Current and Emerging Markers and Tools Used in the Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease–Mineral and Bone Disorder in Non-Dialysis Adult Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. CKD-MBD/SHPT
1.2. Diagnostic Tools in CKD-MBD
1.3. Objective
2. General Markers of Mineral Dysregulation
2.1. Phosphate
2.2. Parathyroid Hormone
2.3. Vitamin D
2.4. Calcium
2.5. FGF-23
2.6. Klotho
3. Diagnostic Tools and Markers of Cardiovascular Dysfunction
3.1. Vascular Calcification in CKD-MBD
3.2. Vascular Calcification Imaging Tools
3.3. Pulse Wave Velocity
3.4. Regulators of Vascular Calcification
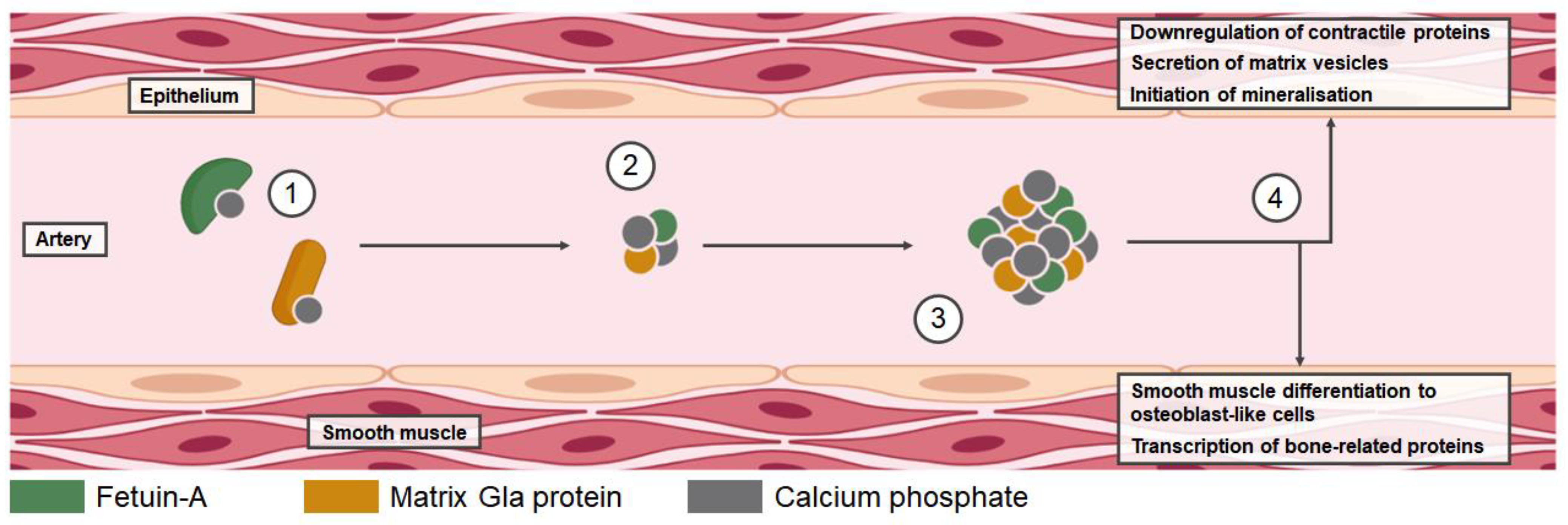
3.5. Fetuin-A
3.6. MGP
3.7. Primary and Secondary CPPs
3.8. Osteocalcin
4. Diagnostic Tools and Markers of Bone Dysregulation
4.1. Mechanism of Bone Deterioration
4.2. Alkaline Phosphatase
4.3. TRAP5b
4.4. P1NP
4.5. Sclerostin
4.6. Bone Histology Tools
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Chronic Kidney Disease, 1990–2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2020, 395, 709–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foreman, K.J.; Marquez, N.; Dolgert, A.; Fukutaki, K.; Fullman, N.; McGaughey, M.; Pletcher, M.A.; Smith, A.E.; Tang, K.; Yuan, C.-W.; et al. Forecasting Life Expectancy, Years of Life Lost, and All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality for 250 Causes of Death: Reference and Alternative Scenarios for 2016-40 for 195 Countries and Territories. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2018, 392, 2052–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, J.; Locatelli, F.; Rodriguez, M. Secondary Hyperparathyroidism: Pathogenesis, Disease Progression, and Therapeutic Options. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD-MBD Update Work Group KDIGO 2017 Clinical Practice Guideline Update for the Diagnosis, Evaluation, Prevention, and Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD). Kidney Int. Suppl. 2017, 7, 1–59. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ureña-Torres, P.A.; Vervloet, M.; Mazzaferro, S.; Oury, F.; Brandenburg, V.; Bover, J.; Cavalier, E.; Cohen-Solal, M.; Covic, A.; Drüeke, T.B.; et al. Novel Insights into Parathyroid Hormone: Report of The Parathyroid Day in Chronic Kidney Disease. Clin. Kidney J. 2019, 12, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketteler, M.; Ambühl, P. Where Are We Now? Emerging Opportunities and Challenges in the Management of Secondary Hyperparathyroidism in Patients with Non-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Nephrol. 2021, 34, 1405–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bover, J.; Arana, C.; Ureña, P.; Torres, A.; Martín-Malo, A.; Fayos, L.; Coll, V.; Lloret, M.J.; Ochoa, J.; Almadén, Y.; et al. Hyporesponsiveness or Resistance to the Action of Parathyroid Hormone in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nefrol. Engl. Ed. 2021, 41, 514–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD-MBD Work Group. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis, Evaluation, Prevention, and Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD). Kidney Int. Suppl. 2009, 76, S1–S130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairallah, P.; Nickolas, T.L. Management of Osteoporosis in CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 13, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervloet, M.G.; Massy, Z.A.; Brandenburg, V.M.; Mazzaferro, S.; Cozzolino, M.; Ureña-Torres, P.; Bover, J.; Goldsmith, D.; CKD-MBD Working Group of ERA-EDTA. Bone: A New Endocrine Organ at the Heart of Chronic Kidney Disease and Mineral and Bone Disorders. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covic, A.; Vervloet, M.; Massy, Z.A.; Torres, P.U.; Goldsmith, D.; Brandenburg, V.; Mazzaferro, S.; Evenepoel, P.; Bover, J.; Apetrii, M.; et al. Bone and Mineral Disorders in Chronic Kidney Disease: Implications for Cardiovascular Health and Ageing in the General Population. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, A.; Bakris, G.L.; Molitch, M.; Smulders, M.; Tian, J.; Williams, L.A.; Andress, D.L. Prevalence of Abnormal Serum Vitamin D, PTH, Calcium, and Phosphorus in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: Results of the Study to Evaluate Early Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2007, 71, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassalotti, J.A.; Uribarri, J.; Chen, S.-C.; Li, S.; Wang, C.; Collins, A.J.; Calvo, M.S.; Whaley-Connell, A.T.; McCullough, P.A.; Norris, K.C.; et al. Trends in Mineral Metabolism: Kidney Early Evaluation Program (KEEP) and the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 1999–2004. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2008, 51, S56–S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotondi, S.; Pasquali, M.; Tartaglione, L.; Muci, M.L.; Mandanici, G.; Leonangeli, C.; Sales, S.; Farcomeni, A.; Mazzaferro, S. Soluble α-Klotho Serum Levels in Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, e872193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalle Carbonare, L.; Valenti, M.T.; Giannini, S.; Gallieni, M.; Stefani, F.; Ciresa, R.; Politi, C.; Fusaro, M. Bone Biopsy for Histomorphometry in Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): State-of-the-Art and New Perspectives. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusaro, M.; Re Sartò, G.V.; Gallieni, M.; Cosmai, L.; Messa, P.; Rossini, M.; Chiodini, I.; Plebani, M.; Evenepoel, P.; Harvey, N.; et al. Time for Revival of Bone Biopsy with Histomorphometric Analysis in Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Moving from Skepticism to Pragmatism. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evenepoel, P.; Cunningham, J.; Ferrari, S.; Haarhaus, M.; Javaid, M.K.; Lafage-Proust, M.-H.; Prieto-Alhambra, D.; Torres, P.U.; Cannata-Andia, J.; European Renal Osteodystrophy (EUROD) workgroup, an initiative of the CKD-MBD working group of the ERA-EDTA, and the committee of Scientific Advisors and National Societies of the IOF. European Consensus Statement on the Diagnosis and Management of Osteoporosis in Chronic Kidney Disease Stages G4-G5D. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauppila, L.I.; Polak, J.F.; Cupples, L.A.; Hannan, M.T.; Kiel, D.P.; Wilson, P.W. New Indices to Classify Location, Severity and Progression of Calcific Lesions in the Abdominal Aorta: A 25-Year Follow-up Study. Atherosclerosis 1997, 132, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adragao, T.; Pires, A.; Lucas, C.; Birne, R.; Magalhaes, L.; Gonçalves, M.; Negrao, A.P. A Simple Vascular Calcification Score Predicts Cardiovascular Risk in Haemodialysis Patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2004, 19, 1480–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervloet, M.G.; Brandenburg, V.M. CKD-MBD working group of ERA-EDTA Circulating Markers of Bone Turnover. J. Nephrol. 2017, 30, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ureña-Torres, P.; D’Marco, L.; Raggi, P.; García-Moll, X.; Brandenburg, V.; Mazzaferro, S.; Lieber, A.; Guirado, L.; Bover, J. Valvular Heart Disease and Calcification in CKD: More Common than Appreciated. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 2046–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bover, J.; Aguilar, A.; Arana, C.; Molina, P.; Lloret, M.J.; Ochoa, J.; Berná, G.; Gutiérrez-Maza, Y.G.; Rodrigues, N.; D’Marco, L.; et al. Clinical Approach to Vascular Calcification in Patients with Non-Dialysis Dependent Chronic Kidney Disease: Mineral-Bone Disorder-Related Aspects. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 642718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bover, J.; Ureña-Torres, P.; Cozzolino, M.; Rodríguez-García, M.; Gómez-Alonso, C. The Non-Invasive Diagnosis of Bone Disorders in CKD. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2021, 108, 512–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, K.; Alderdice, J. Chronic Kidney Disease—Mineral and Bone Disorder: Pathophysiology and Treatment. Pharm. J. 2016, 8, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Duque, E.J.; Elias, R.M.; Moysés, R.M.A. Parathyroid Hormone: A Uremic Toxin. Toxins 2020, 12, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichel, H. Low-Dose Alfacalcidol Controls Secondary Hyperparathyroidism in Predialysis Chronic Kidney Disease. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2010, 114, c268–c276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K.J.; González, E.A. Metabolic Bone Disease in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nicola, L.; Conte, G.; Chiodini, P.; D’Angiò, P.; Donnarumma, G.; Minutolo, R. Interaction between Phosphorus and Parathyroid Hormone in Non-Dialysis CKD Patients under Nephrology Care. J. Nephrol. 2014, 27, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, W.G.; Salusky, I.B.; Jüppner, H. New Lessons from Old Assays: Parathyroid Hormone (PTH), Its Receptors, and the Potential Biological Relevance of PTH Fragments. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc.—Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2002, 17, 1731–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoye, J.U.; Arodiwe, E.B.; Ulasi, I.I.; Ijoma, C.K.; Onodugo, O.D. Prevalence of CKD-MBD in Pre-Dialysis Patients Using Biochemical Markers in Enugu, South-East Nigeria. Afr. Health Sci. 2015, 15, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einbinder, Y.; Benchetrit, S.; Golan, E.; Zitman-Gal, T. Comparison of Intact PTH and Bio-Intact PTH Assays Among Non-Dialysis Dependent Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Ann. Lab. Med. 2017, 37, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melamed, M.L.; Chonchol, M.; Gutiérrez, O.M.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kendrick, J.; Norris, K.; Scialla, J.J.; Thadhani, R. The Role of Vitamin D in CKD Stages 3 to 4: Report of a Scientific Workshop Sponsored by the National Kidney Foundation. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2018, 72, 834–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, P.; Molina, M.D.; Pallardó, L.M.; Torralba, J.; Escudero, V.; Álvarez, L.; Peris, A.; Sánchez-Pérez, P.; González-Rico, M.; Puchades, M.J.; et al. Disorders in Bone-Mineral Parameters and the Risk of Death in Persons with Chronic Kidney Disease Stages 4 and 5: The PECERA Study. J. Nephrol. 2021, 34, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, C.; Hamano, T.; Fujii, N.; Matsui, I.; Tomida, K.; Mikami, S.; Inoue, K.; Obi, Y.; Okada, N.; Tsubakihara, Y.; et al. Combined Use of Vitamin D Status and FGF23 for Risk Stratification of Renal Outcome. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 7, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketteler, M.; Bover, J.; Mazzaferro, S. ERA CKD-MBD Working Groups Treatment of Secondary Hyperparathyroidism in Non-Dialysis CKD: An Appraisal 2022s. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc.—Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2022, 38, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torregrosa, J.-V. Recomendaciones De La Sociedad Espanola De Nefrologia Para El Manejo De Las Alteraciones Del Metabolismo Oseo-Mineral En Los Pacientes Con Enfermedad Renal Cronica. 2021 (SEN-MM). Nefrología 2022, 42, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, P.U.; Troya, M.I.; Dauverge, M.; Bover, J. Independent Effects of Parathyroid Hormone and Phosphate Levels on Hard Outcomes in Non-Dialysis Patients: Food for Thought. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc.—Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2022, 37, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabibzadeh, N.; Karaboyas, A.; Robinson, B.M.; Csomor, P.A.; Spiegel, D.M.; Evenepoel, P.; Jacobson, S.H.; Ureña-Torres, P.-A.; Fukagawa, M.; Al Salmi, I.; et al. The Risk of Medically Uncontrolled Secondary Hyperparathyroidism Depends on Parathyroid Hormone Levels at Haemodialysis Initiation. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc.—Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2021, 36, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waziri, B.; Duarte, R.; Naicker, S. Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD): Current Perspectives. Int. J. Nephrol. Renov. Dis. 2019, 12, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprague, S.M.; Crawford, P.W.; Melnick, J.Z.; Strugnell, S.A.; Ali, S.; Mangoo-Karim, R.; Lee, S.; Petkovich, P.M.; Bishop, C.W. Use of Extended-Release Calcifediol to Treat Secondary Hyperparathyroidism in Stages 3 and 4 Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 2016, 44, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, E.T.; Martínez, M.E.; Jurutka, P.W. Vitamin D: Marker or Mechanism of Action? Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. Publ. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. Cosponsored Am. Soc. Prev. Oncol. 2011, 20, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bover, J.; Massó, E.; Gifre, L.; Alfieri, C.; Soler-Majoral, J.; Fusaro, M.; Calabia, J.; Rodríguez-Pena, R.; Rodríguez-Chitiva, N.; López-Báez, V.; et al. Vitamin D and Chronic Kidney Disease Association with Mineral and Bone Disorder: An Appraisal of Tangled Guidelines. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caravaca, F.; Villa, J.; García de Vinuesa, E.; Martínez del Viejo, C.; Martínez Gallardo, R.; Macías, R.; Ferreira, F.; Cerezo, I.; Hernández-Gallego, R. Relationship between Serum Phosphorus and the Progression of Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease. Nefrologia 2011, 31, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayed, A.; El Nokeety, M.M.; Heikal, A.A.; Abdulazim, D.O.; Naguib, M.M.; Sharaf El Din, U.A.A. Fibroblast Growth Factor-23 Is a Strong Predictor of Insulin Resistance among Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Ren. Fail. 2018, 40, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.; Faul, C. FGF23 Actions on Target Tissues-With and Without Klotho. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, P.U.; Prié, D.; Beck, L.; De Brauwere, D.; Leroy, C.; Friedlander, G. Klotho Gene, Phosphocalcic Metabolism, and Survival in Dialysis. J. Ren. Nutr. Off. J. Counc. Ren. Nutr. Natl. Kidney Found. 2009, 19, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, M.; Aspray, T.J.; Schoenmakers, I. Vitamin D Supplementation for Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses of Trials Investigating the Response to Supplementation and an Overview of Guidelines. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2021, 109, 157–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disthabanchong, S.; Boongird, S. Role of Different Imaging Modalities of Vascular Calcification in Predicting Outcomes in Chronic Kidney Disease. World J. Nephrol. 2017, 6, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenland, P.; Blaha, M.J.; Budoff, M.J.; Erbel, R.; Watson, K.E. Coronary Calcium Score and Cardiovascular Risk. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 434–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erben, R.G. Physiological Actions of Fibroblast Growth Factor-23. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isakova, T.; Xie, H.; Yang, W.; Xie, D.; Anderson, A.H.; Scialla, J.; Wahl, P.; Gutiérrez, O.M.; Steigerwalt, S.; He, J.; et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 and Risks of Mortality and End-Stage Renal Disease in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. JAMA 2011, 305, 2432–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alderson, H.V.; Ritchie, J.P.; Middleton, R.; Larsson, A.; Larsson, T.E.; Kalra, P.A. FGF-23 and Osteoprotegerin but Not Fetuin-A Are Associated with Death and Enhance Risk Prediction in Non-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Stages 3-5. Nephrol. Carlton Vic. 2016, 21, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.; Yang, B.; Zhou, C.; Dai, B.; Liu, Y.; Mao, Z.; Yu, S.; Mei, C. Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 Predicts All-Cause Mortality in a Dose-Response Fashion in Pre-Dialysis Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 2017, 45, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, E.; Yoshida, M.; Sasaki, S. Applicability of Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 for Evaluation of Risk of Vertebral Fracture and Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral Bone Disease in Elderly Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. BMC Nephrol. 2012, 13, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manou, E.; Thodis, E.; Arsos, G.; Pasadakis, P.; Panagoutsos, S.; Papadopoulou, D.; Papagianni, A. Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 and α-Klotho Protein Are Associated with Adverse Clinical Outcomes in Non-Dialysis CKD Patients. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2020, 45, 900–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, G.D.; Xie, J.; An, S.-W.; Huang, C.-L. New Insights into the Mechanism of Action of Soluble Klotho. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuro-o, M.; Matsumura, Y.; Aizawa, H.; Kawaguchi, H.; Suga, T.; Utsugi, T.; Ohyama, Y.; Kurabayashi, M.; Kaname, T.; Kume, E.; et al. Mutation of the Mouse Klotho Gene Leads to a Syndrome Resembling Ageing. Nature 1997, 390, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosu, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Clark, J.D.; Pastor, J.V.; Nandi, A.; Gurnani, P.; McGuinness, O.P.; Chikuda, H.; Yamaguchi, M.; Kawaguchi, H.; et al. Suppression of Aging in Mice by the Hormone Klotho. Science 2005, 309, 1829–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.C.; Kuro-o, M.; Moe, O.W. The Emerging Role of Klotho in Clinical Nephrology. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc.—Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2012, 27, 2650–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.R.; Nam, B.Y.; Kim, D.W.; Kang, M.W.; Han, J.-H.; Lee, M.J.; Shin, D.H.; Doh, F.M.; Koo, H.M.; Ko, K.I.; et al. Circulating α-Klotho Levels in CKD and Relationship to Progression. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2013, 61, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiler, S.; Wen, M.; Roth, H.J.; Fehrenz, M.; Flügge, F.; Herath, E.; Weihrauch, A.; Fliser, D.; Heine, G.H. Plasma Klotho Is Not Related to Kidney Function and Does Not Predict Adverse Outcome in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimamura, Y.; Hamada, K.; Inoue, K.; Ogata, K.; Ishihara, M.; Kagawa, T.; Inoue, M.; Fujimoto, S.; Ikebe, M.; Yuasa, K.; et al. Serum Levels of Soluble Secreted α-Klotho Are Decreased in the Early Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease, Making It a Probable Novel Biomarker for Early Diagnosis. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2012, 16, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Hu, M.C. Klotho/FGF23 Axis in Chronic Kidney Disease and Cardiovascular Disease. Kidney Dis. 2017, 3, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neyra, J.A.; Hu, M.C.; Moe, O.W. Klotho in Clinical Nephrology: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Implications. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Yang, J.; Bi, X.; Yu, Z.; Xiao, T.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, J.; Zhao, J. Serum Klotho, Cardiovascular Events, and Mortality in Nondiabetic Chronic Kidney Disease. Cardiorenal Med. 2020, 10, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yu, L.; Yin, X.; Ye, J.; Li, S. Correlation between Soluble Klotho and Vascular Calcification in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 711904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.-X.; Huang, C.; Duan, Z.-B.; Xu, C.-Y. The Clinical Value of Klotho and FGF23 in Cardiac Valve Calcification Among Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.-X.; Li, S.-S.; Sha, M.-Y.; Kong, J.-W.; Ye, J.-M.; Liu, Q.-F. The Controversy of Klotho as a Potential Biomarker in Chronic Kidney Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 931746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, B.-G.; Tsai, J.-P. Vascular Calcification of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Brief Review. Tzu Chi Med. J. 2021, 33, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, M.; Goettsch, C.; Aikawa, E. Medial and Intimal Calcification in Chronic Kidney Disease: Stressing the Contributions. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2013, 2, e000481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfamariam, B. Involvement of Vitamin K-Dependent Proteins in Vascular Calcification. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 24, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackey, R.H.; Venkitachalam, L.; Sutton-Tyrrell, K. Calcifications, Arterial Stiffness and Atherosclerosis. Adv. Cardiol. 2007, 44, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa-Bellosta, R. New Insights into Endogenous Mechanisms of Protection against Arterial Calcification. Atherosclerosis 2020, 306, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuro-O, M. Klotho and Calciprotein Particles as Therapeutic Targets against Accelerated Ageing. Clin. Sci. Lond. Engl. 1979 2021, 135, 1915–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giachelli, C.M. The Emerging Role of Phosphate in Vascular Calcification. Kidney Int. 2009, 75, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blacher, J.; Guerin, A.P.; Pannier, B.; Marchais, S.J.; London, G.M. Arterial Calcifications, Arterial Stiffness, and Cardiovascular Risk in End-Stage Renal Disease. Hypertension 2001, 38, 938–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, J.; Floege, J.; Fliser, D.; Böhm, M.; Marx, N. Cardiovascular Disease in Chronic Kidney Disease. Circulation 2021, 143, 1157–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marreiros, C.; Viegas, C.; Simes, D. Targeting a Silent Disease: Vascular Calcification in Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 16114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, J.; Oldendorf, M.; Moshage, W.; Heidler, R.; Zeitler, E.; Luft, F.C. Electron Beam Computed Tomography in the Evaluation of Cardiac Calcification in Chronic Dialysis Patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 1996, 27, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinsch, N.; Mahabadi, A.A.; Lehmann, N.; Möhlenkamp, S.; Hoefs, C.; Sievers, B.; Budde, T.; Seibel, R.; Jöckel, K.-H.; Erbel, R. Comparison of Dual-Source and Electron-Beam CT for the Assessment of Coronary Artery Calcium Scoring. Br. J. Radiol. 2012, 85, e300–e306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.K.; Cespedes, A.; Li, D.; Choi, T.-Y.; Budoff, M.J. Mild and Moderate Pre-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Is Associated with Increased Coronary Artery Calcium. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2011, 7, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garland, J.S.; Holden, R.M.; Hopman, W.M.; Gill, S.S.; Nolan, R.L.; Morton, A.R. Body Mass Index, Coronary Artery Calcification, and Kidney Function Decline in Stage 3 to 5 Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. J. Ren. Nutr. Off. J. Counc. Ren. Nutr. Natl. Kidney Found. 2013, 23, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, Y.-W.; Adler, S.G.; Budoff, M.J.; Takasu, J.; Ashai, J.; Mehrotra, R. Coronary Artery Calcification and Mortality in Diabetic Patients with Proteinuria. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarche, M.C.; Hopman, W.M.; Garland, J.S.; White, C.A.; Holden, R.M. Relationship of Coronary Artery Calcification with Renal Function Decline and Mortality in Predialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2019, 34, 1715–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouis, P.; Kousios, A.; Kanari, A.; Kleopa, D.; Papatheodorou, S.I.; Panayiotou, A.G. Association of Non-Invasive Measures of Subclinical Atherosclerosis and Arterial Stiffness with Mortality and Major Cardiovascular Events in Chronic Kidney Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Clin. Kidney J. 2020, 13, 842–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusaro, M.; Luigi Tripepi, G.; Aghi, A.; Politi, C.; Crimi, G.; Bazzocchi, A.; Girolami, M.; Sella, S.; Barbanti Brodano, G.; Schileo, E.; et al. MO547: A Novel Quantitative Computer-Assisted Score Can Improve Repeatability in the Estimate of Vascular Calcifications at the Abdominal Aorta. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2022, 37, gfac073.011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, G.; Capusa, C.; Stancu, S.; Petrescu, L.; Nedelcu, E.D.; Andreiana, I.; Mircescu, G. Abdominal Aortic Calcification and Renal Resistive Index in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: Is There a Connection? J. Nephrol. 2014, 27, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Hellberg, M.; Kouidi, E.; Deligiannis, A.; Höglund, P.; Clyne, N. Relationships between Abdominal Aortic Calcification, Glomerular Filtration Rate, and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Patients with Non-Dialysis Dependent Chronic Kidney Disease. Clin. Nephrol. 2018, 90, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górriz, J.L.; Molina, P.; Cerverón, M.J.; Vila, R.; Bover, J.; Nieto, J.; Barril, G.; Martínez-Castelao, A.; Fernández, E.; Escudero, V.; et al. Vascular Calcification in Patients with Nondialysis CKD over 3 Years. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, R.; Pereira, L.; Magalhães, J.; Quelhas-Santos, J.; Frazão, J. Low Bone Turnover Is Associated with Plain X-Ray Vascular Calcification in Predialysis Patients. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0258284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Berkel, B.; Van Ongeval, C.; Van Craenenbroeck, A.H.; Pottel, H.; De Vusser, K.; Evenepoel, P. Prevalence, Progression and Implications of Breast Artery Calcification in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Clin. Kidney J. 2022, 15, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, S.; Cockcroft, J.; Van Bortel, L.; Boutouyrie, P.; Giannattasio, C.; Hayoz, D.; Pannier, B.; Vlachopoulos, C.; Wilkinson, I.; Struijker-Boudier, H.; et al. Expert Consensus Document on Arterial Stiffness: Methodological Issues and Clinical Applications. Eur. Heart J. 2006, 27, 2588–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Lin, Y.; Ye, C.; Mao, Z.; Rong, S.; Zhao, X.; Mei, C. Effects of Peritoneal Dialysis and Hemodialysis on Arterial Stiffness Compared with Predialysis Patients. Clin. Nephrol. 2011, 75, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanakitcharu, P.; Jitsuparat, Y.; Jirajan, B. Prevalence of Arterial Stiffness and Associated Factors in Thai Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Kidney Transplant Recipients. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. Chotmaihet Thangphaet 2017, 100 (Suppl. S1), S56–S69. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.W.; Han, S.H.; Yoo, T.H.; Chung, W.; Park, S.K.; Chae, D.W.; Ahn, C.; Oh, K.-H. Relationship between Brachial-Ankle and Heart-Femoral Pulse Wave Velocities and the Rapid Decline of Kidney Function. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, Y.Y.; Kim, H.; Oh, K.-H.; Ahn, C.; Park, S.K.; Chae, D.W.; Han, S.H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, C.S.; et al. Arterial Stiffness as a Risk Factor for Subclinical Coronary Artery Calcification in Predialysis Chronic Kidney Disease: From the KNOW-CKD Study. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2019, 44, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olczyk, P.; Małyszczak, A.; Gołębiowski, T.; Letachowicz, K.; Szymczak, A.; Mazanowska, O.; Krajewska, M.; Kusztal, M. Arterial Stiffness Assessed by Oscillometric Method in Kidney Transplant, Predialysis, and Dialysis Patients. Transplant. Proc. 2020, 52, 2337–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgutkaya, A.; Aşçı, G. The Association between Hba1c and Arterial Stiffness among Non-Diabetic Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Vasc. Bras. 2021, 20, e20200245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Sharma, P.K.; Garg, V.K.; Mondal, S.C.; Singh, A.K.; Kumar, N. Role of Fetuin-A in Atherosclerosis Associated with Diabetic Patients. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2012, 64, 1703–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekol Abebe, E.; Tilahun Muche, Z.; Behaile T/Mariam, A.; Mengie Ayele, T.; Mekonnen Agidew, M.; Teshome Azezew, M.; Abebe Zewde, E.; Asmamaw Dejenie, T.; Asmamaw Mengstie, M. The Structure, Biosynthesis, and Biological Roles of Fetuin-A: A Review. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 945287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutikhin, A.G.; Feenstra, L.; Kostyunin, A.E.; Yuzhalin, A.E.; Hillebrands, J.-L.; Krenning, G. Calciprotein Particles: Balancing Mineral Homeostasis and Vascular Pathology. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 1607–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudloff, S.; Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Huynh-Do, U. Tissue Chaperoning-the Expanded Functions of Fetuin-A beyond Inhibition of Systemic Calcification. Pflugers Arch. 2022, 474, 949–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koos, R.; Brandenburg, V.; Mahnken, A.H.; Mühlenbruch, G.; Stanzel, S.; Günther, R.W.; Floege, J.; Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Kelm, M.; Kühl, H.P. Association of Fetuin-A Levels with the Progression of Aortic Valve Calcification in Non-Dialyzed Patients. Eur. Heart J. 2009, 30, 2054–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevinc, C.; Yilmaz, G.; Ustundag, S. The Relationship between Calcification Inhibitor Levels in Chronic Kidney Disease and the Development of Atherosclerosis. Ren. Fail. 2021, 43, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.R.; Ford, M.L.; Tomlinson, L.A.; Rajkumar, C.; McMahon, L.P.; Holt, S.G. Phosphorylated Fetuin-A-Containing Calciprotein Particles Are Associated with Aortic Stiffness and a Procalcific Milieu in Patients with Pre-Dialysis CKD. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc.—Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2012, 27, 1957–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Ji, Y.; Ju, H.; Chen, H.; Sun, M. Circulating Fetuin-A and Risk of All-Cause Mortality in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, D.S.; Grewal, R.; Le, T.H. Vitamin K Deficiency: An Emerging Player in the Pathogenesis of Vascular Calcification and an Iatrogenic Consequence of Therapies in Advanced Renal Disease. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2020, 319, F618–F623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaminon, A.M.G.; Dai, L.; Qureshi, A.R.; Evenepoel, P.; Ripsweden, J.; Söderberg, M.; Witasp, A.; Olauson, H.; Schurgers, L.J.; Stenvinkel, P. Matrix Gla Protein Is an Independent Predictor of Both Intimal and Medial Vascular Calcification in Chronic Kidney Disease. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manghat, P.; Souleimanova, I.; Cheung, J.; Wierzbicki, A.S.; Harrington, D.J.; Shearer, M.J.; Chowienczyk, P.; Fogelman, I.; Nerlander, M.; Goldsmith, D.; et al. Association of Bone Turnover Markers and Arterial Stiffness in Pre-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD). Bone 2011, 48, 1127–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurgers, L.J.; Barreto, D.V.; Barreto, F.C.; Liabeuf, S.; Renard, C.; Magdeleyns, E.J.; Vermeer, C.; Choukroun, G.; Massy, Z.A. The Circulating Inactive Form of Matrix Gla Protein Is a Surrogate Marker for Vascular Calcification in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Preliminary Report. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnatowska, I.; Grzelak, P.; Masajtis-Zagajewska, A.; Kaczmarska, M.; Stefańczyk, L.; Vermeer, C.; Maresz, K.; Nowicki, M. Plasma Desphospho-Uncarboxylated Matrix Gla Protein as a Marker of Kidney Damage and Cardiovascular Risk in Advanced Stage of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2016, 41, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, S.; Beatrice, A.M.; Ghosh, A.; Pramanik, S.; Bhattacharjee, R.; Ghosh, S.; Raychaudhury, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Chowdhury, S. Profile of Chronic Kidney Disease Related-Mineral Bone Disorders in Newly Diagnosed Advanced Predialysis Diabetic Kidney Disease Patients: A Hospital Based Cross-Sectional Study. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2017, 11 (Suppl. S2), S931–S937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusaro, M.; Tripepi, G.; Noale, M.; Plebani, M.; Zaninotto, M.; Piccoli, A.; Naso, A.; Miozzo, D.; Giannini, S.; Avolio, M.; et al. Prevalence of Vertebral Fractures, Vascular Calcifications, and Mortality in Warfarin Treated Hemodialysis Patients. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 13, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusaro, M.; Tondolo, F.; Gasperoni, L.; Tripepi, G.; Plebani, M.; Zaninotto, M.; Nickolas, T.L.; Ketteler, M.; Aghi, A.; Politi, C.; et al. The Role of Vitamin K in CKD-MBD. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2022, 20, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silaghi, C.N.; Ilyés, T.; Van Ballegooijen, A.J.; Crăciun, A.M. Calciprotein Particles and Serum Calcification Propensity: Hallmarks of Vascular Calcifications in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Isoyama, N.; Nakayama, Y.; Hiroyoshi, T.; Fujikawa, K.; Miura, Y.; Kurosu, H.; Matsuyama, H.; Kuro-O, M. Association between Amorphous Calcium-Phosphate Ratios in Circulating Calciprotein Particles and Prognostic Biomarkers in Hemodialysis Patients. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasch, A.; Farese, S.; Gräber, S.; Wald, J.; Richtering, W.; Floege, J.; Jahnen-Dechent, W. Nanoparticle-Based Test Measures Overall Propensity for Calcification in Serum. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1744–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasch, A.; Block, G.A.; Bachtler, M.; Smith, E.R.; Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Arampatzis, S.; Chertow, G.M.; Parfrey, P.; Ma, X.; Floege, J. Blood Calcification Propensity, Cardiovascular Events, and Survival in Patients Receiving Hemodialysis in the EVOLVE Trial. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.R.; Ford, M.L.; Tomlinson, L.A.; Bodenham, E.; McMahon, L.P.; Farese, S.; Rajkumar, C.; Holt, S.G.; Pasch, A. Serum Calcification Propensity Predicts All-Cause Mortality in Predialysis CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundy, J.D.; Cai, X.; Mehta, R.C.; Scialla, J.J.; de Boer, I.H.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Go, A.S.; Dobre, M.A.; Chen, J.; Rao, P.S.; et al. Serum Calcification Propensity and Clinical Events in CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 1562–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Karsenty, G. An Overview of the Metabolic Functions of Osteocalcin. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2015, 13, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacey, A.; Qaradakhi, T.; Brennan-Speranza, T.; Hayes, A.; Zulli, A.; Levinger, I. Potential Role for Osteocalcin in the Development of Atherosclerosis and Blood Vessel Disease. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacey, A.; Hayes, A.; Zulli, A.; Levinger, I. Osteocalcin and Vascular Function: Is There a Cross-Talk? Mol. Metab. 2021, 49, 101205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchelek-Mysliwiec, M.; Wisniewska, M.; Nowosiad-Magda, M.; Safranow, K.; Kwiatkowska, E.; Banach, B.; Dołegowska, B.; Dołegowska, K.; Stepniewska, J.; Domanski, L.; et al. Association between Plasma Concentration of Klotho Protein, Osteocalcin, Leptin, Adiponectin, and Bone Mineral Density in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Horm. Metab. Res. Horm. Stoffwechselforschung Horm. Metab. 2018, 50, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, X.; Cai, G. Osteocalcin Association with Vascular Function in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2022, 24, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ni, Z.; Zhou, W.; Qian, J. Undercarboxylated Osteocalcin as a Biomarker of Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Non-Dialysis Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Biomed. Sci. 2015, 22, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasello, S. Secondary Hyperparathyroidism and Chronic Kidney Disease. Diabetes Spectr. 2008, 21, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, N.A.; Weststrate, A.C.G.; Oosterlaan, F.M.; Verhaar, M.C.; Willems, H.C.; Emmelot-Vonk, M.H.; Hamaker, M.E. The Association between Chronic Kidney Disease, Falls, and Fractures: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Osteoporos. Int. 2020, 31, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drüeke, T.B.; Massy, Z.A. Changing Bone Patterns with Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-G.; Cheng, B.-C.; Lee, W.-C.; Li, L.-C.; Lee, C.-H.; Long, G.; Chen, J.-B. Serum Alkaline Phosphatase Levels Are Not Associated with Increased Death Risk in Prevalent Hemodialysis Patients: 5-Year Experience in a Single Hemodialysis Center. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2016, 41, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, A.; Qureshi, A.R.; Haarhaus, M.; Lindholm, B.; Barany, P.; Heimburger, O.; Stenvinkel, P.; Anderstam, B. Total and Bone-Specific Alkaline Phosphatase Are Associated with Bone Mineral Density over Time in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients Starting Dialysis. J. Nephrol. 2017, 30, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ureña, P.; Hruby, M.; Ferreira, A.; Ang, K.S.; de Vernejoul, M.C. Plasma Total versus Bone Alkaline Phosphatase as Markers of Bone Turnover in Hemodialysis Patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1996, 7, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regidor, D.L.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Mehrotra, R.; Rambod, M.; Jing, J.; McAllister, C.J.; Van Wyck, D.; Kopple, J.D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Serum Alkaline Phosphatase Predicts Mortality among Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 2193–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drechsler, C.; Verduijn, M.; Pilz, S.; Krediet, R.T.; Dekker, F.W.; Wanner, C.; Ketteler, M.; Boeschoten, E.W.; Brandenburg, V.; NECOSAD Study Group. Bone Alkaline Phosphatase and Mortality in Dialysis Patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 1752–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iimori, S.; Mori, Y.; Akita, W.; Kuyama, T.; Takada, S.; Asai, T.; Kuwahara, M.; Sasaki, S.; Tsukamoto, Y. Diagnostic Usefulness of Bone Mineral Density and Biochemical Markers of Bone Turnover in Predicting Fracture in CKD Stage 5D Patients--a Single-Center Cohort Study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc.—Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2012, 27, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haarhaus, M.; Fernström, A.; Magnusson, M.; Magnusson, P. Clinical Significance of Bone Alkaline Phosphatase Isoforms, Including the Novel B1x Isoform, in Mild to Moderate Chronic Kidney Disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc.—Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2009, 24, 3382–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidan, N.; Inci, A.; Coban, M.; Ulman, C.; Kursat, S. Bone Mineral Density and Biochemical Markers of Bone Metabolism in Predialysis Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Investig. Med. Off. Publ. Am. Fed. Clin. Res. 2016, 64, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomida, K.; Hamano, T.; Mikami, S.; Fujii, N.; Okada, N.; Matsui, I.; Nagasawa, Y.; Moriyama, T.; Ito, T.; Imai, E.; et al. Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D as an Independent Determinant of 1-84 PTH and Bone Mineral Density in Non-Diabetic Predialysis CKD Patients. Bone 2009, 44, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davina, J.J.; Priyadarssini, M.; Rajappa, M.; Parameswaran, S.; Sahoo, J.; Mohan Raj, P.S.; Revathy, G.; Palanivel, C.; Marella, M.G. Assessment of Bone Turnover Markers to Predict Mineral and Bone Disorder in Men with Pre-Dialysis Non-Diabetic Chronic Kidney Disease. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2017, 469, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C. The Use of Bone Turnover Markers in Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorders. Nephrol. Carlton Vic. 2017, 22 (Suppl. S2), 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.; Chao, T.-Y.; Lin, Y.-F.; Janckila, A.J.; Yam, L.T. Correlation between Histomorphometric Parameters of Bone Resorption and Serum Type 5b Tartrate-Resistant Acid Phosphatase in Uremic Patients on Maintenance Hemodialysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2003, 41, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malluche, H.H.; Davenport, D.L.; Cantor, T.; Monier-Faugere, M.-C. Bone Mineral Density and Serum Biochemical Predictors of Bone Loss in Patients with CKD on Dialysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salam, S.; Gallagher, O.; Gossiel, F.; Paggiosi, M.; Khwaja, A.; Eastell, R. Diagnostic Accuracy of Biomarkers and Imaging for Bone Turnover in Renal Osteodystrophy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, S.; Inaba, M.; Kurajoh, M.; Shidara, K.; Imanishi, Y.; Ishimura, E.; Nishizawa, Y. Utility of Serum Tartrate-Resistant Acid Phosphatase (TRACP5b) as a Bone Resorption Marker in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: Independence from Renal Dysfunction. Clin. Endocrinol. 2008, 69, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickolas, T.L.; Cremers, S.; Zhang, A.; Thomas, V.; Stein, E.; Cohen, A.; Chauncey, R.; Nikkel, L.; Yin, M.T.; Liu, X.S.; et al. Discriminants of Prevalent Fractures in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1560–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnero, P.; Vergnaud, P.; Hoyle, N. Evaluation of a Fully Automated Serum Assay for Total N-Terminal Propeptide of Type I Collagen in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figurek, A.; Rroji, M.; Spasovski, G. Sclerostin: A New Biomarker of CKD-MBD. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2020, 52, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Guan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, S.; Cao, B.; Ji, Y. Sclerostin as a New Key Factor in Vascular Calcification in Chronic Kidney Disease Stages 3 and 4. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2016, 48, 2043–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenburg, V.M.; Verhulst, A.; Babler, A.; D’Haese, P.C.; Evenepoel, P.; Kaesler, N. Sclerostin in Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral Bone Disorder Think First before You Block It! Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc.—Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2019, 34, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, R.; Pereira, L.; Magalhães, J.; Quelhas-Santos, J.; Martins, S.; Carvalho, C.; Frazão, J.M. Sclerostin and DKK1 Circulating Levels Associate with Low Bone Turnover in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Stages 3 and 4. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, 2401–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massy, Z.; Drueke, T. Adynamic Bone Disease Is a Predominant Bone Pattern in Early Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Nephrol. 2017, 30, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, B.L.; Drake, M.T. Clinical Utility of Serum Sclerostin Measurements. BoneKey Rep. 2013, 2, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delanaye, P.; Cavalier, E.; Bouquegneau, A.; Khwaja, A. Sclerostin Levels in CKD Patients: An Important, but Not Definitive, Step on the Way to Clinical Use. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 1221–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morena, M.; Jaussent, I.; Dupuy, A.-M.; Bargnoux, A.-S.; Kuster, N.; Chenine, L.; Leray-Moragues, H.; Klouche, K.; Vernhet, H.; Canaud, B.; et al. Osteoprotegerin and Sclerostin in Chronic Kidney Disease Prior to Dialysis: Potential Partners in Vascular Calcifications. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc.—Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2015, 30, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Chen, A.; Wang, H.; Cui, J.; Sun, Y.; Xu, L.; Mao, Y. The Relationship between Sclerostin and Carotid Artery Atherosclerosis in Patients with Stage 3-5 Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2020, 52, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanbay, M.; Siriopol, D.; Saglam, M.; Kurt, Y.G.; Gok, M.; Cetinkaya, H.; Karaman, M.; Unal, H.U.; Oguz, Y.; Sari, S.; et al. Serum Sclerostin and Adverse Outcomes in Nondialyzed Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E1854–E1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bembem, K.; Singh, T.; Singh, N.P.; Saxena, A.; Jain, S.L. Bone Histo-Morphology in Chronic Kidney Disease Mineral Bone Disorder. Indian J. Hematol. Blood Transfus. 2017, 33, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malluche, H.H.; Monier-Faugere, M.C. The Role of Bone Biopsy in the Management of Patients with Renal Osteodystrophy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1994, 4, 1631–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malluche, H.H.; Porter, D.S.; Pienkowski, D. Evaluating Bone Quality in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2013, 9, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal-Moscovici, A.; Sprague, S.M. Role of Bone Biopsy in Stages 3 to 4 Chronic Kidney Disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 3 (Suppl. 3), S170–S174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickolas, T.L.; Stein, E.; Cohen, A.; Thomas, V.; Staron, R.B.; McMahon, D.J.; Leonard, M.B.; Shane, E. Bone Mass and Microarchitecture in CKD Patients with Fracture. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1371–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, S.A.; Cheung, A.M.; West, S.L.; Lok, C.E. Bone Mineral Density by DXA and HR PQCT Can Discriminate Fracture Status in Men and Women with Stages 3 to 5 Chronic Kidney Disease. Osteoporos. Int. J. Establ. Result Coop. Eur. Found. Osteoporos. Natl. Osteoporos. Found. USA 2012, 23, 2805–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucur, R.C.; Panjwani, D.D.; Turner, L.; Rader, T.; West, S.L.; Jamal, S.A. Low Bone Mineral Density and Fractures in Stages 3–5 CKD: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Osteoporos. Int. J. Establ. Result Coop. Eur. Found. Osteoporos. Natl. Osteoporos. Found. USA 2015, 26, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connelly, K.; Collister, D.; Tangri, N. Fracture Risk and Treatment in Chronic Kidney Disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2018, 27, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairallah, P.; Nickolas, T.L.; Fusaro, M. How and When to Assess Bone Mineral Density and Bone Quality in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2021, 36, 774–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Song, S.H.; Kim, I.-J.; Jeon, Y.K. Is Dual-Energy Absorptiometry Accurate in the Assessment of Bone Status of Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease? Osteoporos. Int. J. Establ. Result Coop. Eur. Found. Osteoporos. Natl. Osteoporos. Found. USA 2021, 32, 1859–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittencourt, A.L.; Canziani, M.E.F.; Costa, L.D.B.R.; Rochitte, C.E.; Carvalho, A.B. Cortical Bone Density by Quantitative Computed Tomography Mirrors Disorders of Bone Structure in Bone Biopsy of Non-Dialysis CKD Patients. Bone Rep. 2022, 16, 101166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranhos-Neto, F.P.; Lima, G.A.C.; Silva, L.C.; Madeira, M.; Vieira Neto, L.; Mendonça, L.M.C.; Lima, I.C.B.; Delgado, A.G.; Leite, M.; Gomes, C.P.; et al. HR-PQCT Detects Alterations in Bone Microstructure in Men with CKD Stages 3 and 4, Which Are Influenced by Hormonal Changes and Body Composition. Clin. Nephrol. 2018, 89, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, K.; Kitamura, M.; Chiba, K.; Muta, K.; Yokota, K.; Okazaki, N.; Osaki, M.; Mukae, H.; Nishino, T. Comparison of Bone Microstructures via High-Resolution Peripheral Quantitative Computed Tomography in Patients with Different Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease before and after Starting Hemodialysis. Ren. Fail. 2022, 44, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampersad, C.; Whitlock, R.H.; Leslie, W.D.; Rigatto, C.; Komenda, P.; Bohm, C.; Hans, D.; Tangri, N. Trabecular Bone Score in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Osteoporos. Int. 2020, 31, 1905–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalayiannis, A.D.; Crabtree, N.J.; Ferro, C.J.; Wheeler, D.C.; Duncan, N.D.; Smith, C.; Popoola, J.; Varvara, A.; Mitsioni, A.; Kaur, A.; et al. Bone Mineral Density and Vascular Calcification in Children and Young Adults with CKD 4 to 5 or on Dialysis. Kidney Int. Rep. 2023, 8, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoeb, M.; Hamdy, N.A.T.; Malgo, F.; Winter, E.M.; Appelman-Dijkstra, N.M. Added Value of Impact Microindentation in the Evaluation of Bone Fragility: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Sáez, M.J.; Herrera, S.; Prieto-Alhambra, D.; Vilaplana, L.; Nogués, X.; Vera, M.; Redondo-Pachón, D.; Mir, M.; Güerri, R.; Crespo, M.; et al. Bone Density, Microarchitecture, and Material Strength in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients at the Time of Kidney Transplantation. Osteoporos. Int. 2017, 28, 2723–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| General Mineral Dysregulation Markers | |
| Phosphate | Essential for bone growth and mineralization; multiple key roles in cellular maintenance, metabolism and signaling |
| Parathyroid hormone | Regulates serum calcium and phosphate concentration through effects on the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys and bone |
| Calcium | Essential for bone formation; versatile signaling molecule with multiple physiological functions |
| 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) | The main circulating form of vitamin D; serves as a precursor to the active form of vitamin D—1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (1,25(OH)2D) |
| 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (1,25(OH)2D) | Increases absorption of calcium from the gastrointestinal tract and promotes its reabsorption in the kidneys; helps regulate phosphate levels; suppresses the release of PTH from the parathyroid glands |
| Fibroblast growth factor-23 (FGF-23) | Suppresses phosphate reabsorption and calcitriol synthesis in the kidney |
| Klotho | Obligate co-receptor for FGF-23; role in the regulation of survival and vascular calcification |
| Cardiovascular Dysfunction Markers | |
| Matrix Gla protein | Helps regulate vascular calcification by scavenging circulating calcium phosphate and interacting with fetuin-A to form primary calciprotein particles |
| Fetuin-A | Helps regulate vascular calcification by binding to calcium phosphate and interacting with matrix Gla protein to form primary calciprotein particles |
| Primary calciprotein particles (CPPs) | Develop into secondary CPPs, which contribute to vascular calcification |
| Secondary calciprotein particles (CPPs) | Are involved in the initiation and progression of vascular calcification |
| Osteocalcin | Promotes bone mineralization and plays a multifaceted role in cardiovascular health by influencing insulin sensitivity, vascular function, cardiac function and the regulation of calcification processes |
| Markers of Bone Turnover | |
| Bone-specific alkaline phosphatase | Contributes to the process of bone turnover by regulating bone matrix mineralization |
| Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase 5b (TRAP5b) | Released by osteoclasts to break down bone matrix |
| Procollagen type 1 N-terminal propeptide (P1NP) | A marker of bone formation released following extracellular cleavage of type 1 collagen |
| Sclerostin | Inhibits bone formation by osteoblasts and influences vascular calcification |
| Tools that Assess Cardiovascular Health | |
| Coronary artery calcification (CAC) score | Uses computed tomography to measure the amount of calcified plaque in the coronary arteries |
| Kauppila score | Uses lateral lumbar radiographs to quantify abdominal aortic calcification |
| Adragao score | Uses X-rays of the pelvis and hands to assess vascular calcifications of iliac, femoral, radial and digital arteries |
| Pulse wave velocity | Is a measure of arterial stiffness. It is calculated by measuring the time it takes for the arterial pulse to travel between two points (e.g., carotid and femoral arteries) divided by the distance between those points |
| Non-Invasive Tools that Assess Bone | |
| Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) | Uses spectral imaging to measure bone mineral density |
| Peripheral quantitative computed tomography (pQCT) | Is a 3D imaging technique used to quantify bone mineral density in peripheral skeletal sites, e.g., spine, proximal femur, forearm and tibia |
| Trabecular bone score (TBS) | Uses images acquired from lumbar spine DXA to evaluate bone texture variations and bone quality |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fusaro, M.; Pereira, L.; Bover, J. Current and Emerging Markers and Tools Used in the Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease–Mineral and Bone Disorder in Non-Dialysis Adult Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6306. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196306
Fusaro M, Pereira L, Bover J. Current and Emerging Markers and Tools Used in the Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease–Mineral and Bone Disorder in Non-Dialysis Adult Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(19):6306. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196306
Chicago/Turabian StyleFusaro, Maria, Luciano Pereira, and Jordi Bover. 2023. "Current and Emerging Markers and Tools Used in the Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease–Mineral and Bone Disorder in Non-Dialysis Adult Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 19: 6306. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196306
APA StyleFusaro, M., Pereira, L., & Bover, J. (2023). Current and Emerging Markers and Tools Used in the Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease–Mineral and Bone Disorder in Non-Dialysis Adult Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(19), 6306. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196306





