Filling the Gap: The Immune Therapeutic Armamentarium for Relapsed/Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Epidemiological, Immunogenetic and Environmental Background of Hodgkin Lymphoma
3. Pathophysiological Background
3.1. Origin and Molecular Landscape of Malignant Cells in Hodgkin Lymphoma
3.2. Microenvironmental Interactions
3.3. Mechanisms of Resistance
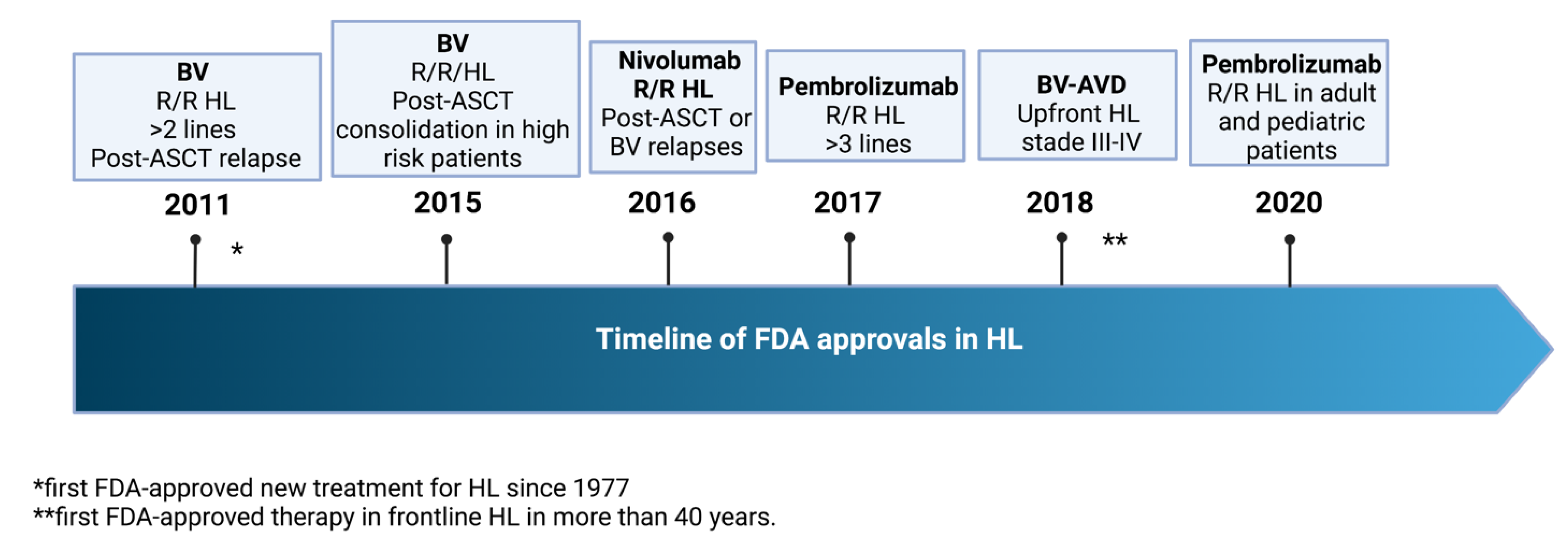
4. Management of Relapsed/Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma
4.1. The Evolving Place of Brentuximab Vedotin
4.2. Targeting the PD-1 Axis
4.2.1. Nivolumab
4.2.2. Pembrolizumab
4.2.3. Other Investigational Anti-PD-1 Inhibitors
4.3. Novel Agents Potentially Effective in R/R HL
4.3.1. Role of Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation
| Agent | Mechanism of Action | NCT | Phase | Study Design | Number of Therapeutic Lines | Start Date/Status | Reference | Results if Available |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 | ||||||||
| PENPULIMAB | Monoclonal antibody (anti-PD-1) | NCT05244642 | III | Randomized, Open, Multi-center Phase III Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Penpulimab Monotherapy vs. Standard Chemotherapy Selected by Investigator | ≥2, relapsed after ASCT | February 2022/Recruiting | Not available | |
| CAMRELIZUMAB (SHR-1210) vs. Chemotherapy | Monoclonal antibody (anti-PD-1) | NCT04342936 | III | Open-label, multicenter, randomized trial to evaluate the efficacy of Camrelizumab monotherapy or chemotherapy | ≥2, relapsed after ASCT | July 2020/Recruiting | Not available | |
| TISLELIZUMAB | Monoclonal antibody (anti-PD-1) | NCT03209973 | II | Single Arm, Multicenter, Phase 2 Study of BGB-A317 as Monotherapy in R/R cHL | Relapsed after ASCT | July 2017/Completed | Song et al. Leukemia 2020 [123] | ORR:87%; CR: 63% |
| TISLELIZUMAB | Monoclonal antibody (anti-PD-1) | NCT04318080 | II | Multicenter, Open-Label Study to evaluate the efficacy of Tislelizumab (BGB-A317) in Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma | Relapsed after ASCT | August 2020/Active Not recruiting | Not available | |
| TISLELIZUMAB | Monoclonal antibody (anti-PD-1) | NCT04486391 | III | Multicenter, open-Label, randomized Controlled Phase 3 Study of Tislelizumab Monotherapy Versus Salvage Chemotherapy | ≥2, relapsed after ASCT | September 2020/Recruiting | Not available | |
| Immunotherapy associations | ||||||||
| IPILIMUMAB +/− Nivolumab | Monoclonal antibodies (anti-CTLA-4, anti-PD-1) | NCT04938232 | II | Open-label, multi-cohort, multi-center of ipilimumab with or without nivolumab. | ≥2 including PD-1 monoclonal antibody, relapsed after ASCT | September 2021/Recruiting | Not available | |
| Brentuximab Vedotin and Nivolumab with or without IPILIMUMAB | Monoclonal antibodies (anti-CD-30, anti-PD-1, anti-CTLA4) | NCT01896999 | I/II | Randomized Phase II Study of the Combinations of Ipilimumab, Nivolumab and Brentuximab Vedotin. | ≥1 | July 2013/Recruiting | Diefenbach et al. Lancet Haematol 2020 [132] | n = 64; (I) BV + Ipilimumab: ORR= 76%; CR = 57%; (II) BV+ nivolumab ORR = 82%; CR = 61%; (III) BV + Ipilimumab + nivolumab: ORR = 82%; CR = 73% |
| MAGROLIMAB and Pembrolizumab | Monoclonal antibodies (anti-CD47, anti-PD-1) | NCT04788043 | II | A Phase 2 Study of Magrolimab and Pembrolizumab | ≥2 | June 2022/Recruiting | Not available | |
| CAMRELIZUMAB (SHR-1210) Alone or in Combination with Decitabine | Monoclonal antibody (anti-PD-1) | NCT03250962 | II | Multicohort, decitabine-plus-SHR1210 single-arm clinical trial. Evaluate the long-term response duration with decitabine-plus-SHR-1210 | ≥4, ≥3 months from ASCT | September 2017/Recruiting | Liu et al. J Immunother Cancer 2021 [133] | n = 61; I) SHR-1210: CR= 32%; II) SHR-1210 + decitabine: CR = 79% |
| CAMRELIZUMAB (SHR-1210) Combined With GEMOX | Monoclonal antibody (anti-PD-1) | NCT04239170 | II, III | Open-label, single arm, Phase 2 study to evaluate efficacy and safety of PD-1 inhibitor Camrelizumab(SHR-1210) combined with Gemox who will receive ASCT | ≥3, relapsed after ASCT | January 2020/Recruiting | Not available | |
| Nivolumab with RUXOLITINIB | Monoclonal antibody (anti-PD-1), JAK2 inhibitor | NCT03681561 | II | Multicenter, open-label, dose escalation/dose-expansion study to evaluate the tolerability, safety, and the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of ruxolitinib when given with fixed dose nivolumab | ≥2, including check point inhibitors | 13 September 2018/Recruiting | Not available | |
| Bispecific Antibody | ||||||||
| AZD7789 | Bispecific Antibody (Anti-PD-1 and Anti-TIM-3) | NCT05216835 | I/II | Open-label, Multi-center Study to Assess Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics and Preliminary Efficacy of AZD778 | ≥2, no previous treatment with anti-TIM-3 | 18 March 2022/Recruiting | Not available | |
| Phase 1 (Part A) Dose Escalation and Phase 2 (Part B) Dose Expansion | ||||||||
| Other immunomodulating agents | ||||||||
| ITACITINIB (INCB039110) and EVEROLIMUS (Afinitor) | JAK 1 inhibitor; mTOR inhibitor | NCT03697408 | I/II | Open-label, single-group, study of itacitinib in combination with everolimus | ≥2, relapsed after ASCT | 11 February 2019/Recruiting | Not available | |
| CAR T-cells | ||||||||
| CART30 cells | Autologous CART-30 cells | NCT02259556 | I/II | CD30-directed Chimeric Antigen Receptor T (CART30) Therapy | ≥2 or relapsed after ASCT | October 2014/Recruiting | Not available | |
| HSP-CAR30 | Autologous CART-30 cells | NCT04653649 | I/IIa | Interventional, single arm, open label, treatment study to evaluate the safety, tolerability and efficacy of HSP-CAR30 | Relapsed after ASCT who have received anti PD-L1 or Brentuximab; or Primarily refractory patients who do not reach CR after rescue | September 2020/Recruiting | Caballero et al., EHA 2022 | Preliminary results: n = 11; ORR = 100%; CR = 62% |
| ATLCAR.CD30 cells | Autologous CART-30 cells | NCT02690545 | Ib/II | Establish a safe dose of ATLCAR.CD30 cells to infuse after lymphodepleting chemotherapy and evaluate relative toxicities | ≥2, CD30+ disease | August 26, 2016/Recruiting | Ramos et al. JCO 2020 [134] | n = 41; CRS = 26%; ORR = 72%; CR = 59%; 1-year PFS = 36%; 1-year OS = 94% |
4.3.2. The Dilemma of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors before Allo-HCT
4.4. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells in Hodgkin Lymphoma
| Design | Anti-PD-1 Molecule | Disease | N# of Patients Receiving Anti-PD-1 before Allo-HCT | Median Time of Anti-PD-1 before Transplant | GvHD Prophylaxis Type | Graft Source | II-IV Grade Acute GvHD | Chronic GvHD | OS | Relapse | NRM | Translational Findings if Available | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retrospective | Nivolumab and Pembrolizumab | HL/NHL | 39 | 62 (7–260) | Heterogeneous | BM and PBSC | 44% | 41% | 89% at 1 year | 14 at 1 year | 11 at 1 year | depletion of PD-1+ T cells and reduction in T-reg cells | Merryman et al. Blood 2017 [139] |
| Retrospective (subanalysis) | Nivolumab | HL | 11 of 75 pts | 30 (15–190) | Heterogeneous | BM and PBSC | 3 of 11 pts. | 1 of 11 pts. | 10 of 11 pts alive | None | 1 of 11 pts. | NA | Beköz et al. Ann Oncol. 2017 [147] |
| Retrospective | Nivolumab, Pembrolizumab, Ipilimumab | HL/NHL/MDS/AML | 14 (N. HL = 10) | 42 (18–231) | PT-Cy, CNI and MMF | BM (n = 12) and PBSC (n = 2) | 6 of 14 pts | None | 13 of 14 pts alive | 2 pts (none with HL) | None | NA | Schoch et al. Blood adv. 2018 [148] |
| Retrospective | NA | HL | 37 of 105 pts | 51 (23–472) | PT-Cy, CNI and MMF | BM (n = 31), PBSC (n = 5), CB (n = 1) | 33% | 3% | 94% at 3 years | 4% at 3 years | 6% at 3 years | NA | Paul et al. BBMT 2020 [142] |
| Retrospective | Nivolumab | HL/NHL/MM | 18 | 83 (34–154) | CNI/PT-Cy-CNI -MMF | NA | 3 pts receiving CNI alone none of the pts receiving PT-Cy | None | 11 of 18 | 3 of 18 pts | 5 of 18 pts | Circulating nivolumab found in plasma for up to 56 days after allo-HCT and binding PD-1 on T cells inducing T cell activation. Ratio T-reg/CD8: reduced in CNI group and increased in PT-Cy group | Nieto et al. Leukemia 2020 [140] |
| Retrospective (subanalysis) | Nivolumab | HL | 39 of 74 | 58 (15–173) | Heterogeneous | BM (n = 2), PBSC (n = 37) | 33% | 35% | 72% at 2 years | 11% | 13% | NA | Martinez et al. [141] |
| Retrospective | Nivolumab | HL | 9 | 44 (27–100) | Heterogeneous | NA | 8 of 9 pts | 3 of 9 pts | 8 of 9 pts | 1 pt in SD | 1 of 9 pts | NA | El Cheikh et al. BMT 2017 [149] |
| Retrospective | Nivolumab and Pembrolizumab | HL | 25 | 59 (23–539) | Heterogeneous | BM (n = 12), PBSC (n = 11), CB (n = 2) | 47% | None | 52% at 1 year | 27% at 1 year | 8% | NA | Ito et al. Int J Hem 2020 [150] |
5. Age Related Considerations
6. Conclusive Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Connors, J.M.; Cozen, W.; Steidl, C.; Carbone, A.; Hoppe, R.T.; Flechtner, H.-H.; Bartlett, N.L. Hodgkin lymphoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2020, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meyer, R.M.; Gospodarowicz, M.K.; Connors, J.M.; Pearcey, R.G.; Wells, W.A.; Winter, J.N.; Horning, S.J.; Dar, A.R.; Shustik, C.; Stewart, D.A.; et al. ABVD Alone versus Radiation-Based Therapy in Limited-Stage Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Straus, D.J.; Jung, S.-H.; Pitcher, B.; Kostakoglu, L.; Grecula, J.C.; Hsi, E.D.; Schöder, H.; Popplewell, L.L.; Chang, J.E.; Moskowitz, C.H.; et al. CALGB 50604: Risk-adapted treatment of nonbulky early-stage Hodgkin lymphoma based on interim PET. Blood 2018, 132, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasse, S.; Bröckelmann, P.J.; Goergen, H.; Plütschow, A.; Müller, H.; Kreissl, S.; Buerkle, C.; Borchmann, S.; Fuchs, M.; Borchmann, P.; et al. Long-Term Follow-UP of Contemporary Treatment in Early-Stage Hodgkin Lymphoma: Updated Analyses of the German Hodgkin Study Group HD7, HD8, HD10, and HD11 Trials. JCO 2017, 35, 1999–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engert, A.; Haverkamp, H.; Kobe, C.; Markova, J.; Renner, C.; Ho, A.; Zijlstra, J.; Král, Z.; Fuchs, M.; Hallek, M.; et al. Reduced-intensity chemotherapy and PET-guided radiotherapy in patients with advanced stage Hodgkin’s lymphoma (HD15 trial): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2012, 379, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linch, D.C.; Goldstone, A.H.; McMillan, A.; Chopra, R.; Vaughan Hudson, G.; Winfield, D.; Hancock, B.; Moir, D.; Milligan, D. Dose intensification with autologous bone-marrow transplantation in relapsed and resistant Hodgkin’s disease: Results of a BNLI randomised trial. Lancet 1993, 341, 1051–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, N.; Pfistner, B.; Sextro, M.; Sieber, M.; Carella, A.M.; Haenel, M.; Boissevain, F.; Zschaber, R.; Müller, P.; Kirchner, H.; et al. Aggressive conventional chemotherapy compared with high-dose chemotherapy with autologous haemopoietic stem-cell transplantation for relapsed chemosensitive Hodgkin’s disease: A randomised trial. Lancet 2002, 359, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, A.; Rodday, A.M.; Kumar, A.J.; Miller, K.B.; Parsons, S.K. Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplant Utilization in Relapsed/Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Population-Level Analysis of Statewide Claims Data. JCO Clin. Cancer Inf. 2022, 6, e2100135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halahleh, K.; Al Sawajneh, S.; Saleh, Y.; Shahin, O.; Abufara, A.; Ma’koseh, M.; Abdel-Razeq, R.; Barakat, F.; Abdelkhaleq, H.; Al-Hassan, N.; et al. Pembrolizumab for the Treatment of Relapsed and Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma After Autologous Transplant and in Transplant-Naïve Patients. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2022, 22, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazarbachi, A.; Boumendil, A.; Finel, H.; Khvedelidze, I.; Romejko-Jarosinska, J.; Tanase, A.; Akhtar, S.; Ben Othman, T.; Ma’koseh, M.; Afanasyev, B.; et al. The outcome of patients with Hodgkin lymphoma and early relapse after autologous stem cell transplant has improved in recent years. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1646–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaCasce, A.S. Treating Hodgkin lymphoma in the new millennium: Relapsed and refractory disease. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chohan, K.; Ansell, S.M. Current salvage therapies in Hodgkin lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 2022, 63, 1267–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veilleux, O.; Claveau, J.-S.; Alaoui, H.; Roy, J.; Ahmad, I.; Delisle, J.-S.; Kiss, T.; Bambace, N.M.; Bernard, L.; Cohen, S.; et al. Real-World Outcomes of Autologous and Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Relapsed/Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma in the Era of Novel Therapies: A Canadian Perspective. Transpl. Cell Ther. 2022, 28, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epperla, N.; Hamadani, M. Double-refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: Tackling relapse after brentuximab vedotin and checkpoint inhibitors. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Progr. 2021, 2021, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, J.L.; Glaser, S.L. Epstein–Barr virus-associated malignancies: Epidemiologic patterns and etiologic implications. Crit. Rev. Oncol/Hematol. 2000, 34, 27–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landgren, O.; Engels, E.A.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Gridley, G.; Mellemkjaer, L.; Olsen, J.H.; Kerstann, K.F.; Wheeler, W.; Hemminki, K.; Linet, M.S.; et al. Autoimmunity and Susceptibility to Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Population-Based Case–Control Study in Scandinavia. JNCI: J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 1321–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biggar, R.J.; Jaffe, E.S.; Goedert, J.J.; Chaturvedi, A.; Pfeiffer, R.; Engels, E.A.; for the HIV/AIDS Cancer Match Study. Hodgkin lymphoma and immunodeficiency in persons with HIV/AIDS. Blood 2006, 108, 3786–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taj, T.; Poulsen, A.H.; Ketzel, M.; Geels, C.; Brandt, J.; Christensen, J.H.; Hvidtfeldt, U.A.; Sørensen, M.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O. Long-term residential exposure to air pollution and Hodgkin lymphoma risk among adults in Denmark: A population-based case–control study. Cancer Causes Control. 2021, 32, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleveland, W.S.; Devlin, S.J. Locally Weighted Regression: An Approach to Regression Analysis by Local Fitting. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1988, 83, 596–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, T.M.; Norman, J.E.; Rappaport, E.; Cozen, W. Childhood Determination of Hodgkin Lymphoma among U.S. Servicemen. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2015, 24, 1707–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weiss, L.M.; Movahed, L.A.; Warnke, R.A.; Sklar, J. Detection of Epstein–Barr Viral Genomes in Reed–Sternberg Cells of Hodgkin’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 320, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mack, T.M.; Cozen, W.; Shibata, D.K.; Weiss, L.M.; Nathwani, B.N.; Hernandez, A.M.; Taylor, C.R.; Hamilton, A.S.; Deapen, D.M.; Rappaport, E.B. Concordance for Hodgkin’s Disease in Identical Twins Suggesting Genetic Susceptibility to the Young-Adult Form of the Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sud, A.; Thomsen, H.; Orlando, G.; Försti, A.; Law, P.J.; Broderick, P.; Cooke, R.; Hariri, F.; Pastinen, T.; Easton, D.F.; et al. Genome-wide association study implicates immune dysfunction in the development of Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2018, 132, 2040–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Nolte, I.M.; Hepkema, B.G.; Stulp, M.; van den Berg, A.; Diepstra, A. Killer Cell Immunoglobulin-Like Receptor Haplotype B Modulates Susceptibility to EBV-Associated Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 829943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozen, W.; Timofeeva, M.N.; Li, D.; Diepstra, A.; Hazelett, D.; Delahaye-Sourdeix, M.; Edlund, C.K.; Franke, L.; Rostgaard, K.; Van Den Berg, D.J.; et al. A meta-analysis of Hodgkin lymphoma reveals 19p13.3 TCF3 as a novel susceptibility locus. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khankhanian, P.; Cozen, W.; Himmelstein, D.S.; Madireddy, L.; Din, L.; van den Berg, A.; Matsushita, T.; Glaser, S.L.; Moré, J.M.; Smedby, K.E.; et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies reveals genetic overlap between Hodgkin lymphoma and multiple sclerosis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 45, 728–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weniger, M.A.; Tiacci, E.; Schneider, S.; Arnolds, J.; Rüschenbaum, S.; Duppach, J.; Seifert, M.; Döring, C.; Hansmann, M.-L.; Küppers, R. Human CD30+ B cells represent a unique subset related to Hodgkin lymphoma cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 2996–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiarle, R.; Podda, A.; Prolla, G.; Gong, J.; Thorbecke, G.J.; Inghirami, G. CD30 in Normal and Neoplastic Cells. Clin. Immunol. 1999, 90, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, R.; Watanabe, T. CD30: Expression and function in health and disease. Semin. Immunol. 1998, 10, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizawa, S.; Nakano, H.; Ishida, T.; Horie, R.; Nagai, M.; Ito, K.; Yagita, H.; Okumura, K.; Inoue, J.; Watanabe, T. Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor-associated Factor (TRAF) 5 and TRAF2 Are Involved in CD30-mediated NFκB Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 2042–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muta, H.; Podack, E.R. CD30: From basic research to cancer therapy. Immunol. Res. 2013, 57, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, J.M.R.; Mehta, A. Diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic role of CD30 in lymphoma. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2017, 10, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bladel, D.A.G.; Stevens, W.B.C.; van den Brand, M.; Kroeze, L.I.; Groenen, P.J.T.A.; van Krieken, J.H.J.M.; Hebeda, K.M.; Scheijen, B. Novel Approaches in Molecular Characterization of Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichel, J.; Chadburn, A.; Rubinstein, P.G.; Giulino-Roth, L.; Tam, W.; Liu, Y.; Gaiolla, R.; Eng, K.; Brody, J.; Inghirami, G.; et al. Flow sorting and exome sequencing reveal the oncogenome of primary Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells. Blood 2015, 125, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tiacci, E.; Ladewig, E.; Schiavoni, G.; Penson, A.; Fortini, E.; Pettirossi, V.; Wang, Y.; Rosseto, A.; Venanzi, A.; Vlasevska, S.; et al. Pervasive mutations of JAK-STAT pathway genes in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2018, 131, 2454–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wienand, K.; Chapuy, B.; Stewart, C.; Dunford, A.J.; Wu, D.; Kim, J.; Kamburov, A.; Wood, T.R.; Cader, F.Z.; Ducar, M.D.; et al. Genomic analyses of flow-sorted Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg cells reveal complementary mechanisms of immune evasion. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 4065–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tilly, H.; Bastard, C.; Delastre, T.; Duval, C.; Bizet, M.; Lenormand, B.; Daucé, J.P.; Monconduit, M.; Piguet, H. Cytogenetic studies in untreated Hodgkin’s disease. Blood 1991, 77, 1298–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, S.; Martin-Subero, J.I.; Gesk, S.; Husken, J.; Giefing, M.; Nagel, I.; Riemke, J.; Chott, A.; Klapper, W.; Parrens, M.; et al. Detection of genomic imbalances in microdissected Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells of classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma by array-based comparative genomic hybridization. Haematologica 2008, 93, 1318–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Re, D.; Zander, T.; Diehl, V.; Wolf, J. Genetic instability in Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Ann. Oncol 2002, 13, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chui, D.T.Y.; Hammond, D.; Baird, M.; Shield, L.; Jackson, R.; Jarrett, R.F. Classical Hodgkin lymphoma is associated with frequent gains of 17q. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2003, 38, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steidl, C.; Telenius, A.; Shah, S.P.; Farinha, P.; Barclay, L.; Boyle, M.; Connors, J.M.; Horsman, D.E.; Gascoyne, R.D. Genome-wide copy number analysis of Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg cells identifies recurrent imbalances with correlations to treatment outcome. Blood 2010, 116, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seitz, V.; Hummel, M.; Marafioti, T.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Assaf, C.; Stein, H. Detection of clonal T-cell receptor gamma-chain gene rearrangements in Reed-Sternberg cells of classic Hodgkin disease. Blood 2000, 95, 3020–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamboa-Cedeño, A.M.; Castillo, M.; Xiao, W.; Waldmann, T.A.; Ranuncolo, S.M. Alternative and canonical NF-kB pathways DNA-binding hierarchies networks define Hodgkin lymphoma and Non-Hodgkin diffuse large B Cell lymphoma respectively. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 145, 1437–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weniger, M.A.; Küppers, R. NF-κB deregulation in Hodgkin lymphoma. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 39, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weniger, M.A.; Küppers, R. Molecular biology of Hodgkin lymphoma. Leukemia 2021, 35, 968–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, J.A.; Nugent, A.; Rempel, R.E.; Moffitt, A.B.; Davis, N.S.; Jiang, X.; Shingleton, J.R.; Zhang, J.; Love, C.; Datta, J.; et al. GNA13 loss in germinal center B cells leads to impaired apoptosis and promotes lymphoma in vivo. Blood 2016, 127, 2723–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camus, V.; Miloudi, H.; Taly, A.; Sola, B.; Jardin, F. XPO1 in B cell hematological malignancies: From recurrent somatic mutations to targeted therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Renné, C.; Willenbrock, K.; Küppers, R.; Hansmann, M.-L.; Bräuninger, A. Autocrine- and paracrine-activated receptor tyrosine kinases in classic Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2005, 105, 4051–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, R.; Nishikori, M.; Kitawaki, T.; Sakai, T.; Hishizawa, M.; Tashima, M.; Kondo, T.; Ohmori, K.; Kurata, M.; Hayashi, T.; et al. PD-1–PD-1 ligand interaction contributes to immunosuppressive microenvironment of Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2008, 111, 3220–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vockerodt, M.; Yap, L.-F.; Shannon-Lowe, C.; Curley, H.; Wei, W.; Vrzalikova, K.; Murray, P.G. The Epstein-Barr virus and the pathogenesis of lymphoma. J. Pathol. 2015, 235, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brice, P.; de Kerviler, E.; Friedberg, J.W. Classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Lancet 2021, 398, 1518–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steidl, C.; Connors, J.M.; Gascoyne, R.D. Molecular pathogenesis of Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Increasing evidence of the importance of the microenvironment. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1812–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggio, E.M.; Van Den Berg, A.; Visser, L.; Diepstra, A.; Kluiver, J.; Emmens, R.; Poppema, S. Common and differential chemokine expression patterns in rs cells of NLP, EBV positive and negative classical Hodgkin lymphomas. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 99, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedvat, C.V.; Jaffe, E.S.; Qin, J.; Filippa, D.A.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Tosato, G.; Nimer, S.D.; Teruya-Feldstein, J. Macrophage-Derived Chemokine Expression in Classical Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: Application of Tissue Microarrays. Mod. Pathol. 2001, 14, 1270–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buri, C.; Körner, M.; Schärli, P.; Cefai, D.; Uguccioni, M.; Mueller, C.; Laissue, J.A.; Mazzucchelli, L. CC chemokines and the receptors CCR3 and CCR5 are differentially expressed in the nonneoplastic leukocytic infiltrates of Hodgkin disease. Blood 2001, 97, 1543–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khnykin, D.; Troen, G.; Berner, J.-M.; Delabie, J. The expression of fibroblast growth factors and their receptors in Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J. Pathol. 2006, 208, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshima, K.; Tutiya, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Suzuki, K.; Suzumiya, J.; Kawasaki, C.; Haraoka, S.; Kikuchi, M. Infiltration of Th1 and Th2 lymphocytes around Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg (H&RS) cells in Hodgkin disease: Relation with expression of CXC and CC chemokines on H&RS cells. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 98, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steidl, C.; Lee, T.; Shah, S.P.; Farinha, P.; Han, G.; Nayar, T.; Delaney, A.; Jones, S.J.; Iqbal, J.; Weisenburger, D.D.; et al. Tumor-associated macrophages and survival in classic Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; Visser, L.; Roelofsen, H.; de Vries, M.; Diepstra, A.; van Imhoff, G.; van der Wal, T.; Luinge, M.; Alvarez-Llamas, G.; Vos, H.; et al. Proteomics analysis of Hodgkin lymphoma: Identification of new players involved in the cross-talk between HRS cells and infiltrating lymphocytes. Blood 2008, 111, 2339–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jundt, F.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Bommert, K.; Emmerich, F.; Müller, G.; Foss, H.D.; Royer, H.D.; Stein, H.; Dörken, B. Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg cells induce fibroblasts to secrete eotaxin, a potent chemoattractant for T cells and eosinophils. Blood 1999, 94, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, A.; Visser, L.; Poppema, S. High expression of the CC chemokine TARC in Reed-Sternberg cells. A possible explanation for the characteristic T-cell infiltratein Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 154, 1685–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, N.A.; Christie, L.E.; Munro, L.R.; Culligan, D.J.; Johnston, P.W.; Barker, R.N.; Vickers, M.A. Immunosuppressive regulatory T cells are abundant in the reactive lymphocytes of Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2004, 103, 1755–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herbst, H.; Foss, H.D.; Samol, J.; Araujo, I.; Klotzbach, H.; Krause, H.; Agathanggelou, A.; Niedobitek, G.; Stein, H. Frequent expression of interleukin-10 by Epstein-Barr virus-harboring tumor cells of Hodgkin’s disease. Blood 1996, 87, 2918–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadin, M.E.; Agnarsson, B.A.; Ellingsworth, L.R.; Newcom, S.R. Immunohistochemical evidence of a role for transforming growth factor beta in the pathogenesis of nodular sclerosing Hodgkin’s disease. Am. J. Pathol. 1990, 136, 1209–1214. [Google Scholar]
- Carey, C.D.; Gusenleitner, D.; Lipschitz, M.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Stack, E.C.; Gjini, E.; Hu, X.; Redd, R.; Freeman, G.J.; Neuberg, D.; et al. Topological analysis reveals a PD-L1-associated microenvironmental niche for Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2017, 130, 2420–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roemer, M.G.M.; Advani, R.H.; Redd, R.A.; Pinkus, G.S.; Natkunam, Y.; Ligon, A.H.; Connelly, C.F.; Pak, C.J.; Carey, C.D.; Daadi, S.E.; et al. Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma with Reduced β2M/MHC Class I Expression Is Associated with Inferior Outcome Independent of 9p24.1 Status. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2016, 4, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, R.; Hou, J.; Newman, E.; Kim, Y.; Donohue, C.; Liu, X.; Thomas, S.H.; Forman, S.J.; Kane, S.E. CD30 Downregulation, MMAE Resistance, and MDR1 Upregulation Are All Associated with Resistance to Brentuximab Vedotin. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 1376–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Othman, T.; Herrera, A.; Mei, M. Emerging Therapies in Relapsed and Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma: What Comes Next After Brentuximab Vedotin and PD-1 Inhibition? Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2021, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bark, H.; Choi, C.-H. PSC833, cyclosporine analogue, downregulates MDR1 expression by activating JNK/c-Jun/AP-1 and suppressing NF-κB. Cancer Chemother. Pharm. 2010, 65, 1131–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Herrera, A.F.; Hou, J.; Chen, L.; Wu, J.; Guo, Y.; Synold, T.W.; Ngo, V.N.; Puverel, S.; Mei, M.; et al. Inhibition of MDR1 Overcomes Resistance to Brentuximab Vedotin in Hodgkin Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 1034–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielson, C.; Fischer, R.; Fraga, G.; Aires, D. Loss of CD30 expression in anaplastic large cell lymphoma following brentuximab therapy. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2016, 15, 894–895. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goyal, A.; Patel, S.; Goyal, K.; Morgan, E.A.; Foreman, R.K. Variable loss of CD30 expression by immunohistochemistry in recurrent cutaneous CD30+ lymphoid neoplasms treated with brentuximab vedotin. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2019, 46, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rohil, R.N.; Torres-Cabala, C.A.; Patel, A.; Tetzlaff, M.T.; Ivan, D.; Nagarajan, P.; Curry, J.L.; Miranda, R.N.; Duvic, M.; Prieto, V.G.; et al. Loss of CD30 expression after treatment with brentuximab vedotin in a patient with anaplastic large cell lymphoma: A novel finding. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2016, 43, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Aguilera, A.; Montalbán, C.; de la Cueva, P.; Sánchez-Verde, L.; Morente, M.M.; García-Cosío, M.; García-Laraña, J.; Bellas, C.; Provencio, M.; Romagosa, V.; et al. Tumor microenvironment and mitotic checkpoint are key factors in the outcome of classic Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2006, 108, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, R.A.; Zaki, M.A.; Mohamed, N.A.; Mansou, O.M.; Refaey, F.A. Prognostic Value of Tumor Associated Macrophage Markers CD163 and CD68 Immunohistochemistry in Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Clin. Lab. 2021, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowshanravan, B.; Halliday, N.; Sansom, D.M. CTLA-4: A moving target in immunotherapy. Blood 2018, 131, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huard, B.; Prigent, P.; Tournier, M.; Bruniquel, D.; Triebel, F. CD4/major histocompatibility complex class II interaction analyzed with CD4- and lymphocyte activation gene-3 (LAG-3)-Ig fusion proteins. Eur. J. Immunol. 1995, 25, 2718–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longley, J.; Johnson, P.W.M. Current treatment paradigms for advanced stage Hodgkin lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 184, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carter, J.; David, K.A.; Kritharis, A.; Evens, A.M. Current Treatment Options for Older Patients with Hodgkin Lymphoma. Curr. Treat. Options. Oncol. 2020, 21, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straus, D.J. Treatment of Newly Diagnosed Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 2020, 20 (Suppl. S1), S87–S88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Neste, E.; Casasnovas, O.; Andre, M.; Touati, M.; Senecal, D.; Edeline, V.; Stamatoullas, A.; Fornecker, L.; Deau, B.; Gastinne, T.; et al. Classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma: The Lymphoma Study Association guidelines for relapsed and refractory adult patients eligible for transplant. Haematologica 2013, 98, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shah, G.L.; Moskowitz, C.H. Transplant strategies in relapsed/refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2018, 131, 1689–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Claro, R.A.; McGinn, K.; Kwitkowski, V.; Bullock, J.; Khandelwal, A.; Habtemariam, B.; Ouyang, Y.; Saber, H.; Lee, K.; Koti, K.; et al. U.S. Food and Drug Administration Approval Summary: Brentuximab Vedotin for the Treatment of Relapsed Hodgkin Lymphoma or Relapsed Systemic Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 5845–5849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Younes, A.; Gopal, A.K.; Smith, S.E.; Ansell, S.M.; Rosenblatt, J.D.; Savage, K.J.; Ramchandren, R.; Bartlett, N.L.; Cheson, B.D.; de Vos, S.; et al. Results of a Pivotal Phase II Study of Brentuximab Vedotin for Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. JCO 2012, 30, 2183–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moskowitz, C.H.; Nademanee, A.; Masszi, T.; Agura, E.; Holowiecki, J.; Abidi, M.H.; Chen, A.I.; Stiff, P.; Gianni, A.M.; Carella, A.; et al. Brentuximab vedotin as consolidation therapy after autologous stem-cell transplantation in patients with Hodgkin’s lymphoma at risk of relapse or progression (AETHERA): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 1853–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, J.M.; Jurczak, W.; Straus, D.J.; Ansell, S.M.; Kim, W.S.; Gallamini, A.; Younes, A.; Alekseev, S.; Illés, Á.; Picardi, M.; et al. Brentuximab Vedotin with Chemotherapy for Stage III or IV Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Palmer, J.M.; Martin, P.; Tsai, N.; Kim, Y.; Chen, B.T.; Popplewell, L.; Siddiqi, T.; Thomas, S.H.; Mott, M.; et al. Results of a Multicenter Phase II Trial of Brentuximab Vedotin as Second-Line Therapy before Autologous Transplantation in Relapsed/Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma. Biol. Blood. Marrow. Transplant. 2015, 21, 2136–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moskowitz, A.J.; Schöder, H.; Yahalom, J.; McCall, S.J.; Fox, S.Y.; Gerecitano, J.; Grewal, R.; Hamlin, P.A.; Horwitz, S.; Kobos, R.; et al. PET-adapted sequential salvage therapy with brentuximab vedotin followed by augmented ifosamide, carboplatin, and etoposide for patients with relapsed and refractory Hodgkin’s lymphoma: A non-randomised, open-label, single-centre, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, A.F.; Palmer, J.; Martin, P.; Armenian, S.; Tsai, N.-C.; Kennedy, N.; Sahebi, F.; Cao, T.; Budde, L.E.; Mei, M.; et al. Autologous stem-cell transplantation after second-line brentuximab vedotin in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaCasce, A.S.; Bociek, R.G.; Sawas, A.; Caimi, P.; Agura, E.; Matous, J.; Ansell, S.M.; Crosswell, H.E.; Islas-Ohlmayer, M.; Behler, C.; et al. Brentuximab vedotin plus bendamustine: A highly active first salvage regimen for relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2018, 132, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, O.A.; Lue, J.K.; Sawas, A.; Amengual, J.E.; Deng, C.; Kalac, M.; Falchi, L.; Marchi, E.; Turenne, I.; Lichtenstein, R.; et al. Brentuximab vedotin plus bendamustine in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin’s lymphoma: An international, multicentre, single-arm, phase 1–2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalac, M.; Lue, J.K.; Lichtenstein, E.; Turenne, I.; Rojas, C.; Amengual, J.E.; Sawas, A.; Deng, C.; Mapara, M.Y.; Connors, J.M.; et al. Brentuximab vedotin and bendamustine produce high complete response rates in patients with chemotherapy refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 180, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Picardi, M.; Della Pepa, R.; Giordano, C.; Pugliese, N.; Mortaruolo, C.; Trastulli, F.; Rascato, M.G.; Cappuccio, I.; Raimondo, M.; Memoli, M.; et al. Brentuximab vedotin followed by bendamustine supercharge for refractory or relapsed Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 1546–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broccoli, A.; Argnani, L.; Botto, B.; Corradini, P.; Pinto, A.; Re, A.; Vitolo, U.; Fanti, S.; Stefoni, V.; Zinzani, P.L.; et al. First salvage treatment with bendamustine and brentuximab vedotin in Hodgkin lymphoma: A phase 2 study of the Fondazione Italiana Linfomi. Blood Cancer J. 2019, 9, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lynch, R.C.; Cassaday, R.D.; Smith, S.D.; Fromm, J.R.; Cowan, A.J.; Warren, E.H.; Shadman, M.S.; Shustov, A.; Till, B.G.; Ujjani, C.S.; et al. Dose-dense brentuximab vedotin plus ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide for second-line treatment of relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma: A single centre, phase 1/2 study. Lancet Haematol. 2021, 8, e562–e571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatoullas, A.; Ghesquières, H.; Feugier, P.; André, M.; Le Bras, F.; Gac, A.-C.; Borel, C.; Gastinne, T.; Quittet, P.; Morschhauser, F.; et al. Final results of brentuximab vedotin combined with ifosfamide-carboplatin-etoposide in first refractory/relapsed Hodgkin lymphoma: A lymphoma study association phase I/II study. Leuk. Lymphoma 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Wyngaert, Z.; Coppo, P.; Cervera, P.; Fabiani, B.; Lemonnier, M.-P.; Corre, E.; Marjanovic, Z.; Aoudjhane, M.; Mohty, M.; Duléry, R. Combination of brentuximab-vedotin and ifosfamide, carboplatin, etoposide in relapsed/refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Eur. J. Haematol. 2021, 106, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, M.J.; Driessen, J.; Zijlstra, J.M.; Plattel, W.J.; Morschhauser, F.; Lugtenburg, P.J.; Brice, P.; Hutchings, M.; Gastinne, T.; Liu, R.; et al. Combining brentuximab vedotin with dexamethasone, high-dose cytarabine and cisplatin as salvage treatment in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: The phase II HOVON/LLPC Transplant BRaVE study. Haematologica 2021, 106, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Sanz, R.; Sureda, A.; de la Cruz, F.; Canales, M.; Gonzalez, A.P.; Pinana, J.L.; Rodriguez, A.; Gutierrez, A.; Domingo-Domenech, E.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, B.; et al. Brentuximab vedotin and ESHAP is highly effective as second-line therapy for Hodgkin lymphoma patients (long-term results of a trial by the Spanish GELTAMO Group). Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gettinger, S.N.; Horn, L.; Gandhi, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Antonia, S.J.; Rizvi, N.A.; Powderly, J.D.; Heist, R.S.; Carvajal, R.D.; Jackman, D.M.; et al. Overall Survival and Long-Term Safety of Nivolumab (Anti–Programmed Death 1 Antibody, BMS-936558, ONO-4538) in Patients With Previously Treated Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. JCO 2015, 33, 2004–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manson, G.; Mear, J.-B.; Herbaux, C.; Schiano, J.-M.; Casasnovas, O.; Stamatoullas, A.; Deau, B.; Schmitt, A.; Garnier, G.; Regny, C.; et al. Long-term efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy in Hodgkin lymphoma with and without allogenic stem cell transplantation. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 115, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momotow, J.; Bühnen, I.; Trautmann-Grill, K.; Kobbe, G.; Hahn, D.; Schroers, R.; Heinrich, B.; Gaska, T.; Forstbauer, H.; Schmidt, B.; et al. Outcomes of anti-programmed death 1 treatment for relapsed/refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: A German Hodgkin Study Group multicentre real-world analysis. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 198, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manson, G.; Herbaux, C.; Schiano, J.-M.; Casasnovas, O.; Stamatoullas, A.; Deau, B.; Schmitt, A.; Regny, C.; Bouabdallah, K.; Chauchet, A.; et al. Can nivolumab alone cure patients with relapse or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma? A 5-year analysis of the French early access program (EPA). Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 198, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armand, P.; Engert, A.; Younes, A.; Fanale, M.; Santoro, A.; Zinzani, P.L.; Timmerman, J.M.; Collins, G.P.; Ramchandren, R.; Cohen, J.B.; et al. Nivolumab for Relapsed/Refractory Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma After Failure of Autologous Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: Extended Follow-Up of the Multicohort Single-Arm Phase II CheckMate 205 Trial. JCO 2018, 36, 1428–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, A.; Santoro, A.; Shipp, M.; Zinzani, P.L.; Timmerman, J.M.; Ansell, S.; Armand, P.; Fanale, M.; Ratanatharathorn, V.; Kuruvilla, J.; et al. Nivolumab for classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma after failure of both autologous stem-cell transplantation and brentuximab vedotin: A multicentre, multicohort, single-arm phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1283–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Advani, R.H.; Moskowitz, A.J.; Bartlett, N.L.; Vose, J.M.; Ramchandren, R.; Feldman, T.A.; LaCasce, A.S.; Christian, B.A.; Ansell, S.M.; Moskowitz, C.H.; et al. Brentuximab vedotin in combination with nivolumab in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: 3-year study results. Blood 2021, 138, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, M.G.; Lee, H.J.; Palmer, J.M.; Chen, R.; Tsai, N.-C.; Chen, L.; McBride, K.; Smith, D.L.; Melgar, I.; Song, J.Y.; et al. Response-adapted anti-PD-1–based salvage therapy for Hodgkin lymphoma with nivolumab alone or in combination with ICE. Blood 2022, 139, 3605–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruvilla, J.; Ramchandren, R.; Santoro, A.; Paszkiewicz-Kozik, E.; Gasiorowski, R.; Johnson, N.A.; Fogliatto, L.M.; Goncalves, I.; de Oliveira, J.S.R.; Buccheri, V.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus brentuximab vedotin in relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma (KEYNOTE-204): An interim analysis of a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 512–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zinzani, P.L.; Lee, H.J.; Armand, P.; Johnson, N.A.; Brice, P.; Radford, J.; Ribrag, V.; Molin, D.; Vassilakopoulos, T.P.; et al. Pembrolizumab in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: 2-year follow-up of KEYNOTE-087. Blood 2019, 134, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moskowitz, A.J.; Shah, G.; Schöder, H.; Ganesan, N.; Drill, E.; Hancock, H.; Davey, T.; Perez, L.; Ryu, S.; Sohail, S.; et al. Phase II Trial of Pembrolizumab Plus Gemcitabine, Vinorelbine, and Liposomal Doxorubicin as Second-Line Therapy for Relapsed or Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. JCO 2021, 39, 3109–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massaro, F.; Meuleman, N.; Bron, D.; Vercruyssen, M.; Maerevoet, M. Brentuximab Vedotin and Pembrolizumab Combination in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Single-Centre Retrospective Analysis. Cancers 2022, 14, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, P.B.; Lu, X.; Chen, Q.; Kane, K.L.; Chmiel, J.S.; Barnea Slonim, L.; Sukhanova, M.; Savas, H.; Evens, A.M.; Advani, R.; et al. Sequential Pembrolizumab and AVD is Highly Effective at any PD-L1 Expression Level in Untreated Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2022. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, P.B.; Savas, H.; Evens, A.M.; Advani, R.H.; Palmer, B.; Pro, B.; Karmali, R.; Mou, E.; Bearden, J.; Dillehay, G.; et al. Pembrolizumab followed by AVD in untreated early unfavorable and advanced-stage classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2021, 137, 1318–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, W.; Nan, Y.; Yang, T.; Liang, X.; Xiao, C.; Guo, B.; Xiang, Y. Sintilimab as salvage treatment in an HIV patient with relapsed/ refractory Hodgkin: A case report. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2020, 9, 2414–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, X.; Lin, T.; Cao, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, J.; Huang, H.; Hu, J.; et al. A Single-Arm, Multicenter, Phase II Study of Camrelizumab in Relapsed or Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 7363–7369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Song, Y.; Chen, X.; Lin, T.; Cao, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, J.; Huang, H.; Hu, J.; et al. Camrelizumab for relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma: Extended follow-up of the multicenter, single-arm, Phase 2 study. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 150, 984–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneim, H.E.; Fan, Y.; Moustaki, A.; Abdelsamed, H.A.; Dash, P.; Dogra, P.; Carter, R.; Awad, W.; Neale, G.; Thomas, P.G.; et al. De Novo Epigenetic Programs Inhibit PD-1 Blockade-Mediated T Cell Rejuvenation. Cell 2017, 170, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pauken, K.E.; Sammons, M.A.; Odorizzi, P.M.; Manne, S.; Godec, J.; Khan, O.; Drake, A.M.; Chen, Z.; Sen, D.R.; Kurachi, M.; et al. Epigenetic stability of exhausted T cells limits durability of reinvigoration by PD-1 blockade. Science 2016, 354, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nie, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Mei, Q.; Dong, L.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Ku, W.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Addition of Low-Dose Decitabine to Anti–PD-1 Antibody Camrelizumab in Relapsed/Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. JCO 2019, 37, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Dong, L.; Li, X.; Yang, Q.; Brock, M.V.; Mei, Q.; Liu, J.; Chen, M.; Shi, F.; et al. Efficacy of Decitabine plus Anti-PD-1 Camrelizumab in Patients with Hodgkin Lymphoma Who Progressed or Relapsed after PD-1 Blockade Monotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 2782–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Zhou, K.; Jin, C.; Qian, Z.; Hou, M.; Fan, L.; Li, F.; Ding, K.; Zhou, H.; Li, X.; et al. Penpulimab for Relapsed or Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Multicenter, Single-Arm, Pivotal Phase I/II Trial (AK105-201). Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 925236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Fan, L.; Zhou, J.; Zou, D.; Li, W.; Yang, H.; Liu, T.; Wang, Q.; et al. Treatment of relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma with the anti-PD-1, tislelizumab: Results of a phase 2, single-arm, multicenter study. Leukemia 2020, 34, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Juhaishi, T.; Borogovac, A.; Ibrahimi, S.; Wieduwilt, M.; Ahmed, S. Reappraising the Role of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Relapsed and Refractory Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: Recent Advances and Outcomes. JPM 2022, 12, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sureda, A.; Domenech, E.; Schmitz, N.; Dreger, P.; on behalf of the Lymphoma Working Party of the European Group for Stem Cell Transplantation. The Role of Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation in Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2014, 15, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sureda, A.; Canals, C.; Arranz, R.; Caballero, D.; Ribera, J.M.; Brune, M.; Passweg, J.; Martino, R.; Valcarcel, D.; Besalduch, J.; et al. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation after reduced intensity conditioning in patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Results of the HDR-ALLO study—A prospective clinical trial by the Grupo Espanol de Linfomas/Trasplante de Medula Osea (GEL/TAMO) and the Lymphoma Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Haematologica 2012, 97, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sureda, A.; Robinson, S.; Canals, C.; Carella, A.M.; Boogaerts, M.A.; Caballero, D.; Hunter, A.E.; Kanz, L.; Slavin, S.; Cornelissen, J.J.; et al. Reduced-Intensity Conditioning Compared With Conventional Allogeneic Stem-Cell Transplantation in Relapsed or Refractory Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: An Analysis From the Lymphoma Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. JCO 2008, 26, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.P.; Sureda, A.; Canals, C.; Russell, N.; Caballero, D.; Bacigalupo, A.; Iriondo, A.; Cook, G.; Pettitt, A.; Socie, G.; et al. Reduced intensity conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation for Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Identification of prognostic factors predicting outcome. Haematologica 2009, 94, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarina, B.; Castagna, L.; Farina, L.; Patriarca, F.; Benedetti, F.; Carella, A.M.; Falda, M.; Guidi, S.; Ciceri, F.; Bonini, A.; et al. Allogeneic transplantation improves the overall and progression-free survival of Hodgkin lymphoma patients relapsing after autologous transplantation: A retrospective study based on the time of HLA typing and donor availability. Blood 2010, 115, 3671–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devetten, M.P.; Hari, P.N.; Carreras, J.; Logan, B.R.; van Besien, K.; Bredeson, C.N.; Freytes, C.O.; Gale, R.P.; Gibson, J.; Giralt, S.A.; et al. Unrelated Donor Reduced-Intensity Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Relapsed and Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009, 15, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bento, L.; Boumendil, A.; Finel, H.; Khvedelidze, I.; Blaise, D.; Fegueux, N.; Castagna, L.; Forcade, E.; Chevallier, P.; Mordini, N.; et al. Tandem autologous-reduced intensity allogeneic stem cell transplantation in high-risk relapsed Hodgkin lymphoma: A retrospective study of the Lymphoma Working Party—EBMT. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2021, 56, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diefenbach, C.S.; Hong, F.; Ambinder, R.F.; Cohen, J.B.; Robertson, M.J.; David, K.A.; Advani, R.H.; Fenske, T.S.; Barta, S.K.; Palmisiano, N.D.; et al. Ipilimumab, nivolumab, and brentuximab vedotin combination therapies in patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: Phase 1 results of an open-label, multicentre, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e660–e670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Dong, L.; Yang, Q.; Chen, M.; Shi, F.; Brock, M.; Liu, M.; Mei, Q.; et al. Improved clinical outcome in a randomized phase II study of anti-PD-1 camrelizumab plus decitabine in relapsed/refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, C.A.; Grover, N.S.; Beaven, A.W.; Lulla, P.D.; Wu, M.-F.; Ivanova, A.; Wang, T.; Shea, T.C.; Rooney, C.M.; Dittus, C.; et al. Anti-CD30 CAR-T Cell Therapy in Relapsed and Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma. JCO 2020, 38, 3794–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garciaz, S.; Coso, D.; Peyrade, F.; Fürst, S.; Duran, S.; Chetaille, B.; Brenot-Rossi, I.; Devillier, R.; Granata, A.; Blaise, D.; et al. Brentuximab vedotin followed by allogeneic transplantation as salvage regimen in patients with relapsed and/or refractory Hodgkin’s lymphoma: BV and allogeneic transplantation in HL. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 32, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatobene, G.; Rocha, V.; St. Martin, A.; Hamadani, M.; Robinson, S.; Bashey, A.; Boumendil, A.; Brunstein, C.; Castagna, L.; Dominietto, A.; et al. Nonmyeloablative Alternative Donor Transplantation for Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: From the LWP-EBMT, Eurocord, and CIBMTR. JCO 2020, 38, 1518–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raiola, A.; Dominietto, A.; Varaldo, R.; Ghiso, A.; Galaverna, F.; Bramanti, S.; Todisco, E.; Sarina, B.; Giordano, L.; Ibatici, A.; et al. Unmanipulated haploidentical BMT following non-myeloablative conditioning and post-transplantation CY for advanced Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2014, 49, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paviglianiti, A.; Tozatto Maio, K.; Rocha, V.; Gehlkopf, E.; Milpied, N.; Esquirol, A.; Chevallier, P.; Blaise, D.; Gac, A.-C.; Leblond, V.; et al. Outcomes of Advanced Hodgkin Lymphoma after Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation: A Eurocord and EBMT Lymphoma and Cellular Therapy & Immunobiology Working Party Study. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018, 24, 2265–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merryman, R.W.; Kim, H.T.; Zinzani, P.L.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Ansell, S.M.; Perales, M.-A.; Avigdor, A.; Halwani, A.S.; Houot, R.; Marchand, T.; et al. Safety and efficacy of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant after PD-1 blockade in relapsed/refractory lymphoma. Blood 2017, 129, 1380–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nieto, J.C.; Roldán, E.; Jiménez, I.; Fox, L.; Carabia, J.; Ortí, G.; Puigdefàbregas, L.; Gallur, L.; Iacoboni, G.; Raheja, P.; et al. Posttransplant cyclophosphamide after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation mitigates the immune activation induced by previous nivolumab therapy. Leukemia 2020, 34, 3420–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, C.; Carpio, C.; Heras, I.; Ríos-Herranz, E.; Buch, J.; Gutierrez, A.; Romero, S.; Zeberio, I.; García-García, I.; Rodriguez-Izquierdo, A.; et al. Potential Survival Benefit for Patients Receiving Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation after Nivolumab Therapy for Relapse/Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma: Real-Life Experience in Spain. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020, 26, 1534–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S.; Zahurak, M.; Luznik, L.; Ambinder, R.F.; Fuchs, E.J.; Bolaños-Meade, J.; Wagner-Johnston, N.; Swinnen, L.J.; Schoch, L.; Varadhan, R.; et al. Non-Myeloablative Allogeneic Transplantation with Post-Transplant Cyclophosphamide after Immune Checkpoint Inhibition for Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020, 26, 1679–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadelain, M. CD19 CAR T Cells. Cell 2017, 171, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- June, C.H.; Sadelain, M. Chimeric Antigen Receptor Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finck, A.V.; Blanchard, T.; Roselle, C.P.; Golinelli, G.; June, C.H. Engineered cellular immunotherapies in cancer and beyond. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, N.S.; Savoldo, B. Challenges of driving CD30-directed CAR-T cells to the clinic. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beköz, H.; Karadurmuş, N.; Paydaş, S.; Türker, A.; Toptaş, T.; Fıratlı Tuğlular, T.; Sönmez, M.; Gülbaş, Z.; Tekgündüz, E.; Kaya, A.H.; et al. Nivolumab for relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: Real-life experience. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 2496–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoch, L.K.; Cooke, K.R.; Wagner-Johnston, N.D.; Gojo, I.; Swinnen, L.J.; Imus, P.; Fuchs, E.J.; Levis, M.; Ambinder, R.F.; Jones, R.J.; et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitors as a bridge to allogeneic transplantation with posttransplant cyclophosphamide. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 2226–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Cheikh, J.; Massoud, R.; Abudalle, I.; Haffar, B.; Mahfouz, R.; Kharfan-Dabaja, M.A.; Jisr, T.; Mougharbel, A.; Ibrahim, A.; Bazarbachi, A. Nivolumab salvage therapy before or after allogeneic stem cell transplantation in Hodgkin lymphoma. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2017, 52, 1074–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, A.; Kim, S.-W.; Matsuoka, K.; Kawakita, T.; Tanaka, T.; Inamoto, Y.; Toubai, T.; Fujiwara, S.; Fukaya, M.; Kondo, T.; et al. Safety and efficacy of anti-programmed cell death-1 monoclonal antibodies before and after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: A multicenter retrospective study. Int. J. Hematol. 2020, 112, 674–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-M.; Wu, Z.-Q.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.-L.; Dai, H.-R.; Wang, X.-H.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Chen, M.-X.; et al. Autologous T Cells Expressing CD30 Chimeric Antigen Receptors for Relapsed or Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma: An Open-Label Phase I Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 1156–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, C.A.; Ballard, B.; Zhang, H.; Dakhova, O.; Gee, A.P.; Mei, Z.; Bilgi, M.; Wu, M.-F.; Liu, H.; Grilley, B.; et al. Clinical and immunological responses after CD30-specific chimeric antigen receptor–redirected lymphocytes. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 3462–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartlett, N.L.; Niedzwiecki, D.; Johnson, J.L.; Friedberg, J.W.; Johnson, K.B.; van Besien, K.; Zelenetz, A.D.; Cheson, B.D.; Canellos, G.P. Gemcitabine, vinorelbine, and pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (GVD), a salvage regimen in relapsed Hodgkin’s lymphoma: CALGB 59804. Ann. Oncol. 2007, 18, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hazane Leroyer, E.; Ziegler, C.; Moulin, C.; Campidelli, A.; Jacquet, C.; Rubio, M.T.; Feugier, P.; Pagliuca, S. Filling the Gap: The Immune Therapeutic Armamentarium for Relapsed/Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6574. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216574
Hazane Leroyer E, Ziegler C, Moulin C, Campidelli A, Jacquet C, Rubio MT, Feugier P, Pagliuca S. Filling the Gap: The Immune Therapeutic Armamentarium for Relapsed/Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(21):6574. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216574
Chicago/Turabian StyleHazane Leroyer, Esther, Caroline Ziegler, Charline Moulin, Arnaud Campidelli, Caroline Jacquet, Marie Thérèse Rubio, Pierre Feugier, and Simona Pagliuca. 2022. "Filling the Gap: The Immune Therapeutic Armamentarium for Relapsed/Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 21: 6574. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216574
APA StyleHazane Leroyer, E., Ziegler, C., Moulin, C., Campidelli, A., Jacquet, C., Rubio, M. T., Feugier, P., & Pagliuca, S. (2022). Filling the Gap: The Immune Therapeutic Armamentarium for Relapsed/Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(21), 6574. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216574






