Navigating through the Lipid Metabolism Maze: Diagnosis and Prognosis Metabolites of Hepatocellular Carcinoma versus Compensated Cirrhosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patient Characteristics and Sample Collection
2.2. Metabolomic Analysis
2.2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2.2. UHPLC-QTOF-ESI+-MS Analysis
2.3. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
2.4. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis for Prognosis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Univariate and Multivariate Analysis of Metabolic Profile
3.2.1. Analysis of Raw Data Based on UHPLC-QTOF-ESI+-MS Peak Intensities
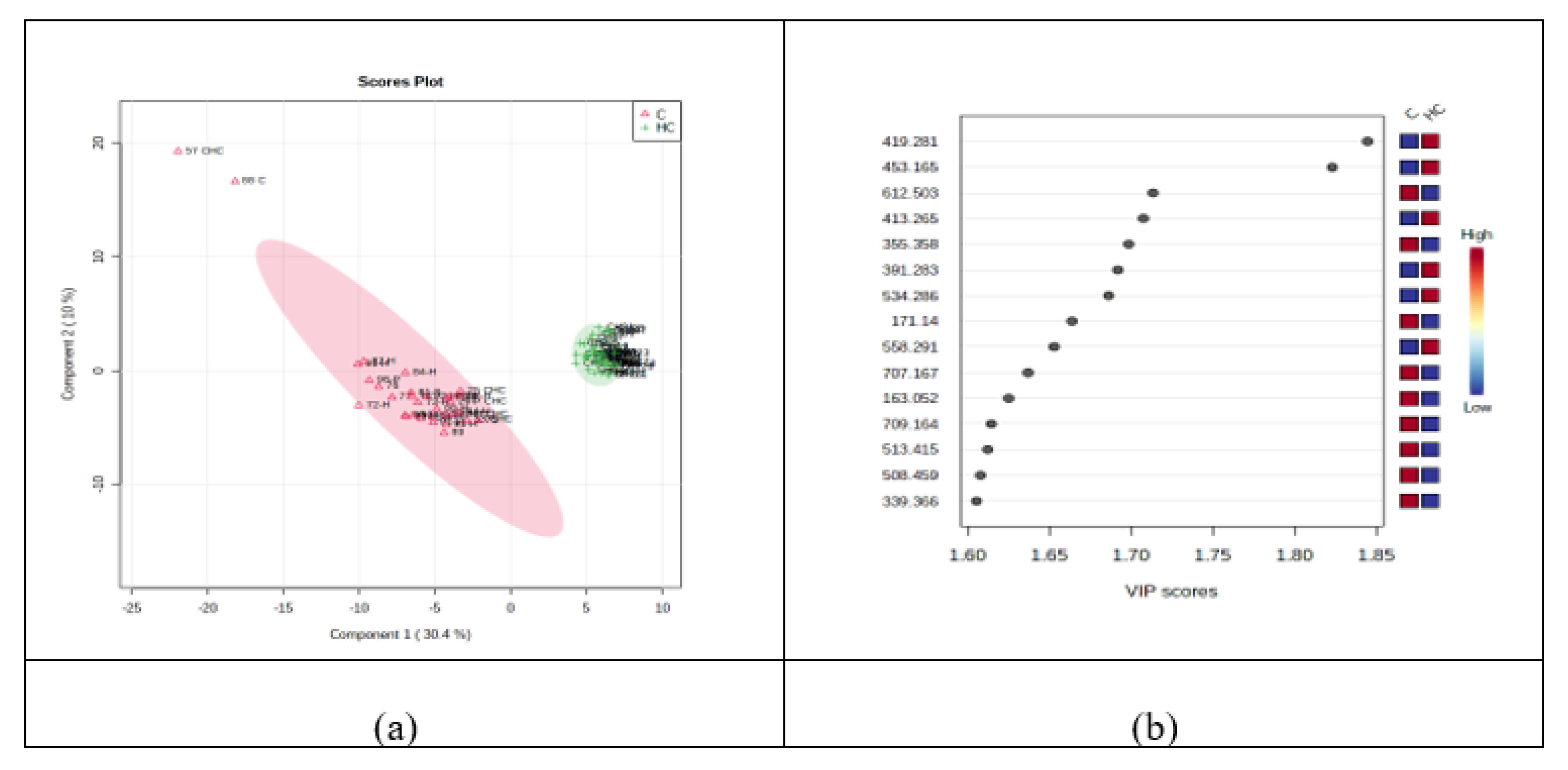
3.2.2. Discrimination Analysis: PCA and PLSDA for HC vs. C Groups
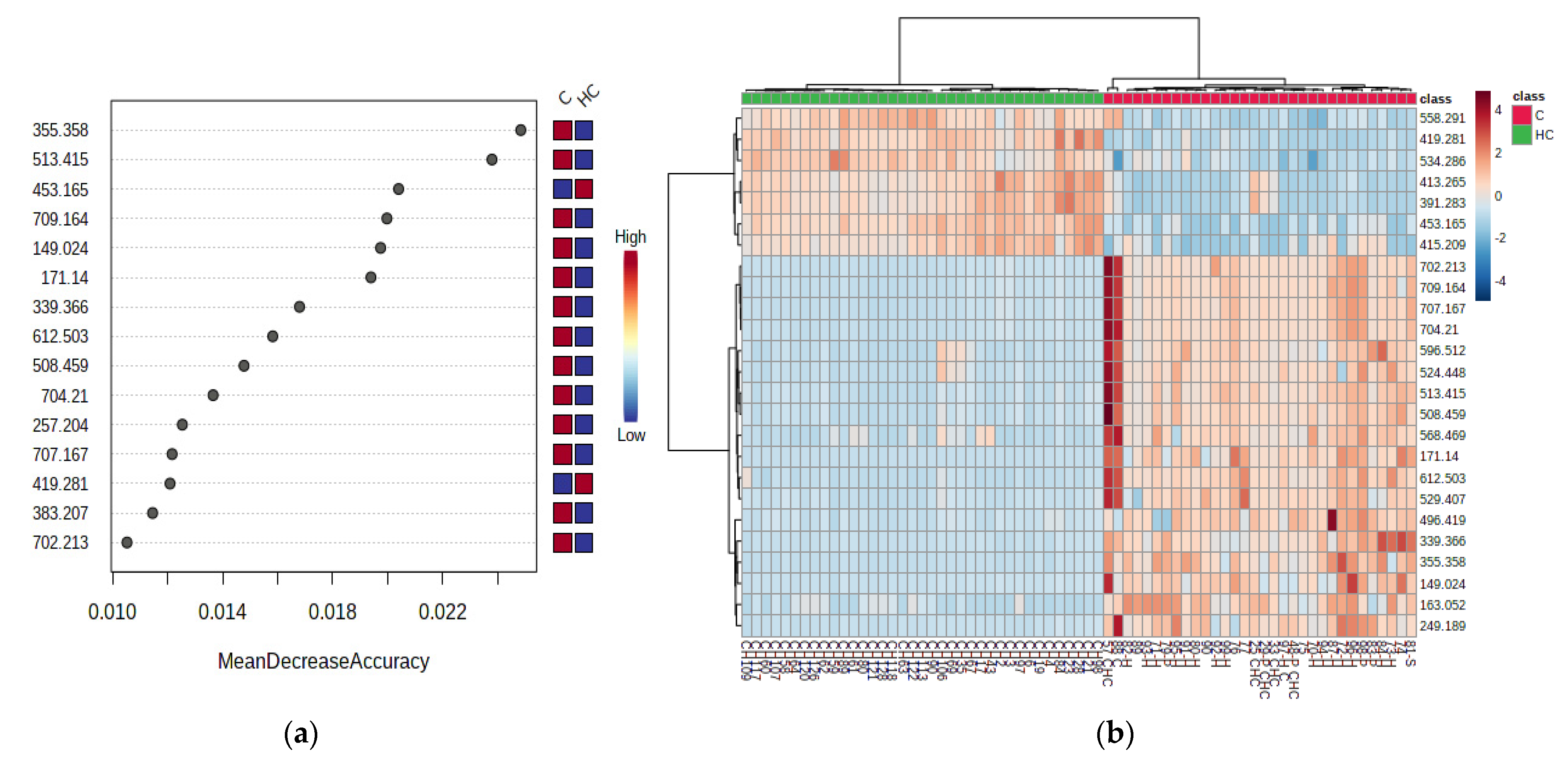
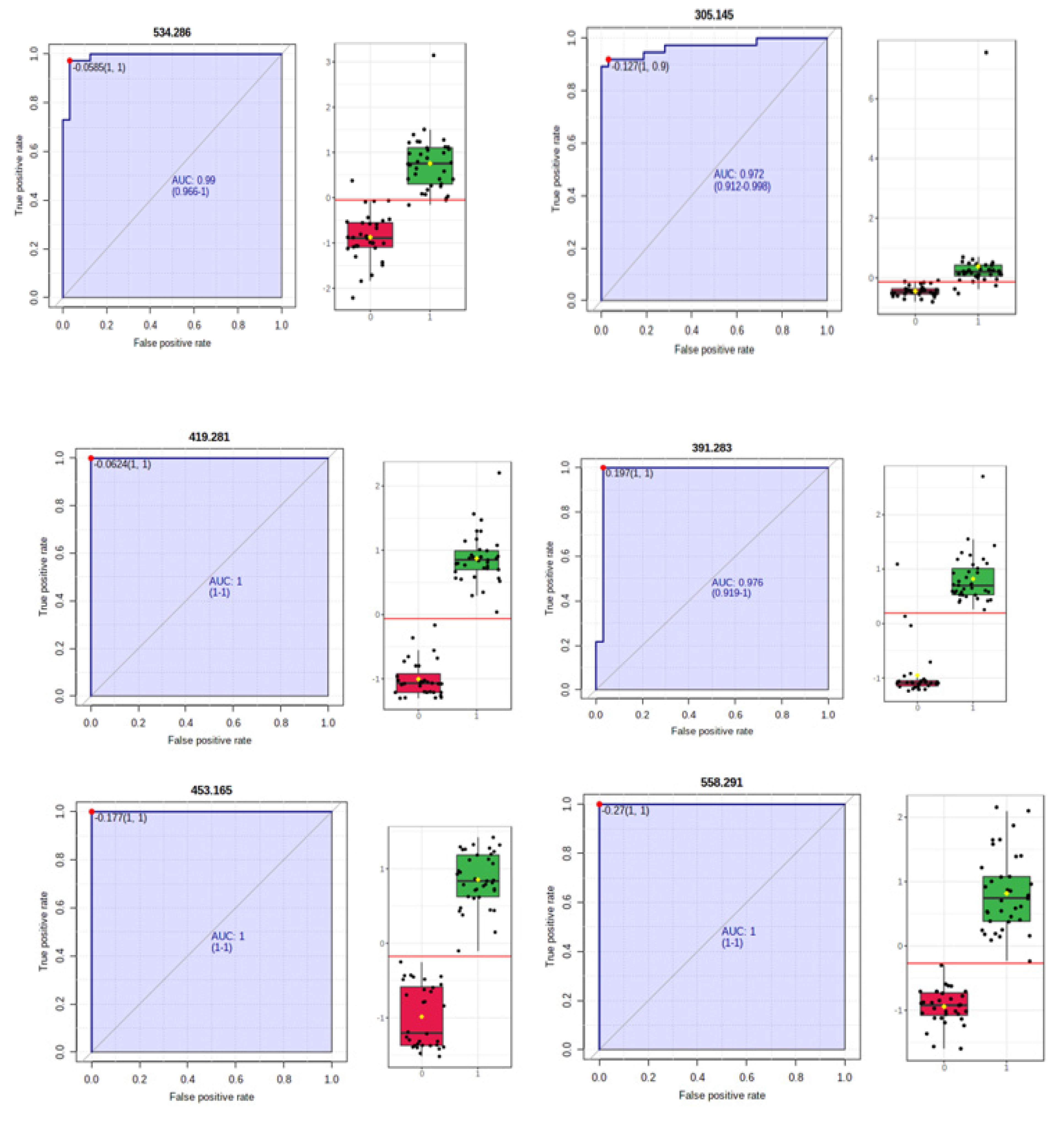
3.2.3. Random Forest Analysis, Heatmaps and Biomarker Analysis for HC vs. C Groups
3.2.4. Correlations between Lipid Metabolites, and Clinical and Biological Characteristics
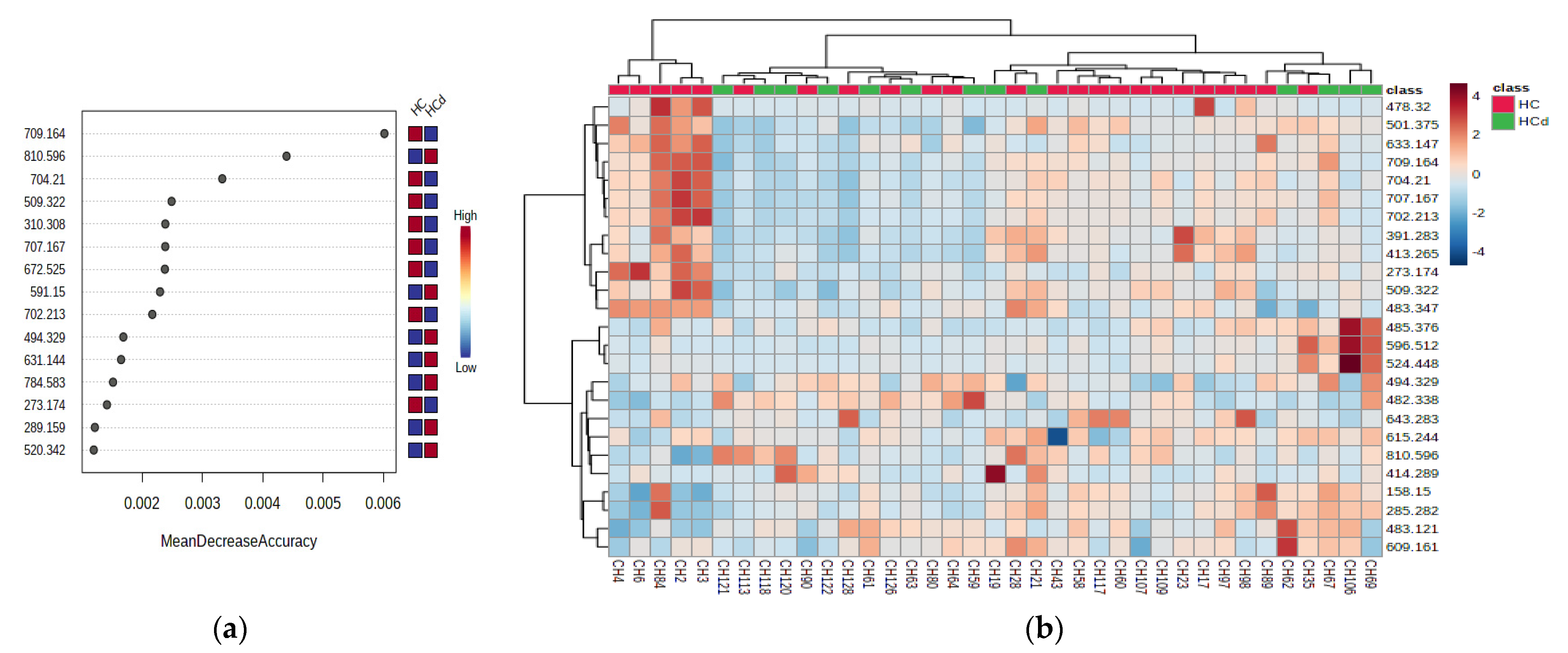
3.2.5. Univariate Analysis to Predict the Death (Comparison of HCd vs. HCs Groups)
3.2.6. Multivariate Analysis for HCd vs. HC Groups
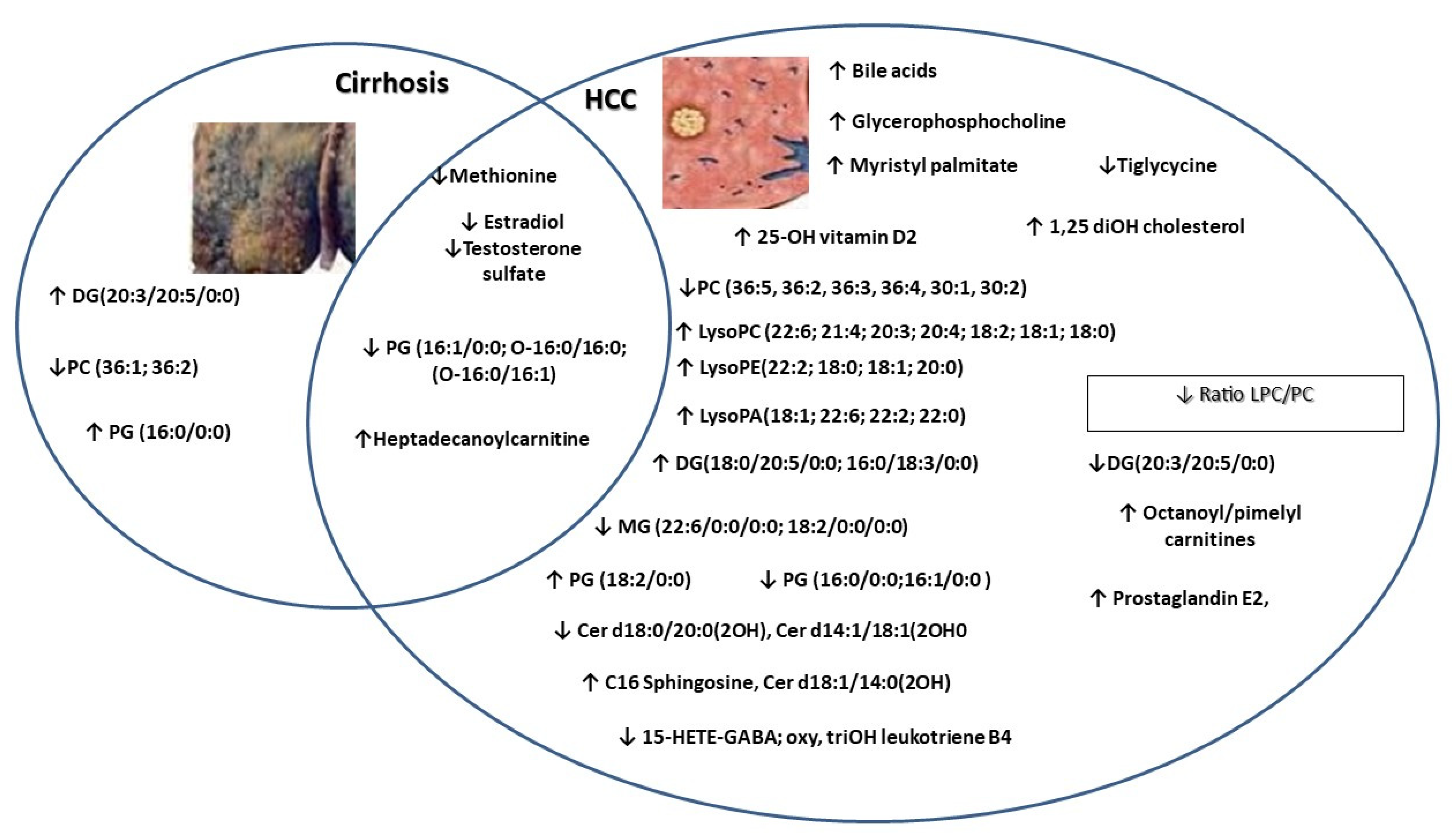
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fitzmaurice, C.; Akinyemiju, T.F.; Al Lami, F.H.; Alam, T.; Alizadeh-Navaei, R.; Allen, C.; Alsharif, U.; Alvis-Guzman, N.; Amini, E.; Anderson, B.O.; et al. Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 29 cancer groups, 1990 to 2016 a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study global burden o. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1553–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinyemiju, T.; Abera, S.; Ahmed, M.; Alam, N.; Alemayohu, M.A.; Allen, C.; Al-Raddadi, R.; Alvis-Guzman, N.; Amoako, Y.; Artaman, A.; et al. The Burden of Primary Liver Cancer and Underlying Etiologies from 1990 to 2015 at the Global, Regional, and National Level. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabibbo, G.; Enea, M.; Attanasio, M.; Bruix, J.; Craxí, A.; Cammà, C. A meta-analysis of survival rates of untreated patients in randomized clinical trials of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaiteerakij, R.; Addissie, B.D.; Roberts, L.R. Update on Biomarkers of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mocan, T.; Simão, A.L.; Castro, R.E.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Słomka, A.; Wang, B.; Strassburg, C.; Wöhler, A.; Willms, A.G.; Kornek, M. Liquid biopsies in hepatocellular carcinoma: Are we winning? J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, A.; Sun, H. Power of metabolomics in diagnosis and biomarker discovery of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2013, 57, 2072–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spratlin, J.L.; Serkova, N.J.; Eckhardt, S.G. Clinical applications of metabolomics in oncology: A review. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenu, I.; Gafencu, G.A.; Popescu, T.; Kacso, G. Lactate-A new frontier in the immunology and therapy of prostate cancer. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2017, 13, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, S.R.; Butler, L.M.; Hoy, A.J. The diversity and breadth of cancer cell fatty acid metabolism. Cancer Metab. 2021, 9, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Han, J.; Xing, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Liang, L.; Li, C.; Dai, S.; Wu, M.; Shen, F.; et al. Dysregulated fatty acid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatic Oncol. 2016, 3, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krautbauer, S.; Meier, E.M.; Rein-Fischboeck, L.; Pohl, R.; Weiss, T.S.; Sigruener, A.; Aslanidis, C.; Liebisch, G.; Buechler, C. Ceramide and polyunsaturated phospholipids are strongly reduced in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2016, 1861, 1767–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyne, N.J.; Pyne, S. Sphingosine 1-phosphate and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunkel, G.T.; MacEyka, M.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Targeting the sphingosine-1-phosphate axis in cancer, inflammation and beyond. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 688–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grammatikos, G.; Schoell, N.; Ferreirós, N.; Bon, D.; Herrmann, E.; Farnik, H.; Köberle, V.; Piiper, A.; Zeuzem, S.; Kronenberger, B.; et al. Serum sphingolipidomic analyses reveal an upregulation of C16-ceramide and sphingosine-1-phosphate in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 18095–18105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buechler, C.; Aslanidis, C. Role of lipids in pathophysiology, diagnosis and therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2020, 1865, 158658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Beggs, K.; Borude, P.; Edwards, G.; Bhushan, B.; Walesky, C.; Roy, N.; Manley, M.W.; Gunewardena, S.; O’Neil, M.; et al. Bile acids promote diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma via increased inflammatory signaling. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 311, G91–G104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cucchetti, A.; Cescon, M.; Golfieri, R.; Piscaglia, F.; Renzulli, M.; Neri, F.; Cappelli, A.; Mazzotti, F.; Mosconi, C.; Colecchia, A.; et al. Hepatic venous pressure gradient in the preoperative assessment of patients with resectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolondi, L.; Burroughs, A.; Dufour, J.F.; Galle, P.R.; Mazzaferro, V.; Piscaglia, F.; Raoul, J.L.; Sangro, B. Heterogeneity of patients with intermediate (BCLC B) Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Proposal for a subclassification to facilitate treatment decisions. Semin Liver Dis. 2012, 32, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, I.T.; Elfert, A.; Helal, M.; Salama, I.; El-Said, H.; Fiehn, O. Remodeling lipids in the transition from chronic liver disease to hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotte, A.K.; Cottet, V.; Aires, V.; Mouillot, T.; Rizk, M.; Vinault, S.; Binquet, C.; De Barros, J.P.P.; Hillon, P.; Delmas, D. Phospholipid profiles and hepatocellular carcinoma risk and prognosis in cirrhotic patients. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 2161–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, L.; Chi, W.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Song, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Jia, J.; Pilo, M.G.; Wang, J.; et al. Cholesterol biosynthesis supports the growth of hepatocarcinoma lesions depleted of fatty acid synthase in mice and humans. Gut 2020, 69, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.; Singh, P.P.; Singh, A.G.; Murad, M.H.; Sanchez, W. Statins are associated with a reduced risk of hepatocellular cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Finkelmeier, F.; Kronenberger, B.; Köberle, V.; Bojunga, J.; Zeuzem, S.; Trojan, J.; Piiper, A.; Waidmann, O. Severe 25-hydroxyvitamin D deficiency identifies a poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma-A prospective cohort study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Jiang, X.; Qiao, Q.; Chen, L.; Matsuda, K.; Jiang, G.; Yu, T.; Wang, Y.; Lin, H.; Liang, X.; et al. Association of circulating 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and its related genetic variations with hepatocellular carcinoma incidence and survival. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, G.Y.; Wang, J.B.; Weinstein, S.J.; Parisi, D.; Horst, R.L.; McGlynn, K.A.; Männistö, S.; Albanes, D.; Freedman, N.D. Association of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D with Liver Cancer Incidence and Chronic Liver Disease Mortality in Finnish Male Smokers of the ATBC Study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2018, 27, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guan, Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, M.; Zhu, W.; Arslan, A.; Takeda, S.; Nguyen, M.H.; Majeti, R.; Thomas, D.; Zheng, M.; et al. The phosphatidylethanolamine biosynthesis pathway provides a new target for cancer chemotherapy. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 746–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, Y.; Horisawa, K.; Udono, M.; Ohkawa, Y.; Suzuki, A. Prolonged inhibition of hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation by combinatorial expression of defined transcription factors. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 3543–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guan, M.; Lin, Y.; Cui, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, J. Aberrant lipid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma revealed by liver lipidomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fisher-Wellman, K.H.; Hagen, J.T.; Neufer, P.D.; Kassai, M.; Cabot, M.C. On the nature of ceramide-mitochondria interactions –Dissection using comprehensive mitochondrial phenotyping. Cell. Signal. 2021, 78, 109838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morad, S.A.F.; Cabot, M.C. Ceramide-orchestrated signalling in cancer cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Liao, Y.; Yin, P.; Zeng, Z.; Li, J.; Lu, X.; Zheng, L.; Xu, G. Metabolic profiling study of early and late recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2014, 966, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Han, M.; Xing, H.; Li, Z.; Yuan, D.; Wu, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.; Li, C.; Liang, L.; et al. Tissue and serum metabolomic phenotyping for diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 1741–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Su, B.; Dong, L.; Jiang, T.; Tan, Y.; Lu, X.; Liu, X.; Lin, X.; Xu, G. Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry-Based Nontargeted Metabolomics Predicts Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Curative Resection. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 3533–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, D.; Ali, O.; Obada, M.; El-Mezayen, H.; El-Said, H. Chromatographic determination of some biomarkers of liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma in Egyptian patients. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2017, 31, e3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Huang, H.; Xu, W.; Chen, D.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Li, L. Fecal metabolome profiling of liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma patients by ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 691, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.; Ouro, A.; Ala-Ibanibo, L.; Presa, N.; Delgado, T.C.; Martínez-Chantar, M.L. Sphingolipids in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma: Ceramide turnover. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| HCC (Group HC) | Cirrhosis (Group C) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| General Data | |||
| Number | 37 | 32 | |
| Age mean SD * | 64.62 (6.29) | 55.97 (8.1) | <0.001 |
| Sex, no (%) ** | |||
| Females | 10 (27.03) | 20 (62.5) | |
| Males | 27 (72.97) | 11 (37.5) | <0.003 |
| Etiology (%) ** | |||
| HCV | 16 (43.24) | 32 (100%) | |
| HVB | 6 (16.21) | ||
| Alcohol | 12 (32.4) | ||
| Cholestatic | 1 (2.7) | ||
| NAFLD | 2 (5.4) | <0.01 | |
| Dead (yes), no (%) | 13 (35.13) | 1 (3.33) | <0.001 |
| Laboratory values | |||
| ALAT * | 37 (21–59) | 74.5 (46.25–108.25) | 0.015 |
| ASAT * | 57 (35–82) | 72.5 (52.25–97.75) | 0.76 |
| γGT * | 61 (33.5–91.5) | 60 (42–129) | 0.67 |
| Total bilirubin * | 1 (0.8–1.6) | 1.15 (0.9–1.35) | 0.67 |
| Creatinine * | 0.73 (0.61–0.95) | 0.72 (0.58–0.84) | 0.2 |
| Albumin * | 3.8 (3.6–4.1) | 4.1 (4–4.3) | <0.01 |
| Hemoglobin * | 14.2 (12.2–15.2) | 14.5 (13.7–15.8) | 0.06 |
| PMN count * | 3.37 (2.5–4.62) | 3.11 (2.52–3.95) | 0.089 |
| Platelet count* | 117 (82–147) | 103 (79–144.5) | 0.725 |
| Na * | 140 (138–142) | 140 (139–143.25) | 0.3 |
| K * | 4.3 (4.07–4.6) | 3.9 (3.8–4.3) | 0.012 |
| AFP * | 10.1 (5.5–58.8) | 13.5 (8.33–19.62) | 0.016 |
| The severity of Liver Disease | |||
| Child–Pugh ** | |||
| A | 31 (74.1%) | 32 (100%) | <0.01 |
| B | 6 (22.2%) | ||
| MELD ** | |||
| ≤9 | 16 (43.24%) | 19 (59.38%) | 0.23 |
| 10–19 | 1 (2.7%) | 13 (40.62 %) | |
| 20 (54.5%) | |||
| Portal pressure * | |||
| HVPG | 15 (11–18) | 14 (11–16) | 0.448 |
| HCC staging | |||
| BCLC ** | |||
| 0 | 4 (11%) | ||
| A | 15 (40%) | ||
| B | 18 (49%) | ||
| Tumor number ** | |||
| <3 | 34 (91.89%) | ||
| 3–5 | 3 (8.11%) | ||
| >5 | 0 | ||
| Milan criteria ** | |||
| In | 19 (51.35%) | ||
| Out | 18 (48.65%) | ||
| m/z | HC/C | HCd/HCs | m/z | HC/C | HCd/HCs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steroids, Incl.Bile Acids | Fatty Acid Derivatives | ||||||
| 419.281 | 1,25 DiOH cholesterol | 6.90 | 0.96 | 453.165 | Myristyl palmitate | 4.12 | 0.97 |
| 391.283 | 12-Ketodeoxycholic acid | 3.24 | 0.89 | 313.255 | Icosanoic (arahidic) acid C20:0 | 2.25 | 0.93 |
| 413.265 | 25-hydroxy vitamin D2 | 3.06 | 0.89 | 331.284 | Docosapentenoic acid (C22:5) | 2.07 | 0.95 |
| 409.328 | Ursocholic acid | 1.38 | 0.9 | 303.181 | Eicosapentenoic acid (C20:5) | 1.85 | 0.86 |
| 473.327 | 3-Sulfodeoxycholic acid | 1.36 | 0.91 | 425.130 | Lauryl palmitate | 1.83 | 1.09 |
| 271.264 | Estrone | 1.17 | 1.13 | 325.250 | Methyl-7-eicosenoic acid | 1.79 | 0.92 |
| 585.268 | Cholic acid glucuronide | 1.14 | 1.19 | 318.291 | N-methyl arachidonoyl amine | 1.76 | 1.07 |
| 289.159 | Testosterone/DHEA | 1.14 | 1.02 | 397.268 | Hexacosanoic acid (C26:0) | 1.59 | 1.02 |
| 421.338 | Dihomodeoxycholic acid | 0.60 | 0.92 | 427.390 | N-stearoyl arginine | 1.23 | 1.03 |
| 369.295 | Testosterone sulfate/DHEAS | 0.55 | 0.92 | 326.354 | Oleoyl Ethanolamide | 1.17 | 1.03 |
| 273.174 | Estradiol | 0.50 | 0.7 | 350.338 | Dihomo-gamma-linolenoyl (C18:3) Ethanolamine | 1.10 | 1.01 |
| Oxylipins | 299.126 | 2-hydroxy oleic acid (C18:1) | 1.06 | 1.04 | |||
| 353.271 | Prostaglandin E2 | 2.54 | 0.93 | 338.341 | Docosenamide (C22) | 1.02 | 1.01 |
| 267.266 | Tetranor 12-HETE | 1.15 | 0.96 | 324.325 | Linoleoyl ethanolamide | 1.01 | 0.95 |
| 406.328 | 15-HETE-GABA | 0.49 | 0.77 | 341.298 | Docosanoic acid (C22:0) | 0.94 | 0.96 |
| 383.207 | 12-Oxo-trihydroxy-leukotriene B4 | 0.22 | 1.06 | 348.319 | O-Arachidonoyl (C20:4, n-6) Ethanolamine | 0.86 | 1.06 |
| Acyl carnitines | 269.217 | Heptadecenoic acid (C17:1) | 0.65 | 1.03 | |||
| 414.289 | Heptadecanoyl carnitine | 3.92 | 2.47 | 501.375 | Palmitoleyl linolenate | 0.55 | 0.93 |
| 290.261 | Adipoyl carnitine | 2.81 | 1.09 | 301.142 | Eicosahexaenoic acid (C20:6) | 0.45 | 0.96 |
| 316.317 | Decanoylcarnitine | 1.90 | 1.1 | 529.407 | Linoleyl linoleate | 0.43 | 1.04 |
| 304.295 | Pimelyl carnitine | 1.78 | 1.03 | 285.282 | Stearic acid | 0.42 | 1.06 |
| 288.266 | Octanoyl carnitine | 1.66 | 1.08 | 295.182 | 2-Hydroxy linolenic acid (C16:3) | 0.40 | 0.97 |
| 230.24 | Butenyl carnitine | 1.28 | 1.01 | 279.160 | Linolenic acid (C18:3) | 0.33 | 0.98 |
| 332.327 | 3-hydroxydecanoyl carnitine | 1.21 | 0.99 | 163.052 | Hydroxy adipic acid | 0.26 | 1.18 |
| 312.326 | Decadienoyl carnitine | 1.18 | 1.01 | 249.189 | Hexadecatetraenoic acid C16:4 | 0.22 | 1.05 |
| 374.259 | Dodecanedioylcarnitine | 1.15 | 0.93 | 229.131 | Myristic acid (C14) | 0.21 | 1.03 |
| 388.355 | 3-Hydroxytetradecanoyl carnitine | 1.09 | 1.04 | 257.204 | Palmitic acid (C16:0) | 0.20 | 0.93 |
| 310.308 | Decatrienoyl carnitine | 0.98 | 0.93 | 339.366 | Dimethyl-2-eicosenoic acid (C22) | 0.16 | 1.09 |
| Aminoacid and choline derivatives | 245.077 | Hydroxy myristic acid (C14) | 0.14 | 1.02 | |||
| 258.265 | Glycerophosphocholine | 1.69 | 1.02 | 305.145 | Arahidonic acid (C20:4) | 2.83 | 1.51 |
| 166.073 | Phenyl alanine | 1.10 | 0.94 | 415.209 | Ascorbyl palmitate | 2.94 | 0.99 |
| 183.082 | Phosphoryl choline | 0.46 | 0.98 | Sphingolipids | |||
| 161.1 | Tryptamine | 0.43 | 0.59 | 274.265 | C16-Sphingosine | 1.64 | 1.07 |
| 149.024 | Methionine | 0.27 | 0.98 | 526.518 | Ceramide (d18:1/14:0 (2OH)) | 1.49 | 1.05 |
| 158.15 | Tiglylglycine | 0.12 | 1.08 | 554.547 | Ceramide (d18:1/16:0 (2OH)) | 1.10 | 1.04 |
| 171.14 | Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate | 0.06 | 1.04 | 354.360 | C16 Sphinganine 1-P | 0.99 | 1.03 |
| 364.346 | a-linolenyl choline (C18:3) | 0.63 | 0.96 | 623.245 | Ceramide (d18:1/22:0) | 0.88 | 1 |
| 366.374 | a-linoleyl choline (C18:2) | 0.87 | 1.09 | 584.464 | Ceramide (d18:0/18:0 (2OH)) | 0.63 | 0.99 |
| Lyso Phospholipids | 582.576 | Ceramide (d18:1/18:0 (2OH)) | 0.61 | 1.08 | |||
| 558.291 | LysoPC (21:4) | 2.83 | 1.07 | 628.495 | Ceramide (t18:0/20:0 (2OH)) | 0.58 | 0.98 |
| 522.357 | LysoPC (18:1) | 2.11 | 1.06 | 540.441 | Ceramide (d18:0/16:0) | 0.58 | 1 |
| 534.286 | LysoPE (22:2) | 2.08 | 1.09 | 672.525 | GlycoCeramide (d18:1/14:0) | 0.58 | 0.93 |
| 437.191 | LysoPA (18:1/0:0) | 1.89 | 0.99 | 703.574 | Sphingomyelin 18:2/16:0 | 0.50 | 1 |
| 524.37 | LysoPC (18:0) | 1.68 | 1.02 | 496.419 | Ceramide (d15:1/16:0) | 0.49 | 0.97 |
| 482.338 | LysoPE (18:0) | 1.54 | 1.25 | 596.512 | Ceramide (d20:0/18:0) | 0.48 | 1.28 |
| 483.121 | LysoPA (22:6/0:0) | 1.51 | 1.23 | 508.459 | Ceramide (d18:2/14:0) & isom. | 0.47 | 1.05 |
| 510.372 | LysoPE (20:0) | 1.49 | 1.21 | 568.469 | Ceramide (d18:0/18:0) | 0.45 | 1.23 |
| 480.332 | LysoPE (18:1) | 1.42 | 1.18 | 524.448 | Ceramide (d14:1/18:1 (2OH)) isomizom | 0.39 | 1.31 |
| 520.342 | LysoPC (18:2) | 1.41 | 1.16 | 612.503 | Ceramide (d18:0/20:0 (2OH)) | 0.36 | 1.08 |
| 495.297 | LysoPA (22:0/0:0) | 1.38 | 0.97 | Monoacyl glycerols | |||
| 546.354 | LysoPC (20:3) | 1.35 | 1.06 | 379.263 | MG (20:4/0:0/0:0) | 1.45 | 0.83 |
| 491.371 | LysoPA (22:2/0:0) | 1.25 | 1.14 | 359.313 | MG (18:0/0:0/0:0) | 1.15 | 0.98 |
| 494.329 | LysoPC (16:1) | 1.22 | 1.27 | 381.304 | MG (20:3/0:0/0:0) | 1.03 | 1.02 |
| 544.341 | LysoPC (20:4) | 1.22 | 1.01 | 357.093 | MG (18:1/0:0/0:0) | 0.78 | 1.05 |
| 568.342 | LysoPC (22:6) | 1.11 | 1.03 | 403.234 | MG (22:6/0:0/0:0) | 0.22 | 0.96 |
| 502.299 | LysoPE (20:4) | 1.09 | 0.9 | 355.358 | MG (0:0/18:2/0:0) | 0.15 | 1.08 |
| 454.294 | LysoPE (16:0) | 1.08 | 0.97 | Diacyl glycerols | |||
| 518.325 | LysoPC (18:3) | 0.98 | 0.98 | 643.283 | DG (18:0/20:5/0:0) | 1.96 | 0.59 |
| 496.342 | LysoPC (16:0) | 0.9 | 0.91 | 591.15 | DG (16:0/18:3/0:0) | 1.6 | 1.14 |
| 542.323 | LysoPC (20:5) | 0.88 | 1.04 | 609.161 | DG (18:1/17:0/0:0) | 1.6 | 1.17 |
| 508.359 | LysoPE (20:1) | 0.74 | 0.93 | 631.144 | DG (18:4/19:0/0:0) | 1.23 | 1.09 |
| 545.402 | LysoPI (14:0/0:0) | 0.63 | 1.02 | 561.403 | DG (14:1/18:3/0:0) | 1.07 | 0.93 |
| 452.392 | LysoPE (16:1) | 0.51 | 0.92 | 607.251 | DG (18:2/17:0/0:0) | 1.01 | 1.03 |
| 478.32 | LysoPE (18:2) | 0.44 | 0.52 | 617.259 | DG (18:2/18:2/0:0) | 0.96 | 1.16 |
| 480.424 | Lyso PC (O-16:1/0:0) | 0.43 | 1.42 | 663.457 | DG (20:4/20:5/0:0) | 0.91 | 0.99 |
| Glycerophospholipids | 599.247 | DG (18:4/17:2/0:0) | 0.85 | 1.07 | |||
| 780.553 | PC (36:5) [M + H] | 2.05 | 1.29 | 601.264 | DG (18:3/17:2/0:0) | 0.83 | 1.09 |
| 758.568 | PC (34:2) [M + H] | 1.09 | 1.01 | 615.244 | DG (18:2/18:3/0:0) | 0.77 | 1.11 |
| 816.59 | PC (38:2) [M + H] | 0.99 | 1.08 | 603.22 | DG (18:2/17:2/0:0) | 0.66 | 1.2 |
| 744.585 | PE (36:2) | 0.96 | 1.17 | 589.428 | DG (16:1/18:3/0:0) | 0.62 | 1.01 |
| 784.583 | PC (36:3) [M + H] | 0.95 | 1.06 | 513.415 | DG (12:0/16:0/0:0) | 0.56 | 1.04 |
| 760.582 | PC (34:1) [M + H] | 0.92 | 0.98 | 635.143 | DG (18:2/19:0/0:0) | 0.48 | 0.94 |
| 734.569 | PC (32:0) [M + H] | 0.90 | 1.1 | 633.147 | DG (18:3/19:0/0:0) | 0.46 | 0.9 |
| 810.596 | PC (36:1) [M + Na] | 0.83 | 1.41 | 579.294 | DG (16:1/17:1/0:0) | 0.37 | 0.94 |
| 808.582 | PC (36:2) [M + Na] | 0.80 | 1.24 | 665.582 | DG (20:3/20:5/0:0) | 0.07 | 1.36 |
| 633.254 | PA (O-16:0/16:1) | 0.79 | 1.08 | Phosphoglycerols | |||
| 786.602 | PC (36:2) [M + H] | 0.78 | 1.02 | 509.322 | PG (18:2/0:0) | 1.32 | 0.78 |
| 806.568 | PC (36:3) [M + Na] | 0.76 | 0.93 | 483.347 | PG (16:1/0:0) | 0.88 | 0.81 |
| 782.564 | PC (36:4)[M + H] | 0.69 | 1.14 | 485.376 | PG (16:0/0:0) | 0.48 | 1.2 |
| 804.55 | PC (36:4) [M + Na] | 0.24 | 1 | 709.164 | PG (O-16:0/16:0) | 0.26 | 0.85 |
| 704.21 | PC (30:1) | 0.24 | 0.83 | 707.167 | PG (O-16:0/16:1) | 0.26 | 0.84 |
| 702.213 | PC (30:2) | 0.23 | 0.83 | ||||
| m/z | Identification | p Value | FC | Log2FC | Tendency HC vs. C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 419.281 | 1,25-dihydroxy cholesterol | 5.94 × 10−26 | 5.98 | 2.5805 | I |
| 453.165 | Myristyl palmitate | 1.45 × 10−24 | 3.35 | 1.7482 | I |
| 391.283 | 12-keto deoxycholic acid | 2.36 × 10−18 | 2.61 | 1.385 | I |
| 534.286 | lysoPE (22:2) | 3.82 × 10−18 | 2.03 | 1.1245 | I |
| 558.291 | LysoPC (21:4) | 5.62 × 10−17 | 2.17 | 1.1177 | I |
| 413.265 | 25-hydroxy vitamin D2 | 6.06 × 10−19 | 2.48 | 1.3153 | I |
| 355.358 | MG (18:2/0:0/0:0) | 1.34 × 10−18 | 0.12 | −3.0437 | D |
| 612.503 | Ceramide (d18:0/20:0 (2OH)) | 3.56 × 10−19 | 0.28 | −1.8195 | D |
| 171.140 | Decenoic acid (C10:0) | 2.40 × 10−17 | 0.04 | −4.4131 | D |
| 707.167 | PG (O-16:0/16:1) | 1.83 × 10−16 | 0.20 | −2.3198 | D |
| 163.052 | Hydroxy adipic acid | 4.27 × 10−16 | 0.21 | −2.22 | D |
| 709.164 | PG (O-16:0/16:0) | 8.98 × 10−16 | 0.20 | −2.3214 | D |
| 513.415 | PG (18:0/0:0) | 1.04 × 10−15 | 0.44 | −1.1718 | D |
| 508.459 | Ceramide (d18:2/14:0) & isom | 1.42 × 10−15 | 0.37 | −1.4338 | D |
| 339.366 | Dimethyl eicosanoic acid (C20:1) | 1.67 × 10−15 | 0.13 | −2.8875 | D |
| 415.209 | Ascorbyl palmitate | 3.74 × 10−13 | 2.50 | 1.3232 | D |
| 702.213 | PC (30:2) | 1.31 × 10−14 | 0.17 | −2.5291 | D |
| 704.210 | PC (30:1) | 6.58 × 10−15 | 0.18 | −2.4645 | D |
| 596.512 | Cer (d18:0/20:0) and isom | 2.41 × 10−13 | 0.37 | −1.3964 | D |
| 524.448 | Ceramide (d18:1/15:0) | 7.40 × 10−13 | 0.30 | −1.6999 | D |
| 568.459 | Ceramide (d18:0/18:0) | 1.37 × 10−12 | 0.35 | −1.4968 | D |
| 529.407 | Linoleyl linoleate & isomers | 1.72 × 10−14 | 0.33 | −1.5771 | D |
| 496.419 | Ceramide (d15:1/16:0) | 1.04 × 10−12 | 0.41 | −1.2777 | D |
| 149.024 | Methionine | 2.63 × 10−13 | 0.21 | −2.2327 | D |
| 249.189 | C16:4 fatty acid | 2.46 × 10−15 | 0.18 | −2.4734 | D |
| 257.204 | Palmitic acid C16:0 | 4.62 × 10−12 | 0.15 | −2.7155 | D |
| 383.207 | 16,16-dimethyl-PGE1 | 4.46 × 10−4 | 0.15 | −2.6836 | D |
| m/z | Identification | p Value (t-Tests) | Log2 FC | Variation (HC vs. C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 419.281 | 1,25 dihydroxy Cholesterol | 1.5071 × 10−33 | −2.138 | I |
| 453.165 | Myristyl palmitate | 1.4840 × 10−29 | −2.041 | I |
| 558.291 | LysoPC (21:4) | 9.5558 × 10−24 | −1.501 | I |
| 534.286 | LysoPE (22:2) | 7.8846 × 10−18 | −1.056 | I |
| 513.415 | PG (18:0/0:0) | 5.1513 × 10−28 | 0.838 | D |
| 508.459 | Ceramide (d18:2/14:0) & isom | 1.2346 × 10−32 | 1.092 | D |
| 633.147 | DG (18:3/19:0/0:0)[iso2] | 5.7123 × 10−13 | 1.113 | D |
| 612.503 | Ceramide (d18:0/20:0 (2OH)) | 2.3868 × 10−28 | 1.481 | D |
| 709.164 | PG (O-16:0/16:0) | 2.9093 × 10−34 | 1.953 | D |
| 707.167 | PG (O-16:0/16:1) | 6.0675 × 10−40 | 1.953 | D |
| 704.21 | PC (30:1) | 2.3366 × 10−43 | 2.079 | D |
| 702.213 | PC (30:2) | 2.4668 × 10−36 | 2.142 | D |
| 339.366 | Dimethyl eicosanoic acid (C20:1) | 9.6275 × 10−15 | 2.602 | D |
| 355.358 | MG (0:0/18:2/0:0) | 8.10591 × 10−19 | 2.750 | D |
| 171.14 | Decenoic acid (C10:0) | 5.9068 × 10−22 | 4.051 | D |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | HR | 95% CI | p | HR | 95%CI | p |
| Arachidonic acid | 1.56 | (0.52–4.69) | 0.429 | 12.08 | (2.95–49.93) | 0.027 |
| 1,25 dihydroxy Cholesterol | 5.29 | (1.86–15.08) | 0.002 | 10.61 | (1.37–82.3) | 0.024 |
| Myristyl palmitate | 16.67 | (2.3–120.69) | 0.005 | 31.63 | (1.51–661.66) | 0.026 |
| 12-keto deoxycholic acid | 4.96 | (1.45–17) | 0.011 | 12.98 | (1.39–121.39) | 0.025 |
| LysoPC (21:4) | 4.86 | (1.81–13.01) | 0.002 | 10.46 | (1.41–77.54) | 0.022 |
| LysoPE (22:2) | 1.54 | (1.16–2.03) | 0.002 | 2.37 | (1.07–5.24) | 0.032 |
| m/z | Identification | AUC | p-Value | HCd vs. HC | m/z | Identification | AUC | p-Value | HCd vs. HC |
| 702.213 | PC (30:2) | 0.820 | 0.027 | D | 391.283 | 12-Ketodeoxycholic acid | 0.714 | 0.064 | D |
| 704.210 | PC (30:1) | 0.807 | 0.017 | D | 413.265 | 25-hydroxy vitamin D2 | 0.692 | 0.072 | D |
| 707.167 | PG (O-16:0/16:1) | 0.804 | 0.025 | D | 273.174 | Estradiol | 0.692 | 0.061 | D |
| 709.164 | PG (O-16:0/16:0) | 0.791 | 0.025 | D | 483.121 | PG (16:1/0:0) | 0.684 | 0.064 | I |
| 509.322 | PG (18:2/0:0) | 0.772 | 0.017 | D | 501.375 | Palmitoleyl linolenate | 0.682 | 0.062 | D |
| 810.596 | PC (36:1) | 0.762 | 0.034 | I | 633.254 | PA (O-16:0/16:1) | 0.639 | 0.085 | D |
| 494.329 | LysoPC (16:1) | 0.761 | 0.017 | I | 591.150 | DG (16:0/18:3/0:0) | 0.637 | 0.127 | I |
| 414.289 | Heptadecanoyl carnitine | 0.642 | 0.046 | I | 496.342 | LysoPC (16:0) | 0.634 | 0.139 | D |
| 672.525 | GlycoCeramide (d18:1/14:0) | 0.631 | 0.160 | D | 631.144 | DG (18:4/19:0/0:0) | 0.625 | 0.240 | I |
| 784.583 | PC (36:3) | <0.600 | >0.05 | I | 310.308 | Decatrienoyl carnitine | <0.600 | >0.05 | D |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nenu, I.; Stefanescu, H.; Procopet, B.; Sparchez, Z.; Minciuna, I.; Mocan, T.; Leucuta, D.; Morar, C.; Grigorescu, M.; Filip, G.A.; et al. Navigating through the Lipid Metabolism Maze: Diagnosis and Prognosis Metabolites of Hepatocellular Carcinoma versus Compensated Cirrhosis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11051292
Nenu I, Stefanescu H, Procopet B, Sparchez Z, Minciuna I, Mocan T, Leucuta D, Morar C, Grigorescu M, Filip GA, et al. Navigating through the Lipid Metabolism Maze: Diagnosis and Prognosis Metabolites of Hepatocellular Carcinoma versus Compensated Cirrhosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(5):1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11051292
Chicago/Turabian StyleNenu, Iuliana, Horia Stefanescu, Bogdan Procopet, Zeno Sparchez, Iulia Minciuna, Tudor Mocan, Daniel Leucuta, Corina Morar, Mircea Grigorescu, Gabriela Adriana Filip, and et al. 2022. "Navigating through the Lipid Metabolism Maze: Diagnosis and Prognosis Metabolites of Hepatocellular Carcinoma versus Compensated Cirrhosis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 5: 1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11051292
APA StyleNenu, I., Stefanescu, H., Procopet, B., Sparchez, Z., Minciuna, I., Mocan, T., Leucuta, D., Morar, C., Grigorescu, M., Filip, G. A., & Socaciu, C. (2022). Navigating through the Lipid Metabolism Maze: Diagnosis and Prognosis Metabolites of Hepatocellular Carcinoma versus Compensated Cirrhosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(5), 1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11051292








