Percutaneous Deep Venous Arterialization for Limb Salvage in No Option Patients with Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Interpreting DVA
2. Percutaneous DVA (pDVA)
2.1. Benefits of pDVA
2.2. Adverse Effects and Disadvantages of pDVA
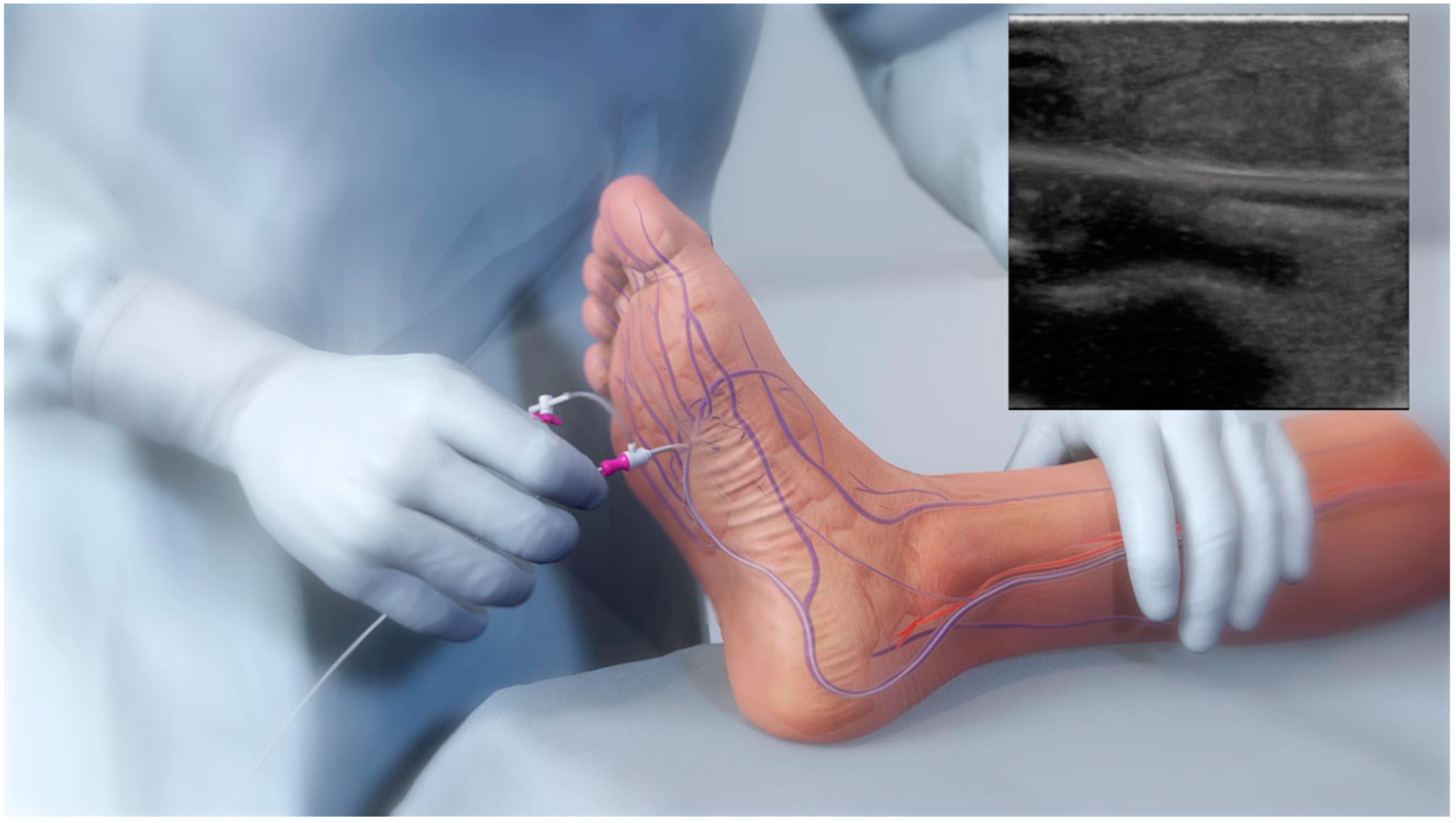
2.3. pDVA Techniques
2.4. Selection Criteria for pDVA Intervention
2.5. DVA Techniques
2.6. Benefits of LimFlow System—A Purpose-Built Device
2.7. The pDVA Procedure Using the LimFlow System
3. Studies Involving the LimFlow Device
3.1. PROMISE I
3.2. PROMISE II
3.3. ALPS
3.4. PROMISE International
3.5. PROMISE UK
3.6. PROMISE III
4. Discussion
DVA Failure Types
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shu, J.; Santulli, G. Update on peripheral artery disease: Epidemiology and evidence-based facts. Atherosclerosis 2018, 275, 379–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkoudis, N.A.; Katsanos, K.; Inchingolo, R.; Paraskevopoulos, I.; Mariappan, M.; Spiliopoulos, S. Quantifying tissue perfusion after peripheral endovascular procedures: Novel tissue perfusion endpoints to improve outcomes. World J. Cardiol. 2021, 13, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruchart, J.C.; Nierman, M.C.; Stroes, E.S.; Kastelein, J.J.; Duriez, P. New risk factors for atherosclerosis and patient risk assessment. Circulation 2004, 109 (Suppl. S1), III15–III19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norgren, L.; Hiatt, W.R.; Dormandy, J.A.; Nehler, M.R.; Harris, K.A.; Fowkes, F.G.R. Inter-Society Consensus for the Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease (TASC II). J. Vasc. Surg. 2007, 45, S5–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, M.W.; Undavalli, C.; Asi, N.; Wang, Z.; Elamin, M.B.; Conte, M.S.; Murad, M.H. The natural history of untreated severe or critical limb ischemia. J. Vasc. Surg. 2015, 62, 1642–1651.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uccioli, L.; Meloni, M.; Izzo, V.; Giurato, L.; Merolla, S.; Gandini, R. Critical limb ischemia: Current challenges and future prospects. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2018, 14, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caro, J.; Migliaccio-Walle, K.; Ishak, K.J.; Proskorovsky, I. The morbidity and mortality following a diagnosis of peripheral arterial disease: Long-term follow-up of a large database. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2005, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bevan, G.H.; White Solaru, K.T. Evidence-Based Medical Management of Peripheral Artery Disease. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, M.S.; Bradbury, A.W.; Kolh, P.; White, J.V.; Dick, F.; Fitridge, R.; Mills, J.L.; Ricco, J.-B.; Suresh, K.R.; Murad, M.H.; et al. Global vascular guidelines on the management of chronic limb-threatening ischemia. J. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 69, 3S–125S.e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreve, M.A.; Vos, C.G.; Vahl, A.C.; De Vries, J.P.P.M.; Kum, S.; de Borst, G.J.; Ünlü, Ç. Venous Arterialisation for Salvage of Critically Ischaemic Limbs: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2017, 53, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francois-Franck, M. Note à propos de la communication de M Raimond Petit sur la susture artério-veneuse. Compt. Rend. Hebd. Soc. Biol. 1896, 48, 150. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, V.T.; Gologorsky, R.; Kibrik, P.; Chandra, V.; Prent, A.; Lee, J.; Dua, A. Open, percutaneous, and hybrid deep venous arterialization technique for no-option foot salvage. J. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 71, 2152–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szilagyi, D.E.; Jay, G.D., 3rd; Munnell, E.R. Femoral arteriovenous anastomosis in the treatment of occlusive arterial disease. AMA Arch. Surg. 1951, 63, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheil, G.R. Treatment of critical ischaemia of the lower limb by venous arterialization: An interim report. Br. J. Surg. 1977, 64, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozek, C.; Zhang, F.; Lineaweaver, W.C.; Chin, B.T.; Newlin, L.; Eiman, T.; Buncke, H.J. Arterialization of the venous system in a rat lower limb model. Br. J. Plast Surg. 1997, 50, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, A.M.; Baffour, R.; Burdon, T.; Devarennes, B.; Ricci, M.A.; Common, A.; Lisbona, R.; Sniderman, A.D.; Symes, J.F. A demonstration of vascular proliferation in response to arteriovenous reversal in the ischemic canine hind limb. J. Surg. Res. 1989, 47, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baffour, R.; Danylewick, R.; Burdon, T.; Sniderman, A.; Common, A.; Graham, A.; Symes, J.F. An angiographic study of ischaemia as a determinant of neovascularisation in arteriovenous reversal. Surg. Gynaecol. Obstet. 1988, 166, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.W.; Hsu, C.H.; Jhang, Y.C.; Wang, C.C.; Chang, C.T.; Chen, H.C. Percutaneous Deep Vein Arterialization for a Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia Patient in Taiwan. Acta Cardiol. Sin. 2021, 37, 434–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saab, F.A.; Mustapha, J.A.; Ansari, M.; Pupp, G.; Madassery, K.; N’Dandu, Z.; Wiechmann, B.N.; Bernstein, R.; Mize, A.; Pliagas, G. Percutaneous Deep Venous Arterialization: Treatment of Patients with End-Stage Plantar Disease. J. Soc. Cardiovasc. Angiogr. Interv. 2022, 1, 100437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreve, M.A.; Lichtenberg, M.; Ünlü, Ç.; Branzan, D.; Schmidt, A.; van den Heuvel, D.A.; Blessing, E.; Brodmann, M.; Cabane, V.; Lin, W.T.Q. PROMISE international; a clinical post marketing trial investigating the percutaneous deep vein arterialization (LimFlow) in the treatment of no-option chronic limb ischemia patient. CVIR Endovasc. 2019, 2, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ysa, A.; Lobato, M.; Mikelarena, E.; Arruabarrena, A.; Gómez, R.; Apodaka, A.; Metcalfe, M.; Fonseca, J.L. Homemade Device to Facilitate Percutaneous Venous Arterialization in Patients with No-Option Critical Limb Ischemia. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2019, 26, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichihashi, S.; Shimohara, Y.; Bolstad, F.; Iwakoshi, S.; Kichikawa, K. Simplified Endovascular Deep Venous Arterialization for Non-option CLI Patients by Percutaneous Direct Needle Puncture of Tibial Artery and Vein under Ultrasound Guidance (AV Spear Technique). Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 43, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliara, B.; Cappellari, T.F. A Novel Technique to Create an Arteriovenous Fistula during Total Percutaneous Deep Foot Venous Arterialisation Using an IVUS Guided Catheter. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2018, 55, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandini, R.; Merolla, S.; Scaggiante, J.; Meloni, M.; Giurato, L.; Uccioli, L.; Konda, D. Endovascular Distal Plantar Vein Arterialization in Dialysis Patients with No-Option Critical Limb Ischemia and Posterior Tibial Artery Occlusion: A Technique for Limb Salvage in a Challenging Patient Subset. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2018, 25, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichihashi, S.; Iwakoshi, S.; Nakai, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hirose, T.; Furuichi, K.; Tamura, Y.; Tanaka, T. Role of Percutaneous Deep Venous Arterialization for Patients with Chronic Limb-threatening Ischemia. Interv. Radiol. 2023, 8, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kum, S.; Tan, Y.K.; Schreve, M.A.; Ferraresi, R.; Varcoe, R.L.; Schmidt, A.; Scheinert, D.; Mustapha, J.A.; Lim, D.A.; Ho, D. Midterm Outcomes from a Pilot Study of Percutaneous Deep Vein Arterialization for the Treatment of No-Option Critical Limb Ischemia. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2017, 24, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreve, M.A.; Minnee, R.C.; Bosma, J.; Leijdekkers, V.J.; Idu, M.M.; Vahl, A.C. Comparative study of venous arterialization and pedal bypass in a patient cohort with critical limb ischemia. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2014, 28, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Baker, M.; Sommerset Rvt, J.; Miranda, J.A. How I Do It: Hybrid Superficial Venous Arterialization and Endovascular Deep Venous Arterialization. J. Vasc. Surg. Cases Innov. Tech. 2023, 9, 101160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraresi, R.; Casini, A.; Losurdo, F.; Caminiti, M.; Ucci, A.; Longhi, M.; Schreve, M.; Lichtenberg, M.; Kum, S.; Clerici, G. Hybrid Foot Vein Arterialization in No-Option Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia: A Preliminary Report. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2019, 26, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrescu, V.; Ngongang, C.; Vincent, G.; Ledent, G.; Hubermont, G. Deep calf veins arterialization for inferior limb preservation in diabetic patients with extended ischaemic wounds, unfit for direct arterial reconstruction: Preliminary results according to an angiosome model of perfusion. Cardiovasc. Revasc. Med. 2011, 12, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montelione, N.; Catanese, V.; Gabellini, T.; Codispoti, F.A.; Nenna, A.; Spinelli, F.; Stilo, F. Duplex and Angiographic-Assisted Evaluation of Outcomes of Endovascular Embolization after Surgical Deep Vein Arterialization for the Treatment No-Option Critical Limb Ischemia Patients. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, T.; Miyamoto, A.; Ohura, N.; Yamauchi, Y. Percutaneous deep venous arterialization with balloon angioplasty salvaged a life-threatening critical limb in a hemodialysis patient after repeated pedal angioplasty failed: A case report. Clin. Case Rep. 2023, 11, e7589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clair, D.G.; Mustapha, J.A.; Shishehbor, M.H.; Schneider, P.A.; Henao, S.; Bernardo, N.N.; Deaton, D.H. PROMISE I: Early feasibility study of the LimFlow System for percutaneous deep vein arterialization in no-option chronic limb-threatening ischemia: 12-month results. J. Vasc. Surg. 2021, 74, 1626–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishehbor, M.H.; Powell, R.J.; Montero-Baker, M.F.; Dua, A.; Martínez-Trabal, J.L.; Bunte, M.C.; Lee, A.C.; Mugglin, A.S.; Mills, J.L.; Farber, A.; et al. Transcatheter Arterialization of Deep Veins in Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.; Schreve, M.A.; Huizing, E.; Del Giudice, C.; Branzan, D.; Ünlü, Ç.; Varcoe, R.L.; Ferraresi, R.; Midterm, S.K. Outcomes of Percutaneous Deep Venous Arterialization With a Dedicated System for Patients With No-Option Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia: The ALPS Multicenter Study. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2020, 27, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietzsch, J.B.; Ederhof, M.; Geisler, B.P.; Schneider, P.A. Cost-Effectiveness of Percutaneous Deep Vein Arterialization for Patients with No-Option Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia: An Exploratory Analysis Based on the PROMISE I Study. J. Crit. Limb Ischem. 2021, 1, E148–E157. [Google Scholar]
- Zaman, N.S.; Shackles, C.; Moriarty, K.T.; Herman, K.; Rundback, J.H. Patterns of Failure in Deep Venous Arterialization and Implications for Management. J. Crit. Limb Ischem. 2022, 2, E58–E63. [Google Scholar]
- Huizing, E.; Schreve, M.A.; Kum, S.; Papageorgiou, G.; de Vries, J.P.P.; de Borst, G.J.; Ünlü, Ç. Development of a Prediction Model for the Occurrence of Stenosis or Occlusion after Percutaneous Deep Venous Arterialization. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Advantages | Adverse Effects |
|---|---|
| Minimally invasive approach | Allergic reactions |
| Less chance of infection | Vascular complications (bleeding, hematoma) |
| Absence of wounds | Arterial and venous thromboembolic events (angina, stroke, limb ischemia, MI, PE, DVT) |
| Contrast-induced nephropathy and renal failure | |
| Local or systemic infection | |
| Stent thrombosis, in-stent stenosis | |
| Unsuccessful disruption of valves |
| Name | Purpose | Enrollment | AFS | Reintervention | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PROMISE I U.S. | To assess the safety, efficacy, and feasibility of the LimFlow system. | n = 32 | 91% (30-day) 74% (6-month) 70% (12-month) | n = 16 (52%) | Published April 2021 [35] |
| PROMISE II U.S. | To investigate the effectiveness and safety of the LimFlow System | n = 105 | 66.1% (6-month) | n = 38 (36.5%) | Published March 2023 [20] |
| PROMISE III U.S. | To provide additional data for the LimFlow system | n = 100 | Ongoing | ||
| ALPS Study | To evaluate the midterm results of pDVA performed with the LimFlow device in no-option CLTI patients | n = 32 | 83.9% (6-month) 71% (12-month) 67.2% (24-month) | n = 17 (59.4%) | Published May 2018 [35] |
| PROMISE International | To evaluate the clinical effectiveness and safety of the LimFlow System | n = 35 | Enrollment completed | ||
| PROMISE UK | To evaluate the clinical effectiveness and safety of the LimFlow System | n = 28 | Enrollment completed |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spiliopoulos, S.; Davoutis, E.; Arkoudis, N.-A.; Sritharan, K.; Lechareas, S. Percutaneous Deep Venous Arterialization for Limb Salvage in No Option Patients with Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7324. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237324
Spiliopoulos S, Davoutis E, Arkoudis N-A, Sritharan K, Lechareas S. Percutaneous Deep Venous Arterialization for Limb Salvage in No Option Patients with Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(23):7324. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237324
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpiliopoulos, Stavros, Efstathia Davoutis, Nikolaos-Achilleas Arkoudis, Kaji Sritharan, and Symeon Lechareas. 2023. "Percutaneous Deep Venous Arterialization for Limb Salvage in No Option Patients with Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 23: 7324. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237324
APA StyleSpiliopoulos, S., Davoutis, E., Arkoudis, N.-A., Sritharan, K., & Lechareas, S. (2023). Percutaneous Deep Venous Arterialization for Limb Salvage in No Option Patients with Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(23), 7324. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237324








