Efficacy of Tegoprazan in Patients with Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease: A Preliminary Feasibility Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Randomization
2.3. Study Assessments
2.3.1. LPRD Symptom Assessment
2.3.2. LPRD Sign Assessment
2.3.3. Study Efficacy
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
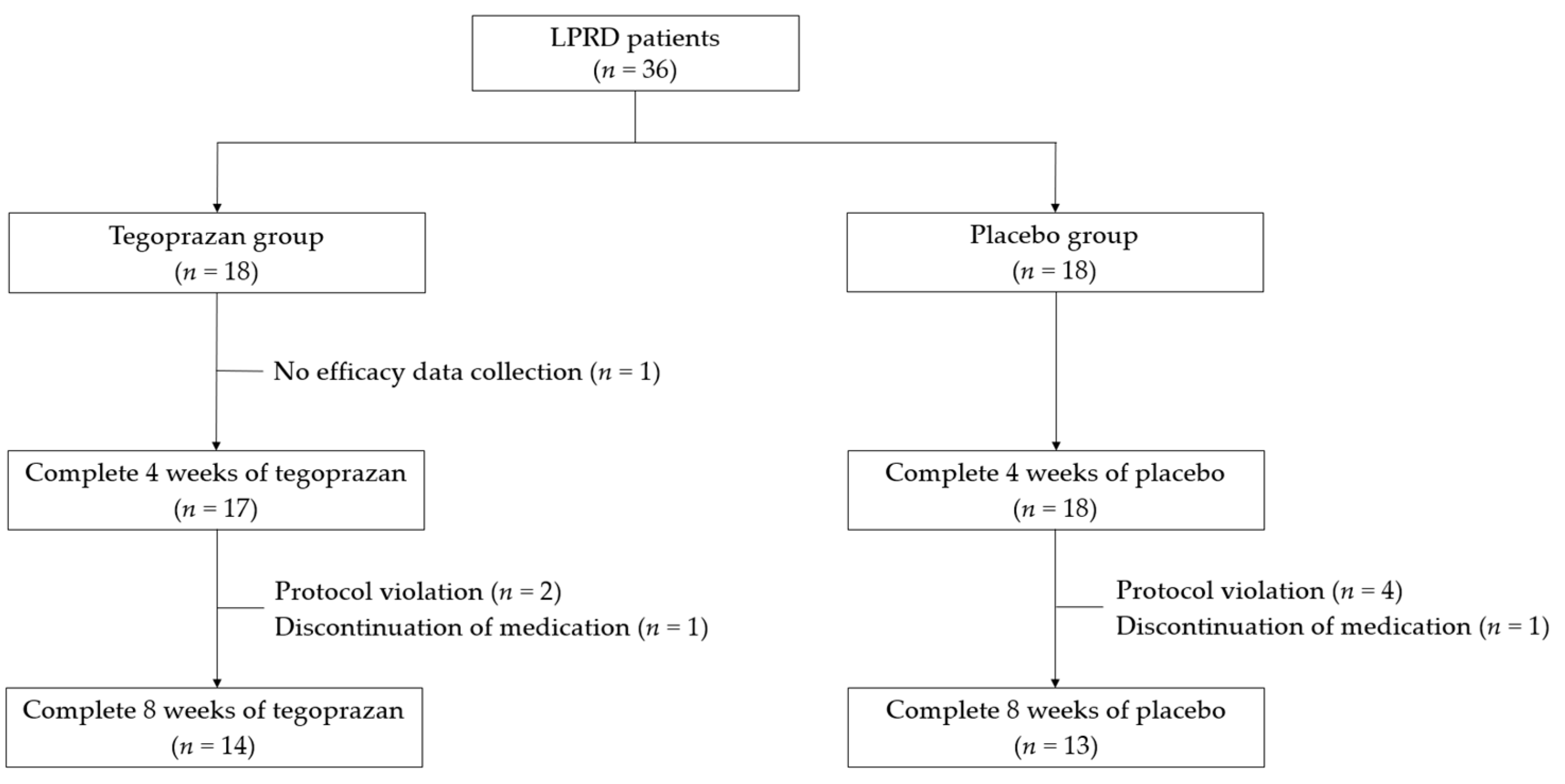
3.1. Patient Allocation and Baseline Clinicodemographic Characteristics
3.2. Efficacy Assessment
3.2.1. Complete Resolution Rates of LPRD Symptoms after 4 and 8 Weeks of Medication
3.2.2. Changes in the Total RSI and RFS Scores from Baseline at 4 and 8 Weeks of Medication
- (1)
- Changes in the total RSI scores after 4 and 8 weeks of medication
- (2)
- Changes in total RFS scores after 4 and 8 weeks of medication
- (3)
- Changes in the individual RSI items after 4 and 8 weeks of medication
- (4)
- Changes in the individual RFS items after 4 and 8 weeks of medication
3.3. Adverse Events
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Lechien, J.R.; Saussez, S.; Karkos, P.D. Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease: Clinical presentation, diagnosis and therapeutic challenges in 2018. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 26, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koufman, J.A. The otolaryngologic manifestations of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): A clinical investigation of 225 patients using ambulatory 24-h pH monitoring and an experimental investigation of the role of acid and pepsin in the development of laryngeal injury. Laryngoscope 1991, 101, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belafsky, P.C.; Postma, G.N.; Koufman, J.A. Validity and reliability of the reflux symptom index (RSI). J. Voice Off. J. Voice Found. 2002, 16, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belafsky, P.C.; Postma, G.N.; Koufman, J.A. The validity and reliability of the reflux finding score (RFS). Laryngoscope 2001, 111, 1313–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzka, D.A.; Kahrilas, P.J. Advances in the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Bmj 2020, 371, m3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaezi, M.F.; Hicks, D.M.; Abelson, T.I.; Richter, J.E. Laryngeal signs and symptoms and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): A critical assessment of cause and effect association. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Off. Clin. Pract. J. Am. Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2003, 1, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormseth, E.J.; Wong, R.K. Reflux laryngitis: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 94, 2812–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.A.; Harb, A.H.; Vaezi, M.F. Oropharyngeal Reflux Monitoring and Atypical Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2016, 18, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichel, O.; Dressel, H.; Wiederanders, K.; Issing, W.J. Double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with esomeprazole for symptoms and signs associated with laryngopharyngeal reflux. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. Off. J. Am. Acad. 2008, 139, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, P.K.; Ng, M.L.; Cheung, T.K.; Wong, B.Y.; Tan, V.P.; Fong, D.Y.; Wei, W.I.; Wong, B.C. Rabeprazole is effective in treating laryngopharyngeal reflux in a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Off. Clin. Pract. J. Am. Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2010, 8, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzic, S.A.; Turkalj, M.; Zupan, A.; Labor, M.; Plavec, D.; Baudoin, T. Eight weeks of omeprazole 20 mg significantly reduces both laryngopharyngeal reflux and comorbid chronic rhinosinusitis signs and symptoms: Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Otolaryngol. Off. J. ENT-UK Off. J. Neth. Soc. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. Cervico-Facial Surg. 2018, 43, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wo, J.M.; Koopman, J.; Harrell, S.P.; Parker, K.; Winstead, W.; Lentsch, E. Double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with single-dose pantoprazole for laryngopharyngeal reflux. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 1972–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordzij, J.P.; Khidr, A.; Evans, B.A.; Desper, E.; Mittal, R.K.; Reibel, J.F.; Levine, P.A. Evaluation of omeprazole in the treatment of reflux laryngitis: A prospective, placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blind study. Laryngoscope 2001, 111, 2147–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.; Hicks, D.M.; Khandwala, F.; Richter, J.E.; Abelson, T.I.; Milstein, C.; Vaezi, M.F. Laryngopharyngeal reflux: Prospective cohort study evaluating optimal dose of proton-pump inhibitor therapy and pretherapy predictors of response. Laryngoscope 2005, 115, 1230–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, C.N. Evaluation and management of laryngopharyngeal reflux. JAMA 2005, 294, 1534–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, T.; Furuta, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Sugimoto, M.; Kasugai, K.; Kusano, M.; Okada, H.; Suzuki, T.; Higuchi, T.; Kagami, T.; et al. Randomised trial of acid inhibition by vonoprazan 10/20 mg once daily vs rabeprazole 10/20 mg twice daily in healthy Japanese volunteers (SAMURAI pH study). Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N.; Take, Y. Tegoprazan, a Novel Potassium-Competitive Acid Blocker to Control Gastric Acid Secretion and Motility. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2018, 364, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Choi, H.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Nam, J.Y.; Kim, B.; Song, G.S.; Lim, H.S.; Bae, K.S. Randomised clinical trial: Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of single and multiple oral doses of tegoprazan (CJ-12420), a novel potassium-competitive acid blocker, in healthy male subjects. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 50, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Son, B.K.; Kim, G.H.; Jung, H.K.; Jung, H.Y.; Chung, I.K.; Sung, I.K.; Kim, J.I.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; et al. Randomised phase 3 trial: Tegoprazan, a novel potassium-competitive acid blocker, vs. esomeprazole in patients with erosive oesophagitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshima, T.; Miwa, H. Potent Potassium-competitive Acid Blockers: A New Era for the Treatment of Acid-related Diseases. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 24, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Cho, K.B.; Chun, H.J.; Lee, S.W.; Kwon, J.G.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, S.G.; Jung, H.Y.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, J.S.; et al. Randomised clinical trial: Comparison of tegoprazan and placebo in non-erosive reflux disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 54, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julious, S.A. Sample size of 12 per group rule of thumb for a pilot study. Pharm. Stat. J. Appl. Stat. Pharm. Ind. 2005, 4, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Cao, G.; Yu, J.; Wang, J.; Cheng, N.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; Zhang, B.; Lu, J.; et al. Safety, Tolerability and Pharmacokinetics of Single Ascending and Multiple Oral Doses of Tegoprazan in Healthy Chinese Subjects. Clin. Drug Investig. 2021, 41, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Choi, H.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Nam, J.Y.; Kim, B.; Song, G.S.; Lim, H.S.; Bae, K.S. Effect of Food on the Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of a Single Oral Dose of Tegoprazan. Clin. Ther. 2021, 43, 1371–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.K.; Choi, M.G.; Choi, S.C.; Lee, K.M.; Kim, T.O.; Park, S.H.; Moon, J.S.; Lim, Y.J.; Kang, D.H.; Cheon, G.J.; et al. Randomised clinical trial: Tegoprazan, a novel potassium-competitive acid blocker, or lansoprazole in the treatment of gastric ulcer. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 52, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.J.; Lee, Y.C.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, J.I.; Moon, J.S.; Lim, Y.J.; Baik, G.H.; Son, B.K.; Lee, H.L.; Kim, K.O.; et al. Triple Therapy-Based on Tegoprazan, a New Potassium-Competitive Acid Blocker, for First-Line Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase III, Clinical Trial. Gut Liver 2022, 16, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Serag, H.B.; Lee, P.; Buchner, A.; Inadomi, J.M.; Gavin, M.; McCarthy, D.M. Lansoprazole treatment of patients with chronic idiopathic laryngitis: A placebo-controlled trial. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 96, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steward, D.L.; Wilson, K.M.; Kelly, D.H.; Patil, M.S.; Schwartzbauer, H.R.; Long, J.D.; Welge, J.A. Proton pump inhibitor therapy for chronic laryngo-pharyngitis: A randomized placebo-control trial. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. Off. J. Am. Acad. 2004, 131, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhou, X.; Fan, Z.; Qin, Y.; Zhan, J. Meta-analysis of Proton Pump Inhibitors in the Treatment of Pharyngeal Reflux Disease. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 9105814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Ma, H.; Wang, J. Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy for the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 50, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weihrauch, T.R.; Gauler, T.C. Placebo-efficacy and adverse effects in controlled clinical trials. Arzneimittelforschung 1999, 49, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, V.; Graf, S.; Schlag, C.; Schuster, T.; Feussner, H.; Schmid, R.M.; Bajbouj, M. First agreement analysis and day-to-day comparison of pharyngeal pH monitoring with pH/impedance monitoring in patients with suspected laryngopharyngeal reflux. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2012, 16, 1096–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechien, J.R.; Akst, L.M.; Hamdan, A.L.; Schindler, A.; Karkos, P.D.; Barillari, M.R.; Calvo-Henriquez, C.; Crevier-Buchman, L.; Finck, C.; Eun, Y.G.; et al. Evaluation and Management of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease: State of the Art Review. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. Off. J. Am. Acad. 2019, 160, 762–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bortoli, N.; Nacci, A.; Savarino, E.; Martinucci, I.; Bellini, M.; Fattori, B.; Ceccarelli, L.; Costa, F.; Mumolo, M.G.; Ricchiuti, A.; et al. How many cases of laryngopharyngeal reflux suspected by laryngoscopy are gastroesophageal reflux disease-related? World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2012, 18, 4363–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkos, P.D.; Wilson, J.A. Empiric treatment of laryngopharyngeal reflux with proton pump inhibitors: A systematic review. Laryngoscope 2006, 116, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Rouby, N.; Lima, J.J.; Johnson, J.A. Proton pump inhibitors: From CYP2C19 pharmacogenetics to precision medicine. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2018, 14, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaezi, M.F.; Richter, J.E.; Stasney, C.R.; Spiegel, J.R.; Iannuzzi, R.A.; Crawley, J.A.; Hwang, C.; Sostek, M.B.; Shaker, R. Treatment of chronic posterior laryngitis with esomeprazole. Laryngoscope 2006, 116, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Tegoprazan 50 mg | Placebo | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 17) | (n = 18) | ||
| Age (years) | 60.6 ± 12.2 | 58.4 ± 8.3 | 0.141 * |
| Sex | 0.088 † | ||
| Men | 3 (17.6) | 8 (44.4) | |
| Women | 14 (82.4) | 10 (55.6) | |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 23.5 ± 3.1 | 25.0 ± 3.0 | 0.142 * |
| Waist (cm) | 86.5 ± 6.8 | 89.3 ± 7.2 | 0.227 * |
| Alcohol consumption | 3 (17.7) | 6 (33.3) | 0.443 † |
| Smoking | 0 (0.0) | 1 (5.6) | 1.000 † |
| Reflux symptom index | 21.2 ± 6.2 | 22.1 ± 5.3 | 0.633 * |
| Reflux finding score | 10.4 ± 2.4 | 10.8 ± 1.8 | 0.502 * |
| Week 4 | p-Value | Week 8 | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tegoprazan | Placebo | Tegoprazan | Placebo | |||
| Full-analysis set | ||||||
| Number of patients | 17 | 18 | 17 | 18 | ||
| Complete resolution rate | 2 (11.8) | 4 (22.2) | 0.658 | 5 (29.4) | 5 (27.8) | 1.000 |
| Per-protocol set | ||||||
| Number of patients | 14 | 13 | 14 | 13 | ||
| Complete resolution rate | 1 (7.1) | 4 (30.8) | 0.165 | 4 (28.6) | 5 (38.5) | 0.695 |
| Group | Baseline | Week 4 | p-Value * | Week 8 | p-Value † | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSI score | Tegoprazan (n = 17) | 21.2 ± 6.2 | 16.8 ± 7.0 | 0.003 | 15.2 ± 7.8 | 0.002 |
| Placebo (n = 18) | 22.1 ± 5.3 | 15.9 ± 7.6 | <0.001 | 16.2 ± 9.6 | 0.002 | |
| p-value ‡ | 0.394 | 0.949 | ||||
| RFS score | Tegoprazan (n = 17) | 10.4 ± 2.4 | 8.5 ± 1.4 | <0.001 | 8.1 ± 1.4 | <0.001 |
| Placebo (n = 18) | 10.8 ± 1.8 | 9.1 ± 1.3 | <0.001 | 9.2 ± 1.8 | <0.001 | |
| p-value § | 0.279 | 0.073 |
| Group | Baseline | Week 4 | p-Value * | Week 8 | p-Value † | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSI score | Tegoprazan (n = 14) | 20.8 ± 6.5 | 17.0 ± 7.3 | 0.019 | 15.1 ± 8.2 | 0.010 |
| Placebo (n = 13) | 20.3 ± 4.9 | 14.1 ± 7.3 | <0.001 | 14.2 ± 9.8 | 0.008 | |
| p-value ‡ | 0.250 | 0.886 | ||||
| RFS score | Tegoprazan (n = 14) | 10.7 ± 2.2 | 8.6 ± 1.4 | <0.001 | 8.2 ± 1.4 | <0.001 |
| Placebo (n = 13) | 10.5 ± 1.5 | 8.6 ± 1.0 | <0.001 | 9.0 ± 1.9 | 0.002 | |
| p-value § | 0.936 | 0.219 |
| Tegoprazan (p-Value *) | Placebo (p-Value *) | Difference (p-Value †) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Changes in score between baseline and week 4 | |||
| RSI score | |||
| Hoarseness | −1.2 ± 1.9 (0.016) | −1.0 ± 1.4 (0.008) | −0.2 ± 1.7 (0.678) |
| Throat clearing | −0.5 ± 1.4 (0.146) | −0.9 ± 1.8 (0.049) | 0.4 ± 1.6 (0.449) |
| Throat mucus | −0.1 ± 1.5 (0.750) | −1.1 ± 1.2 (0.002) | 0.9 ± 1.4 (0.032) |
| Difficulty swallowing | 0.1 ± 0.9 (0.789) | −0.2 ± 0.9 (0.500) | 0.3 ± 0.9 (0.349) |
| Coughing after meals | −0.2 ± 1.0 (0.361) | −0.3 ± 1.5 (0.345) | 0.1 ± 1.3 (0.959) |
| Breathing difficulty | −0.4 ± 0.9 (0.188) | −0.2 ± 1.4 (0.495) | −0.1 ± 1.1 (0.912) |
| Annoying cough | −0.5 ± 1.5 (0.257) | −0.3 ± 1.3 (0.491) | −0.2 ± 1.4 (0.622) |
| Throat sensation | −0.7 ± 0.9 (0.023) | −1.2 ± 1.3 (0.001) | 0.6 ± 1.1 (0.190) |
| Heartburn | −0.9 ± 2.1 (0.058) | −0.9 ± 1.1 (0.002) | 0.0 ± 1.7 (0.774) |
| RFS score | |||
| Subglottic edema | −0.9 ± 1.0 (0.008) | −0.2 ± 1.4 (0.727) | −0.7 ± 1.2 (0.114) |
| Ventricular obliteration | 0.0 ± 0.7 (1.000) | −0.4 ± 0.9 (0.125) | 0.4 ± 0.8 (0.112) |
| Erythema | 0.1 ± 0.5 (1.000) | −0.1 ± 0.5 (1.000) | 0.2 ± 0.5 (0.176) |
| Vocal fold edema | −0.5 ± 0.6 (0.016) | −0.4 ± 0.7 (0.063) | −0.1 ± 0.7 (0.764) |
| Diffuse laryngeal edema | −0.2 ± 0.6 (0.250) | −0.1 ± 0.3 (0.500) | −0.1 ± 0.5 (0.568) |
| Posterior commissure hypertrophy | −0.2 ± 0.4 (0.125) | −0.1 ± 0.4 (1.000) | −0.2 ± 0.4 (0.235) |
| Granuloma/granulation tissue | 0.0 ± 0.0 | −0.1 ± 0.5 (1.000) | 0.1 ± 0.3 (0.360) |
| Thick endolaryngeal mucus | −0.1 ± 1.3 (1.000) | −0.3 ± 1.2 (0.453) | 0.2 ± 1.3 (0.637) |
| Changes in score between baseline and week 8 | |||
| RSI score | |||
| Hoarseness | −1.1 ± 1.8 (0.019) | −1.0 ± 1.5 (0.013) | −0.1 ± 1.7 (0.834) |
| Throat clearing | −0.8 ± 1.6 (0.036) | −1.0 ± 1.4 (0.008) | 0.2 ± 1.5 (0.643) |
| Throat mucus | −0.7 ± 1.8 (0.124) | −1.0 ± 1.2 (0.004) | 0.3 ± 1.5 (0.398) |
| Difficulty swallowing | 0.1 ± 1.1 (0.820) | 0.1 ± 1.3 (1.000) | 0.1 ± 1.2 (0.473) |
| Coughing after meals | −0.2 ± 0.8 (0.398) | −0.4 ± 1.3 (0.283) | 0.2 ± 1.1 (0.439) |
| Breathing difficulties | −0.6 ± 1.2 (0.056) | −0.3 ± 1.1 (0.240) | −0.3 ± 1.2 (0.491) |
| Annoying cough | −0.7 ± 1.7 (0.127) | −0.5 ± 1.4 (0.125) | −0.2 ± 1.6 (0.568) |
| Throat sensations | −1.1 ± 1.4 (0.005) | −1.1 ± 1.0 (0.001) | −0.1 ± 1.2 (0.932) |
| Heartburn | −0.8 ± 2.1 (0.120) | −0.7 ± 2.1 (0.099) | −0.2 ± 2.1 (0.919) |
| RFS score | |||
| Subglottic edema | −0.8 ± 1.0 (0.016) | 0.0 ± 1.2 (1.000) | −0.8 ± 1.1 (0.044) |
| Ventricular | 0.0 ± 1.0 (1.000) | −0.4 ± 0.9 (0.125) | 0.4 ± 0.9 (0.184) |
| Erythema | 0.0 ± 1.0 (1.000) | −0.1 ± 0.5 (1.000) | 0.1 ± 0.8 (0.704) |
| Vocal fold edema | −0.6 ± 0.6 (0.004) | −0.4 ± 0.6 (0.031) | −0.2 ± 0.6 (0.290) |
| Diffuse laryngeal edema | −0.2 ± 0.7 (0.313) | −0.1 ± 0.3 (0.500) | −0.1 ± 0.5 (0.586) |
| Posterior commissure hypertrophy | −0.2 ± 0.6 (0.250) | −0.1 ± 0.3 (0.500) | −0.1 ± 0.5 (0.568) |
| Granuloma/granulation tissue | 0.0 ± 0.0 | −0.1 ± 0.5 (1.000) | 0.1 ± 0.3 (0.360) |
| Thick endolaryngeal mucus | −0.4 ± 1.1 (0.375) | −0.3 ± 1.2 (0.453) | −0.0 ± 1.2 (1.000) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, H.K.; Kim, G.H.; Cheon, Y.-I.; Shin, S.-C.; Lee, B.J. Efficacy of Tegoprazan in Patients with Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease: A Preliminary Feasibility Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6116. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196116
Jeon HK, Kim GH, Cheon Y-I, Shin S-C, Lee BJ. Efficacy of Tegoprazan in Patients with Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease: A Preliminary Feasibility Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(19):6116. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196116
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Hye Kyung, Gwang Ha Kim, Yong-Il Cheon, Sung-Chan Shin, and Byung Joo Lee. 2023. "Efficacy of Tegoprazan in Patients with Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease: A Preliminary Feasibility Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 19: 6116. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196116
APA StyleJeon, H. K., Kim, G. H., Cheon, Y.-I., Shin, S.-C., & Lee, B. J. (2023). Efficacy of Tegoprazan in Patients with Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease: A Preliminary Feasibility Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(19), 6116. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196116







