Impact of Intravenous Trehalose Administration in Patients with Niemann–Pick Disease Types A and B
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Test Substances
2.3. Endpoints and Assessments
2.3.1. Primary Endpoints
2.3.2. Secondary Endpoints
2.3.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of Patients
3.2. Quality of Life Assessment
3.3. Serum Lysosphingomyelin Levels (lyso-SM and lyso-SM509)
3.4. Serum ALT and AST Levels
3.5. Oxidative Stress Index (OSI)
3.6. Sonographic Liver and Spleen Dimensions
3.7. Lung HRCT
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schuchman, E.H.; Desnick, R.J. Types A and B niemann-pick disease. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 120, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerón-Rodríguez, M.; Vázquez-Martínez, E.R.; García-Delgado, C.; Ortega-Vázquez, A.; Valencia-Mayoral, P.; Ramírez-Devars, L.; Arias-Villegas, C.; Monroy-Muñoz, I.E.; López, M.; Cervantes, A.; et al. Niemann-Pick disease A or B in four pediatric patients and SMPD1 mutation carrier frequency in the Mexican population. Ann. Hepatol. 2019, 18, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuchman, E.H.; Wasserstein, M.P. Types A and B niemann-pick disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 29, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordieres-Ortega, L.; Galeano-Valle, F.; Mallén-Pérez, M.; Muñoz-Delgado, C.; Apaza-Chavez, J.E.; Menárguez-Palanca, F.J.; Alvarez-Sala Walther, L.A.; Demelo-Rodríguez, P. Niemann-Pick disease type-B: A unique case report with compound heterozygosity and complicated lipid management. BMC Med. Genet. 2020, 21, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pick, L., II. Niemann-Pick’s disease and other forms of so-called xanthomatosis. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1933, 185, 615–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGovern, M.M.; Wasserstein, M.P.; Kirmse, B.; Duvall, W.L.; Schiano, T.; Thurberg, B.L.; Richards, S.; Cox, G.F. Novel first-dose adverse drug reactions during a phase I trial of olipudase alfa (recombinant human acid sphingomyelinase) in adults with Niemann-Pick disease type B (acid sphingomyelinase deficiency). Genet. Med. Off. J. Am. Coll. Med. Genet. 2016, 18, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, G.R.; Praciano, A.M.; Rodrigues, J.P.; Viana, C.F.; Brandão, K.P.; Valenca, J.T., Jr.; Garcia, J.H. Liver transplantation in patients with niemann-pick disease--single-center experience. Transplant. Proc. 2015, 47, 2929–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, S.; Coulter, J.; Besley, G.; Ellis, I.; Desnick, R.; Schuchman, E.; Vellodi, A. Niemann–Pick disease: Sixteen-year follow-up of allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in a type B variant. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2003, 26, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Zheng, G.; Feng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Lou, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Shang, P.; et al. Trehalose ameliorates oxidative stress-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and ER stress via selective autophagy stimulation and autophagic flux restoration in osteoarthritis development. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, A.B.; Krakowka, S.; Dexter, L.B.; Schmid, H.; Wolterbeek, A.P.; Waalkens-Berendsen, D.H.; Shigoyuki, A.; Kurimoto, M. Trehalose: A review of properties, history of use and human tolerance, and results of multiple safety studies. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2002, 40, 871–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBosch, B.J.; Heitmeier, M.R.; Mayer, A.L.; Higgins, C.B.; Crowley, J.R.; Kraft, T.E.; Chi, M.; Newberry, E.P.; Chen, Z.; Finck, B.N.; et al. Trehalose inhibits solute carrier 2A (SLC2A) proteins to induce autophagy and prevent hepatic steatosis. Sci. Signal. 2016, 9, ra21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari-Robati, M.; Akbari, M.; Khaksari, M.; Mirzaee, M. Trehalose attenuates spinal cord injury through the regulation of oxidative stress, inflammation and GFAP expression in rats. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2019, 42, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinpour-Moghaddam, K.; Caraglia, M.; Sahebkar, A. Autophagy induction by trehalose: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic impacts. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 6524–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifeh, M.; Barreto, G.E.; Sahebkar, A. Trehalose as a promising therapeutic candidate for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 1173–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifeh, M.; Read, M.I.; Barreto, G.E.; Sahebkar, A. Trehalose against Alzheimer’s disease: Insights into a potential therapy. BioEssays 2020, 42, 1900195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahebkar, A.; Hatamipour, M.; Tabatabaei, S.A. Trehalose administration attenuates atherosclerosis in rabbits fed a high-fat diet. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 9455–9459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, J.E.; Sarkar, S.; Rubinsztein, D.C. Trehalose reduces aggregate formation and delays pathology in a transgenic mouse model of oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 15, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaltzman, R.; Elyoseph, Z.; Lev, N.; Gordon, C.R. Trehalose in machado-joseph disease: Safety, tolerability, and efficacy. Cerebellum 2020, 19, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifeh, M.; Barreto, G.E.; Sahebkar, A. Therapeutic potential of trehalose in neurodegenerative diseases: The knowns and unknowns. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 2026–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi, P.; Tse, D.Y.; Di Ronza, A.; Seymour, M.L.; Martano, G.; Cooper, J.D.; Pereira, F.A.; Passafaro, M.; Wu, S.M.; Sardiello, M. Trehalose reduces retinal degeneration, neuroinflammation and storage burden caused by a lysosomal hydrolase deficiency. Autophagy 2018, 14, 1419–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuele, E. Can trehalose prevent neurodegeneration? Insights from experimental studies. Curr. Drug Targets 2014, 15, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assoni, G.; Frapporti, G.; Colombo, E.; Gornati, D.; Perez-Carrion, M.D.; Polito, L.; Seneci, P.; Piccoli, G.; Arosio, D. Trehalose-based neuroprotective autophagy inducers. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 40, 127929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taya, K.; Hirose, K.; Hamada, S. Trehalose inhibits inflammatory cytokine production by protecting IkappaB-alpha reduction in mouse peritoneal macrophages. Arch. Oral Biol. 2009, 54, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabandé-Rodríguez, E.; Boya, P.; Labrador, V.; Dotti, C.G.; Ledesma, M.D. High sphingomyelin levels induce lysosomal damage and autophagy dysfunction in Niemann Pick disease type A. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cologna, S.M.; Cluzeau, C.V.; Yanjanin, N.M.; Blank, P.S.; Dail, M.K.; Siebel, S.; Toth, C.L.; Wassif, C.A.; Lieberman, A.P.; Porter, F.D. Human and mouse neuroinflammation markers in Niemann-Pick disease, type C1. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2014, 37, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Cañamás, A.; Benvegnù, S.; Rueda, C.B.; Rábano, A.; Satrústegui, J.; Ledesma, M.D. Sphingomyelin-induced inhibition of the plasma membrane calcium ATPase causes neurodegeneration in type A Niemann-Pick disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Yaribeygi, A.; Sathyapalan, T.; Sahebkar, A. Molecular mechanisms of trehalose in modulating glucose homeostasis in diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2019, 13, 2214–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtake, S.; Wang, Y.J. Trehalose: Current use and future applications. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 2020–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunge, E.; Essink-Bot, M.-L.; Kobussen, M.; van Suijlekom-Smit, L.; Moll, H.; Raat, H. Reliability and validity of health status measurement by the TAPQOL. Arch. Dis. Child. 2005, 90, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo, G.; Burlina, A.P.; Ranieri, E.; Colucci, F.; Rubert, L.; Pascarella, A.; Duro, G.; Tummolo, A.; Padoan, A.; Plebani, M.; et al. Plasma and dried blood spot lysosphingolipids for the diagnosis of different sphingolipidoses: A comparative study. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2019, 57, 1863–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Alamdari, D.H.; Moohebati, M.; Sahebkar, A.; Nematy, M.; Safarian, M.; Azimi-Nezhad, M.; Parizadeh, S.M.; Tavallaie, S.; Koliakos, G.; et al. Determination of prooxidant—Antioxidant balance after acute coronary syndrome using a rapid assay: A pilot study. Angiology 2009, 60, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Ranke, F.M.; Pereira Freitas, H.M.; Mançano, A.D.; Rodrigues, R.S.; Hochhegger, B.; Escuissato, D.; Araujo Neto, C.A.; da Silva, T.K.; Marchiori, E. Pulmonary involvement in Niemann-Pick disease: A state-of-the-art review. Lung 2016, 194, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Lozano, A.; Villamandos García, D.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Fiuza-Luces, C.; Pareja-Galeano, H.; Garatachea, N.; Nogales Gadea, G.; Lucia, A. Niemann-Pick disease treatment: A systematic review of clinical trials. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myerowitz, R.; Puertollano, R.; Raben, N. Impaired autophagy: The collateral damage of lysosomal storage disorders. EBioMedicine 2021, 63, 103166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, C.D.; Lieberman, A.P. The pathogenesis of Niemann–Pick type C disease: A role for autophagy? Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2008, 10, e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Canonico, B.; Cesarini, E.; Salucci, S.; Luchetti, F.; Falcieri, E.; Di Sario, G.; Palma, F.; Papa, S. Defective autophagy, mitochondrial clearance and lipophagy in Niemann-Pick type B lymphocytes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusmini, P.; Cortese, K.; Crippa, V.; Cristofani, R.; Cicardi, M.E.; Ferrari, V.; Vezzoli, G.; Tedesco, B.; Meroni, M.; Messi, E.; et al. Trehalose induces autophagy via lysosomal-mediated TFEB activation in models of motoneuron degeneration. Autophagy 2019, 15, 631–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, M.; Li, L.; Xu, S.; Huang, D.; Ju, M.; Huang, J.; Chen, K.; Gu, H. Trehalose, sucrose and raffinose are novel activators of autophagy in human keratinocytes through an mTOR-independent pathway. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Higgins, C.B.; Mayer, A.L.; Mysorekar, I.U.; Razani, B.; Graham, M.J.; Hruz, P.W.; DeBosch, B.J. TFEB-dependent induction of thermogenesis by the hepatocyte SLC2A inhibitor trehalose. Autophagy 2018, 14, 1959–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Ren, J. mTOR-Independent autophagy inducer trehalose rescues against insulin resistance-induced myocardial contractile anomalies: Role of p38 MAPK and Foxo1. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 111, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, T.D.; Jeong, S.-J.; Zhang, X.; Sergin, I.; Razani, B. TFEB and trehalose drive the macrophage autophagy-lysosome system to protect against atherosclerosis. Autophagy 2018, 14, 724–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, V.H.; Herr, D.R.; Panton, D.; Fyrst, H.; Saba, J.D.; Harris, G.L. Disruption of sphingolipid metabolism elicits apoptosis-associated reproductive defects in Drosophila. Dev. Biol. 2007, 309, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mignard, V.; Dubois, N.; Lanoé, D.; Joalland, M.P.; Oliver, L.; Pecqueur, C.; Heymann, D.; Paris, F.; Vallette, F.M.; Lalier, L. Sphingolipid distribution at mitochondria-associated membranes (MAMs) upon induction of apoptosis. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 1025–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maekawa, M.; Jinnoh, I.; Matsumoto, Y.; Narita, A.; Mashima, R.; Takahashi, H.; Iwahori, A.; Saigusa, D.; Fujii, K.; Abe, A.; et al. Structural determination of lysosphingomyelin-509 and discovery of novel class lipids from patients with Niemann–Pick disease type C. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghidoni, R.; Caretti, A.; Signorelli, P. Role of sphingolipids in the pathobiology of lung inflammation. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 487508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandru, H.; Boggaram, V. The role of sphingosine 1-phosphate in the TNF-alpha induction of IL-8 gene expression in lung epithelial cells. Gene 2007, 391, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyan, Z.S.; Karadağ, B.; Ersu, R.; Kiyan, G.; Kotiloğlu, E.; Sirvanci, S.; Ercan, F.; Dağli, T.; Karakoç, F.; Dağli, E. Early pulmonary involvement in Niemann-Pick type B disease: Lung lavage is not useful. Pediatric Pulmonol. 2005, 40, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.J.; Park, J.W. The role of sphingolipids in endoplasmic reticulum stress. FEBS Lett. 2020, 594, 3632–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knupp, J.; Martinez-Montañés, F.; Van Den Bergh, F.; Cottier, S.; Schneiter, R.; Beard, D.; Chang, A. Sphingolipid accumulation causes mitochondrial dysregulation and cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 2044–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizunoe, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Sudo, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Yasukawa, H.; Natori, D.; Hoshino, A.; Negishi, A.; Okita, N.; Komatsu, M.; et al. Trehalose protects against oxidative stress by regulating the Keap1-Nrf2 and autophagy pathways. Redox Biol. 2018, 15, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhao, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Z. Trehalose targets Nrf2 signal to alleviate d-galactose induced aging and improve behavioral ability. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 521, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.F.; Kuo, Y.T.; Chen, T.Y.; Chien, C.T. Quercetin-rich guava (Psidium guajava) juice in combination with trehalose reduces autophagy, apoptosis and pyroptosis formation in the kidney and pancreas of type II diabetic rats. Molecules 2016, 21, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portbury, S.D.; Hare, D.J.; Sgambelloni, C.; Perronnes, K.; Portbury, A.J.; Finkelstein, D.I.; Adlard, P.A. Trehalose improves cognition in the transgenic Tg2576 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 60, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portbury, S.D.; Hare, D.J.; Finkelstein, D.I.; Adlard, P.A. Trehalose improves traumatic brain injury-induced cognitive impairment. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, A.; Marconi, M.; Musillo, C.; Chiarotti, F.; Bellisario, V.; Matarrese, P.; Gambardella, L.; Vona, R.; Lombardi, M.; Foglieni, C.; et al. Trehalose administration in C57BL/6N old mice affects healthspan improving motor learning and brain anti-oxidant defences in a sex-dependent fashion: A pilot study. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 129, 110755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGovern, M.M.; Avetisyan, R.; Sanson, B.-J.; Lidove, O. Disease manifestations and burden of illness in patients with acid sphingomyelinase deficiency (ASMD). Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2017, 12, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGovern, M.M.; Wasserstein, M.P.; Giugliani, R.; Bembi, B.; Vanier, M.T.; Mengel, E.; Brodie, S.E.; Mendelson, D.; Skloot, G.; Desnick, R.J.; et al. A prospective, cross-sectional survey study of the natural history of Niemann-Pick disease type B. Pediatrics 2008, 122, e341–e349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasserstein, M.P.; Desnick, R.J.; Schuchman, E.H.; Hossain, S.; Wallenstein, S.; Lamm, C.; McGovern, M.M. The natural history of type B Niemann-Pick disease: Results from a 10-year longitudinal study. Pediatrics 2004, 114, e672–e677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
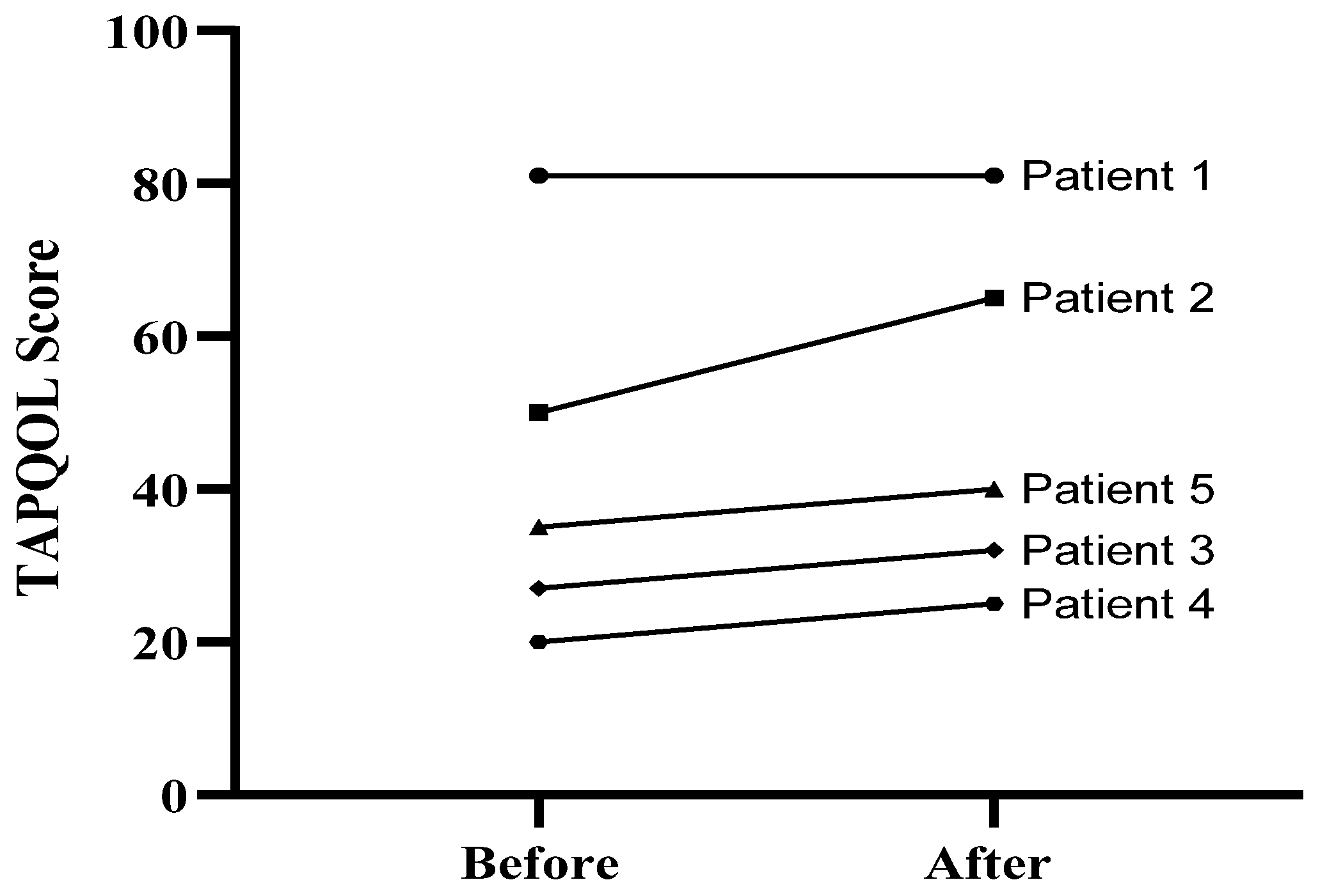



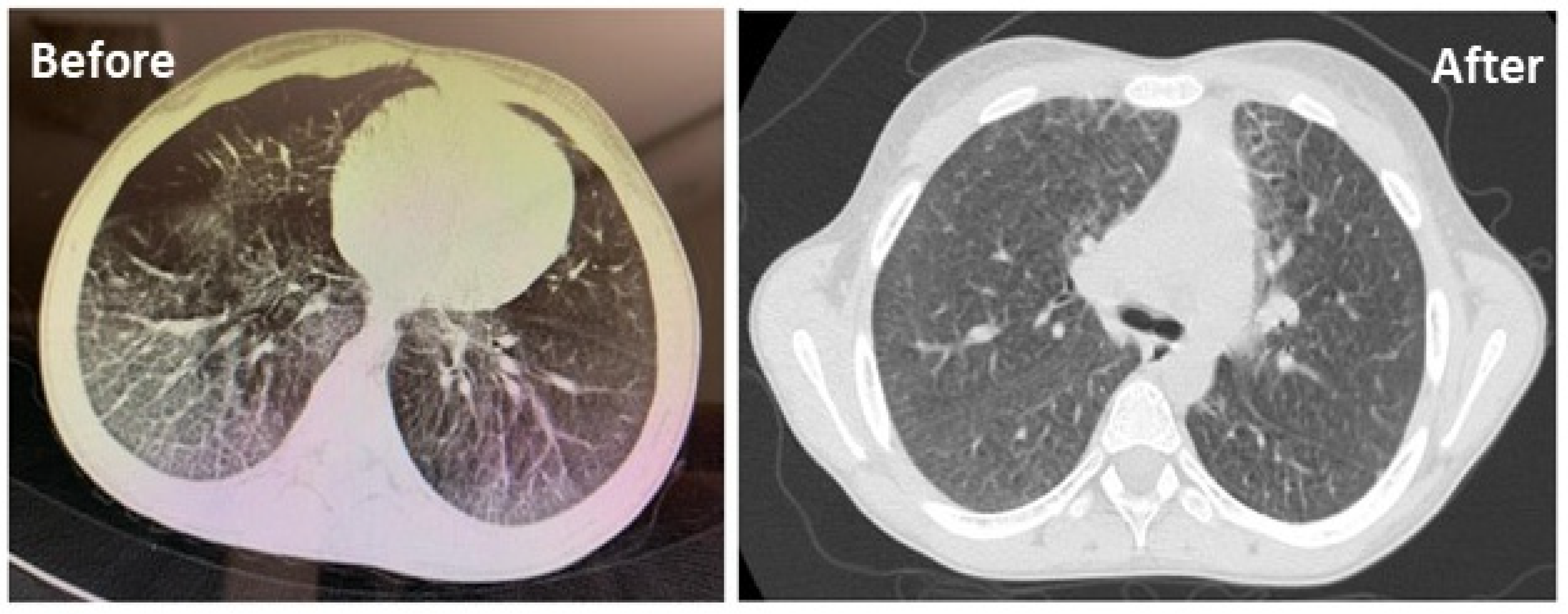
| Patient ID | Spleen cranio-Caudal Diameter (mm) | Liver Diameter Changes, Measuring the Liver Span below the Costal Margin by Ultrasound Scan (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | After | Before | After | |
| 01 | 204 | 224 | 30 | 30 |
| 02 | 125 | 122 | 10 | 30 |
| 03 | 120 | 138 | 30 | 10 |
| 04 | 150 | 145 | 10 | 30 |
| 05 | 115 | 115 | 30 | 30 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mobini, M.; Radbakhsh, S.; Kubaski, F.; Eshraghi, P.; Vakili, S.; Vakili, R.; Khalili, M.; Varesvazirian, M.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Alamdaran, S.A.; et al. Impact of Intravenous Trehalose Administration in Patients with Niemann–Pick Disease Types A and B. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010247
Mobini M, Radbakhsh S, Kubaski F, Eshraghi P, Vakili S, Vakili R, Khalili M, Varesvazirian M, Jamialahmadi T, Alamdaran SA, et al. Impact of Intravenous Trehalose Administration in Patients with Niemann–Pick Disease Types A and B. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(1):247. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010247
Chicago/Turabian StyleMobini, Moein, Shabnam Radbakhsh, Francyne Kubaski, Peyman Eshraghi, Saba Vakili, Rahim Vakili, Manijeh Khalili, Majid Varesvazirian, Tannaz Jamialahmadi, Seyed Ali Alamdaran, and et al. 2022. "Impact of Intravenous Trehalose Administration in Patients with Niemann–Pick Disease Types A and B" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 1: 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010247
APA StyleMobini, M., Radbakhsh, S., Kubaski, F., Eshraghi, P., Vakili, S., Vakili, R., Khalili, M., Varesvazirian, M., Jamialahmadi, T., Alamdaran, S. A., Sayedi, S. J., Rajabi, O., Emami, S. A., Reiner, Ž., & Sahebkar, A. (2022). Impact of Intravenous Trehalose Administration in Patients with Niemann–Pick Disease Types A and B. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(1), 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010247









