Bidirectional Association between Metabolic Control in Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus and Periodontitis Inflammatory Burden: A Cross-Sectional Study in an Italian Population
Abstract
1. Introduction
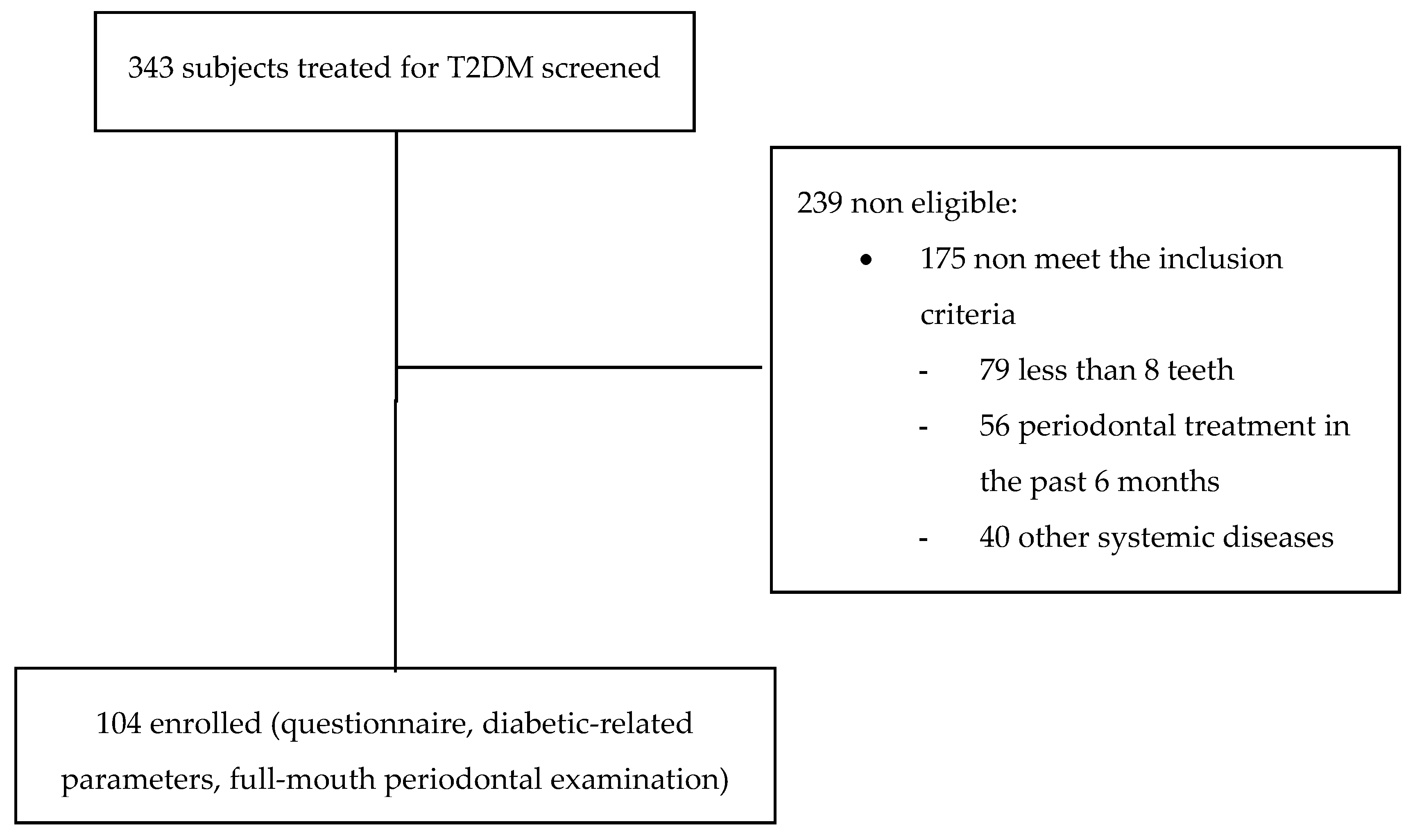
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ogurtsova, K.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Huang, Y.; Linnenkamp, U.; Guariguata, L.; Cho, N.H.; Cavan, D.; Shaw, J.E.; Makaroff, L.E. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 2017, 128, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes Care 2017, 40 (Suppl. 1), S11–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathers, C.D.; Loncar, D. Projections of global mortality and burden of disease from 2002 to 2030. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, J.M.; Cooper, M.E. Mechanisms of diabetic complications. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 137–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lind, M.; Odén, A.; Fahlén, M.; Eliasson, B. A systematic review of HbA1c variables used in the study of diabetic complications. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2008, 2, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lӧe, H. Periodontal disease: The sixth complication of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 1993, 16, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, B.; Park, B.; Barthold, P.M. Periodontitis and type II diabetes: A two-way relationship. Int. J. Evid. Based Healthc. 2013, 11, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, M.; Ceriello, A.; Buysschaert, M.; Chapple, I.; Demmer, R.T.; Graziani, F.; Herrera, D.; Jepsen, S.; Lione, L.; Madianos, P.; et al. Scientific evidence on the links between periodontal diseases and diabetes: Consensus report and guidelines of the joint workshop on periodontal diseases and diabetes by the International Diabetes Federation and the European Federation of Periodontology. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-Z.; Yuan, Y.-H.; Liu, H.-H.; Li, S.-S.; Zhang, B.-W.; Chen, W.; An, Z.-J.; Chen, S.-Y.; Wu, Y.-Z.; Han, B.; et al. Epidemiologic relationship between periodontitis and type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavarry, N.G.; Vettore, M.V.; Sansone, C.; Sheiham, A. The relationship between diabetes mellitus and destructive periodontal disease: A meta-analysis. Oral Health Prev. Dent. 2009, 7, 107–127. [Google Scholar]
- Lalla, E.; Papapanou, P.N. Diabetes mellitus and periodontitis: A tale of two common interrelated diseases. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 7, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapple, I.L.; Genco, R. Working group 2 of the joint EFP/AAP workshop. Diabetes and periodontal diseases: Consensus report of the joint EFP/AAP Workshop on Periodontitis and Systemic Diseases. J. Periodontol. 2013, 40 (Suppl. 14), 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumvoll, M.; Goldstein, B.J.; van Haeften, T.W. Type 2 diabetes: Principles of pathogenesis and therapy. Lancet 2005, 365, 1333–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, D.T.; Ding, Z.; Yang, Y. The impact of diabetes on periodontal diseases. Periodontology 2000 2020, 82, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziani, F.; Gennai, S.; Solini, A.; Petrini, M. A systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiologic observational evidence on the effect of periodontitis on diabetes an update of the EFP-AAP review. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, 167–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aral, C.A.; Nalbantoğlu, Ö.; Nur, B.G.; Altunsoy, M.; Aral, K. Metabolic control and periodontal treatment decreases elevated oxidative stress in the early phases of type 1 diabetes onset. Arch. Oral Biol. 2017, 82, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, G.C. The complete periodontal examination. Periodontolology 2000 2004, 34, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesse, W.; Abbas, F.; van der Ploeg, I.; Spijkervet, F.K.; Dijkstra, P.U.; Vissink, A. Periodontal inflamed surface area: Quantifying inflammatory burden. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2008, 35, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hujoel, P.P.; White, B.A.; Garcia, R.I.; Listgarten, M.A. The dentogingival epithelial surface area revisited. J. Periodont. Res. 2001, 36, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesse, W.; Linde, A.; Abbas, F.; Spijkervet, F.K.; Dijkstra, P.U.; de Brabander, E.C.; Gerstenbluth, I.; Vissink, A. Dose–response relationship between periodontal inflamed surface area and HbA1c in type 2 diabetics. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2009, 36, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leira, Y.; Martín-Lancharro, P.; Blanco, J. Periodontal inflamed surface area and periodontal case definition classification. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2018, 76, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Ahn, S.; Lee, J.T.; Yun, P.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Song, Y.W.; Chang, Y.S.; Lee, H.J. Periodontal inflamed surface area as a novel numerical variable describing periodontal conditions. J. Periodontal Implant. Sci. 2017, 47, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, S.K.; Lavu, V.; Rao, S. Chronic periodontitis prevalence and the inflammatory burden in a sample population from South India. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2018, 29, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, M.J.; Potter, R.M.; Blodgett, J.; Ebersole, J.L. Periodontal disease in Hispanic Americans with type 2 diabetes. J. Periodontol. 2008, 79, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.T.; Chen, T.H.; Wang, P.E.; Lai, H.; Lo, M.T.; Chen, P.Y.C.; Chiu, S.Y.H. A population-based study on the association between type 2 diabetes and periodontal disease in 12,123 middle-aged Taiwanese (KCIS No. 21). J. Clin. Periodontol. 2009, 36, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonora, E.; Cataudella, S.; Marchesini, G.; Miccoli, R.; Vaccaro, O.; Fadini, G.P.; Martini, L.; Rossi, E. Under te mandate of the Italian Diabetes Society. Clinical burden of diabetes in Italy in 2018: A look at a systemic disease from the ARNO Diabetes Observatory. BMJ Open Diab. Res. Care 2020, 8, e001191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, K.G.; Zimmet, P.Z. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet. Med. 1998, 15, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, R.C.; Eke, P.I. Case definitions for use in population-based surveillance of periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 2007, 78, 1387–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eke, P.I.; Page, R.C.; Wei, L.; Thornton-Evans, G.; Genco, R.J. Update of the case definitions for population-based surveillance of periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 2012, 83, 1449–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonetti, M.S.; Greenwell, H.; Kornman, K.S. Staging and grading of periodontitis: Framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. 20), S159–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, H.; Martin, S. Environmental/lifestyle factors in the pathogenesis and prevention of type 2 diabetes. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtfreter, B.; Albandar, J.M.; Dietrich, T.; Dye, B.A.; Eaton, K.A.; Eke, P.I.; Papapanou, P.N.; Kocher, T.; Joint EU/USA Periodontal Epidemiology Working Group. Standards of reporting chronic periodontitis prevalence and severity in epidemiological studies: Proposed standards from the Joint EU/USA Periodontal Epidemiology Working Group. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2015, 42, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preshaw, P.M.; de Silva, N.; McCracken, G.I.; Fernando, D.J.S.; Dalton, C.F.; Steen, N.D.; Heasman, P.A. Compromised periodontal status in an urban Sri Lankan population with type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2010, 37, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susanto, H.; Nesse, W.; Dijkstra, P.U.; Hoedemaker, E.; van Reenen, Y.H.; Agustina, D.; Vissink, A.; Abbas, F. Periodontal inflamed surface area and C-reactive protein as predictors of HbA1c: A study in Indonesia. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2012, 16, 1237–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-K.; Lee, S.G.; Choi, Y.-H.; Won, K.-C.; Moon, J.S.; Merchant, A.T.; Lee, H.-K. Association between diabetes-related factors and clinical periodontal parameters in type-2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Oral Health 2013, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.G.; Idris, S.B.; Ahmed, M.F.; Bøe, O.E.; Mustafa, K.; Ibrahim, S.O.; Åstrøm, A.N. Association between oral health status and type 2 diabetes mellitus among Sudanese adults: A matched case-control study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.W.; Noh, J.H.; Kim, D.-J. The prevalence and associated factors of periodontitis according to fasting plasma glucose in the Korean adults. Medicine 2016, 95, e3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimetti, M.; Perotto, S.; Castiglione, A.; Mariani, G.M.; Ferrarotti, F.; Romano, F. Prevalence of periodontitis in an adult population from an urban area in North Italy: Findings from a cross-sectional population-based epidemiological survey. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2015, 42, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abduljabbar, T.; Al-sahaly, F.; Al-kathami, M.; Afza, S.; Vohra, F. Comparison of periodontal and peri-implant inflammatory parameters among patients with prediabetes, type 2 diabetes mellitus and non-diabetic controls. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2017, 75, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowall, B.; Holtfreter, B.; Volzke, H.; Schipf, S.; Mundt, T.; Rathmann, W.; Kocher, T. Pre-diabetes and well-controlled diabetes are not associated with periodontal disease: The SHIP Trend Study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2015, 42, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campus, G.; Salem, A.; Uzzau, S.; Baldoni, E.; Tonolo, G. Diabetes and periodontal disease. A case-control study. J. Periodontol. 2005, 76, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannidou, E.; Malekzadeh, T.; Dongari-Bagtzoglou, A. Effect of periodontal treatment on serum C-reactive protein levels: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Periodontol. 2006, 77, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polak, D.; Sanui, T.; Nishimura, F.; Shapira, L. Diabetes as a risk factor for periodontal disease-Plausible mechanisms. Periodontology 2000 2020, 83, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanto, H.; Nesse, W.; Dijkstra, P.U.; Agustina, D.; Vissink, A.; Abbas, F. Periodontitis prevalence and severity in Indonesians with type 2 diabetes. J. Periodontol. 2011, 82, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sora, N.D.; Marlow, N.M.; Bandyopadhyay, D.; Leite, R.S.; Slate, E.H.; Fernandes, J.K. Metabolic syndrome and periodontitis in Gullah African Americans with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2013, 40, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirwan, J.P.; Sacks, J.; Nieuwoudt, S. The essential role of exercise in the management of type 2 diabetes. Cleve. Clin. J. Med. 2017, 84 (7 Suppl. 1), S15–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiiszewski, P.M.; Janssen, I.; Ross, R. Does waist circumference predict diabetes and cardiovascular disease beyond commonly evaluated cardio metabolic risk factors? Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 3105–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, F.; Bongiovanni, L.; Bianco, L.; Di Scipio, F.; Yang, Z.; Sprio, A.E.; Berta, G.N.; Aimetti, M. Biomarker levels in gingival crevicular fluid of generalized aggressive periodontitis patients after non-surgical periodontal treatment. Clin. Oral Invest. 2018, 22, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, F.; Del Buono, W.; Bianco, L.; Arana, M.; Mariani, G.M.; Di Scipio, F.; Berta, G.N.; Aimetti, M. Gingival crevicular fluid cytokines in moderate and deep pocket sites of Stage III periodontitis patients in different rated of clinical progression. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, B.G. Systemic markers of inflammation of periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 2006, 76, 2106–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polak, D.; Shapira, L. An update of the evidence for pathogenic mechanisms that may link periodontitis and diabetes. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, 150–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecoro, G.; Annunziata, M.; Iuorio, M.T.; Nastri, L.; Guida, L. Periodontitis, low-grade inflammation and systemic health: A scoping review. Medicina 2020, 56, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, R.C. The pathobiology of periodontal diseases may affect systemic diseases: Inversion of a paradigm. Ann. Periodontol. 1998, 3, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preshaw, P.M.; Foster, N.; Taylor, J.I. Cross-susceptibility between periodontal disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus: An immunobiological perspective. Periodontology 2000 2007, 45, 138–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, F.; Soga, Y.; Iwamoto, Y.; Kudo, C.; Murayama, Y. Periodontal disease as part of the insulin resistance syndrome in diabetic patients. J. Int. Acad. Periodontol. 2005, 7, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Shoelson, S.E.; Lee, J.; Goldfine, A.B. Inflammation and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engebretson, S.; Chertog, R.; Nichols, A.; Hey-Hadavi, J.; Celenti, R.; Grbic, J. Plasma levels of tumour necrosis factor-alpha in patients with chronic periodontitis and type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2007, 34, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madianos, P.M.; Koromantzos, P.A. An update of the evidence on the potential impact of periodontal therapy on diabetes outcomes. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, C.; Muñoz, F.; Andriankaja, O.M.; Ritchie, C.S.; Martínez, S.; Vergara, J.; Vivaldi, J.; Lòpez, L.; Campos, M.; Joshipura, K.J. Cross-sectional associations of impaired glucose metabolism measures with bleeding on probing and periodontitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, F.; Perotto, S.; Castiglione, A.; Aimetti, M. Prevalence of periodontitis: Misclassification, under-recognition or over-diagnosis using partial and full-mouth periodontal examination protocols. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2019, 77, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, P.M.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S.; Eliasson, B.; Cederholm, J.; Steering Committee of the Swedish National Diabetes Register. Smoking is associated with increased HbA1c values and microalbuminuria in patients with diabetes-data from the National Diabetes Register in Sweden. Diabetes Metab. 2004, 30, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, F.R.M.; Nascimento, G.G.; Scheutz, F.; Lòpez, R. Effect of smoking on periodontitis: A systematic review and meta-regression. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2018, 54, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | Poor Glycemic Control (n= 66) | Good Glycemic Control (n = 38) | Total (n = 104) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 65.9 ± 9.7 (43–80) | 64.4 ± 10.8 (40–78) | 65.3 ± 10.1 (40–80) | 0.459 |
| Sex | 0.076 | |||
| Males | 43 (70.5) | 18 (29.5) | 61 (58.7) | |
| Females | 23 (53.5) | 20 (46.5) | 43 (41.3) | |
| Education level | 0.796 | |||
| <high school | 33 (64.7) | 18 (35.3) | 51 (48.1) | |
| high school or higher | 33 (62.3) | 20 (37.7) | 53 (51.9) | |
| Smoking | 0.788 | |||
| Yes | 4 (66.7) | 2 (33.3) | 6 (5.8) | |
| No | 62 (63.3) | 36 (36.7) | 98 (94.2) | |
| Alcohol consumption | 0.384 | |||
| Yes | 42 (61.8) | 26 (38.2) | 68 (64.4) | |
| No | 24 (66.7) | 12 (33.3) | 36 (34.6) | |
| Balanced diet | 0.105 | |||
| Yes | 4 (40.0) | 6 (60.0) | 10 (9.6) | |
| No | 62 (66.0) | 32 (34.0) | 94 (90.4) | |
| Leisure-time physical activity | 0.019 | |||
| Yes | 21 (50.0) | 21 (50.0) | 42 (40.4) | |
| No | 45 (72.6) | 17 (27.4) | 62 (59.6) | |
| Duration of diabetes (years) | 15.1 ± 9.9 (1–42) | 12.8 ± 11.7 (1–52) | 14.2 ± 10.7 (1–52) | 0.306 |
| Family history of T2DM | 0.395 | |||
| Yes | 47 (66.2) | 24 (33.8) | 71 (68.3) | |
| No | 19 (57.6) | 14 (42.4) | 33 (31.7) | |
| Chronic complications of diabetes | 0.009 | |||
| None | 22 (53.7) | 19 (46.3) | 41 (39.4) | |
| 1 | 21 (56.8) | 16 (43.2) | 37 (35.6) | |
| 2 or more | 23 (88.5) | 3 (11.5) | 26 (25.0) | |
| HbA1c (%) | 8.0 ± 1.0 (7.0–11.6) | 6.3 ± 0.5 (5.0–6.9) | 7.4 ± 1.2 (5.0–11.6) | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29.6 ± 5.1 (18.8–40.8) | 28.1 ± 6.1 (17.0–43.0) | 29.1 ± 5.5 (17.0–43.0) | 0.162 |
| WC (cm) | 104.4 ± 12.6 (71.0–134.0) | 94.9 ± 15.2 (60.0–130.0) | 100.9 ± 14.3 (60.0–134.0) | 0.001 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 150.9 ± 81.4 851.0–507.0) | 145.0 ± 77.7 (57.0–377.0) | 148.8 ± 79.7 (51.0–107.0) | 0.719 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 47.2 ± 15.1 (23.0–90.0) | 53.8 ± 16.7 (31.0–88.0) | 49.6 ± 15.9 (23.0–80.0) | 0.042 |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 94.9 ± 29.2 (47.6–147.0) | 92.8 ± 31.9 (22.4–158.2) | 94.1 ± 30.1 (22.4–158.2) | 0.738 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 171.8 ± 31.1 (122.0–227.0) | 177.2 ± 31.7 (101.0–224.0) | 173.7 ± 31.3 (101.0–227.0) | 0.399 |
| hs-CPR (mg/L) | 2.9 ± 2.3 (0.2–8.5) | 1.8 ± 2.3 (0.0–9.9) | 2.5 ± 2.3 (0.0–9.9) | 0.030 |
| Number of teeth | 21.9 ± 4.9 (6–28) | 22.7 ± 4.6 (9–28) | 22.2 ± 4.8 (6–28) | 0.410 |
| Periodontitis | <0.001 | |||
| No/mild periodontitis | 1 (11.1) | 8 (88.9) | 9 (8.7) | |
| Moderate periodontitis | 13 (46.4) | 15 (53.6) | 28 (26.9) | |
| Severe periodontitis | 52 (77.6) | 15 (22.4) | 67 (64.4) | |
| Full-mouth PISA (mm2) | 1342.3 ± 487.9 (422.0–2732.0) | 946.1 ± 454.1 (229.0–2252.0) | 1204.1 ± 507.7 (229.0–2732.0) | <0.001 |
| Variable | No/Mild Periodontitis (n = 9) | Moderate Periodontitis (n = 28) | Severe Periodontitis (n = 67) | Total | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 60.1 ± 17.1 (40–79) | 66.0 ± 9.7 (47–80) | 65.8 ± 8.9 (43–80) | 65.3 ± 10.1 (40–80) | 0.266 |
| Sex | 0.240 | ||||
| Males | 3 (4.9) | 16 (26.2) | 42 (68.9) | 61 (58.7) | |
| Females | 6 (14.0) | 12 (27.9) | 25 (58.1) | 43 (41.3) | |
| Education level | 0.902 | ||||
| <high school | 5 (9.8) | 14 (27.5) | 32 (62.7) | 51 (48.1) | |
| high school or higher | 4 (7.5) | 14 (26.4) | 35 (66.0) | 53 (51.9) | |
| Smoking | 0.696 | ||||
| Yes | 1 (16.7) | 1 (16.7) | 4 (66.6) | 6 (5.8) | |
| No | 8 (8.2) | 27 (27.5) | 63 (64.3) | 98 (94.2) | |
| Alcohol consumption | 0.455 | ||||
| Yes | 5 (7.3) | 15 (22.1) | 48 (70.6) | 68 (65.4) | |
| No | 4 (11.1) | 13 (36.1) | 19 (52.8) | 36 (34.6) | |
| Balanced diet | 0.196 | ||||
| Yes | 0 | 1 (10.0) | 9 (90.0) | 10 (9.6) | |
| No | 9 (9.6) | 27 (28.7) | 58 (61.7) | 94 (90.4) | |
| Leisure-time physical activity | 0.904 | ||||
| Yes | 4 (9.5) | 12 (28.6) | 26 (61.9) | 42 (40.4) | |
| No | 5 (8.1) | 16 (25.8) | 41 (66.1) | 62 (59.6) | |
| Duration of diabetes (yrs) | 14.9 ± 11.2 (1–38) | 12.9 ± 11.9 (1–52) | 14.7 ± 10.1 (1–42) | 14.2 ± 10.7 (1–52) | 0.754 |
| Family history of T2DM | 0.015 | ||||
| Yes | 7 (9.9) | 13 (18.3) | 51 (71.8) | 71 (68.3) | |
| No | 2 (6.1) | 15 (45.4) | 16 (48.5) | 33 (31.7) | |
| Chronic complications of diabetes | 0.002 | ||||
| None | 5 (12.2) | 12 (29.3) | 24 (58.5) | 41 (39.4) | |
| 1 | 4 (10.8) | 15 (40.5) | 18 (48.6) | 37 (35.6) | |
| 2 or more | 0 (0.0) | 1 (3.8) | 25 (96.2) | 26 (25.0) | |
| Glycemic control | <0.001 | ||||
| Good | 8 (21.1) | 15 (39.5) | 15 (39.5) | 38 (36.5) | |
| Poor | 1 (1.5) | 13 (19.7) | 52 (78.8) | 66 (63.5) | |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.1 ± 0.7 (5.0–7.3) | 7.1 ± 1.3 (5.4–10.0) | 7.6 ± 1.1 (5.2–11.6) | 7.4 ± 1.2 (5.0 –11.6) | 0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 31.0 ± 6.3 (23.0–43.0) | 27.9 ± 6.0 (18.0– 40.3) | 29.3 ± 5.1 (17.0–40.8) | 29.1 ± 5.5 (17.0–43.0) | 0.295 |
| WC (cm) | 100.2 ± 11.3 (80.0–115.0) | 98.4± 16.9 (66.0–130.0) | 102.0 ± 13.5 (60.0M–134.0) | 100.9 ± 14.3 (60.0–134.0) | 0.533 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 136.1 ± 92.5 (57.0–374.0) | 176.1 ± 109.4 (63.0–107.0) | 139.0 ± 59.6 (51.0–358.0) | 148.8 ± 79.7 (51.0–107.0) | 0.103 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 52.2 ± 17.4 (38.0–83.0) | 47.1 ± 15.6 (23.0–83.0) | 50.3 ± 16.0 (24.0–90.0) | 49.6 ± 15.9 (23.0–80.0) | 0.592 |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 94.8 ± 43.6 (22.4–154.0) | 91.9 ± 31.9 (38.4 –158.2) | 95.0 ± 27.7 (47.6 –147.0) | 94.1 ± 30.1 (22.4–158.2) | 0.903 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 179.1 ± 29.0 (124.0–217.0) | 174.6 ± 35.5 (101.0–207.0) | 172.6 ± 30.0 (122.0–226.0) | 173.7 ± 31.3 (101.0–227.0) | 0.832 |
| hs-CPR (mg/L) | 0.7 ± 0.06 (0.0–2.0) | 1.5 ± 1.2 (0.0–4.7) | 3.1 ± 2.5 (0.2–9.9) | 2.5 ± 2.3 (0.0–9.9) | <0.001 |
| Number of teeth | 24.1 ± 3.8 (18–28) | 22.1± 4.8 (10–28) | 22.0 ± 4.9 (6–28) | 22.2 ± 4.8 (6–28) | 0.472 |
| Full-mouth PISA (mm2) | 415.5 ± 105.5 (229.0 – 575.0) | 859.4 ± 199.5 (494.0 –1298.0) | 1454.1 ± 431.3 (585.0 – 2732.0) | 1204.1 ± 507.7 (229.0 –2732.0) | < 0.001 |
| Model and Variables | Severe Periodontitis (Dichotomous) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% IC | p Value | |
| Model 1 | |||
| Glycemic control (poor vs. good) | 4.574 | 1.724 to 12.138 | 0.002 |
| Family history of T2DM (yes vs. no) | 3.323 | 1.189 to 9.283 | 0.022 |
| hs-CRP (mg/L) | 1.656 | 1.187 to 2.306 | 0.003 |
| Model 2 | |||
| HbA1c (%) | 1.608 | 1.034 to 2.502 | 0.035 |
| Family history of T2DM (yes vs. no) | 3.257 | 1.194 to 8.885 | 0.021 |
| hs-CRP (mg/L) | 1.692 | 1.213 to 2.360 | 0.002 |
| PISA (mm2) | |||
| ß | 95% IC | p Value | |
| Model 3 | |||
| Glycemic control (poor vs. good) | 297.419 | 104.887 to 489.951 | 0.003 |
| Chronic diabetes complications (at least one vs. none) | 205.264 | 19.895 to 390.632 | 0.030 |
| hs-CRP (mg/L) | 46.002 | 6.136 to 85.868 | 0.024 |
| Model 4 | |||
| HbA1c (%) | 89.601 | 11.265 to 167.937 | 0.025 |
| Chronic diabetes complications (at least one vs. none) | 219.628 | 30.917 to 408.339 | 0.023 |
| hs-CRP (mg/L) | 49.949 | 9.412 to 90.486 | 0.016 |
| Model and Variables | Poorly Controlled T2DM (Dichotomous) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% IC | p Value | |
| Model 5 | |||
| Severe periodontitis (yes vs. no) | 8.509 | 2.988 to 24.230 | <0.001 |
| Leisure-time physical activity (yes vs. no) | 0.384 | 0.143 to 1.033 | 0.058 |
| Balanced diet (yes vs. no) | 0.125 | 0.027 to 0.580 | 0.008 |
| WC (cm) | 1.057 | 1.018 to 1.096 | 0.004 |
| Model 6 | |||
| PISA (mm2) | 1.002 | 1.001 to 1.003 | <0.001 |
| Leisure-time physical activity (yes vs. no) | 0.397 | 0.150 to 1.051 | 0.063 |
| Balanced diet (yes vs. no) | 0.140 | 0.027 to 0.725 | 0.019 |
| WC (cm) | 1.062 | 1.023 to 1.103 | 0.002 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romano, F.; Perotto, S.; Mohamed, S.E.O.; Bernardi, S.; Giraudi, M.; Caropreso, P.; Mengozzi, G.; Baima, G.; Citterio, F.; Berta, G.N.; et al. Bidirectional Association between Metabolic Control in Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus and Periodontitis Inflammatory Burden: A Cross-Sectional Study in an Italian Population. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081787
Romano F, Perotto S, Mohamed SEO, Bernardi S, Giraudi M, Caropreso P, Mengozzi G, Baima G, Citterio F, Berta GN, et al. Bidirectional Association between Metabolic Control in Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus and Periodontitis Inflammatory Burden: A Cross-Sectional Study in an Italian Population. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(8):1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081787
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomano, Federica, Stefano Perotto, Sara Elamin Osman Mohamed, Sara Bernardi, Marta Giraudi, Paola Caropreso, Giulio Mengozzi, Giacomo Baima, Filippo Citterio, Giovanni Nicolao Berta, and et al. 2021. "Bidirectional Association between Metabolic Control in Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus and Periodontitis Inflammatory Burden: A Cross-Sectional Study in an Italian Population" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 8: 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081787
APA StyleRomano, F., Perotto, S., Mohamed, S. E. O., Bernardi, S., Giraudi, M., Caropreso, P., Mengozzi, G., Baima, G., Citterio, F., Berta, G. N., Durazzo, M., Gruden, G., & Aimetti, M. (2021). Bidirectional Association between Metabolic Control in Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus and Periodontitis Inflammatory Burden: A Cross-Sectional Study in an Italian Population. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(8), 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081787







