Assessment of Thigh MRI Radiomics and Clinical Characteristics for Assisting in Discrimination of Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
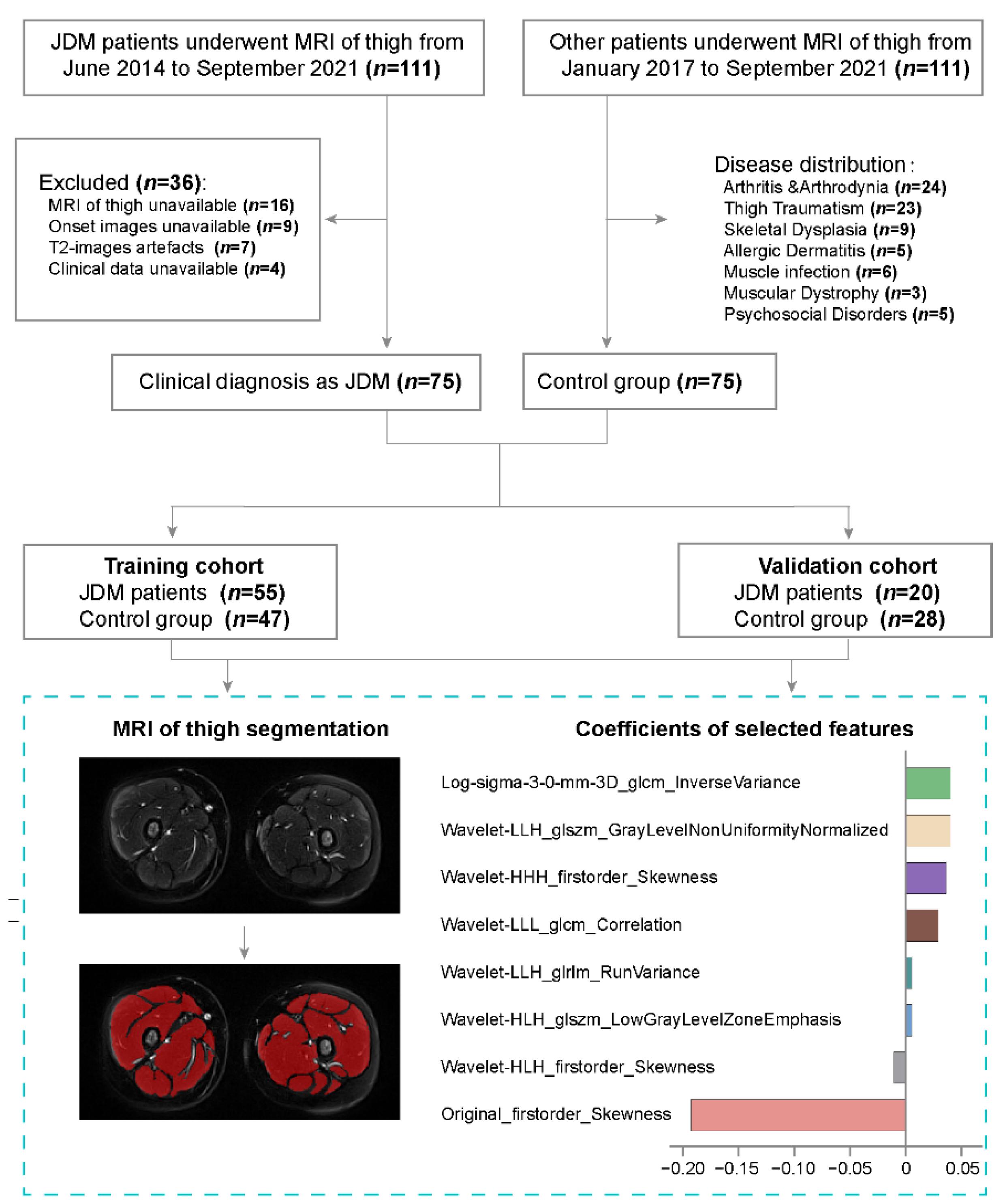
2.1. Patients
2.2. MRI Acquisition
2.3. MRI Segmentation
2.4. Radiomics Feature Extraction
2.5. Feature Selection
2.6. Diagnostic Performance Evaluation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of the Included Children
3.2. Radiomics Feature Selection and Radiomics Score Construction
3.3. Clinical Predictors of JDM in Children
3.4. Development and Validation of the JDM-Discriminating Nomogram
3.5. Radiomics Score Assessment via Linear Discriminant Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cobos, G.A.; Femia, A.; Vleugels, R.A. Dermatomyositis: An Update on Diagnosis and Treatment. Am. J. Clin. Derm. 2020, 21, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCann, L.J.; Juggins, A.D.; Maillard, S.M.; Wedderburn, L.R.; Davidson, J.E.; Murray, K.J.; Pilkington, C.A. The Juvenile Dermatomyositis National Registry and Repository (UK and Ireland)—clinical characteristics of children recruited within the first 5 yr. Rheumatology 2006, 45, 1255–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCann, L.J.; Livermore, P.; Wilkinson, M.G.L.; Wedderburn, L.R. Juvenile dermatomyositis. Where are we now? Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christen-Zaech, S.; Seshadri, R.; Sundberg, J.; Paller, A.S.; Pachman, L.M. Persistent association of nailfold capillaroscopy changes and skin involvement over thirty-six months with duration of untreated disease in patients with juvenile dermatomyositis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imataka, G.; Arisaka, O. Long-term, high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in a patient with banker-type juvenile dermatomyositis. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 69, 747–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pachman, L.M.; Hayford, J.R.; Chung, A.; Daugherty, C.A.; Pallansch, M.A.; Fink, C.W.; Gewanter, H.L.; Jerath, R.; Lang, B.A.; Sinacore, J.; et al. Juvenile dermatomyositis at diagnosis: Clinical characteristics of 79 children. J. Rheumatol. 1998, 25, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Mamyrova, G.; Katz, J.D.; Jones, R.V.; Targoff, I.N.; Lachenbruch, P.A.; Jones, O.Y.; Miller, F.W.; Rider, L.G. Clinical and laboratory features distinguishing juvenile polymyositis and muscular dystrophy. Arthritis Care Res. 2013, 65, 1969–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Constantin, T.; Ponyi, A.; Orbán, I.; Molnár, K.; Dérfalvi, B.; Dicso, F.; Kálovics, T.; Müller, J.; Garami, M.; Sallai, A.; et al. National registry of patients with juvenile idiopathic inflammatory myopathies in Hungary--clinical characteristics and disease course of 44 patients with juvenile dermatomyositis. Autoimmunity 2006, 39, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohan, A.; Peter, J.B. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (first of two parts). N. Engl. J. Med. 1975, 292, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohan, A.; Peter, J.B. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (second of two parts). N. Engl. J. Med. 1975, 292, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lundberg, I.E.; Tjärnlund, A.; Bottai, M.; Werth, V.P.; Pilkington, C.; Visser, M.d.; Alfredsson, L.; Amato, A.A.; Barohn, R.J.; Liang, M.H.; et al. 2017 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for adult and juvenile idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and their major subgroups. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1955–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunawardena, H. The Clinical Features of Myositis-Associated Autoantibodies: A Review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 52, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betteridge, Z.; Tansley, S.; Shaddick, G.; Chinoy, H.; Cooper, R.G.; New, R.P.; Lilleker, J.B.; Vencovsky, J.; Chazarain, L.; Danko, K.; et al. Frequency, mutual exclusivity and clinical associations of myositis autoantibodies in a combined European cohort of idiopathic inflammatory myopathy patients. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 101, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, T.C.M.; Lederman, H.; Terreri, M.T.; Caldana, W.I.; Zanoteli, E.; Hilário, M.O.E. Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of muscular involvement in juvenile dermatomyositis/polymyositis patients. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2014, 43, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, I.; Akioka, S.; Kobayashi, N.; Iwata, N.; Takezaki, S.; Nakaseko, H.; Sato, S.; Nishida, Y.; Nozawa, T.; Yamasaki, Y.; et al. Clinical practice guidance for juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM) 2018-Update. Mod. Rheumatol. 2020, 30, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rizzo, S.; Botta, F.; Raimondi, S.; Origgi, D.; Fanciullo, C.; Morganti, A.G.; Bellomi, M. Radiomics: The facts and the challenges of image analysis. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2018, 2, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannil, M.; Burgstaller, J.M.; Thanabalasingam, A.; Winklhofer, S.; Betz, M.; Held, U.; Guggenberger, R. Texture analysis of paraspinal musculature in MRI of the lumbar spine: Analysis of the lumbar stenosis outcome study (LSOS) data. Skelet. Radiol. 2018, 47, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilmeier, U.; Wamba, J.M.; Joseph, G.B.; Darakananda, K.; Callan, J.; Neumann, J.; Link, T.M. Baseline knee joint effusion and medial femoral bone marrow edema, in addition to MRI-based T2 relaxation time and texture measurements of knee cartilage, can help predict incident total knee arthroplasty 4–7 years later: Data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Skelet. Radiol. 2019, 48, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukichi, T.; Yoshida, K.; Matsushima, S.; Kawakami, G.; Noda, K.; Furuya, K.; Kurosaka, D. MRI of skeletal muscles in patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies: Characteristic findings and diagnostic performance in dermatomyositis. RMD Open 2019, 5, e000850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tustison, N.J.; Avants, B.B.; Cook, P.A.; Zheng, Y.; Egan, A.; Yushkevich, P.A.; Gee, J.C. N4ITK: Improved N3 bias correction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2010, 29, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yushkevich, P.A.; Piven, J.; Hazlett, H.C.; Smith, R.G.; Ho, S.; Gee, J.C.; Gerig, G. User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: Significantly improved efficiency and reliability. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Griethuysen, J.J.M.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Fillion-Robin, J.-C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression Shrinkage and Selection Via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, D.J.; Lindsley, C.B.; Rennebohm, R.M.; Ballinger, S.H.; Bowyer, S.L.; Giannini, E.H.; Hicks, J.E.; Levinson, J.E.; Mier, R.; Pachman, L.M.; et al. Development of validated disease activity and damage indices for the juvenile idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. II. The Childhood Myositis Assessment Scale (CMAS): A quantitative tool for the evaluation of muscle function. The Juvenile Dermatomyositis Disease Activity Collaborative Study Group. Arthritis Rheum. 1999, 42, 2213–2219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huber, A.M.; Lovell, D.J.; Pilkington, C.A.; Rennebohm, R.M.; Rider, L.G. Confusion concerning multiple versions of the childhood myositis assessment scale. Arthritis Care Res. 2014, 66, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, S.M.; Jones, R.; Owens, C.; Pilkington, C.; Woo, P.; Wedderburn, L.R.; Murray, K.J. Quantitative assessment of MRI T2 relaxation time of thigh muscles in juvenile dermatomyositis. Rheumatology 2004, 43, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerami, P.; Schope, J.M.; McDonald, L.; Walling, H.W.; Sontheimer, R.D. A systematic review of adult-onset clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis (dermatomyositis siné myositis): A missing link within the spectrum of the idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2006, 54, 597–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; de Jong, E.E.C.; van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; Larue, R.; Even, A.J.G.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, V.E.; Pilkington, C.A.; Feldman, B.M.; Davidson, J.E. An international consensus survey of the diagnostic criteria for juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM). Rheumatology 2006, 45, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rider, L.G.; Giannini, E.H.; Harris-Love, M.; Joe, G.; Isenberg, D.; Pilkington, C.; Lachenbruch, P.A.; Miller, F.W. Defining Clinical Improvement in Adult and Juvenile Myositis. J. Rheumatol. 2003, 30, 603–617. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tansley, S.L.; McHugh, N.J.; Wedderburn, L.R. Adult and juvenile dermatomyositis: Are the distinct clinical features explained by our current understanding of serological subgroups and pathogenic mechanisms? Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wedderburn, L.R.; McHugh, N.J.; Chinoy, H.; Cooper, R.G.; Salway, F.; Ollier, W.E.R.; McCann, L.J.; Varsani, H.; Dunphy, J.; North, J.; et al. HLA class II haplotype and autoantibody associations in children with juvenile dermatomyositis and juvenile dermatomyositis-scleroderma overlap. Rheumatology 2007, 46, 1786–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolstencroft, P.W.; Fiorentino, D.F. Dermatomyositis Clinical and Pathological Phenotypes Associated with Myositis-Specific Autoantibodies. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2018, 20, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchbinder, R.; Forbes, A.; Hall, S.; Dennett, X.; Giles, G. Incidence of malignant disease in biopsy-proven inflammatory myopathy. A population-based cohort study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001, 134, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deakin, C.T.; Yasin, S.A.; Simou, S.; Arnold, K.A.; Tansley, S.L.; Betteridge, Z.E.; McHugh, N.J.; Varsani, H.; Holton, J.L.; Jacques, T.S.; et al. Muscle Biopsy Findings in Combination With Myositis-Specific Autoantibodies Aid Prediction of Outcomes in Juvenile Dermatomyositis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 2806–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albayda, J.; Pinal-Fernandez, I.; Huang, W.; Parks, C.; Paik, J.; Casciola-Rosen, L.; Danoff, S.K.; Johnson, C.; Christopher-Stine, L.; Mammen, A.L. Antinuclear Matrix Protein 2 Autoantibodies and Edema, Muscle Disease, and Malignancy Risk in Dermatomyositis Patients. Arthritis Care Res. 2017, 69, 1771–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tansley, S.L.; Betteridge, Z.E.; Gunawardena, H.; Jacques, T.S.; Owens, C.M.; Pilkington, C.; Arnold, K.; Yasin, S.; Moraitis, E.; Wedderburn, L.R.; et al. Anti-MDA5 autoantibodies in juvenile dermatomyositis identify a distinct clinical phenotype: A prospective cohort study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristic | Training Cohort, No. (%) | Validation Cohort, No. (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JDM n = 55 | Control n = 47 | p-Value | JDM n = 20 | Control n = 28 | p-Value | |
| Demographics and basic clinical characteristic | ||||||
| Age, mean ± SD, y | 6.9 ± 3.3 | 7.8 ± 4.0 | 0.23 | 7.7 ± 4.7 | 8.9 ± 3.9 | 0.36 |
| Sex | ||||||
| Male | 30 (54.5) | 36(76.6) | 0.02 * | 11 (55.0) | 13 (46.4) | 0.77 |
| Female | 25 (45.4) | 11 (23.4) | 9 (45.0) | 15 (53.6) | ||
| Height, mean ± SD, cm | 121.1 ± 19.6 | 125.8 ± 24.2 | 0.27 | 122.4 ± 24.6 | 131.0 ± 21.4 | 0.21 |
| Weight, mean ± SD, kg | 24.3 ± 11.7 | 28.7 ± 15.1 | 0.10 | 27.6 ± 14.9 | 30.5 ± 12.4 | 0.46 |
| Muscle strength (CMAS), Mean ± SD 1 | 43.3 ± 5.7 | 49.8 ± 2.6 | <0.01 ** | 43.4 ± 6.3 | 49.8 ± 2.2 | <0.01 ** |
| WBC | ||||||
| Median (IQR), /μL | 7.4 (6.7–9.0) | 7.1 (5.9–9.7) | 0.63 | 6.7 (5.5–8.4) | 7.4 (5.9–8.1) | 0.57 |
| In reference range | 51 (92.7) | 42 (89.4) | 0.73 | 16 (80.0) | 24 (85.7) | 0.70 |
| Outside reference range | 4 (7.3) | 5 (10.6) | 4 (20.0) | 4 (14.3) | ||
| ESR | ||||||
| Median (IQR), mm/h | 9.0 (7.0–20.0) | 6.0 (3.0–11.5) | <0.01 ** | 13.5 (6.0–22.3) | 6.0 (3.0–9.0) | <0.05 * |
| In reference range | 39 (71.9) | 42 (89.4) | <0.01 ** | 14 (70.0) | 26 (92.9) | 0.05 |
| Outside reference range | 16 (29.1) | 5 (10.6) | 6 (30.0) | 2 (7.1) | ||
| CRP | ||||||
| Median (IQR), mg/L | 0.5 (0.5–3.0) | 0.5 (0.5–2.2) | 0.54 | 0.7 (0.5–4.8) | 0.5 (0.5–3.2) | 0.31 |
| In reference range | 53 (96.4) | 45 (95.7) | 0.99 | 17 (85.0) | 24 (85.7) | 0.99 |
| Outside reference range | 2 (3.6) | 2 (4.3) | 3 (15.0) | 4 (14.3) | ||
| Logarithm of CK | ||||||
| Median (IQR), U/L | 2.61 (2.27–3.50) | 0.23 (0.18–0.32) | <0.01 ** | 2.50 (2.36–3.10) | 2.12 (1.97–2.21) | <0.01 ** |
| In reference range | 25 (45.5) | 41 (87.2) | <0.01 ** | 10 (50) | 27 (96.4) | <0.01 ** |
| Outside reference range | 30 (54.5) | 6 (12.8) | 10 (50) | 1 (3.6) | ||
| JDM-associated characteristic | ||||||
| EMG 2 | ||||||
| Myogenic damage | 49 (89.9) | 6 (12.8) | <0.01 ** | 19 (95.0) | 2 (7.1) | <0.01 ** |
| Normal and others | 6 (10.1) | 41 (87.2) | 1 (5.0) | 26 (92.9) | ||
| Myositis antibody positive 3 | 21 (38.2) | 2 (4.3) | <0.01 ** | 6 (30.0) | 0 (0) | <0.01 ** |
| Anti-NXP2 positive | 5 (9.1) | 0 (0) | 2 (10) | 0 (0) | ||
| Anti-MDA5 positive | 5 (9.1) | 0 (0) | 3 (15) | 0 (0) | ||
| Biopsy | ||||||
| Biopsy positive | 35 (94.6) | 1 (7.7) | <0.01 ** | 16 (94.1) | 0 (0) | <0.01 ** |
| Biopsy negative | 2 (5.4) | 12 (92.3) | 1 (5.9) | 5 (100) | ||
| MRI | ||||||
| Abnormal signal in thighs | 49 (87.3) | 0 (0) | <0.01 ** | 18 (90) | 0 (0) | <0.01 ** |
| Normal and others | 6 (12.7) | 47 (100) | 2 (10) | 28 (100) | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, M.; Zheng, F.; Ma, X.; Liu, L.; Shen, C.; Wu, J.; Wang, C.; Yang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zou, L.; et al. Assessment of Thigh MRI Radiomics and Clinical Characteristics for Assisting in Discrimination of Juvenile Dermatomyositis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6712. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226712
Hu M, Zheng F, Ma X, Liu L, Shen C, Wu J, Wang C, Yang L, Xu Y, Zou L, et al. Assessment of Thigh MRI Radiomics and Clinical Characteristics for Assisting in Discrimination of Juvenile Dermatomyositis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(22):6712. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226712
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Minfei, Fei Zheng, Xiaohui Ma, Linke Liu, Chencong Shen, Jianqiang Wu, Chaoying Wang, Li Yang, Yiping Xu, Lixia Zou, and et al. 2022. "Assessment of Thigh MRI Radiomics and Clinical Characteristics for Assisting in Discrimination of Juvenile Dermatomyositis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 22: 6712. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226712
APA StyleHu, M., Zheng, F., Ma, X., Liu, L., Shen, C., Wu, J., Wang, C., Yang, L., Xu, Y., Zou, L., Fei, L., Lu, M., & Xu, X. (2022). Assessment of Thigh MRI Radiomics and Clinical Characteristics for Assisting in Discrimination of Juvenile Dermatomyositis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(22), 6712. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226712






