b) Following vessel damage, the endothelium (EC) is disrupted to reveal subendothelial collagen. Globular VWF binds to this surface via its A3 domain and unravels into an elongated conformation in response to the shear forces exerted by the flowing blood. This reveals the A1 domain that can then capture platelets via the GPIbα receptor on the platelet surface. Unravelling of VWF also unravels the VWF A2 domain into a linear polypeptide conformation that reveals the binding sites for ADAMTS13 and the Tyr1605-Met1606 cleavage site, making it susceptible to proteolysis by ADAMTS13. (c) ADAMTS13 recognizes unfolded VWF through multiple interactions. (1) The CUB domains bind the VWF D4-CK domains, which (2) induces their dissociation from the Spacer domain. (3) The Spacer and (4) cysteine (Cys)-rich domain exosites recognize the C-terminal region of the unfolded A2 domain to bring the enzyme and substrate into proximity. (d) Once bound, (5) the disintegrin-like (Dis) domain exosite engages VWF residues Asp1614–Asp1622. This interaction (6) induces an allosteric change in the MP domain. This causes a conformational change, disrupting the “gatekeepertriad” that otherwise occludes the active site cleft, to reveal the S1′ pocket. Once allosterically activated, (7) the MP domain proteolyzes the scissile bond. Petri et al. [54], pp. 1–16. The corresponding author, James Crawley agreed to use of the Figure. No changes were made to the original figure. Creative Commons License: http://creativecommons.org/liceses/by/4.0/.
Though a severe ADAMTS13 deficiency is necessary for the development of TTP, enzyme deficiency alone may not be sufficient to induce the clinical syndrome [40,55,56,57,58]. Activation of the complement system has also been suggested to play a role in acute TTP [59,60,61,62]. In fact, ULVWF multimers serve as a scaffold for the assembly and activation of the alternative pathway of the complement system [61]. VWF acts as a cofactor for complement factor I mediated cleavage and inactivation of complement C3b, thereby regulating alternative pathway activation. This regulatory process is dependent on VWF multimer size with the smaller, physiologic VWF multimers enhancing cleavage of C3b and the ULVWF multimers losing this function [62]. Further studies have demonstrated a correlation between the presence of ULVWF multimers and higher levels of sC5b-9, C3a, and C5a [63]. Experimental mouse models have recently demonstrated a synergistic effect of ADAMTS13 deficiency and complement dysregulation. Mice with Adamts13−/− or heterozygous complement factor H (CFH) hyperfunctional mutation (cfhW/R) alone remained asymptomatic. However, mice that were both Adamts13−/− and cfhW/R went on to develop clinical TMA findings [64]. Clinically, complement activation has also been reported to be associated with increased mortality from an acute TTP episode [60]. These and other findings have led to a “second hit” hypothesis, suggesting that another stressor in conjunction with severe deficiency of ADAMTS13 activity is usually required to develop clinical TTP [65,66].
3.2. Congenital ADAMTS13 Deficiency
cTTP (also known as Upshaw–Schulman syndrome OMIM 274150) is an autosomal recessive condition caused by biallelic mutations in the ADAMTS13 gene located on chromosome 9q34 [14]. Approximately 200 causative mutations have been identified in more than 150 patients, which span the entire ADAMTS13 gene [14,39,40,41,42,67,68]. The majority of ADAMTS13 mutations are confined to single families [40,42]. Missense mutations are most common (59%), followed by nonsense mutations (13%), deletions (13%), splice site mutations (9%), and insertions (6%) [67]. There is some geographic variability and certain mutations have increased frequency in different regions. Two mutations in particular, p.R1060W [39,41,42,68,69,70,71,72] and insertion c.4143_4144dupA [42,68,69,73] are more prominent in cTTP patients with European ancestry. The p.R1060W mutation, a single nucleotide variant located on exon 24, also occurred in a high proportion (75–80%) of cTTP patients that presented during pregnancy in the French and UK cohorts [70,71]. Though no definite genotype–phenotype relationships have been established [41,67], earlier onset of disease appears to be related to earlier sequence mutations in the prespacer region of ADAMTS13 [41,72,74]. Often, mutations in ADAMTS13 result in secretion deficiencies but they can also affect ADAMTS13 activity [67,74,75,76]. Indeed, in an effort to explain the variance of clinical phenotype, residual ADAMTS13 activity of different genotypes was measured and the results showed that residual ADAMTS13 activity <3% was correlated with earlier age of disease onset, need for prophylactic plasma infusions, and an annual event rate >1 [42,74]. However, this does not fully explain the phenotypic differences in cTTP as studies have demonstrated that many patients homozygous for the c.4143_4144dupA mutation had ADAMTS13 activity <1% but widely varying clinical courses [42,69,73].
3.3. Acquired ADAMTS13 Deficiency
3.3.1. Risk Factors
iTTP is due to acquired anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibodies [11,12]. Certain factors, such as African ancestry and female sex, predispose to the development of these antibodies [29,30,31,32,33]. Human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DRB1*11 and HLA-DQB*03:01 alleles are also overrepresented in white iTTP patients, with HLA-DRB1*04 having a protective effect [77,78,79,80]. The frequency of the HLA-DRB1*04 allele is dramatically decreased in iTTP patients with African ancestry, indicating that a low natural frequency of this allele may contribute to the greater risk in this population. However, there does not appear to be an increased risk of mortality in these patients [33]. An analysis of Japanese patients identified HLA-DRB1*08:03, HLA-DRB3/4/5*blank, HLA-DQA1*01:03, and HLA-DQB1*06:01 as predisposing factors for iTTP, with HLA-DRB1*15:01 and HLA-DRB5*01:01 being identified as weakly protective [81]. In contrast to white iTTP patients, HLA-DRB1*11 and HLA-DRB1*04 were not associated with iTTP in the Japanese [81].
3.3.2. Anti-ADAMTS13 Autoantibodies
Anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibodies are largely divided into two categories: inhibitory and non-inhibitory. Inhibitory antibodies neutralize the proteolytic activity of ADAMTS13 and non-inhibitory antibodies bind to the protease, accelerating its clearance from plasma [11,12,82,83,84]. It was previously widely held that inhibitory antibodies were the main cause of ADAMTS13 deficiency, but recent studies have demonstrated that antigen depletion also significantly contributes to deficiency [85]. Even a small amount of anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibodies can induce ADAMTS13 deficiency [86]. Anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibodies have been found against all domains of ADAMTS13, indicating a polyclonal immune response. However, the spacer domain of ADAMTS13 has been identified as an immunogenic region, as anti-spacer antibodies are present in most iTTP patients [85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92]. Recently, anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibodies that induce the open conformation of ADAMTS13 have been identified [18,93]. The role these conformation-changing antibodies play in the pathophysiology of TTP and their clinical significance is still being explored.
The most common isotype class of anti-ADAMT13 autoantibodies are IgG, followed by IgA and IgM (20% of cases). Among the IgG isotype, the IgG4 subclass is most common, followed by IgG1 [83,91,94,95,96,97,98]. During acute episodes of iTTP, approximately 75% of cases have detectable free anti-ADAMTS13 IgG [29]. The anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibody isotype may contribute to the severity of the disease phenotype. High IgA antibody titers were suggested to be associated with lower platelet counts, increased mortality, and a worse prognosis [94,95,96]. Though no bacterial or viral infections are known to directly lead to iTTP, molecular mimicry between ADAMTS13 and certain pathogens such as influenza A [99], Helicobacter pylori [100], Legionella [101], hepatitis C virus [102], and HIV [103] may evoke an immune response [91,104].
3.3.3. Immune Complexes
In addition to free anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibodies, immune complexes containing ADAMTS13 have also been found in 39–93% of patients during acute iTTP [105,106,107]. Given that C3a and C5a are elevated during the acute iTTP episode, this could suggest that the complement is activated through the classic pathway, via ADAMTS13 antigen-antibody immune complexes; the elevated levels of factor Bb, however, suggest activation of the alternative pathway [60,63,104,105,108]. The clinical significance of complement activation in TTP is still unclear, though it further supports the “second hit” hypothesis that another physiologic stressor in conjunction with severe ADAMTS13 deficiency is required to induce the clinical syndrome [65,66].
3.3.4. Primary and Secondary iTTP
iTTP is classified as primary when no obvious underlying associated disease can be determined and as secondary when a defined underlying disorder is identified [27]. The majority of iTTP cases are primary. Secondary iTTP can be associated with infections as mentioned previously, though the best evidence is its association with HIV [103,109,110]. Acute stressors, such as pancreatitis, may induce secondary iTTP [111]. Many drugs have also been implicated in secondary TMA but are only rarely accompanied by ADAMTS13 deficiency, indicating that they mostly represent a separate drug-induced TMA (DI-TMA) and not TTP [112]. One exception is ticlopidine, which has been associated with severely deficient ADAMTS13 and this condition may be considered as secondary iTTP [113]. Notably, not all thienopyridine-derivatives (ticlopidine, clopidogrel, and prasugrel) are associated with TTP. Of 97 cases of TMA associated with ticlopidine, 80% had severely deficient ADAMT13 activity confirming the diagnosis of TTP. A clear causal relationship, however, has not been confirmed between the use of ticlopidine and the development of anti-ADAMTS13 antibodies. In 197 patients with clopidogrel associated TMA, 0% had severely deficient ADAMTS13 [114], which is consistent with DI-TMA, not TTP. Secondary iTTP can also be associated with various autoimmune conditions, though it is most commonly associated with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) [23,24,115,116,117]. In either primary or secondary iTTP, prompt therapy is essential. Secondary iTTP typically also requires treatment of the underlying condition in addition to standard TTP therapies.
4. Diagnosis
4.1. Clinical Presentation
Previously, TTP was defined by a clinical “pentad” consisting of fever, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, neurological deficits, and renal insufficiency [4]. However, the pentad was reported at a time before the effectiveness of plasma-based therapy in treating TTP was firmly established. Today, the presence of thrombocytopenia and MAHA alone, without an alternative explanation, should prompt serious consideration of the diagnosis of TTP or another TMA. Large cohort studies from various registries worldwide indicate that less than 10% of patients with acute TTP present with all five symptoms [29,30,31,35,36,37]. In fact, the clinical features of acute TTP can be extraordinarily diverse and a high degree of suspicion is required to diagnose TTP and promptly initiate appropriate management [118]. The differential diagnosis for patients with possible TTP is broad and described in Table 1. In obstetric patients with TMA, hemolysis, elevated liver enzyme, and low platelet (HELLP) syndrome and preeclampsia should be ruled out prior to evaluating for other conditions such as iTTP, cTTP, or complement-mediated hemolytic-uremic syndrome (CM-HUS) [27,112,119].

Table 1.
Differential diagnosis for patients presenting with MAHA-T [27,112].
Acute TTP almost uniformly presents with severe thrombocytopenia (typically <30 × 109/L) and microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, often with evidence of erythrocyte fragmentation on the peripheral blood smear [119]. Frequently, other classical parameters of hemolysis are also present, including an undetectable haptoglobin concentration accompanied by an elevated reticulocyte count, elevated total bilirubin (predominantly unconjugated), and an elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level, a marker for both red cell destruction and organ ischemia [120]. Coombs’ testing is usually negative and coagulation parameters are not severely deranged in TTP.
Signs and symptoms of organ ischemia due to microthrombi formation are variable at presentation. More than 60% of patients have neurological manifestations which range broadly from mild confusion or altered sensorium to stroke, seizures, or coma [25,29,30,36,37]. Gastrointestinal ischemia is present in 35% of patients and can result in abdominal pain, nausea, and diarrhea [29]. Evidence of myocardial ischemia is present in a quarter of acute TTP patients and can be characterized by an abnormal electrocardiogram, or more commonly, elevated cardiac troponin-I measurements. Cardiac symptoms consistent with congestive heart failure or myocardial infarction can also be seen [121]. Renal injury is not uncommon in TTP, though acute renal failure requiring renal replacement therapy is quite rare in iTTP. Hematuria and proteinuria are the most commonly seen renal manifestations. Though modest renal insufficiency may occur, most patients present with a creatinine below 2 mg/dL [122,123,124,125]. Severely deficient ADAMTS13 activity serves to confirm the diagnosis of TTP [11,12,27].
4.2. ADAMTS13 Investigation
4.2.1. ADAMTS13 Activity
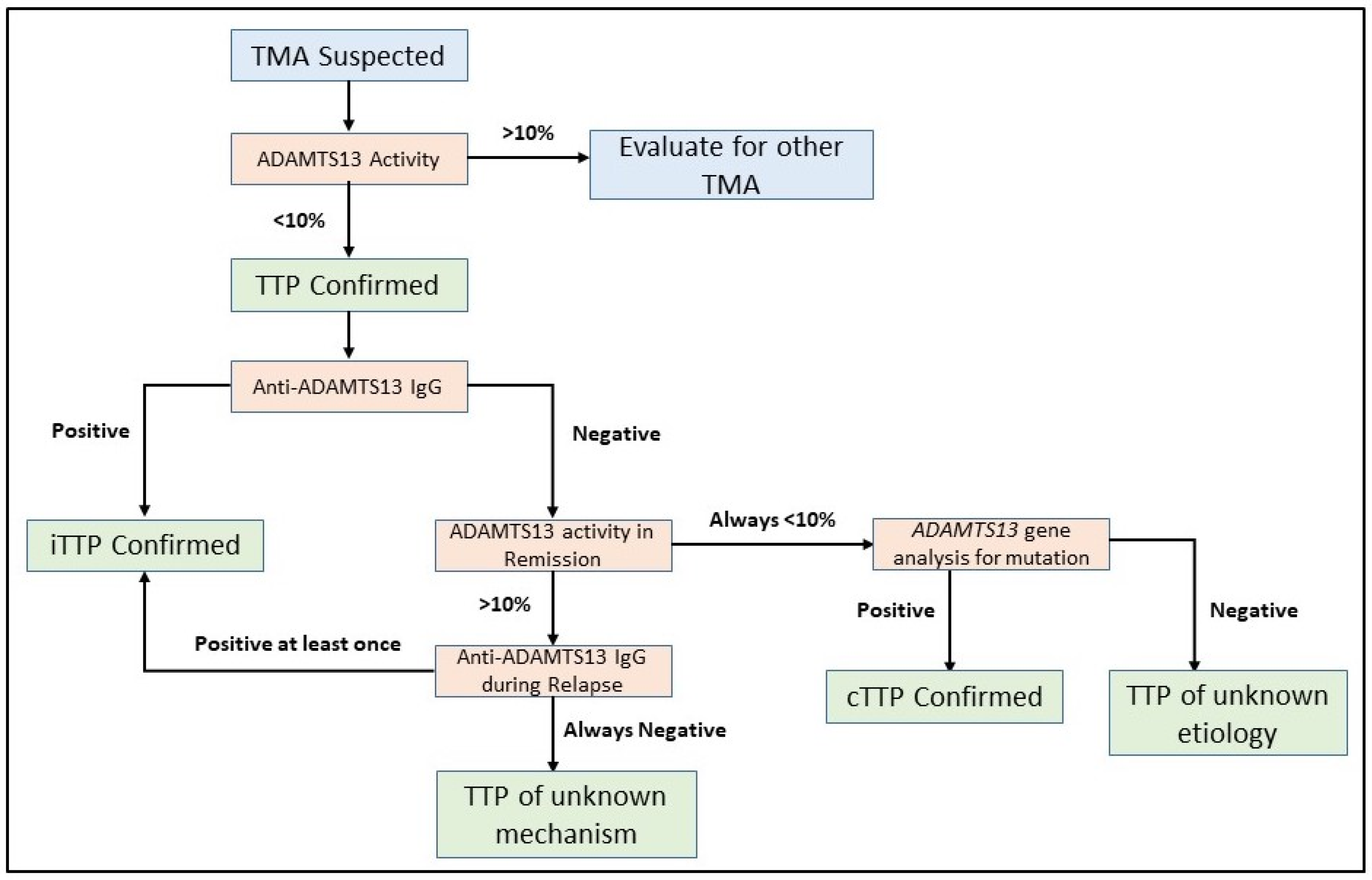
Assaying the ADAMTS13 activity is the first test which should be undertaken in patients with a suspected TMA. Severe ADAMTS13 deficiency, which is defined by an activity level <10%, is required to confirm the diagnosis of TTP (Figure 2) [119]. ADAMTS13 activity assays are based on degradation of either full-length VWF or synthetic peptides of VWF by ADAMTS13 in the plasma sample being tested. VWF cleavage products are detected by fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRETS), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs), surface-enhanced laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight (SELDI-TOF)-mass spectrometry, electrophoresis, reduced collagen binding, or reduced ristocetin-induced platelet agglutination [11,12,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133]. Though multiple assays have been developed, the FRETS-VWF73-based assay [128,134] is most commonly used in clinical settings [135] and is considered as the reference method for ADAMTS13 activity, typically calibrated against the World Health Organization International Standard ADAMTS13 plasma (normal 100%) [136]. However, ADAMTS13 activity testing is labor intensive, time consuming, and limited to reference laboratories typically. Though the FRETS assay can be completed quickly, the turnaround time for results can be three to six days as it is typically performed only in reference centers. Given the variability in ADAMTS13 testing turnaround time for any individual center, point-based scoring systems which predict the probability of severely deficient ADAMTS13 have been developed to avoid delays in prompt treatment initiation [122,137,138]. Importantly, these scores are not meant to replace ADAMTS13 testing but to aid decision making until test results are available. Recently, fully automated chemiluminescence immunoassays have been developed with drastically reduced analytical times of approximately 30 min [139,140]. In addition, a semiquantitative ADAMTS13 activity assay has also been developed which provides an easily interpreted four-level indicator of ADAMTS13 activity, allowing identification of activity levels < 10% [141]. A potential advantage of such an assay is rapid screening for severely deficient ADAMTS13 activity which can be utilized at non-specialized centers to facilitate referral to tertiary centers for additional testing and management.
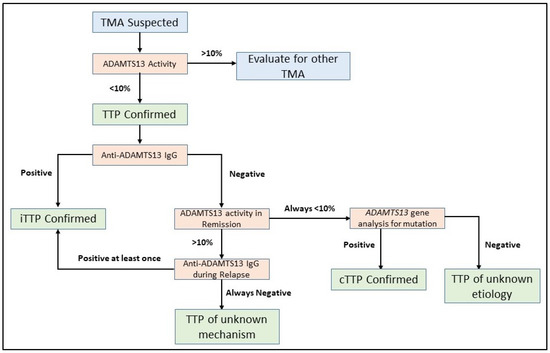
Figure 2.
Flowchart for ADAMTS13 investigation in TTP. Severely deficient ADAMTS13 activity of <10% is required to establish a diagnosis of TTP. Further investigation of anti-ADAMTS13 IgG inhibitory autoantibodies are required to document the mechanism of ADAMTS13 deficiency. ADAMTS13 gene analysis for biallelic mutations is reserved for selected situations to confirm a diagnosis of cTTP. In some cases, the underlying mechanism of ADAMTS13 activity deficiency is not immediately clear and repeated measurements of ADAMTS13 activity in remission and anti-ADAMTS13 IgG during relapse events can help establish a diagnosis.
4.2.2. Anti-ADAMTS13 Autoantibodies
When severely deficient ADAMTS13 activity is confirmed, the next step of investigation is to determine if an antibody inhibitor to ADAMTS13 is present [11,12]. Understanding the mechanism of ADAMTS13 deficiency is critical in differentiating iTTP from cTTP and has important treatment implications. This distinction is also especially important in children and obstetrical patients, owing to higher rates of cTTP in these cohorts [29,34,71]. ADAMTS13 autoantibodies, predominantly anti-ADAMTS13 IgG, can be readily detected using in-house or commercial ELISA kits by laboratories [83,94]. A Bethesda assay can only detect ADAMTS13 autoantibodies which functionally inhibit ADAMTS13 (inhibitory antibodies), unlike the anti-ADAMTS13 IgG ELISA which can detect both inhibitory and non-inhibitory antibodies [25,142]. For both inhibitory and non-inhibitory anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibodies, assays only detect free autoantibodies whereas those bound to ADAMTS13 (immune complexes) are not detected by standard assays. In patients who have persistent severe ADAMTS13 deficiency during periods of remission and in whom no inhibitory autoantibody is detected, ADAMTS13 gene analysis should be pursued to confirm a diagnosis of cTTP [38].
4.2.3. ADAMTS13 Antigen
ADAMTS13 antigen can be measured by ELISA but this is not yet part of routine clinical practice. A recent study evaluated the prognostic value of anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibody titers and antigen levels in patients with iTTP [143]. Patients in the lowest quartile, with an antigen level <1.5%, had a mortality rate of 18% compared with a mortality rate of ~4% for those in the highest quartile, with an antigen level >11%. Those in the lowest antigen quartile and the highest antibody quartile had the highest mortality rate of 27%. This suggests that there could be some prognostic value for this test and that it has the potential to be incorporated in clinical practice in the future.
4.3. Emerging Biomarkers
It has previously been demonstrated that ADAMTS13 circulates in the “open” conformation in iTTP patients during the acute phase [93]. Recently, anti-ADAMT13 autoantibodies were revealed to induce the open ADAMTS13 conformation. Additionally, the open ADAMTS13 conformation preceded significant decrement in ADAMTS13 activity in one patient followed longitudinally [18]. While these findings warrant further study, there are many potentially important implications with regard to treatment and long term follow-up. As discussed previously, though it is a major risk factor, not all patients who have undetectable ADAMTS13 activity in remission uniformly go on to relapse [55,56,58,144]. However, being able to identify the open versus closed conformation of ADAMTS13 may potentially be useful to decide on the necessity of prophylactic therapy in select iTTP patients during remission.
5. Acute Management
TTP is a clinical emergency and in patients with suspected TTP treatment should be initiated promptly as delays in therapy may result in significant morbidity and mortality. Often therapy decisions are required prior to the availability of confirmatory ADAMTS13 testing. A blood sample for ADAMTS13 activity testing should immediately be obtained from a patient with TMA and frontline therapy can then commence based on clinical presentation alone. Severe ADAMTS13 deficiency is still required to confirm the diagnosis but should not delay the initiation of treatment [145]. Below are definitions of treatment response from the International Working Group for Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura [27]:
- Clinical response—a normalization of the platelet count to a level greater than the lower limit of the established reference range (150 × 109/L) and the LDH level to <1.5 × the upper limit of normal (ULN). If initial presentation is severe with evidence of significant end-organ damage, stabilization of these parameters with improvement in function should also be required to qualify for a clinical response.
- Clinical remission—a sustained clinical response which is maintained for >30 days after the cessation of plasma exchange.
- Exacerbation—a decreasing platelet count with rising LDH and the need to restart plasma exchange therapy within 30 days of cessation after an initial clinical response is noted.
- Relapse—a fall in platelet count below the lower limit of the established reference range (~150 × 109/L), with or without clinical symptoms, during a clinical remission that requires reinitiating therapy. ADAMTS13 activity will most likely be <10%.
- Refractory TTP—persistent thrombocytopenia (platelet count <50 × 109/L, without increment) and persistently elevated LDH (>1.5 × ULN) despite five plasma exchange treatments in conjunction with adequate steroid treatment. If platelet count remains <30 × 109/L, this is classified as severe refractory TTP.
5.1. iTTP
Patients with both primary and secondary iTTP should be treated similarly in the acute inpatient setting. Importantly, patients with secondary iTTP should also have the underlying etiology managed appropriately in addition to the acute iTTP event. For example, in a patient with secondary iTTP due to underlying HIV infection, appropriate antiretroviral therapy would also be warranted in addition to management of TTP.
5.1.1. Plasma Exchange
Therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE) with fresh frozen plasma (FFP) replacement is the foundation of front-line therapy for TTP [8]. The proposed mechanism of TPE is that it supplies adequate levels of ADAMTS13 while removing circulating anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibodies. Delays in therapy can lead to early mortality, which may be preventable with prompt initiation of TPE [146]. Typically 1–1.5× plasma volume exchange is performed for the first three days, followed by 1× plasma volume exchange each day thereafter [8]. While there is no optimal duration of therapy or pre-specified number of procedures required, therapy should be continued daily until clinical response is achieved and sustained for two days. In patients with refractory TTP or evidence of progressive end organ damage, more intensive therapy, such as twice daily TPE, may be considered [147]. The efficacy of this approach is difficult to determine as it is usually accompanied by the addition or intensification of concurrent therapies. Generally, there are no significant differences between readily available therapeutic plasma replacement products [148,149]. Previously, cryosupernatant plasma devoid of ULVWF multimers was suggested to be more efficacious than fresh frozen plasma [150], but equivalency of these plasma products was demonstrated in a small randomized controlled trial [151].
5.1.2. Immune Suppression
In conjunction with TPE, immunosuppressive therapy is a cornerstone of acute iTTP management. The general principle of therapy is to target antibody production to allow for recovery of circulating levels of ADAMTS13. Therapy is typically started concurrently with TPE.
Glucocorticoids: steroids are widely used in conjunction with TPE at the initiation of therapy for acute iTTP. Though there are no randomized clinical trials comparing TPE with steroids vs. TPE alone, there is high biological plausibility for concurrent immunosuppression given the autoimmune nature of the condition. A small prospective randomized controlled trial comparing prednisone with cyclosporine A as an adjunct to TPE demonstrated that prednisone was superior in the initial treatment of iTTP [152]. This is also the only prospective randomized trial confirming the efficacy of steroids in the acute setting in decreasing anti-ADAMTS13 IgG and thereby increasing ADAMTS13 activity. No optimal dose or route of administration has been identified. High dose pulse steroids with methylprednisolone 10 mg/kg/day for three days followed by 2.5 mg/kg/day thereafter may be more efficacious than 1 mg/kg/day dosing [153]. Most standards of practice recommend oral prednisone 1 mg/kg/day or equivalent [149], gradually tapered over 3–4 weeks after clinical response is achieved. In patients with severe presentations or neurological symptoms, intravenous methylprednisolone 1 g/day for three days can be considered.
Rituximab: rituximab is a monoclonal antibody against CD20, specifically targeting B-cells. Rituximab is given most commonly during the acute phase of iTTP, typically during the first days of hospitalization or shortly thereafter. A non-randomized prospective phase 2 trial has shown its safety and efficacy in the front-line setting [154]. Additionally, this trial and many observational cohort studies suggest that rituximab given in the acute phase results in fewer relapses [20,154,155,156,157]. While a lower relapse rate did not reach statistical significance in all studies [158,159], a recent meta-analysis shows that rituximab administered during an acute iTTP episode not only lowers the relapse rate vs. control, but also reduces mortality [160]. Rituximab also appears to be effective in patients with refractory TTP or poor response to TPE [20,157,158]. The standard dosing for rituximab is 375 mg/m2 given weekly for a total of four doses, which is recommended for both initial iTTP episodes and the acute phase of relapsing episodes. Emerging evidence for the efficacy of low dose rituximab (100 mg–200 mg/per dose) comes from a small prospective trial [161] and retrospective studies [162] but it has not yet been widely incorporated into standard practice.
Alternative immunosuppressive therapies: in patients with contraindications to steroids or with refractory disease, cyclosporine A can be effective [19,163]. Mycophenolate mofetil has also been used with success in some case reports [164,165]. Prior to the use of rituximab, vincristine was used for refractory disease, but this is no longer preferred [166]. Bortezomib, a proteasome inhibitor targeting plasma cells, has been used successfully as an alternative agent to rituximab [167,168]. Cyclophosphamide and/or splenectomy are also options for refractory or chronically relapsing cases [169].
5.1.3. Anti-VWF Strategy
Caplacizumab: caplacizumab, a humanized immunoglobulin originally from llamas, targeting the A1 domain of VWF and thereby preventing its interaction with platelets is the first medication approved specifically to treat TTP. In the recent phase 2 TITAN [21] and phase 3 HERCULES [22] trials, caplacizumab along with TPE and immunosuppression significantly reduced time to platelet count normalization and the exacerbation rate when compared with placebo. The initial dose is 10 mg given intravenously prior to the first TPE, followed by 10 mg daily and subcutaneously thereafter. Caplacizumab is well tolerated and has a good safety profile with the most common side effect being minor bleeding, which is often easily managed [170]. By blocking microvascular thrombi formation it is hypothesized that tissue ischemia can be decreased. Caplacizumab effectively blocks the end-organ damage caused by TTP; however, concomitant immunosuppression is required as the underlying deficient ADAMTS13 function is not addressed by this therapy. It is unsurprising then that exacerbations and early relapses can occur when the drug is discontinued while ADAMTS13 activity remains severely deficient. As a result, treatment is typically continued until the recovery of ADAMTS13 activity. As a novel agent, one limitation of incorporating caplacizumab into current standard practice is its high cost. At its current price level (in the United States) as of 2020, a recent analysis suggested that the addition of caplacizumab to the front line treatment for all patients with iTTP would not be cost-effective [171]. As caplacizumab is increasingly utilized, treatment response definitions may need to be revisited in the future as platelet count alone may not be an accurate measure of disease activity.
N-acetylcysteine: N-acetylcysteine (NAC) is a mucolytic approved by the Food and Drug Administration which is predominantly used to treat lung diseases. Its efficacy in TTP has been examined given that VWF multimers polymerize in a similar manner to mucins. NAC was found to degrade ULVWF multimer strings and inhibited VWF-dependent platelet aggregation and collagen binding in vitro [172,173]. NAC has been effective in some cases of severe and refractory iTTP but only a few case reports exist to date [174,175]. Animal models examining NAC have produced mixed results. NAC was able to prevent iTTP in mice but NAC administration was not successful in resolving TTP in either mice or baboons [176].
Emerging anti-VWF therapies: in 2012, ARC1779, a nucleic acid macromolecule, or aptamer, that blocks platelet binding by the A1 domain of VWF, was evaluated in TTP patients in a small trial [177]. Nine patients were recruited to the study, seven of whom received ARC1779. The study was halted for financial reasons before sufficient patients could be enrolled to ascertain the efficacy but there were no bleeding complications, despite ARC1779 suppression of VWF function in patients with severe thrombocytopenia. Development of ARC1779 has not been continued, but the safety profile from this trial encouraged the development of second generation anti-VWF aptamers. A novel DNA aptamer, TAGX-0004, showed a stronger ability to inhibit ristocetin- or botrocetin-induced platelet agglutination/aggregation than ARC1779 and a similar inhibitory effect to caplacizumab [178]. Another synthetic aptamer, BT200, has shown inhibition of human VWF in vitro and prevented arterial thrombosis in non-human primates [179]. Further studies incorporating this approach are in development.
5.2. cTTP
Acute episodes in patients with known cTTP can be successfully treated with plasma infusions (FFP, 10–15 mL/kg/day). Treatment is continued until clinical response is achieved [38,41,42]. In patients with a recurring cTTP phenotype, prophylactic plasma infusions may be required. Prophylactic plasma infusions have also been shown to improve chronic symptoms not related to an acute episode [39,41]. In patients who receive chronic plasma infusions, the ADAMTS13 activity half-life has been reported to be 2.5–5.4 days [180,181,182]. Consequently, ADAMTS13 activity is expected to return to baseline activity after approximately 5–10 days. Treatments are usually given every 2–3 weeks, depending on clinical symptoms, platelet counts, and patient preferences [38,41,42,181,182].
5.3. Emerging Therapies
Upfront therapy of TTP has seen innovative strategies in the last five years. Recombinant ADAMTS13 (BAX 930, rADAMTS13) has shown promise in a recent phase 1/2 study in cTTP patients [183]. A phase 3 clinical trial to assess the efficacy of rADAMTS13 for prophylactic and on-demand treatment of cTTP compared to plasma infusion therapy is ongoing (https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT03393975). There is also evidence that rADAMTS13 may be effective in patients with iTTP, a hypothesis that is presently being prospectively studied as well (https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03922308) [184].
With ever growing treatment options for the acute phase of TTP, the classic treatment paradigm is constantly being re-examined. Though TPE is the cornerstone of acute therapy, there are not insignificant risks associated with the procedures required and replacement plasma products [23]. There are an increasing number of case reports detailing treatment of acute iTTP with caplacizumab and immunosuppression, without TPE, in the context of religious beliefs prohibiting blood products [185], shared decision making [186,187], and anaphylaxis to plasma [188]. As novel treatments become readily available, acute TTP management may soon enter an era without obligatory reliance on plasma exchange.
6. Special Populations
6.1. Pregnancy
TTP in the pregnant patient presents many difficulties and challenges. These patients should be managed by a multidisciplinary team typically including hematologists, high-risk obstetricians, and, occasionally, neonatologists. Prompt recognition and differentiation from preeclampsia or HELLP syndrome followed by appropriate treatment is critical, as maternal/fetal morbidity and mortality are high if unrecognized [70]. Pregnancy can trigger acute episodes in cTTP patients who have previously been asymptomatic. Approximately 25–30% of all obstetrical TTP cases were due to cTTP in some cohorts [29,34,71]. Thus, a high suspicion for cTTP is warranted in pregnant patients and appropriate diagnostic workup should be pursued if there is no evidence of an inhibitor or anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibodies. Acute management of cTTP in pregnancy includes plasma infusions but more severe cases may require TPE [38].
In pregnant patients with iTTP, the acute phase should be managed with TPE with the addition of corticosteroids if tolerated [70]. Though corticosteroids may confer some risks if given during the first trimester, these are largely outweighed by the potential benefits in this clinical context. Further immunosuppression with rituximab has not been studied in pregnant iTTP patients and its use is not standard. Routine use of caplacizumab is not recommended given the theoretical risk of fetal hemorrhage.
In remission after an episode during pregnancy, cTTP patients may require prophylactic therapy prior to and during their next pregnancy. The recently published International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH) guidelines for management of TTP state that pregnant cTTP patients should receive prophylactic plasma infusions to prevent relapse [189].
In remission after any acute episode, iTTP patients who are pregnant or could become pregnant should have ADAMTS13 monitored periodically. Severely deficient ADAMTS13 activity in pregnancy appears to uniformly predict relapse of iTTP [190]. Though there is currently a lack of strong evidence, prophylactic therapy for pregnant patients with a history of iTTP and severely deficient ADAMTS13 activity in remission is suggested due to the risk of mortality to both mother and fetus associated with relapse [191]. No standard prophylactic regimen has yet been determined for this indication.
6.2. Jehovah’s Witnesses/Contraindication to Blood Products
Certain groups, including Jehovah’s Witnesses, may not accept exogenous blood products on the basis of religious or other beliefs. As TPE is the foundation of management of acute episodes, this presents a unique challenge in the management of these patients. Various regimens have previously been tried, including vincristine [192] and plasma exchange with albumin [193] or cryosupernatant [194] replacement. With the use of caplacizumab alongside improved immunosuppressive therapy, successful treatment without TPE has been described not only in this patient population [185] but also in other selected patients, including one with anaphylaxis to plasma [186,187,188].
7. Long-Term Follow-Up and Remission Management
TTP was previously thought to only be an acute illness but long-term follow-up of TTP survivors reveals many potential chronic complications and morbidity in addition to the risk of relapse [23,24,195,196,197]. Severely deficient ADAMTS13 activity (<10–20%) in remission suggests an increased risk of relapse and maintaining activity above this level appears adequate to prevent relapse [55,56,198]. Therefore, serial ADAMTS13 activity should be monitored in patients after remission. This is routinely accompanied by a chemistry panel, complete blood count, and measurement of LDH level. After resolution of an acute episode, ADAMTS13 activity can be measured monthly for 3 months, then every 3 months for 1 year, then every 6–12 months if stable. If ADAMTS13 activity consistently decreases, then more frequent monitoring may be appropriate [191]. However, ADAMTS13 activity is not a perfect predictive biomarker and not all patients with severely deficient activity go on to relapse [58]. Further studies highlighting the role of complement activation in the presence of ULVWF multimers suggest that the addition of other biomarkers may more accurately predict relapse in asymptomatic patients [63]. Emerging biomarkers such as the “open” vs. “closed” conformation of ADAMTS13 may also help to better predict which patients with severely deficient activity will ultimately progress to another episode [18,93].
In asymptomatic patients with ADAMTS13 activity persistently <10%, preemptive therapy with rituximab can effectively prevent relapse [144,160,198]. Cyclosporine has also been used for prophylaxis [199] and can be an option for patients who do not respond to rituximab. For the chronically relapsing patient, splenectomy is a viable option. Though falling out of favor with the development of improved immunomodulatory therapy, splenectomy has both a high and a durable response rate in some case series with a 10-year relapse-free survival of 70% [200]. Splenectomy is usually efficacious, with a nonresponse rate as low as 8% in some reports [201]. It has also been shown to induce durable remissions and reduce relapse rate in some of these challenging patients [200,202]. Though previously splenectomy had increased risk for adverse events, especially when used in refractory TTP [203], improvements in surgical technique have decreased complications considerably, especially when laparoscopic technique is utilized [201].
Long-term complications are prevalent in both iTTP and cTTP patients. Many adverse health sequelae are seen in TTP survivors, including higher rates of obesity, stroke, hypertension, mood disorders, cognitive impairment, and reduced quality of life [42,195,196,204,205,206]. TTP survivors also appear to have a higher all-cause mortality than reference populations [24,197]. Low-normal levels of ADAMTS13 activity have recently been implicated as a risk factor for coronary artery disease [207,208], stroke [209], and all-cause/cardiovascular mortality [210] in the general population. While the mechanism for the development of these complications is not known, reduced ADAMTS13 activity may contribute to cardiovascular risk. Further studies investigating this relationship as well as other potential mechanisms leading to the development of these chronic complications are warranted.
8. Conclusions/Summary
TTP is a life-threatening illness which requires prompt recognition and management given its high mortality if left untreated. Acute management and long-term follow-up are evolving as new therapies and potential biomarkers emerge. Given the rarity of this disease, TTP registries and multicenter cohort studies are critical to continue advancing the field.
Author Contributions
S.S. conducted the literature review and drafted the manuscript. B.L. critically reviewed and edited the manuscript. S.R.C. critically reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This review article received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
S.S. has no conflict of interest; B.L. is chairman of the Data Safety Monitoring Committees for studies on recombinant ADAMTS13 in congenital and acquired TTP (now run by Takeda); he is on the Advisory Board of Sanofi for the development of caplacizumab for acquired TTP; he received congress travel support and/or lecture fees from Ablynx, Alexion, Siemens, Bayer, Roche, and Sanofi; S.R.C. has received research funding and consulting/speaking fees from Sanofi-Genzyme and Takeda.
References
- Moschcowitz, E. Hyaline Thrombosis of the Terminal Arterioles and Capillaries: A Hitherto Undescribed Disease. Proc. N. Y. Pathol. Soc. 1924, 24, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Moschowitz, E. An acute febrile pleiochromic anemia with hyaline thrombosis of the terminal arterioles and capillaries: An undescribed disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 1925, 36, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, K.; Bornstein, F.P.; Wile, S.A. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura; hemorrhagic diathesis with generalized platelet thromboses. Blood 1947, 2, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amorosi, E.L.; Ultmann, J.E. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Pupura: Report of 16 cases and Review of the Literature. Medicine 1966, 45, 139–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrnes, J.J.; Khurana, M. Treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura with plasma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1977, 297, 1386–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upshaw, J.D. Congenital deficiency of a factor in normal plasma that reverses microangiopathic hemolysis and thrombocytopenia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1978, 298, 1350–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moake, J.L.; Rudy, C.K.; Troll, J.H.; Weinstein, M.J.; Colannino, N.M.; Azocar, J.; Seder, R.H.; Hong, S.L.; Deykin, D. Unusually large plasma factor VIII:von Willebrand factor multimers in chronic relapsing thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N. Engl. J. Med. 1982, 307, 1432–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, G.A.; Shumak, K.H.; Buskard, N.A.; Blanchette, V.S.; Kelton, J.G.; Nair, R.C.; Spasoff, R.A. Comparison of plasma exchange with plasma infusion in the treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Canadian Apheresis Study Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, M.; Robles, R.; Lämmle, B. Partial purification and characterization of a protease from human plasma cleaving von Willebrand factor to fragments produced by in vivo proteolysis. Blood 1996, 87, 4223–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.M. Physiologic cleavage of von Willebrand factor by a plasma protease is dependent on its conformation and requires calcium ion. Blood 1996, 87, 4235–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, M.; Robles, R.; Galbusera, M.; Remuzzi, G.; Kyrle, P.A.; Brenner, B.; Krause, M.; Scharrer, I.; Aumann, V.; Mittler, U.; et al. von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and the hemolytic-uremic syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 1578–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, H.M.; Lian, E.C. Antibodies to von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease in acute thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 1585–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soejima, K.; Mimura, N.; Hirashima, M.; Maeda, H.; Hamamoto, T.; Nakagaki, T.; Nozaki, C. A novel human metalloprotease synthesized in the liver and secreted into the blood: Possibly, the von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease? J. Biochem. 2001, 130, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, G.G.; Nichols, W.C.; Lian, E.C.; Foroud, T.; McClintick, J.N.; McGee, B.M.; Yang, A.Y.; Siemieniak, D.R.; Stark, K.R.; Gruppo, R.; et al. Mutations in a member of the ADAMTS gene family cause thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Nature 2001, 413, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerritsen, H.E.; Robles, R.; Lämmle, B.; Furlan, M. Partial amino acid sequence of purified von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease. Blood 2001, 98, 1654–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujikawa, K.; Suzuki, H.; McMullen, B.; Chung, D. Purification of human von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease and its identification as a new member of the metalloproteinase family. Blood 2001, 98, 1662–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Chung, D.; Takayama, T.K.; Majerus, E.M.; Sadler, J.E.; Fujikawa, K. Structure of von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease (ADAMTS13), a metalloprotease involved in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 41059–41063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roose, E.; Schelpe, A.S.; Tellier, E.; Sinkovits, G.; Joly, B.S.; Dekimpe, C.; Kaplanski, G.; Le Besnerais, M.; Mancini, I.; Falter, T.; et al. Open ADAMTS13, induced by antibodies, is a biomarker for subclinical immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2020, 136, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataland, S.R.; Jin, M.; Ferketich, A.K.; Kennedy, M.S.; Kraut, E.H.; George, J.N.; Wu, H.M. An evaluation of cyclosporin and corticosteroids individually as adjuncts to plasma exchange in the treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br. J. Haematol. 2007, 136, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froissart, A.; Buffet, M.; Veyradier, A.; Poullin, P.; Provôt, F.; Malot, S.; Schwarzinger, M.; Galicier, L.; Vanhille, P.; Vernant, J.P.; et al. Efficacy and safety of first-line rituximab in severe, acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura with a suboptimal response to plasma exchange. Experience of the French Thrombotic Microangiopathies Reference Center. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 40, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyvandi, F.; Scully, M.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Cataland, S.; Knöbl, P.; Wu, H.; Artoni, A.; Westwood, J.P.; Mansouri Taleghani, M.; Jilma, B.; et al. Caplacizumab for Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, M.; Cataland, S.R.; Peyvandi, F.; Coppo, P.; Knöbl, P.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Metjian, A.; de la Rubia, J.; Pavenski, K.; Callewaert, F.; et al. Caplacizumab Treatment for Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, E.E.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Terrell, D.R.; Vesely, S.K.; George, J.N. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: Diagnostic criteria, clinical features, and long-term outcomes from 1995 through 2015. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deford, C.C.; Reese, J.A.; Schwartz, L.H.; Perdue, J.J.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Lämmle, B.; Terrell, D.R.; Vesely, S.K.; George, J.N. Multiple major morbidities and increased mortality during long-term follow-up after recovery from thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2013, 122, 2023–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Vesely, S.K.; Terrell, D.R.; Lämmle, B.; George, J.N. Survival and relapse in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2010, 115, 1500–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moake, J.L. Thrombotic microangiopathies. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, M.; Cataland, S.; Coppo, P.; de la Rubia, J.; Friedman, K.D.; Kremer Hovinga, J.; Lämmle, B.; Matsumoto, M.; Pavenski, K.; Sadler, E.; et al. Consensus on the standardization of terminology in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and related thrombotic microangiopathies. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarode, R.; Bandarenko, N.; Brecher, M.E.; Kiss, J.E.; Marques, M.B.; Szczepiorkowski, Z.M.; Winters, J.L. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: 2012 American Society for Apheresis (ASFA) consensus conference on classification, diagnosis, management, and future research. J. Clin. Apher. 2014, 29, 148–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotte, E.; Azoulay, E.; Galicier, L.; Rondeau, E.; Zouiti, F.; Boisseau, P.; Poullin, P.; de Maistre, E.; Provôt, F.; Delmas, Y.; et al. Epidemiology and pathophysiology of adulthood-onset thrombotic microangiopathy with severe ADAMTS13 deficiency (thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura): A cross-sectional analysis of the French national registry for thrombotic microangiopathy. Lancet Haematol. 2016, 3, e237–e245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, M.; Yarranton, H.; Liesner, R.; Cavenagh, J.; Hunt, B.; Benjamin, S.; Bevan, D.; Mackie, I.; Machin, S. Regional UK TTP registry: Correlation with laboratory ADAMTS 13 analysis and clinical features. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 142, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, J.A.; Muthurajah, D.S.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Vesely, S.K.; Terrell, D.R.; George, J.N. Children and adults with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura associated with severe, acquired Adamts13 deficiency: Comparison of incidence, demographic and clinical features. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2013, 60, 1676–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miesbach, W.; Menne, J.; Bommer, M.; Schönermarck, U.; Feldkamp, T.; Nitschke, M.; Westhoff, T.H.; Seibert, F.S.; Woitas, R.; Sousa, R.; et al. Incidence of acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in Germany: A hospital level study. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martino, S.; Jamme, M.; Deligny, C.; Busson, M.; Loiseau, P.; Azoulay, E.; Galicier, L.; Pène, F.; Provôt, F.; Dossier, A.; et al. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura in Black People: Impact of Ethnicity on Survival and Genetic Risk Factors. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joly, B.S.; Stepanian, A.; Leblanc, T.; Hajage, D.; Chambost, H.; Harambat, J.; Fouyssac, F.; Guigonis, V.; Leverger, G.; Ulinski, T.; et al. Child-onset and adolescent-onset acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura with severe ADAMTS13 deficiency: A cohort study of the French national registry for thrombotic microangiopathy. Lancet Haematol. 2016, 3, e537–e546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blombery, P.; Kivivali, L.; Pepperell, D.; McQuilten, Z.; Engelbrecht, S.; Polizzotto, M.N.; Phillips, L.E.; Wood, E.; Cohney, S. Diagnosis and management of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) in Australia: Findings from the first 5 years of the Australian TTP/thrombotic microangiopathy registry. Intern. Med. J. 2016, 46, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, Y.; Matsumoto, M. Registry of 919 patients with thrombotic microangiopathies across Japan: Database of Nara Medical University during 1998–2008. Intern. Med. 2010, 49, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.J.; Chong, S.Y.; Kim, I.H.; Kim, J.H.; Jung, C.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.C.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, J.E.; et al. Clinical features of severe acquired ADAMTS13 deficiency in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: The Korean TTP registry experience. Int. J. Hematol. 2011, 93, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; George, J.N. Hereditary Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1653–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, B.S.; Boisseau, P.; Roose, E.; Stepanian, A.; Biebuyck, N.; Hogan, J.; Provot, F.; Delmas, Y.; Garrec, C.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; et al. ADAMTS13 Gene Mutations Influence ADAMTS13 Conformation and Disease Age-Onset in the French Cohort of Upshaw-Schulman Syndrome. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 118, 1902–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, Y.; Matsumoto, M.; Isonishi, A.; Yagi, H.; Kokame, K.; Soejima, K.; Murata, M.; Miyata, T. Natural history of Upshaw-Schulman syndrome based on ADAMTS13 gene analysis in Japan. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9 (Suppl. 1), 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwan, F.; Vendramin, C.; Liesner, R.; Clark, A.; Lester, W.; Dutt, T.; Thomas, W.; Gooding, R.; Biss, T.; Watson, H.G.; et al. Characterization and treatment of congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2019, 133, 1644–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dorland, H.A.; Taleghani, M.M.; Sakai, K.; Friedman, K.D.; George, J.N.; Hrachovinova, I.; Knöbl, P.N.; von Krogh, A.S.; Schneppenheim, R.; Aebi-Huber, I.; et al. The International Hereditary Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Registry: Key findings at enrollment until 2017. Haematologica 2019, 104, 2107–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Inada, M.; Lee, T.P.; Benten, D.; Lyubsky, S.; Bouhassira, E.E.; Gupta, S.; Tsai, H.M. ADAMTS13 is expressed in hepatic stellate cells. Lab. Investig. 2005, 85, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, M.; Tatsumi, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Fujimoto, M.; Matsuyama, T.; Ishikawa, M.; Iwamoto, T.A.; Mori, T.; Wanaka, A.; Fukui, H.; et al. Localization of ADAMTS13 to the stellate cells of human liver. Blood 2005, 106, 922–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- South, K.; Luken, B.M.; Crawley, J.T.; Phillips, R.; Thomas, M.; Collins, R.F.; Deforche, L.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Lane, D.A. Conformational activation of ADAMTS13. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18578–18583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deforche, L.; Roose, E.; Vandenbulcke, A.; Vandeputte, N.; Feys, H.B.; Springer, T.A.; Mi, L.Z.; Muia, J.; Sadler, J.E.; Soejima, K.; et al. Linker regions and flexibility around the metalloprotease domain account for conformational activation of ADAMTS-13. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 2063–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muia, J.; Zhu, J.; Gupta, G.; Haberichter, S.L.; Friedman, K.D.; Feys, H.B.; Deforche, L.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Westfield, L.A.; Roth, R.; et al. Allosteric activation of ADAMTS13 by von Willebrand factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18584–18589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.F.; Moake, J.L.; Nolasco, L.; Bernardo, A.; Arceneaux, W.; Shrimpton, C.N.; Schade, A.J.; McIntire, L.V.; Fujikawa, K.; López, J.A. ADAMTS-13 rapidly cleaves newly secreted ultralarge von Willebrand factor multimers on the endothelial surface under flowing conditions. Blood 2002, 100, 4033–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanardelli, S.; Chion, A.C.; Groot, E.; Lenting, P.J.; McKinnon, T.A.; Laffan, M.A.; Tseng, M.; Lane, D.A. A novel binding site for ADAMTS13 constitutively exposed on the surface of globular VWF. Blood 2009, 114, 2819–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Halvorsen, K.; Zhang, C.Z.; Wong, W.P.; Springer, T.A. Mechanoenzymatic cleavage of the ultralarge vascular protein von Willebrand factor. Science 2009, 324, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sixma, J.J.; van Zanten, G.H.; Huizinga, E.G.; van der Plas, R.M.; Verkley, M.; Wu, Y.P.; Gros, P.; de Groot, P.G. Platelet adhesion to collagen: An update. Thromb. Haemost. 1997, 78, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savage, B.; Almus-Jacobs, F.; Ruggeri, Z.M. Specific synergy of multiple substrate-receptor interactions in platelet thrombus formation under flow. Cell 1998, 94, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroi, M.; Jung, S.M.; Nomura, S.; Sekiguchi, S.; Ordinas, A.; Diaz-Ricart, M. Analysis of the involvement of the von Willebrand factor-glycoprotein Ib interaction in platelet adhesion to a collagen-coated surface under flow conditions. Blood 1997, 90, 4413–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petri, A.; Kim, H.J.; Xu, Y.; de Groot, R.; Li, C.; Vandenbulcke, A.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Emsley, J.; Crawley, J.T.B. Crystal structure and substrate-induced activation of ADAMTS13. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Casper, T.C.; Cataland, S.R.; Kennedy, M.S.; Lin, S.; Li, Y.J.; Wu, H.M. Relationship between ADAMTS13 activity in clinical remission and the risk of TTP relapse. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 141, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyvandi, F.; Lavoretano, S.; Palla, R.; Feys, H.B.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Battaglioli, T.; Valsecchi, C.; Canciani, M.T.; Fabris, F.; Zver, S.; et al. ADAMTS13 and anti-ADAMTS13 antibodies as markers for recurrence of acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura during remission. Haematologica 2008, 93, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, M.; Lämmle, B. Aetiology and pathogenesis of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and haemolytic uraemic syndrome: The role of von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2001, 14, 437–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, E.E.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Terrell, D.R.; Vesely, S.K.; George, J.N. Clinical importance of ADAMTS13 activity during remission in patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2016, 128, 2175–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réti, M.; Farkas, P.; Csuka, D.; Rázsó, K.; Schlammadinger, Á.; Udvardy, M.L.; Madách, K.; Domján, G.; Bereczki, C.; Reusz, G.S.; et al. Complement activation in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.C.; Yang, S.; Haven, S.; Holers, V.M.; Lundberg, A.S.; Wu, H.; Cataland, S.R. Complement activation and mortality during an acute episode of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 1925–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.; Sartain, S.; Moake, J. Ultralarge von Willebrand factor-induced platelet clumping and activation of the alternative complement pathway in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and the hemolytic-uremic syndromes. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 29, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Liang, X.; Kroll, M.H.; Chung, D.W.; Afshar-Kharghan, V. von Willebrand factor is a cofactor in complement regulation. Blood 2015, 125, 1034–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Jay, L.; Lin, S.; Han, C.; Yang, S.; Cataland, S.R.; Masias, C. Interrelationship between ADAMTS13 activity, von Willebrand factor, and complement activation in remission from immune-mediated trhrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 189, e18–e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Zhang, D.; Cao, W.; Song, W.C.; Zheng, X.L. Synergistic effects of ADAMTS13 deficiency and complement activation in pathogenesis of thrombotic microangiopathy. Blood 2019, 134, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyata, T.; Fan, X. A second hit for TMA. Blood 2012, 120, 1152–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, T.A.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Schatzberg, D.; Wagner, D.D.; Lämmle, B. Circulating DNA and myeloperoxidase indicate disease activity in patients with thrombotic microangiopathies. Blood 2012, 120, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotta, L.A.; Garagiola, I.; Palla, R.; Cairo, A.; Peyvandi, F. ADAMTS13 mutations and polymorphisms in congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Hum. Mutat. 2010, 31, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Heeb, S.R.; Skowronska, M.; Schaller, M. Pathophysiology of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and hemolytic uremic syndrome. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Krogh, A.S.; Quist-Paulsen, P.; Waage, A.; Langseth, Ø.; Thorstensen, K.; Brudevold, R.; Tjønnfjord, G.E.; Largiadèr, C.R.; Lämmle, B.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A. High prevalence of hereditary thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in central Norway: From clinical observation to evidence. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 14, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, M.; Thomas, M.; Underwood, M.; Watson, H.; Langley, K.; Camilleri, R.S.; Clark, A.; Creagh, D.; Rayment, R.; Mcdonald, V.; et al. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and pregnancy: Presentation, management, and subsequent pregnancy outcomes. Blood 2014, 124, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moatti-Cohen, M.; Garrec, C.; Wolf, M.; Boisseau, P.; Galicier, L.; Azoulay, E.; Stepanian, A.; Delmas, Y.; Rondeau, E.; Bezieau, S.; et al. Unexpected frequency of Upshaw-Schulman syndrome in pregnancy-onset thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2012, 119, 5888–5897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri, R.S.; Cohen, H.; Mackie, I.J.; Scully, M.; Starke, R.D.; Crawley, J.T.; Lane, D.A.; Machin, S.J. Prevalence of the ADAMTS-13 missense mutation R1060W in late onset adult thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneppenheim, R.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Becker, T.; Budde, U.; Karpman, D.; Brockhaus, W.; Hrachovinová, I.; Korczowski, B.; Oyen, F.; Rittich, S.; et al. A common origin of the 4143insA ADAMTS13 mutation. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 96, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotta, L.A.; Wu, H.M.; Mackie, I.J.; Noris, M.; Veyradier, A.; Scully, M.A.; Remuzzi, G.; Coppo, P.; Liesner, R.; Donadelli, R.; et al. Residual plasmatic activity of ADAMTS13 is correlated with phenotype severity in congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2012, 120, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokame, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Soejima, K.; Yagi, H.; Ishizashi, H.; Funato, M.; Tamai, H.; Konno, M.; Kamide, K.; Kawano, Y.; et al. Mutations and common polymorphisms in ADAMTS13 gene responsible for von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11902–11907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaimauer, B.; Fuhrmann, J.; Mohr, G.; Wernhart, W.; Bruno, K.; Ferrari, S.; Konetschny, C.; Antoine, G.; Rieger, M.; Scheiflinger, F. Modulation of ADAMTS13 secretion and specific activity by a combination of common amino acid polymorphisms and a missense mutation. Blood 2006, 107, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppo, P.; Busson, M.; Veyradier, A.; Wynckel, A.; Poullin, P.; Azoulay, E.; Galicier, L.; Loiseau, P.; Microangiopathies, F.R.C.F.T. HLA-DRB1*11: A strong risk factor for acquired severe ADAMTS13 deficiency-related idiopathic thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in Caucasians. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 856–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, M.; Brown, J.; Patel, R.; McDonald, V.; Brown, C.J.; Machin, S. Human leukocyte antigen association in idiopathic thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: Evidence for an immunogenetic link. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, M.L.; Hitzler, W.; Scharrer, I. The role of human leukocyte antigens as predisposing and/or protective factors in patients with idiopathic thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Ann. Hematol. 2012, 91, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, I.; Giacomini, E.; Pontiggia, S.; Artoni, A.; Ferrari, B.; Pappalardo, E.; Gualtierotti, R.; Trisolini, S.M.; Capria, S.; Facchini, L.; et al. The HLA Variant rs6903608 Is Associated with Disease Onset and Relapse of Immune-Mediated Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura in Caucasians. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, K.; Kuwana, M.; Tanaka, H.; Hosomichi, K.; Hasegawa, A.; Uyama, H.; Nishio, K.; Omae, T.; Hishizawa, M.; Matsui, M.; et al. HLA loci predisposing to immune TTP in Japanese: Potential role of the shared ADAMTS13 peptide bound to different HLA-DR. Blood 2020, 135, 2413–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheiflinger, F.; Knöbl, P.; Trattner, B.; Plaimauer, B.; Mohr, G.; Dockal, M.; Dorner, F.; Rieger, M. Nonneutralizing IgM and IgG antibodies to von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease (ADAMTS-13) in a patient with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2003, 102, 3241–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieger, M.; Mannucci, P.M.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Herzog, A.; Gerstenbauer, G.; Konetschny, C.; Zimmermann, K.; Scharrer, I.; Peyvandi, F.; Galbusera, M.; et al. ADAMTS13 autoantibodies in patients with thrombotic microangiopathies and other immunomediated diseases. Blood 2005, 106, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feys, H.B.; Liu, F.; Dong, N.; Pareyn, I.; Vauterin, S.; Vandeputte, N.; Noppe, W.; Ruan, C.; Deckmyn, H.; Vanhoorelbeke, K. ADAMTS-13 plasma level determination uncovers antigen absence in acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and ethnic differences. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.R.; de Groot, R.; Scully, M.A.; Crawley, J.T. Pathogenicity of Anti-ADAMTS13 Autoantibodies in Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. EBioMedicine 2015, 2, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luken, B.M.; Turenhout, E.A.; Hulstein, J.J.; Van Mourik, J.A.; Fijnheer, R.; Voorberg, J. The spacer domain of ADAMTS13 contains a major binding site for antibodies in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 93, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soejima, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Kokame, K.; Yagi, H.; Ishizashi, H.; Maeda, H.; Nozaki, C.; Miyata, T.; Fujimura, Y.; Nakagaki, T. ADAMTS-13 cysteine-rich/spacer domains are functionally essential for von Willebrand factor cleavage. Blood 2003, 102, 3232–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaus, C.; Plaimauer, B.; Studt, J.D.; Dorner, F.; Lämmle, B.; Mannucci, P.M.; Scheiflinger, F. Epitope mapping of ADAMTS13 autoantibodies in acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2004, 103, 4514–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.L.; Wu, H.M.; Shang, D.; Falls, E.; Skipwith, C.G.; Cataland, S.R.; Bennett, C.L.; Kwaan, H.C. Multiple domains of ADAMTS13 are targeted by autoantibodies against ADAMTS13 in patients with acquired idiopathic thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Haematologica 2010, 95, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Moriki, T.; Igari, A.; Nakagawa, T.; Wada, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Fujimura, Y.; Murata, M. Epitope analysis of autoantibodies to ADAMTS13 in patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Thromb. Res. 2011, 128, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pos, W.; Sorvillo, N.; Fijnheer, R.; Feys, H.B.; Kaijen, P.H.; Vidarsson, G.; Voorberg, J. Residues Arg568 and Phe592 contribute to an antigenic surface for anti-ADAMTS13 antibodies in the spacer domain. Haematologica 2011, 96, 1670–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grillberger, R.; Casina, V.C.; Turecek, P.L.; Zheng, X.L.; Rottensteiner, H.; Scheiflinger, F. Anti-ADAMTS13 IgG autoantibodies present in healthy individuals share linear epitopes with those in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Haematologica 2014, 99, e58–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roose, E.; Schelpe, A.S.; Joly, B.S.; Peetermans, M.; Verhamme, P.; Voorberg, J.; Greinacher, A.; Deckmyn, H.; De Meyer, S.F.; Coppo, P.; et al. An open conformation of ADAMTS-13 is a hallmark of acute acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, S.; Scheiflinger, F.; Rieger, M.; Mudde, G.; Wolf, M.; Coppo, P.; Girma, J.P.; Azoulay, E.; Brun-Buisson, C.; Fakhouri, F.; et al. Prognostic value of anti-ADAMTS 13 antibody features (Ig isotype, titer, and inhibitory effect) in a cohort of 35 adult French patients undergoing a first episode of thrombotic microangiopathy with undetectable ADAMTS 13 activity. Blood 2007, 109, 2815–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, S.; Mudde, G.C.; Rieger, M.; Veyradier, A.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Scheiflinger, F. IgG subclass distribution of anti-ADAMTS13 antibodies in patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7, 1703–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettoni, G.; Palla, R.; Valsecchi, C.; Consonni, D.; Lotta, L.A.; Trisolini, S.M.; Mancini, I.; Musallam, K.M.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Peyvandi, F. ADAMTS-13 activity and autoantibodies classes and subclasses as prognostic predictors in acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 1556–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrdinová, J.; D’Angelo, S.; Graça, N.A.G.; Ercig, B.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Veyradier, A.; Voorberg, J.; Coppo, P. Dissecting the pathophysiology of immune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: Interplay between genes and environmental triggers. Haematologica 2018, 103, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luken, B.M.; Kaijen, P.H.; Turenhout, E.A.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; van Mourik, J.A.; Fijnheer, R.; Voorberg, J. Multiple B-cell clones producing antibodies directed to the spacer and disintegrin/thrombospondin type-1 repeat 1 (TSP1) of ADAMTS13 in a patient with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 2355–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosugi, N.; Tsurutani, Y.; Isonishi, A.; Hori, Y.; Matsumoto, M.; Fujimura, Y. Influenza A infection triggers thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura by producing the anti-ADAMTS13 IgG inhibitor. Intern. Med. 2010, 49, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchini, M. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: Proposal of a new pathogenic mechanism involving Helicobacter pylori infection. Med. Hypotheses 2005, 65, 1128–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, T.; Fernandez-Castro, G.; Montero, A.J.; Stefanovic, A.; Lian, E. A case of severe thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura with concomitant Legionella pneumonia: Review of pathogenesis and treatment. Am. J. Ther. 2011, 18, e180–e185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagita, M.; Uemura, M.; Nakamura, T.; Kunitomi, A.; Matsumoto, M.; Fujimura, Y. Development of ADAMTS13 inhibitor in a patient with hepatitis C virus-related liver cirrhosis causes thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J. Hepatol. 2005, 42, 420–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunther, K.; Garizio, D.; Nesara, P. ADAMTS13 activity and the presence of acquired inhibitors in human immunodeficiency virus-related thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Transfusion 2007, 47, 1710–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbij, F.C.; Fijnheer, R.; Voorberg, J.; Sorvillo, N. Acquired TTP: ADAMTS13 meets the immune system. Blood Rev. 2014, 28, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotta, L.A.; Valsecchi, C.; Pontiggia, S.; Mancini, I.; Cannavò, A.; Artoni, A.; Mikovic, D.; Meloni, G.; Peyvandi, F. Measurement and prevalence of circulating ADAMTS13-specific immune complexes in autoimmune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 12, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.; Palavra, K.; Gruber, B.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Knöbl, P.; Caron, C.; Cromwell, C.; Aledort, L.; Plaimauer, B.; Turecek, P.L.; et al. Persistence of circulating ADAMTS13-specific immune complexes in patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Haematologica 2014, 99, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, I.; Ferrari, B.; Valsecchi, C.; Pontiggia, S.; Fornili, M.; Biganzoli, E.; Peyvandi, F.; Investigators, I.G.o.T. ADAMTS13-specific circulating immune complexes as potential predictors of relapse in patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 39, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westwood, J.P.; Langley, K.; Heelas, E.; Machin, S.J.; Scully, M. Complement and cytokine response in acute Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 164, 858–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, D.; Sayer, R.; Miller, R.; Edwards, S.; Kelly, A.; Baglin, T.; Hunt, B.; Benjamin, S.; Patel, R.; Machin, S.; et al. Human immunodeficiency virus associated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura--favourable outcome with plasma exchange and prompt initiation of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 153, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malak, S.; Wolf, M.; Millot, G.A.; Mariotte, E.; Veyradier, A.; Meynard, J.L.; Korach, J.M.; Malot, S.; Bussel, A.; Azoulay, E.; et al. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated thrombotic microangiopathies: Clinical characteristics and outcome according to ADAMTS13 activity. Scand. J. Immunol. 2008, 68, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swisher, K.K.; Doan, J.T.; Vesely, S.K.; Kwaan, H.C.; Kim, B.; Lämmle, B.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; George, J.N. Pancreatitis preceding acute episodes of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura-hemolytic uremic syndrome: Report of five patients with a systematic review of published reports. Haematologica 2007, 92, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masias, C.; Vasu, S.; Cataland, S.R. None of the above: Thrombotic microangiopathy beyond TTP and HUS. Blood 2017, 129, 2857–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.M.; Rice, L.; Sarode, R.; Chow, T.W.; Moake, J.L. Antibody inhibitors to von Willebrand factor metalloproteinase and increased binding of von Willebrand factor to platelets in ticlopidine-associated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Ann. Intern. Med. 2000, 132, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, S.; Dunn, B.L.; Qureshi, Z.P.; Bandarenko, N.; Kwaan, H.C.; Pandey, D.K.; McKoy, J.M.; Barnato, S.E.; Winters, J.L.; Cursio, J.F.; et al. Ticlopidine-, clopidogrel-, and prasugrel-associated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: A 20-year review from the Southern Network on Adverse Reactions (SONAR). Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2012, 38, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roriz, M.; Landais, M.; Desprez, J.; Barbet, C.; Azoulay, E.; Galicier, L.; Wynckel, A.; Baudel, J.L.; Provôt, F.; Pène, F.; et al. Risk Factors for Autoimmune Diseases Development After Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Medicine 2015, 94, e1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schattner, A.; Friedman, J.; Klepfish, A. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura as an initial presentation of primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin. Rheumatol. 2002, 21, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, T.; Kuwana, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Isonishi, A.; Inokuma, S.; Fujimura, Y. Heterogeneous pathogenic processes of thrombotic microangiopathies in patients with connective tissue diseases. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 102, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.N.; Chen, Q.; Deford, C.C.; Al-Nouri, Z. Ten patient stories illustrating the extraordinarily diverse clinical features of patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and severe ADAMTS13 deficiency. J. Clin. Apher. 2012, 27, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.N.; Nester, C.M. Syndromes of thrombotic microangiopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1847–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veyradier, A.; Meyer, D. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and its diagnosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 2420–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhamou, Y.; Boelle, P.Y.; Baudin, B.; Ederhy, S.; Gras, J.; Galicier, L.; Azoulay, E.; Provôt, F.; Maury, E.; Pène, F.; et al. Cardiac troponin-I on diagnosis predicts early death and refractoriness in acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Experience of the French Thrombotic Microangiopathies Reference Center. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppo, P.; Schwarzinger, M.; Buffet, M.; Wynckel, A.; Clabault, K.; Presne, C.; Poullin, P.; Malot, S.; Vanhille, P.; Azoulay, E.; et al. Predictive features of severe acquired ADAMTS13 deficiency in idiopathic thrombotic microangiopathies: The French TMA reference center experience. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesely, S.K.; George, J.N.; Lämmle, B.; Studt, J.D.; Alberio, L.; El-Harake, M.A.; Raskob, G.E. ADAMTS13 activity in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura-hemolytic uremic syndrome: Relation to presenting features and clinical outcomes in a prospective cohort of 142 patients. Blood 2003, 102, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, S.; Westwood, J.P.; Ellis, D.; Laing, C.; Mc Guckin, S.; Benjamin, S.; Scully, M. The utility of ADAMTS13 in differentiating TTP from other acute thrombotic microangiopathies: Results from the UK TTP Registry. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 171, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafrani, L.; Mariotte, E.; Darmon, M.; Canet, E.; Merceron, S.; Boutboul, D.; Veyradier, A.; Galicier, L.; Azoulay, E. Acute renal failure is prevalent in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura associated with low plasma ADAMTS13 activity. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obert, B.; Tout, H.; Veyradier, A.; Fressinaud, E.; Meyer, D.; Girma, J.P. Estimation of the von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease in plasma using monoclonal antibodies to vWF. Thromb. Haemost. 1999, 82, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerritsen, H.E.; Turecek, P.L.; Schwarz, H.P.; Lämmle, B.; Furlan, M. Assay of von Willebrand factor (vWF)-cleaving protease based on decreased collagen binding affinity of degraded vWF: A tool for the diagnosis of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). Thromb. Haemost. 1999, 82, 1386–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokame, K.; Nobe, Y.; Kokubo, Y.; Okayama, A.; Miyata, T. FRETS-VWF73, a first fluorogenic substrate for ADAMTS13 assay. Br. J. Haematol. 2005, 129, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thouzeau, S.; Capdenat, S.; Stépanian, A.; Coppo, P.; Veyradier, A. Evaluation of a commercial assay for ADAMTS13 activity measurement. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 110, 852–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, B.; Stepanian, A.; Hajage, D.; Thouzeau, S.; Capdenat, S.; Coppo, P.; Veyradier, A. Evaluation of a chromogenic commercial assay using VWF-73 peptide for ADAMTS13 activity measurement. Thromb. Res. 2014, 134, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Cataland, S.; Bissell, M.; Wu, H.M. A rapid test for the diagnosis of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura using surface enhanced laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight (SELDI-TOF)-mass spectrometry. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, S.; Matsumoto, M.; Matsuyama, T.; Isonishi, A.; Hiura, H.; Fujimura, Y. Novel monoclonal antibody-based enzyme immunoassay for determining plasma levels of ADAMTS13 activity. Transfusion 2006, 46, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhm, M.; Vigh, T.; Scharrer, I. Evaluation and clinical application of a new method for measuring activity of von Willebrand factor-cleaving metalloprotease (ADAMTS13). Ann. Hematol. 2002, 81, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripodi, A.; Peyvandi, F.; Chantarangkul, V.; Palla, R.; Afrasiabi, A.; Canciani, M.T.; Chung, D.W.; Ferrari, S.; Fujimura, Y.; Karimi, M.; et al. Second international collaborative study evaluating performance characteristics of methods measuring the von Willebrand factor cleaving protease (ADAMTS-13). J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 1534–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masias, C.; Cataland, S.R. The role of ADAMTS13 testing in the diagnosis and management of thrombotic microangiopathies and thrombosis. Blood 2018, 132, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, A.R.; Heath, A.B.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Factor, S.o.v.W. Establishment of the WHO 1st International Standard ADAMTS13, plasma (12/252): Communication from the SSC of the ISTH. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 1151–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, M.J.; Wilson, A.R.; Rodgers, G.M. Performance of a clinical prediction score for thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in an independent cohort. Vox Sang 2013, 105, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendapudi, P.K.; Hurwitz, S.; Fry, A.; Marques, M.B.; Waldo, S.W.; Li, A.; Sun, L.; Upadhyay, V.; Hamdan, A.; Brunner, A.M.; et al. Derivation and external validation of the PLASMIC score for rapid assessment of adults with thrombotic microangiopathies: A cohort study. Lancet Haematol. 2017, 4, e157–e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favresse, J.; Lardinois, B.; Chatelain, B.; Jacqmin, H.; Mullier, F. Evaluation of the Fully Automated HemosIL Acustar ADAMTS13 Activity Assay. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 118, 942–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsecchi, C.; Mirabet, M.; Mancini, I.; Biganzoli, M.; Schiavone, L.; Faraudo, S.; Mane-Padros, D.; Giles, D.; Serra-Domenech, J.; Blanch, S.; et al. Evaluation of a New, Rapid, Fully Automated Assay for the Measurement of ADAMTS13 Activity. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 119, 1767–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, G.W.; Meijer, D.; Griffiths, M.; Rushen, L.; Brown, A.; Budde, U.; Dittmer, R.; Schocke, B.; Leyte, A.; Geiter, S.; et al. A multi-center evaluation of TECHNOSCREEN. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1686–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vendramin, C.; Thomas, M.; Westwood, J.P.; Scully, M. Bethesda Assay for Detecting Inhibitory Anti-ADAMTS13 Antibodies in Immune-Mediated Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. TH Open 2018, 2, e329–e333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alwan, F.; Vendramin, C.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Langley, K.; McDonald, V.; Austin, S.; Clark, A.; Lester, W.; Gooding, R.; Biss, T.; et al. Presenting ADAMTS13 antibody and antigen levels predict prognosis in immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2017, 130, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hie, M.; Gay, J.; Galicier, L.; Provôt, F.; Presne, C.; Poullin, P.; Bonmarchand, G.; Wynckel, A.; Benhamou, Y.; Vanhille, P.; et al. Preemptive rituximab infusions after remission efficiently prevent relapses in acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2014, 124, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadler, J.E.; Moake, J.L.; Miyata, T.; George, J.N. Recent advances in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2004, 407–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.; Mazzara, R.; Monteagudo, J.; Sanz, C.; Puig, L.; Martínez, A.; Ordinas, A.; Castillo, R. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura/hemolytic uremic syndrome: A multivariate analysis of factors predicting the response to plasma exchange. Ann. Hematol. 1995, 70, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.; Li, X.; Duvall, D.; Terrell, D.R.; Vesely, S.K.; George, J.N. Twice-daily plasma exchange for patients with refractory thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: The experience of the Oklahoma Registry, 1989 through 2006. Transfusion 2008, 48, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussaint-Hacquard, M.; Coppo, P.; Soudant, M.; Chevreux, L.; Mathieu-Nafissi, S.; Lecompte, T.; Gross, S.; Guillemin, F.; Schneider, T. Type of plasma preparation used for plasma exchange and clinical outcome of adult patients with acquired idiopathic thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: A French retrospective multicenter cohort study. Transfusion 2015, 55, 2445–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, M.; Hunt, B.J.; Benjamin, S.; Liesner, R.; Rose, P.; Peyvandi, F.; Cheung, B.; Machin, S.J. Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and other thrombotic microangiopathies. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 158, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, G.; Shumak, K.H.; Sutton, D.M.; Buskard, N.A.; Nair, R.C. Cryosupernatant as replacement fluid for plasma exchange in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Members of the Canadian Apheresis Group. Br. J. Haematol. 1996, 94, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeigler, Z.R.; Shadduck, R.K.; Gryn, J.F.; Rintels, P.B.; George, J.N.; Besa, E.C.; Bodensteiner, D.; Silver, B.; Kramer, R.E. Cryoprecipitate poor plasma does not improve early response in primary adult thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). J. Clin. Apher. 2001, 16, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cataland, S.R.; Kourlas, P.J.; Yang, S.; Geyer, S.; Witkoff, L.; Wu, H.; Masias, C.; George, J.N.; Wu, H.M. Cyclosporine or steroids as an adjunct to plasma exchange in the treatment of immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 2075–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balduini, C.L.; Gugliotta, L.; Luppi, M.; Laurenti, L.; Klersy, C.; Pieresca, C.; Quintini, G.; Iuliano, F.; Re, R.; Spedini, P.; et al. High versus standard dose methylprednisolone in the acute phase of idiopathic thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: A randomized study. Ann. Hematol. 2010, 89, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, M.; McDonald, V.; Cavenagh, J.; Hunt, B.J.; Longair, I.; Cohen, H.; Machin, S.J. A phase 2 study of the safety and efficacy of rituximab with plasma exchange in acute acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2011, 118, 1746–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, E.E.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Terrell, D.R.; Vesely, S.K.; George, J.N. Rituximab reduces risk for relapse in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2016, 127, 3092–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel Karim, N.; Haider, S.; Siegrist, C.; Ahmad, N.; Zarzour, A.; Ying, J.; Yasin, Z.; Sacher, R. Approach to management of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura at university of cincinnati. Adv. Hematol. 2013, 2013, 195746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinott, N.; Mashiach, T.; Horowitz, N.A.; Schliamser, L.; Sarig, G.; Keren-Politansky, A.; Dann, E.J. A 14-Year Experience in the Management of Patients with Acquired Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura in Northern Israel. Acta Haematol. 2015, 134, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhl, L.; Kiss, J.E.; Malynn, E.; Terrell, D.R.; Vesely, S.K.; George, J.N. Rituximab for thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: Lessons from the STAR trial. Transfusion 2017, 57, 2532–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falter, T.; Herold, S.; Weyer-Elberich, V.; Scheiner, C.; Schmitt, V.; von Auer, C.; Messmer, X.; Wild, P.; Lackner, K.J.; Lämmle, B.; et al. Relapse Rate in Survivors of Acute Autoimmune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Treated with or without Rituximab. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 118, 1743–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owattanapanich, W.; Wongprasert, C.; Rotchanapanya, W.; Owattanapanich, N.; Ruchutrakool, T. Comparison of the Long-Term Remission of Rituximab and Conventional Treatment for Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2019, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwicker, J.I.; Muia, J.; Dolatshahi, L.; Westfield, L.A.; Nieters, P.; Rodrigues, A.; Hamdan, A.; Antun, A.G.; Metjian, A.; Sadler, J.E.; et al. Adjuvant low-dose rituximab and plasma exchange for acquired TTP. Blood 2019, 134, 1106–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, M.S.; Hofmann, S.; Shen, Y.M.; Nagalla, S.; Rambally, S.; Usmani, A.; Sarode, R. Comparison of low fixed dose versus standard-dose rituximab to treat thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in the acute phase and preemptively during remission. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2020, 102885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosari, A.; Redaelli, R.; Caimi, T.M.; Mostarda, G.; Morra, E. Cyclosporine therapy in refractory/relapsed patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Am. J. Hematol. 2009, 84, 313–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, H.N.; Thomas-Dewing, R.R.; Hunt, B.J. Mycophenolate mofetil in a case of relapsed, refractory thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Eur. J. Haematol. 2007, 78, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioredda, F.; Cappelli, E.; Mariani, A.; Beccaria, A.; Palmisani, E.; Grossi, A.; Ceccherini, I.; Venè, R.; Micalizzi, C.; Calvillo, M.; et al. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and defective apoptosis due to CASP8/10 mutations: The role of mycophenolate mofetil. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 3432–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziman, A.; Mitri, M.; Klapper, E.; Pepkowitz, S.H.; Goldfinger, D. Combination vincristine and plasma exchange as initial therapy in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: One institution’s experience and review of the literature. Transfusion 2005, 45, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shortt, J.; Oh, D.H.; Opat, S.S. ADAMTS13 antibody depletion by bortezomib in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patriquin, C.J.; Thomas, M.R.; Dutt, T.; McGuckin, S.; Blombery, P.A.; Cranfield, T.; Westwood, J.P.; Scully, M. Bortezomib in the treatment of refractory thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 173, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloncle, F.; Buffet, M.; Coindre, J.P.; Munoz-Bongrand, N.; Malot, S.; Pène, F.; Mira, J.P.; Galicier, L.; Guidet, B.; Baudel, J.L.; et al. Splenectomy and/or cyclophosphamide as salvage therapies in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: The French TMA Reference Center experience. Transfusion 2012, 52, 2436–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoebl, P.; Cataland, S.; Peyvandi, F.; Coppo, P.; Scully, M.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Metjian, A.; de la Rubia, J.; Pavenski, K.; Minkue Mi Edou, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of open-label caplacizumab in patients with exacerbations of acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in the HERCULES study. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshua, G.; Sinha, P.; Hendrickson, J.E.; Tormey, C.A.; Bendapudi, P.; Lee, A.I. Cost effectiveness of caplacizumab in acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Reheman, A.; Gushiken, F.C.; Nolasco, L.; Fu, X.; Moake, J.L.; Ni, H.; López, J.A. N-acetylcysteine reduces the size and activity of von Willebrand factor in human plasma and mice. J. Clin. Invest. 2011, 121, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, N.; Nolasco, L.; Moake, J. Generation and breakdown of soluble ultralarge von Willebrand factor multimers. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2012, 38, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rottenstreich, A.; Hochberg-Klein, S.; Rund, D.; Kalish, Y. The role of N-acetylcysteine in the treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2016, 41, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.W.; Rambally, S.; Kamboj, J.; Reilly, S.; Moake, J.L.; Udden, M.M.; Mims, M.P. Treatment of refractory thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura with N-acetylcysteine: A case report. Transfusion 2014, 54, 1221–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tersteeg, C.; Roodt, J.; Van Rensburg, W.J.; Dekimpe, C.; Vandeputte, N.; Pareyn, I.; Vandenbulcke, A.; Plaimauer, B.; Lamprecht, S.; Deckmyn, H.; et al. N-acetylcysteine in preclinical mouse and baboon models of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2017, 129, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataland, S.R.; Peyvandi, F.; Mannucci, P.M.; Lämmle, B.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Machin, S.J.; Scully, M.; Rock, G.; Gilbert, J.C.; Yang, S.; et al. Initial experience from a double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical outcome study of ARC1779 in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Am. J. Hematol. 2012, 87, 430–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, K.; Someya, T.; Harada, K.; Yagi, H.; Matsui, T.; Matsumoto, M. Novel aptamer to von Willebrand factor A1 domain (TAGX-0004) shows total inhibition of thrombus formation superior to ARC1779 and comparable to caplacizumab. Haematologica 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Gilbert, J.C.; Hatala, P.; Harvey, W.; Liang, Z.; Gao, S.; Kang, D.; Jilma, B. The development and characterization of a long acting anti-thrombotic von Willebrand factor (VWF) aptamer. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, M.; Robles, R.; Morselli, B.; Sandoz, P.; Lämmle, B. Recovery and half-life of von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease after plasma therapy in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Thromb. Haemost. 1999, 81, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kovarova, P.; Hrdlickova, R.; Blahutova, S.; Cermakova, Z. ADAMTS13 kinetics after therapeutic plasma exchange and plasma infusion in patients with Upshaw-Schulman syndrome. J. Clin. Apher. 2019, 34, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.; Vendramin, C.; Oosterholt, S.; Della Pasqua, O.; Scully, M. Pharmacokinetics of plasma infusion in congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 17, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, M.; Knöbl, P.; Kentouche, K.; Rice, L.; Windyga, J.; Schneppenheim, R.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Kajiwara, M.; Fujimura, Y.; Maggiore, C.; et al. Recombinant ADAMTS-13: First-in-human pharmacokinetics and safety in congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2017, 130, 2055–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaimauer, B.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Juno, C.; Wolfsegger, M.J.; Skalicky, S.; Schmidt, M.; Grillberger, L.; Hasslacher, M.; Knöbl, P.; Ehrlich, H.; et al. Recombinant ADAMTS13 normalizes von Willebrand factor-cleaving activity in plasma of acquired TTP patients by overriding inhibitory antibodies. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chander, D.P.; Loch, M.M.; Cataland, S.R.; George, J.N. Caplacizumab Therapy without Plasma Exchange for Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumar, S.; George, J.N.; Cataland, S.R. Shared decision making, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, and caplacizumab. Am. J. Hematol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Völker, L.A.; Brinkkoetter, P.T.; Knöbl, P.N.; Krstic, M.; Kaufeld, J.; Menne, J.; Buxhofer-Ausch, V.; Miesbach, W. Treatment of acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura without plasma exchange in selected patients under caplacizumab. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, M.S.; Sanchez, F.; Friedman, K. Caplacizumab for treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in a patient with anaphylaxis to fresh-frozen plasma. Transfusion 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.L.; Vesely, S.K.; Cataland, S.R.; Coppo, P.; Geldziler, B.; Iorio, A.; Matsumoto, M.; Mustafa, R.A.; Pai, M.; Rock, G.; et al. ISTH guidelines for treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masias, C.; Carter, K.; Wu, H.; Yang, S.; Flowers, A.; Cataland, S. Severely Deficient ADAMTS13 Activity Predicts Relapse of Immune-Mediated Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura in Pregnancy. Blood 2019, 134, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.L.; Vesely, S.K.; Cataland, S.R.; Coppo, P.; Geldziler, B.; Iorio, A.; Matsumoto, M.; Mustafa, R.A.; Pai, M.; Rock, G.; et al. Good practice statements (GPS) for the clinical care of patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walia, S.S.; Walia, M.S.; Walia, H.S. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura treated with vincristine in a Jehovah’s witness. Asian J. Transfus. Sci. 2011, 5, 180–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, J.N.; Sandler, S.A.; Stankiewicz, J. Management of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura without plasma exchange: The Jehovah’s Witness experience. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 2161–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.Y.; Greenberg, C.S. Successful Management of Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura in a Jehovah’s Witness: An Individualized Approach With Joint Decision-Making. J. Patient Exp. 2020, 7, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cataland, S.R.; Scully, M.A.; Paskavitz, J.; Maruff, P.; Witkoff, L.; Jin, M.; Uva, N.; Gilbert, J.C.; Wu, H.M. Evidence of persistent neurologic injury following thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Am. J. Hematol. 2011, 86, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, S.; Abbas, H.; McCrae, K.R. Increased morbidity during long-term follow-up of survivors of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Am. J. Hematol. 2015, 90, E208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.N. TTP: Long-term outcomes following recovery. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2018, 2018, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jestin, M.; Benhamou, Y.; Schelpe, A.S.; Roose, E.; Provôt, F.; Galicier, L.; Hié, M.; Presne, C.; Poullin, P.; Wynckel, A.; et al. Preemptive rituximab prevents long-term relapses in immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2018, 132, 2143–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataland, S.R.; Jin, M.; Lin, S.; Kraut, E.H.; George, J.N.; Wu, H.M. Effect of prophylactic cyclosporine therapy on ADAMTS13 biomarkers in patients with idiopathic thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Am. J. Hematol. 2008, 83, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappers-Klunne, M.C.; Wijermans, P.; Fijnheer, R.; Croockewit, A.J.; van der Holt, B.; de Wolf, J.T.; Löwenberg, B.; Brand, A. Splenectomy for the treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br. J. Haematol. 2005, 130, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, L.; Gray, D.K. Case series: Splenectomy: Does it still play a role in the management of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura? Can. J. Surg. 2010, 53, 349–355. [Google Scholar]
- Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Studt, J.D.; Demarmels Biasiutti, F.; Solenthaler, M.; Alberio, L.; Zwicky, C.; Fontana, S.; Taleghani, B.M.; Tobler, A.; Lämmle, B. Splenectomy in relapsing and plasma-refractory acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Haematologica 2004, 89, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bell, W.R.; Braine, H.G.; Ness, P.M.; Kickler, T.S. Improved survival in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura-hemolytic uremic syndrome. Clinical experience in 108 patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, S.; Oluwole, O.; Cataland, S.; McCrae, K.R. Post-traumatic stress disorder and depression in survivors of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Thromb. Res. 2017, 151, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upreti, H.; Kasmani, J.; Dane, K.; Braunstein, E.M.; Streiff, M.B.; Shanbhag, S.; Moliterno, A.R.; Sperati, C.J.; Gottesman, R.F.; Brodsky, R.A.; et al. Reduced ADAMTS13 activity during TTP remission is associated with stroke in TTP survivors. Blood 2019, 134, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falter, T.; Schmitt, V.; Herold, S.; Weyer, V.; von Auer, C.; Wagner, S.; Hefner, G.; Beutel, M.; Lackner, K.; Lämmle, B.; et al. Depression and cognitive deficits as long-term consequences of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Transfusion 2017, 57, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonneveld, M.A.; Kavousi, M.; Ikram, M.A.; Hofman, A.; Rueda Ochoa, O.L.; Turecek, P.L.; Franco, O.H.; Leebeek, F.W.; de Maat, M.P. Low ADAMTS-13 activity and the risk of coronary heart disease—A prospective cohort study: The Rotterdam Study. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 14, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongers, T.N.; de Bruijne, E.L.; Dippel, D.W.; de Jong, A.J.; Deckers, J.W.; Poldermans, D.; de Maat, M.P.; Leebeek, F.W. Lower levels of ADAMTS13 are associated with cardiovascular disease in young patients. Atherosclerosis 2009, 207, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonneveld, M.A.; de Maat, M.P.; Portegies, M.L.; Kavousi, M.; Hofman, A.; Turecek, P.L.; Rottensteiner, H.; Scheiflinger, F.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Ikram, M.A.; et al. Low ADAMTS13 activity is associated with an increased risk of ischemic stroke. Blood 2015, 126, 2739–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonneveld, M.A.; Franco, O.H.; Ikram, M.A.; Hofman, A.; Kavousi, M.; de Maat, M.P.; Leebeek, F.W. Von Willebrand Factor, ADAMTS13, and the Risk of Mortality: The Rotterdam Study. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 2446–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).