Three Ablation Techniques for Atrial Fibrillation during Concomitant Cardiac Surgery: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Risk of Bias in Assessments
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection and Characteristics
3.2. Quality Assessment
3.3. Postoperative Outcomes
3.4. Operative Procedure Time
3.5. Hospital Admissions and Stays
4. Discussion
Strength and Limitations
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lippi, G.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Cervellin, G. Global epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: An increasing epidemic and public health challenge. Int. J. Stroke 2021, 16, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, P.M.; Cox, J.L.; Kislitsina, O.N.; Kruse, J.; Churyla, A.; Malaisrie, S.C.; Mehta, C.K. Surgery and Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation: History, Current Practice, and Future Directions. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 11, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Yan, F.; Ouyang, P.; Xie, Z.; Wang, H.; Yang, W.; Pan, X. Bi-atrial or left atrial ablation of atrial fibrillation during concomitant cardiac surgery: A Bayesian network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2021, 32, 2316–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad-Omer, S.M.; Ryad, R.; Limbana, T.; Zahid, T.; Jahan, N. Catheter Ablation vs. Medical Treatment in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Cureus 2020, 12, e9700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buist, T.J.; Zipes, D.P.; Elvan, A. Atrial fibrillation ablation strategies and technologies: Past, present, and future. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2020, 110, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrance, C.P.; Henn, M.C.; Damiano, R.J., Jr. Surgical ablation for atrial fibrillation: Techniques, indications, and results. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2015, 30, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruaengsri, C.; Schill, M.R.; Khiabani, A.J.; Schuessler, R.B.; Melby, S.J.; Damiano, R.J. The Cox-maze IV procedure in its second decade: Still the gold standard? Eur. J. Cardio Thorac. Surg. 2018, 53 (Suppl. 1), i19–i25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackstone, E.H.; Chang, H.L.; Rajeswaran, J.; Parides, M.K.; Ishwaran, H.; Li, L.; Ehrlinger, J.; Gelijns, A.C.; Moskowitz, A.J.; Argenziano, M.; et al. Biatrial maze procedure versus pulmonary vein isolation for atrial fibrillation during mitral valve surgery: New analytical approaches and end points. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2019, 157, 234–243.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calò, L.; Lamberti, F.; Loricchio, M.L.; De Ruvo, E.; Colivicchi, F.; Bianconi, L.; Pandozi, C.; Santini, M. Left Atrial Ablation Versus Biatrial Ablation for Persistent and Permanent Atrial Fibrillation: A Prospective and Randomized Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47, 2504–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalybekova, A.T.; Rakhmonov, S.S.; Lukinov, V.L.; Chernyavsky, A.M. Comparative characteristics of a pacemaker implantation after biatrial or left atrial ablation of atrial fibrillation in combination with coronary artery bypass grafting in patients with ischemic heart disease and long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation. Kardiologiia 2021, 61, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, G.A.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Pereson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses. Available online: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 12 February 2019).
- Viswanathan, M.; Ansari, M.T.; Berkman, N.D.; Chang, S.; Hartling, L.; McPheeters, M. AHRQ Assessing the Risk of Bias of Individual Studies in Systematic Reviews of Health Care Intervention. 2021. Available online: https://effectivehealthcare.ahrq.gov/products/methods-guidance-bias-individual-studies/methods (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Sterne, J.A. Chapter 8: Assessing Risk of Bias in a Randomized Trial. 2022. Available online: https://training.cochrane.org/handbook/current/chapter-08 (accessed on 26 March 2023).
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, R.K.; Bradbury, N.; Xin, Y.; Cooper, N.; Sutton, A. MetaInsight: An interactive web-based tool for analyzing, interrogating, and visualizing network meta-analyses using R-shiny and netmeta. Res. Synth. Methods 2019, 10, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lima, G.G.; Kalil, R.A.; Leiria, T.L.; Hatem, D.M.; Kruse, C.L.; Abrahão, R.; Sant’Anna, J.R.; Prates, P.R.; Nesralla, I.A. Randomized study of surgery for patients with permanent atrial fibrillation as a result of mitral valve disease. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2004, 77, 2089–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deneke, T.; Khargi, K.; Lemke, B.; Lawo, T.; Lindstaedt, M.; Germing, A.; Brodherr, T.; Bösche, L.; Mügge, A.; Laczkovics, A.; et al. Intra-operative cooled-tip radiofrequency linear atrial ablation to treat permanent atrial fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. 2007, 28, 2909–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghavidel, A.A.; Javadpour, H.; Shafiee, M.; Tabatabaie, M.-B.; Raiesi, K.; Hosseini, S. Cryoablation for surgical treatment of chronic atrial fibrillation combined with mitral valve surgery: A clinical observation. Eur. J. Cardio Thorac. Surg. 2008, 33, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, V.; Kumar, S.; Javali, S.; Rajesh, T.; Pai, V.; Khandekar, J.; Agrawal, N.; Patwardhan, A.M. Efficacy of Three Different Ablative Procedures to Treat Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Valvular Heart Disease: A Randomised Trial. Heart Lung Circ. 2008, 17, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, Á.; Kalil, R.A.; Schuch, L.; Abrahão, R.; Sant’Anna, J.R.M.; de Lima, G.; Nesralla, I.A. Randomized study of surgical isolation of the pulmonary veins for correction of permanent atrial fibrillation associated with mitral valve disease. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2009, 138, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Meng, X.; Li, H.; Cui, Y.; Han, J.; Xu, C. Prospective randomized comparison of left atrial and biatrial radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of atrial fibrillation. Eur. J. Cardio Thorac. Surg. 2009, 35, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogachev-Prokophiev, A.; Zheleznev, S.; Pivkin, A.; Pokushalov, E.; Romanov, A.; Nazarov, V.; Karaskov, A. Assessment of concomitant paroxysmal atrial fibrillation ablation in mitral valve surgery patients based on continuous monitoring: Does a different lesion set matter? Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2014, 18, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillinov, A.M.; Gelijns, A.C.; Parides, M.K.; DeRose, J.J.; Moskowitz, A.J.; Voisine, P.; Ailawadi, G.; Bouchard, D.; Smith, P.K.; Mack, M.J.; et al. Surgical Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation during Mitral-Valve Surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1399–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, G.J.; Panikker, S.; Morgan, M.; Hall, M.; Waktare, J.; Markides, V.; Hussain, W.; Salukhe, T.; Modi, S.; Jarman, J.; et al. Biatrial linear ablation in sustained nonpermanent AF: Results of the substrate modification with ablation and antiarrhythmic drugs in nonpermanent atrial fibrillation (SMAN-PAF) trial. Heart Rhythm. 2016, 13, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ad, N.; Holmes, S.D.; Lamont, D.; Shuman, D.J. Left-Sided Surgical Ablation for Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Who Are Undergoing Concomitant Cardiac Surgical Procedures. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 103, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogachev-Prokophiev, A.V.; Ovcharov, M.A.; Lavinykov, S.O.; Pivkin, A.N.; Sharifulin, R.M.; Afanasyev, A.V.; Sapegin, A.V.; Zheleznev, S.I. Surgical Atrial Fibrillation Ablation With and Without Left Atrium Reduction for Patients Scheduled for Mitral Valve Surgery: A Prospective Randomised Study. Heart Lung Circ. 2021, 30, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hald, M.O.; Lauritzen, D.J.; Heiberg, J.; Juhl, W.; Moss, E.; Vodstrup, H.J. Biatrial ablation vs. Pulmonary vein isolation in atrial fibrillation patients undergoing cardiac surgery: A retrospective study. Scand. Cardiovasc. J. 2021, 55, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stulak, J.M.; Suri, R.M.; Burkhart, H.M.; Daly, R.C.; Dearani, J.A.; Greason, K.L.; Joyce, L.D.; Park, S.J.; Schaff, H.V. Surgical ablation for atrial fibrillation for two decades: Are the results of new techniques equivalent to the Cox maze III procedure? J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 147, 1478–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onorati, F.; Mariscalco, G.; Rubino, A.S.; Serraino, F.; Santini, F.; Musazzi, A.; Klersy, C.; Sala, A.; Renzulli, A. Impact of Lesion Sets on Mid-Term Results of Surgical Ablation Procedure for Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geuzebroek, G.S.; Ballaux, P.K.; van Hemel, N.M.; Kelder, J.C.; Defauw, J.J. Medium-term outcome of different surgical methods to cure atrial fibrillation: Is less worse? Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2008, 7, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, Y.; Petersen, J.; Aydin, A.; Alassar, Y.; Reichenspurner, H.; Pecha, S. Complete Left-Atrial Lesion Set versus Pulmonary Vein Isolation Only in Patients with Paroxysmal AF Undergoing CABG or AVR. Medicina 2022, 58, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henn, M.C.; Lancaster, T.S.; Miller, J.R.; Sinn, L.A.; Schuessler, R.B.; Moon, M.R.; Melby, S.J.; Maniar, H.S.; Damiano, R.J. Late outcomes after the Cox maze IV procedure for atrial fibrillation. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 150, 1168–1178.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albåge, A.; Péterffy, M.; Källner, G. Learning what works in surgical cryoablation of atrial fibrillation: Results of different application techniques and benefits of prospective follow-up. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2011, 13, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, P.M.; Kruse, J.; Shalli, S.; Ilkhanoff, L.; Goldberger, J.J.; Kadish, A.H.; Arora, R.; Lee, R. Where does atrial fibrillation surgery fail? Implications for increasing effectiveness of ablation. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2010, 139, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guden, M.; Akpinar, B.; Caynak, B.; Turkoglu, C.; Ozyedek, Z.; Sanisoglu, I.; Sagbas, E.; Aytekin, S.; Oztekin, S.D. Left Versus Bi-Atrial Intraoperative Saline-Irrigated Radiofrequency Modified Maze Procedure for Atrial Fibrillation. Card. Electrophysiol. Rev. 2003, 7, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecha, S.; Schäfer, T.; Yildirim, Y.; Ahmadzade, T.; Willems, S.; Reichenspurner, H.; Wagner, F.M. Predictors for permanent pacemaker implantation after concomitant surgical ablation for atrial fibrillation. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 147, 984–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualis, J.; Castaño, M.; Martínez-Comendador, J.M.; Marcos, J.M.; Martín, C.; Estévez-Loureiro, R.; Gómez-Plana, J.; Martín, E.; Otero, J. Crioablación biauricular frente a la ablación aislada de la aurícula izquierda en fibrilación auricular persistente. Recurrencia a medio-largo plazo. [Biatrial vs. isolated left atrial cryoablation for the treatment of long-lasting permanent atrial fibrillation. Midterm recurrence rate]. Arch. Cardiol. México 2016, 86, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecha, S.; Hartel, F.; Ahmadzade, T.; Aydin, M.A.; Willems, S.; Reichenspurner, H.; Wagner, F.M. Event recorder monitoring to compare the efficacy of a left versus biatrial lesion set in patients undergoing concomitant surgical ablation for atrial fibrillation. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 148, 2161–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, L.K.; Cedola, S.R.; Cogan, J.; Jiang, J.; Yang, J.; Takayama, H.; Argenziano, M. Right atrial lesions do not improve the efficacy of a complete left atrial lesion set in the surgical treatment of atrial fibrillation, but they do increase procedural morbidity. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2013, 145, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.B.; Bang, J.H.; Jung, S.H.; Choo, S.J.; Chung, C.H.; Lee, J.W. Left Atrial Ablation Versus Biatrial Ablation in the Surgical Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2011, 92, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breda, A.S.C.R.; Ragognette, R.G.; Machado, L.N.; Neff, C.B.; De Matos, L.L.; Meneghine, A.; Pires, A.C. Comparison of Uniatrial and Biatrial Radiofrequency Ablation Procedures in Atrial Fibrillation: Initial Results. Heart Surg. Forum 2011, 14, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deneke, T.; Khargi, K.; Voss, D.; Lemke, B.; Lawo, T.; Laczkovics, A.; Mügge, A.; Bösche, L.I.; Lindstaedt, M.; Germing, A.; et al. Long-term sinus rhythm stability after intraoperative ablation of permanent atrial fibrillation. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2009, 32, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, W.H.; Prince, H.B.; Wheatley, I.G.H.; Herbert, M.A.; Worley, C.M.; Prince, S.L.; Dewey, T.M.; Mack, M.J. Experience with Various Surgical Options for the Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation. Heart Surg. Forum 2004, 7, E333–E336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takami, Y.; Yasuura, K.; Takagi, Y.; Ohara, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Usui, A.; Masumoto, H.; Sakai, Y.; Teranishi, K. Partial Maze Procedure Is Effective Treatment for Chronic Atrial Fibrillation Associated with Valve Disease. J. Card. Surg. 1999, 14, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takasaki, T.; Sueda, T.; Imai, K.; Orihashi, K.; Takahashi, S.; Kurosaki, T.; Morita, S.; Uchida, N. Mid-term results of the box pulmonary vein isolation and the cryo-maze procedure for chronic atrial fibrillation associated with mitral valve disease. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2012, 60, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charitos, E.I.; Ziegler, P.D.; Stierle, U.; Graf, B.; Sievers, H.-H.; Hanke, T. Long-term outcomes after surgical ablation for atrial fibrillation in patients with continuous heart rhythm monitoring devices. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 21, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churyla, A.; Iddriss, A.; Andrei, A.-C.; Kruse, J.; Malaisrie, S.C.; Passman, R.; Li, Z.; Lee, R.; McCarthy, P.M. Biatrial or Left Atrial Lesion Set for Ablation During Mitral Surgery: Risks and Benefits. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 103, 1858–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Mei, B.; Feng, K.; Lin, W.; Chen, G.; Liang, M.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z. Long-Term Results of Surgical Atrial Fibrillation Radiofrequency Ablation: Comparison of Two Methods. Heart Lung Circ. 2018, 27, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, H.; Miyata, H.; Motomura, N.; Sasaki, K.; Kunihara, T.; Takamoto, S. Comparison of early outcomes of surgical ablation procedures for atrial fibrillation concomitant to non-mitral cardiac surgery: A Japan Adult Cardiovascular Surgery Database study. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2017, 65, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Usui, A.; Ueda, Y. Surgical Treatment of Chronic Atrial Fibrillation—Unipolar Radiofrequency Ablation versus Cryoablation, and Left Atrial versus Bi-atrial Maze Procedures. J. Arrhythm. 2006, 22, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeRose, J.J.; Mancini, D.M.; Chang, H.L.; Argenziano, M.; Dagenais, F.; Ailawadi, G.; Perrault, L.P.; Parides, M.K.; Taddei-Peters, W.C.; Mack, M.J.; et al. Pacemaker Implantation After Mitral Valve Surgery With Atrial Fibrillation Ablation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 2427–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Song, Y.; Hu, S.; Wang, W. Efficiency of radiofrequency ablation for surgical treatment of chronic atrial fibrillation in rheumatic valvular disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 174, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sef, D.; Trkulja, V.; Raja, S.G.; Hooper, J.; Turina, M.I. Comparing mid-term outcomes of Cox-Maze procedure and pulmonary vein isolation for atrial fibrillation after concomitant mitral valve surgery: A systematic review. J. Card. Surg. 2022, 37, 3801–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappabianca, G.; Ferrarese, S.; Tutino, C.; Corazzari, C.; Matteucci, M.; Mantovani, V.; Musazzi, A.; Ponti, R.; Beghi, C. Safety and efficacy of biatrial vs left atrial surgical ablation during concomitant cardiac surgery: A meta-analysis of clinical studies with a focus on the causes of pacemaker implantation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2019, 30, 2150–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClure, G.R.; Belley-Cote, E.P.; Jaffer, I.H.; Dvirnik, N.; An, K.R.; Fortin, G.; Spence, J.; Healey, J.; Singal, R.K.; Whitlock, R.P. Surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Europace 2018, 20, 1442–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Non-SR | BAA | LAA | PVI |
|---|---|---|---|
| BAA | BAA | 1.08(0.94, 1.23) | 1.36 (1.08, 1.7) * |
| LAA | 0.93 (0.81, 1.07) | LAA | 1.26 (1.01, 1.6) * |
| PVI | 0.74 (0.59, 0.93) * | 0.79 (0.63, 0.99) * | PVI |
| Pacemaker Implantation | BAA | LAA | PVI |
| BAA | BAA | 0.52 (0.37, 0.71) * | 0.48 (0.3, 0.8) * |
| LAA | 1.93 (1.4, 2.69) * | LAA | 0.93 (0.56, 1.62) |
| PVI | 2.08 (1.26, 3.38) * | 1.08 (0.62, 1.8) | PVI |
| Reoperation | BAA | LAA | PVI |
| BAA | BAA | 0.71 (0.28, 1.45) | 0.31 (0.1, 0.64) * |
| LAA | 1.4 (0.69, 3.61) | LAA | 0.43 (0.16, 1.05) |
| PVI | 3.26 (1.56, 9.53) * | 2.34 (0.95, 6.29) | PVI |
| Bleeding | BAA | LAA | PVI |
| BAA | BAA | 0.58 (0.22, 1.5) | 0.74 (0.18, 2.43) |
| LAA | 1.71 (0.67, 4.57) | LAA | 1.26 (0.32, 4.24) |
| PVI | 1.35 (0.41, 5.54) | 0.79 (0.24, 3.16) | PVI |
| Renal Failure | BAA | LAA | PVI |
| BAA | BAA | 0.58 (0.22, 1.48) | 0.75 (0.19, 2.36) |
| LAA | 1.71 (0.68, 4.51) | LAA | 1.27 (0.32, 4.15) |
| PVI | 1.34 (0.42, 5.35) | 0.79 (0.24, 3.11) | PVI |
| CVA | BAA | LAA | PVI |
| BAA | BAA | 0.76 (0.14, 3.18) | 0.89 (0.1, 6.43) |
| LAA | 1.32 (0.31, 7.05) | LAA | 1.17 (0.13, 10.56) |
| PVI | 1.12 (0.16, 9.68) | 0.86 (0.09, 7.45) | PVI |
| All-cause Mortality | BAA | LAA | PVI |
| BAA | BAA | 1.06 (0.59, 1.78) | 1.29 (0.52, 2.69) |
| LAA | 0.94 (0.56, 1.7) | LAA | 1.22 (0.5, 2.68) |
| PVI | 0.78 (0.37, 1.93) | 0.82 (0.37, 1.99) | PVI |
| Xc | BAA | LAA | PVI |
|---|---|---|---|
| BAA | BAA | −2.35 (−10.46, 5.43) | −16.2 (−29.78, −3.2) |
| LAA | 2.35 (−5.43, 10.46) | LAA | −13.86 (−26.34, −1.45) |
| PVI | 16.2 (3.2, 29.78) * | 13.86 (1.45, 26.34) * | PVI |
| CPB | BAA | LAA | PVI |
| BAA | BAA | −18.91 (−29.25, −8.77) * | −27.39 (−41.04, −13.95) * |
| LAA | 18.91 (8.77, 29.35) * | LAA | −8.48 (−23.14, 6.23) |
| PVI | 27.39 (13.95, 41.04) * | 8.48 (−6.23, 23.14) | PVI |
| Ablation | BAA | LAA | PVI |
| BAA | BAA | −7.4 (−15.56, 0.65) | −20.39 (−31.85, −9.44) * |
| LAA | 7.4 (−0.65, 15.56) | LAA | −13 (−24.32, −2.03) * |
| PVI | 20.39 (9.44, 31.85) * | 13 (2.03, 24.32) * | PVI |
| Admission | BAA | LAA | PVI |
|---|---|---|---|
| BAA | BAA | 1.8 (0.36, 7.16) | 0.84 (0.08, 9.1) |
| LAA | 0.55 (0.14, 2.76) | LAA | 0.47 (0.03, 8.47) |
| PVI | 1.18 (0.11, 13.14) | 2.14 (0.12, 32.16) | PVI |
| Length of stay | BAA | LAA | PVI |
| BAA | BAA | −1.5 (−4.07, 1.1) | −1.83 (−5.56, 1.81) |
| LAA | 1.5 (−1.1, 4.07) | LAA | 0.33 (−3.52, 2.79) |
| PVI | 1.83 (−1.81, 5.56) | 0.33 (−2.79, 3.52) | PVI |
| Treatment | Non-SR | Pacemaker Implantation | Reoperation | Bleeding | Renal Failure | Cerebrovascular Accidents | All-cause Mortality | Xc Time | CPB Time | Ablation Time | Hospital Admissions | Length of Stay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
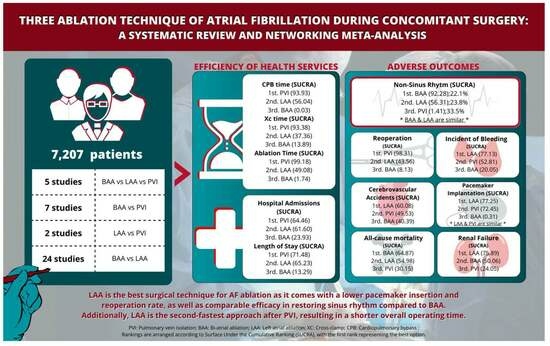
| BAA | 1 (92.28) | 2 (0.31) | 1 (8.13) | 1 (20.05) | 1 (50.06) | 1 (40.39) | 1 (64.87) | 2 (13.89) | 2 (0.03) | 2 (1.74) | 1 (61.60) | 1 (13.29) |
| LAA | 1 (56.31) | 1 (77.25) | 1 (43.56) | 1 (77.13) | 1 (75.89) | 1 (60.08) | 1 (54.98) | 2 (37.36) | 1 (56.04) | 2 (49.08) | 1 (23.93) | 1 (65.23) |
| PVI | 2 (1.41) | 1 (72.45) | 1 (98.31) | 1 (52.81) | 1 (24.05) | 1 (49.53) | 1 (30.15) | 1 (98.76) | 1 (93.93) | 1 (99.18) | 1 (64.46) | 1 (71.48) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hanafy, D.A.; Erdianto, W.P.; Husen, T.F.; Nathania, I.; Vidya, A.P.; Angelica, R.; Suwatri, W.T.; Lintangella, P.; Prasetyo, P.; Sugisman. Three Ablation Techniques for Atrial Fibrillation during Concomitant Cardiac Surgery: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5716. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175716
Hanafy DA, Erdianto WP, Husen TF, Nathania I, Vidya AP, Angelica R, Suwatri WT, Lintangella P, Prasetyo P, Sugisman. Three Ablation Techniques for Atrial Fibrillation during Concomitant Cardiac Surgery: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(17):5716. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175716
Chicago/Turabian StyleHanafy, Dudy Arman, Wahyu Prima Erdianto, Theresia Feline Husen, Ilona Nathania, Ananda Pipphali Vidya, Ruth Angelica, Widya Trianita Suwatri, Pasati Lintangella, Priscillia Prasetyo, and Sugisman. 2023. "Three Ablation Techniques for Atrial Fibrillation during Concomitant Cardiac Surgery: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 17: 5716. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175716
APA StyleHanafy, D. A., Erdianto, W. P., Husen, T. F., Nathania, I., Vidya, A. P., Angelica, R., Suwatri, W. T., Lintangella, P., Prasetyo, P., & Sugisman. (2023). Three Ablation Techniques for Atrial Fibrillation during Concomitant Cardiac Surgery: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(17), 5716. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175716