Autophagy Inhibition in Trophoblasts Induces Aberrant Shift in CXCR4+ Decidual NK Cell Phenotype Leading to Pregnancy Loss
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Tissue Samples
2.2. Cell Isolation and Culture
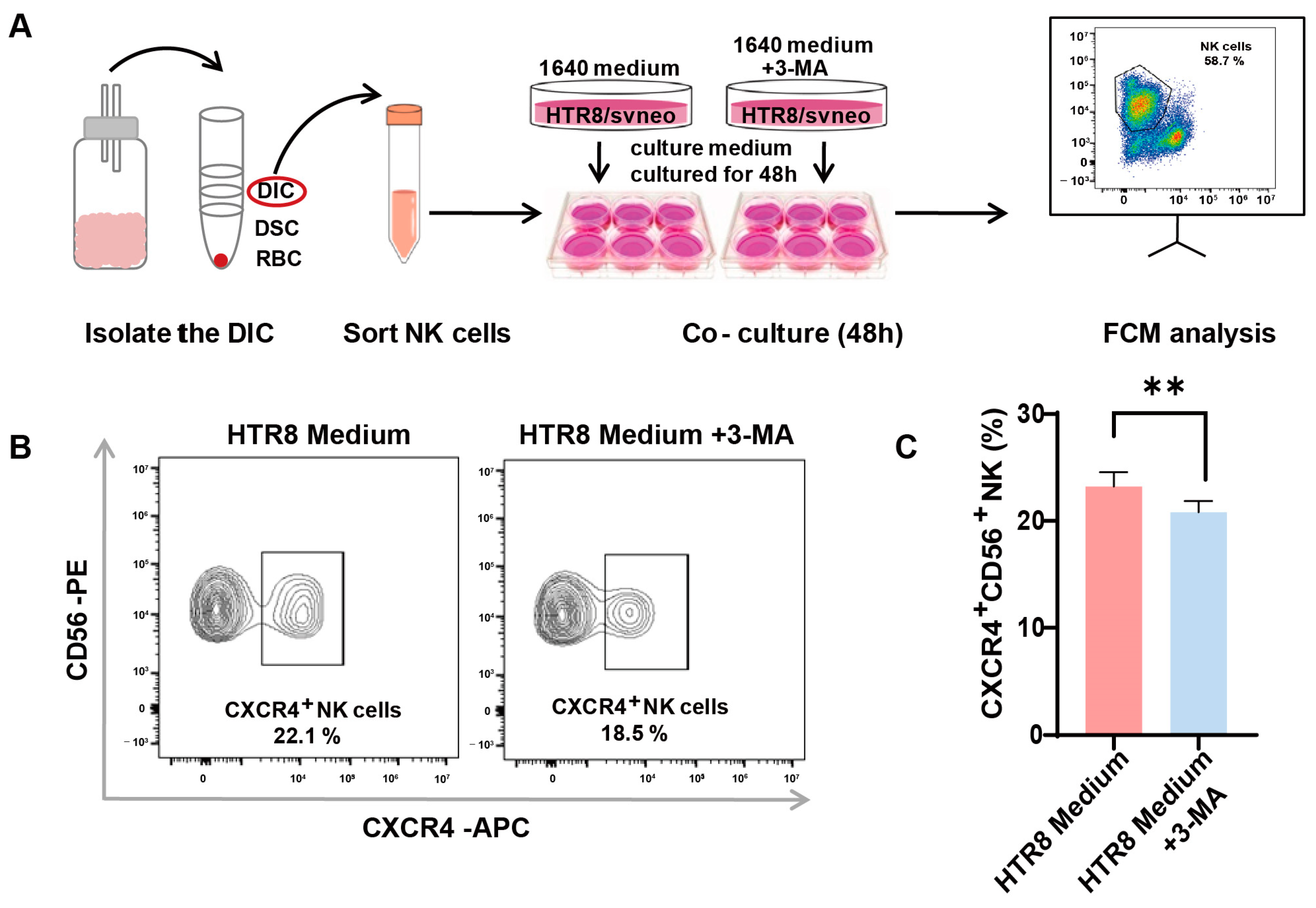
2.3. Co-Culture System
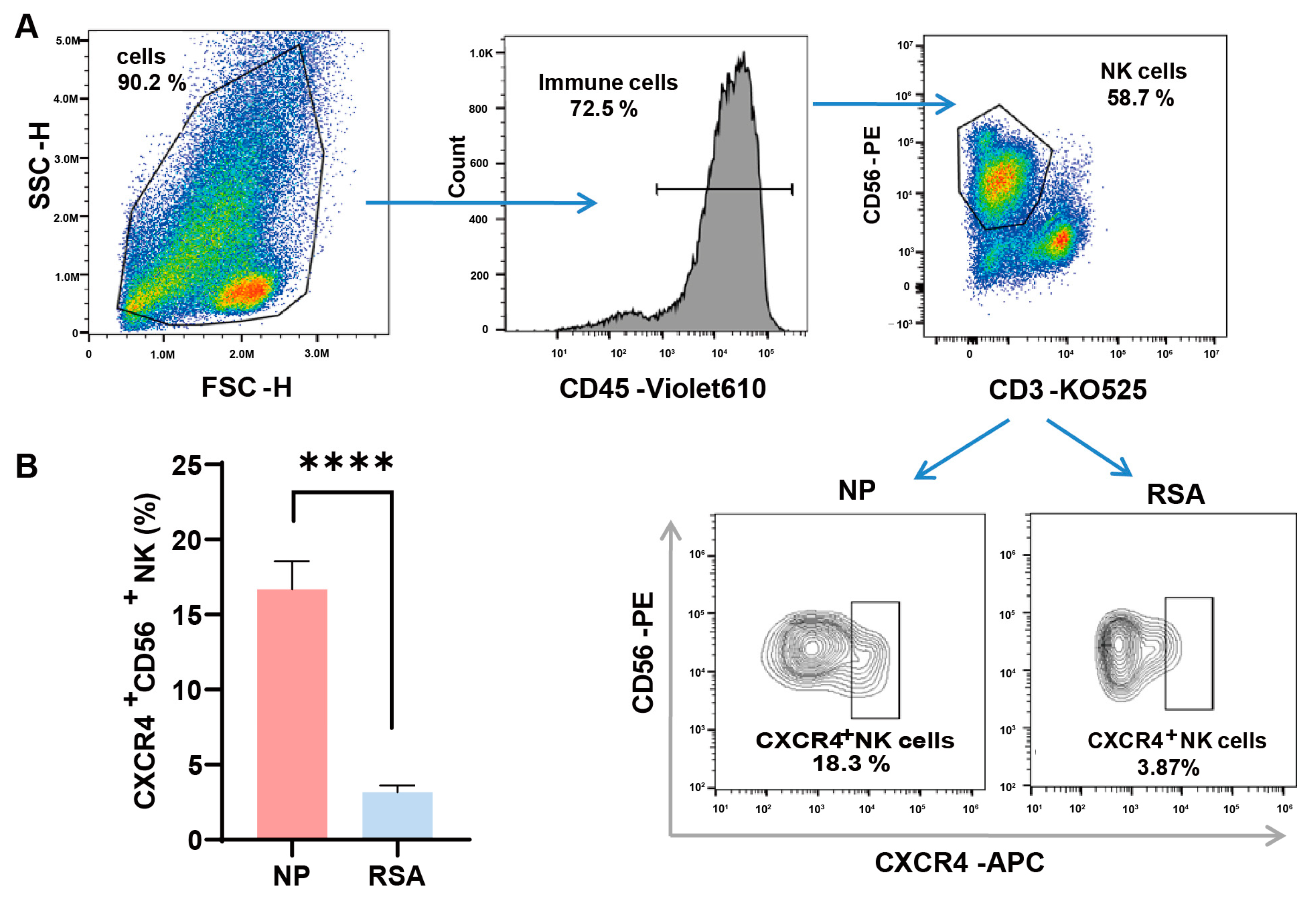
2.4. Flow Cytometry Assays
2.5. Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR (qRT-PCR)
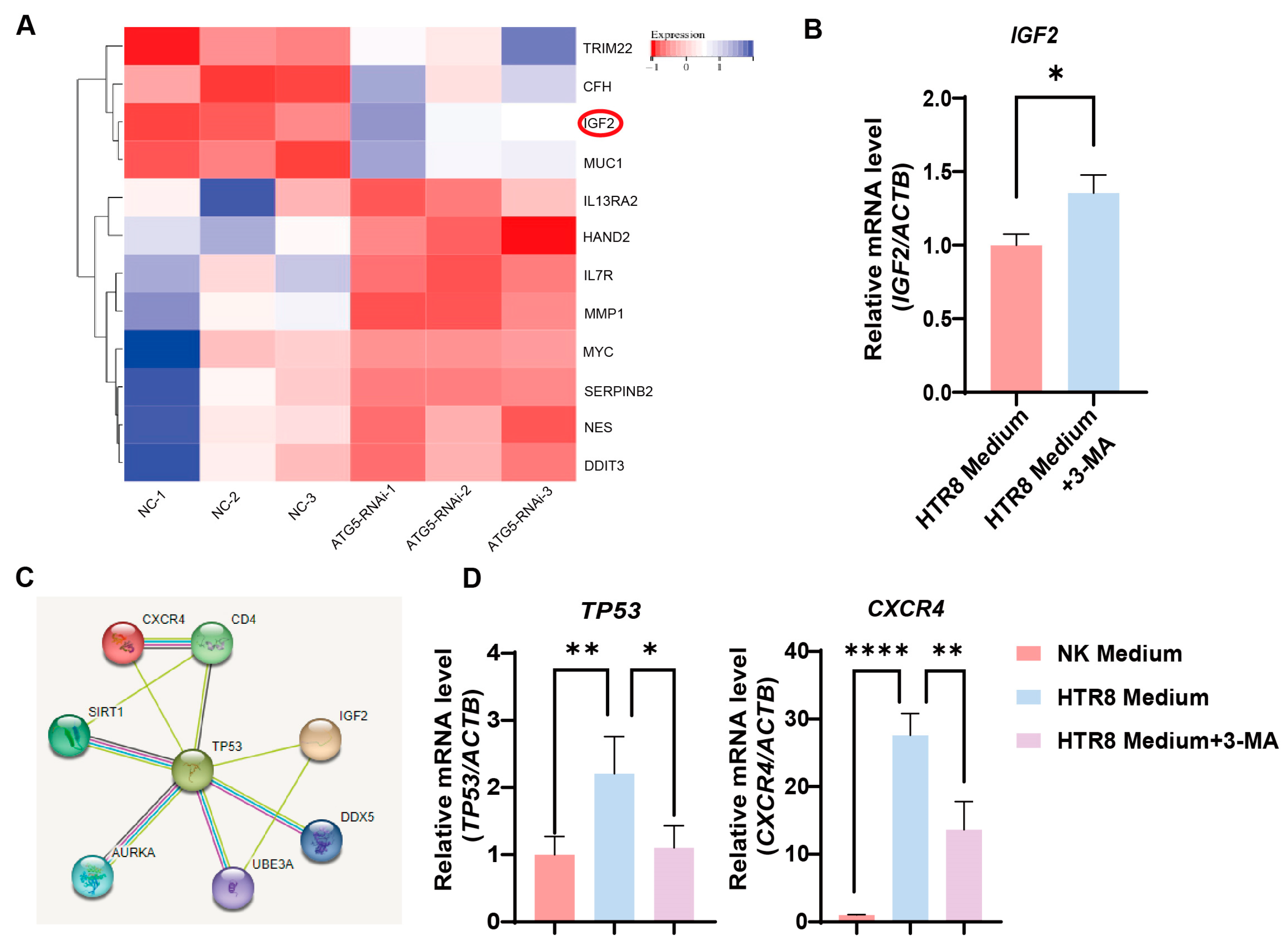
2.6. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Reduced CXCR4 Expression in dNK Cells of RSA Patients
3.2. Enhanced CXCR4 Expression in dNK Cells Co-Cultured with Trophoblast-Derived Supernatant
3.3. Autophagy Inhibition in Trophoblasts Restricts CXCR4 Expression in dNK Cells
3.4. Trophoblast Autophagy Modulates CXCR4 Expression in NK-92 Cells via IGF2
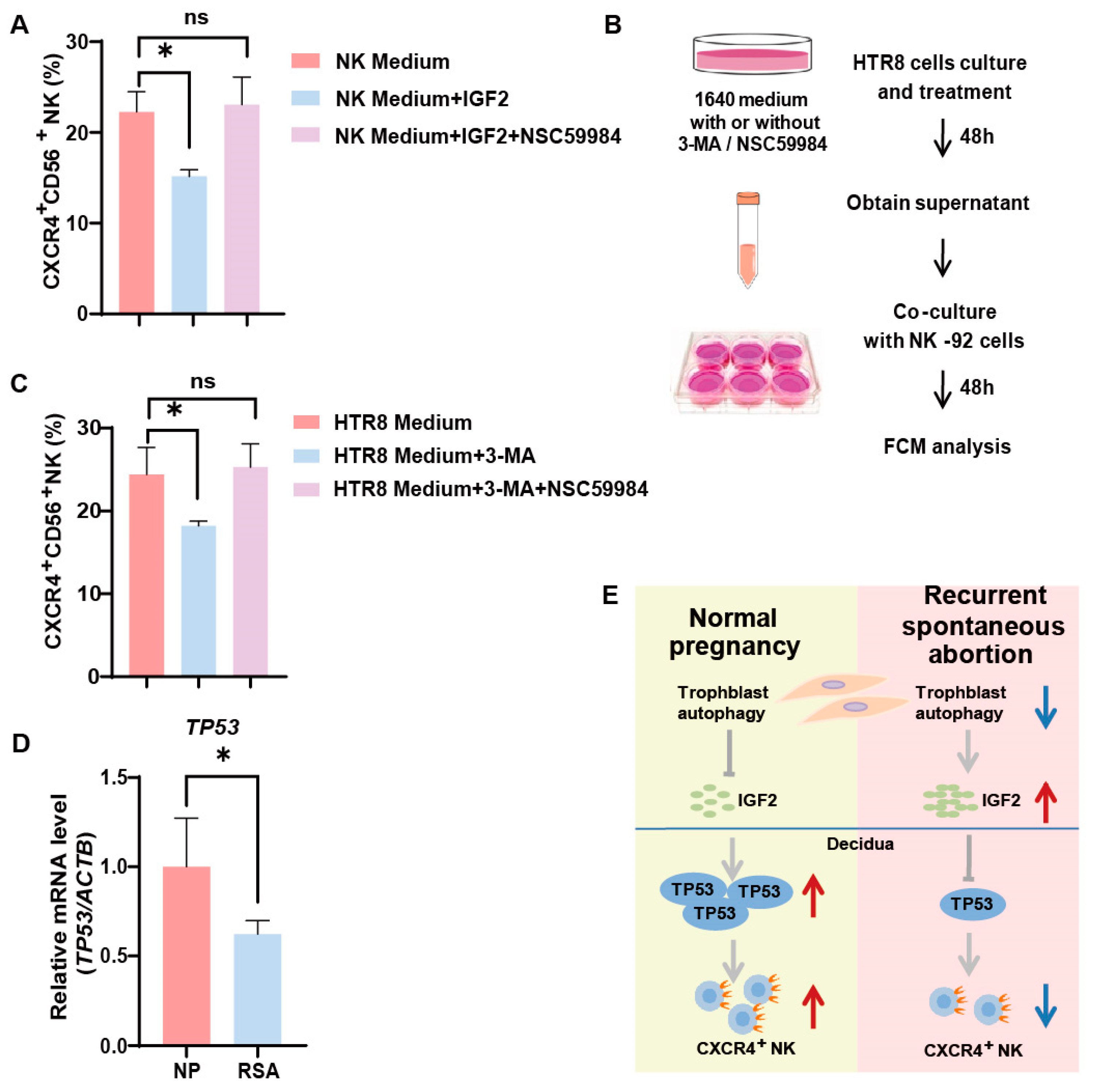
3.5. Trophoblast Autophagy Influences NK Cells via IGF2-TP53-CXCR4 Axis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NP | Normal pregnancy |
| RSA | Recurrent spontaneous abortion |
| IGF2 | Insulin-like growth factor 2 |
| 3-MA | 3-methyladenine |
| DIC | Decidual immune cell |
| RBC | Red blood cell |
| FCM | Flow cytometry |
References
- Shao, T.Y.; Kinder, J.M.; Harper, G.; Pham, G.; Peng, Y.; Liu, J.; Gregory, E.J.; Sherman, B.E.; Wu, Y.; Iten, A.E.; et al. Reproductive outcomes after pregnancy-induced displacement of preexisting microchimeric cells. Science 2023, 381, 1324–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trowsdale, J.; Betz, A.G. Mother’s little helpers: Mechanisms of maternal-fetal tolerance. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitriadis, E.; Menkhorst, E.; Saito, S.; Kutteh, W.H.; Brosens, J.J. Recurrent pregnancy loss. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshmukh, H.; Way, S.S. Immunological Basis for Recurrent Fetal Loss and Pregnancy Complications. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2019, 14, 185–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Xu, Q.H.; Ma, L.N.; Luo, J.; Muyayalo, K.P.; Wang, L.L.; Huang, D.H.; Xiao, X.J.; Cheng, S.B.; Mor, G.; et al. Trophoblast-derived Lactic Acid Orchestrates Decidual Macrophage Differentiation via SRC/LDHA Signaling in Early Pregnancy. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 599–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.L.; Lai, Z.Z.; Shi, J.W.; Zhou, W.J.; Mei, J.; Ye, J.F.; Zhang, T.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J.Y.; Li, D.J.; et al. A defective lysophosphatidic acid-autophagy axis increases miscarriage risk by restricting decidual macrophage residence. Autophagy 2022, 18, 2459–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, D.; Xu, L.; Chen, J.J.; Sang, Y.F.; Piao, H.L.; Jing, X.L.; Yu, M.; Fu, Q.; et al. Decidual CXCR4+ CD56bright NK cells as a novel NK subset in maternal-foetal immune tolerance to alleviate early pregnancy failure. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Yang, H.L.; Zhou, W.J.; Lai, Z.Z.; Qiu, X.M.; Fu, Q.; Zhao, J.Y.; Wang, J.; Li, D.J.; Li, M.Q. Rapamycin prevents spontaneous abortion by triggering decidual stromal cell autophagy-mediated NK cell residence. Autophagy 2021, 17, 2511–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlebacher, A. Immunology of the maternal-fetal interface. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 31, 387–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagel, S. The developmental role of natural killer cells at the fetal-maternal interface. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 2009, 201, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, F.; Burzynski, C.A.; Fang, Y.Y.; Tal, A.; Chen, A.Y.; Kisa, J.; Agrawal, K.; Kluger, Y.; Taylor, H.S.; Tal, R. Maternal CXCR4 deletion results in placental defects and pregnancy loss mediated by immune dysregulation. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e172216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Z.Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, W.J.; Liang, Z.; Shi, J.W.; Yang, H.L.; Xie, F.; Chen, W.D.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, C.; et al. Single-cell transcriptome profiling of the human endometrium of patients with recurrent implantation failure. Theranostics 2022, 12, 6527–6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.X.; Yang, S.L.; Li, M.Q.; Wang, H.Y. Autophagy suppression of trophoblast cells induces pregnancy loss by activating decidual NK cytotoxicity and inhibiting trophoblast invasion. Cell Commun. Signal 2020, 18, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, H.; Huang, X.; Ying, H.; Zhang, S.; Pan, Y.; Zhu, H. Dysregulation of Histone Deacetylases Inhibits Trophoblast Growth during Early Placental Development Partially through TFEB-Dependent Autophagy-Lysosomal Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.Y.; Shen, H.H.; Zhou, W.J.; Mei, J.; Lu, H.; Tan, X.F.; Zhu, R.; Zhou, W.H.; Li, D.J.; Zhang, T.; et al. Insight of Autophagy in Spontaneous Miscarriage. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 1150–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Shi, J.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, Z.; Li, M.; Shao, J. An abnormal LPA/LPAR1-NHE1 axis leads to the autophagy deficiency of trophoblast cells in recurrent spontaneous abortion. Reproduction 2023, 166, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, J.; Yuan, E.; Yan, G. Association between HIF-1α, BNIP3, and autophagy in the chorionic villi of missed abortion. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2023, 49, 1710–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.L.; Hassan, A.B. Cell survival and proliferation are modified by insulin-like growth factor 2 between days 9 and 10 of mouse gestation. Development 2001, 128, 3819–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandovici, I.; Georgopoulou, A.; Perez-Garcia, V.; Hufnagel, A.; Lopez-Tello, J.; Lam, B.Y.H.; Schiefer, S.N.; Gaudreau, C.; Santos, F.; Hoelle, K.; et al. The imprinted Igf2-Igf2r axis is critical for matching placental microvasculature expansion to fetal growth. Dev. Cell 2022, 57, 63–79.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.S.; Monteiro, M.P.; Costa, M.M.; Moreira, A.; Alves, M.G.; Oliveira, P.F.; Jarak, I.; Pignatelli, D. IGF2 role in adrenocortical carcinoma biology. Endocrine 2019, 66, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabapathy, K.; Lane, D.P. Understanding p53 functions through p53 antibodies. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 11, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohnke, Y.; Schneider-Merck, T.; Fahnenstich, J.; Kempf, R.; Christian, M.; Milde-Langosch, K.; Brosens, J.J.; Gellersen, B. Wild-type p53 protein is up-regulated upon cyclic adenosine monophosphate-induced differentiation of human endometrial stromal cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 5233–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haley, V.L.; Barnes, D.J.; Sandovici, I.; Constancia, M.; Graham, C.F.; Pezzella, F.; Buhnemann, C.; Carter, E.J.; Hassan, A.B. Igf2 pathway dependency of the Trp53 developmental and tumour phenotypes. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| IGF2 | Forward | CAATGGGGAAGTCGATGCTG |
| (human) | Reverse | GGAAACAGCACTCCTCAACG |
| TP53 | Forward | AGGTTGGCTCTGACTGTACC |
| (human) | Reverse | TCTTCTTTGGCTGGGGAGAG |
| CXCR4 | Forward | TGTCATCACGCTTCCCTTCT |
| (human) | Reverse | TCATCTGCCTCACTGACGTT |
| ACTB | Forward | GGCATCCTCACCCTGAAGTA |
| (human) | Reverse | TAGCACAGCCTGGATAGCAA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, N.; Shen, H.; Wang, Z.; Qin, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, X. Autophagy Inhibition in Trophoblasts Induces Aberrant Shift in CXCR4+ Decidual NK Cell Phenotype Leading to Pregnancy Loss. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7491. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237491
Liu N, Shen H, Wang Z, Qin X, Li M, Zhang X. Autophagy Inhibition in Trophoblasts Induces Aberrant Shift in CXCR4+ Decidual NK Cell Phenotype Leading to Pregnancy Loss. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(23):7491. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237491
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Nan, Huihui Shen, Zehua Wang, Xueyun Qin, Mingqing Li, and Xinyan Zhang. 2023. "Autophagy Inhibition in Trophoblasts Induces Aberrant Shift in CXCR4+ Decidual NK Cell Phenotype Leading to Pregnancy Loss" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 23: 7491. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237491
APA StyleLiu, N., Shen, H., Wang, Z., Qin, X., Li, M., & Zhang, X. (2023). Autophagy Inhibition in Trophoblasts Induces Aberrant Shift in CXCR4+ Decidual NK Cell Phenotype Leading to Pregnancy Loss. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(23), 7491. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237491






