Renal Denervation as a Complementary Treatment Option for Uncontrolled Arterial Hypertension: A Situation Assessment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
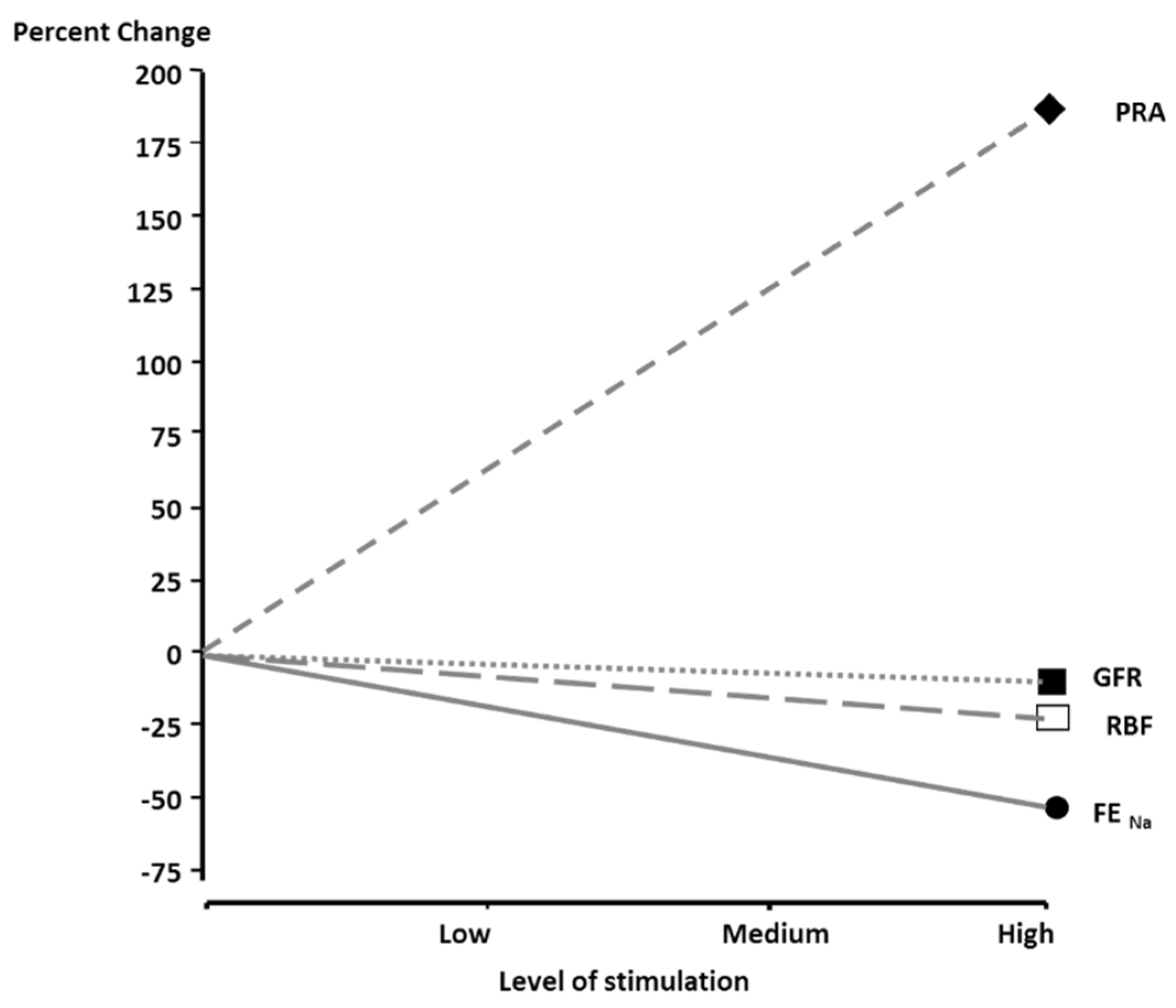
2. Rationale for Renal Denervation in Hypertension
3. Renal Denervation—State of the Evidence
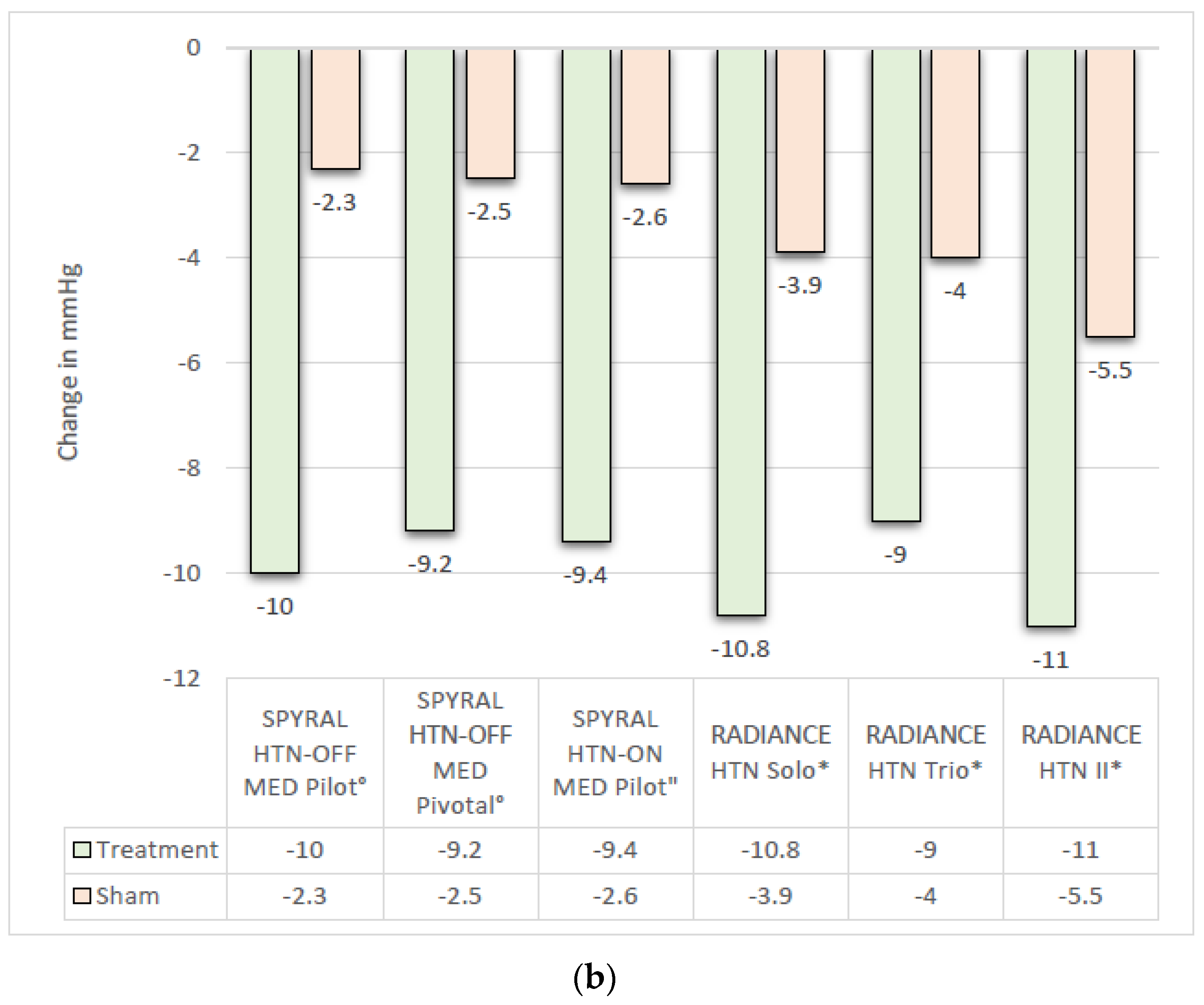
3.1. Efficacy
3.2. Neutral Trials
3.3. Safety of Renal Denervation Procedures
3.4. Influence of Ethnicity
4. Long-Term Effects of Renal Denervation
5. Cardiovascular Outcomes after RDN
6. Cost-Effectiveness of Renal Denervation
7. Where Does Renal Denervation Fit in the Antihypertensive Treatment Toolkit?
8. Consensus Points
8.1. Point 1
8.2. Point 2
8.3. Point 3
8.4. Point 4
8.5. Point 5
8.6. Point 6
9. Open Questions
10. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: A pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet 2021, 398, 957–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, M.H.; Angell, S.Y.; Asma, S.; Boutouyrie, P.; Burger, D.; Chirinos, J.A.; Damasceno, A.; Delles, C.; Gimenez-Roqueplo, A.-P.; Hering, D.; et al. A call to action and a lifecourse strategy to address the global burden of raised blood pressure on current and future generations: The Lancet Commission on hypertension. Lancet 2016, 388, 2665–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettehad, D.; Emdin, C.A.; Kiran, A.; Anderson, S.G.; Callender, T.; Emberson, J.; Chalmers, J.; Rodgers, A.; Rahimi, K. Blood pressure lowering for prevention of cardiovascular disease and death: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2016, 387, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandzari, D.E.; Townsend, R.R.; Bakris, G.; Basile, J.; Bloch, M.J.; Cohen, D.L.; East, C.; Ferdinand, K.C.; Fisher, N.; Kirtane, A.; et al. Renal denervation in hypertension patients: Proceedings from an expert consensus roundtable cosponsored by SCAI and NKF. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2021, 98, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaschke, T.F.; Osterberg, L.; Vrijens, B.; Urquhart, J. Adherence to medications: Insights arising from studies on the unreliable link between prescribed and actual drug dosing histories. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 52, 275–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visseren, F.L.J.; Mach, F.; Smulders, Y.M.; Carballo, D.; Koskinas, K.C.; Bäck, M.; Benetos, A.; Biffi, A.; Boavida, J.-M.; Capodanno, D.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2022, 29, 5–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Addolorato, G.; Ammirati, E.; Baddour, L.M.; Barengo, N.C.; Beaton, A.; Benjamin, E.J.; Benziger, C.P.; et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019: Update From the GBD 2019 Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; de Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2018, 36, 1953–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, R.R.; Mahfoud, F.; Kandzari, D.E.; Kario, K.; Pocock, S.; Weber, M.A.; Ewen, S.; Tsioufis, K.; Tousoulis, D.; Sharp, A.S.P.; et al. Catheter-based renal denervation in patients with uncontrolled hypertension in the absence of antihypertensive medications (SPYRAL HTN-OFF MED): A randomised, sham-controlled, proof-of-concept trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 2160–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfoud, F.; Weber, M.; Schmieder, R.E.; Lobo, M.D.; Blankestijn, P.J.; Persu, A.; Fischell, T.A.; Parise, H.; Pathak, A.; Kandzari, D.E. Catheter-based alcohol-mediated renal denervation for the treatment of uncontrolled hypertension: Design of two sham-controlled, randomized, blinded trials in the absence (TARGET BP OFF-MED) and presence (TARGET BP I) of antihypertensive medications. Am. Heart J. 2021, 239, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, M.; Schmieder, R.E.; Mahfoud, F.; Weber, M.A.; Daemen, J.; Davies, J.; Basile, J.; Kirtane, A.J.; Wang, Y.; Lobo, M.D.; et al. Endovascular ultrasound renal denervation to treat hypertension (RADIANCE-HTN SOLO): A multicentre, international, single-blind, randomised, sham-controlled trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 2335–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahfoud, F.; Azizi, M.; Ewen, S.; Pathak, A.; Ukena, C.; Blankestijn, P.J.; Böhm, M.; Burnier, M.; Chatellier, G.; Durand Zaleski, I.; et al. Proceedings from the 3rd European Clinical Consensus Conference for clinical trials in device-based hypertension therapies. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 1588–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmieder, R.E.; Mahfoud, F.; Mancia, G.; Azizi, M.; Böhm, M.; Dimitriadis, K.; Kario, K.; Kroon, A.A.; D Lobo, M.; Ott, C.; et al. European Society of Hypertension position paper on renal denervation 2021. J. Hypertens 2021, 39, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kario, K.; Kim, B.-K.; Aoki, J.; Wong, A.Y.-T.; Lee, Y.-H.; Wongpraparut, N.; Nguyen, Q.N.; Ahmad, W.A.W.; Lim, S.T.; Ong, T.K.; et al. Renal Denervation in Asia: Consensus Statement of the Asia Renal Denervation Consortium. Hypertension 2020, 75, 590–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, M.D.; Sharp, A.S.P.; Kapil, V.; Davies, J.; de Belder, M.A.; Cleveland, T.; Bent, C.; Chapman, N.; Dasgupta, I.; Levy, T.; et al. Joint UK societies’ 2019 consensus statement on renal denervation. Heart 2019, 105, 1456–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbato, E.; Azizi, M.; Schmieder, R.E.; Lauder, L.; Böhm, M.; Brouwers, S.; Bruno, R.M.; Dudek, D.; Kahan, T.; Kandzari, D.E.; et al. Renal denervation in the management of hypertension in adults. A clinical consensus statement of the ESC Council on Hypertension and the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI). Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 1313–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, J.W.; Tyshynsky, R.; Vulchanova, L. Function of Renal Nerves in Kidney Physiology and Pathophysiology. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2021, 83, 429–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiBona, G.F.; Esler, M. Translational medicine: The antihypertensive effect of renal denervation. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2010, 298, R245–R253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esler, M.; Jennings, G.; Korner, P.; Willett, I.; Dudley, F.; Hasking, G.; Anderson, W.; Lambert, G. Assessment of human sympathetic nervous system activity from measurements of norepinephrine turnover. Hypertension 1988, 11, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumantir, M.S.; Vaz, M.; Jennings, G.L.; Collier, G.; Kaye, D.M.; Seals, D.R.; Wiesner, G.H.; Brunner-La Rocca, H.P.; Esler, M.D. Neural mechanisms in human obesity-related hypertension. J. Hypertens. 1999, 17, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, E.J.; Kopp, U.C.; DiBona, G.F. Neural control of renal function. Compr. Physiol. 2011, 1, 731–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandzari, D.E.; Böhm, M.; Mahfoud, F.; Townsend, R.R.; Weber, M.A.; Pocock, S.; Tsioufis, K.; Tousoulis, D.; Choi, J.W.; East, C.; et al. Effect of renal denervation on blood pressure in the presence of antihypertensive drugs: 6-month efficacy and safety results from the SPYRAL HTN-ON MED proof-of-concept randomised trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 2346–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhm, M.; Kario, K.; Kandzari, D.E.; Mahfoud, F.; Weber, M.A.; Schmieder, R.E.; Tsioufis, K.; Pocock, S.; Konstantinidis, D.; Choi, J.W.; et al. Efficacy of catheter-based renal denervation in the absence of antihypertensive medications (SPYRAL HTN-OFF MED Pivotal): A multicentre, randomised, sham-controlled trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 1444–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, M.; Daemen, J.; Lobo, M.D.; Mahfoud, F.; Sharp, A.S.P.; Schmieder, R.E.; Wang, Y.; Saxena, M.; Lurz, P.; Sayer, J.; et al. 12-Month Results From the Unblinded Phase of the RADIANCE-HTN SOLO Trial of Ultrasound Renal Denervation. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2020, 13, 2922–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, M.; Sanghvi, K.; Saxena, M.; Gosse, P.; Reilly, J.P.; Levy, T.; Rump, L.C.; Persu, A.; Basile, J.; Bloch, M.J.; et al. Ultrasound renal denervation for hypertension resistant to a triple medication pill (RADIANCE-HTN TRIO): A randomised, multicentre, single-blind, sham-controlled trial. Lancet 2021, 297, 2476–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfoud, F.; Kandzari, D.E.; Kario, K.; Townsend, R.R.; Weber, M.A.; Schmieder, R.E.; Tsioufis, K.; Pocock, S.; Dimitriadis, K.; Choi, J.W.; et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of renal denervation in the presence of antihypertensive drugs (SPYRAL HTN-ON MED): A randomised, sham-controlled trial. Lancet 2022, 399, 1401–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kario, K.; Mahfoud, F.; Kandzari, D.E.; Townsend, R.R.; Weber, M.A.; Schmieder, R.E.; Tsioufis, K.; Pocock, S.; Brar, S.; Hettrick, D.A.; et al. Long-term reduction in morning and nighttime blood pressure after renal denervation: 36-month results from SPYRAL HTN-ON MED trial. Hypertens. Res. 2023, 46, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, M.; Fahy, M.; Hickey, G.L.; Pocock, S.; Brar, S.; DeBruin, V.; Weber, M.A.; Mahfoud, F.; Kandzari, D.E. A re-examination of the SPYRAL HTN-OFF MED Pivotal trial with respect to the underlying model assumptions. Contemp. Clin. Trials Commun. 2021, 23, 100818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, M.; Townsend, R.R.; Kario, K.; Kandzari, D.; Mahfoud, F.; Weber, M.A.; Schmieder, R.E.; Tsioufis, K.; Hickey, G.L.; Fahy, M.; et al. Rationale and design of two randomized sham-controlled trials of catheter-based renal denervation in subjects with uncontrolled hypertension in the absence (SPYRAL HTN-OFF MED Pivotal) and presence (SPYRAL HTN-ON MED Expansion) of antihypertensive medications: A novel approach using Bayesian design. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2020, 109, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, M.; Saxena, M.; Wang, Y.; Jenkins, J.S.; Devireddy, C.; Rader, F.; Fisher, N.D.L.; Schmieder, R.E.; Mahfoud, F.; Lindsey, J.; et al. Endovascular Ultrasound Renal Denervation to Treat Hypertension: The RADIANCE II Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2023, 329, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirtane, A.J.; Sharp, A.S.P.; Mahfoud, F.; Fisher, N.D.L.; Schmieder, R.E.; Daemen, J.; Lobo, M.D.; Lurz, P.; Basile, J.; Bloch, M.J.; et al. Patient-Level Pooled Analysis of Ultrasound Renal Denervation in the Sham-Controlled RADIANCE II, RADIANCE-HTN SOLO, and RADIANCE-HTN TRIO Trials. JAMA Cardiol. 2023, 8, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, M.; Schmieder, R.E.; Mahfoud, F.; Weber, M.A.; Daemen, J.; Lobo, M.D.; Sharp, A.S.P.; Bloch, M.J.; Basile, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Six-Month Results of Treatment-Blinded Medication Titration for Hypertension Control After Randomization to Endovascular Ultrasound Renal Denervation or a Sham Procedure in the RADIANCE-HTN SOLO Trial. Circulation 2019, 139, 2542–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahfoud, F.; Renkin, J.; Sievert, H.; Bertog, S.; Ewen, S.; Böhm, M.; Lengelé, J.-P.; Wojakowski, W.; Schmieder, R.; van der Giet, M.; et al. Alcohol-Mediated Renal Denervation Using the Peregrine System Infusion Catheter for Treatment of Hypertension. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2020, 13, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertog, S.; Sharma, A.; Mahfoud, F.; Pathak, A.; Schmieder, R.E.; Sievert, K.; Papademetriou, V.; Weber, M.A.; Haratani, N.; Lobo, M.D.; et al. Alcohol-Mediated Renal Sympathetic Neurolysis for the Treatment of Hypertension: The PeregrineTM Infusion Catheter. Cardiovasc. Revasc Med. 2021, 24, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, M. Catheter-based renal denervation for treatment of hypertension. Lancet 2017, 390, 2124–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kario, K.; Bhatt, D.L.; Kandzari, D.E.; Brar, S.; Flack, J.M.; Gilbert, C.; Oparil, S.; Robbins, M.; Townsend, R.R.; Bakris, G. Impact of Renal Denervation on Patients With Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Resistant Hypertension—Insights From the SYMPLICITY HTN-3 Trial. Circ. J. 2016, 80, 1404–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.W.; Li, Y.; Boggia, J.; Thijs, L.; Richart, T.; Staessen, J.A. Predictive role of the nighttime blood pressure. Hypertension 2011, 57, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancia, G. Short- and long-term blood pressure variability: Present and future. Hypertension 2012, 60, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, D.L.; Kandzari, D.E.; O’Neill, W.W.; D’Agostino, R.; Flack, J.M.; Katzen, B.T.; Leon, M.B.; Liu, M.; Mauri, L.; Negoita, M.; et al. A Controlled Trial of Renal Denervation for Resistant Hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1393–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krum, H.; Schlaich, M.; Whitbourn, R.; Sobotka, P.A.; Sadowski, J.; Bartus, K.; Kapelak, B.; Walton, A.; Sievert, H.; Thambar, S.; et al. Catheter-based renal sympathetic denervation for resistant hypertension: A multicentre safety and proof-of-principle cohort study. Lancet 2009, 373, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esler, M. Renal sympathetic denervation in patients with treatment-resistant hypertension (The Symplicity HTN-2 Trial): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 1903–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persu, A.; Jin, Y.; Azizi, M.; Baelen, M.; Völz, S.; Elvan, A.; Severino, F.; Rosa, J.; Adiyaman, A.; Fadl Elmula, F.E.; et al. Blood pressure changes after renal denervation at 10 European expert centers. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2014, 28, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worthley, S.G.; Tsioufis, C.P.; Worthley, M.I.; Sinhal, A.; Chew, D.P.; Meredith, I.T.; Malaiapan, Y.; Papademetriou, V. Safety and efficacy of a multi-electrode renal sympathetic denervation system in resistant hypertension: The EnligHTN I trial. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 2132–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfoud, F.; Ukena, C.; Schmieder, R.E.; Cremers, B.; Rump, L.C.; Vonend, O.; Weil, J.; Schmidt, M.; Hoppe, U.C.; Zeller, T.; et al. Ambulatory Blood Pressure Changes After Renal Sympathetic Denervation in Patients With Resistant Hypertension. Circulation 2013, 128, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, C.; Mahfoud, F.; Schmid, A.; Ditting, T.; Sobotka, P.A.; Veelken, R.; Spies, A.; Ukena, C.; Laufs, U.; Uder, M.; et al. Renal denervation in moderate treatment-resistant hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 1880–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, M.; Sapoval, M.; Gosse, P.; Monge, M.; Bobrie, G.; Delsart, P.; Midulla, M.; Mounier-Véhier, C.; Courand, P.-Y.; Lantelme, P.; et al. Optimum and stepped care standardised antihypertensive treatment with or without renal denervation for resistant hypertension (DENERHTN): A multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 1957–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandzari, D.E.; Bhatt, D.L.; Brar, S.; Devireddy, C.M.; Esler, M.; Fahy, M.; Flack, J.M.; Katzen, B.T.; Lea, J.; Lee, D.P.; et al. Predictors of blood pressure response in the SYMPLICITY HTN-3 trial. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahfoud, F.; Böhm, M.; Azizi, M.; Pathak, A.; Durand Zaleski, I.; Ewen, S.; Tsioufis, K.; Andersson, B.; Blankestijn, P.J.; Burnier, M.; et al. Proceedings from the European clinical consensus conference for renal denervation: Considerations on future clinical trial design. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 2219–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.A.; Kirtane, A.J.; Weir, M.R.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Das, T.; Berk, M.; Mendelsohn, F.; Bouchard, A.; Larrain, G.; Haase, M.; et al. The REDUCE HTN: REINFORCE: Randomized, Sham-Controlled Trial of Bipolar Radiofrequency Renal Denervation for the Treatment of Hypertension. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2020, 13, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kario, K.; Yokoi, Y.; Okamura, K.; Fujihara, M.; Ogoyama, Y.; Yamamoto, E.; Urata, H.; Cho, J.-M.; Kim, C.-J.; Choi, S.-H.; et al. Catheter-based ultrasound renal denervation in patients with resistant hypertension: The randomized, controlled REQUIRE trial. Hypertens. Res. 2022, 45, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmieder, R.E.; Bosch, A. Editorial comment: Renal denervation. Hypertens. Res. 2022, 45, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SPYRAL HTN-ON MED: Renal Denervation in the Presence of Anti-Hypertensive Medications. Available online: https://www.acc.org/latest-in-cardiology/articles/2022/11/01/22/00/http%3a%2f%2fwww.acc.org%2flatest-in-cardiology%2farticles%2f2022%2f11%2f01%2f22%2f00%2fmon-5pm-spyral-htn-on-aha-2022 (accessed on 19 January 2023).
- Mahfoud, F.; Böhm, M.; Schmieder, R.; Narkiewicz, K.; Ewen, S.; Ruilope, L.; Schlaich, M.; Williams, B.; Fahy, M.; Mancia, G. Effects of renal denervation on kidney function and long-term outcomes: 3-year follow-up from the Global SYMPLICITY Registry. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 3474–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, M.F.; Reitsma, J.B.; Morpey, M.; Gremmels, H.; Bots, M.L.; Pisano, A.; Bolignano, D.; Zoccali, C.; Blankestijn, P.J. Renal safety of catheter-based renal denervation: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 1440–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templin, C.; Jaguszewski, M.; Ghadri, J.R.; Sudano, I.; Gaehwiler, R.; Hellermann, J.P.; Schoenenberger-Berzins, R.; Landmesser, U.; Erne, P.; Noll, G.; et al. Vascular lesions induced by renal nerve ablation as assessed by optical coherence tomography: Pre- and post-procedural comparison with the Simplicity catheter system and the EnligHTN multi-electrode renal denervation catheter. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 2141–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rippy, M.K.; Zarins, D.; Barman, N.C.; Wu, A.; Duncan, K.L.; Zarins, C.K. Catheter-based renal sympathetic denervation: Chronic preclinical evidence for renal artery safety. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2011, 100, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakakura, K.; Tunev, S.; Yahagi, K.; O’Brien, A.J.; Ladich, E.; Kolodgie, F.D.; Melder, R.J.; Joner, M.; Virmani, R. Comparison of histopathologic analysis following renal sympathetic denervation over multiple time points. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2015, 8, e001813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, R.R.; Walton, A.; Hettrick, D.A.; Hickey, G.L.; Weil, J.; Sharp, A.S.P.; Blankestijn, P.J.; Böhm, M.; Mancia, G. Review and meta-analysis of renal artery damage following percutaneous renal denervation with radiofrequency renal artery ablation. EuroIntervention 2020, 16, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safian, R.D.; Textor, S.C. Renal-artery stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caps, M.T.; Perissinotto, C.; Zierler, R.E.; Polissar, N.L.; Bergelin, R.O.; Tullis, M.J.; Cantwell-Gab, K.; Davidson, R.C.; Strandness, D.E. Prospective study of atherosclerotic disease progression in the renal artery. Circulation 1998, 98, 2866–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawicki, P.T.; Kaiser, S.; Heinemann, L.; Frenzel, H.; Berger, M. Prevalence of renal artery stenosis in diabetes mellitus--an autopsy study. J. Intern. Med. 1991, 229, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mast, Q.; Beutler, J.J. The prevalence of atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis in risk groups: A systematic literature review. J. Hypertens. 2009, 27, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, D.L.; Vaduganathan, M.; Kandzari, D.E.; Leon, M.B.; Rocha-Singh, K.; Townsend, R.R.; Katzen, B.T.; Oparil, S.; Brar, S.; DeBruin, V.; et al. Long-term outcomes after catheter-based renal artery denervation for resistant hypertension: Final follow-up of the randomised SYMPLICITY HTN-3 Trial. Lancet 2022, 400, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.-K.; Kim, H.-S.; Park, S.-J.; Park, C.G.; Seung, K.B.; Gwon, H.-C.; Choi, D.-J.; Ahn, T.H.; Kim, C.J.; Kwon, H.M.; et al. Long-term outcomes after renal denervation in an Asian population: Results from the Global SYMPLICITY Registry in South Korea (GSR Korea). Hypertens. Res. 2021, 44, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kario, K.; Yamamoto, E.; Tomita, H.; Okura, T.; Saito, S.; Ueno, T.; Yasuhara, D.; Shimada, K. SYMPLICITY HTN-Japan Investigators Sufficient and Persistent Blood Pressure Reduction in the Final Long-Term Results from SYMPLICITY HTN-Japan—Safety and Efficacy of Renal Denervation at 3 Years. Circ. J. 2019, 83, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juknevičius, V.; Berūkštis, A.; Juknevičienė, R.; Jasiūnas, E.; Šerpytis, P.; Laucevičius, A. Long-Term Effects of Renal Artery Denervation. Medicina 2021, 57, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists’ Collaboration Pharmacological blood pressure lowering for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease across different levels of blood pressure: An individual participant-level data meta-analysis. Lancet 2021, 397, 1625–1636. [CrossRef]
- Schmieder, R.E.; Mahfoud, F.; Mancia, G.; Narkiewicz, K.; Ruilope, L.; Hutton, D.; Cao, K.; Hettrick, D.A.; Fahy, M.; Schlaich, M.P.; et al. Clinical Event Reductions in High-Risk Patients After Renal Denervation Projected from the Global SYMPLICITY Registry. Eur. Heart J. Qual. Care Clin. Outcomes 2022, qcac056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisler, B.P.; Egan, B.M.; Cohen, J.T.; Garner, A.M.; Akehurst, R.L.; Esler, M.D.; Pietzsch, J.B. Cost-effectiveness and clinical effectiveness of catheter-based renal denervation for resistant hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, E.K.; Reid, C.M.; Zomer, E.; Kelly, D.J.; Liew, D. Cost-Effectiveness of Renal Denervation Therapy for Treatment-Resistant Hypertension: A Best Case Scenario. Am. J. Hypertens. 2018, 31, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, T.L.; De Brouwer, B.F.E.; Van Keep, M.M.L.; Blankestijn, P.J.; Bots, M.L.; Koffijberg, H. Cost-effectiveness of renal denervation therapy for the treatment of resistant hypertension in The Netherlands. J. Med. Econ. 2015, 18, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahfoud, F.; Mancia, G.; Schmieder, R.; Narkiewicz, K.; Ruilope, L.; Schlaich, M.; Whitbourn, R.; Zirlik, A.; Zeller, T.; Stawowy, P.; et al. Renal Denervation in High-Risk Patients With Hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 2879–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.; Leong, K.M.W.; Houlder, S.; Getov, S.; Lee, R.; Rajkumar, C. The relationship between dipping profile in blood pressure and neurologic deficit in early acute ischemic stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2011, 20, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, G.L.; Bailey, K.R.; Mosley, T.; Knopman, D.S.; Jack, C.R.; Canzanello, V.J.; Turner, S.T. Association of ambulatory blood pressure with ischemic brain injury. Hypertension 2007, 49, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkubo, T.; Imai, Y.; Tsuji, I.; Nagai, K.; Watanabe, N.; Minami, N.; Kato, J.; Kikuchi, N.; Nishiyama, A.; Aihara, A.; et al. Relation between nocturnal decline in blood pressure and mortality. The Ohasama Study. Am. J. Hypertens. 1997, 10, 1201–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kario, K.; Pickering, T.G.; Umeda, Y.; Hoshide, S.; Hoshide, Y.; Morinari, M.; Murata, M.; Kuroda, T.; Schwartz, J.E.; Shimada, K. Morning surge in blood pressure as a predictor of silent and clinical cerebrovascular disease in elderly hypertensives: A prospective study. Circulation 2003, 107, 1401–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Thijs, L.; Hansen, T.W.; Kikuya, M.; Boggia, J.; Richart, T.; Metoki, H.; Ohkubo, T.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Kuznetsova, T.; et al. Prognostic value of the morning blood pressure surge in 5645 subjects from 8 populations. Hypertension 2010, 55, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.E.; Ritchey, M.D.; Park, S.; Chang, A.; Odom, E.C.; Durthaler, J.; Jackson, S.L.; Loustalot, F. National Rates of Nonadherence to Antihypertensive Medications Among Insured Adults With Hypertension, 2015. Hypertension 2019, 74, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnier, M.; Egan, B.M. Adherence in Hypertension: A Review of Prevalence, Risk Factors, Impact, and Management. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 1124–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, M.N.; Miller, N.H.; DeGeest, S. Adherence and persistence with taking medication to control high blood pressure. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2011, 5, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnier, M. Drug adherence in hypertension. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 125, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Food and Drug Administration. Factors to Consider When Making Benefit-Risk Determinations in Medical Device Premarket Approval and De Novo Classifications; US Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2019.
- Schmieder, R.E.; Kandzari, D.E.; Wang, T.-D.; Lee, Y.-H.; Lazarus, G.; Pathak, A. Differences in patient and physician perspectives on pharmaceutical therapy and renal denervation for the management of hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2021, 39, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmieder, R.E.; Högerl, K.; Jung, S.; Bramlage, P.; Veelken, R.; Ott, C. Patient preference for therapies in hypertension: A cross-sectional survey of German patients. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2019, 108, 1331–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandzari, D.E.; Weber, M.A.; Poulos, C.; Coulter, J.; Cohen, S.A.; DeBruin, V.; Jones, D.; Pathak, A. Patient Preferences for Pharmaceutical and Device-Based Treatments for Uncontrolled Hypertension: Discrete Choice Experiment. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2023, 16, e008997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M.; Aronow, W.S.; Casey, D.E.; Collins, K.J.; Dennison Himmelfarb, C.; DePalma, S.M.; Gidding, S.; Jamerson, K.A.; Jones, D.W.; et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2018, 138, e426–e483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, A.; Kanukula, R.; Atkins, E.; Wang, X.; Islam, S.; Kishore, S.P.; Jaffe, M.G.; Patel, A.; Rodgers, A. Efficacy and safety of dual combination therapy of blood pressure-lowering drugs as initial treatment for hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Hypertens. 2019, 37, 1768–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhm, M.; Mahfoud, F.; Townsend, R.R.; Kandzari, D.E.; Pocock, S.; Ukena, C.; Weber, M.A.; Hoshide, S.; Patel, M.; Tyson, C.C.; et al. Ambulatory heart rate reduction after catheter-based renal denervation in hypertensive patients not receiving anti-hypertensive medications: Data from SPYRAL HTN-OFF MED, a randomized, sham-controlled, proof-of-concept trial. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosse, P.; Cremer, A.; Kirtane, A.J.; Lobo, M.D.; Saxena, M.; Daemen, J.; Wang, Y.; Stegbauer, J.; Weber, M.A.; Abraham, J.; et al. Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring to Predict Response to Renal Denervation: A Post Hoc Analysis of the RADIANCE-HTN SOLO Study. Hypertension 2021, 77, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilder, J. Basimetric approach (law of initial value) to biological rhythms. Ann. N. Y Acad. Sci. 1962, 98, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfoud, F.; Townsend, R.R.; Kandzari, D.E.; Kario, K.; Schmieder, R.E.; Tsioufis, K.; Pocock, S.; David, S.; Patel, K.; Rao, A.; et al. Changes in Plasma Renin Activity After Renal Artery Sympathetic Denervation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 2909–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, M.; Schmieder, R.E.; Kirtane, A.J.; Mahfoud, F.; Daemen, J.; Basile, J.; Lurz, P.; Gosse, P.; Sanghvi, K.; Fisher, N.D.L.; et al. Predictors of blood pressure response to ultrasound renal denervation in the RADIANCE-HTN SOLO study. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2022, 36, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Chen, W.; Lai, Y.; Du, H.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Ling, Z.; Fan, J.; Xiao, P.; Zhang, B.; et al. Selective Renal Denervation Guided by Renal Nerve Stimulation in Canine. Hypertension 2019, 74, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gal, P.; de Jong, M.R.; Smit, J.J.J.; Adiyaman, A.; Staessen, J.A.; Elvan, A. Blood pressure response to renal nerve stimulation in patients undergoing renal denervation: A feasibility study. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2015, 29, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoogerwaard, A.F.; de Jong, M.R.; Adiyaman, A.; Smit, J.J.J.; Delnoy, P.P.H.M.; Heeg, J.-E.; van Hasselt, B.A.A.M.; Ramdat Misier, A.R.; Rienstra, M.; van Gelder, I.C.; et al. Renal sympathetic denervation induces changes in heart rate variability and is associated with a lower sympathetic tone. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2019, 108, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandzari, D.E.; Kario, K.; Mahfoud, F.; Cohen, S.A.; Pilcher, G.; Pocock, S.; Townsend, R.; Weber, M.A.; Boehm, M. The SPYRAL HTN Global Clinical Trial Program: Rationale and design for studies of renal denervation in the absence (SPYRAL HTN OFF-MED) and presence (SPYRAL HTN ON-MED) of antihypertensive medications. Am. Heart J. 2016, 171, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, L.; Kario, K.; Basile, J.; Daemen, J.; Davies, J.; Kirtane, A.J.; Mahfoud, F.; Schmieder, R.E.; Weber, M.; Nanto, S.; et al. A multinational clinical approach to assessing the effectiveness of catheter-based ultrasound renal denervation: The RADIANCE-HTN and REQUIRE clinical study designs. Am. Heart J. 2018, 195, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wagener, M.; Dolan, E.; Arnous, S.; Galvin, J.; Murphy, A.W.; Casserly, I.; Eustace, J.; O’Connor, S.; McCreery, C.; Shand, J.; et al. Renal Denervation as a Complementary Treatment Option for Uncontrolled Arterial Hypertension: A Situation Assessment. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5634. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175634
Wagener M, Dolan E, Arnous S, Galvin J, Murphy AW, Casserly I, Eustace J, O’Connor S, McCreery C, Shand J, et al. Renal Denervation as a Complementary Treatment Option for Uncontrolled Arterial Hypertension: A Situation Assessment. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(17):5634. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175634
Chicago/Turabian StyleWagener, Max, Eamon Dolan, Samer Arnous, Joseph Galvin, Andrew W. Murphy, Ivan Casserly, Joseph Eustace, Stephen O’Connor, Charles McCreery, James Shand, and et al. 2023. "Renal Denervation as a Complementary Treatment Option for Uncontrolled Arterial Hypertension: A Situation Assessment" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 17: 5634. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175634
APA StyleWagener, M., Dolan, E., Arnous, S., Galvin, J., Murphy, A. W., Casserly, I., Eustace, J., O’Connor, S., McCreery, C., Shand, J., Wall, C., Matiullah, S., & Sharif, F. (2023). Renal Denervation as a Complementary Treatment Option for Uncontrolled Arterial Hypertension: A Situation Assessment. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(17), 5634. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175634






