Audiological Outcomes and Associated Factors after Pediatric Cochlear Reimplantation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
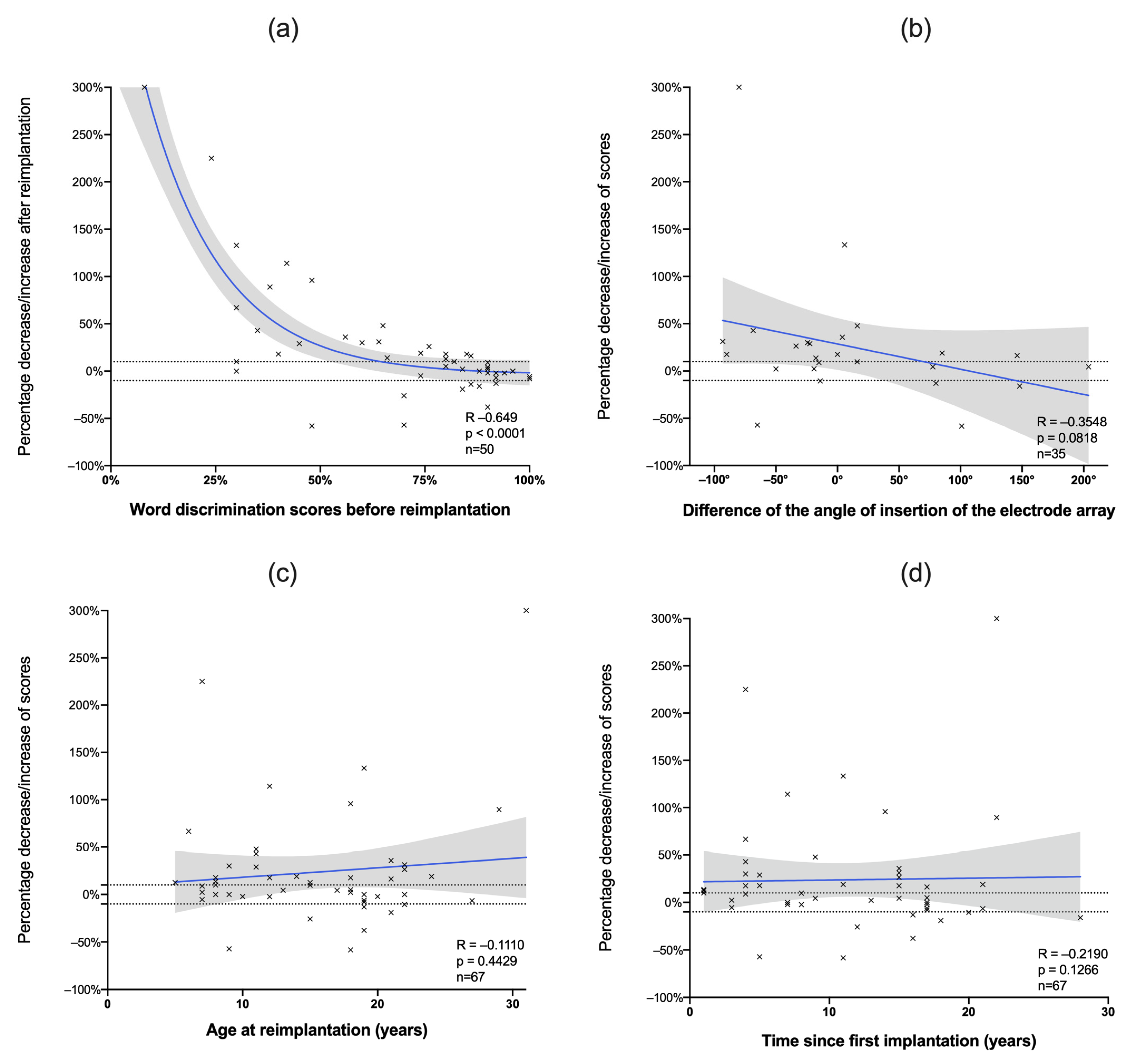
3.1. Audiological Outcomes
3.2. Factors Associated with Audiological Performance
3.3. Success of Reimplantation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization Deafness and Hearing Loss. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/deafness-and-hearing-loss (accessed on 4 September 2019).
- Lieu, J.E.C.; Kenna, M.; Anne, S.; Davidson, L. Hearing Loss in Children: A Review. JAMA 2020, 324, 2195–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illg, A.; Haack, M.; Lesinski-Schiedat, A.; Büchner, A.; Lenarz, T. Long-Term Outcomes, Education, and Occupational Level in Cochlear Implant Recipients Who Were Implanted in Childhood. Ear Hear. 2017, 38, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullen, R.D.; Fayad, J.N.; Luxford, W.M.; Buchman, C.A. Revision Cochlear Implant Surgery in Children. Otol. Neurotol. 2008, 29, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.D.; Connell, S.S.; Balkany, T.J.; Eshraghi, A.E.; Telischi, F.F.; Angeli, S.A. Incidence and Indications for Revision Cochlear Implant Surgery in Adults and Children. Laryngoscope 2009, 119, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Distinguin, L.; Blanchard, M.; Rouillon, I.; Parodi, M.; Loundon, N. Pediatric Cochlear Reimplantation: Decision-Tree Efficacy. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2018, 135, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterkers, F.; Merklen, F.; Piron, J.P.; Vieu, A.; Venail, F.; Uziel, A.; Mondain, M. Outcomes after Cochlear Reimplantation in Children. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 79, 840–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhadania, S.; Vishwakarma, R.; Keshri, A. Cochlear Implant Device Failure in the Postoperative Period: An Institutional Analysis. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2018, 13, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moberly, A.C.; Welling, D.B.; Nittrouer, S. Detecting Soft Failures in Pediatric Cochlear Implants: Relating Behavior to Language Outcomes. Otol. Neurotol. 2013, 34, 1648–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sunde, J.; Webb, J.B.; Moore, P.C.; Gluth, M.B.; Dornhoffer, J.L. Cochlear Implant Failure, Revision, and Reimplantation. Otol. Neurotol. 2013, 34, 1670–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roßberg, W.; Timm, M.; Matin, F.; Zanoni, A.; Krüger, C.; Giourgas, A.; Bültmann, E.; Lenarz, T.; Kral, A.; Lesinski-Schiedat, A. First Results of Electrode Reimplantation and Its Hypothetical Dependence from Artificial Brain Maturation. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 278, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcomb, M.A.; Burton, J.A.; Dornhoffer, J.R.; Camposeo, E.L.; Meyer, T.A.; McRackan, T.R. When to Replace Legacy Cochlear Implants for Technological Upgrades: Indications and Outcomes: CI Reimplantation for Technology Upgrade. Laryngoscope 2019, 129, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, Y.-F.; Hunter, J.B.; Kutz, J.W.; Isaacson, B.; Lee, K.H. Revision Pediatric Cochlear Implantation in a Large Tertiary Center since 1986. Cochlear Implant. Int. 2020, 21, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, T.A.; Pisoni, D.B. Some Computational Analyses of the PBK Test: Effects of Frequency and Lexical Density on Spoken Word Recognition. Ear Hear. 1999, 20, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Connor, S.E.J.; Bell, D.J.; O’Gorman, R.; Fitzgerald-O’Connor, A. CT and MR Imaging Cochlear Distance Measurements May Predict Cochlear Implant Length Required for a 360° Insertion. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 1425–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rivas, A.; Marlowe, A.L.; Chinnici, J.E.; Niparko, J.K.; Francis, H.W. Revision Cochlear Implantation Surgery in Adults: Indications and Results. Otol. Neurotol. 2008, 29, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henson, A.M.; Slattery, W.H.; Luxford, W.M.; Mills, D.M. Cochlear Implant Performance after Reimplantation: A Multicenter Study. Am. J. Otol. 1999, 20, 56–64. [Google Scholar]
- van der Marel, K.S.; Briaire, J.J.; Verbist, B.M.; Joemai, R.M.S.; Boermans, P.-P.B.M.; Peek, F.A.W.; Frijns, J.H.M. Cochlear Reimplantation with Same Device: Surgical and Audiologic Results: Results of Cochlear Reimplantation. Laryngoscope 2011, 121, 1517–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orús Dotú, C.; Venegas Pizarro, M.d.P.; De Juan Beltrán, J.; De Juan Delago, M. Reimplantación coclear en el mismo oído: Hallazgos, peculiaridades de la técnica quirúrgica y complicaciones. Acta Otorrinolaringológica Esp. 2010, 61, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkany, T.J.; Hodges, A.V.; Gómez-Marín, O.; Bird, P.A.; Dolan-Ash, S.; Butts, S.; Telischi Mee, F.F.; Lee, D. Cochlear Reimplantation. Laryngoscope 1999, 109, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, M.; Ferron, P.; Bergeron, F.; Bussieres, R. Cochlear Reimplantation: Causes of Failure, Outcomes, and Audiologic Performance. Laryngoscope 2007, 117, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migirov, L.; Taitelbaum-Swead, R.; Hildesheimer, M.; Kronenberg, J. Revision Surgeries in Cochlear Implant Patients: A Review of 45 Cases. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2007, 264, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, M.; Michel, G.; Boyer, J.; Bordure, P. Auditory Performance after Cochlear Reimplantation. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2021, S1879729621002581, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Ren, H.-B.; Jiang, L.; Liu, L.-Y.; Han, F.-G.; Wang, S.-F. Reference Function of Old Electrical Stimulation Electrode in Cochlear-Reimplantation in Children. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2020, 137, 415–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adunka, O.; Kiefer, J.; Unkelbach, M.H.; Radeloff, A.; Gstoettner, W. Evaluating Cochlear Implant Trauma to the Scala Vestibuli. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2005, 30, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschendorff, A.; Kromeier, J.; Klenzner, T.; Laszig, R. Quality Control After Insertion of the Nucleus Contour and Contour Advance Electrode in Adults. Ear Hear. 2007, 28, 75S–79S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, R.K.; Pyman, B.C.; Clark, G.M.; Webb, R.L. Banded Intracochlear Electrode Array: Evaluation of Insertion Trauma in Human Temporal Bones. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1985, 94, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Etiologies of Deafness | n | % |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic | ||
| Nonsyndromic | 19 | 28 |
| Syndromic 1 | 12 | 18 |
| Unknown | 23 | 34 |
| Meningitis | 7 | 10 |
| CMV | 2 | 3 |
| Labyrinthitis | 2 | 3 |
| Perinatal anoxia | 1 | 2 |
| Prematurity | 1 | 2 |
| Total | 67 | 100 |
| Percentage Decrease/Increase in Word Discrimination | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Female | +7.50 [−3.02–28.7] | 0.96 |
| Male | +9.32 [−1.63–26.4] | ||
| Etiology | Unknown | +15.1 [3.89–33.4] | 0.5 |
| Genetic nonsyndromic | 0 [−2.21–4.44] | ||
| Genetic syndromic | +5.00 [−8.82–38.8] | ||
| Meningitis | +16.9 [3.75–20.9] | ||
| Other | +4.17 [−27.1–35.4] | ||
| Indication of reimplantation | Hard failure | +12.5 [2.38–42.9] | 0.052 |
| Soft failure | +10.0 [−1.09–27.6] | ||
| Medical indication | −13.0 [−31.7–4.75] | ||
| Head trauma | −2.13 [−3.77–3.81] | ||
| Adherence to speech rehabilitation | Optimal | +8.89 [−2.15–31.0] | <0.01 |
| Suboptimal | −19.0 [−47.5–−7.63] |
| Etiology | Age | Time since Implantation | Indication | Surgical Findings | Word Discrimination Scores (after Reimplantation and Gain) | Comments | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient 1 | Perinatal anoxia 1 | 18 years | 11 years | Soft failure | Complete insertion | 20% (−58%) | Suspicion of evolutive auditory neuropathy |
| Patient 2 | NSHL | 15 years | 12 years | Head trauma | Scala vestibuli insertion | 52% (−26%) | Scala vestibuli insertion of the electrode array |
| Patient 3 | SHL 2 | 21 years | 18 years | Soft failure | Complete insertion | 68% (−10%) | Suboptimal speech rehabilitation |
| Patient 4 | NSHL | 8 years | 7 years | Medical reasons 3 | Complete insertion | 96% (+0%) | Pain after reimplantation remains stable—suspicion of migraine |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blanc, F.; Blanchet, C.; Sicard, M.; Merklen, F.; Venail, F.; Mondain, M. Audiological Outcomes and Associated Factors after Pediatric Cochlear Reimplantation. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3148. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113148
Blanc F, Blanchet C, Sicard M, Merklen F, Venail F, Mondain M. Audiological Outcomes and Associated Factors after Pediatric Cochlear Reimplantation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(11):3148. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113148
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlanc, Fabian, Catherine Blanchet, Marielle Sicard, Fanny Merklen, Frederic Venail, and Michel Mondain. 2022. "Audiological Outcomes and Associated Factors after Pediatric Cochlear Reimplantation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 11: 3148. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113148
APA StyleBlanc, F., Blanchet, C., Sicard, M., Merklen, F., Venail, F., & Mondain, M. (2022). Audiological Outcomes and Associated Factors after Pediatric Cochlear Reimplantation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(11), 3148. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113148





