A Novel Lightweight Approach to COVID-19 Diagnostics Based on Chest X-ray Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
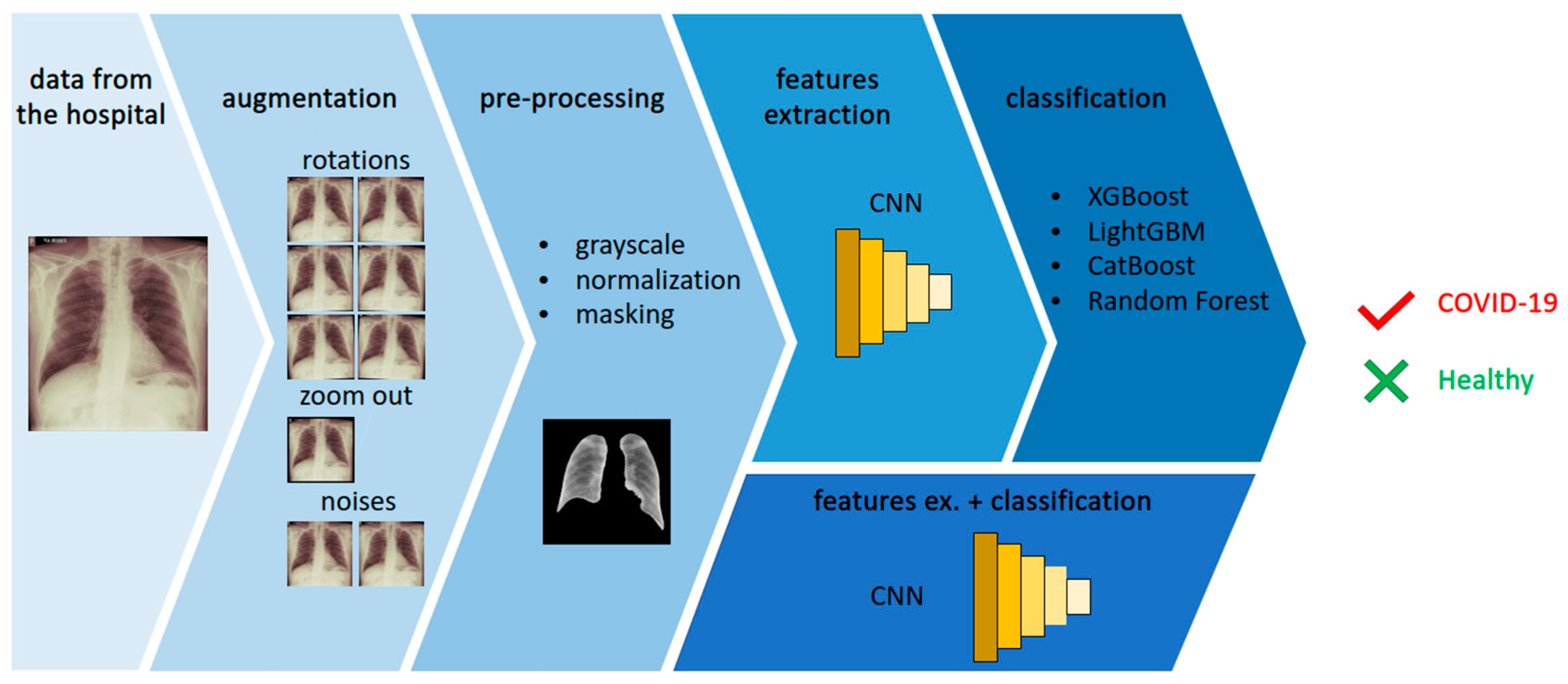
- We propose a novel approach to chest X-ray image analysis in order to diagnose COVID-19 using an original CNN-based features extraction method.
- We obtained a new dataset containing samples from confirmed COVID-19 cases as well as from uninfected patients. The infection status of both groups was confirmed by a PCR test. We performed an augmentation in order to increase the dataset’s size.
- We implemented the proposed features extraction for different classifiers, obtaining promising results.
2. Related Work
- Human agencies and oversight;
- Technical robustness and safety;
- Privacy and data governance;
- Transparency;
- Diversity, non-discrimination and fairness;
- Societal and environmental well-being;
- Accountability.
3. Materials and Methods
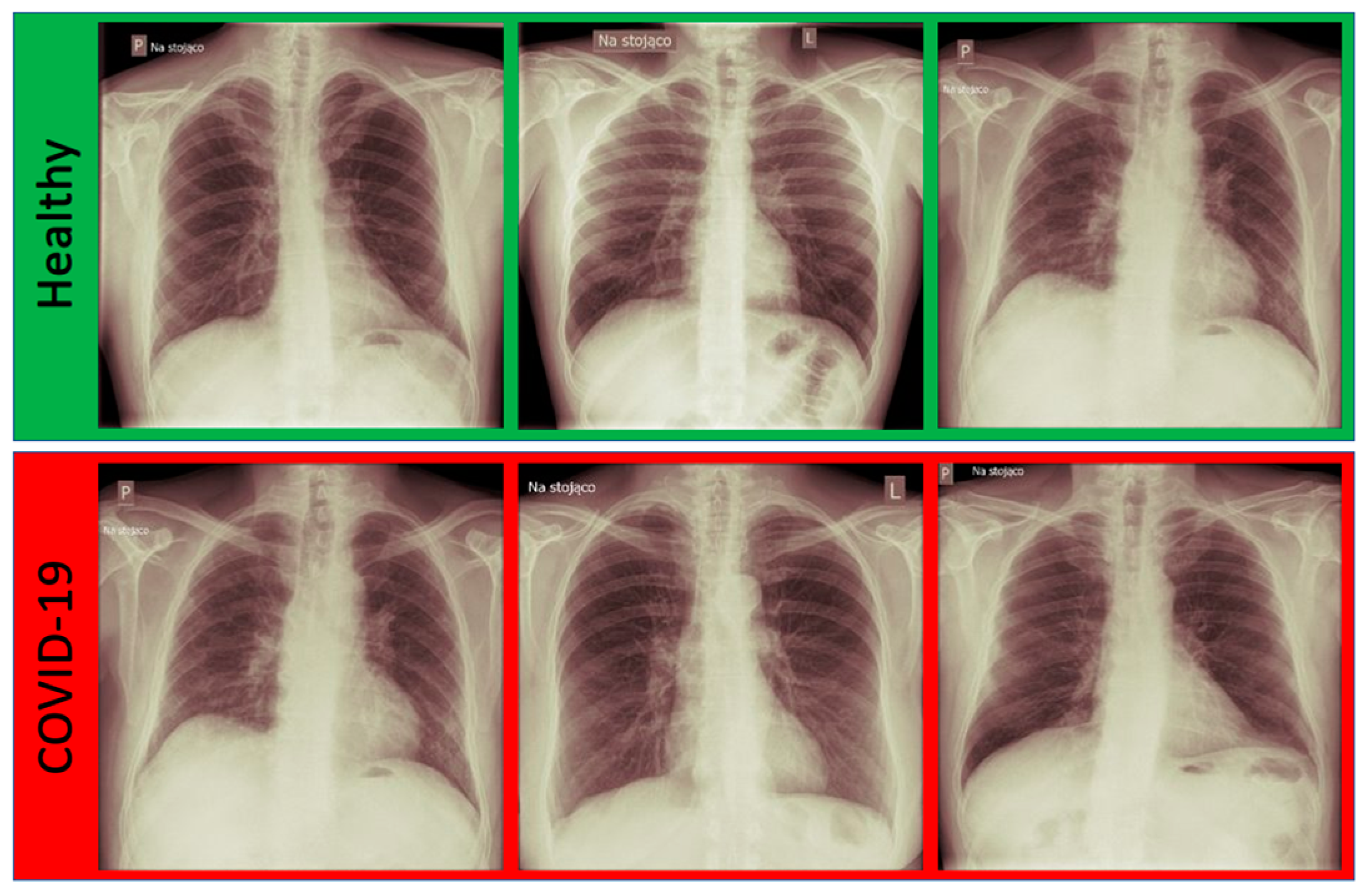
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Data Augmentation
- rotations—1°, 2° and 3° both clockwise and anti-clockwise;
- noises—a random Gaussian noise and a salt and pepper noise were added;
- zooming out—the image was resized to obtain 95% of its original size.
3.3. Data Pre-Processing
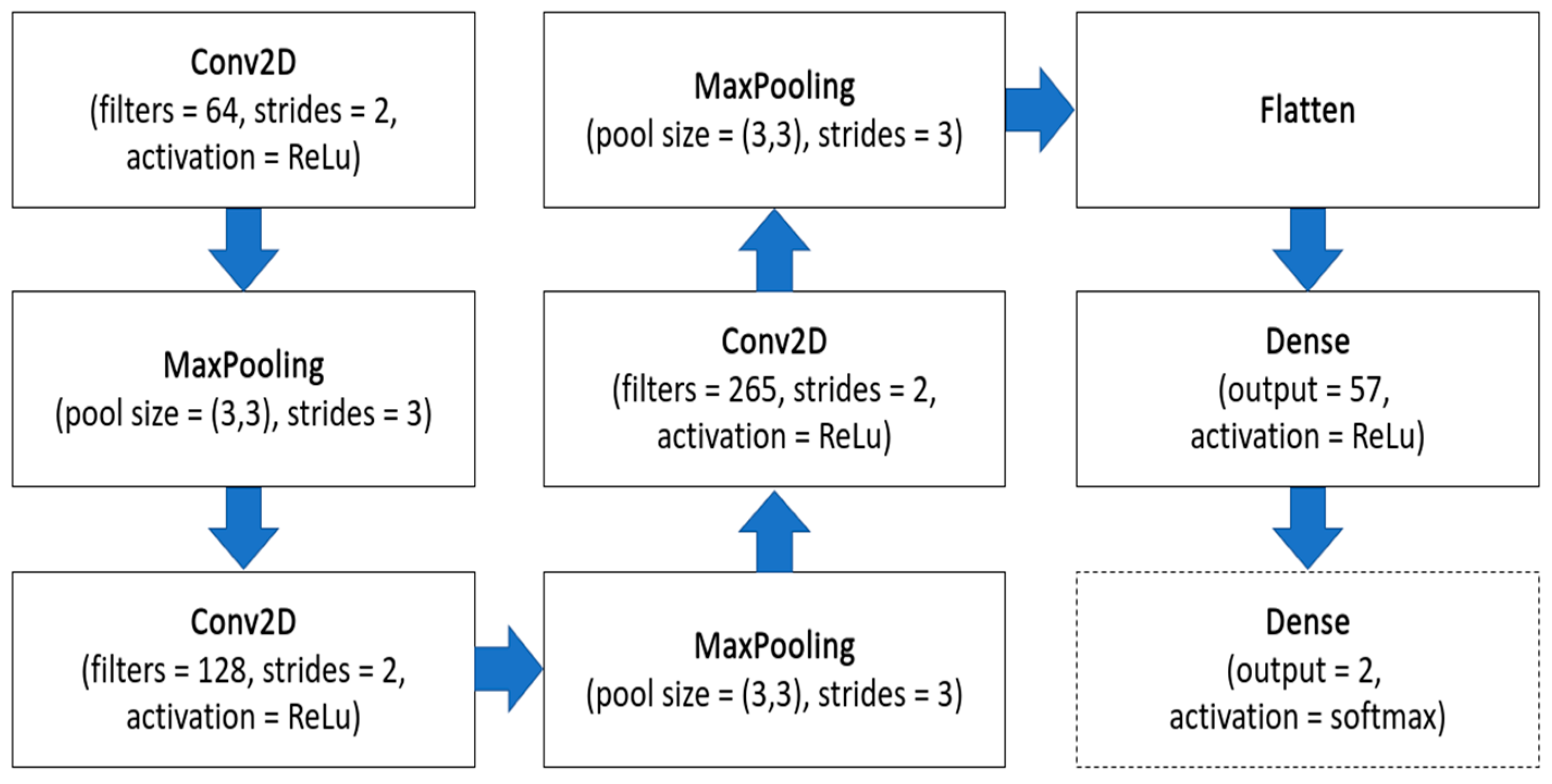
3.4. ML-Based Methods
4. Results
- TP—true positives—COVID-19-infected patients classified as sick;
- FP—false positives—healthy patient images classified as COVID-19 infected;
- FN—false negatives—COVID-19-infected patients classified as healthy;
- TN—true negatives—healthy patients classified as healthy.
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, J. SARS-CoV-2: An Emerging Coronavirus that Causes a Global Threat. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 1678–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahamtan, A.; Ardebili, A. Real-time RT-PCR in COVID-19 detection: Issues affecting the results. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 20, 453–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Tian, T.; Zhao, Z. Transmission Dynamics and Control Strategies of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China. J. Biol. Syst. 2020, 28, 543–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeny, M.; Neshat, A.A.; Hussain, M.A.; Kia, S.; Marhamati, M.; Jahanbakhshi, A.; Hamarneh, G. Learning-to-augment strategy using noisy and denoised data: Improving generalizability of deep CNN for the detection of COVID-19 in X-ray images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 136, 104704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassania, S.H.; Kassanib, P.H.; Wesolowskic, M.J.; Schneidera, K.A.; Detersa, R. Automatic Detection of Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) in X-ray and CT Images: A Machine Learning Based Approach. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 41, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, G.; Mittal, D.; Thakur, D.; Mittal, M.K. A deep learning approach to detect Covid-19 coronavirus with X-ray images. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 40, 1391–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.H.; Sohail, A.; Khan, A.; Hassan, M.; Lee, Y.S.; Alam, J.; Basit, A.; Zubair, S. COVID-19 detection in chest X-ray images using deep boosted hybrid learning. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 137, 104816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, A.M.; Chowdhury, M.E.; Khandakar, A.; Rahman, T.; Qiblawey, Y.; Khurshid, U.; Kiranyaz, S.; Ibtehaz, N.; Rahman, M.S.; Al-Maadeed, S.; et al. COVID-19 infection localization and severity grading from chest X-ray images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 139, 105002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunese, L.; Mercaldo, F.; Reginelli, A.; Santone, A. Explainable Deep Learning for Pulmonary Disease and Coronavirus COVID-19 Detection from X-rays. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 196, 105608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Murali, B.; Mitra, A.K. An Efficient Deep Learning Model to Detect COVID-19 Using Chest X-ray Images. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civit-Masot, J.; Luna-Perejón, F.; Domínguez Morales, M.; Civit, A. Deep Learning System for COVID-19 Diagnosis Aid Using X-ray Pulmonary Images. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayesha, S.; Yu, Z.; Nutini, A. COVID-19 Variants and Transfer Learning for the Emerging Stringency Indices. Neural Process. Lett. 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamad, M.M.; Aktar, S.; Rashed-Al-Mahfuz, M.; Uddin, S.; Liò, P.; Xu, H.; Summers, M.A.; Quinn, J.M.W.; Moni, M.A. A machine learning model to identify early stage symptoms of SARS-Cov-2 infected patients. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 160, 113661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan, S.; Subbaram, K.; Ali, S.; Kannan, H. The role of artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques: Race for covid-19 vaccine. Arch. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 15, e103232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EC. On Artificial Intelligence—A European Approach to Excellence and Trusty. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/sites/default/files/commission-white-paper-artificial-intelligence-feb2020_en.pdf/ (accessed on 2 July 2022).
- Schwartz, R.; Dodge, J.; Smith, N.A.; Etzioni, O. Green ai. Commun. ACM 2020, 63, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T. Greening the artificial intelligence for a sustainable planet: An editorial commentary. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenherr, N.; Pawlitzek, R.; Michel, B. New universal sustainability metrics to assess edge intelligence. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2021, 31, 100580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giełczyk, A.; Marciniak, A.; Tarczewska, M.; Lutowski, Z. Pre-processing methods in chest X-ray image classification. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0265949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.J.; Alom, M.S.; Ali, M.S. Deep learning based detection and segmentation of COVID-19 & pneumonia on chest X-ray image. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology for Sustainable Development (ICICT4SD), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 27–28 February 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 210–214. [Google Scholar]
- Munusamy, H.; Muthukumar, K.J.; Gnanaprakasam, S.; Shanmugakani, T.R.; Sekar, A. FractalCovNet architecture for COVID-19 chest X-ray image classification and CT-scan image segmentation. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 41, 1025–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimbekov, R.; Vassilenko, I.; Turlassov, A. Lung Segmentation Library. Available online: https://github.com/alimbekovKZ/lungs_segmentation/ (accessed on 15 May 2022).
- Rajagopal, R. Comparative analysis of COVID-19 X-ray images classification using convolutional neural network, transfer learning, and machine learning classifiers using deep features. Pattern Recognit. Image Anal. 2021, 31, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laeli, A.R.; Rustam, Z.; Pandelaki, J. Tuberculosis Detection based on Chest X-rays using Ensemble Method with CNN Feature Extraction. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Decision Aid Sciences and Application (DASA), Sakheer, Bahrain, 7–8 December 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 682–686. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Bagging predictors. Mach. Learn. 1996, 24, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T. Lightgbm: A highly efficient gradient boosting decision tree. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Prokhorenkova, L.; Gusev, G.; Vorobev, A.; Dorogush, A.V.; Gulin, A. CatBoost: Unbiased boosting with categorical features. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 3–8 December 2018; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Nasiri, H.; Hasani, S. Automated detection of COVID-19 cases from chest X-ray images using deep neural network and XGBoost. Radiography 2022, 28, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Júnior, D.A.D.; da Cruz, L.B.; Diniz, J.O.B.; da Silva, G.L.F.; Junior, G.B.; Silva, A.C.; de Paiva, A.C.; Nunes, R.A.; Gattass, M. Automatic method for classifying COVID-19 patients based on chest X-ray images, using deep features and PSO-optimized XGBoost. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 183, 115452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jawahar, M.; Prassanna, J.; Ravi, V.; Anbarasi, L.J.; Jasmine, S.G.; Manikandan, R.; Sekaran, R.; Kannan, S. Computer-aided diagnosis of COVID-19 from chest X-ray images using histogram-oriented gradient features and Random Forest classifier. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, M.R.; Karray, S.; Sousa, I.T.D. LightGBM: An effective decision tree gradient boosting method to predict customer loyalty in the finance industry. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference Science and Education, Toronto, ON, Canada, 19–21 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Misshuari, I.W.; Herdiana, R.; Farikhin, A.; Saputra, J. Factors that Affect Customer Credit Payments During COVID-19 Pandemic: An Application of Light Gradient Boosting Machine (LightGBM) and Classification and Regression Tree (CART). In Proceedings of the 11th Annual International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, Singapore, 7–11 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolaou, V.; Massaro, S.; Fakhimi, M.; Stergioulas, L.; Garn, W. COVID-19 diagnosis from chest x-rays: Developing a simple, fast, and accurate neural network. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2021, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbano, C.A.; Tartaglione, E.; Berzovini, C.; Calandri, M.; Grangetto, M. A two-step explainable approach for COVID-19 computer-aided diagnosis from chest x-ray images. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.10223. [Google Scholar]
- Ezzoddin, M.; Nasiri, H.; Dorrigiv, M. Diagnosis of COVID-19 Cases from Chest X-ray Images Using Deep Neural Network and LightGBM. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Machine Vision and Image Processing (MVIP), Ahvaz, Iran, 23–24 February 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Lin, Z.Q.; Wong, A. Covid-net: A tailored deep convolutional neural network design for detection of covid-19 cases from chest x-ray images. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajpal, S.; Lakhyani, N.; Singh, A.K.; Kohli, R.; Kumar, N. Using handpicked features in conjunction with ResNet-50 for improved detection of COVID-19 from chest X-ray images. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 145, 110749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| F. Extractor | Classifier | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | CNN | 0.86 | 0.75 | 1.00 | 0.86 |
| CNN | XGBoost | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| CNN | Random Forest | 0.91 | 0.86 | 1.00 | 0.92 |
| CNN | LightGBM | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| CNN | CatBoost | 0.91 | 0.86 | 1.00 | 0.92 |
| Authors | Method | Acc. | Prec. | Rec. | F1 | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rajagopal [27] | CNN + SVM | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.96 | - |
| Júnior et al. [30] | VGG19 + XGBoost | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | - |
| Nasari et al. [29] | DenseNet169 + XGBoost | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.92 | 0.97 | - |
| Ezzoddin et al. [36] | DenseNet169 + LightGBM | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.99 | - |
| Laeli et al. [28] | CNN + RF | 0.99 | - | - | - | 0.99 |
| Proposed | CNN + LightGBM | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giełczyk, A.; Marciniak, A.; Tarczewska, M.; Kloska, S.M.; Harmoza, A.; Serafin, Z.; Woźniak, M. A Novel Lightweight Approach to COVID-19 Diagnostics Based on Chest X-ray Images. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5501. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195501
Giełczyk A, Marciniak A, Tarczewska M, Kloska SM, Harmoza A, Serafin Z, Woźniak M. A Novel Lightweight Approach to COVID-19 Diagnostics Based on Chest X-ray Images. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(19):5501. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195501
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiełczyk, Agata, Anna Marciniak, Martyna Tarczewska, Sylwester Michal Kloska, Alicja Harmoza, Zbigniew Serafin, and Marcin Woźniak. 2022. "A Novel Lightweight Approach to COVID-19 Diagnostics Based on Chest X-ray Images" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 19: 5501. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195501
APA StyleGiełczyk, A., Marciniak, A., Tarczewska, M., Kloska, S. M., Harmoza, A., Serafin, Z., & Woźniak, M. (2022). A Novel Lightweight Approach to COVID-19 Diagnostics Based on Chest X-ray Images. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(19), 5501. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195501










