Plasma Endocan as a Biomarker of Thrombotic Events in COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Studied Population
2.2. Endocan Measurement
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
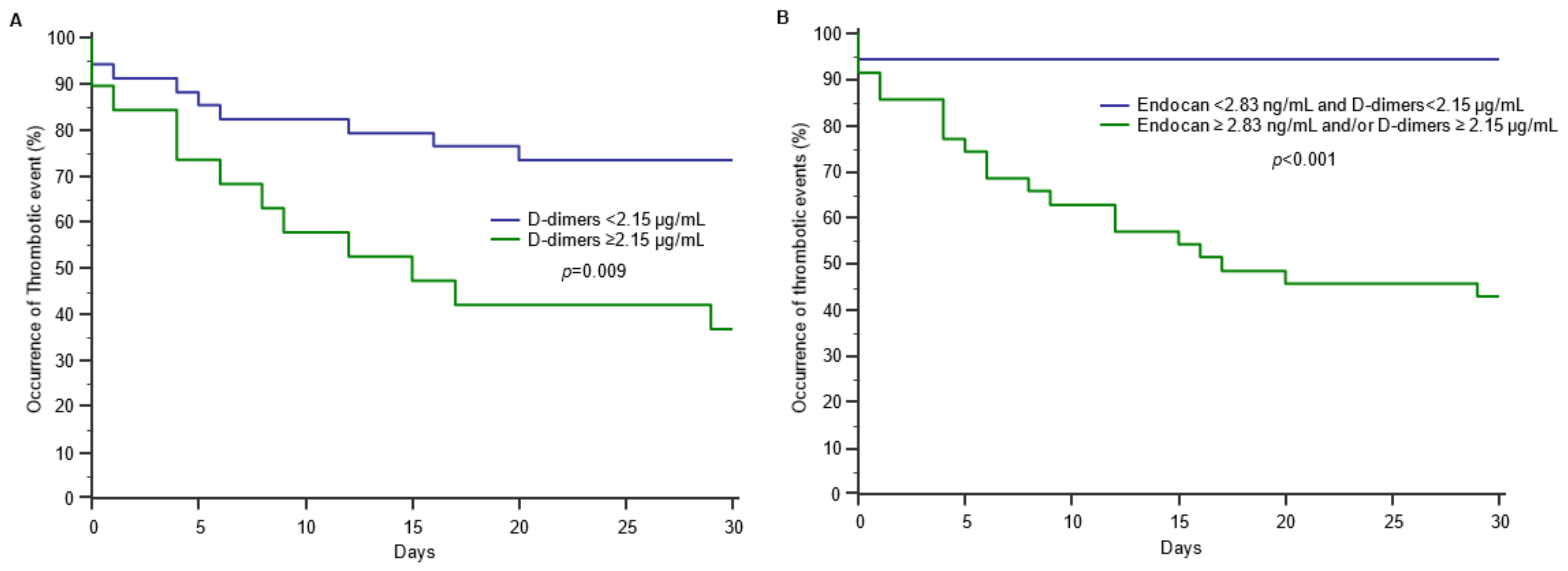
3.1. Endocan and Thrombotic Events in COVID-19
3.2. Endocan and COVID-19 Severity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsai, J.C.; Zhang, J.; Minami, T.; Voland, C.; Zhao, S.; Yi, X.; Lassalle, P.; Oettgen, P.; Aird, W.C. Cloning and characterization of the human lung endothelial-cell-specific molecule-1 promoter. J. Vasc. Res. 2002, 39, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassalle, P.; Molet, S.; Janin, A.; Heyden, J.V.; Tavernier, J.; Fiers, W.; Devos, R.; Tonnel, A.B. ESM-1 is a novel human endothelial cell-specific molecule expressed in lung and regulated by cytokines. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 20458–20464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.M.; Zuo, L.; Zhou, Q.; Gui, S.Y.; Shi, R.; Wu, Q.; Wei, W.; Wang, Y. Expression and distribution of endocan in human tissues. Biotech. Histochem. 2012, 87, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Béchard, D.; Gentina, T.; Delehedde, M.; Scherpereel, A.; Lyon, M.; Aumercier, M.; Vazeux, R.; Richet, C.; Degand, P.; Jude, B.; et al. Endocan is a novel chondroitin sulfate/dermatan sulfate proteoglycan that promotes hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor mitogenic activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 48341–48349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherpereel, A.; Depontieu, F.; Grigoriu, B.; Cavestri, B.; Tsicopoulos, A.; Gentina, T.; Jourdain, M.; Pugin, J.; Tonnel, A.B.; Lassalle, P. Endocan, a new endothelial marker in human sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 34, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherpereel, A.; Gentina, T.; Grigoriu, B.; Sénéchal, S.; Janin, A.; Tsicopoulos, A.; Plénat, F.; Béchard, D.; Tonnel, A.B.; Lassalle, P. Overexpression of endocan induces tumor formation. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 6084–6089. [Google Scholar]
- Kali, A.; Shetty, K.S. Endocan: A novel circulating proteoglycan. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2014, 46, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béchard, D.; Scherpereel, A.; Hammad, H.; Gentina, T.; Tsicopoulos, A.; Aumercier, M.; Pestel, J.; Dessaint, J.P.; Tonnel, A.B.; Lassalle, P. Human endothelial-cell specific molecule-1 binds directly to the integrin CD11a/CD18 (LFA-1) and blocks binding to intercellular adhesion molecule-1. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 3099–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissier, S.; Lancel, S.; Marechal, X.; Mordon, S.; Depontieu, F.; Scherpereel, A.; Chopin, C.; Neviere, R. Calpain inhibitors improve myocardial dysfunction and inflammation induced by endotoxin in rats. Shock 2004, 21, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas Caires, N.; Gaudet, A.; Portier, L.; Tsicopoulos, A.; Mathieu, D.; Lassalle, P. Endocan, sepsis, pneumonia, and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, S.J.; Chuang, C.Y.; Tang, C.H.; Lin, C.H.; Bien, M.Y.; Yu, M.C.; Bai, K.J.; Yang, S.F.; Chien, M.H. Plasma endothelial cell-specific molecule-1 (ESM-1) in management of community-acquired pneumonia. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2014, 52, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güzel, A.; Duran, L.; Köksal, N.; Torun, A.C.; Alaçam, H.; Ekiz, B.C.; Murat, N. Evaluation of serum endothelial cell specific molecule-1 (endocan) levels as a biomarker in patients with pulmonary thromboembolism. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2014, 25, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balta, Ş. COVID-19 and Endocan Levels. Angiology 2021, 72, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balta, S.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Demirkol, S.; Ozturk, C.; Kurtoglu, E.; Demir, M.; Celik, T.; Turker, T.; Iyisoy, A. Endocan—A novel inflammatory indicator in newly diagnosed patients with hypertension: A pilot study. Angiology 2014, 65, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icli, A.; Cure, E.; Cure, M.C.; Uslu, A.U.; Balta, S.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Ozturk, C.; Arslan, S.; Sakız, D.; Sahin, M.; et al. Endocan Levels and Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Angiology 2016, 67, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balta, S.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Demirkol, S.; Ozturk, C.; Celik, T.; Iyisoy, A. Endocan: A novel inflammatory indicator in cardiovascular disease? Atherosclerosis 2015, 243, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.I.; Siriopol, D.; Saglam, M.; Kurt, Y.G.; Unal, H.U.; Eyileten, T.; Gok, M.; Cetinkaya, H.; Oguz, Y.; Sari, S.; et al. Plasma endocan levels associate with inflammation, vascular abnormalities, cardiovascular events, and survival in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2014, 86, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribes, A.; Vardon-Bounes, F.; Mémier, V.; Poette, M.; Au-Duong, J.; Garcia, C.; Minville, V.; Sié, P.; Bura-Rivière, A.; Voisin, S.; et al. Thromboembolic events and COVID-19. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2020, 77, 100735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosino, P.; Di Minno, A.; Maniscalco, M.; Di Minno, M.N.D. COVID-19 and venous thromboembolism: Current insights and prophylactic strategies. Ann. Med. 2020, 52, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medetalibeyoglu, A.; Emet, S.; Kose, M.; Akpinar, T.S.; Senkal, N.; Catma, Y.; Kaytaz, A.M.; Genc, S.; Omer, B.; Tukek, T. Serum Endocan Levels on Admission Are Associated With Worse Clinical Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Pilot Study. Angiology 2021, 72, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görgün, S.; Cindoruk, Ş.; Özgen, E.; Yadigaroğlu, M.; Demir, M.T.; Yücel, M.; Akpınar, Ç.K.; Güzel, M. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Serum Endocan Levels in Patients With COVID-19. Angiology 2021, 72, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzel, D.; Kalkan, E.A.; Eren, F.; Zengin, O.; Erel, O.; Sahiner, E.S.; Inan, O.; Ates, I. Can Serum Endocan Levels be Used as an Early Prognostic Marker for Endothelial Dysfunction in COVID-19? Angiology 2022, 73, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascreau, T.; Tcherakian, C.; Zuber, B.; Farfour, E.; Vasse, M.; Lassalle, P. A high blood endocan profile during COVID-19 distinguishes moderate from severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudet, A.; Ghozlan, B.; Dupont, A.; Parmentier-Decrucq, E.; Rosa, M.; Jeanpierre, E.; Bayon, C.; Tsicopoulos, A.; Duburcq, T.; Susen, S.; et al. Derivation and Validation of a Predictive Score for Respiratory Failure Worsening Leading to Secondary Intubation in COVID-19: The CERES Score. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honore, P.M.; Redant, S.; Preseau, T.; Cismas, B.V.; Kaefer, K.; Barreto Gutierrez, L.; Anane, S.; Attou, R.; Gallerani, A.; De Bels, D. Is endocan correlated to ARDS severity or an epiphenomenon of thrombo-embolic disease in COVID. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laloglu, E.; Alay, H. Endocan as a potential marker in diagnosis and predicting disease severity in COVID-19 patients: A promising biomarker for patients with false-negative RT-PCR. Upsala J. Med. Sci. 2022, 127, e8211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducastel, M.; Chenevier-Gobeaux, C.; Ballaa, Y.; Meritet, J.F.; Brack, M.; Chapuis, N.; Pene, F.; Carlier, N.; Szwebel, T.A.; Roche, N.; et al. Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Biomarkers for the Prediction of Severity and ICU Admission in Unselected Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.COVID-19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/overview/management-of-COVID-19/ (accessed on 16 September 2020).
- Gaudet, A.; Chenevier-Gobeaux, C.; Parmentier, E.; Delobel, J.E.; Dubucquoi, S.; Mathieu, D.; Lassalle, P.; De Freitas Caires, N. Endocan is a stable circulating molecule in ICU patients. Clin. Biochem. 2017, 50, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilaki, E.; Brodsky, R.A. Severe COVID-19 infection and thrombotic microangiopathy: Success does not come easily. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 189, e227–e230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iba, T.; Connors, J.M.; Levy, J.H. The coagulopathy, endotheliopathy, and vasculitis of COVID-19. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 69, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iba, T.; Levy, J.H.; Levi, M.; Connors, J.M.; Thachil, J. Coagulopathy of Coronavirus Disease 2019. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, 1358–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menter, T.; Haslbauer, J.D.; Nienhold, R.; Savic, S.; Hopfer, H.; Deigendesch, N.; Frank, S.; Turek, D.; Willi, N.; Pargger, H.; et al. Postmortem examination of COVID-19 patients reveals diffuse alveolar damage with severe capillary congestion and variegated findings in lungs and other organs suggesting vascular dysfunction. Histopathology 2020, 77, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, M.; Verleden, S.E.; Kuehnel, M.; Haverich, A.; Welte, T.; Laenger, F.; Vanstapel, A.; Werlein, C.; Stark, H.; Tzankov, A.; et al. Pulmonary Vascular Endothelialitis, Thrombosis, and Angiogenesis in COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuovo, G.J.; Magro, C.; Shaffer, T.; Awad, H.; Suster, D.; Mikhail, S.; He, B.; Michaille, J.J.; Liechty, B.; Tili, E. Endothelial cell damage is the central part of COVID-19 and a mouse model induced by injection of the S1 subunit of the spike protein. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2021, 51, 151682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hu, T.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Jing, H.; Wang, C.; Hu, T.; Shi, J. Mechanisms of COVID-19 thrombosis in an inflammatory environment and new anticoagulant targets. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 3925–3941. [Google Scholar]
- Gaudet, A.; Portier, L.; Mathieu, D.; Hureau, M.; Tsicopoulos, A.; Lassalle, P.; De Freitas Caires, N. Cleaved endocan acts as a biologic competitor of endocan in the control of ICAM-1-dependent leukocyte diapedesis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 107, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Jiang, L.; Yu, X.H.; Hu, M.; Zhang, Y.K.; Liu, X.; He, P.; Ouyang, X. Endocan: A Key Player of Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 8, 798699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemzadeh, M.; Ahmadi, J.; Hosseini, E. Platelet-leukocyte crosstalk in COVID-19: How might the reciprocal links between thrombotic events and inflammatory state affect treatment strategies and disease prognosis? Thromb. Res. 2022, 213, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | No Thrombotic Event | Thrombotic Event | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | |||
| N | 63 | 16 | |
| Age—years | 62 (47–73) | 54 (50–66) | 0.427 |
| Male—n (%) | 31 (49) | 13 (81) | 0.019 |
| Cardiovascular disease—n (%) | 27 (43) | 6 (68) | 0.700 |
| Overweight/obesity—n (%) | 24 (38) | 10 (63) | 0.080 |
| Hypertension—n (%) | 19 (30) | 5 (31) | 0.841 |
| Diabetes—n (%) | 15 (24) | 2 (13) | 0.631 |
| Chronic respiratory failure—n (%) | 3 (5) | 0 (0) | 0.600 |
| Systemic AI disease—n (%) | 2 (3) | 0 (0) | 0.686 |
| Symptoms at admission | |||
| Temperature >38 °C—n (%) | 41 (65) | 14 (88) | 0.084 |
| Dyspnea—n (%) | 36 (57) | 14 (88) | 0.025 |
| Myalgias—n (%) | 21 (33) | 5 (31) | 0.875 |
| Fatigue—n (%) | 29 (46) | 5 (31) | 0.289 |
| Diarrhea—n (%) | 19 (30) | 3 (19) | 0.366 |
| Oxygenation—n (%) | 41 (65) | 15 (94) | 0.030 |
| Admission flow (L/min) | 3 (2–4) | 5 (2–14) | 0.043 |
| Tomodensitometry performed—n (%) | 34 (54) | 11 (69) | 0.283 |
| Extension at TDM—n (%) | |||
| <10% | 3 (9) | 0 (0) | |
| 10–25% | 13 (38) | 4 (36) | |
| 25–50% | 11 (32) | 2 (18) | |
| 50–75% | 2 (6) | 3 (27) | |
| >75% | 5 (15) | 2 (18) | |
| Increased O2 need—n (%) | 21 (33) | 13 (81) | 0.002 |
| Intensive care Unit admission—n (%) | 16 (25) | 11 (69) | 0.001 |
| COVID-19 severity | <0.001 | ||
| Stage 0 | 18 | 0 | |
| Stage 1 | 18 | 3 | |
| Stage 2 | 14 | 2 | |
| Stage 3 | 13 | 11 | |
| Type of thrombotic event—n (%) | |||
| Pulmonary embolism (PE) | 0 (0) | 11 (69) | |
| Venous thromboembolism (VTE) | 0 (0) | 5 (31) | |
| Follow-up | |||
| Length of stay (days) | 9 (6–22) | 27 (9–49) | 0.021 |
| Death—n (%) | 1 (2) | 3 (19) | 0.054 |
| Blood routine biomarkers at admission | |||
| CRP—mg/L (IQR) | 75 (27–132) | 147 (79–246) | 0.017 |
| D-dimers—µg/mL (IQR) | 1.15 (0.42–2.15) | 6.76 (2.83–10.0) | 0.003 |
| Neutrophils—G/L (IQR) | 4.3 (2.8–7.2) | 6.2 (4.4–8.7) | 0.133 |
| Neutrophil/lymphocytes ratio (IQR) | 4.5 (2.1–8.7) | 4.9 (3.2–11.1) | 0.531 |
| Platelets—G/L (IQR) | 242 (187–356) | 237 (169–305) | 0.545 |
| Endocan—ng/mL (IQR) | 1.81 (0.71–10.5) | 16.2 (5.53–26.7) | <0.001 |
| CRP | Neutrophils | Neutrophils/Lymphocytes Ratio | D-Dimers | Platelets | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Endocan | 0.468 ** | 0.390 ** | 0.347 * | 0.345 * | 0.093 |
| CRP | 0.402 ** | 0.257 | 0.445 ** | 0.043 | |
| Neutrophils | 0.725 ** | 0.517 ** | 0.307 ** | ||
| Neutrophils/Lymphocytes ratio | 0.291 * | 0.068 | |||
| D-dimers | 0.237 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chenevier-Gobeaux, C.; Ducastel, M.; Meritet, J.-F.; Ballaa, Y.; Chapuis, N.; Pene, F.; Carlier, N.; Roche, N.; Szwebel, T.-A.; Terrier, B.; et al. Plasma Endocan as a Biomarker of Thrombotic Events in COVID-19 Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5560. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195560
Chenevier-Gobeaux C, Ducastel M, Meritet J-F, Ballaa Y, Chapuis N, Pene F, Carlier N, Roche N, Szwebel T-A, Terrier B, et al. Plasma Endocan as a Biomarker of Thrombotic Events in COVID-19 Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(19):5560. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195560
Chicago/Turabian StyleChenevier-Gobeaux, Camille, Morgane Ducastel, Jean-François Meritet, Yassine Ballaa, Nicolas Chapuis, Frédéric Pene, Nicolas Carlier, Nicolas Roche, Tali-Anne Szwebel, Benjamin Terrier, and et al. 2022. "Plasma Endocan as a Biomarker of Thrombotic Events in COVID-19 Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 19: 5560. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195560
APA StyleChenevier-Gobeaux, C., Ducastel, M., Meritet, J.-F., Ballaa, Y., Chapuis, N., Pene, F., Carlier, N., Roche, N., Szwebel, T.-A., Terrier, B., & Borderie, D. (2022). Plasma Endocan as a Biomarker of Thrombotic Events in COVID-19 Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(19), 5560. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195560









