The Effect of PRP Augmentation of Arthroscopic Repairs of Shoulder Rotator Cuff Tears on Postoperative Clinical Scores and Retear Rates: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
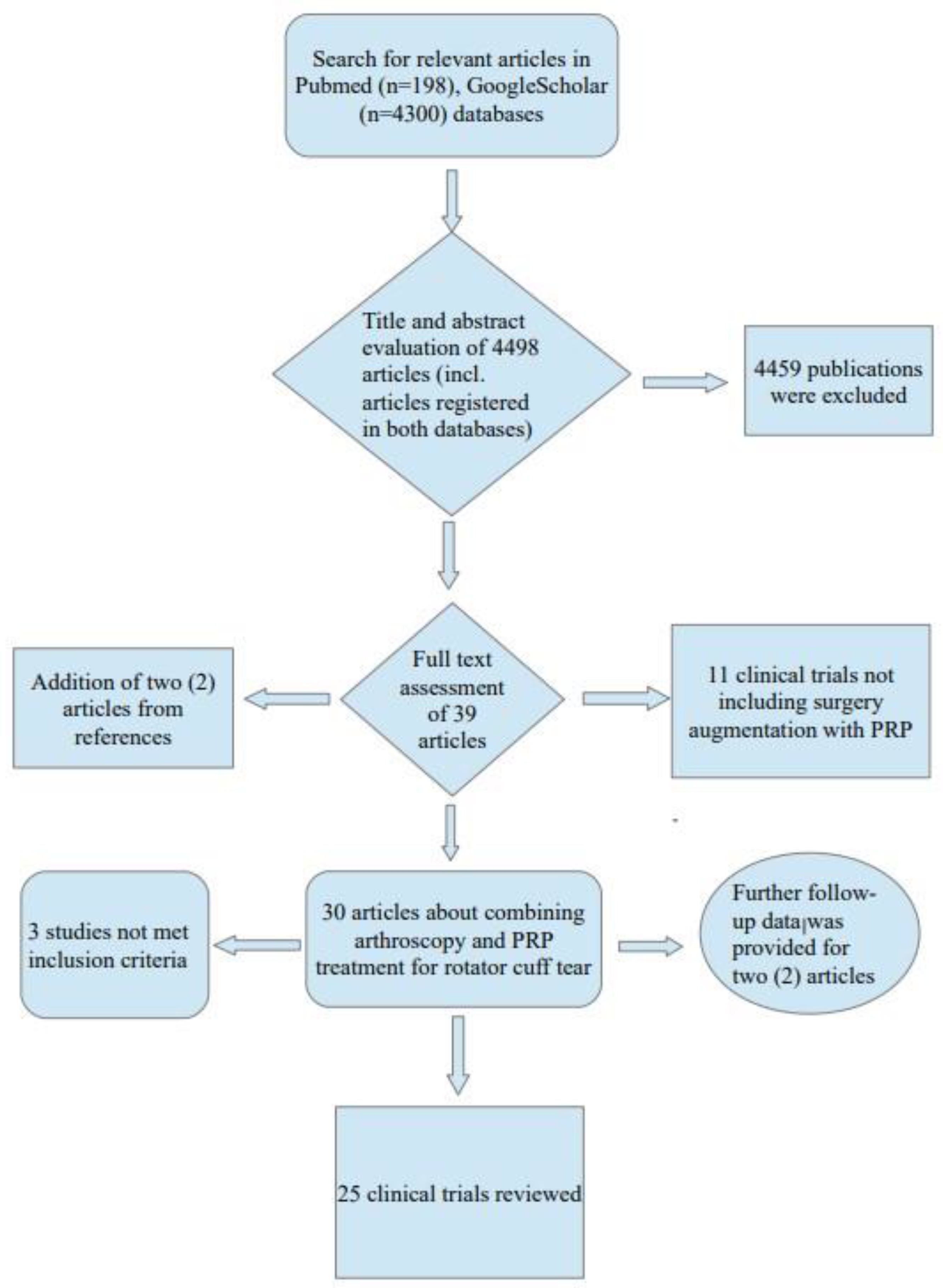
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion Criteria and Study Design
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Quality and Risk of Bias Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Arthroscopic Repair Techniques and Tear Characteristics
3.2. The Issue of Varying PRP Products
3.3. Administration Time and Dosage Scheme
3.4. Postoperative and Rehabilitation Protocols and Follow-Up Period
3.5. Clinical Results
3.6. Retear Rates and Imaging Results
3.7. Adverse Effects
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teunis, T.; Lubberts, B.; Reilly, B.T.; Ring, D. A systematic review and pooled analysis of the prevalence of rotator cuff disease with increasing age. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2014, 23, 1913–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galatz, L.M.; Ball, C.M.; Teefey, S.A.; Middleton, W.D.; Yamaguchi, K. The outcome and repair integrity of completely arthroscopically repaired large and massive rotator cuff tears. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2004, 86, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, C.; Fuchs, B.; Hodler, J. The results of repair of massive tears of the rotator cuff. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2000, 82, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, B.; Zumstein, M.; Pfirrmann, C.W.; Gerber, C. Long-term outcome after structural failure of rotator cuff repairs. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2006, 88, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebert, J.; Wang, A.; Smith, A.; Nairn, R.; Breidahl, W.; Zheng, M.H.; Ackland, T. A midterm evaluation of postoperative platelet-rich plasma injections on arthroscopic supraspinatus repair. Am. J. Sport. Med. 2017, 45, 2965–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhart, S.S.; Denard, P.J.; Konicek, J.; Hanypsiak, B.T. Biomechanical validation of load-sharing rip-stop fixation for the repair of tissue deficient rotator cuff tears. Am. J. Sport. Med. 2014, 42, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorbach, O.; Bachelier, F.; Vees, J.; Kohn, D.; Pape, D. Cyclic loading of rotator cuff reconstructions: Single-row repair with modified suture configurations versus double-row repair. Am. J. Sport. Med. 2008, 36, 1504–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salata, M.J.; Sherman, S.L.; Lin, E.C.; Sershon, R.A.; Gupta, A.; Shewman, E.; Wang, V.M.; Cole, B.J.; Romeo, A.A.; Verma, N.N. Biomechanical evaluation of transosseous rotator cuff repair: Do anchors really matter? Am. J. Sport. Med. 2013, 41, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, E.V.; Silverio, L.; Sperling, J.W. Strategies in biologic augmentation of rotator cuff repair: A review. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 1476–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castricini, R.; Longo, U.G.; De Benedetto, M.; Panfoli, N.; Pirani, P.; Zini, R.; Maffulli, N.; Denaro, V. Platelet-Rich Plasma Augmentation for Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Sport. Med. 2011, 39, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagna, A.; Cesari, E.; Gigante, A.; Conti, M.; Garofalo, R. Metalloproteases and their inhibitors are altered in both torn and intact rotator cuff tendons. Musculoskelet. Surg. 2013, 97, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, E.T.; Hannon, C.P.; Pauzenberger, L.; Fat, D.L.; Moran, C.J.; Mullett, H. Nonoperative Treatment of Rotator Cuff Disease With Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2019, 35, 1584–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baksh, N.; Hannon, C.P.; Murawski, C.D.; Smyth, N.A.; Kennedy, J.G. Platelet-rich plasma in tendon models: A systematic review of basic science literature. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2013, 29, 596–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohan Ehrenfest, D.M.; Rasmusson, L.; Albrektsson, T. Classification of platelet concentrates: From pure platelet-rich plasma (P-PRP) to leucocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF). Trends Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filiardo, G.; Di Matteo, B.; Kon, E.; Merli, G.; Marcacci, M. Platelet-rich plasma in tendon-related disorders: Results and indications. Knee Surg. Sport. Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2018, 26, 1984–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Management of Rotator Cuff Pathology Appropriate Use Criteria. Available online: https://www.aaos.org/rcauc (accessed on 4 December 2022).
- LaPrade, R.F.; Geeslin, A.G.; Murray, I.R.; Musahl, V.; Zlotnicki, J.P.; Petrigliano, F.; Mann, B.J. Biologic Treatments for Sports Injuries II Think Tank-Current Concepts, Future Research, and Barriers to Advancement, Part 1: Biologics Overview, Ligament Injury, Tendinopathy. Am. J. Sport. Med. 2016, 44, 3270–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jones, I.A.; Togashi, R.; Park, C.; Vangsness, C.T. Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Improvement of Pain and Function in Rotator Cuff Tears: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis With Bias Assessment. Am. J. Sport. Med. 2020, 48, 2028–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antuña, S.; Barco, R.; Diez, J.M.M.; Márquez, J.M.S. Platelet-rich fibrin in arthroscopic repair of massive rotator cuff tears: A prospective randomized pilot clinical trial. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2013, 79, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barber, F.A.; Hrnack, S.A.; Snyder, S.J.; Hapa, O. Rotator Cuff Repair Healing Influenced by Platelet-Rich Plasma Construct Augmentation. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2011, 27, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergeson, A.G.; Tashjian, R.Z.; Greis, P.E.; Crim, J.; Stoddard, G.J.; Burks, R.T. Effects of Platelet-Rich Fibrin Matrix on Repair Integrity of At-Risk Rotator Cuff Tears. Am. J. Sport. Med. 2012, 40, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, A.J.; Murphy, R.; Dakin, S.G.; Rombach, I.; Wheway, K.; Watkins, B.; Franklin, S.L. Platelet rich plasma injection with arthroscopic acromioplasty for chronic rotator cuff tendinopathy. Am. J. Sport. Med. 2015, 43, 2891–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charousset, C.; Zaoui, A.; Bellaiche, L.; Piterman, M. Does Autologous Leukocyte-Plateletet Rich Plasma Improve Tendon Healing in Arthroscopic Repair of Large or Massive Rotator Cuff Tears? Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2014, 30, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ambrosi, R.; Palumbo, F.; Paronzini, A.; Ragone, V.; Facchini, R.M. Platelet-rich plasma supplementation in arthroscopic repair of full-thickness rotator cuff tears: A randomized clinical trial. Musculoskelet. Surg. 2016, 100, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukan, R.; Bommier, A.; Rousseau, M.A.; Boyer, P. Arthroscopic knotless tape bridging with autologous platelet rich fibrin gel augmentation: Functional and structural results. Physician Sportsmed. 2019, 47, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flury, M.; Rickenbacher, D.; Schwyzer, H.K.; Jung, C.; Schneider, M.M.; Stahnke, K.; Goldhahn, J.; Audigé, L. Does Pure Platelet-Rich Plasma Affect Postoperative Clinical Outcomes After Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair? A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Sport. Med. 2016, 44, 2136–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumina, S.; Campagna, V.; Ferrazza, G.; Giannicola, G.; Fratalocchi, F.; Milani, A.; Postacchini, F. Use of platelet-leukocyte membrane in arthroscopic repair of large rotator cuff tears: A prospective randomized study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2012, 94, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwinner, C.; Gerhardt, C.; Haneveld, H.; Scheibel, M. Two-staged application of PRP in arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: A matched-pair analysis. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2016, 136, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hak, A.; Rajaratnam, K.; Ayeni, O.R.; Moro, J.; Peterson, D.; Sprague, S.; Bhandari, M. A Double-Blinded Placebo Randomized Controlled Trial Evaluating Short-term Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Reducing Postoperative Pain After Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair: A Pilot Study. Sport. Health 2015, 7, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jo, C.H.; Kim, J.E.; Yoon, K.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, S.B.; Lee, J.H.; Han, H.S.; Rhee, S.H.; Shin, S. Does platelet-rich plasma accelerate recovery after rotator cuff repair? A prospective cohort study. Am. J. Sport. Med. 2011, 39, 2082–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, C.H.; Shin, J.S.; Lee, Y.G.; Shin, W.H.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.Y.; Yoon, K.S.; Shin, S. Platelet-rich plasma for arthroscopic repair of large to massive rotator cuff tears: A randomized, single-blind, parallel-group trial. Am. J. Sport. Med. 2013, 41, 2240–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, C.H.; Shin, J.S.; Shin, W.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Yoon, K.S.; Shin, S. Platelet-rich plasma for arthroscopic repair of medium to large rotator cuff tears: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Sport. Med. 2015, 43, 2102–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malavolta, E.A.; Gracitelli, M.E.C.; Assunção, J.H.; Ferreira Neto, A.A.; Bordalo-Rodrigues, M.; de Camargo, O.P. Clinical and Structural Evaluations of Rotator Cuff Repair With and Without Added Platelet-Rich Plasma at 5-Year Follow-up: A Prospective Randomized Study. Am. J. Sport. Med. 2018, 46, 3134–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malavolta, E.A.; Gracitelli, M.E.C.; Ferreira Neto, A.A.; Assunção, J.H.; Bordalo-Rodrigues, M.; de Camargo, O.P. Platelet-rich plasma in rotator cuff repair: A prospective randomized study. Am. J. Sport. Med. 2014, 42, 2446–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malavolta, E.A.; Gracitelli, M.E.; Sunada, E.E.; Benegas, E.; de Santis Prada, F.; Neto, R.B.; Rodrigues, M.B.; Neto, A.A.; de Camargo, O.P. Platelet-Rich Plasma In Arthroscopic Repairs Of Complete Tears Of The Rotator Cuff. Rev. Bras. Ortop. 2015, 47, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marquez, J.M.S.; Diez, J.M.M.; Barco, R.; Antuña, S. Functional results after arthroscopic repair of massive rotator cuff tears; influence of the application platelet-rich plasma combined with fibrin. Rev. Esp. Cir. Ortop. Traumatol. 2011, 55, 282–287. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, V.; Bandi, A.; Madi, S.; Agarwal, L.; Acharya, K.K.; Maddukuri, S.; Sambhaji, C.; Willems, W.J. Does application of moderately concentrated platelet-rich plasma improve clinical and structural outcome after arthroscopic repair of medium-sized to large rotator cuff tear? A randomized controlled trial. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2016, 25, 1312–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randelli, P.; Arrigoni, P.; Ragone, V.; Aliprandi, A.; Cabitza, P. Platelet rich plasma in arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: A prospective RCT study, 2-year follow-up. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2011, 20, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodeo, S.A.; Delos, D.; Williams, R.J.; Adler, R.S.; Pearle, A.; Warren, R.F. The effect of platelet-rich fibrin matrix on rotator cuff tendon healing: A prospective, randomized clinical study. Am. J. Sport. Med. 2012, 40, 1234–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow, M.; Hussain, F.; Pagkalos, J.; Kowalski, T.; Green, M.; Massoud, S.; James, S. The Effect of Delayed Injection of Leukocyte-Rich Platelet-Rich Plasma Following Rotator Cuff Repair on Patient Function: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2020, 36, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; McCann, P.; Colliver, J.; Koh, E.; Ackland, T.; Joss, B.; Zheng, M.; Breidahl, B. Do postoperative platelet-rich plasma injections accelerate early tendon healing and functional recovery after arthroscopic supraspinatus repair? A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Sport. Med. 2015, 43, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, S.C.; Kauffman, J.I.; Parise, C.; Weber, S.J.; Katz, S.D. Platelet-rich fibrin matrix in the management of arthroscopic repair of the rotator cuff: A prospective, randomized, double-blinded study. Am. J. Sport. Med. 2013, 41, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J. The effect of platelet-rich plasma on arthroscopic double-row rotator cuff repair: A clinical study with 12-month follow-up. Acta Orthop. Traumatol. Turc. 2016, 50, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumstein, M.A.; Rumian, A.; Thélu, C.É.; Lesbats, V.; O’Shea, K.; Schaer, M.; Boileau, P. SECEC Research Grant 2008 II: Use of platelet- and leucocyte-rich fibrin (L-PRF) does not affect late rotator cuff tendon healing: A prospective randomized controlled study. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2016, 25, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aurégan, J.C.; Klouche, S.; Levy, B.; Bauer, T.; Rousselin, B.; Ferrand, M.; Hardy, P. Autologous Conditioned Plasma for tendon healing following arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. Prospective comparative assessment with magnetic resonance arthrography at 6 months’ follow-up. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2019, 105, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buford, D.A. Rotator Cuff Healing With and Without Platelet Rich Plasma Application. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2011, 27, e37–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Jüni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savovic, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.; et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wells, G.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses. 2013. Available online: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 4 December 2022).
- Longo, U.G.; Carnevale, A.; Piergentili, I.; Berton, A.; Candela, V.; Schena, E.; Denaro, V. Retear rates after rotator cuff surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabija, D.I.; Jain, N.B. Minimal Clinically Important Difference of Shoulder Outcome Measures and Diagnoses: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 98, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukkonen, J.; Kauko, T.; Vahlberg, T.; Joukainen, A.; Aärimaa, V. Investigating minimal clinically important difference for Constant score in patients undergoing rotator cuff surgery. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2013, 22, 1650–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Chen, J.Y.; Lie, H.M.E.; Hao, Y.; Lie, D.T.T. Minimal Clinically Important Difference of Oxford, Constant, and UCLA shoulder score for arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. J. Orthop. 2019, 19, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perser, K.; Godfrey, D.; Bisson, L. Meta-analysis of Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes After Arthroscopic Single-Row Versus Double-Row Rotator Cuff Repair. Sport. Health 2011, 3, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashjian, R.Z.; Shin, J.; Broschinsky, K.; Yeh, C.C.; Martin, B.; Chalmers, P.N.; Greis, P.E.; Burks, R.T.; Zhang, Y. Minimal clinically important differences in the American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons, Simple Shoulder Test, and visual analog scale pain scores after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2020, 29, 1406–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugaya, H.; Maeda, K.; Matsuki, K.; Moriishi, J. Functional and structural outcome after arthroscopic full-thickness rotator cuff repair: Single-row versus dual-row fixation. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2005, 21, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltzman, B.M.; Jain, A.; Campbell, K.A.; Mascarenhas, R.; Romeo, A.A.; Verma, N.N.; Cole, B.J. Does the Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma at the Time of Surgery Improve Clinical Outcomes in Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair When Compared With Control Cohorts? A Systematic Review of Meta-analyses. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2016, 32, 906–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Xue, Q. Application of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Orthop. J. Sport. Med. 2021, 9, 23259671211016847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vavken, P.; Sadoghi, P.; Palmer, M.; Rosso, C.; Mueller, A.M.; Szoelloesy, G.; Valderrabano, V. Platelet-Rich Plasma Reduces Retear Rates After Arthroscopic Repair of Small- and Medium-Sized Rotator Cuff Tears but Is Not Cost-Effective. Am. J. Sport. Med. 2015, 43, 3071–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chafik, D.; Yamaguchi, K. Outcomes after rotator cuff repair: Does healing matter? Semin. Arthroplast. 2009, 20, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henn, R.F.; Kang, L.; Tashjian, R.Z.; Green, A. Patients’ preoperative expectations predict the outcome of rotator cuff repair. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2007, 89, 1913–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iagulli, N.D.; Field, L.D.; Hobgood, E.R.; Ramsey, J.R.; Savoie, F.H. Comparison of partial versus complete arthroscopic repair of massive rotator cuff tears. Am. J. Sport. Med. 2012, 40, 1022–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baums, M.H.; Spahn, G.; Buchhorn, G.H.; Schultz, W.; Hofmann, L.; Klinger, H.M. Biomechanical and magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of a single- and double-row rotator cuff repair in an in vivo sheep model. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2012, 28, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, F.A. PRP as an Adjunct to Rotator Cuff Tendon Repair. Sport. Med. Arthrosc. Rev. 2018, 26, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragoo, J.L.; Braun, H.J.; Durham, J.L.; Ridley, B.A.; Odegaard, J.I.; Luong, R.; Arnoczky, S.P. Comparison of the acute inflammatory response of two commercial platelet-rich plasma systems in healthy rabbit tendons. Am. J. Sport. Med. 2012, 40, 1274–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Xu, W.; Dong, Q.; Huang, Q.; Xie, Z.; Mao, Y. Outcomes of single-row versus double-row arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: A systematic review and meta-analysis of current evidence. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2013, 29, 1437–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascarenhas, R.; Chalmers, P.N.; Sayegh, E.T.; Bhandari, M.; Verma, N.N.; Cole, B.J.; Romeo, A.A. Is double-row rotator cuff repair clinically superior to single-row rotator cuff repair: A systematic review of overlapping meta-analyses. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2014, 30, 1156–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukan, R.; Ledinot, P.; Donadio, J.; Boyer, P. Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair With a Knotless Suture Bridge Technique: Functional and Radiological Outcomes After a Minimum Follow-Up of 5 Years. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2019, 35, 2003–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, J.E.; Dunn, W.R.; Sanders, R.; An, Q.; Baumgarten, K.M.; Bishop, J.Y.; Brophy, R.H.; Carey, J.L.; Holloway, B.G.; Jones, G.L.; et al. Effectiveness of physical therapy in treating atraumatic full-thickness rotator cuff tears: A multicenter prospective cohort study. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2013, 22, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Selection Bias | Performance Bias | Detection Bias | Attrition Bias | Reporting Bias | Other Bias | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Random sequence generation | Allocation concealment | Blinding of participants and researchers | Blinding of outcome assessment | Incomplete outcome data | Selective reporting | ||
| Castricini et al. [10] | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Randelli et al. [38] | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Marquez et al. [36] | + | ? | - | - | + | + | + |
| Gumina et al. [27] | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Rodeo et al. [39] | + | + | + | - | + | + | ? |
| Weber et al. [42] | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Antuna et al. [19] | + | + | - | + | + | + | + |
| Jo et al. [31] | + | ? | - | - | + | + | + |
| Malavolta et al. [33,34] | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | + |
| Jo et al. [32] | + | ? | - | ? | + | + | + |
| Ebert, Wang et al. [5,41] | + | ? | - | - | + | + | + |
| Flury et al. [26] | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Pandey et al. [37] | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| D’Ambrosi et al. [24] | + | + | ? | + | + | + | + |
| Zumstein et al. [44] | + | ? | + | + | + | + | + |
| Snow et al. [40] | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Selection | Comparability | Outcome | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Representativeness of the exposed cohort | Selection of the non-exposed cohort | Ascertainment of exposure | Demonstration that outcome of interest was not present at start | Comparability of cohorts on the basis of the design or analysis | Assessment of outcome | Was follow-up long enough for outcomes to occur | Adequacy of follow up of cohorts | ||
| Barber et al. [20] | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | 9 |
| Jo et al. [30] | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | 9 |
| Bergeson et al. [21] | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | 9 |
| Buford [46] | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | 7 | ||
| Charousset et al. [23] | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | 8 | |
| Zhang et al. [43] | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | 9 |
| Gwinner et al. [28] | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | 9 |
| Dukan et al. [25] | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | 9 |
| Auregan et al. [45] | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎ | ⁎⁎ | ⁎ | 7 | ||
| PRP + Arthroscopy | Arthroscopy | Mean Difference | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Mean | SD | Total | Mean | SD | Total | Weight | IV, Fixed, 95% CI |
| Auregan et al. [45] | 77 | 13.5 | 26 | 72.4 | 12.3 | 23 | 2.2% | 4.6 [−2.62, 11.82] |
| Castricini et al. [10] | 88.4 | 7.62 | 43 | 88.4 | 7.78 | 45 | 10.8% | 0 [−3.22, 3.22] |
| Charousset et al. [23] | 77.3 | 9.9 | 31 | 78.1 | 7.7 | 30 | 5.7% | −0.8 [−5.24, 3.64] |
| D’Ambrosi et al. [24] | 81 | 11.2 | 20 | 78.5 | 9 | 20 | 2.8% | 2.5 [−3.8, 8.8] |
| Dukan et al. [25] | 86.7 | 11.1 | 32 | 81.6 | 14.4 | 37 | 3.1% | 5.1 [−0.93, 11.13] |
| Ebert, Wang et al. [5,41] | 86.2 | 11.4 | 27 | 85.2 | 11.3 | 28 | 3.1% | 1.0 [−5.0, 7.0] |
| Flury et al. [26] | 82.7 | 8 | 49 | 82.1 | 9.5 | 52 | 9.6% | 0.6 [−2.82, 4.02] |
| Gumina et al. [27] | 77.9 | 5.7 | 39 | 74.2 | 6.1 | 37 | 15.9% | 3.7 [1.04, 6.36] |
| Gwinner et al. [28] | 79 | 13 | 18 | 77 | 13 | 18 | 1.6% | 2.0 [−6.49, 10.49] |
| Jo et al. [30] | 79.12 | 13.42 | 19 | 82 | 13.02 | 23 | 1.7% | −2.88 [−10.93, 5.17] |
| Jo et al. [31] | 74.82 | 14.3 | 24 | 69.84 | 16.29 | 24 | 1.5% | 4.98 [−3.69, 13.65] |
| Jo et al. [32] | 74.67 | 9.17 | 37 | 70.87 | 9.76 | 37 | 6% | 3.8 [−0.52, 8.12] |
| Malavolta et al. [33,34] | 82.1 | 11 | 26 | 82 | 9.5 | 25 | 3.5% | 0.1 [−5.53, 5.73] |
| Marquez et al. [36] | 65.6 | 13.1 | 14 | 64.1 | 13.6 | 14 | 1.1% | 1.5 [−8.39, 11.39] |
| Pandey et al. [37] | 93.2 | 4.97 | 52 | 87.6 | 8.12 | 50 | 16.3% | 5.6 [2.98, 8.22] |
| Randelli et al. [38] | 82.4 | 6.3 | 22 | 78.7 | 10 | 23 | 4.8% | 3.7 [−1.16, 8.56] |
| Snow et al. [40] | 72.8 | 19.36 | 40 | 72.6 | 18.54 | 47 | 1.8% | 0.2 [−7.81, 8.21] |
| Zhang et al. [43] | 81.5 | 7.7 | 30 | 80.3 | 6.7 | 30 | 8.4% | 1.2 [−2.45, 4.85] |
| Total (95% CI) | 549 | 563 | 100% | 2.46 [1.4, 3.52] | ||||
| PRP + Arthroscopy | Arthroscopy | Mean Difference | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Mean | SD | Total | Mean | SD | Total | Weight | IV, Fixed, 95% CI |
| Flury et al. [26] | 92 | 12 | 50 | 92.5 | 12.8 | 54 | 12.2% | −0.5 [−5.27, 4.27] |
| Jo et al. [30] | 87.61 | 24.83 | 19 | 89.92 | 17.03 | 23 | 1.6% | −2.31 [−15.47, 10.85] |
| Jo et al. [31] | 88.94 | 13.61 | 24 | 85.56 | 17.26 | 24 | 3.6% | 3.38 [−5.41, 12.17] |
| Jo et al. [32] | 87.96 | 13.1 | 37 | 83.65 | 14.56 | 37 | 7% | 4.31 [−2.0, 10.62] |
| Pandey et al. [37] | 87.9 | 5.73 | 52 | 86.1 | 6.2 | 50 | 51.7% | 1.8 [−0.52, 4.12] |
| Rodeo et al. [39] | 91.3 | 9.53 | 19 | 96.43 | 5.55 | 22 | 11.7% | −5.13 [−10.0, −0.26] |
| Snow et al. [40] | 80.1 | 21.46 | 40 | 74.2 | 25.36 | 47 | 2.9% | 5.9 [−3.94, 15.74] |
| Weber et al. [42] | 82.48 | 8.77 | 29 | 82.52 | 12.45 | 30 | 9.3% | −0.04 [−5.52, 5.44] |
| Total (95% CI) | 270 | 287 | 100% | 0.82 [−0.85, 2.49] | ||||
| PRP + Arthroscopy | Arthroscopy | Mean Difference | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Mean | SD | Total | Mean | SD | Total | Weight | IV, Fixed, 95% CI |
| Charousset et al. [23] | 9.9 | 2.9 | 35 | 10.2 | 2 | 35 | 6.9% | −0.3 [−1.47, 0.87] |
| Gumina et al. [27] | 10.5 | 0.8 | 39 | 10.1 | 1 | 37 | 56% | 0.4 [−0.01, 0.81] |
| Jo et al. [30] | 9.83 | 3.31 | 19 | 10.57 | 1.73 | 23 | 3.4% | −0.74 [−2.39, 0.91] |
| Jo et al. [31] | 10.33 | 2.3 | 24 | 9.88 | 2.79 | 24 | 4.5% | 0.45 [−1.0, 1.9] |
| Jo et al. [32] | 10.24 | 2.14 | 37 | 9.76 | 2.27 | 37 | 9.3% | 0.48 [−0.53, 1.49] |
| Randelli et al. [38] | 11.3 | 0.9 | 22 | 10.9 | 1.4 | 23 | 19.9% | 0.4 [−0.28, 1.08] |
| Total (95% CI) | 176 | 179 | 100% | 0.32 [0.02, 0.63] | ||||
| PRP + Arthroscopy | Arthroscopy | Mean Difference | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Mean | SD | Total | Mean | SD | Total | Weight | IV, Fixed, 95% CI |
| Charousset et al. [23] | 29.1 | 2.3 | 35 | 30.3 | 3.2 | 35 | 21.2% | −1.2 [−2.51, 0.11] |
| Jo et al. [30] | 31.78 | 6.15 | 19 | 30.83 | 4.96 | 23 | 3.1% | 0.95 [−2.48, 4.38] |
| Jo et al. [31] | 30.13 | 3.98 | 24 | 29.21 | 6.04 | 24 | 4.3% | 0.92 [−1.97, 3.81] |
| Jo et al. [32] | 30.73 | 4.15 | 37 | 29.54 | 4.86 | 37 | 8.5% | 1.19 [−0.87, 3.25] |
| Malavolta et al. [33,34] | 32.1 | 4.6 | 26 | 32.5 | 3.8 | 25 | 6.8% | −0.4 [−2.71, 1.91] |
| Pandey et al. [37] | 34.75 | 0.72 | 52 | 32.22 | 3.55 | 50 | 35.9% | 2.53 [1.53, 3.53] |
| Randelli et al. [38] | 33.3 | 2.2 | 22 | 31.3 | 4.1 | 23 | 9.9% | 2.0 [0.09, 3.91] |
| Weber et al. [42] | 27.94 | 4.98 | 30 | 29.59 | 1.68 | 30 | 10.2% | −1.65 [−3.53, 0.23] |
| Total (95% CI) | 245 | 247 | 100% | 0.83 [0.23, 1.43] | ||||
| Arthroscopy + PRP | Arthroscopy | Risk Ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Retear incidents | Patients number | Retear incidents | Patients number | Weight | M-H, Fixed, 95% CI |
| Antuna et al. [19] | 13 | 14 | 10 | 14 | 5.9% | 1.3 [0.91, 1.87] |
| Auregan et al. [45] | 10 | 26 | 7 | 23 | 4.4% | 1.26 [0.58, 2.77] |
| Barber et al. [20] | 6 | 20 | 12 | 20 | 7.1% | 0.5 [0.23, 1.07] |
| Bergeson et al. [21] | 9 | 16 | 8 | 21 | 4.1% | 1.48 [0.74, 2.96] |
| Buford [46] | 2 | 50 | 3 | 50 | 1.8% | 0.67 [0.12, 3.82] |
| Castricini et al. [10] | 1 | 40 | 4 | 38 | 2.4% | 0.24 [0.03, 2.03] |
| Charousset et al. [23] | 11 | 31 | 12 | 30 | 7.2% | 0.89 [0.46, 1.69] |
| D’Ambrosi et al. [24] | 0 | 20 | 0 | 20 | Not estimable | |
| Dukan et al. [25] | 3 | 32 | 5 | 37 | 2.7% | 0.69 [0.18, 2.68] |
| Ebert, Wang et al. [5,41] | 2 | 29 | 3 | 30 | 1.7% | 0.69 [0.12, 3.83] |
| Flury et al. [26] | 5 | 49 | 9 | 53 | 5.1% | 0.6 [0.22, 1.67] |
| Gumina et al. [27] | 0 | 39 | 3 | 37 | 2.1% | 0.14 [0.01, 2.54] |
| Gwinner et al. [28] | 2 | 18 | 5 | 18 | 2.9% | 0.4 [0.09, 1.8] |
| Jo et al. [30] | 4 | 15 | 7 | 17 | 3.9% | 0.65 [0.24, 1.78] |
| Jo et al. [31] | 4 | 20 | 10 | 18 | 6.2% | 0.36 [0.14, 0.95] |
| Jo et al. [32] | 1 | 33 | 6 | 30 | 3.7% | 0.15 [0.02, 1.19] |
| Malavolta et al. [33,34] | 0 | 22 | 1 | 22 | 0.9% | 0.33 [0.01, 7.76] |
| Marquez et al. [36] | 9 | 14 | 6 | 14 | 3.5% | 1.5 [0.73, 3.08] |
| Pandey et al. [37] | 2 | 52 | 10 | 50 | 6.0% | 0.19 [0.04, 0.83] |
| Randelli et al. [38] | 9 | 22 | 12 | 23 | 6.9% | 0.78 [0.41, 1.48] |
| Rodeo et al. [39] | 12 | 36 | 6 | 31 | 3.8% | 1.72 [0.73, 4.05] |
| Snow et al. [40] | 6 | 39 | 8 | 38 | 4.8% | 0.73 [0.28, 1.91] |
| Weber et al. [42] | 12 | 28 | 7 | 24 | 4.4% | 1.47 [0.69, 3.13] |
| Zhang et al. [43] | 4 | 30 | 9 | 30 | 5.3% | 0.44 [0.15, 1.29] |
| Zumstein et al. [44] | 6 | 17 | 6 | 18 | 3.4% | 1.06 [0.42, 2.65] |
| Total (95% CI) | 133 | 712 | 169 | 706 | 100% | 0.78 [0.65, 0.94] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trantos, I.A.; Vasiliadis, E.S.; Giannoulis, F.S.; Pappa, E.; Kakridonis, F.; Pneumaticos, S.G. The Effect of PRP Augmentation of Arthroscopic Repairs of Shoulder Rotator Cuff Tears on Postoperative Clinical Scores and Retear Rates: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12020581
Trantos IA, Vasiliadis ES, Giannoulis FS, Pappa E, Kakridonis F, Pneumaticos SG. The Effect of PRP Augmentation of Arthroscopic Repairs of Shoulder Rotator Cuff Tears on Postoperative Clinical Scores and Retear Rates: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(2):581. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12020581
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrantos, Ioannis Angelos, Elias S. Vasiliadis, Filippos S. Giannoulis, Eleni Pappa, Fotios Kakridonis, and Spyros G. Pneumaticos. 2023. "The Effect of PRP Augmentation of Arthroscopic Repairs of Shoulder Rotator Cuff Tears on Postoperative Clinical Scores and Retear Rates: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 2: 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12020581
APA StyleTrantos, I. A., Vasiliadis, E. S., Giannoulis, F. S., Pappa, E., Kakridonis, F., & Pneumaticos, S. G. (2023). The Effect of PRP Augmentation of Arthroscopic Repairs of Shoulder Rotator Cuff Tears on Postoperative Clinical Scores and Retear Rates: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(2), 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12020581






