3D DXA Hip Differences in Patients with Acromegaly or Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Outcome Measures
2.2.1. Areal Bone Mineral Density
2.2.2. 3D-DXA Modelling
2.2.3. Anthropometric Measures
2.2.4. Serum Measurements
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
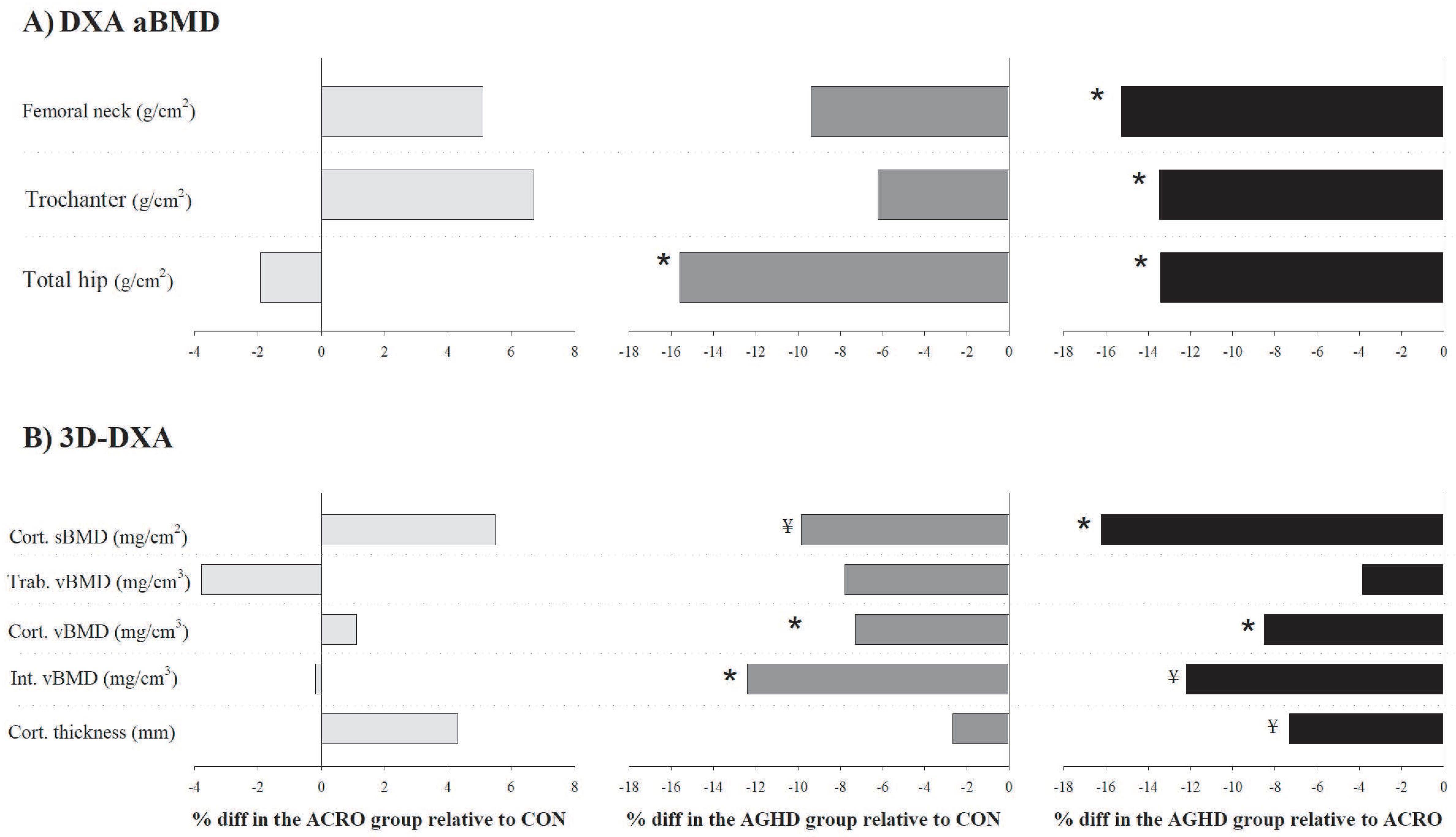
4.1. Differences in aBMD among Groups
4.2. Cortical and Trabecular Bone Differences Assessed by 3D-DXA
4.3. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giustina, A.; Mazziotti, G.; Canalis, E. Growth Hormone, Insulin-Like Growth Factors, and the Skeleton. Endocr. Rev. 2008, 29, 535–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazziotti, G.; Biagioli, E.; Maffezzoni, F.; Spinello, M.; Serra, V.; Maroldi, R.; Floriani, I.; Giustina, A. Bone turnover, bone mineral density, and fracture risk in acromegaly: A meta-analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazziotti, G.; Maffezzoni, F.; Frara, S.; Giustina, A. Acromegalic osteopathy. Pituitary 2017, 20, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffezzoni, F.; Maddalo, M.; Frara, S.; Mezzone, M.; Zorza, I.; Baruffaldi, F.; Doglietto, F.; Mazziotti, G.; Maroldi, R.; Giustina, A. High-resolution-cone beam tomography analysis of bone microarchitecture in patients with acromegaly and radiological vertebral fractures. Endocrine 2016, 54, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbonare, L.D.; Micheletti, V.; Cosaro, E.; Valenti, M.T.; Mottes, M.; Francia, G.; Davì, M.V. Bone histomorphometry in acromegaly patients with fragility vertebral fractures. Pituitary 2017, 21, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.P.B.; Amlashi, F.G.; Yu, E.W.; Pulaski-Liebert, K.J.; Gerweck, A.V.; Fazeli, P.; Lawson, E.A.; Nachtigall, L.B.; Biller, B.M.K.; Miller, K.K.; et al. Bone microarchitecture and estimated bone strength in men with active acromegaly. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 177, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeira, M.; Neto, L.V.; Paranhos-Neto, F.D.P.; Lima, I.C.B.; De Mendonça, L.M.C.; Gadelha, M.R.; De Farias, M.L.F. Acromegaly has a negative influence on trabecular bone, but not on cortical bone, as assessed by high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 1734–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doga, M.; Bonadonna, S.; Gola, M.; Mazziotti, G.; Giustina, A. Growth hormone deficiency in the adult. Pituitary 2006, 9, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, H.; Blok, G.; Van Lingen, A.; Teule, G.; Lips, P.; Van Der Veen, E. Consequences of childhood-onset growth hormone deficiency for adult bone mass. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1994, 9, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Halloran, D.J.; Tsatsoulis, A.; Whitehouse, R.W.; Holmes, S.J.; Adams, J.E.; Shalet, S.M. Increased bone density after recombinant human growth hormone (GH) therapy in adults with isolated GH deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1993, 76, 1344–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yan, K.; Yuping, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.J.; Gong, F.Y.; Zhu, H.J.; Xia, W.-B.; Pan, H. Bone microarchitecture and volumetric bone density impairment in young male adults with childhood-onset growth hormone deficiency. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 180, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glüer, C.C. 30 years of DXA technology innovations. Bone 2017, 104, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, E.M.; Silva, B.C.; Boutroy, S.; Zhou, B.; Wang, J.; Udesky, J.; Zhang, C.; McMahon, D.J.; Romano, M.; Dworakowski, E.; et al. Primary hyperparathyroidism is associated with abnormal cortical and trabecular microstructure and reduced bone stiffness in postmenopausal women. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2013, 28, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Humbert, L.; Martelli, Y.; Fonolla, R.; Steghofer, M.; Di Gregorio, S.; Malouf, J.; Romera, J.; Barquero, L.M.D.R. 3D-DXA: Assessing the Femoral Shape, the Trabecular Macrostructure and the Cortex in 3D from DXA images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winzenrieth, R.; Humbert, L.; Di Gregorio, S.; Bonel, E.; García, M.; Del Rio, L. Effects of osteoporosis drug treatments on cortical and trabecular bone in the femur using DXA-based 3D modeling. Osteoporos. Int. 2018, 29, 2323–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, K.K.Y. Consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of adults with GH deficiency II: A statement of the GH Research Society in association with the European Society for Pediatric Endocrinology, Lawson Wilkins Society, European Society of Endocrinology, Japan Endocrine Society, and Endocrine Society of Australia. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2007, 157, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewiecki, E.M.; Binkley, N.; Morgan, S.L.; Shuhart, C.R.; Camargos, B.; Carey, J.J.; Gordon, C.M.; Jankowski, L.G.; Lee, J.-K.; Leslie, W.D. Best practices for dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry measurement and reporting: International society for clinical densitometry guidance. J. Clin. Densitom. 2016, 19, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia-Marco, L.; García-Fontana, B.; Ubago-Guisado, E.; Vlachopoulos, D.; García-Martín, A.; Muñoz-Torres, M. Analysis of bone impairment by 3D DXA hip measures in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism: A pilot study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, B.C.; Cusano, N.E.; Bilezikian, J.P. Primary hyperparathyroidism. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 32, 593–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, J. Quantitative methods in psychology: A power primer. Psychol. Bull. 1992, 112, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canalis, E.; Giustina, A.; Bilezikian, J.P. Mechanisms of anabolic therapies for osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mazziotti, G.; Frara, S.; Giustina, A. Pituitary diseases and bone. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 440–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueland, T.; Fougner, S.L.; Godang, K.; Schreiner, T.; Bollerslev, J. Serum GH and IGF-I are significant determinants of bone turnover but not bone mineral density in active acromegaly: A prospective study of more than 70 consecutive patients. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 155, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, T.; Nery, L.; Posen, S. Spinal and peripheral bone mineral densities in acromegaly: The effects of excess growth hormone and hypogonadism. Ann. Intern. Med. 1989, 111, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzat, S. Biochemical assessment of bone formation and resorption in acromegaly. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1993, 76, 1452–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.M.; Hopkins, M.; Fraser, W.; Ooi, C.; Durham, B.; Vora, J. Parathyroid hormone secretory pattern, circulating activity, and effect on bone turnover in adult growth hormone deficiency. Bone 2003, 32, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bex, M.; Abs, R.; Maiter, D.; Beckers, A.; Lamberigts, G.; Bouillon, R. The effects of growth hormone replacement therapy on bone metabolism in adult-onset growth hormone deficiency: A 2-year open randomized controlled multicenter trial. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2002, 17, 1081–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapaport, R.; Cook, D.M. Transition of childhood-onset growth hormone-deficient patients to adult healthcare. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Rev. 2006, 4 (Suppl. S1), 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Radovick, S.; Divall, S. Approach to the growth hormone-deficient child during transition to adulthood. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia-Marco, L.; Vicente-Rodríguez, G.; Valtueña, J.; Rey-López, J.; Martínez, A.D.; Mesana, M.; Widhalm, K.; Ruiz, J.; González-Gross, M.; Castillo, M.; et al. Bone mass and bone metabolism markers during adolescence: The HELENA study. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2010, 74, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubago-Guisado, E.; Vlachopoulos, D.; Barker, A.R.; Christoffersen, T.; Metcalf, B.; Gracia-Marco, L. Effect of maturational timing on bone health in male adolescent athletes engaged in different sports: The PRO-BONE study. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2018, 22, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, R.D.; Columb, B.; Adams, J.E.; Shalet, S.M. Low bone mass is an infrequent feature of the adult growth hormone deficiency syndrome in middle-age adults and the elderly. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 1124–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holmes, S.J.; Economou, G.; Whitehouse, R.W.; Adams, J.E.; Shalet, S.M. Reduced bone mineral density in patients with adult onset growth hormone deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1994, 78, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toogood, A.A.; Adams, J.E.; O’Neill, P.A.; Shalet, S.M. Elderly patients with adult-onset growth hormone deficiency are not osteopenic 1. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 1462–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, H.D.; Ahmad, A.M.; Durham, B.H.; Peter, R.; Prabhakar, V.K.B.; Corlett, P.; Vora, J.P.; Fraser, W.D. PTH circadian rhythm and PTH target-organ sensitivity is altered in patients with adult growth hormone deficiency with low BMD. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2007, 22, 1798–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazziotti, G.; Lania, A.G.A.; Canalis, E. Management of endocrine disease: Bone disorders associated with acromegaly: Mechanisms and treatment. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 181, R45–R56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kužma, M.; Vanuga, P.; Sagova, I.; Pavai, D.; Jackuliak, P.; Killinger, Z.; Binkley, N.C.; Winzenrieth, R.; Genant, H.K.; Payer, J. Non-invasive DXA-derived bone structure assessment of acromegaly patients: A cross-sectional study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 180, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malgo, F.; Hamdy, N.A.T.; Rabelink, T.J.; Kroon, H.M.; Claessen, K.M.J.A.; Pereira, A.M.; Biermasz, N.R.; Appelman-Dijkstra, N.M. Bone material strength index as measured by impact microindentation is altered in patients with acromegaly. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 176, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treece, G.; Gee, A. Cortical bone mapping: Measurement and statistical analysis of localised skeletal changes. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2018, 16, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bravenboer, N.; Holzmann, P.; de Boer, H.; Blok, G.J.; Lips, P. Histomorphometric analysis of bone mass and bone metabolism in growth hormone deficient adult men. Bone 1996, 18, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, N.H.; Nimphius, S.; Rantalainen, T.; Ireland, A.; Siafarikas, A.; Newton, R.U. Mechanical basis of bone strength: Influence of bone material, bone structure and muscle action. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2017, 17, 114–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Greenspan, S.L.; Myers, E.R.; Maitland, L.A.; Kido, T.H.; Krasnow, M.B.; Hayes, W.C. Trochanteric bone mineral density is associated with type of hip fracture in the elderly. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1994, 9, 1889–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarantino, U.; Rao, C.; Tempesta, V.; Gasbarra, E.; Feola, M. Hip fractures in the elderly: The role of cortical bone. Injury 2016, 47 (Suppl. 4), S107–S111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, S.J.; Clarke, B.L.; Peacock, M.; Bandeira, F.; Boutroy, S.; Cusano, N.E.; Dempster, D.; Lewiecki, E.M.; Liu, J.-M.; Minisola, S.; et al. Current issues in the presentation of asymptomatic primary hyperparathyroidism: Proceedings of the Fourth International Workshop. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 3580–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| CON (n = 33) | ACRO (n = 20) | AGHD (n = 14) | Overall p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (n,%) Male | 8, 24.2 | 5, 25.0 | 3, 21.4 | 0.969 | |||
| Female | 25, 75.8 | 15, 75.0 | 11, 78.6 | ||||
| Hypogonadism (n,%) | N/A | 6, 30.0 | 12, 87.5 | - | |||
| Prevalent fracture (n,%) | N/A | 1, 5.0 | 2, 14.3 | - | |||
| Smoking (n,%) | 7, 21.2 | 5, 25.0 | 5, 35.7 | 0.579 | |||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| Age (years) | 56.1 | 12.0 | 54.8 | 11.5 | 57.4 | 12.3 | 0.816 |
| Duration of disease (years) | N/A | 10 | 7 | 22 | 10 | - | |
| Duration of GH replacement therapy (years) | N/A | - | - | 19 | 7 | - | |
| Height (m) | 1.62 | 0.10 | 1.65 | 0.08 | 1.56 | 0.09 | 0.020 |
| Weight (kg) | 72.4 | 11.7 | 78.5 | 16.5 | 68.9 | 10.2 | 0.096 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.7 | 4.6 | 28.8 | 5.0 | 28.6 | 5.2 | 0.711 |
| IGF-I (ng/mL) | N/A | 191.2 | 141.7 | 145 | 39.3 | - | |
| GH (ng/mL) | N/A | 1.65 | 2.0 | 0.72 | 0.78 | - | |
| aBMD | |||||||
| Femoral neck (g/cm2) | 0.779 | 0.137 | 0.833 | 0.161 | 0.705 | 0.117 | 0.040 |
| Femoral neck T-score | −0.855 | 1.001 | −0.320 | 1.258 | −1.400 | 0.981 | 0.020 |
| Trochanter (g/cm2) | 0.682 | 0.099 | 0.741 | 0.127 | 0.642 | 0.100 | 0.031 |
| Total hip (g/cm2) | 0.953 | 0.124 | 0.950 | 0.156 | 0.823 | 0.142 | 0.011 |
| 3D-DXA | |||||||
| Cortical sBMD (mg/cm2) | 163.32 | 20.28 | 175.75 | 31.53 | 148.86 | 22.80 | 0.010 |
| Trabecular vBMD (mg/cm3) | 183.40 | 36.44 | 181.97 | 57.41 | 169.18 | 41.98 | 0.594 |
| Cortical vBMD (mg/cm3) | 836.14 | 59.04 | 851.96 | 69.97 | 779.79 | 45.55 | 0.003 |
| Integral vBMD (mg/cm3) | 327.83 | 47.14 | 334.72 | 68.10 | 291.27 | 54.41 | 0.066 |
| Cortical thickness (mm) | 1.95 | 0.16 | 2.06 | 0.25 | 1.90 | 0.21 | 0.060 |
| CON (n = 33) | ACRO (n = 20) | AGHD (n = 14) | Pairwise p-Value (Effect Size) * | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SE | Mean | SE | Mean | SE | Overall p-Value | CON-ACRO | CON-AGHD | AGHD-ACRO | |
| aBMD | ||||||||||
| Femoral neck (g/cm2) | 0.781 | 0.019 | 0.823 | 0.025 | 0.714 | 0.029 | 0.024 | NS (0.36) | NS (0.63) | 0.020 (0.99) * |
| Trochanter (g/cm2) | 0.685 | 0.015 | 0.732 | 0.019 | 0.645 | 0.023 | 0.016 | NS (0.57) | NS (0.43) | 0.015 (1.01) * |
| Total hip (g/cm2) | 0.957 | 0.020 | 0.939 | 0.025 | 0.828 | 0.030 | 0.002 | NS (0.13) | 0.002 (1.13) | 0.018 (0.99) * |
| 3D-DXA | ||||||||||
| Cortical sBMD (mg/cm2) | 164.19 | 3.43 | 173.74 | 4.41 | 149.467 | 5.26 | 0.004 | NS (0.50) | 0.071 (0.72) ¥ | 0.003 (1.22) * |
| Trabecular vBMD (mg/cm3) | 184.81 | 6.51 | 178.07 | 8.38 | 171.44 | 9.90 | 0.518 | NS (0.18) | NS (0.36) | NS (0.18) |
| Cortical vBMD (mg/cm3) | 838.16 | 9.35 | 847.66 | 12.03 | 781.16 | 14.34 | 0.002 | NS (0.19) | 0.004 (1.05) * | 0.002 (1.24) * |
| Integral vBMD (mg/cm3) | 330.05 | 8.04 | 329.42 | 10.35 | 293.60 | 12.33 | 0.040 | NS (0.00) | 0.048 (0.78) * | 0.087 (0.78) ¥ |
| Cortical thickness (mm) | 1.955 | 0.030 | 2.043 | 0.038 | 1.904 | 0.045 | 0.057 | NS (0.54) | NS (0.28) | 0.066 (0.82) ¥ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gracia-Marco, L.; Gonzalez-Salvatierra, S.; Garcia-Martin, A.; Ubago-Guisado, E.; Garcia-Fontana, B.; Gil-Cosano, J.J.; Muñoz-Torres, M. 3D DXA Hip Differences in Patients with Acromegaly or Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040657
Gracia-Marco L, Gonzalez-Salvatierra S, Garcia-Martin A, Ubago-Guisado E, Garcia-Fontana B, Gil-Cosano JJ, Muñoz-Torres M. 3D DXA Hip Differences in Patients with Acromegaly or Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(4):657. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040657
Chicago/Turabian StyleGracia-Marco, Luis, Sheila Gonzalez-Salvatierra, Antonia Garcia-Martin, Esther Ubago-Guisado, Beatriz Garcia-Fontana, José Juan Gil-Cosano, and Manuel Muñoz-Torres. 2021. "3D DXA Hip Differences in Patients with Acromegaly or Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 4: 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040657








