Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics of Pediatric COVID-19 Population—A Bibliometric Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
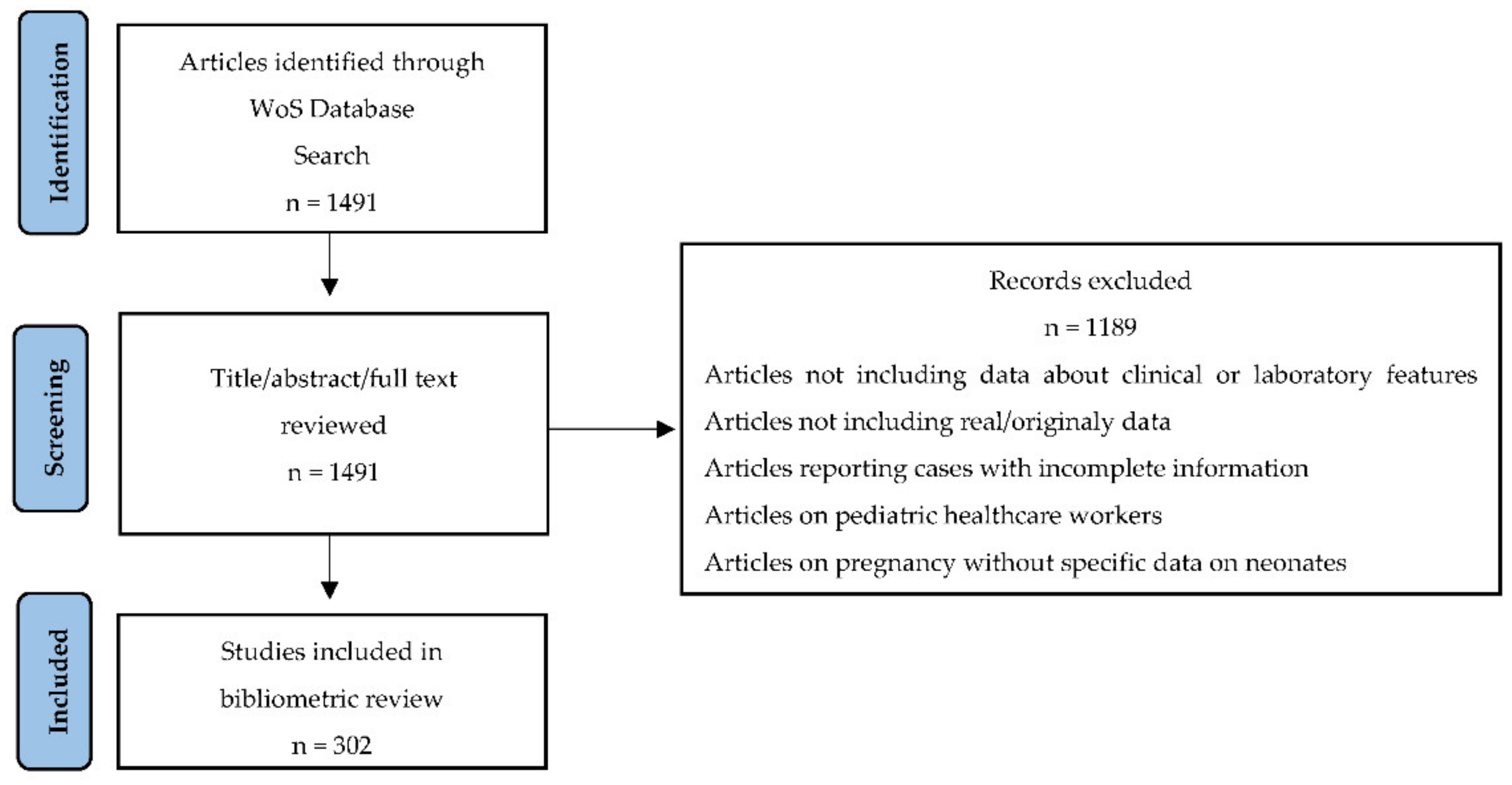
2. Materials and Methods
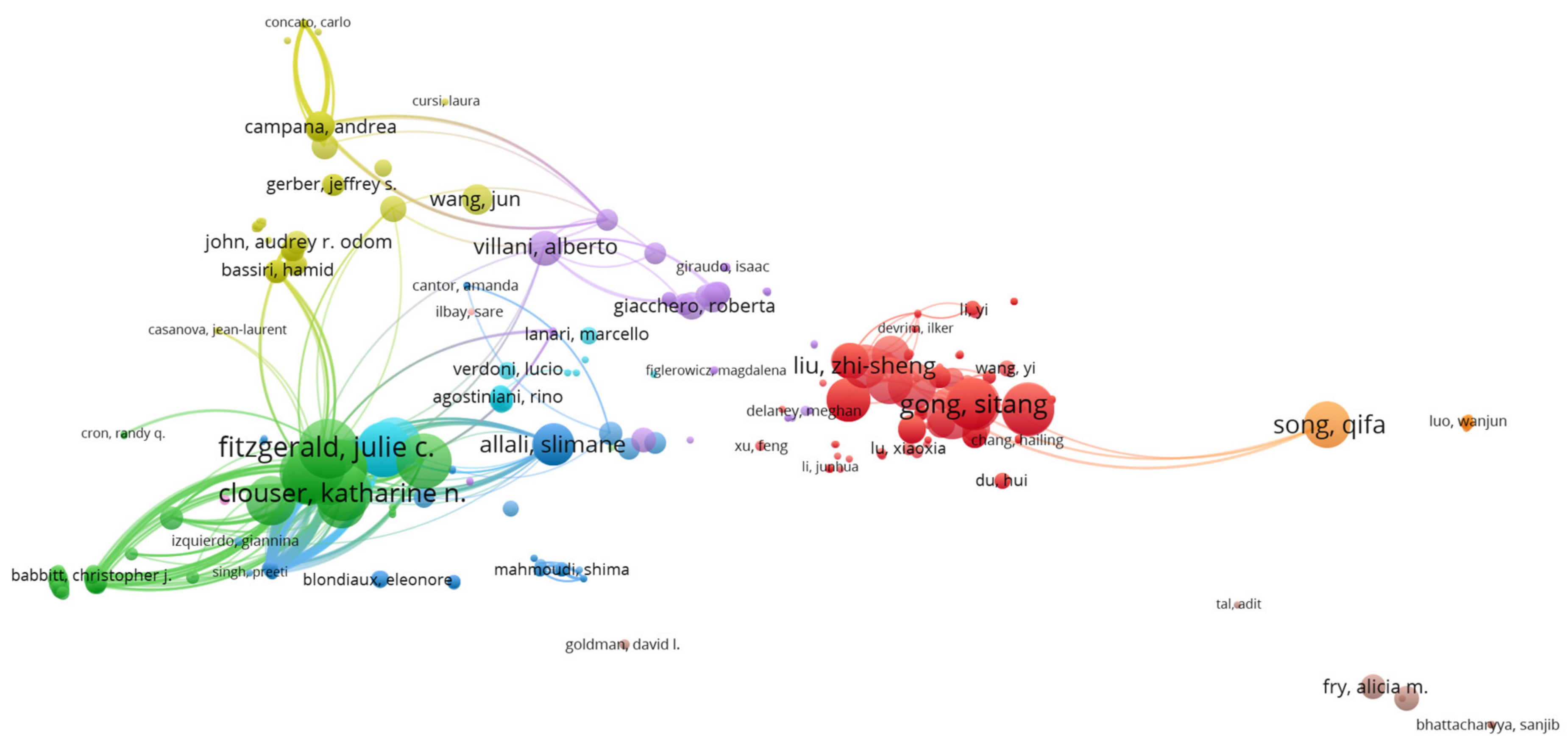
3. Results
- -
- Shao, Jianbo (Wuhan Maternal and Child Healthcare Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, China, 8 documents, 588 citations, 66 TLS)
- -
- Li, Hui (Department of Hematology, Wuhan Maternal and Child Healthcare Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 7 documents, 368 citations, 72 TLS)
- -
- Villani, Alberto (Department of Emergency, Acceptance and General Pediatrics, Bambino Gesù Children’s Hospital, Rome, Italy, 6 documents, 299 citations, 115 TLS)
- -
- Rossi, Paolo (Academic Department of Pediatrics, Research Unit of Clinical Immunology and Vaccinology, Bambino Gesù Children’s Hospital, Chair of Pediatrics, Department of Systems Medicine, University of Rome “Tor Vergata,” Rome, Italy, 5 documents, 181 citations, 110 TLS)
- -
- Xiao, Han (Institute of Maternal and Child Health, Wuhan Children’s Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 5 documents, 337 citations, 45 TLS)
- -
- Fitzgerald, Julie (Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care Medicine, The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, USA, 4 documents, 862 citations, 176 TLS)
- -
- Son, Mary Beth F. (Division of Immunology, Department of Pediatrics, Boston Children’s Hospital, Boston, USA, 4 documents, 858 citations, 168 TLS)
- -
- Newburger, Jane (Department of Cardiology, Boston Children’s Hospital, Department of Pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston, USA, 3 documents, 839 citations, 121 TLS)
- -
- Clouser, Katharine (Hackensack University Medical Center, New Jersey, USA, 4 documents, 788 citations, 173 TLS)
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rhodes, K.M.; Turner, R.M.; Higgins, J.P.T. Predictive distributions were developed for the extent of heterogeneity in meta-analysesof continuous outcome data. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2015, 68, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moed, H.F. New developments in the use of citation analysis in research evaluation. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2009, 57, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turatto, F.; Mazzalai, E.; Pagano, F.; Migliara, G.; Villari, P.; De Vito, C. A Systematic Review and Bibliometric Analysis of the Scientific Literature on the Early Phase of COVID-19 in Italy. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, T.; Guo, W.; Guo, W.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, J.; Dong, C.; Na, R.; Zheng, L.; et al. A systematic review andmeta-analysis of children with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, L.; Cattrall, J.W.; Harris, C.; Newell, K.; Thomson, B.; Pritchard, M.G.; Bannister, P.G.; Sigfrid, L.; Solomon, T.; Horby, P.W.; et al. Evaluating clinical characteristics studies produced early in the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, K.; Zeng, W.; Ye, M.; Zheng, L.; Song, C.; Hu, S.; Duan, C.; Wei, Y.; Peng, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Clinical, laboratory, and imaging features of pediatric COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2021, 100, e25230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, O.; Muttalib, F.; Tang, K.; Jiang, L.; Lassi, Z.S.; Bhutta, Z. Clinical Characteristics, Treatment and Outcomes of PaediatricCOVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arch. Dis. Child. 2021, 106, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, T.H.; Nadal, J.A.; Nogueira, R.J.N.; Pereira, R.M.; Brandão, M.B. Clinical manifestations of children with COVID-19: Asystematic review. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2020, 55, 1892–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. VOSviewer Manual; Univeristeit Leiden: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, M.R.; Martek, I.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Aibinu, A.A.; Arashpour, M.; Chileshe, N. Critical evaluation of off-site construction research: A Scientometric analysis. Autom. Constr. 2018, 87, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosseck, G.; Țîru, L.G.; Bran, R.A. Education for sustainable development: Evolution and perspectives: A bibliometric review of research, 1992–2018. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomaszewska, E.J.; Florea, A. Urban smart mobility in the scientific literature—Bibliometric analysis. Eng. Manag. Prod. Serv. 2018, 10, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maniu, I.; Costea, R.; Maniu, G.; Neamtu, B.M. Inflammatory Biomarkers in Febrile Seizure: A Comprehensive Bibliometric, Review and Visualization Analysis. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldstein, L.R.; Rose, E.B.; Horwitz, S.M.; Collins, J.P.; Newhams, M.M.; Son, M.B.F.; Newburger, J.W.; Kleinman, L.C.; Heidemann, S.M.; Martin, A.A.; et al. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in U.S. Children and Adolescents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhu, B.; Liang, H.; Fang, C.; Gong, Y.; Guo, Q.; Sun, X.; Zhao, D.; Shen, J.; et al. Characteristics of pediatric SARS-CoV-2 infection and potential evidence for persistent fecal viral shedding. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 502–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whittaker, E.; Bamford, A.; Kenny, J.; Kaforou, M.; Jones, C.E.; Shah, P.; Ramnarayan, P.; Fraisse, A.; Miller, O.; Davies, P.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of 58 Children with a Pediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome Temporally Associated with SARS-CoV-2. JAMA 2020, 324, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Wu, J.; Hong, L.; Luo, Y.; Song, Q.; Chen, D. Clinical and epidemiological features of 36 children withcoronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Zhejiang, China: An observational cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, W.; Shao, J.; Guo, Y.; Peng, X.; Li, Z.; Hu, D. Clinical and Ct features in pediatric patients with COVID-19 infection: Different points from adults. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2020, 55, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toubiana, J.; Poirault, C.; Corsia, A.; Bajolle, F.; Fourgeaud, J.; Angoulvant, F.; Debray, A.; Basmaci, R.; Salvador, E.; Biscardi, S.; et al. Kawasaki-like multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children duringthe COVID-19 pandemic in Paris, France: Prospective observational study. BMJ 2020, 369, m2094. [Google Scholar]
- Dufort, E.M.; Koumans, E.H.; Chow, E.J.; Rosenthal, E.M.; Muse, A.; Rowlands, J.; Barranco, M.A.; Maxted, A.M.; Rosenberg, E.S.; Easton, D.; et al. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children in New York state. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Li, H.; Lu, X.X.; Xiao, H.; Ren, J.; Zhang, F.R.; Liu, Z.S. Clinical features of severe pediatric patientswith coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan: A single center’s observational study. World J. Pediatr. 2020, 16, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Liao, C.; Fan, Q.-H.; Chen, H.-B.; Zhao, X.-G.; Xie, Z.-G.; Li, X.-L.; Chen, C.-B.; Lu, X.-X.; Liu, Z.-S.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Children with Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Hubei, China. Curr. Med. Sci. 2020, 40, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Consiglio, C.R.; Cotugno, N.; Sardh, F.; Pou, C.; Amodio, D.; Rodriguez, L.; Tan, Z.; Zicari, S.; Ruggiero, A.; Pascucci, G.R.; et al. The Immunology of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children with COVID-19. Cell 2020, 183, 968–981.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Ma, X.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Bian, P.; Han, Y.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Geng, J.; et al. The different clinical characteristics of corona virus disease cases between children and their families in China—The character of children with COVID-19. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Liu, F.; Li, J.; Zhang, T.; Wang, D.; Lan, W. Clinical and CT imaging features of the COVID-19 pneumonia: Focus on pregnant women and children. J. Infect. 2020, 80, e7–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, L.; Whitaker, M.; O’Halloran, A.; Kambhampati, A.; Chai, S.J.; Reingold, A.; Armistead, I.; Kawasaki, B.; Meek, J.; Yousey-Hindes, K. Hospitalization rates and characteristics of children aged <18 years hospitalized with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19-COVID-NET, 14 States, March 1–July 25, 2020. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 1081. [Google Scholar]
- Swann, O.V.; Holden, K.A.; Turtle, L.C.W.; Pollock, L.; Fairfield, C.J.; Drake, T.M.; Seth, S.; Fegan, C.; Hardwick, H.E.; Halpin, S.; et al. Clinical characteristics of children and young people admitted to hospital with COVID-19 in United Kingdom: Prospectivemulticentre observational cohort study. BMJ 2020, 370, m3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, P.; Evans, C.; Kanthimathinathan, H.K.; Lillie, J.; Brierley, J.; Waters, G.; Johnson, M.; Griffiths, B.; du Pre, P.; Mohammad, Z.; et al. Intensive care admissions of children with paediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome temporallyassociated with SARS-CoV-2 (PIMS-TS) in the UK: A multicentre observational study. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cui, H.; Li, K.; Fang, Y.; Li, S. Chest computed tomography in children with COVID-19 respiratoryinfection. Pediatr. Radiol. 2020, 50, 796–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garazzino, S.; Montagnani, C.; Donà, D.; Meini, A.; Felici, E.; Vergine, G.; Bernardi, S.; Giacchero, R.; Lo Vecchio, A.; Marchisio, P.; et al. Multicentre Italian study of SARS-CoV-2 infection in children and adolescents, preliminary data as at 10 April 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaud, M.; Starck, J.; Levy, M.; Marais, C.; Chareyre, J.; Khraiche, D.; Leruez-Ville, M.; Quartier, P.; Léger, P.L.; Geslain, G.; et al. Acute myocarditis and multisystem inflammatory emerging disease following SARS-CoV-2 infection in critically ill children. Ann. Intensive Care 2020, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zachariah, P.; Johnson, C.L.; Halabi, K.C.; Ahn, D.; Sen, A.I.; Fischer, A.; Banker, S.L.; Giordano, M.; Manice, C.S.; Diamond, R.; et al. Epidemiology, Clinical Features, and Disease Severity in Patients withCoronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in a Children’s Hospital in New York City, New York. JAMA Pediatr. 2020, 174, e202430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Cui, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Zheng, J.; Zheng, G.; Guo, W.; Cai, C.; He, S.; Xu, Y. Detectable SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA infeces of three children during recovery period of COVID-19 pneumonia. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazova, S.; Alexandrova, T.; Gorelyova-Stefanova, N.; Atanasov, K.; Tzotcheva, I.; Velikova, T. Liver Involvement in Childrenwith COVID-19 and Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome: A Single-Center Bulgarian Observational Study. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, I.; Singh, Y.; Sanchez-de-Toledo, J.; Theocharis, P.; Chikermane, A.; Di Filippo, S.; Kuciñska, B.; Mannarino, S.; Tamariz-Martel, A.; Gutierrez-Larraya, F.; et al. Acute Cardiovascular Manifestations in 286 Children with Multisystem InflammatorySyndrome Associated with COVID-19 Infection in Europe. Circulation 2021, 143, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatelli, R.; Antona, C.V.; Rivera, I.R.; Zenteno, P.A.; Acosta, Y.T.; Huertas-Quiñones, M.; Murillo, C.A.; Torres, F.M.; Cabalin, C.F.; Camacho, A.G.; et al. Pediatric multisystem SARS-CoV-2 with versus without cardiac involvement: A multicenter study from Latin America. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 180, 2879–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondiaux, E.; Parisot, P.; Redheuil, A.; Tzaroukian, L.; Levy, Y.; Sileo, C.; Schnuriger, A.; Lorrot, M.; Guedj, R.; Ducou le Pointe, H. Cardiac MRI in Children with Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome Associated with COVID-19. Radiology 2020, 297, E283–E288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, N.H.; Fremed, M.; Starc, T.; Weller, R.; Cheung, E.; Ferris, A.; Silver, E.S.; Liberman, L. MIS-C and cardiac conduction abnormalities. Pediatrics 2020, 146, 2020009738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRovere, K.L.; Riggs, B.J.; Poussaint, T.Y.; Young, C.C.; Newhams, M.M.; Maamari, M.; Walker, T.C.; Singh, A.R.; Dapul, H.; Hobbs, C.V.; et al. Neurologic involvement in children and adolescents hospitalized in the United States for COVID-19 ormultisystem inflammatory syndrome. JAMA Neurol. 2021, 78, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Deng, W.; Liu, M.; He, Y.; Huang, L.; Lv, M.; Li, J.; Du, H. Symptomatic infection is associated with prolongedduration of viral shedding in mild coronavirus disease 2019: A retrospective study of 110 children in Wuhan. Pediatric Infect. Dis. J. 2020, 39, e95–e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mutair, A.; Alhumaid, S.; Alhuqbani, W.N.; Zaidi, A.R.Z.; Alkoraisi, S.; Al-Subaie, M.F.; AlHindi, A.M.; Abogosh, A.K.; Alrasheed, A.K.; Alsharafi, A.A. Clinical, epidemiological, and laboratory characteristics of mild-to-moderate COVID-19 patientsin Saudi Arabia: An observational cohort study. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2020, 25, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinyazdi, M.; Esmaeilian, S.; Jahankhah, R.; Teimouri, A.; Sherbaf, F.G.; Rafiee, F.; Jalli, R.; Hooshmandi, S. Clinical, laboratory, and chest CT features of severe versus non-severe pediatric patients with COVID-19 infection among different age groups. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Thoon, K.C.; Chong, C.Y.; Maiwald, M.; Kam, K.Q.; Nadua, K.; Tan, N.W.; Yung, C.F. Comparative Analysis ofSymptomatic and Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Children. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2020, 49, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totan, M.; Gligor, F.G.; Duică, L.; Grigore, N.; Silișteanu, S.; Maniu, I.; Antonescu, E. A Single-Center (Sibiu, Romania), Retrospective Study (March–November 2020) of COVID-19 Clinical and Epidemiological Features in Children. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, E.A.; Colosimo, E.A.; e Silva, A.C.S.; Mak, R.H.; Martelli, D.B.; Silva, L.R.; Martelli, H.; Oliveira, M.C.L. Clinical characteristics and risk factors for death among hospitalised children and adolescents with COVID-19 in Brazil: An analysis of a nationwide database. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2021, 5, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, A.; Mahto, D.; Kumar, V.; Gulati, S.; Pemde, H.; Saha, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Pandit, K.; Paharia, K.; Basu, S. Comparison of clinical and laboratory profile of survivors and non-survivors of SARS-CoV-2-related multisystem inflammatory syndrome of childhood in India: An observational study. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2022, 58, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Yu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Z. Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 in children compared with adults in Shandong Province, China. Infection 2020, 48, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Lai, C.X.; Huang, P.Y.; Liu, J.M.; Wang, X.F.; Tang, Q.Y.; Zhou, X.; Xian, W.J.; Chen, R.K.; Li, X.; et al. Comparison ofClinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Pediatric and Adult Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Shenzhen, China. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2020, 33, 906–915. [Google Scholar]
- Shaiba, L.A.; Altirkawi, K.; Hadid, A.; Alsubaie, S.; Alharbi, O.; Alkhalaf, H.; Alharbi, M.; Alruqaie, N.; Alzomor, O.; Almughaileth, F.; et al. COVID-19 Disease in Infants Less Than 90 Days: Case Series. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Lu, X.-X.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, F.-R.; Liu, Z.-S. SARS-CoV-2 infection in infants under 1 year of age in Wuhan City, China. World J. Pediatr. 2020, 16, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Cheng, H.; Wang, J.; Ding, L.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, S.; Chang, L.; Rong, Z. Clinical analysis of neonates born to mothers with or without COVID-19: A retrospective analysis of 48 cases from two neonatal intensive care units in Hubei Province. Am. J. Perinatol. 2020, 37, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Dong, X.; Zhang, J.-J.; Cao, Y.-Y.; Akdis, M.; Huang, P.-Q.; Chen, H.-W.; Li, Y.; Liu, G.-H.; Akdis, C.A.; et al. Clinical characteristics of 182 pediatric COVID-19 patients with different severities and allergic status. Allergy 2021, 76, 510–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Zhu, F.; Wang, C.; Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Lu, X.; Ma, J.; et al. Children Infected with SARS-CoV-2 From Family Clusters. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, S.Q.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, K.; Chen, Y.; Chu, Q.; Wei, Y.C.; Zhou, F.L.; Bu, B.T.; Tu, H.L.; et al. Characteristics of immune and inflammatory responses among different age groups of pediatric patients with COVID-19 in China. World J. Pediatr. 2021, 17, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Hu, W.; Hall, I.P.; Yue, J.; Lu, H.; Ruan, L.; Ye, M.; Mei, J. Reduced inflammatory responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection in children presenting to hospital with COVID-19 in China. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 34, 100831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Song, X.; Lu, H.; Mao, Y.; Liu, C.; Yuan, Y.; Fan, Q. Clinical analysis of seven pediatric patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Jingzhou, Hubei, China: A retrospective study. Transl. Pediatr. 2021, 10, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Yan, X.; Gao, L.; Ding, S.; Bai, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Cui, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Lu, G.; et al. Comparison of clinical characteristics among COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 pediatric pneumonias: A multicenter cross-sectional study. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 663884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, B.; Guo, Y.; Hu, Z.; Peng, C.; Lei, X.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, W.; et al. Comparative study of hospitalized children with acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.M.; Zhou, A.F.; Zhang, X.B.; Xu, H.; Wang, X.-F.; Ye, Q.-F.; Shang, F.-N.; He, Y.-L.; Ma, S.-L.; Cui, Y.-X.; et al. Safety and efficacy of oral lopinavir/ritonavir in pediatric patients with coronavirus disease: A nationwide comparative analysis. Eur. Rev.Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 549–555. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Zhu, H.; Yuan, C.; Yao, C.; Luo, W.; Shen, X.; Wang, J.; Shao, J.; Xiang, Y. Clinical and Immune Features of Hospitalized Pediatric Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2010895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, F.; Du, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, P.; Lu, X. Comparison of hospitalized patients with pneumonia caused by COVID-19 and influenza A in children under 5 years. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 98, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Luo, W.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Mei, H.; Shao, J.; Song, Q. Clinical features and follow-up of pediatric patients hospitalized for COVID-19. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2021, 56, 1967–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diorio, C.; Henrickson, S.E.; Vella, L.A.; McNerney, K.O.; Chase, J.M.; Burudpakdee, C.; Lee, J.H.; Jasen, C.; Balamuth, F.; Barrett, D.M.; et al. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children and COVID-19 are distinct presentations of SARS-CoV-2. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 5967–5975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corwin, D.J.; Sartori, L.F.; Chiotos, K.; John, A.R.O.; Cohn, K.; Bassiri, H.; Behrens, E.M.; Teachey, D.T.; Henrickson, S.E.; Diorio, C.J.; et al. Distinguishing multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children from Kawasaki disease and benign inflammatory illnesses in the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2020, 36, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelo-Soccio, L.; Lara-Corrales, I.; Paller, A.S.; Bean, E.; Rangu, S.; Oboite, M.; Flohr, C.; Ahmad, R.C.; Calberg, V.; Gilliam, A.; et al. Acral Changes in pediatric patients during COVID 19 pandemic: Registry report from the COVID 19 response task force of the society of pediatric dermatology (SPD) and pediatric dermatology research alliance (PeDRA). Pediatr. Dermatol. 2021, 38, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diorio, C.; Anderson, E.M.; McNerney, K.O.; Goodwin, E.C.; Chase, J.C.; Bolton, M.J.; Arevalo, C.P.; Weirick, M.E.; Gouma, S.; Vella, L.A.; et al. Convalescent plasma for pediatric patients with SARS-CoV-2-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2020, 67, e28693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, W.R.; Geoghegan, S.; Posch, L.C.; Bell, L.M.; Coffin, S.E.; Sammons, J.S.; Harris, R.M.; Odom John, A.R.; Luan, X.; Gerber, J.S. The epidemiology of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in a pediatric healthcare network in the United States. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2020, 9, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, A.; Cantor, A.; Rudolph, B.; Miller, J.; Kogan-Liberman, D.; Gao, Q.; Da Silva, B.; Margolis, K.G.; Ovchinsky, N.; Martinez, M. Liver involvement in children with SARS-CoV-2 infection: Two distinct clinical phenotypes caused by the same virus. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 2068–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, D.G.; Rodríguez-Belvís, M.V.; Gonzalez, P.F.; Ortega, G.D.; Segarra, O.; Benitez, E.M.; Tirado, D.G.; Romero, R.G.; López, R.V.; Crehuá-Gaudiza, E.; et al. COVID-19 gastrointestinal manifestations are independent predictors of PICU admission in hospitalized pediatric patients. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2020, 39, e459–e462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrero-Hernández, M.; García-Salido, A.; Leoz-Gordillo, I.; Alonso-Cadenas, J.A.; Gochi-Valdovinos, A.; González Brabin, A.; de Lama Caro-Patón, G.; Nieto-Moro, M.; De-Azagra-Garde, A.M.-; Serrano-González, A. Severe SARS-CoV-2 infectionin children with suspected acute abdomen: A case series from a tertiary hospital in Spain. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2020, 39, E195–E198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andina, D.; Noguera-Morel, L.; Bascuas-Arribas, M.; Gaitero-Tristán, J.; Alonso-Cadenas, J.A.; Escalada-Pellitero, S.; Hernández-Martín, Á.; De La Torre-Espi, M.; Colmenero, I.; Torrelo, A. Chilblains in children in the setting of COVID-19 pandemic. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2020, 37, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldarale, F.; Giacomelli, M.; Garrafa, E.; Tamassia, N.; Morreale, A.; Poli, P.; Timpano, S.; Baresi, G.; Zunica, F.; Cattalini, M.; et al. Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells Depletion and Elevation of IFN-γDependent Chemokines CXCL9 and CXCL10 in Children with Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 654587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Rank | Documents | Citations | Total Link Strength | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Authorship | Citations | Bibliographic Coupling | |||
| 1 | USA (76) | USA (3751) | USA (73) | USA (434) | USA (28,680) |
| 2 | China (67) | China (3426) | England (65) | China (251) | China (19,916) |
| 3 | Turkey (41) | England (946) | Italy (46) | England (207) | Turkey (17,967) |
| 4 | Italy (26) | France (727) | Spain (45) | Turkey (119) | Italy (11,416) |
| 5 | England (21) | Italy (493) | France (36) | France (107) | England (10,435) |
| 6 | India; Spain (15) | Scotland (322) | Brazil (33) | Italy (92) | France (7761) |
| 7 | France (14) | Spain (230) | Germany; China (26) | Scotland (79) | Brazil (7381) |
| 8 | Brazil; Saudi Arabia (12) | Sweden (184) | Scotland (24) | Brazil (54) | India (6718) |
| 9 | Iran (11) | Wales (152) | Argentina; Peru; Switzerland (23) | Spain (48) | Spain (6627) |
| 10 | Scotland (6) | Turkey (90) | Chile (22) | India (41) | Saudi Arabia (5465) |
| Rank | Most Productive Journals Documents/Citations/ TLS/IF2020; WoS Category, JCR | Most Cited Journals Citations/Documents/ TLS/IF2020; WoS Category, JCR | Most Co-Cited Journals Citations/TLS/ IF2020; WoS Category, JCR |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 14/189/45/2.129 immunology, infectious disease, pediatrics Q3 | New England Journal of Medicine 1070/2/86/91.245 medicine, general & internal Q1 | New England Journal of Medicine 481/8705/91.245 medicine, general & internal Q1 |
| 2 | Pediatric Pulmonology 11/492/50/3.039 pediatrics Q2, respiratory system Q3 | Nature Medicine 665/2/11/53.440 biochemistry & molecular biology, cell biology, medicine, research & experimental Q1 | Lancet Infectious Disease 323/5861/25.071 infectious diseases Q1 |
| 3 | Frontiers in Pediatrics 10/26/18/3.418 pediatrics Q1 | Jama—Journal of American Medical Association 604/2/48/56.272 medicine, general & internal Q1 | Pediatrics 299/5458/7.124 pediatrics Q1 |
| 4 | Journal of Medical Virology 7/173/15/2.327 virology Q3 | Lancet Infectious Disease 538/1/52/25.071 infectious diseases Q1 | JAMA—Journal of American Medical Association 287/5330/56.272 medicine, general & internal Q1 |
| 5 | World Journal of Pediatrics 6/298/32/2.764 pediatrics Q2 | BMJ—British Medical Journal 526/2/38/39.890 medicine, general & internal Q1 | JAMA Pediatrics 143/2837/16.193 pediatrics Q1 |
| First Author Year [ref.] | Document Title | Journal | Citations (Rank) 8 October 2021/ 20 June 2022 | Links |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feldstein 2020 [15] | Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in US Children and Adolescents | NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE | 695 (1)/ 1066 (1) | 46 |
| Xu 2020 [16] | Characteristics of pediatric SARS-CoV-2 infection and potential evidence for persistent fecal viral shedding | NATURE MEDICINE | 658 (2)/ 789 (3) | 11 |
| Whittaker 2020 [17] | Clinical Characteristics of 58 Children with a Pediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome Temporally Associated With SARS-CoV-2 | JAMA—JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN MEDICAL ASSOCIATION | 554 (3)/ 851 (2) | 41 |
| Qiu 2020 [18] | Clinical and epidemiological features of 36 children with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Zhejiang, China: an observational cohort study | LANCET INFECTIOUS DISEASES | 538 (4)/ 645 (4) | 52 |
| Xia 2020 [19] | Clinical and CT features in pediatric patients with COVID-19 infection: Different points from adults | PEDIATRIC PULMONOLOGY | 462 (5)/ 550 (6) | 36 |
| Toubiana 2020 [20] | Kawasaki-like multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children during the COVID-19 pandemic in Paris, France: prospective observational study | BMJ | 395 (6)/ 508 (7) | 24 |
| Dufort 2020 [21] | Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children in New York State | NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE | 375 (7)/ 579 (5) | 42 |
| Sun 2020 [22] | Clinical features of severe pediatric patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan: a single center’s observational study | WORLD JOURNAL OF PEDIATRICS | 277 (8)/ 336 (8) | 23 |
| Zheng 2020 [23] | Clinical Characteristics of Children with Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Hubei, China | CURRENT MEDICAL SCIENCE | 190 (9)/ 227 (13) | 9 |
| Consiglio 2020 [24] | The Immunology of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children with COVID-19 | CELL | 174 (10)/ 304 (9) | 14 |
| Su 2020 [25] | The different clinical characteristics of corona virus disease cases between children and their families in China—the character of children with COVID-19 | EMERGING MICROBES & INFECTIONS | 153 (11)/ 177 (16) | 10 |
| Liu 2020 [26] | Clinical and CT imaging features of the COVID-19 pneumonia: Focus on pregnant women and children | JOURNAL OF INFECTION | 137 (12)/ 196 (15) | 3 |
| Kim 2020 [27] | Hospitalization Rates and Characteristics of Children Aged < 18 Years Hospitalized with Laboratory-Confirmed COVID-19-COVID-NET, 14 States, 1 March–25 July 2020 | MMWR—MORBIDITY AND MORTALITY WEEKLY REPORT | 132 (13)/ 241 (12) | 12 |
| Swann 2020 [28] | Clinical characteristics of children and young people admitted to hospital with COVID-19 in United Kingdom: prospective multicentre observational cohort study | BMJ-BRITISH MEDICAL JOURNAL | 131 (14)/ 253 (10) | 16 |
| Davies 2020 [29] | Intensive care admissions of children with paediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome temporally associated with SARS-CoV-2 (PIMS-TS) in the UK: a multicentre observational study | LANCET CHILD & ADOLESCENT HEALTH | 129 (15)/ 203 (14) | 11 |
| Li 2020 [30] | Chest computed tomography in children with COVID-19 respiratory infection | PEDIATRIC RADIOLOGY | 120 (16)/ 121 (20) | 12 |
| Garazzino 2020 [31] | Multicentre Italian study of SARS-CoV-2 infection in children and adolescents, preliminary data as at 10 April 2020 | EUROSURVEILLANCE | 116 (17)/ 148 (18) | 16 |
| Grimaud 2020 [32] | Acute myocarditis and multisystem inflammatory emerging disease following SARS-CoV-2 infection in critically ill children | ANNALS OF INTENSIVE CARE | 109 (18)/ 155 (17) | 6 |
| Zachariah 2020 [33] | Epidemiology, Clinical Features, and Disease Severity in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in a Children’s Hospital in New York City, New York | JAMA PEDIATRICS | 107 (19)/ 248 (11) | 23 |
| Zhang 2020 [34] | Detectable SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA in feces of three children during recovery period of COVID-19 pneumonia | JOURNAL OF MEDICAL VIROLOGY | 106 (20)/ 119 (19) | 5 |
| Terms Related to: | |
|---|---|
| Symptoms | |
| Systemic | Fever (133), fatigue (14), myalgia (8), anemia (4) |
| Respiratory | Cough (75), sore throat (17), dry cough (10), dyspnea (9), tachypnea (6), rhinorrhea (8), runny nose (4), nasal congestion (4), rhinitis (3), nasal discharge (2) |
| Gastrointestinal | Gastrointestinal (32), diarrhea/diarrhea (21/4), abdominal pain/discomfort/symptoms (18/2/2), vomiting (14), nausea (3) |
| Neurological | Headache (22), dizziness (2), irritability (2), encephalopathy (4), hypoxia (2) |
| Olfactory | Taste (8), smell/anosmia (6/3), ageusia/dysgeusia (4/3) |
| Dermatological | Rash (19), dermatologic (2), skin/mucocutaneous rash (3/2), cheilitis (2) |
| Ocular | Conjunctivitis (5), conjunctival injection (5) |
| Rheumatic | Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (5), arthritis rheumatol (15) |
| Cardiac | Myocarditis (10), hypertension (8), chest pain (5), cardiac arrhythmia (3), tachycardia (2) |
| Laboratory markers | |
| Biochemistry | C reactive protein/CRP (72/26), lactate dehydrogenase/LDH (15/12), ALT/alanine aminotransferase (7/2), aspartate aminotransferase/AST (3/4), creatinine kinase/creatine kinase mb (4/3), sodium/hyponatremia (2/2), zinc (3), total bilirubin (3), albumin/hypoalbuminemia (2/2), alpha hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase (2) |
| Cardiac | B-type natriuretic peptide/BNP (6/3), troponin (4) |
| Coagulation | D-dimer (43), fibrinogen (10), prothrombin time (2) |
| Hematology | Lymphocyte/lymphopenia/lymphocytosis/lymphopenium/lymphopaenia (44/36/5/3/2), absolute lymphocyte count (4), procalcitonin (30), neutrophil/neutropenia (19/5), absolute lymphocyte count (3), platelet (15), WBC/white blood cell count (8/7), thrombocytopenia (10), T cell/T cell response (6/2), CD4 (5), CD8 T cell (3), B cell (4), MPV (8), erythrocyte sedimentation rate/ESR (5/4), hemoglobin (5), leukocytosis/leukopenia/leukocyte (4/4/3), neutrophil lymphocyte ratio (3), hematologic (3) |
| Immunology | Ferritin (27), interleukin/IL-6/interleukin-6 (13/4/4), chemokine (4), IFN gama/interferon gamma (10/3), cytokine storm (10), TNF alpha (9), Th Ts (2), immunoglobulin/IgG/IgM/IgA (12/7/7/3), total immunoglobulin E (2) |
| Treatment | Mechanical ventilation (19), invasive/noninvasive ventilation (8/3), oxygen therapy (4), antiviral therapy (3), azithromycin (3), corticosteroid (12), hydroxychloroquine (2), interferon alfa (1), intravenous immunoglobulin (12), lopinavir ritonavir (3), methylprednisolone (2), ribavirin (2), ritonavir (2), glucocorticoid (4), anakinra (5), antibiotic (4) |
| Coinfections | Influenza A (4), respiratory syncytial virus (4), influenza virus (2), mycoplasma pneumonia (2), adenovirus (2), rhinovirus (3) |
| Radiological/imaging | Chest CT finding/scan/examination/image/feature (6/5/4/3/2), chest radiograph/radiography/x-ray/imaging/finding/feature (10/5/9/8/6/4), abnormal CT finding/scan (5/2), abnormal radiological finding (2), lung (9), lung injury/involvement/lobe (6/4/3), ground glass opacity (29), patchy shadow (4), bilateral involvement/bilateral pneumonia (3/2), pleural effusion (3), interstitial opacity (2), sub-pleural area (2). |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maniu, I.; Maniu, G.; Totan, M. Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics of Pediatric COVID-19 Population—A Bibliometric Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5987. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11205987
Maniu I, Maniu G, Totan M. Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics of Pediatric COVID-19 Population—A Bibliometric Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(20):5987. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11205987
Chicago/Turabian StyleManiu, Ionela, George Maniu, and Maria Totan. 2022. "Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics of Pediatric COVID-19 Population—A Bibliometric Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 20: 5987. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11205987
APA StyleManiu, I., Maniu, G., & Totan, M. (2022). Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics of Pediatric COVID-19 Population—A Bibliometric Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(20), 5987. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11205987





