Refractive Error and Axial Length and Their Related Factors in 8-Year-Old Japanese Children: The Yamanashi Adjunct Study of the Japan Environment and Children’s Study (JECS)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Participants and Methods
2.1. Enrolled Participants and Investigated Parameters
2.2. Statistical Test
3. Result
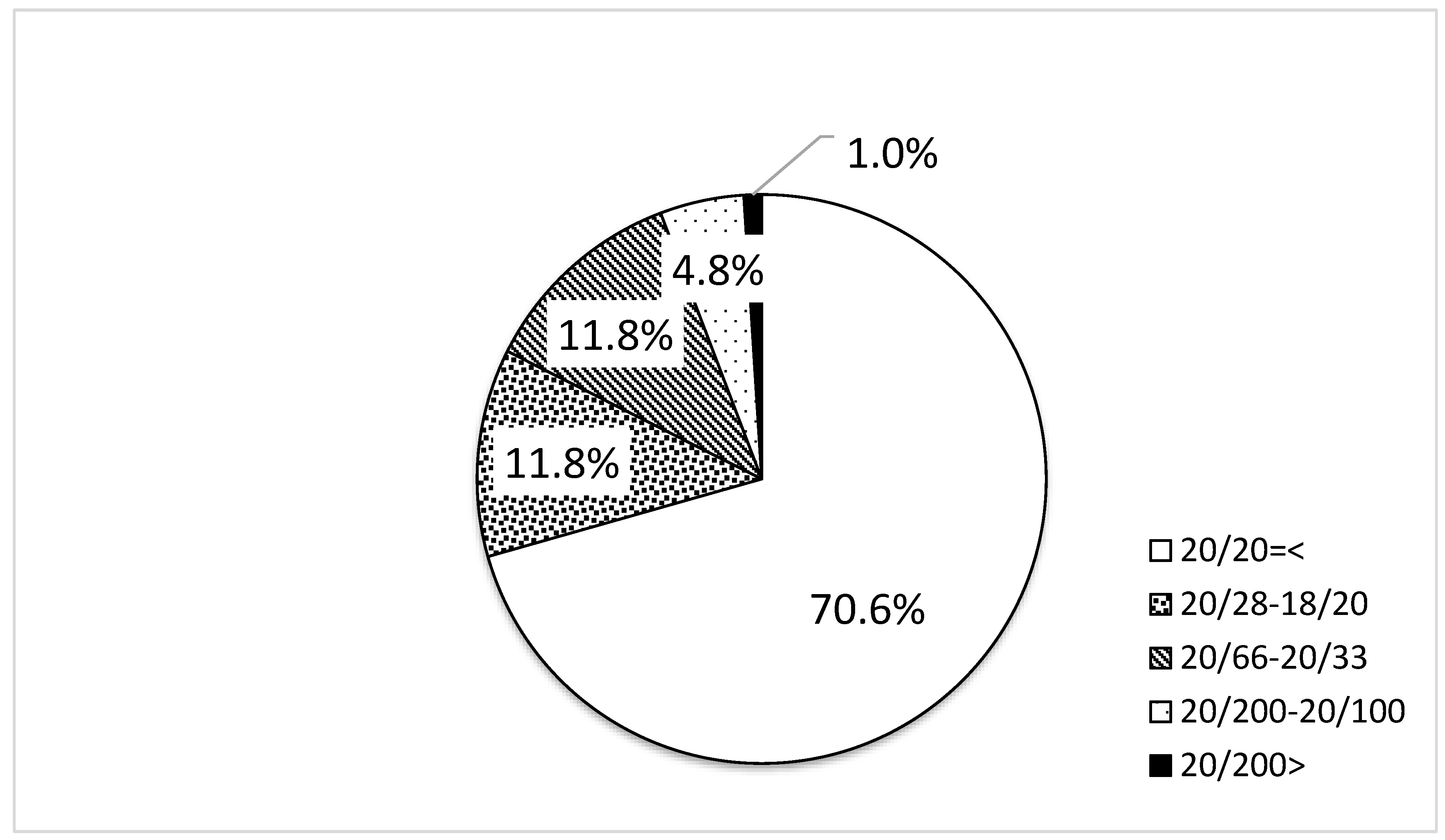
3.1. Distribution of Uncorrected Visual Acuity
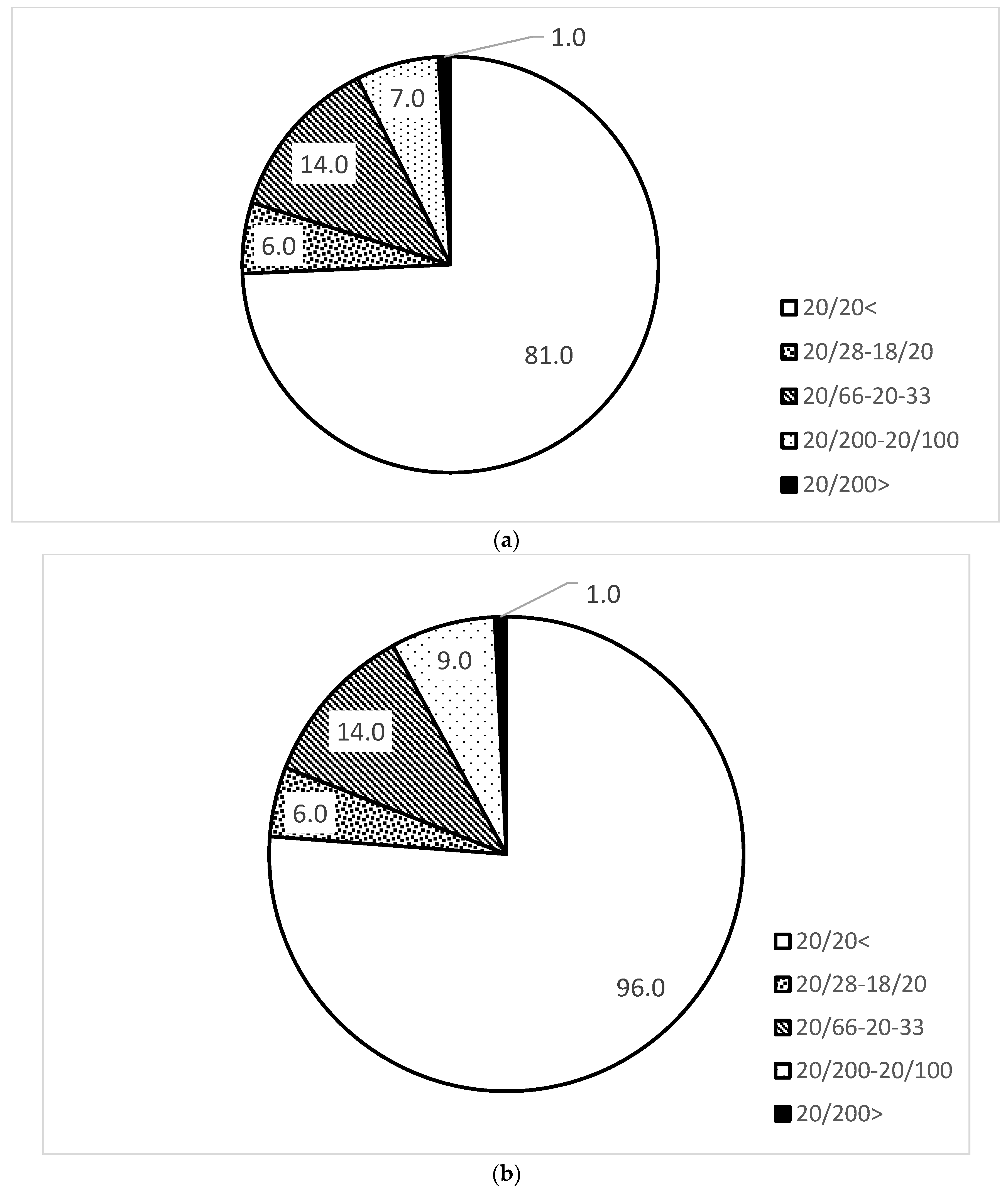
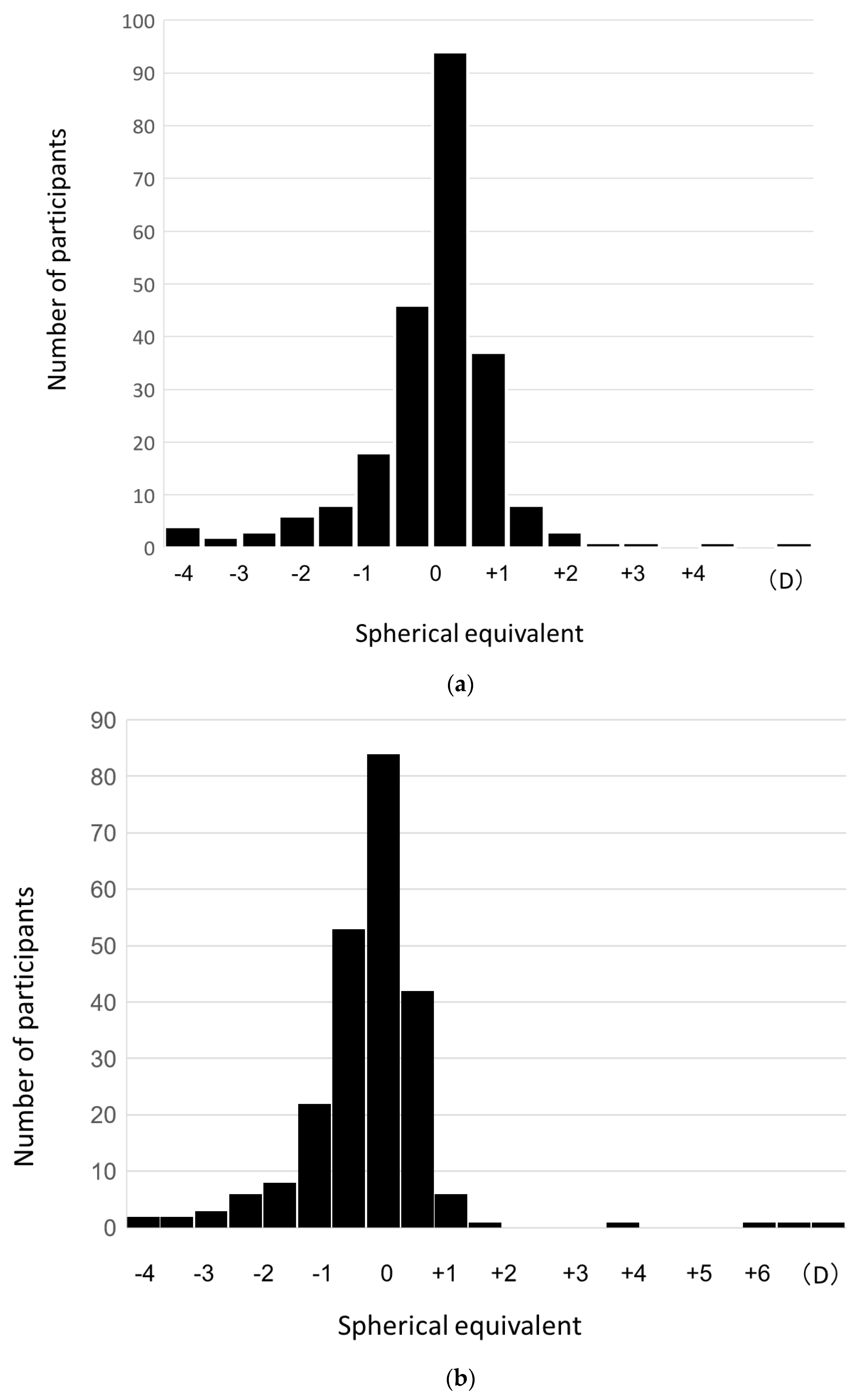
3.2. Distribution of Refractive Error
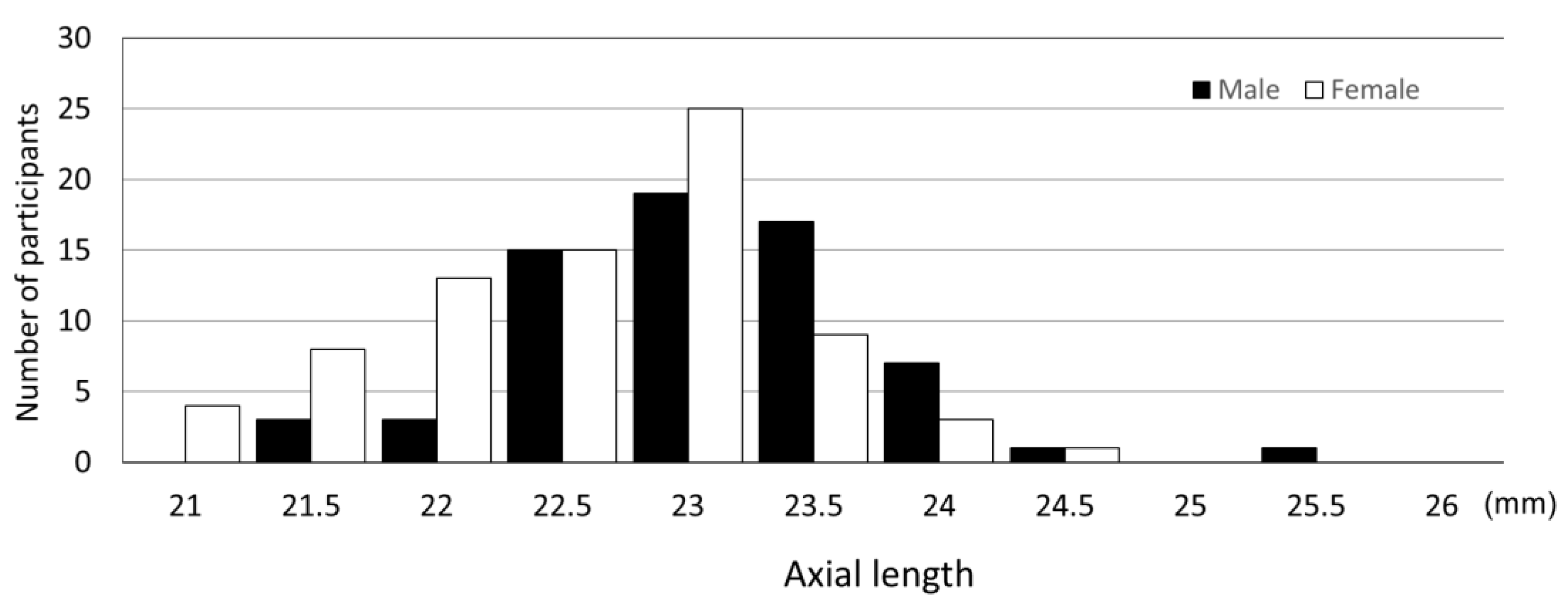
3.3. Distribution of Axial Length
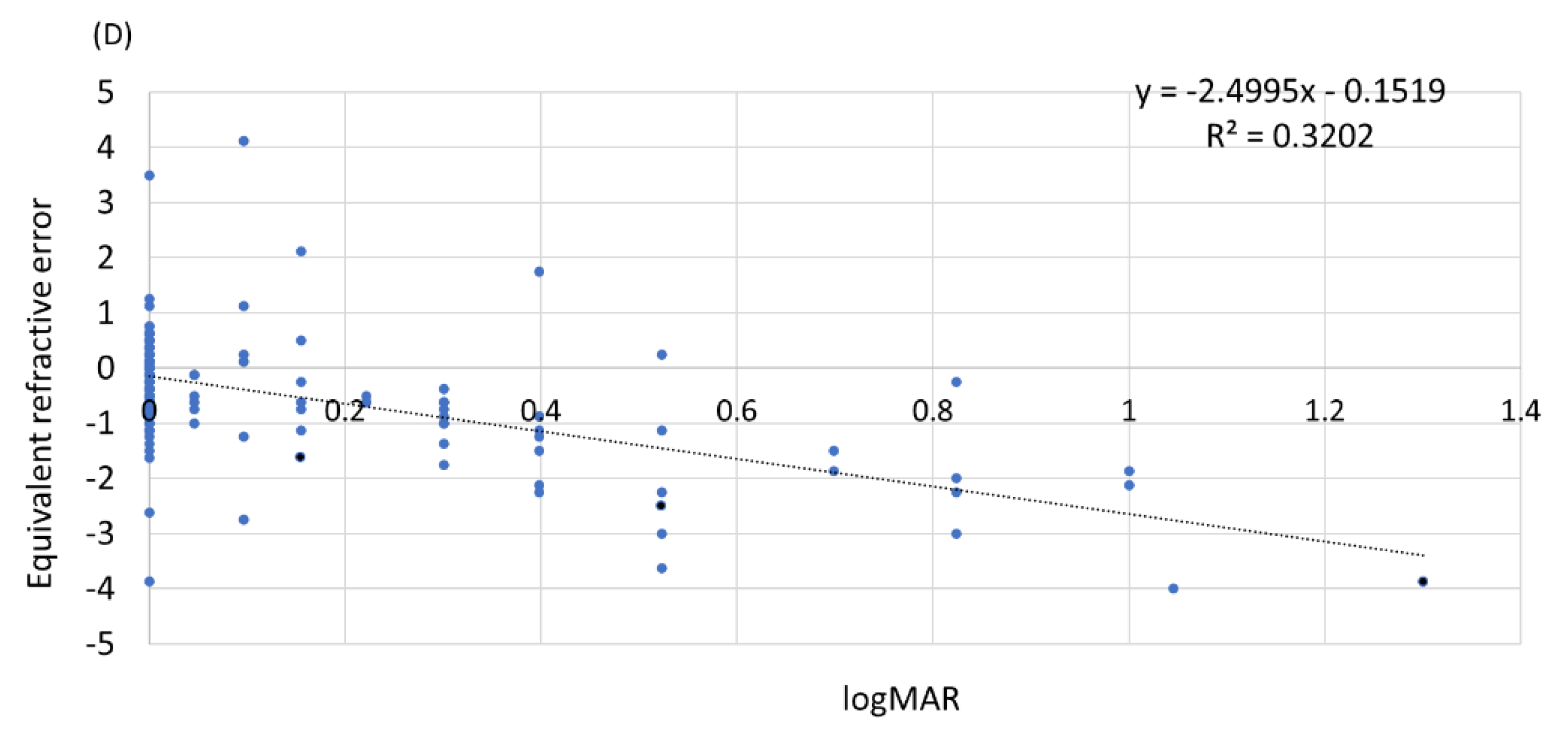
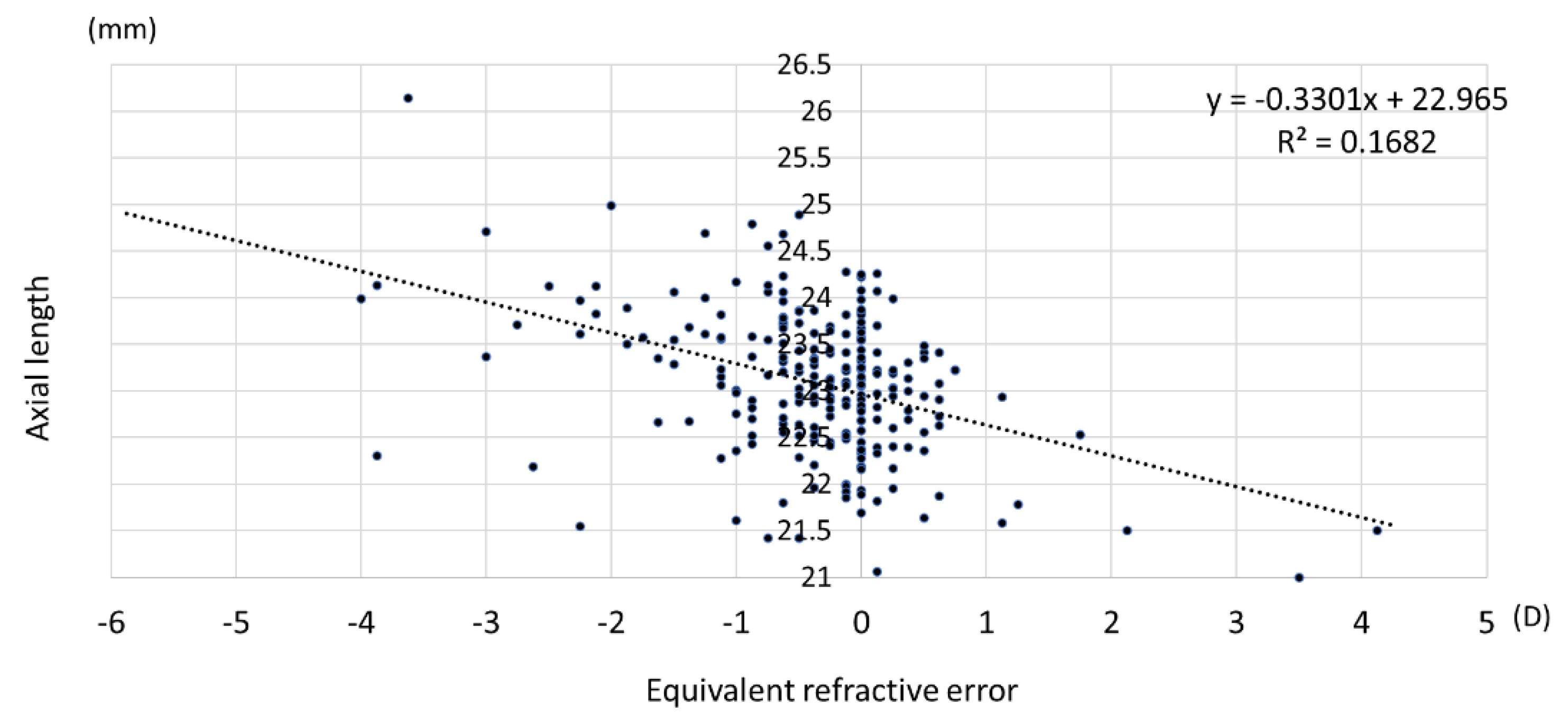
3.4. Relationship among Uncorrected Visual Acuity, Refractive Error, and Axial Length
3.5. Relationship between Axial Length, Refractive Error, and Body Height
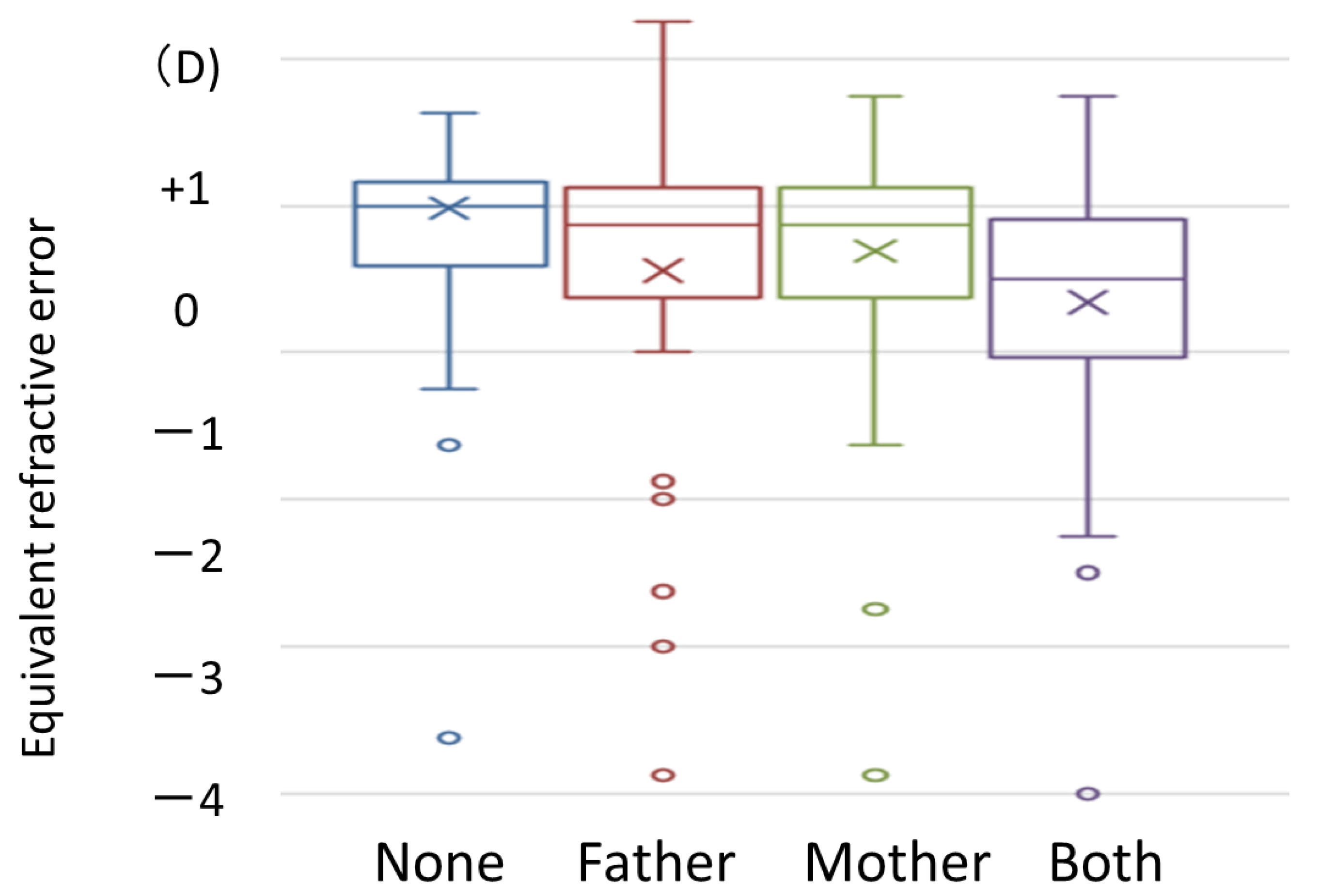
3.6. Association between Parents’ Use of Eyeglasses or Contact Lenses and Children’s Refraction Error
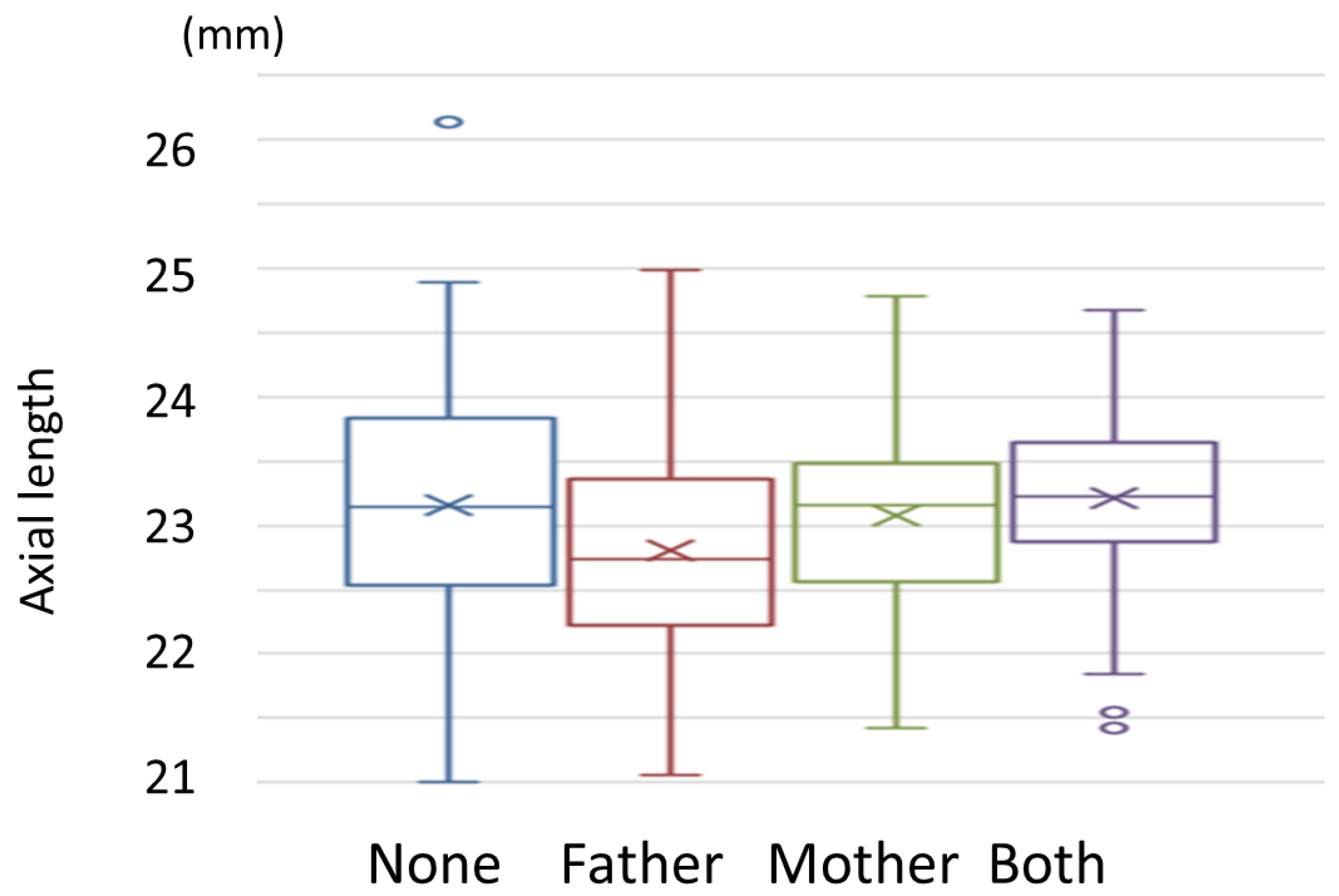
3.7. Association between Parents’ Use of Eyeglasses or Contact Lenses and Children’s Axial Length
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chon, B.; Qiu, M.; Lin, S.C. Myopia and glaucoma in the South Korean population. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 6570–6577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flitcroft, D.I. The complex interactions of retinal, optical and environmental factors in myopia aetiology. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2012, 31, 622–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holden, B.A.; Fricke, T.R.; Wilson, D.A.; Jong, M.; Naidoo, K.S.; Sankaridurg, P.; Wong, T.Y.; Naduvilath, T.J.; Resnikoff, S. Global Prevalence of Myopia and High Myopia and Temporal Trends from 2000 through 2050. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michikawa, T.; Nitta, H.; Nakayama, S.F.; Ono, M.; Yonemoto, J.; Tamura, K.; Suda, E.; Ito, H.; Takeuchi, A.; Kawamoto, T. The Japan Environment and Children’s Study (JECS): A Preliminary Report on Selected Characteristics of Approximately 10 000 Pregnant Women Recruited During the First Year of the Study. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzybowski, A.; Kanclerz, P.; Tsubota, K.; Lanca, C.; Saw, S.M. A review on the epidemiology of myopia in school children worldwide. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020, 20, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choong, Y.F.; Chen, A.H.; Goh, P.P. A comparison of autorefraction and subjective refraction with and without cycloplegia in primary school children. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2006, 142, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Sun, Y.; Li, S.M.; Hu, J.P.; Cao, K.; An, W.; Guo, J.Y.; Li, H.; Wang, N. Effect of body stature on refraction and ocular biometry in Chinese young adults: The Anyang University Students Eye Study. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2021, 104, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terasaki, H.; Yamashita, T.; Asaoka, R.; Yoshihara, N.; Kakiuchi, N.; Sakamoto, T. Sex Differences in Rate of Axial Elongation and Ocular Biometrics in Elementary School Students. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2021, 15, 4297–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, L.; Friedman, D.S.; Repka, M.X.; Katz, J.; Ibironke, J.; Hawes, P.; Tielsch, J.M. Prevalence of refractive error among preschool children in an urban population: The Baltimore Pediatric Eye Disease Study. Ophthalmology 2009, 116, 739–746.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Lin, H.; Li, C.; Liu, L.; Xiao, H.; Lin, Y.; Huang, X.; Chen, Y. Longitudinal association between myopia and parental myopia and outdoor time among students in Wenzhou: A 2.5-year longitudinal cohort study. BMC Ophthalmol. 2021, 21, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, H.; Jafarzadehpur, E.; Ghaderi, S.; Yekta, A.; Ostadimoghaddam, H.; Norouzirad, R.; Khabazkhoob, M. Ocular components during the ages of ocular development. Acta Ophthalmol. 2015, 93, e74–e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutti, D.O.; Mitchell, G.L.; Jones, L.A.; Friedman, N.E.; Frane, S.L.; Lin, W.K.; Moeschberger, M.L.; Zadnik, K. Axial growth and changes in lenticular and corneal power during emmetropization in infants. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 3074–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, L.T.; Gong, Y.; Ah-Kee, E.Y.; Xiao, G.; Zhang, X.; Yu, S. Impact of parental history of myopia on the development of myopia in mainland china school-aged children. Ophthalmol. Eye Dis. 2014, 6, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Shakarchi, A.F.; Block, S.S.; Friedman, D.S.; Repka, M.X.; Collins, M.E. Noncycloplegic Compared with Cycloplegic Refraction in a Chicago School-Aged Population. Ophthalmology 2022, 129, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, H.; Khabazkhoob, M.; Asharlous, A.; Soroush, S.; Yekta, A.; Dadbin, N.; Fotouhi, A. Cycloplegic autorefraction versus subjective refraction: The Tehran Eye Study. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 100, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junghans, B.M.; Crewther, S.G. Prevalence of myopia among primary school children in eastern Sydney. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2003, 86, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Yang, D.; Guo, K.; Guo, Y.; Jing, X.; Pan, C.W. Pre- and Postcycloplegic Refractions in Children and Adolescents. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mimouni, M.; Zoller, L.; Horowitz, J.; Wygnanski-Jaffe, T.; Morad, Y.; Mezer, E. Cycloplegic autorefraction in young adults: Is it mandatory? Graefes. Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2016, 254, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, B.; Wang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Jin, N.; Rong, H.; Wang, X.; Nian, H.; Guo, L.; Liang, M.; Wei, R. Prediction of spherical equivalent difference before and after cycloplegia in school-age children with machine learning algorithms. Front Public Health 2023, 11, 1096330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magome, K.; Morishige, N.; Ueno, A.; Matsui, T.A.; Uchio, E. Prediction of cycloplegic refraction for noninvasive screening of children for refractive error. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okabe, N.; Takahashi, A.; Shigemoto, Y.; Kogure, C.; Ooka, T.; Shinohara, R.; Otawa, S.; Kobayashi, A.; Horiuchi, S.; Kushima, M.; et al. Refractive Error and Axial Length and Their Related Factors in 8-Year-Old Japanese Children: The Yamanashi Adjunct Study of the Japan Environment and Children’s Study (JECS). J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5929. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185929
Okabe N, Takahashi A, Shigemoto Y, Kogure C, Ooka T, Shinohara R, Otawa S, Kobayashi A, Horiuchi S, Kushima M, et al. Refractive Error and Axial Length and Their Related Factors in 8-Year-Old Japanese Children: The Yamanashi Adjunct Study of the Japan Environment and Children’s Study (JECS). Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(18):5929. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185929
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkabe, Natsuki, Airi Takahashi, Yumi Shigemoto, Chio Kogure, Tadao Ooka, Ryoji Shinohara, Sanae Otawa, Anna Kobayashi, Sayaka Horiuchi, Megumi Kushima, and et al. 2023. "Refractive Error and Axial Length and Their Related Factors in 8-Year-Old Japanese Children: The Yamanashi Adjunct Study of the Japan Environment and Children’s Study (JECS)" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 18: 5929. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185929
APA StyleOkabe, N., Takahashi, A., Shigemoto, Y., Kogure, C., Ooka, T., Shinohara, R., Otawa, S., Kobayashi, A., Horiuchi, S., Kushima, M., Yamagata, Z., Kashiwagi, K., & The Yamanashi Adjunct Study of the Japan Environment and Children's Study Group. (2023). Refractive Error and Axial Length and Their Related Factors in 8-Year-Old Japanese Children: The Yamanashi Adjunct Study of the Japan Environment and Children’s Study (JECS). Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(18), 5929. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185929






