Prevalence and Factors Associated with Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Transient Ischemic Attack or Ischemic Stroke in Northern Vietnam
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
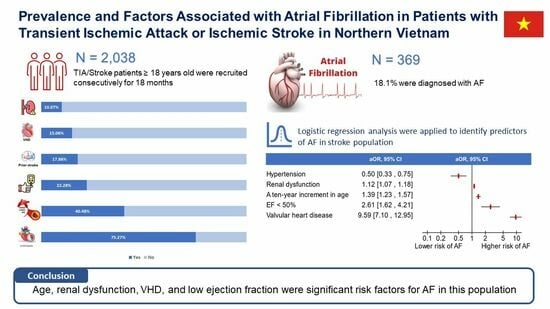
3. Results
3.1. Prevalence
3.2. Risk Factor
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolf, P.A.; Abbott, R.D.; Kannel, W.B. Atrial fibrillation as an independent risk factor for stroke: The Framingham Study. Stroke 1991, 22, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friberg, L.; Rosenqvist, M.; Lindgren, A.; Terént, A.; Norrving, B.; Asplund, K. High Prevalence of Atrial Fibrillation among Patients with Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2014, 45, 2599–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinzon, R.T.; Buwana, F. The clinical outcome comparison of ischemic stroke with and without atrial fibrillation. J. Clin. Med. Kazakhstan 2019, 2, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Tsivgoulis, G.; Teoh, H.L.; Ong, B.K.; Chan, B.P. Stroke Risk Factors and Outcomes Among Various Asian Ethnic Groups in Singapore. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2012, 21, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorasoot, N.; Khempet, W.; Kongbunkiat, K.; Kasemsap, N.; Tiamkao, S.; Sawanyawisuth, K. Does atrial fibrillation worsen stroke outcomes in acute ischemic stroke treated with rt-PA? J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2019, 102, 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- Tirschwell, D.L.; Ton, T.G.N.; Ly, K.A.; Van Ngo, Q.; Vo, T.T.; Pham, C.H.; Longstreth, W.T.; Fitzpatrick, A.L. A prospective cohort study of stroke characteristics, care, and mortality in a hospital stroke registry in Vietnam. BMC Neurol. 2012, 12, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwong, W.Y.; Aziz, Z.A.; Sidek, N.N.; Bots, M.L.; Selvarajah, S.; Kappelle, L.J.; Sivasampu, S.; Vaartjes, I. Prescription of secondary preventive drugs after ischemic stroke: Results from the Malaysian National Stroke Registry. BMC Neurol. 2017, 17, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, D.T.; Dao, X.C.; Luong, N.K.; Nguyen, T.K.; Nguyen, H.T.; Nguyen, T.N. Current State of Stroke Care in Vietnam. Stroke Vasc. Interv. Neurol. 2022, 2, e000331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.-A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, R.M.; Badano, L.P.; Mor-Avi, V.; Afilalo, J.; Armstrong, A.; Ernande, L.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Foster, E.; Goldstein, S.A.; Kuznetsova, T.; et al. Recommendations for Cardiac Chamber Quantification by Echocardiography in Adults: An Update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2015, 16, 233–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahanian, A.; Beyersdorf, F.; Praz, F.; Milojevic, M.; Baldus, S.; Bauersachs, J.; Capodanno, D.; Conradi, L.; De Bonis, M.; De Paulis, R.; et al. 2021 ESC/EACTS Guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease: Developed by the Task Force for the management of valvular heart disease of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 561–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cockcroft, D.W.; Gault, H. Prediction of Creatinine Clearance from Serum Creatinine. Nephron 1976, 16, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, H.P.; Bendixen, B.H.; Kappelle, L.J.; Biller, J.; Love, B.B.; Gordon, D.L.; Marsh, E.E. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke 1993, 24, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, B.H.; Hill, M.D.; Quinn, F.R.; Butcher, K.S.; Menon, B.K.; Gulamhusein, S.; Siddiqui, M.; Coutts, S.B.; Jeerakathil, T.; Smith, E.E.; et al. Effect of Implantable vs. Prolonged External Electrocardiographic Monitoring on Atrial Fibrillation Detection in Patients With Ischemic Stroke. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2021, 325, 2160–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhouli, M.; Alqahtani, F.; Aljohani, S.; Alvi, M.; Holmes, D.R. Burden of Atrial Fibrillation–Associated Ischemic Stroke in the United States. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2018, 4, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otite, F.O.; Khandelwal, P.; Chaturvedi, S.; Romano, J.G.; Sacco, R.L.; Malik, A.M. Increasing atrial fibrillation prevalence in acute ischemic stroke and TIA. Neurology 2016, 87, 2034–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, T.D.; Phuong, D.V.V.; Tien, D.N.; Nguyen, H.T.; Tran, C.C.; Duong, H.Q.; Nguyen, H.N.; Nguyen, S.H.; Bui, H.T.; Dang, D.P.; et al. Sex disparity in stroke outcomes in a multicenter prospective stroke registry in Viet Nam. Int. J. Stroke 2023. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodani, E.; Atarashi, H. Prevalence of atrial fibrillation in Asia and the world. J. Arrhythmia 2012, 28, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, S.E.; Shroff, G.R.; Li, S.; Herzog, C.A. Impact of Chronic Kidney Disease on Risk of Incident Atrial Fibrillation and Subsequent Survival in Medicare Patients. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2012, 1, e002097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lip, G.Y.H.; Jensen, M.; Melgaard, L.; Skjøth, F.; Nielsen, P.B.; Larsen, T.B. Stroke and bleeding risk scores in patients with atrial fibrillation and valvular heart disease: Evaluating ‘valvular heart disease’ in a nationwide cohort study. EP Eur. 2019, 21, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wańkowicz, P.; Staszewski, J.; Dębiec, A.; Nowakowska-Kotas, M.; Szylińska, A.; Rotter, I. Ischemic Stroke Risk Factors in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Treated with New Oral Anticoagulants. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladiran, O.; Nwosu, I. Stroke risk stratification in atrial fibrillation: A review of common risk factors. J. Community Hosp. Intern. Med. Perspect. 2019, 9, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdecchia, P.; Angeli, F.; Reboldi, G. Hypertension and Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 352–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poh, M.Q.W.; Tham, C.H.; Chee, J.D.M.S.; Saffari, S.E.; Tan, K.W.K.; Tan, L.W.; Ng, E.Y.; Yeo, C.P.X.; Seet, C.Y.H.; Xie, J.P.; et al. Predicting Atrial Fibrillation after Ischemic Stroke: Clinical, Genetics, and Electrocardiogram Modelling. Cerebrovasc. Dis. Extra 2022, 13, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Overall (n = 2038) | Atrial Fibrillation (AF) | p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without AF (n = 1669) | With AF (n = 369) | ||||||
| /n | SD/% | /n | SD/% | /n | SD/% | ||
| Age (years) | 65.7 | 12.6 | 64.8 | 12.6 | 69.7 | 12.1 | <0.0001 |
| Male gender, n (%) | 1324 | 64.97 | 1124 | 67.35 | 200 | 54.20 | <0.001 |
| HTN, n (%) | 1534 | 75.27 | 1298 | 77.77 | 236 | 63.96 | <0.001 |
| Hyperlipidemia, n (%) | 825 | 40.48 | 662 | 39.66 | 163 | 44.17 | 0.110 |
| Smoking, n (%) | 51 | 2.50 | 43 | 2.58 | 8 | 2.17 | 0.854 |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 454 | 22.28 | 392 | 23.49 | 62 | 16.80 | 0.005 |
| IHD, n (%) | 99 | 4.86 | 71 | 4.25 | 28 | 7.59 | 0.007 |
| PVD, n (%) | 144 | 7.07 | 113 | 6.77 | 31 | 8.40 | 0.269 |
| CKD (eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2), n (%) | 218 | 10.70 | 156 | 9.35 | 62 | 16.80 | <0.001 |
| Gout, n (%) | 67 | 3.29 | 59 | 3.54 | 8 | 2.17 | 0.257 |
| Previous stroke, n (%) | 364 | 17.86 | 285 | 17.08 | 79 | 21.41 | 0.049 |
| Drugs | |||||||
| Antiplatelet, n (%) | 179 | 8.78 | 153 | 9.17 | 26 | 7.05 | 0.193 |
| Antihypertension, n (%) | 1152 | 56.53 | 967 | 57.94 | 185 | 50.14 | 0.006 |
| Statin, n (%) | 80 | 3.93 | 64 | 3.83 | 16 | 4.34 | 0.654 |
| OAC, n (%) | 124 | 6.08 | 34 | 2.10 | 89 | 24.12 | <0.001 |
| VHD, n (%) | 307 | 15.06 | 121 | 7.25 | 186 | 50.41 | <0.001 |
| eGFR (ml/min/1.73 m2), ± SD | 93.1 | 30.0 | 95.6 | 30.4 | 81.9 | 25.0 | <0.0001 |
| Glucose, median (IQR) (n = 1463) | 7.1 | 5.9–8.9 | 7.1 | 5.8–9.0 | 7.1 | 6.2–8.5 | 0.4909 |
| Cholesterol, median (IQR) (n = 1692) | 4.7 | 4.0–5.4 | 4.8 | 4.1–5.5 | 4.4 | 3.7–5.2 | <0.0001 |
| Triglycerid, median (IQR) (n = 1687) | 1.7 | 1.2–2.5 | 1.8 | 1.2–2.6 | 1.2 | 1.0–1.7 | <0.0001 |
| HDL, median (IQR) (n = 1666) | 1.1 | 0.9–1.3 | 1.1 | 0.9–1.3 | 1.2 | 1.0–1.4 | <0.0001 |
| LDL, median (IQR) (n = 1685) | 2.8 | 2.2–3.5 | 2.9 | 2.3–3.5 | 2.6 | 2.0–3.3 | 0.0003 |
| EF ≤ 40%, n (%) | 45 | 2.21 | 23 | 1.38 | 22 | 5.96 | <0.001 |
| EF 41–49% | 74 | 3.63 | 30 | 1.80 | 44 | 11.92 | |
| Total n = 2038 | Univariate | Multivariate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted OR | CI 95% | p | Adjusted OR | CI 95% | p-Value | |
| Age (per 10 years) | 1.40 | 1.27–1.54 | <0.001 | 1.39 | 1.23–1.57 | <0.001 |
| Male sex | 0.57 | 0.46–0.72 | <0.001 | 0.79 | 0.60–1.05 | 0.106 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.66 | 0.49–0.88 | 0.005 | 0.81 | 0.57–1.15 | 0.236 |
| Hypertension | 0.51 | 0.40–0.65 | <0.001 | 0.50 | 0.33–0.74 | 0.001 |
| Coronary artery disease | 1.85 | 1.18–2.91 | 0.008 | 1.12 | 0.64–1.95 | 0.694 |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 1.26 | 0.83–1.91 | 0.270 | - | - | - |
| eGFR decrease (per 10 mL/min/1.73 m2) | 1.19 | 1.14–1.24 | <0.001 | 1.12 | 1.06–1.17 | <0.001 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 1.20 | 0.96–1.51 | 0.111 | - | - | - |
| Hypertension treatment | 0.73 | 0.58–0.92 | 0.006 | 0.99 | 0.69–1.43 | 0.953 |
| Valvular heart disease | 13.00 | 9.87–17.13 | <0.001 | 9.59 | 7.10–12.95 | <0.001 |
| EF < 50% | 6.64 | 4.53–9.73 | <0.001 | 2.61 | 1.62–4.21 | <0.001 |
| BMI (per 1 kg/m2) | 0.94 | 0.89–0.98 | 0.009 | 1.04 | 0.98–1.09 | 0.221 |
| Smoking | 0.84 | 0.39–1.80 | 0.650 | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Phong, P.D.; Tung, B.N.; Hung, P.M.; Quang, N.N.; Hoai, N.T.T.; Dung, N.V.; Nguyen, T.N.; Phuong, D.V.; Ton, M.D. Prevalence and Factors Associated with Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Transient Ischemic Attack or Ischemic Stroke in Northern Vietnam. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5516. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175516
Phong PD, Tung BN, Hung PM, Quang NN, Hoai NTT, Dung NV, Nguyen TN, Phuong DV, Ton MD. Prevalence and Factors Associated with Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Transient Ischemic Attack or Ischemic Stroke in Northern Vietnam. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(17):5516. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175516
Chicago/Turabian StylePhong, Phan Dinh, Bui Nguyen Tung, Pham Manh Hung, Nguyen Ngoc Quang, Nguyen Thi Thu Hoai, Nguyen Viet Dung, Thanh N. Nguyen, Dao Viet Phuong, and Mai Duy Ton. 2023. "Prevalence and Factors Associated with Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Transient Ischemic Attack or Ischemic Stroke in Northern Vietnam" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 17: 5516. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175516
APA StylePhong, P. D., Tung, B. N., Hung, P. M., Quang, N. N., Hoai, N. T. T., Dung, N. V., Nguyen, T. N., Phuong, D. V., & Ton, M. D. (2023). Prevalence and Factors Associated with Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Transient Ischemic Attack or Ischemic Stroke in Northern Vietnam. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(17), 5516. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175516