Use of Human Albumin Administration for the Prevention and Treatment of Hyponatremia in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
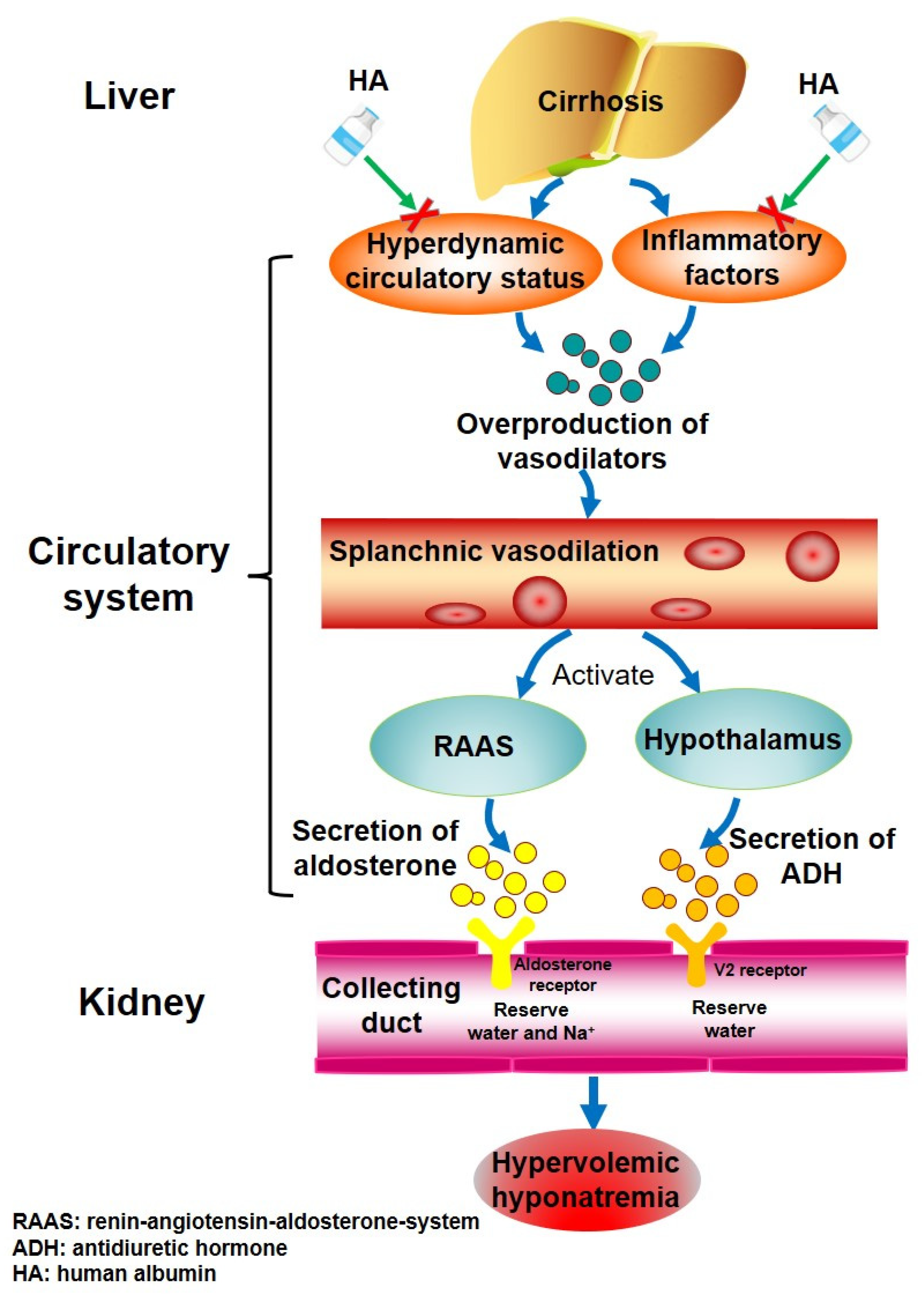
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Registration
2.2. Literature Search
2.3. Study Selection Criteria
2.4. Definitions and Outcomes
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. Study Quality Assessment
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Study Quality
3.4. HA for the Prevention of Hyponatremia
3.4.1. Incidence of Hyponatremia
3.4.2. Serum Sodium Level
3.5. HA for the Treatment of Hyponatremia
3.5.1. Resolution of Hyponatremia
3.5.2. Serum Sodium Level
3.6. Quality of Evidence
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alukal, J.J.; John, S.; Thuluvath, P.J. Hyponatremia in Cirrhosis: An Update. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 1775–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aithal, G.P.; Palaniyappan, N.; China, L.; Härmälä, S.; Macken, L.; Ryan, J.M.; Wilkes, E.A.; Moore, K.; Leithead, J.A.; Hayes, P.C.; et al. Guidelines on the management of ascites in cirrhosis. Gut 2021, 70, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, P.; Wong, F.; Watson, H.; Ginès, P. CAPPS-Investigators. Hyponatremia in cirrhosis: Results of a patient population survey. Hepatology 2006, 44, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginès, P.; Guevara, M. Hyponatremia in cirrhosis: Pathogenesis, clinical significance, and management. Hepatology 2008, 48, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attar, B. Approach to Hyponatremia in Cirrhosis. Clin. Liver Dis. 2019, 13, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.R.; Biggins, S.W.; Kremers, W.K.; Wiesner, R.H.; Kamath, P.S.; Benson, J.T.; Edwards, E.; Therneau, T.M. Hyponatremia and mortality among patients on the liver-transplant waiting list. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.-M.; Choi, S.-N.; Yu, J.H.; Yoon, H.-K.; Kim, W.H.; Jung, C.-W.; Suh, K.-S.; Lee, K.H. Intraoperative hyponatremia is an independent predictor of one-year mortality after liver transplantation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 18023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borroni, G.; Maggi, A.; Sangiovanni, A.; Cazzaniga, M.; Salerno, F. Clinical relevance of hyponatraemia for the hospital outcome of cirrhotic patients. Dig. Liver Dis. 2000, 32, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/governance/policy-initiatives/liver/ (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Sigal, S.H.; Amin, A.; Chiodo, J.A., 3rd; Sanyal, A. Management Strategies and Outcomes for Hyponatremia in Cirrhosis in the Hyponatremia Registry. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 2018, 1579508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hix, J.K.; Silver, S.; Sterns, R.H. Diuretic-associated hyponatremia. Semin. Nephrol. 2011, 31, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbalis, J.G.; Goldsmith, S.R.; Greenberg, A.; Korzelius, C.; Schrier, R.W.; Sterns, R.H.; Thompson, C.J. Diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of hyponatremia: Expert panel recommendations. Am. J. Med. 2013, 126, S1–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berl, T.; Rastegar, A. A patient with severe hyponatremia and hypokalemia: Osmotic demyelination following potassium repletion. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2010, 55, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pose, E.; Solà, E.; Piano, S.; Gola, E.; Graupera, I.; Guevara, M.; Cárdenas, A.; Angeli, P.; Ginès, P. Limited Efficacy of Tolvaptan in Patients with Cirrhosis and Severe Hyponatremia: Real-Life Experience. Am. J. Med. 2017, 130, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas, A.; Ginès, P.; Marotta, P.; Czerwiec, F.; Oyuang, J.; Guevara, M.; Afdhal, N.H. Tolvaptan, an oral vasopressin antagonist, in the treatment of hyponatremia in cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, S.; Thuluvath, P.J. Hyponatremia in cirrhosis: Pathophysiology and management. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 3197–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraceni, P.; Angeli, P.; Prati, D.; Bernardi, M.; Liumbruno, G.M.; Bennardello, F.; Piccoli, P.; Velati, C. AISF-SIMTI position paper: The appropriate use of albumin in patients with liver cirrhosis. Blood Transfus. 2016, 14, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fukui, H.; Saito, H.; Ueno, Y.; Uto, H.; Obara, K.; Sakaida, I.; Shibuya, A.; Seike, M.; Nagoshi, S.; Segawa, M.; et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for liver cirrhosis 2015. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 629–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with decompensated cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 406–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Runyon, B.A.; Committee, A.P.G. Management of adult patients with ascites due to cirrhosis: An update. Hepatology 2009, 49, 2087–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Xu, X.; Duan, Z.; Ding, H.; Li, W.; Jia, J.; Wei, L.; Linghu, E. Chinese guidelines on the management of ascites and its related complications in cirrhosis. Hepatol. Int. 2019, 13, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, M.; Caraceni, P.; Navickis, R.J.; Wilkes, M.M. Albumin infusion in patients undergoing large-volume paracentesis: A meta-analysis of randomized trials. Hepatology 2012, 55, 1172–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, C.S.; Krupa, L.; Mahtani, A.; Kaye, D.; Rushbrook, S.M.; Phillips, M.G.; Gelson, W. Albumin reduces paracentesis-induced circulatory dysfunction and reduces death and renal impairment among patients with cirrhosis and infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 295153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kütting, F.; Schubert, J.; Franklin, J.; Bowe, A.; Hoffmann, V.; Demir, M.; Pelc, A.; Nierhoff, D.; Töx, U.; Steffen, H. Insufficient evidence of benefit regarding mortality due to albumin substitution in HCC-free cirrhotic patients undergoing large volume paracentesis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonetti, R.G.; Perricone, G.; Nikolova, D.; Bjelakovic, G.; Gluud, C. Plasma expanders for people with cirrhosis and large ascites treated with abdominal paracentesis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 6, CD004039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.J.; Zhuo, S.J.; Huang, B.; Su, S. A meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of human serum albumin treatment in patients with ascites due to cirrhosis undergoing drainage. Asian J. Surg. 2021, 44, 1116–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, D.B.; Budhathoki, P.; Sedhai, Y.R.; Baniya, R.; Awal, S.; Yadav, J.; Awal, L.; Davis, B.; Kashiouris, M.G.; Cable, C.A. Safety and efficacy of human serum albumin treatment in patients with cirrhotic ascites undergoing paracentesis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Hepatol. 2021, 26, 100547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Sutton, A.J.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Terrin, N.; Jones, D.R.; Lau, J.; Carpenter, J.; Rücker, G.; Harbord, R.M.; Schmid, C.H.; et al. Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lau, J.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Terrin, N.; Schmid, C.H.; Olkin, I. The case of the misleading funnel plot. BMJ 2006, 333, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Begg, C.B.; Mazumdar, M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 1994, 50, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.D.; Vist, G.E.; Kunz, R.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Alonso-Coello, P.; Schünemann, H.J. GRADE: An emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2008, 336, 924–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhaveri, K.D.; Chawla, A.; Xu, C.; Hazzan, A. Intravenous albumin infusion is an effective therapy for hyponatremia in patient with malignant ascites. Indian J. Nephrol. 2014, 24, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, V.; Vijayaraghavan, R.; Maiwall, R.; Sahney, A.; Thomas, S.S.; Ali, R.; Jain, P.; Kumar, G.; Sarin, S.K. Paracentesis-Induced Circulatory Dysfunction with Modest-Volume Paracentesis Is Partly Ameliorated by Albumin Infusion in Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. Hepatology 2020, 72, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen Sarma, M.; Yachha, S.K.; Bhatia, V.; Srivastava, A.; Poddar, U. Safety, complications and outcome of large volume paracentesis with or without albumin therapy in children with severe ascites due to liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 1126–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormick, P.A.; Mistry, P.; Kaye, G.; Burroughs, A.K.; McIntyre, N. Intravenous albumin infusion is an effective therapy for hyponatraemia in cirrhotic patients with ascites. Gut 1990, 31, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ginès, P.; Titó, L.; Arroyo, V.; Planas, R.; Panes, J.; Viver, J.; Torres, M.; Humbert, P.; Rimola, A.; Llach, J.; et al. Randomized comparative study of therapeutic paracentesis with and without intravenous albumin in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 1988, 94, 1493–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planas, R.; Ginès, P.; Arroyo, V.; Llach, J.; Panés, J.; Vargas, V.; Salmerón, J.M.; Ginès, A.; Toledo, C.; Rimola, A.; et al. Dextran-70 versus albumin as plasma expanders in cirrhotic patients with tense ascites treated with total paracentesis. Results of a randomized study. Gastroenterology 1990, 99, 1736–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, F.; Badalamenti, S.; Lorenzano, E.; Moser, P.; Incerti, P. Randomized comparative study of hemaccel vs. albumin infusion after total paracentesis in cirrhotic patients with refractory ascites. Hepatology 1991, 13, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassio, E.; Terg, R.; Landeira, G.; Abecasis, R.; Salemne, M.; Podesta, A.; Rodriguez, P.; Levi, D.; Kravetz, D. Paracentesis with Dextran 70 vs. paracentesis with albumin in cirrhosis with tense ascites. Results of a randomized study. J. Hepatol. 1992, 14, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Compeán, D.; Villarreal, J.Z.; Cuevas, H.B.; Cantü, D.A.G.; Estrella, M.; Tamez, E.G.; Castillo, R.V.; Barragán, R.F. Total therapeutic paracentesis (TTP) with and without intravenous albumin in the treatment of cirrhotic tense ascites: A randomized controlled trial. Liver 1993, 13, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández Pérez, R.E.; Aguilar Ramírez, J.R.; Hernández López, J.M.; Gómez Maganda y Silva, T.G. Massive paracentesis and administration of dextran 70 vs. albumin in cirrhotic patients with tense ascites. Rev. Gastroenterol. Mex 1995, 60, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Gines, A.; Fernandez-Esparrach, G.; Monescillo, A.; Vila, C.; Domenech, E.; Abecasis, R.; Angeli, P.; Ruiz-Del-Arbol, L.; Planas, R.; Sola, R.; et al. Randomized trial comparing albumin, dextran 70, and polygeline in cirrhotic patients with ascites treated by paracentesis. Gastroenterology 1996, 111, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, C.; Bernard, B.; Roulot, D.; Vitte, R.L.; Ink, O. Randomized comparative multicenter study of hydroxyethyl starch versus albumin as a plasma expander in cirrhotic patients with tense ascites treated with paracentesis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1998, 10, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentilini, P.; Casini-Raggi, V.; Di Fiore, G.; Romanelli, R.G.; Buzzelli, G.; Pinzani, M.; La Villa, G.; Laffi, G. Albumin improves the response to diuretics in patients with cirrhosis and ascites: Results of a randomized, controlled trial. J. Hepatol. 1999, 30, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaak, D.; Paquet, K.J.; Kuhn, R. Prospective study comparing human albumin vs. reinfusion of ultrafiltrate-ascitic fluid after total paracentesis in cirrhotic patients with tense ascites. Z. Gastroenterol. 2001, 39, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Compean, D.; Blanc, P.; Larrey, D.; Daures, J.-P.; Hirtz, J.; Mendoza, E.; Maldonado, H.; Michel, H. Treatment of cirrhotic tense ascites with Dextran-40 versus albumin associated with large volume paracentesis: A randomized controlled trial. Ann. Hepatol. 2002, 1, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, R.; Asselah, T.; Condat, B.; De Kerguenec, C.; Pessione, F.; Bernard, B.; Poynard, T.; Binn, M.; Grangé, J.D.; Valla, D.; et al. Comparison of the effect of terlipressin and albumin on arterial blood volume in patients with cirrhosis and tense ascites treated by paracentesis: A randomised pilot study. Gut 2002, 50, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sola-Vera, J.; Miñana, J.; Ricart, E.; Planella, M.; González, B.; Torras, X.; Rodríguez, J.; Such, J.; Pascual, S.; Soriano, G.; et al. Randomized trial comparing albumin and saline in the prevention of paracentesis-induced circulatory dysfunction in cirrhotic patients with ascites. Hepatology 2003, 37, 1147–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, R.; Valla, D.-C.; Durand-Zaleski, I.; Bronowicki, J.-P.; Durand, F.; Chaput, J.-C.; Dadamessi, I.; Silvain, C.; Bonny, C.; Oberti, F.; et al. Comparison of outcome in patients with cirrhosis and ascites following treatment with albumin or a synthetic colloid: A randomised controlled pilot trail. Liver Int. 2006, 26, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Kumar, R.; Nain, C.K.; Singh, B.; Sharma, A.K. Terlipressin versus albumin in paracentesis-induced circulatory dysfunction in cirrhosis: A randomized study. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 21, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalan, R.; Mookerjee, R.; Cheshire, L.; Williams, R.; Davies, N. Albumin infusion for severe hyponatremia in patients with refractory ascites: A randomized clinical trial. J. Hepatol. 2007, 46, S95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appenrodt, B.; Wolf, A.; Grünhage, F.; Trebicka, J.; Schepke, M.; Rabe, C.; Lammert, F.; Sauerbruch, T.; Heller, J. Prevention of paracentesis-induced circulatory dysfunction: Midodrine vs albumin. A randomized pilot study. Liver Int. 2008, 28, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Dheerendra, P.C.; Singh, B.; Nain, C.K.; Chawla, D.; Sharma, N.; Bhalla, A.; Mahi, S.K. Midodrine versus albumin in the prevention of paracentesis-induced circulatory dysfunction in cirrhotics: A randomized pilot study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Khalek, E.E.; Arif, S.E. Randomized trial comparing human albumin and hydroxyethyl starch 6% as plasma expanders for treatment of patients with liver cirrhosis and tense ascites following large volume paracentesis. Arab. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 11, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, K.; Miñano, C.; Shea, M.; Inayat, I.B.; Hashem, H.J.; Gilles, H.; Heuman, D.; Garcia-Tsao, G. The Combination of Octreotide and Midodrine Is Not Superior to Albumin in Preventing Recurrence of Ascites After Large-Volume Paracentesis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamdy, H.; ElBaz, A.A.; Hassan, A.; Hassanin, O. Comparison of midodrine and albumin in the prevention of paracentesis-induced circulatory dysfunction in cirrhotic patients: A randomized pilot study. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 48, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.U.; Ur Rahim, I.; Latif, M. Hemaccel as a cheaper alternative to human albumin for plasma expansion during paracentesis in cirrhotic patients. Pak. J. Med. Health Sci. 2015, 9, 948–950. [Google Scholar]
- Abootalebi, A.; Khazaei, S.; Minakari, M.; Nasr-Isfahani, M.; Esmailian, M.; Heydari, F. Comparing the Effects of Hydroxyethyl Starch and Albumin in Cirrhotic Patients with Tense Ascites; a Randomized Clinical Trial. Adv. J. Emerg. Med. 2017, 1, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, N.T.; Barraza, L.H.; Anam, A.K.; Patel, P.; Schneider, Y.; Jesudian, A. Benefit of albumin infusion in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis and hyponatremia: A retrospective cohort study. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Res. 2017, 6, 2441–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Tandon, P.; O’leary, J.G.; Biggins, S.W.; Wong, F.; Kamath, P.S.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Maliakkal, B.; Lai, J.C.; Fallon, M.; et al. The Impact of Albumin Use on Resolution of Hyponatremia in Hospitalized Patients with Cirrhosis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solà, E.; Solé, C.; Simón-Talero, M.; Martín-Llahí, M.; Castellote, J.; Martinez, R.G.; Moreira, R.; Torrens, M.; Márquez, F.; Fabrellas, N.; et al. Midodrine and albumin for prevention of complications in patients with cirrhosis awaiting liver transplantation. A randomized placebo-controlled trial. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 1250–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosry, A.; Soliman, Z.A.; Eletreby, R.; Hamza, I.; Ismail, A.; Elkady, M.A. Oral midodrine is comparable to albumin infusion in cirrhotic patients with refractory ascites undergoing large-volume paracentesis: Results of a pilot study. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 31, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- China, L.; Freemantle, N.; Forrest, E.; Kallis, Y.; Ryder, S.D.; Wright, G.; O’Brien, A. Targeted Albumin Therapy Does Not Improve Short-Term Outcome in Hyponatremic Patients Hospitalized with Complications of Cirrhosis: Data from the ATTIRE Trial. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 116, 2292–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smart, H.L.; Triger, D.R. A randomised prospective trial comparing daily paracentesis and intravenous albumin with recirculation in diuretic refractory ascites. J. Hepatol. 1990, 10, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccherini, G.; Baldassarre, M.; Tufoni, M.; Nardelli, S.; Piano, S.; Alessandria, C.; Neri, S.; Foschi, F.G.; Levantesi, F.; Bedogni, G.; et al. Correction and prevention of hyponatremia in patients with cirrhosis and ascites—Post hoc analysis of the ANSWER study database. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, V.; García-Martinez, R.; Salvatella, X. Human serum albumin, systemic inflammation, and cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salerno, F.; Navickis, R.J.; Wilkes, M.M. Albumin infusion improves outcomes of patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: A meta-analysis of randomized trials. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, 123–130.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sort, P.; Navasa, M.; Arroyo, V.; Aldeguer, X.; Planas, R.; Ruiz-Del-Arbol, L.; Castells, L.; Vargas, V.; Soriano, G.; Guevara, M.; et al. Effect of intravenous albumin on renal impairment and mortality in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, F.; Pappas, S.C.; Curry, M.P.; Reddy, K.R.; Rubin, R.A.; Porayko, M.K.; Gonzalez, S.A.; Mumtaz, K.; Lim, N.; Simonetto, D.A.; et al. Terlipressin plus Albumin for the Treatment of Type 1 Hepatorenal Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 818–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraceni, P.; Riggio, O.; Angeli, P.; Alessandria, C.; Neri, S.; Foschi, F.G.; Levantesi, F.; Airoldi, A.; Boccia, S.; Svegliati-Baroni, G.; et al. Long-term albumin administration in decompensated cirrhosis (ANSWER): An open-label randomised trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 2417–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Bernardi, M.; Yoshida, E.M.; Li, H.; Guo, X.; Méndez-Sánchez, N.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Deng, J.; Qi, X. Albumin infusion may decrease the incidence and severity of overt hepatic encephalopathy in liver cirrhosis. Aging 2019, 11, 8502–8525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwakiri, Y.; Groszmann, R.J. The hyperdynamic circulation of chronic liver diseases: From the patient to the molecule. Hepatology 2006, 43, S121–S131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, J. Vascular deterioration in cirrhosis: The big picture. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2007, 41 (Suppl. S3), S247–S253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clària, J.; Stauber, R.E.; Coenraad, M.J.; Moreau, R.; Jalan, R.; Pavesi, M.; Amorós, A.; Titos, E.; Alcaraz-Quiles, J.; Oettl, K.; et al. Systemic inflammation in decompensated cirrhosis: Characterization and role in acute-on-chronic liver failure. Hepatology 2016, 64, 1249–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martell, M.; Coll, M.; Ezkurdia, N.; Raurell, I.; Genescà, J. Physiopathology of splanchnic vasodilation in portal hypertension. World J. Hepatol. 2010, 2, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funder, J.W. Aldosterone and Mineralocorticoid Receptors-Physiology and Pathophysiology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, S.; Marples, D.; Frøkiaer, J.; Knepper, M.; Agre, P. The aquaporin family of water channels in kidney: An update on physiology and pathophysiology of aquaporin-2. Kidney Int. 1996, 49, 1718–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knepper, M.A. Molecular physiology of urinary concentrating mechanism: Regulation of aquaporin water channels by vasopressin. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 272, F3–F12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.M.; Carter, D.C. Atomic structure and chemistry of human serum albumin. Nature 1992, 358, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilkinson, P.; Sherlock, S. The effect of repeated albumin infusions in patients with cirrhosis. Lancet 1962, 2, 1125–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, V. Review article: Albumin in the treatment of liver diseases—New features of a classical treatment. Aliment. Pharm. Ther. 2002, 16 (Suppl. S5), 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, G.J.; Martin, G.S.; Evans, T.W. Albumin: Biochemical properties and therapeutic potential. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraceni, P.; Angeli, P.; Prati, D.; Bernardi, M.; Berti, P.; Bennardello, F.; Fiorin, F.; Piccoli, P. AISF-SIMTI position paper on the appropriate use of albumin in patients with liver cirrhosis: A 2020 update. Blood Transfus. 2021, 19, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiva, J.G.; Salgado, J.M.; Estradas, J.; Torre, A.; Uribe, M. Pathophysiology of ascites and dilutional hyponatremia: Contemporary use of aquaretic agents. Ann. Hepatol. 2007, 6, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, V.; Rodés, J.; Gutiérrez-Lizárraga, M.A.; Revert, L. Prognostic value of spontaneous hyponatremia in cirrhosis with ascites. Am. J. Dig. Dis. 1976, 21, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sersté, T.; Gustot, T.; Rautou, P.-E.; Francoz, C.; Njimi, H.; Durand, F.; Valla, D.; Lebrec, D.; Moreau, R. Severe hyponatremia is a better predictor of mortality than MELDNa in patients with cirrhosis and refractory ascites. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara, M.; E Baccaro, M.; Torre, A.; Gómez-Ansón, B.; Ríos, J.; Torres, F.; Rami, L.; Monté-Rubio, G.C.; Martín-Llahí, M.; Arroyo, V.; et al. Hyponatremia is a risk factor of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: A prospective study with time-dependent analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 1382–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossen, L.; Ginès, P.; Vilstrup, H.; Watson, H.; Jepsen, P. Serum sodium as a risk factor for hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis and ascites. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 34, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginès, A.; Escorsell, A.; Ginès, P.; Saló, J.; Jiménez, W.; Inglada, L.; Navasa, M.; Clària, J.; Rimola, A.; Arroyo, V.; et al. Incidence, predictive factors, and prognosis of the hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis with ascites. Gastroenterology 1993, 105, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janičko, M.; Veselíny, E.; Abraldes, J.G.; Jarčuška, P. Serum sodium identifies patients with cirrhosis at high risk of hepatorenal syndrome. Z. Gastroenterol. 2013, 51, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licata, A.; Maida, M.; Bonaccorso, A.; Macaluso, F.S.; Cappello, M.; Craxì, A.; Almasio, P.L. Clinical course and prognostic factors of hepatorenal syndrome: A retrospective single-center cohort study. World J. Hepatol. 2013, 5, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwabl, P.; Bucsics, T.; Soucek, K.; Mandorfer, M.; Bota, S.; Blacky, A.; Hirschl, A.M.; Ferlitsch, A.; Trauner, M.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M.; et al. Risk factors for development of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and subsequent mortality in cirrhotic patients with ascites. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 2121–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dănulescu, R.M.; Stanciu, C.; Trifan, A. Evaluation of Prognostic Factors in Decompensated Liver Cirrhosis with Ascites and Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis. Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat. Iasi 2015, 119, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sigal, S.H. Hyponatremia in cirrhosis. J. Hosp. Med. 2012, 7 (Suppl. S4), S14–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; The PRISMA Group. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| First Author (Year) | Country | Study Design | Sample Size (n) | Alcoholic Cirrhosis (%) | Definition of Hyponatremia | Control Group | HA Dose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ginès (1988) [36] | Spain | RCT | 105 | 65.71% (69/105) | Decrease in serum Na > 5 mmol/L or serum Na < 130 mmol/L after treatment. | No intervention | 40 g per time of LVP. |
| Smart (1990) [64] | UK | RCT | 40 | 45.00% (18/40) | Serum Na < 130 mmol/L. | Filtration | 40 g per time of LVP. |
| Planas (1990) [37] | Spain | RCT | 88 | 67.05% (59/88) | Decrease in serum Na > 5 mmol/L or serum Na < 130 mmol/L after treatment. | Dextran | 8 g/L of ascites removed. |
| Salerno (1991) [38] | Italy | RCT | 54 | 46.30% (25/54) | Decrease in serum Na > 5 mmol/L or serum Na < 130 mmol/L after treatment. | Hemaccel | 6 g/L of ascites removed. |
| Fassio (1992) [39] | Argentina | RCT | 41 | 82.93% (34/41) | Decrease in serum Na > 5 mmol/L or serum Na < 130 mmol/L after treatment. | Dextran | 6 g/L of ascites removed. |
| Garcia-Compean (1993) [40] | Mexico | RCT | 35 | 71.43% (25/35) | Decrease in serum Na > 5 mmol/L or serum Na < 130 mmol/L after treatment. | No intervention | 5 g/L of ascites removed. |
| Hernández Pérez (1995) [41] | Mexico | RCT | 16 | NA | NA | Dextran | 6 g/L of ascites removed. |
| Ginès (1996) [42] | Spain | RCT | 190 | 70.00% (133/190) | Decrease in serum Na > 5 mmol/L or serum Na < 130 mmol/L after treatment. | Dextran | 8 g/L of ascites removed. |
| Altman (1998) [43] | France | RCT | 60 | 83.33% (50/60) | Decrease in serum Na > 10 mmol/L to serum Na < 120 mmol/L after treatment. | Hydroxyethyl starch | 8 g/L of ascites removed. |
| Gentilini (1999) [44] | Italy | RCT | 68 | 23.53% (16/68) | NA | No intervention | 12.5 g/day. |
| Zaak (2001) [45] | Germany | Cohort | 35 | 88.57% (31/35) | NA | Filtration | 5 g/L of ascites removed. |
| García-Compean (2002) [46] | Mexico | RCT | 96 | 80.21% (77/96) | Decrease in serum Na > 5 mmol/L after treatment. | Dextran | NA |
| Moreau (2002) [47] | France | RCT | 20 | 85.00% (17/20) | Decrease in serum Na > 5 mmol/L or serum Na < 130 mmol/L after treatment. | Terlipressin | 8 g/L of ascites removed. |
| Sola-Vera (2003) [48] | Spain | RCT | 72 | 55.56% (40/72) | Decrease in serum Na > 10 mmol/L to serum Na < 125 mmol/L after treatment. | Saline | 8 g/L of ascites removed. |
| Moreau (2006) [49] | France | RCT | 68 | 100.00% (68/68) | Decrease in serum Na > 5 mmol/L to serum Na < 130 mmol/L after treatment. | Polygeline | NA |
| Singh (2006) [50] | India | RCT | 40 | 70.00% (28/40) | Decrease in serum Na > 5 mmol/L to serum Na < 130 mmol/L after treatment. | Terlipressin | 8 g/L of ascites removed. |
| Appenrodt (2008) [52] | Germany | RCT | 24 | 79.20% (19/24) | NA | Midodrine | 8 g/L of ascites removed. |
| Singh (2008) [53] | India | RCT | 40 | 65.00% (26/40) | Decrease in serum Na > 5 mmol/L to serum Na < 130 mmol/L after treatment. | Midodrine | 8 g/L of ascites removed. |
| Abdel-Khalek (2010) [54] | Egypt | RCT | 135 | NA | Decrease in serum Na > 5 mmol/L to serum Na < 130 mmol/L after treatment. | Hydroxyethyl starch | 8 g/L of ascites removed. |
| Bari (2012) [55] | USA | RCT | 25 | 52.00% (13/25) | NA | Octreotide | 8 g/L of ascites removed. |
| Hamdy (2014) [56] | Egypt | RCT | 50 | NA | NA | Midodrine | 8 g/L of ascites removed. |
| Khan (2015) [57] | Pakistan | RCT | 50 | NA | NA | Hemaccel | 6 g/L of ascites removed. |
| Abootalebi (2017) [58] | Iran | RCT | 72 | NA | NA | Hydroxyethyl starch | 5 g/L of ascites removed. |
| Solà (2018) [61] | Spain | RCT | 173 | 56.07% (97/173) | NA | Placebo | 40 g/15 days. |
| Yosry (2019) [62] | Egypt | RCT | 50 | 0 (0/50) | Decrease in serum Na > 5 mmol/L or serum Na < 130 mmol/L after treatment. | Midodrine | 8 g/L of ascites removed. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, Z.; Wang, L.; Lin, H.; Tacke, F.; Cheng, G.; Qi, X. Use of Human Albumin Administration for the Prevention and Treatment of Hyponatremia in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5928. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195928
Bai Z, Wang L, Lin H, Tacke F, Cheng G, Qi X. Use of Human Albumin Administration for the Prevention and Treatment of Hyponatremia in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(19):5928. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195928
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Zhaohui, Le Wang, Hanyang Lin, Frank Tacke, Gang Cheng, and Xingshun Qi. 2022. "Use of Human Albumin Administration for the Prevention and Treatment of Hyponatremia in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 19: 5928. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195928
APA StyleBai, Z., Wang, L., Lin, H., Tacke, F., Cheng, G., & Qi, X. (2022). Use of Human Albumin Administration for the Prevention and Treatment of Hyponatremia in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(19), 5928. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195928







