Changes in Plasma Levels of ADAMTS13 and von Willebrand Factor in Patients Undergoing Elective Joint Arthroplasty
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Sample Collection and Measurement
2.3. Assay for Plasma ADAMTS13 Activity
2.4. Assay for Plasma VWF Antigen
2.5. Clinical Data Collection
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Population
3.2. Plasma Levels of ADAMTS13 Activity, VWF Antigen and Ratio of ADAMTS13/VWF
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fisher, W.D. Impact of venous thromboembolism on clinical management and therapy after hip and knee arthroplasty. Can. J. Surg. 2011, 54, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Januel, J.M.; Chen, G.; Ruffieux, C.; Quan, H.; Douketis, J.D.; Crowther, M.A.; Colin, C.; Ghali, W.A.; Burnand, B.; Group, I. Symptomatic in-hospital deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism following hip and knee arthroplasty among patients receiving recommended prophylaxis: A systematic review. JAMA 2012, 307, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnelli, G. Prevention of venous thromboembolism in surgical patients. Circulation 2004, 110, IV4–IV12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppert, A.; Steinle, T.; Lees, M. Economic burden of venous thromboembolism: A systematic review. J. Med. Econ. 2011, 14, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, V.V.; Phan, K.; Levy, Y.D.; Bruce, W.J. Aspirin as Thromboprophylaxis in Hip and Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Arthroplast. 2016, 31, 2608–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, Y.; Nakatsuka, H.; Namba, Y.; Mitani, S.; Yoshitake, N.; Sugimoto, E.; Hazama, K. The incidence of pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis and their predictive risk factors after lower extremity arthroplasty: A retrospective analysis based on diagnosis using multidetector CT. J. Anesth. 2015, 29, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofa, D.; Rajaee, S.S.; Smith, E.L. Nationwide trends in total shoulder arthroplasty and hemiarthroplasty for osteoarthritis. Am. J. Orthop. 2014, 43, 166–172. [Google Scholar]
- Schiff, R.L.; Kahn, S.R.; Shrier, I.; Strulovitch, C.; Hammouda, W.; Cohen, E.; Zukor, D. Identifying orthopedic patients at high risk for venous thromboembolism despite thromboprophylaxis. Chest 2005, 128, 3364–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerts, W.H.; Bergqvist, D.; Pineo, G.F.; Heit, J.A.; Samama, C.M.; Lassen, M.R.; Colwell, C.W. Prevention of venous thromboembolism: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest 2008, 133, 381S–453S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, C.M.; Shields, E.J.; Wiater, B.P.; Wiater, J.M. Venous Thromboembolism After Shoulder Arthoplasty and Arthroscopy. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2019, 27, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyman, S.; Sherman, S.; Carter, T.I.; Bach, P.B.; Mandl, L.A.; Marx, R.G. Prevalence and risk factors for symptomatic thromboembolic events after shoulder arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2006, 448, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, E.; Iannuzzi, J.C.; Thorsness, R.; Noyes, K.; Voloshin, I. Postoperative Morbidity by Procedure and Patient Factors Influencing Major Complications Within 30 Days Following Shoulder Surgery. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2014, 2, 2325967114553164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.S.; Ramsey, M.L.; Lau, E.; Williams, G.R. Risk of venous thromboembolism after shoulder arthroplasty in the Medicare population. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2015, 24, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imberti, D.; Dentali, F.; Ivaldo, N.; Murena, L.; Paladini, P.; Castagna, A.; Barillari, G.; Guerra, E.; Tonello, C.; Castoldi, F.; et al. Venous Thromboembolism in Patients Undergoing Shoulder Arthroscopy: Findings From the RECOS Registry. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2015, 21, 486–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.A.; Jensen, M.R.; Harmsen, W.S.; Gabriel, S.E.; Lewallen, D.G. Cardiac and thromboembolic complications and mortality in patients undergoing total hip and total knee arthroplasty. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 2082–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashjian, R.Z.; Lilly, D.T.; Isaacson, A.M.; Georgopoulos, C.E.; Bettwieser, S.P.; Burks, R.T.; Greis, P.E.; Presson, A.P.; Granger, E.K.; Zhang, Y. Incidence of and Risk Factors for Symptomatic Venous Thromboembolism After Shoulder Arthroplasty. Am. J. Orthop. 2016, 45, E379–E385. [Google Scholar]
- Wronka, K.S.; Pritchard, M.; Sinha, A. Incidence of symptomatic venous thrombo-embolism following shoulder surgery. Int. Orthop. 2014, 38, 1415–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farng, E.; Zingmond, D.; Krenek, L.; Soohoo, N.F. Factors predicting complication rates after primary shoulder arthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011, 20, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameson, S.S.; James, P.; Howcroft, D.W.; Serrano-Pedraza, I.; Rangan, A.; Reed, M.R.; Candal-Couto, J. Venous thromboembolic events are rare after shoulder surgery: Analysis of a national database. J. Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011, 20, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ling, J.; Ma, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Pan, J.; Yang, H. Changes in von Willebrand factor and ADAMTS-13 in patients following arthroplasty. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 3015–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lung, B.E.; Kanjiya, S.; Bisogno, M.; Komatsu, D.E.; Wang, E.D. Risk factors for venous thromboembolism in total shoulder arthroplasty. JSES Open Access 2019, 3, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadler, J.E. von Willebrand factor. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 22777–22780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lollar, P. The association of factor VIII with von Willebrand factor. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1991, 66, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skornova, I.; Simurda, T.; Stasko, J.; Zolkova, J.; Sokol, J.; Holly, P.; Dobrotova, M.; Plamenova, I.; Hudecek, J.; Brunclikova, M.; et al. Multimer Analysis of Von Willebrand Factor in Von Willebrand Disease with a Hydrasys Semi-Automatic Analyzer-Single-Center Experience. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wit, T.R.; van Mourik, J.A. Biosynthesis, processing and secretion of von Willebrand factor: Biological implications. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2001, 14, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Goto, S. Role of von Willebrand factor for the onset of arterial thrombosis. Clin. Lab. 2001, 47, 327–334. [Google Scholar]
- Nichols, T.C.; Bellinger, D.A.; Reddick, R.L.; Read, M.S.; Koch, G.G.; Brinkhous, K.M.; Griggs, T.R. Role of von Willebrand factor in arterial thrombosis. Studies in normal and von Willebrand disease pigs. Circulation 1991, 83, IV56–IV64. [Google Scholar]
- Nichols, T.C.; Bellinger, D.A.; Tate, D.A.; Reddick, R.L.; Read, M.S.; Koch, G.G.; Brinkhous, K.M.; Griggs, T.R. von Willebrand factor and occlusive arterial thrombosis. A study in normal and von Willebrand’s disease pigs with diet-induced hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis 1990, 10, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazetto, B.M.; Orsi, F.L.; Barnabe, A.; De Paula, E.V.; Flores-Nascimento, M.C.; Annichino-Bizzacchi, J.M. Increased ADAMTS13 activity in patients with venous thromboembolism. Thromb. Res. 2012, 130, 889–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Chung, D.; Takayama, T.K.; Majerus, E.M.; Sadler, J.E.; Fujikawa, K. Structure of von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease (ADAMTS13), a metalloprotease involved in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 41059–41063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, G.G.; Nichols, W.C.; Lian, E.C.; Foroud, T.; McClintick, J.N.; McGee, B.M.; Yang, A.Y.; Siemieniak, D.R.; Stark, K.R.; Gruppo, R.; et al. Mutations in a member of the ADAMTS gene family cause thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Nature 2001, 413, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furlan, M.; Robles, R.; Lammle, B. Partial purification and characterization of a protease from human plasma cleaving von Willebrand factor to fragments produced by in vivo proteolysis. Blood 1996, 87, 4223–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, H.M.; Lian, E.C. Antibodies to von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease in acute thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N. Eng. J. Med. 1998, 339, 1585–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.L. ADAMTS13 and von Willebrand Factor in Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 66, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, J.; Zheng, L.; Zheng, X.L. ADAMTS13 Biomarkers in Management of Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.L.; Vesely, S.K.; Cataland, S.R.; Coppo, P.; Geldziler, B.; Iorio, A.; Matsumoto, M.; Mustafa, R.A.; Pai, M.; Rock, G.; et al. ISTH guidelines for the diagnosis of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 2486–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moake, J.L. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: The systemic clumping “plague”. Annu. Rev. Med. 2002, 53, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zindovic, I.; Sjogren, J.; Bjursten, H.; Ingemansson, R.; Larsson, M.; Svensson, P.J.; Strandberg, K.; Wierup, P.; Nozohoor, S. The role of von Willebrand factor in acute type A aortic dissection and aortic surgery. Thromb. Res. 2019, 178, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groeneveld, D.J.; Alkozai, E.M.; Adelmeijer, J.; Porte, R.J.; Lisman, T. Balance between von Willebrand factor and ADAMTS13 following major partial hepatectomy. Br. J. Surg. 2016, 103, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haegele, S.; Fuxsteiner, J.; Pereyra, D.; Koeditz, C.; Rumpf, B.; Schuetz, C.; Schwarz, C.; Brostjan, C.; Gruenberger, T.; Starlinger, P. Elevated ADAMTS13 Activity is Associated with Poor Postoperative Outcome in Patients Undergoing Liver Resection. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Wada, H.; Kamikura, Y.; Matsumoto, T.; Mori, Y.; Kaneko, T.; Nobori, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Fujimura, Y.; Shiku, H. Decreased ADAMTS13 activity in plasma from patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Thromb. Res. 2007, 119, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur, P.; Plicner, D.; Zdziarska, J.; Sadowski, J.; Undas, A. Decreased von Willebrand factor ristocetin cofactor activity and increased ADAMTS13 antigen increase postoperative drainage after coronary artery bypass grafting. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2014, 45, e26–e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Simurda, T.; Kubisz, P.; Dobrotova, M.; Necas, L.; Stasko, J. Perioperative Coagulation Management in a Patient with Congenital Afibrinogenemia during Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2016, 42, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flevas, D.A.; Megaloikonomos, P.D.; Dimopoulos, L.; Mitsiokapa, E.; Koulouvaris, P.; Mavrogenis, A.F. Thromboembolism prophylaxis in orthopaedics: An update. EFORT Open Rev. 2018, 3, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokame, K.; Nobe, Y.; Kokubo, Y.; Okayama, A.; Miyata, T. FRETS-VWF73, a first fluorogenic substrate for ADAMTS13 assay. Br. J. Haematol. 2005, 129, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raife, T.J.; Cao, W.; Atkinson, B.S.; Bedell, B.; Montgomery, R.R.; Lentz, S.R.; Johnson, G.F.; Zheng, X.L. Leukocyte proteases cleave von Willebrand factor at or near the ADAMTS13 cleavage site. Blood 2009, 114, 1666–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, R.T.; McDaniel, J.K.; Cao, W.; Shroyer, M.; Wagener, B.M.; Zheng, X.L.; Pittet, J.F. Low Plasma ADAMTS13 Activity Is Associated with Coagulopathy, Endothelial Cell Damage and Mortality after Severe Paediatric Trauma. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 118, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Cao, W.; McDaniel, J.K.; Pham, H.P.; Raju, D.; Nawalinski, K.; Frangos, S.; Kung, D.; Zager, E.; Kasner, S.E.; et al. Plasma ADAMTS13 activity and von Willebrand factor antigen and activity in patients with subarachnoid haemorrhage. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 117, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongers, T.N.; de Maat, M.P.; van Goor, M.L.; Bhagwanbali, V.; van Vliet, H.H.; Gomez Garcia, E.B.; Dippel, D.W.; Leebeek, F.W. High von Willebrand factor levels increase the risk of first ischemic stroke: Influence of ADAMTS13, inflammation, and genetic variability. Stroke 2006, 37, 2672–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.Q.; Chauhan, A.K.; Canault, M.; Patten, I.S.; Yang, J.J.; Dockal, M.; Scheiflinger, F.; Wagner, D.D. von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease ADAMTS13 reduces ischemic brain injury in experimental stroke. Blood 2009, 114, 3329–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, H.M.; Siegerink, B.; Luken, B.M.; Crawley, J.T.; Algra, A.; Lane, D.A.; Rosendaal, F.R. High VWF, low ADAMTS13, and oral contraceptives increase the risk of ischemic stroke and myocardial infarction in young women. Blood 2012, 119, 1555–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonneveld, M.A.; de Maat, M.P.; Portegies, M.L.; Kavousi, M.; Hofman, A.; Turecek, P.L.; Rottensteiner, H.; Scheiflinger, F.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Ikram, M.A.; et al. Low ADAMTS13 activity is associated with an increased risk of ischemic stroke. Blood 2015, 126, 2739–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, M.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, X.L. Low ADAMTS13 predicts adverse outcomes in hospitalized patients suspected with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2021; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Pepin, M.; Kleinjan, A.; Hajage, D.; Buller, H.R.; Di Nisio, M.; Kamphuisen, P.W.; Salomon, L.; Veyradier, A.; Stepanian, A.; Mahe, I. ADAMTS-13 and von Willebrand factor predict venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 14, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakaya, B.; Tombak, A.; Serin, M.S.; Tiftik, N. Change in plasma a disintegrin and metalloprotease with thrombospondin type-1 repeats-13 and von Willebrand factor levels in venous thromboembolic patients. Hematology 2016, 21, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Yokoyama, Y.; Matsushita, T.; Kainuma, M.; Ebata, T.; Igami, T.; Sugawara, G.; Takahashi, Y.; Nagino, M. Increased von Willebrand Factor to ADAMTS13 ratio as a predictor of thrombotic complications following a major hepatectomy. Arch. Surg. 2012, 147, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N.; Wada, H.; Usui, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Habe-Ito, N.; Matsumoto, T.; Uemoto, S.; Nobori, T.; Isaji, S. Behavior of ADAMTS13 and Von Willebrand factor levels in patients after living donor liver transplantation. Thromb. Res. 2013, 131, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habe, K.; Wada, H.; Ito-Habe, N.; Hatada, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Ohishi, K.; Maruyama, K.; Imai, H.; Mizutani, H.; Nobori, T. Plasma ADAMTS13, von Willebrand factor (VWF) and VWF propeptide profiles in patients with DIC and related diseases. Thromb. Res. 2012, 129, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Majerus, E.M.; Sadler, J.E. ADAMTS13 and TTP. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2002, 9, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadler, J.E. von Willebrand factor: Two sides of a coin. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 1702–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, C.B.; Cao, W.; Zheng, X.L. ADAMTS13 and von Willebrand factor interactions. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2015, 22, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moake, J.L. Thrombotic microangiopathies. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, A.T.; Suckau, J.; Frank, K.; Desch, A.; Goertz, L.; Wagner, A.H.; Hecker, M.; Goerge, T.; Umansky, L.; Beckhove, P.; et al. von Willebrand factor fibers promote cancer-associated platelet aggregation in malignant melanoma of mice and humans. Blood 2015, 125, 3153–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansigan, F.; Isufi, I.; Tagoe, C.E. Microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia resembling thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in systemic lupus erythematosus: The role of ADAMTS13. Rheumatology 2011, 50, 824–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, J.; Sanaka, T.; Gohchi, K.; Matsui, K.; Uchida, S.; Matsumoto, M.; Fujimura, Y. Occurrence of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in a systemic lupus erythematosus patient with antiphospholipid antibodies in association with a decreased activity of von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease. Lupus 2002, 11, 463–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannucci, P.M.; Vanoli, M.; Forza, I.; Canciani, M.T.; Scorza, R. Von Willebrand factor cleaving protease (ADAMTS-13) in 123 patients with connective tissue diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus and systemic sclerosis). Haematologica 2003, 88, 914–918. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.A.; Knobl, P.; Varadi, K.; Turecek, P.L. Changes in von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease (ADAMTS13) activity after infusion of desmopressin. Blood 2003, 101, 946–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.A.; Varadi, K.; Turecek, P.L.; Jilma, B.; Knobl, P. Changes in ADAMTS13 (von-Willebrand-factor-cleaving protease) activity after induced release of von Willebrand factor during acute systemic inflammation. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 93, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornara, B.T.; Gudmundsen, T.E.; Dahl, O.E. Frequency and timing of clinical venous thromboembolism after major joint surgery. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 2006, 88, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.H.; Romano, P.S.; Zhou, H.; Rodrigo, J.; Bargar, W. Incidence and time course of thromboembolic outcomes following total hip or knee arthroplasty. Arch. Intern. Med. 1998, 158, 1525–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, R.A.; Inacio, M.C.; Burke, M.F.; Costouros, J.G.; Yian, E.H. Risk of thromboembolism in shoulder arthroplasty: Effect of implant type and traumatic indication. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2013, 471, 1576–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dattani, R.; Smith, C.D.; Patel, V.R. The venous thromboembolic complications of shoulder and elbow surgery: A systematic review. Bone Jt. J. 2013, 95-B, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aibinder, W.R.; Sanchez-Sotelo, J. Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis in Shoulder Surgery. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 49, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Characteristic | N = 22 |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | |
| Mean ± SD | 68 ± 11 |
| Range | 41–84 |
| Gender | 15/7 |
| Male/Female | |
| Operative Shoulder (R/L) | 10/12 |
| Procedure | |
| Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty | 3 |
| Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty | 17 |
| Pre-operative sample only | 2 |
| ADAMTS13 Activity (IU/dL) | ||||||
| Pre-Operative | Immediate Post-Operative | POD 1 | POD 2 | 2 Weeks | 6 Weeks | |
| N | 21 | 20 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 18 |
| Median | 113.7 | 81.0 | 90.4 | 95.5 | 113.5 | 123.8 |
| Range | 55.4–162.7 | 48.3–148.5 | 48.5–137.6 | 42.5–161.1 | 68.5–173.6 | 47.4–194.3 |
| Mean ± SD | 111.9 ± 28.9 | 87.7 ± 28.9 | 89.4 ± 24.4 | 93.7 ± 28.5 | 116.7 ± 30.4 | 125.4 ± 38.2 |
| p-Value (Δ from Preoperative value) | - | 0.0021 | 0.0003 | 0.0010 | 0.567 | 0.266 |
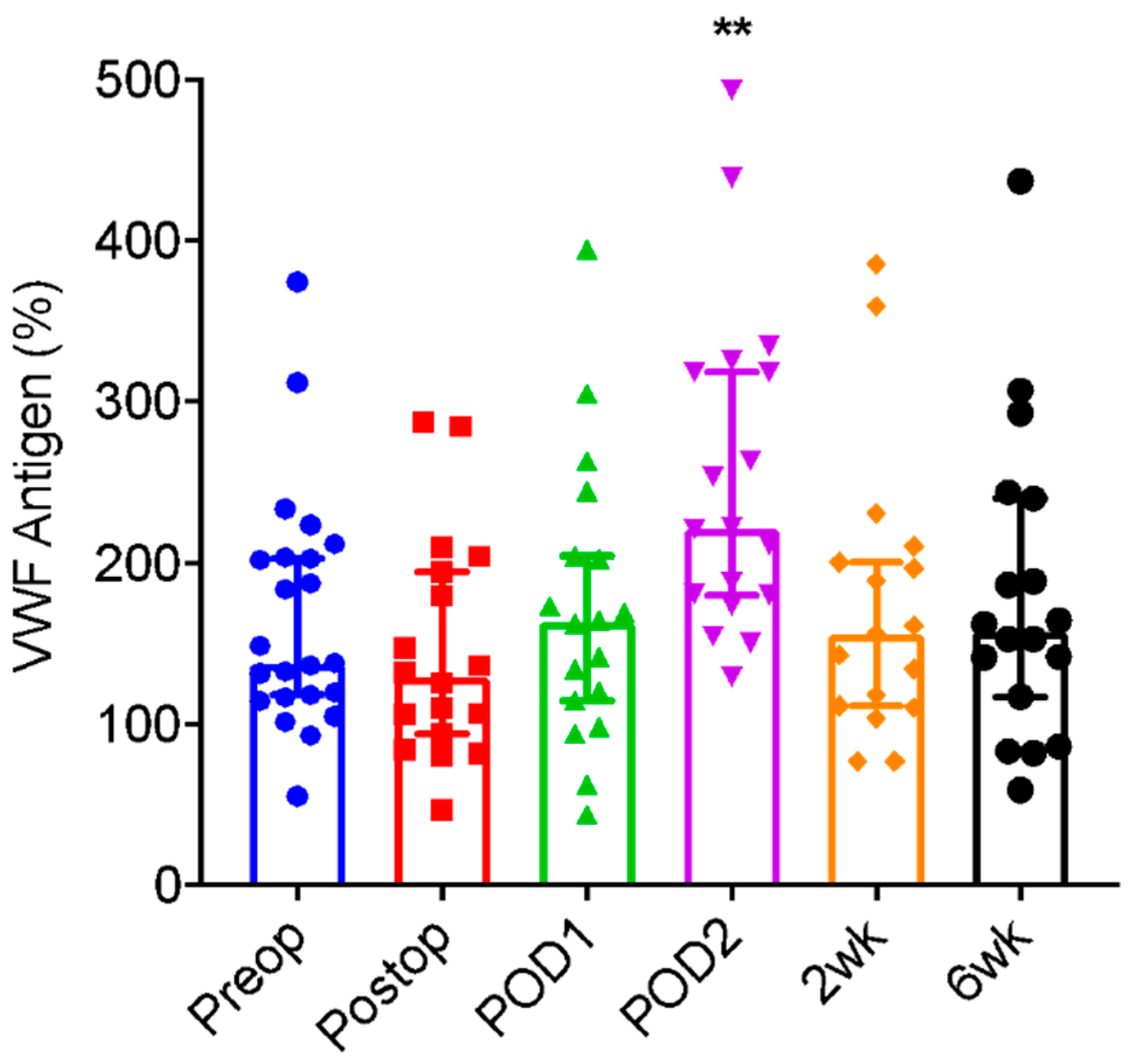
| VWF Antigen (%) | ||||||
| Pre-Operative | Immediate Post-Operative | POD 1 | POD 2 | 2 weeks | 6 Weeks | |
| N | 23 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 18 |
| Median | 138.1 | 128.9 | 163.8 | 221.4 | 156.2 | 157.6 |
| Range | 55.6–374.9 | 46.8–287.7 | 44.0–394.7 | 129.3–493.4 | 77.5–385.7 | 59.6–437.1 |
| Mean ± SD | 167.5 ± 73.5 | 145.1 ± 68.7 | 172.1 ± 87.9 | 253.2 ± 101.0 | 174.5 ± 87.6 | 180.1 ± 95.2 |
| p-Value (Δ from Preoperative value) | - | 0.248 | 0.632 | 0.0034 | 0.425 | 0.487 |
| ADAMTS13/VWF Ratio | ||||||
| Pre-Operative | Immediate Post-Operative | POD 1 | POD 2 | 2 weeks | 6 Weeks | |
| N | 22 | 17 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 18 |
| Median | 0.64 | 0.60 | 0.54 | 0.36 | 0.84 | 0.71 |
| Range | 0.13–1.3 | 0.27–1.1 | 0.22–1.3 | 0.20–0.90 | 0.26–1.5 | 0.31–2.0 |
| Mean ± SD | 0.70 ± 0.32 | 0.65 ± 0.20 | 0.65 ± 0.34 | 0.41 ± 0.20 | 0.82 ± 0.39 | 0.88 ± 0.53 |
| p-Value (Δ from Preoperative value) | - | 0.338 | 0.120 | 0.0016 | 0.647 | 0.976 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.K.; Schick, S.; Williams, M.; Wills, B.; Pinto, M.; Viner, G.; Brabston, E.; Momaya, A.; Zheng, X.L.; Ponce, B. Changes in Plasma Levels of ADAMTS13 and von Willebrand Factor in Patients Undergoing Elective Joint Arthroplasty. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6436. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216436
He JK, Schick S, Williams M, Wills B, Pinto M, Viner G, Brabston E, Momaya A, Zheng XL, Ponce B. Changes in Plasma Levels of ADAMTS13 and von Willebrand Factor in Patients Undergoing Elective Joint Arthroplasty. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(21):6436. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216436
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Jun Kit, Samuel Schick, Marshall Williams, Bradley Wills, Martim Pinto, Gean Viner, Eugene Brabston, Amit Momaya, X. Long Zheng, and Brent Ponce. 2022. "Changes in Plasma Levels of ADAMTS13 and von Willebrand Factor in Patients Undergoing Elective Joint Arthroplasty" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 21: 6436. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216436
APA StyleHe, J. K., Schick, S., Williams, M., Wills, B., Pinto, M., Viner, G., Brabston, E., Momaya, A., Zheng, X. L., & Ponce, B. (2022). Changes in Plasma Levels of ADAMTS13 and von Willebrand Factor in Patients Undergoing Elective Joint Arthroplasty. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(21), 6436. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216436







