Tidal Volume in Pediatric Ventilation: Do You Get What You See?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Tidal Volume in Pediatric Ventilation: Technical Challenges and Clinical Consequences
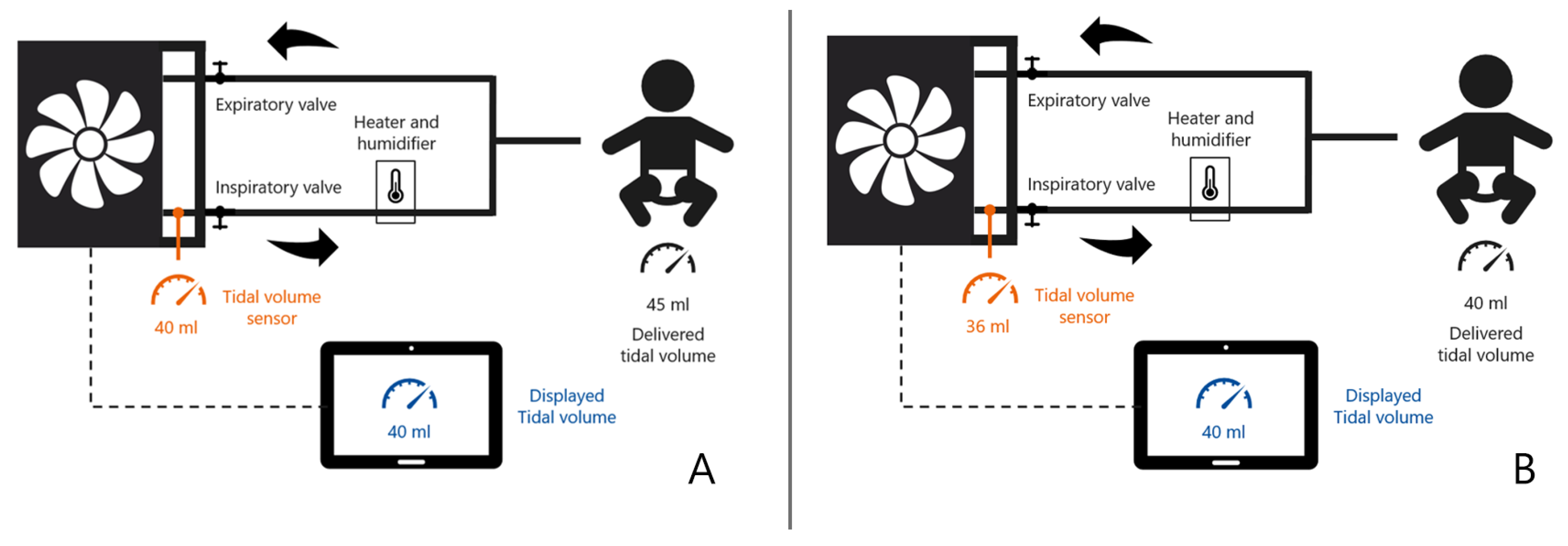
2.1. How Ventilators Measure Tidal Volumes
2.2. How Ventilators Report Tidal Volume
3. Pediatric Ventilation Tidal Volume: Impact of a Software Upgrade in a Prospective Cohort Study
3.1. Data Collection
3.2. Results
3.3. Discussion of the Results
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Castle, R.A.; Dunne, C.J.; Mok, Q.; Wade, A.M.; Stocks, J. Accuracy of Displayed Values of Tidal Volume in the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 30, 2566–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyton. Textbook of Medical Physiology, 11th ed.; Sigma-Aldrich: St. Louis, MI, USA, 2005; Available online: http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/ (accessed on 26 October 2021).
- Michael Badgwell, J.; Swan, J.; Foster, A.C. Volume-Controlled Ventilation Is Made Possible in Infants by Using Compliant Breathing Circuits with Large Compression Volume. Anesth. Analg. 1996, 82, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, K.I.; Klingenberg, C.; Morley, C.J.; Davis, P.G. Volume-Targeted versus Pressure-Limited Ventilation for Preterm Infants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neonatology 2011, 100, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingenberg, C.; Wheeler, K.I.; Davis, P.G.; Morley, C.J. A Practical Guide to Neonatal Volume Guarantee Ventilation. J. Perinatol. 2011, 31, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haddad, M.; Sharma, S. Physiology, Lung. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Duchateau, P.; Guérin, C. Tidal Volume Delivery From ICU Ventilators at BTPS Conditions: A Bench Study. Respir. Care 2013, 58, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hankinson, J.L.; Viola, J.O. Dynamic BTPS Correction Factors for Spirometric Data. J. Appl. Physiol. 1983, 55, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hankinson, J.L.; Viola, J.O.; Petsonk, E.L.; Ebeling, T.R. BTPS Correction for Ceramic Flow Sensor. Chest 1994, 105, 1481–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndd Medizintechnik, AG. BTPS Correction for Flow and Volume; Ndd Medizintechnik AG: Andover, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Getinge. User’s Manual Servo-i Ventilator System V7.0; Getinge: Goteborg, Sweden, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Brower, R.G.; Matthay, M.A.; Morris, A.; Schoenfeld, D.; Thompson, B.T.; Wheeler, A. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network. Ventilation with Lower Tidal Volumes as Compared with Traditional Tidal Volumes for Acute Lung Injury and the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lyazidi, A.; Thille, A.W.; Carteaux, G.; Galia, F.; Brochard, L.; Richard, J.-C.M. Bench Test Evaluation of Volume Delivered by Modern ICU Ventilators during Volume-Controlled Ventilation. Intensive Care Med. 2010, 36, 2074–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| All Patients | ATPD Ventilated Patients | BTPS Ventilated Patients | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 454 ** (1,063,901 observations) | n = 221 (532,930 observations) | n = 235 (551,937 observations) | ||
| Age, median (IQR), months | 5.6 (28.1) | 11.3 (63.0) | 4.3 (9.6) | <0.001 |
| Weight, median (IQR), kg | 6.1 (8.3) | 8.4 (15.3) | 5.45 (4.7) | <0.001 |
| Body temperature, mean (SD), degree Celsius *** | 37.0 (0.8) | 36.9 (0.8) | 37.0 (0.8) | <0.001 |
| Tidal volume per kg, mean (SD), mL/kg * | 7.29 (1.36) | 7.31 (1.32) | 7.27 (1.39) | <0.001 |
| Respiratory rate, mean (SD), /min * | 36 (7) | 35 (8) | 37 (6) | <0.001 |
| Peak pressure, mean (SD), cm H2O * | 21.0 (5.6) | 21.8 (5.4) | 20.2 (5.6) | <0.001 |
| Minute Volume per kg, mean (SD), mL/kg | 264 (75) | 259 (83) | 267 (66) | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koomen, E.; Nijman, J.; Nieuwenstein, B.; Kappen, T. Tidal Volume in Pediatric Ventilation: Do You Get What You See? J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010098
Koomen E, Nijman J, Nieuwenstein B, Kappen T. Tidal Volume in Pediatric Ventilation: Do You Get What You See? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(1):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010098
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoomen, Erik, Joppe Nijman, Ben Nieuwenstein, and Teus Kappen. 2022. "Tidal Volume in Pediatric Ventilation: Do You Get What You See?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 1: 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010098
APA StyleKoomen, E., Nijman, J., Nieuwenstein, B., & Kappen, T. (2022). Tidal Volume in Pediatric Ventilation: Do You Get What You See? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(1), 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010098






