Neuroimaging of Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Imaging to Identify ICH Etiology
2.1. CTA and DSA for Macrovascular Causes
2.2. Value of CT-Perfusion
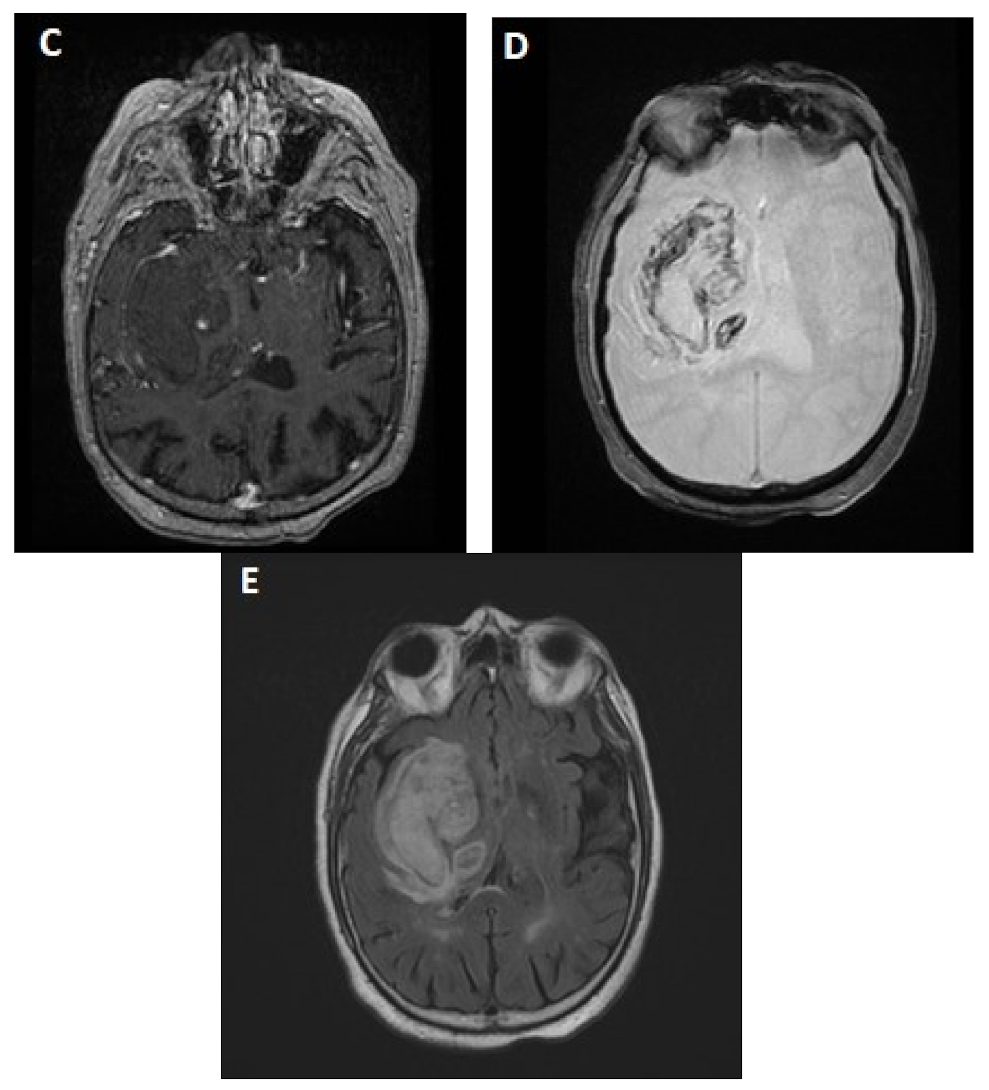
2.3. MRI
3. Imaging to Predict Ich Expansion
3.1. MRI and ICH Expansion
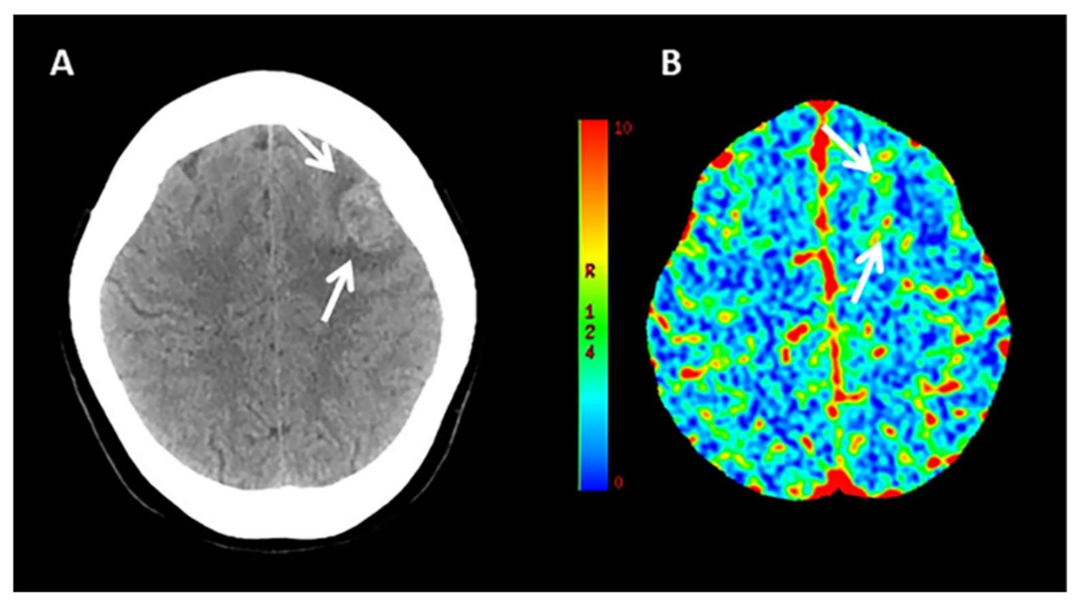
3.2. Value of CT-Perfusion
4. Imaging to Predict Outcome
4.1. MRI
4.2. CT-Perfusion
5. Imaging Acute ICH in Clinical Practice
6. Future Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poon, M.T.C.; Fonville, A.F.; Salman, R.A.S. Long-term prognosis after intracerebral haemorrhage: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2014, 85, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.O.; Nguyen, M.; Roth, G.A.; Nichols, E.; Alam, T.; Abate, D.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; Abraha, H.N.; Abu-Rmeileh, N.M.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shahi Salman, R.; Labovitz, D.L.; Stapf, C. Spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage. BMJ 2009, 339, b2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantoni, L. Cerebral small vessel disease: From pathogenesis and clinical characteristics to therapeutic challenges. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.A.; Samarasekera, N.; Lerpiniere, C.; Humphreys, C.; McCarron, M.O.; White, P.M.; Nicoll, J.A.R.; Sudlow, C.L.M.; Cordonnier, C.; Wardlaw, J.M.; et al. The Edinburgh CT and genetic diagnostic criteria for lobar intracerebral haemorrhage associated with cerebral amyloid angiopathy: Model development and diagnostic test accuracy study. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charidimou, A.; Linn, J.; Vernooij, M.W.; Opherk, C.; Akoudad, S.; Baron, J.C.; Greenberg, S.M.; Jäger, H.R.; Werring, D.J. Cortical superficial siderosis: Detection and clinical significance in cerebral amyloid angiopathy and related conditions. Brain 2015, 138, 2126–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charidimou, A.; Peeters, A.P.; Jäger, R.; Fox, Z.; Vandermeeren, Y.; Laloux, P.; Baron, J.C.; Werring, D.J. Cortical superficial siderosis and intracerebral hemorrhage risk in cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Neurology 2013, 81, 1666–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charidimou, A.; Boulouis, G.; Greenberg, S.M.; Viswanathan, A. Cortical superficial siderosis and bleeding risk in cerebral amyloid angiopathy: A meta-analysis. Neurology 2019, 93, e2192–e2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charidimou, A.; Martinez-Ramirez, S.; Shoamanesh, A.; Oliveira-Filho, J.; Frosch, M.; Vashkevich, A.; Ayres, A.; Rosand, J.; Gurol, M.E.; Greenberg, S.M.; et al. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy with and without hemorrhage: Evidence for different disease phenotypes. Neurology 2015, 84, 1206–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, S.M.; Vernooij, M.W.; Cordonnier, C.; Salman, R.A.; Edin, F.; Warach, S.; Lenore, J.; Buchem, M.; Van, A.; Breteler, M.M.B. Cerebral microbleeds:A field guide to their detection and interpretation. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charidimou, A.; Gang, Q.; Werring, D.J. Sporadic cerebral amyloid angiopathy revisited: Recent insights into pathophysiology and clinical spectrum. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2012, 83, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linn, J.; Halpin, A.; Demaerel, P.; Ruhland, J.; Giese, A.D.; Dichgans, M.; Van Buchem, M.A.; Bruckmann, H.; Greenberg, S.M. Prevalence of superficial siderosis in patients with cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Neurology 2010, 74, 1346–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulouis, G.; Charidimou, A.; Greenberg, S.M. Sporadic cerebral amyloid angiopathy: Pathophysiology, neuroimaging features, and clinical implications. Semin. Neurol. 2016, 36, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.L.; Chan, M.S.Y.; Poon, W.S. Spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage: Which patients need diagnostic cerebral angiography?: A prospective study of 206 cases and review of the literature. Stroke 1997, 28, 1406–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilkens, N.A.; Van Asch, C.J.J.; Werring, D.J.; Wilson, D.; Rinkel, G.J.E.; Algra, A.; Velthuis, B.K.; De Kort, G.A.P.; Witkamp, T.D.; Van Nieuwenhuizen, K.M.; et al. Predicting the presence of macrovascular causes in non-traumatic intracerebral haemorrhage: The DIAGRAM prediction score. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2018, 89, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manninen, A.L.; Isokangas, J.M.; Karttunen, A.; Siniluoto, T.; Nieminen, M.T. A comparison of radiation exposure between diagnostic CTA and DSA examinations of cerebral and cervicocerebral vessels. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 2038–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemphill, J.C.; Greenberg, S.M.; Anderson, C.S.; Becker, K.; Bendok, B.R.; Cushman, M.; Fung, G.L.; Goldstein, J.N.; Macdonald, R.L.; Mitchell, P.H.; et al. Guidelines for the Management of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2015, 46, 2032–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.I.; Mendelow, A.D.; Hanley, D.F. Intracerebral haemorrhage. Lancet 2009, 373, 1632–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, T.P.C.; Bauman, G.; Yartsev, S.; Fainardi, E.; MacDonald, D.; Lee, T.Y. Dynamic perfusion CT in brain tumors. Eur. J. Radiol. 2015, 84, 2386–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainardi, E.; Borrelli, M.; Saletti, A.; Schivalocchi, R.; Azzini, C.; Cavallo, M.; Ceruti, S.; Tamarozzi, R.; Chieregato, A. CT perfusion mapping of hemodynamic disturbances associated to acute spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Neuroradiology 2008, 50, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordonnier, C.; Demchuk, A.; Ziai, W.; Anderson, C.S. Intracerebral haemorrhage: Current approaches to acute management. Lancet 2018, 392, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.J.; Krings, T. Whole-brain perfusion CT patterns of brain arteriovenous malformations: A pilot study in 18 patients. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, 2061–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, K.A.; Rosand, J.; Karluk, D.; Greenberg, S.M. Clinical diagnosis of cerebral amyloid angiopathy: Validation of the boston criteria. Neurology 2001, 56, 537–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charidimou, A.; Boulouis, G.; Gurol, M.E.; Ayata, C.; Bacskai, B.J.; Frosch, M.P.; Viswanathan, A.; Greenberg, S.M. Emerging concepts in sporadic cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Brain 2017, 140, 1829–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, S.M.; Charidimou, A. Diagnosis of cerebral amyloid angiopathy evolution of the Boston criteria. Stroke 2018, 49, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.T.; Fischbein, N.J.; André, J.B.; Wijman, C.; Rosenberg, J.; Zaharchuk, G. Identification of venous signal on arterial spin labeling improves diagnosis of dural arteriovenous fistulas and small arteriovenous malformations. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagadeesan, B.D.; Delgado Almandoz, J.E.; Benzinger, T.L.S.; Moran, C.J. Postcontrast susceptibility-weighted imaging: A novel technique for the detection of arteriovenous shunting in vascular malformations of the brain. Stroke 2011, 42, 3127–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brouwers, H.B.; Greenberg, S.M. Hematoma expansion following acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2013, 35, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowlatshahi, D.; Demchuk, A.M.; Flaherty, M.L.; Ali, M.; Lyden, P.L.; Smith, E.E.M. Defining hematoma expansion in intracerebral hemorrhage: Relationship with patient outcomes. Neurology 2011, 76, 1238–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, T.; Bösel, J. Options to restrict hematoma expansion after spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 2010, 41, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.Z.; Jiang, R.; Gu, M.; He, C.; Guan, J. The accuracy of spot sign in predicting hematoma expansion after intracerebral hemorrhage: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demchuk, A.M.; Dowlatshahi, D.; Rodriguez-Luna, D.; Molina, C.A.; Blas, Y.S.; Dzialowski, I.; Kobayashi, A.; Boulanger, J.M.; Lum, C.; Gubitz, G.; et al. Prediction of haematoma growth and outcome in patients with intracerebral haemorrhage using the CT-angiography spot sign (PREDICT): A prospective observational study. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwers, H.B.; Chang, Y.; Falcone, G.J.; Cai, X.; Ayres, A.M.; Battey, T.W.K.; Vashkevich, A.; McNamara, K.A.; Valant, V.; Schwab, K.; et al. Predicting hematoma expansion after primary intracerebral hemorrhage. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morotti, A.; Brouwers, H.B.; Romero, J.M.; Jessel, M.J.; Vashkevich, A.; Schwab, K.; Afzal, M.R.; Cassarly, C.; Greenberg, S.M.; Martin, R.H.; et al. Intensive blood pressure reduction and spot sign in intracerebral hemorrhage. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 950–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladstone, D.J.; Aviv, R.I.; Demchuk, A.M.; Hill, M.D.; Thorpe, K.E.; Khoury, J.C.; Sucharew, H.J.; Al-Ajlan, F.; Butcher, K.; Dowlatshahi, D.; et al. Effect of recombinant activated coagulation factor VII on hemorrhage expansion among patients with spot sign-positive acute intracerebral hemorrhage: The SPOTLIGHT and STOP-IT randomized clinical trials. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 1493–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morotti, A.; Arba, F.; Boulouis, G.; Charidimou, A. Noncontrast CT markers of intracerebral hemorrhage expansion and poor outcome. Neurology 2020, 95, 632–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morotti, A.; Boulouis, G.; Dowlatshahi, D.; Li, Q.; Barras, C.D.; Delcourt, C.; Yu, Z.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, Z.; Aviv, R.I.; et al. Standards for detecting, interpreting, and reporting noncontrast computed tomographic markers of intracerebral hemorrhage expansion. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 86, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporns, P.B.; Kemmling, A.; Schwake, M.; Minnerup, J.; Nawabi, J.; Broocks, G.; Wildgruber, M.; Fiehler, J.; Heindel, W.; Hanning, U. Triage of 5 noncontrast computed tomography markers and spot sign for outcome prediction after intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 2018, 49, 2317–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporns, P.B.; Schwake, M.; Kemmling, A.; Minnerup, J.; Schwindt, W.; Niederstadt, T.; Schmidt, R.; Hanning, U. Comparison of spot sign, blend sign and black hole sign for outcome prediction in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. J. Stroke 2017, 19, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulouis, G.; Morotti, A.; Brouwers, H.B.; Charidimou, A.; Jessel, M.J.; Auriel, E.; Pontes-Neto, O.; Ayres, A.; Vashkevich, A.; Schwab, K.M.; et al. Association between hypodensities detected by computed tomography and hematoma expansion in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporns, P.B.; Kemmling, A.; Minnerup, J.; Hanning, U.; Heindel, W. Imaging-based outcome prediction in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir. 2018, 160, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawabi, J.; Elsayed, S.; Kniep, H.; Sporns, P.; Schlunk, F.; McDonough, R.; Broocks, G.; Dührsen, L.; Schön, G.; Götz, T.; et al. Inter- and intrarater agreement of spot sign and noncontrast CT markers for early intracerebral hemorrhage expansion. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morotti, A.; Boulouis, G.; Charidimou, A.; Schwab, K.; Kourkoulis, C.; Anderson, C.D.; Gurol, M.E.; Viswanathan, A.; Romero, J.M.; Greenberg, S.M.; et al. Integration of computed tomographic angiography spot Sign and noncontrast computed tomographic hypodensities to predict hematoma expansion. Stroke 2018, 49, 2067–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shahi Salman, R.; Frantzias, J.; Lee, R.J.; Lyden, P.D.; Battey, T.W.K.; Ayres, A.M.; Goldstein, J.N.; Mayer, S.A.; Steiner, T.; Wang, X.; et al. Absolute risk and predictors of the growth of acute spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage: A systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data. Lancet. Neurol. 2018, 17, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morotti, A.; Romero, J.M.; Jessel, M.J.; Brouwers, H.B.; Gupta, R.; Schwab, K.; Vashkevich, A.; Ayres, A.; Anderson, C.D.; Gurol, M.E.; et al. Effect of CTA tube current on spot sign detection and accuracy for prediction of intracerebral hemorrhage expansion. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 1781–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowlatshahi, D.; Morotti, A.; Al-Ajlan, F.S.; Boulouis, G.; Warren, A.D.; Petrcich, W.; Aviv, R.I.; Demchuk, A.M.; Goldstein, J.N. Interrater and intrarater measurement reliability of noncontrast computed tomography predictors of intracerebral hemorrhage expansion. Stroke 2019, 50, 1260–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviv, R.I.; Huynh, T.; Huang, Y.; Ramsay, D.; Van Slyke, P.; Dumont, D.; Asmah, P.; Alkins, R.; Liu, R.; Hynynen, K. An in vivo, MRI-integrated real-time model of active contrast extravasation in acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 1693–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, S.A.; Leigh, R. Imaging active intracerebral hemorrhage after attempted endovascular thrombectomy. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulouis, G.; Van Etten, E.S.; Charidimou, A.; Auriel, E.; Morotti, A.; Pasi, M.; Haley, K.E.; Brouwers, H.B.; Ayres, A.M.; Vashkevich, A.; et al. Association of key magnetic resonance imaging markers of cerebral small vessel disease with hematoma volume and expansion in patients with lobar and deep intracerebral hemorrhage. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 1440–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoamanesh, A.; Morotti, A.; Romero, J.M.; Oliveira-Filho, J.; Schlunk, F.; Jessel, M.J.; Ayres, A.M.; Vashkevich, A.; Schwab, K.; Afzal, M.R.; et al. Cerebral microbleeds and the effect of intensive blood pressure reduction on hematoma expansion and functional outcomes a secondary analysis of the ATACH-2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koennecke, H.C. Cerebral microbleeds on MRI: Prevalence, associations, and potential clinical implications. Neurology 2006, 66, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Nattanmai, P.; George, P.; Newey, C.R. Spot sign in acute intracerebral hemorrhage in magnetic resonance imaging: A case report and review of the literature. Neurologist 2018, 23, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindlbeck, K.A.; Santaella, A.; Galinovic, I.; Krause, T.; Rocco, A.; Nolte, C.H.; Villringer, K.; Fiebach, J.B. Spot sign in acute intracerebral hemorrhage in dynamic T1-Weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Stroke 2016, 47, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, D.; Jhaveri, M.D.; Prabhakaran, S. Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics at onset of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Arch. Neurol. 2011, 68, 826–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.R.; Jain, M.; Kanthala, A.R.; Damania, D.; Stead, L.G.; Wang, H.Z.; Jahromi, B.S. Association of CT perfusion parameters with hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 1895–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batchelor, C.; Pordeli, P.; D’Esterre, C.D.; Najm, M.; Al-Ajlan, F.S.; Boesen, M.E.; McDougall, C.; Hur, L.; Fainardi, E.; Shankar, J.J.S.; et al. Use of noncontrast computed tomography and computed tomographic perfusion in predicting intracerebral hemorrhage after intravenous Alteplase therapy. Stroke 2017, 48, 1548–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morotti, A.; Busto, G.; Bernardoni, A.; Tamborino, C.; Fainardi, E. Association between perihematomal cerebral blood volume and intracerebral hemorrhage expansion: A computed tomography perfusion study. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 85, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemphill, J.C.; Bonovich, D.C.; Besmertis, L.; Manley, G.T.; Johnston, S.C. The ICH score: A simple, reliable grading scale for intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 2001, 32, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kothari, R.U.; Brott, T.; Broderick, J.P.; Barsan, W.G.; Sauerbeck, L.R.; Zuccarello, M.; Khoury, J. The ABCs of measuring intracerebral hemorrhage volumes. Stroke 1996, 27, 1304–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lun, R.; Yogendrakumar, V.; Demchuk, A.M.; Aviv, R.I.; Rodriguez-Luna, D.; Molina, C.A.; Silva, Y.; Dzialowski, I.; Kobayashi, A.; Boulanger, J.M.; et al. Calculation of prognostic scores, using delayed imaging, outperforms baseline assessments in acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 2020, 51, 1107–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporns, P.B.; Schwake, M.; Schmidt, R.; Kemmling, A.; Minnerup, J.; Schwindt, W.; Cnyrim, C.; Zoubi, T.; Heindel, W.; Niederstadt, T.; et al. Computed tomographic blend sign is associated with computed tomographic angiography spot sign and predicts secondary neurological deterioration after intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 2017, 48, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwers, H.B.; Goldstein, J.N.; Romero, J.M.; Rosand, J. Clinical applications of the computed tomography angiography spot sign in acute intracerebral hemorrhage a review. Stroke 2012, 43, 3427–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sato, S.; Delcourt, C.; Heeley, E.; Arima, H.; Zhang, S.; Al-Shahi Salman, R.; Stapf, C.; Woo, D.; Flaherty, M.L.; Vagal, A.; et al. Significance of cerebral small-vessel disease in acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 2016, 47, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lioutas, V.A.; Wu, B.; Norton, C.; Helenius, J.; Modak, J.; Selim, M. Cerebral small vessel disease burden and functional and radiographic outcomes in intracerebral hemorrhage. J. Neurol. 2018, 265, 2803–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, S.; Labreuche, J.; Bombois, S.; Rossi, C.; Boulouis, G.; Hénon, H.; Duhamel, A.; Leys, D.; Cordonnier, C. Dementia risk after spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage: A prospective cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herweh, C.; Jüttler, E.; Schellinger, P.D.; Klotz, E.; Jenetzky, E.; Orakcioglu, B.; Sartor, K.; Schramm, P. Evidence against a perihemorrhagic penumbra provided by perfusion computed tomography. Stroke 2007, 38, 2941–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morotti, A.; Busto, G.; Bernardoni, A.; Leuci, E.; Casetta, I.; Fainardi, E. Comparison of perihematomal perfusion in deep and lobar intracerebral hemorrhage. Neuroradiology 2020, 62, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayal, A.H.; Gupta, R.; Yonas, H.; Jovin, T.; Uchino, K.; Hammer, M.; Wechsler, L.; Gebel, J.M. Quantitative perihematomal blood flow in spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage predicts in-hospital functional outcome. Stroke 2007, 38, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmela, M.B.; Mortazavi, S.; Jagadeesan, B.D.; Broderick, D.F.; Burns, J.; Deshmukh, T.K.; Harvey, H.B.; Hoang, J.; Hunt, C.H.; Kennedy, T.A.; et al. Appropriate use criteria ACR; Appropriateness criteria â cerebrovascular disease expert panel on neurologic imaging. J Am Coll Radiol. 2017, 14, 34–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravani, H.; Mayer, S.A.; Demchuk, A.; Jahromi, B.S.; Gladstone, D.J.; Flaherty, M.; Broderick, J.; Aviv, R.I. Emergency noninvasive angiography for acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.; Ogungbemi, A.; Ambler, G.; Jones, I.; Werring, D.J.; Jäger, H.R. Developing an algorithm to identify patients with intracerebral haemorrhage secondary to a macrovascular cause. Eur. Stroke J. 2017, 2, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbabshirani, M.R.; Fornwalt, B.K.; Mongelluzzo, G.J.; Suever, J.D.; Geise, B.D.; Patel, A.A.; Moore, G.J. Advanced machine learning in action: Identification of intracranial hemorrhage on computed tomography scans of the head with clinical workflow integration. npj Digit. Med. 2018, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawabi, J.; Kniep, H.; Elsayed, S.; Friedrich, C.; Sporns, P.; Rusche, T.; Böhmer, M.; Morotti, A.; Schlunk, F.; Dührsen, L.; et al. Imaging-based outcome prediction of acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Transl. Stroke Res. 2021. Online ahe. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwindling, L.; Ragoschke-Schumm, A.; Kettner, M.; Helwig, S.; Manitz, M.; Roumia, S.; Lesmeister, M.; Grunwald, I.Q.; Fassbender, K. Prehospital imaging-based triage of head trauma with a mobile stroke unit: First evidence and literature review. J. Neuroimaging 2016, 26, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hov, M.R.; Ryen, A.; Finsnes, K.; Storflor, J.; Lindner, T.; Gleditsch, J.; Lund, C.G. Pre-hospital ct diagnosis of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Scand. J. Trauma. Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2017, 25, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, V.J.; Kasturiarachi, B.M.; Lin, E.; Bansal, V.; Zaidat, O.O. Review of the mobile stroke unit experience worldwide. Interv. Neurol. 2018, 7, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faghihi, R.; Zeinali-Rafsanjani, B.; Mosleh-Shirazi, M.A.; Saeedi-Moghadam, M.; Lotfi, M.; Jalli, R.; Iravani, V. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy and its clinical applications: A review. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Sci. 2017, 48, 233–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.E.; Gabr, R.E.; George, S.D.; Zhao, X.; Boren, S.B.; Zhang, X.; Ting, S.M.; Sun, G.; Hasan, K.M.; Savitz, S.; et al. Serial metabolic evaluation of perihematomal tissues in the intracerebral hemorrhage pig model. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Common causes |
| Hypertension |
| Cerebral amyloid angiopathy |
| Uncommon causes |
| Arteriovenous malformations |
| Coagulopathy |
| Intracranial aneurysm |
| Cavernous angioma |
| Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis |
| Dural arteriovenous fistula |
| Moyamoya disease |
| Hemorrhagic transformation of ischemic infarct |
| Illicit drug abuse |
| Tumor |
| Vasculitis |
| Infective endocarditis |
| Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome |
| Possible Causes of Secondary ICH | Red Flags | Suggested Investigations |
|---|---|---|
| Arteriovenous malformation | young age; Lobar ICH; | MRI; CTA/MRA/DSA |
| Coagulopathy | History of anticoagulant use; Large and irregularly shaped hematoma | NCCT/CTA |
| Cavernous angioma | Recurrent ICH in the same location; Lobar or brainstem ICH | Hemorrhage surrounded by hypointense halo or rim on T2-weighted imaging; Punctuate hypointense foci on T2*GRE/SWI |
| Moyamoya disease | Onset of ICH at young age; Ischemic symptoms; Migraine-like headache; | MRI showing “ivy sign”-linear high signals; DSA showing typical “puff-of-smoke” appearance |
| Intracranial aneurysm | Associated Subarachnoid hemorrhage | CTA/MRA/DSA showing intracranial aneurysm |
| Venous sinus thrombosis | Young and middle-aged patients; Moderate to severe headache; Lobar ICH | MRI showing infarcts not restricted to typical arterial territories; CTV/DSA |
| Tumor | Lobar ICH; disproportionate edema; Mass effect | MRI showing mass lesion |
| Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome | Headache; Encephalopathy; Seizures; Visual disturbance; Lobar ICH | MRI abnormalities in posterior or watershed region |
| Infective endocarditis | Fever; Valvular regurgitation | MRI showing associated infarcts; Echocardiogram showing valvular vegetation |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sporns, P.B.; Psychogios, M.-N.; Boulouis, G.; Charidimou, A.; Li, Q.; Fainardi, E.; Dowlatshahi, D.; Goldstein, J.N.; Morotti, A. Neuroimaging of Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10051086
Sporns PB, Psychogios M-N, Boulouis G, Charidimou A, Li Q, Fainardi E, Dowlatshahi D, Goldstein JN, Morotti A. Neuroimaging of Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(5):1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10051086
Chicago/Turabian StyleSporns, Peter B., Marios-Nikos Psychogios, Grégoire Boulouis, Andreas Charidimou, Qi Li, Enrico Fainardi, Dar Dowlatshahi, Joshua N. Goldstein, and Andrea Morotti. 2021. "Neuroimaging of Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 5: 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10051086
APA StyleSporns, P. B., Psychogios, M.-N., Boulouis, G., Charidimou, A., Li, Q., Fainardi, E., Dowlatshahi, D., Goldstein, J. N., & Morotti, A. (2021). Neuroimaging of Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(5), 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10051086








