Diagnosing Middle Ear Malformation by Pure-Tone Audiometry Using a Three-Dimensional Finite Element Model: A Case-Control Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. Participants
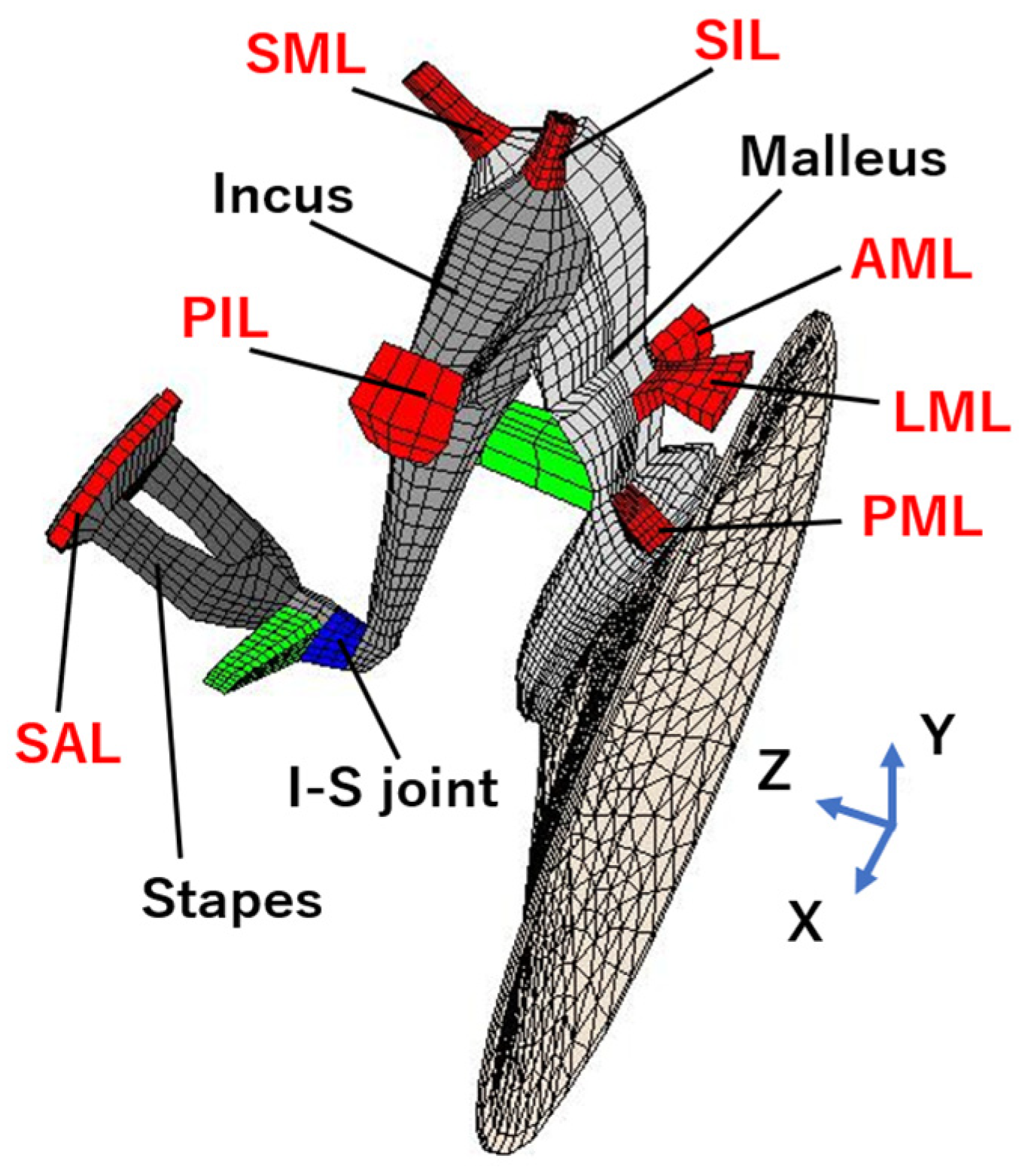
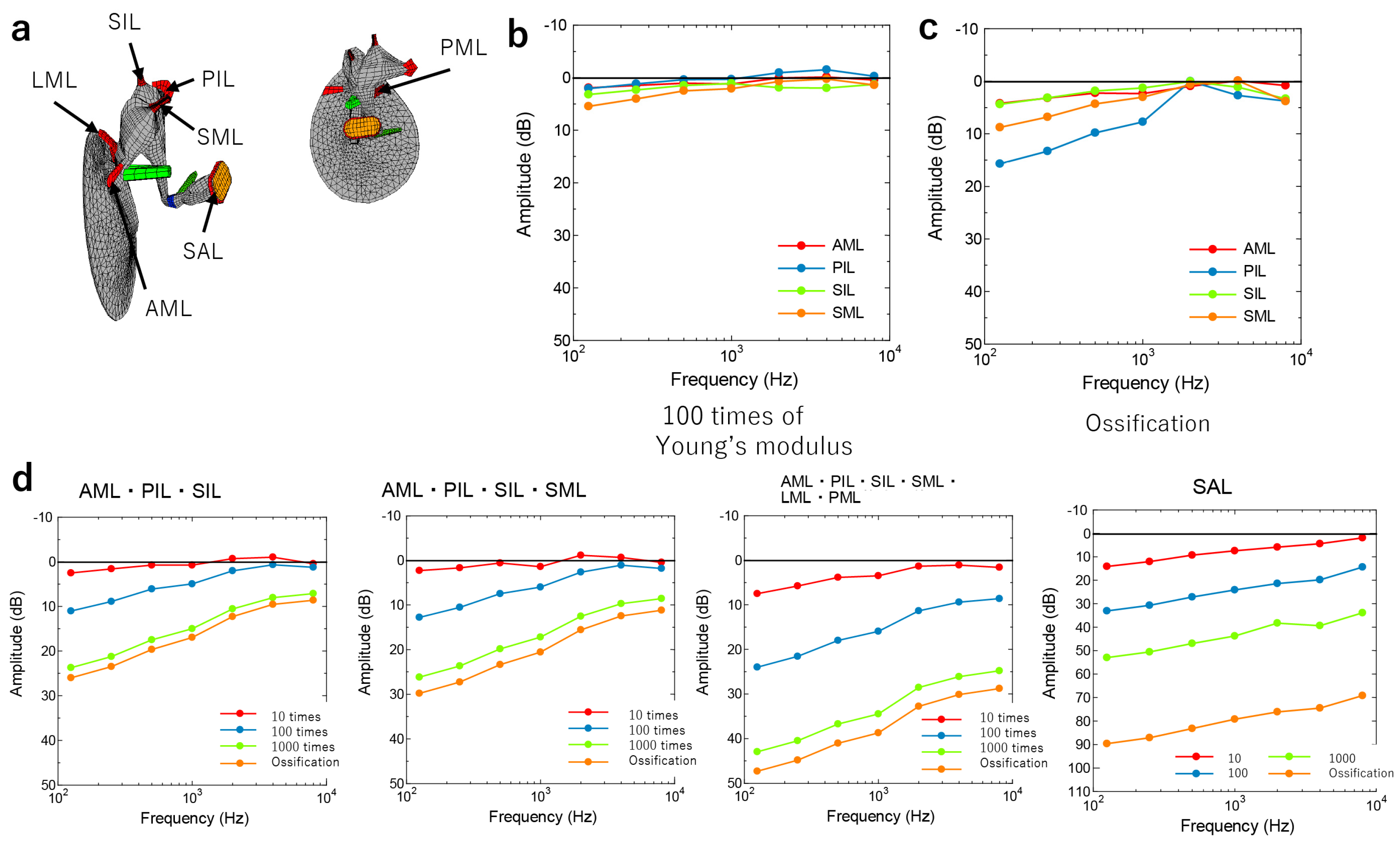
2.3. Theoretical Analysis
3. Results
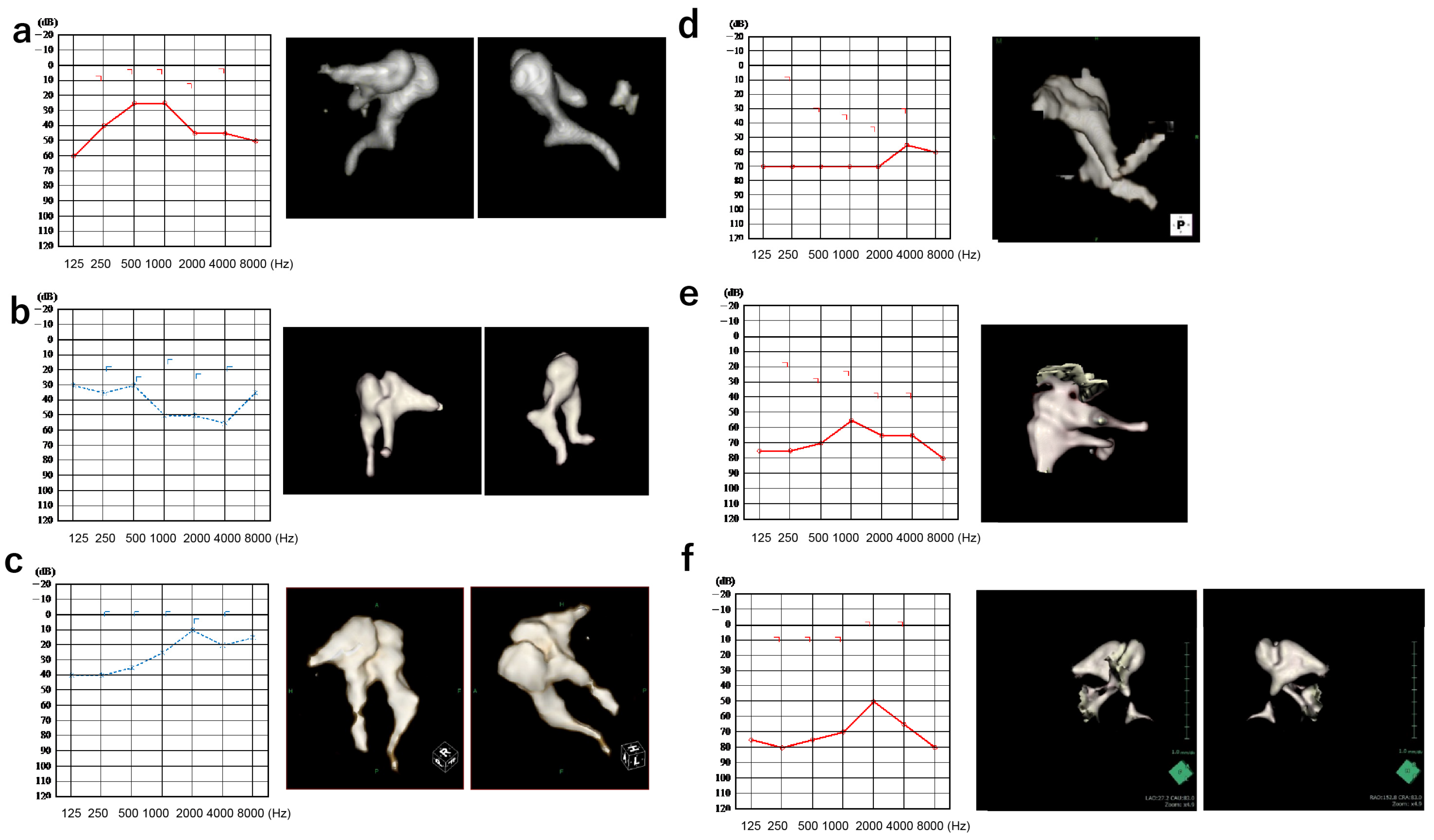
3.1. Patients
3.2. Comparison of Simulated and Actual Audiograms
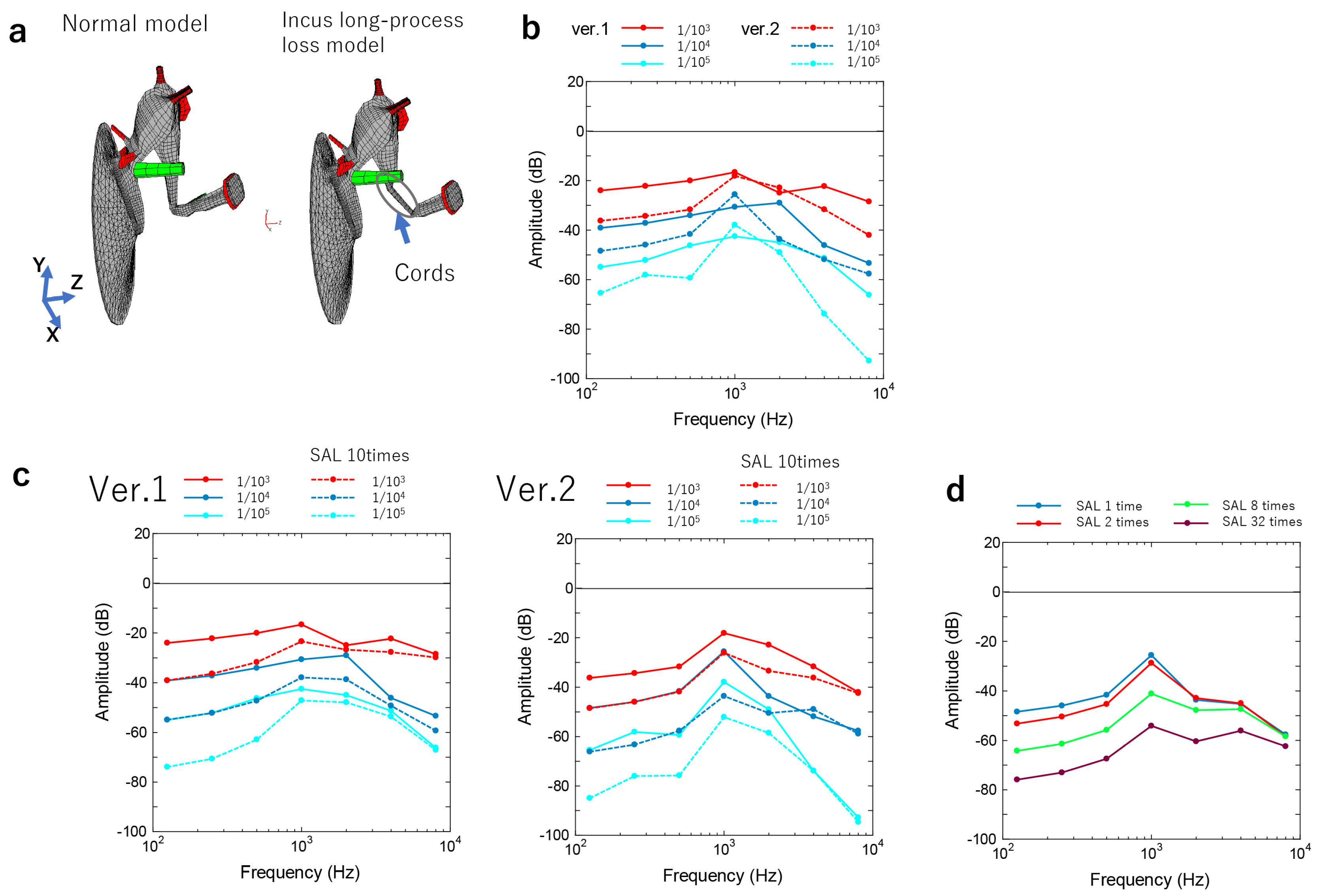
3.2.1. Incus–Stapes Joint Disarticulation due to Dysplasia of the Long Bone or Stapes Superstructure
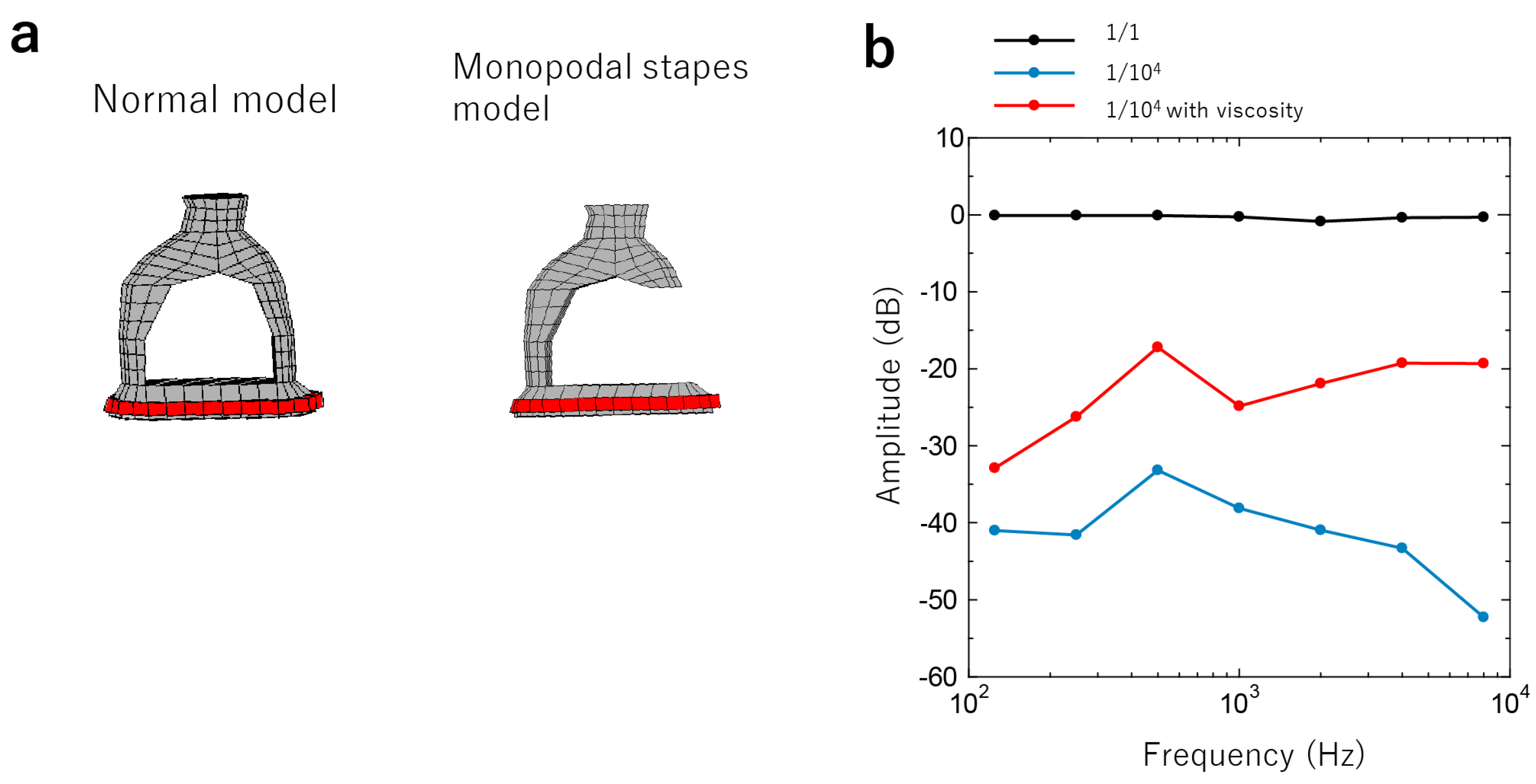
3.2.2. Stapes Fixation
3.2.3. Adhesion of the Head of the Malleus or the Body of the Incus to the Surrounding Bone Wall
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Merchant, G.R.; Merchant, S.N.; Rosowski, J.J.; Nakajima, H.H. Controlled Exploration of the Effects of Conductive Hearing Loss on Wideband Acoustic Immittance in Human Cadaveric Preparations. Heart Res. 2016, 341, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teunissen, E.B.; Cremers, C.W.R.J. Classification of Congenital Middle Ear Anomalies Report on 144 Ears. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1993, 102, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Furukawa, T.; Ohshima, S.; Takahashi, K.; Takata, Y.; Furukawa, M.; Hiraumi, H.; Yamauchi, D.; Yuasa, Y.; Goto, S.; et al. Multicenter Study of Congenital Middle Ear Anomalies. Report on 246 Ears. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, E2323–E2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funasaka, S. Congenital Ossicular Anomalies without Malformations of the External Ear. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 1979, 224, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delrue, S.; Verhaert, N.; Van Dinther, J.; Zarowski, A.; Somers, T.; Desloovere, C.; Offeciers, E. Surgical Management and Hearing Outcome of Traumatic Ossicular Injuries. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2016, 12, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantokoudis, G.; Schlapfer, N.; Kellinghaus, M.; Hakim, A.; Von Werdt, M.; Caversaccio, M.D.; Wagner, F. Traumatic Dislocation of Middle Ear Ossicles: A New Computed Tomography Classification Predicting Hearing Outcome. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutcher, W.L.; Tassone, P.; Pelosi, S. Ossicular Chain Mobilisation versus Reconstruction in Surgery for Isolated Malleus and/or Incus Fixation: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2018, 132, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidman, M.D.; Babu, S. A New Approach for Malleus/Incus Fixation: No Prosthesis Necessary. Otol. Neurotol. 2004, 25, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlauch, R.S.; Nelson, P. Puretone Evaluation. In Handbook of Clinical Audiology; Taylor and Francis Inc.: Abingdon, UK, 2014; pp. 29–47. ISBN 9781469891859. [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima, H.H.; Ravicz, M.E.; Merchant, S.N.; Peake, W.T.; Rosowski, J.J. Experimental Ossicular Fixations and the Middle Ear’s Response to Sound: Evidence for a Flexible Ossicular Chain. Heart Res. 2005, 204, 60–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahmand, R.B.; Merchant, G.R.; Lookabaugh, S.A.; Röösli, C.; Ulku, C.H.; McKenna, M.J.; De Venecia, R.K.; Halpin, C.F.; Rosowski, J.J.; Nakajima, H.H. The Audiometric and Mechanical Effects of Partial Ossicular Discontinuity. Ear Heart 2016, 37, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttenbrink, K.B. The Mechanics and the Function of the Middle-Ear. Part 1: Normal Ossicular Chain and Middle-Ear Muscles. Laryngorhinootologie 1992, 71, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koike, T.; Wada, H.; Kobayashi, T. Modeling of the Human Middle Ear Using the Finite-Element Method. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2002, 111, 1306–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, H.; Metoki, T.; Kobayashi, T. Analysis of Dynamic Behavior of Human Middle Ear Using a Finite-element Method. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1992, 92, 3157–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Paolis, A.; Bikson, M.; Nelson, J.T.; de Ru, J.A.; Packer, M.; Cardoso, L. Analytical and Numerical Modeling of the Hearing System: Advances towards the Assessment of Hearing Damage. Heart Res. 2017, 349, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, H.J.; Bornitz, M.; Hardtke, H.J.; Schmidt, R.; Hofmann, G.; Vogel, U.; Zahnert, T.; Hüttenbrink, K.B. Modelling of Components of the Human Middle Ear and Simulation of Their Dynamic Behaviour. Audiol. Neurotol. 1999, 4, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, K.N.; Cai, H.; Puria, S. The Effects of Varying Tympanic-Membrane Material Properties on Human Middle-Ear Sound Transmission in a Three-Dimensional Finite-Element Model. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 142, 2836–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirabayashi, M.; Kurihara, S.; Ito, R.; Kurashina, Y.; Motegi, M.; Okano, H.J.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kojima, H.; Asakura, T. Combined Analysis of Finite Element Model and Audiometry Provides Insights into the Pathogenesis of Conductive Hearing Loss. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 967475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, M.; Hill, D.L.G.; Denton, E.R.E.; Jarosz, J.M.; Cox, T.C.S.; Rohlfing, T.; Goodey, J.; Hawkes, D.J. Voxel Similarity Measures for 3-D Serial MR Brain Image Registration. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2000, 19, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, A.; Matsushima, S.; Fukuda, T.; Yamauchi, H.; Fujioka, H.; Hasumi, J.; Yoshimoto, S.; Shoji, T.; Kurihara, S.; Yamamoto, Y.; et al. Improved Assessment of Middle Ear Recurrent/Residual Cholesteatomas Using Temporal Subtraction CT. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2022, 40, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.D. Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1980; p. 672. [Google Scholar]
- Michels, T.C.; Duffy, M.T.; Rogers, D.J. Hearing Loss in Adults: Differential Diagnosis and Treatment. Am. Fam. Physician 2019, 100, 98–108. [Google Scholar]
- Wada, H.; Koike, T.; Kobayashi, T. Clinical Applicability of the Sweep Frequency Measuring Apparatus for Diagnosis of Middle Ear Diseases. Ear Heart 1998, 19, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppannan, A.; Barman, A. Wideband Absorbance Pattern in Adults with Otosclerosis and Ossicular Chain Discontinuity. Auris Nasus Larynx 2021, 48, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Koo, M. Mass and Stiffness Impact on the Middle Ear and the Cochlear Partition. J. Audiol. Otol. 2015, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, H. Relation of Audiograms to the Impedance Formula. Acta Otolaryngol. 1948, 36, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmento, K.M.A.; Sampaio, A.L.L.; Santos, T.G.T.; de Oliveira, C.A.C.P. High-Frequency Conductive Hearing Loss as a Diagnostic Test for Incomplete Ossicular Discontinuity in Non-Cholesteatomatous Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Liu, H.; Lutfy, J.; Funnell, W.R.J.; Daniel, S.J. A Nonlinear Finite-Element Model of the Newborn Ear Canal. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 120, 3789–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Category | Age | Sex | PTA 4 (dB HL) | AB Gap (dB HL) | TG | SR | DPOAE | CT | Diagnosis | Surgery | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Incus | 24 | M | 31.7 | 27.5 | Ad | + | - | None | Incus long process, complete loss | Tympanoplasty IIIiM |
| 2 | Incus | 47 | M | 43.3 | 25.0 | Ad | - | - | None | Incus long process, incomplete loss | Tympanoplasty III |
| 3 | Stapes | 9 | F | 23.3 | 18.8 | A | - | NA | None | Monopodal stapes | Tympanoplasty IVi |
| 4 | Stapes | 50 | M | 70.0 | 30.0 | A | - | NA | STD around stapes | Monopodal stapes Adhesion to the petrosus | TympanoplastyI |
| 5 | Adhesion | 56 | M | 23.3 | 28.8 | A | - | - | Adhesion of malleus to tympanic cavity | Adhesion of the malleus to the tympanic cavity Fixation of stapes | Tympanoplasty+ Stapedotomy |
| 6 | Adhesion + abnormal EAC | 18 | F | 65.0 | 60.0 | A | NA | NA | Narrow EAC Adhesion of malleus and incus | Narrow EAC Adhesion of malleus and incus | Tympanoplasty IIIc |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kita, S.-i.; Miwa, T.; Kanai, R.; Morita, Y.; Lee, S.; Koike, T.; Kanemaru, S.-i. Diagnosing Middle Ear Malformation by Pure-Tone Audiometry Using a Three-Dimensional Finite Element Model: A Case-Control Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7493. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237493
Kita S-i, Miwa T, Kanai R, Morita Y, Lee S, Koike T, Kanemaru S-i. Diagnosing Middle Ear Malformation by Pure-Tone Audiometry Using a Three-Dimensional Finite Element Model: A Case-Control Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(23):7493. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237493
Chicago/Turabian StyleKita, Shin-ichiro, Toru Miwa, Rie Kanai, Yoji Morita, Sinyoung Lee, Takuji Koike, and Shin-ichi Kanemaru. 2023. "Diagnosing Middle Ear Malformation by Pure-Tone Audiometry Using a Three-Dimensional Finite Element Model: A Case-Control Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 23: 7493. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237493
APA StyleKita, S.-i., Miwa, T., Kanai, R., Morita, Y., Lee, S., Koike, T., & Kanemaru, S.-i. (2023). Diagnosing Middle Ear Malformation by Pure-Tone Audiometry Using a Three-Dimensional Finite Element Model: A Case-Control Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(23), 7493. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237493






