Morbid Obesity and Thyroid Cancer Rate. A Review of Literature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Thyroid Cancer
3. Obesity, Inflammation and Cancer Development
4. Obesity and Thyroid Cancer
5. Studies in Animal Models
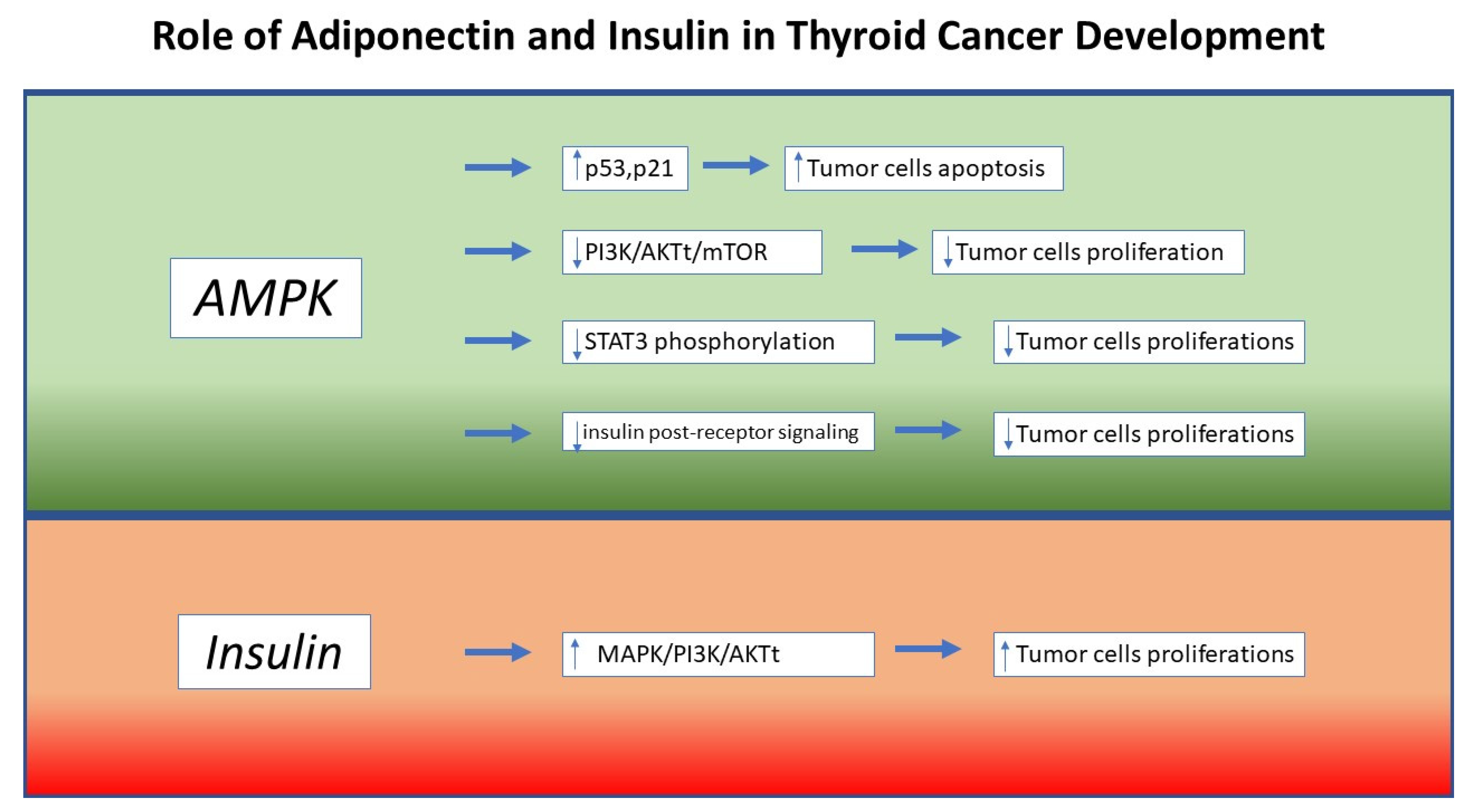
6. Molecular Mechanisms
7. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Trends in adult body-mass index in 200 countries from 1975 to 2014: A pooled analysis of 1698 population-based measurement studies with 19.2 million participants. Lancet 2016, 387, 1377–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Renehan, A.G.; Tyson, M.; Egger, M.; Heller, R.F.; Zwahlen, M. Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Lancet 2008, 371, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Steliarova-Foucher, E.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Rosso, S.; Coebergh, J.W.W.; Comber, H.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: Estimates for 40 countries in 2012. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 1374–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guignard, R.; Truong, T.; Rougier, Y.; Baron-Dubourdieu, D.; Guénel, P. Alcohol drinking, tobacco smoking, and anthropometric characteristics as risk factors for thyroid cancer: A countrywide case-control study in New Caledonia. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 166, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.M.; Sung, J.; Ha, M. Obesity and risk of cancer in postmenopausal Korean women. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3395–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howlader, N.; Noone, A.M.; Krapcho, M.; Miller, D.; Bishop, K.; Altekruse, S.F.; Kosary, C.L.; Yu, M.; Ruhl, J.; Tatalovich, Z.; et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2018, National Cancer Institute. Bethesda. 2016. Available online: http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2013/ (accessed on 28 November 2020).
- Cabanillas, M.E.; McFadden, D.G.; Durante, C. Thyroid cancer. Lancet 2016, 388, 2783–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.; Naishadham, D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013, 63, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manié, S.; Santoro, M.; Fusco, A.; Billaud, M. The RET receptor: Function in development and dysfunction in congenital malformation. Trends Genet. 2001, 17, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforov, Y.E.; Nikiforova, M.N. Molecular genetics and diagnosis of thyroid cancer. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 7, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weetman, A.P. Cellular immune responses in autoimmune thyroid disease. Clin. Endocrinol. 2004, 61, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellone, M.D.; Cirafici, A.M.; Vita, G.D.; Falco, V.D.; Malorni, L.; Tallini, G.; Fagin, J.A.; Fusco, A.; Melillo, R.M.; Santoro, M. Ras-mediated apoptosis of PC CL 3 rat thyroid cells induced by RET/PTC oncogenes. Oncogene. 2003, 22, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guarino, V.; Castellone, M.D.; Avilla, E.; Melillo, R.M. Thyroid cancer and inflammation. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2010, 321, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okayasu, I. The Relationship of Lymphocytic Thyroiditis to the Development of Thyroid Carcinoma. Endocr. Pathol. 1997, 8, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryder, M.; Ghossein, R.A.; Ricarte-Filho, J.C.; Knauf, J.A.; Fagin, J.A. Increased density of tumor-associated macrophages is associated with decreased survival in advanced thyroid cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2008, 15, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO. Obesity and Overweight. 2017. Available online: http://www.who.int (accessed on 27 November 2020).
- Gallagher, E.J.; LeRoith, D. Obesity and Diabetes: The Increased Risk of Cancer and Cancer-Related Mortality. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 727–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Swinburn, B.A.; Sacks, G.; Hall, K.D.; McPherson, K.; Finegood, D.T.; Moodie, M.L.; Gortmaker, S.L. The global obesity pandemic: Shaped by global drivers and local environments. Lancet 2011, 378, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/disease-prevention/nutrition/a-healthy-lifestyle/body-mass-index-bmi (accessed on 23 April 2021).
- Olefsky, J.M.; Glass, C.K. Macrophages, inflammation and insulin resistance. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2010, 72, 219–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, T.; Lyon, C.J.; Bergin, S.; Caligiuri, M.A.; Hsueh, W.A. Obesity, Inflammation, and Cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2016, 11, 421–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avgerinos, K.I.; Spyrou, N.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Dalamaga, M. Obesity and cancer risk: Emerging biological mechanisms and perspectives. Metabolism 2019, 92, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Coussens, L.M. Accessories to the crime: Functions of cells recruited to the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 2012, 21, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balkwill, F.; Mantovani, A. Inflammation and cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet 2001, 357, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.S.; Vieira, A.R.; Aune, D.; Bandera, E.V.; Greenwood, D.C.; McTiernan, A.; Rosenblatt, D.N.; Thune, I.; Vieira, R.; Norat, T. Body mass index and survival in women with breast cancer-systematic literature review and meta-analysis of 82 follow-up studies. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 1901–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, H.T.; Hetland, R.B.; Nygaard, U.C.; Steffensen, I.L. Genetic and Diet-Induced Obesity Increased Intestinal Tumorigenesis in the Double Mutant Mouse Model Multiple Intestinal Neoplasia X Obese via Disturbed Glucose Regulation and Inflammation. J. Obes. 2015, 2015, 343479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolb, R.; Sutterwala, F.S.; Zhang, W. Obesity and cancer: Inflammation bridges the two. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2016, 29, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cnop, M.; Foufelle, F.; Velloso, L.A. Endoplasmic reticulum stress, obesity and diabetes. Trends. Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivennikov, S.I.; Greten, F.R.; Karin, M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell 2010, 140, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolb, R.; Liu, G.H.; Janowski, A.M.; Sutterwala, F.S.; Zhang, W. Inflammasomes in cancer: A double-edged sword. Protein. Cell. 2014, 5, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggioni, R.; Fantuzzi, G.; Fuller, J.; Dinarello, C.A.; Feingold, K.R.; Grunfeld, C. IL-1 beta mediates leptin induction during inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 274, R204–R208. [Google Scholar]
- Rustgi, V.K.; Li, Y.; Gupta, K.; Minacapelli, C.D.; Bhurwal, A.; Catalano, C.; Elsaid, M.I. Bariatric Surgery Reduces Cancer Risk in Adults with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Severe Obesity. Gastroenterology 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schauer, D.P.; Feigelson, H.S.; Koebnick, C.; Caan, B.; Weinmann, S.; Leonard, A.C.; Powers, J.D.; Yenumula, P.R.; Arterburn, D.E. Bariatric Surgery and the Risk of Cancer in a Large Multisite Cohort. Ann. Surg. 2019, 269, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.G.; Guo, X.G.; Ba, C.X.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y.Y.; Wang, J.; Cao, H.Y. Overweight, obesity and thyroid cancer risk: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. J. Int. Med. Res. 2012, 40, 2041–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmid, D.; Ricci, C.; Behrens, G.; Leitzmann, M.F. Adiposity and risk of thyroid cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 1042–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, P.; Wu, Y.; Hou, X.; Peng, Z.; Yang, W.; Guan, L.; Hu, L.; Zhi, J.; Gao, M.; et al. Correlation between obesity and clinicopathological characteristics in patients with papillary thyroid cancer: A study of 1579 cases: A retrospective study. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.S.; Huang, S.; Park, S. Association of Polygenetic Risk Scores Related to Cell Differentiation and Inflammation with Thyroid Cancer Risk and Genetic Interaction with Dietary Intake. Cancers 2021, 13, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Huang, M.; Wang, L.; Ye, W.; Tong, Y.; Wang, H. Obesity and risk of thyroid cancer: Evidence from a meta-analysis of 21 observational studies. Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 283–291. [Google Scholar]
- Rotondi, M.; Castagna, M.G.; Cappelli, C.; Ciuoli, C.; Coperchini, F.; Chiofalo, F.; Maino, F.; Palmitesta, P.; Chiovato, L.; Pacini, F. Obesity Does Not Modify the Risk of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer in a Cytological Series of Thyroid Nodules. Eur. Thyroid. J. 2016, 5, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farfel, A.; Kark, J.D.; Derazne, E.; Tzur, D.; Barchana, M.; Lazar, L.; Afek, A.; Shamiss, A. Predictors for thyroid carcinoma in Israel: A national cohort of 1,624,310 adolescents followed for up to 40 years. Thyroid 2014, 24, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.G.; Park, J.W.; Willingham, M.C.; Cheng, S.Y. Diet-induced obesity increases tumor growth and promotes anaplastic change in thyroid cancer in a mouse model. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 2936–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.W.; Han, C.R.; Zhao, L.; Willingham, M.C.; Cheng, S.Y. Inhibition of STAT3 activity delays obesity-induced thyroid carcinogenesis in a mouse model. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Z.; Saha, A.K.; Xiang, X.; Ruderman, N.B. AMPK, the metabolic syndrome and cancer. Trends. Pharmacol. Sci. 2005, 26, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, G.R.; Kemp, B.E. AMPK in Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 1025–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, T.; Garcia, R.; Turkson, J.; Jove, R. STATs in oncogenesis. Oncogene 2000, 19, 2474–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Izadi, V.; Farabad, E.; Azadbakht, L. Serum Adiponectin level and different kind of cancers: A review of recent evidence. ISRN Oncol. 2012, 2012, 982769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.; Roberts, R.; Vora, N. Energy homoeostasis: The roles of adipose tissue-derived hormones, peptide YY and Ghrelin. Obes. Facts 2009, 2, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyer, C.; Funanashi, T.; Tanaka, S.; Hotta, K.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Pratley, R.E.; Tataranni, P.A. Hypoadipoactinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: Close association with insulin-resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 1930–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeid, S.; Hebbard, L. Role of adiponectin and its receptors in cancer. Cancer Biol. Med. 2012, 9, 213–220. [Google Scholar]
- Hebbard, L.W.; Garlatti, M.; Young, L.J.T.; Cardiff, R.D.; Oshima Robert, G.; Ranscht, B. T-cadherin supports angiogenesis and adiponectin association with the vasculature in a mouse mammary tumor model. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dossus, L.; Franceschi, S.; Biessy, C.; Navionis, A.S.; Travis, R.C.; Weiderpass, E.; Scalbert, A.; Romieu, I.; Tjønneland, A.; Olsen, A.; et al. Adipokines and inflammation markers and risk of differentiated thyroid carcinoma: The EPIC study. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 142, 1332–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsiades, N.; Pazaitou-Panayiotou, K.; Aronis, K.N.; Moon, H.S.; Chamberland, J.P.; Liu, X.; Diakopoulos, K.N.; Kyttaris, V.; Panagiotou, V.; Mylvaganam, G.; et al. Circulating adiponectin is inversely associated with risk of thyroid cancer: In vivo and in vitro studies. J. Clin. Endocrinol Metab. 2011, 96, E2023–E2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, S.P.; Liu, C.L.; Hsu, Y.C.; Chang, Y.C.; Huang, S.Y.; Lee, J.J. Expression and biologic significance of adiponectin receptors in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 65, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciacca, L.; Vella, V.; Frittitta, L.; Tumminia, A.; Manzella, L.; Squatrito, S.; Belfiore, A.; Vigneri, R. Long-acting insulin analogs and cancer. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 28, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollak, M. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor signalling in neoplasia. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, M.; Yaghmaei, P.; Pooyamanesh, Z.; Yeganeh, M.Z.; Rad, L.H. Leptin: A correlated Peptide to papillary thyroid carcinoma? J. Thyroid. Res. 2011, 2011, 832163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uddin, S.; Bavi, P.; Siraj, A.K.; Ahmed, M.; Al-Rasheed, M.; Hussain, A.R.; Ahmed, M.; Amin, T.; Alzahrani, A.; Al-Dayel, F.; et al. Leptin-R and its association with PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2010, 17, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nam, S.; Park, S.; Park, H.S.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, S.I. Association between insulin resistance and luminal B subtype breast cancer in postmenopausal women. Medicine 2016, 95, e2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argirion, I.; Weinstein, S.J.; Mannisto, S.; Albanes, D.; Mondul, A.M. Serum insulin, glucose, indices of insulin resistance, and risk of lung cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2017, 26, 1519–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Braun, S.; Worms, K.B.; LeRoith, D. The link between the metabolic syndrome and cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 1003–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, B. Thyroid and obesity: An intriguing relationship. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 3614–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fontenelle, L.C.; Feitosa, M.M.; Severo, J.S.; Freitas, T.E.C.; Morais, J.B.S.; Torres-Leal, F.L.; Henriques, G.S.; Marreiro, D.D.N. Thyroid function in human obesity: Underlying mechanisms. Horm. Metab. Res. 2016, 48, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malaguarnera, R.; Frasca, F.; Garozzo, A.; Giani, F.; Pandini, G.; Vella, V.; Vigneri, R.; Belfiore, A. Insulin receptor isoforms and insulin-like growth factor receptor in human follicular cell precursors from papillary thyroid cancer and normal thy-roid. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belfiore, A.; Malaguarnera, R. Insulin receptor and cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2011, 18, R125–R147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Mao, X.; Wu, X.; Long, X.; Liu, C. The association between insulin re-sistance and vascularization of thyroid nodules. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pappa, T.; Alevizaki, M. Obesity and thyroid cancer: A clinical update. Thyroid 2014, 24, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.G.; Cheng, S.Y. Mechanisms Linking Obesity and Thyroid Cancer Development and Progression in Mouse Models. Horm. Cancer. 2018, 9, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Woo, J.W.; Park, I.; Lee, J.H.; Choe, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.S. Influence of Body Mass Index and Body Surface Area on the Behavior of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Thyroid 2016, 26, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, E.D.; Spiegelman, B.M. What we talk about when we talk about fat. Cell 2014, 156, 20–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Canu, G.L.; Medas, F.; Cappellacci, F.; Podda, M.G.; Romano, G.; Erdas, E.; Calò, P.G. Can thyroidectomy be considered safe in obese patients? A retrospective cohort study. BMC Surg. 2020, 20, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buerba, R.; Roman, S.A.; Sosa, J.A. Thyroidectomy and parathyroidectomy in patients with high body mass index are safe overall: Analysis of 26,864 patients. Surgery 2011, 150, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Masone, S.; Velotti, N.; Savastano, S.; Filice, E.; Serao, R.; Vitiello, A.; Berardi, G.; Schiavone, V.; Musella, M. Morbid Obesity and Thyroid Cancer Rate. A Review of Literature. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1894. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10091894
Masone S, Velotti N, Savastano S, Filice E, Serao R, Vitiello A, Berardi G, Schiavone V, Musella M. Morbid Obesity and Thyroid Cancer Rate. A Review of Literature. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(9):1894. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10091894
Chicago/Turabian StyleMasone, Stefania, Nunzio Velotti, Silvia Savastano, Emanuele Filice, Rossana Serao, Antonio Vitiello, Giovanna Berardi, Vincenzo Schiavone, and Mario Musella. 2021. "Morbid Obesity and Thyroid Cancer Rate. A Review of Literature" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 9: 1894. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10091894
APA StyleMasone, S., Velotti, N., Savastano, S., Filice, E., Serao, R., Vitiello, A., Berardi, G., Schiavone, V., & Musella, M. (2021). Morbid Obesity and Thyroid Cancer Rate. A Review of Literature. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(9), 1894. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10091894





