Psychological Screening, Standards and Spinal Cord Injury: Introducing Change in NHS England Commissioned Services
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Procedure
2.2. Participants
2.3. Ethics
2.4. Study Variables
2.5. Coding and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Admission Data
3.2. Subgroup with Admission and Discharge Data
3.3. Regression Analyses
4. Discussion
Limitations and Suggestions for Future Research
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| Acronym | Meaning |
| ADAPPSsf | Appraisals of DisAbility Primary and Secondary Scale short form. This is a six-item scale that assesses a participant’s appraisal of their injury and provides an indication of adjustment to SCI/D and screens for a full-scale version |
| CPG | Clinical Practice Guideline |
| CRG | Clinical Reference Group, which oversees the service provision for a range of health conditions for NHS England and sets the service specification and standards for care |
| EBM | Evidence-based medicine |
| GAD-7 | General Anxiety Disorder-7 is a seven-item measure used to assess the presence of anxiety symptoms |
| ISCoS | The International Spinal Cord Society |
| MCSI | Midlands Centre for Spinal Injuries |
| MDT | Multidisciplinary Team |
| NHS | National Health Service, which is the universal health care provider in the UK; the NHS provision is devolved into separate bodies for England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland |
| NICE | National Institute for Health and Care Excellence is an overarching body that creates recommendations for treatment protocols and medication |
| NSIC | National Spinal Injuries Centre at Stoke Mandeville |
| PHQ-9 | Patient Health Questionnaire is a nine-item measure used to assess the presence of depression symptoms |
| PwSCI/D | People with spinal cord injuries/disorders |
| SCI/D | Spinal cord injuries/disorders |
| SCICs | Spinal cord injury centres provide inpatient rehabilitation in the UK |
| SCIPAG | UK and Ireland Spinal Cord Injury Psychology Advisory Group review and promote psychological service provision and care standards across the SCICs |
| SIG | Special interest group |
| SMS-NAC | Stoke Mandeville Spinal Needs Assessment Checklist, which is used to assess inpatient’s knowledge, skills, and physical or verbal independence across 10 domains of rehabilitation for SCI/D |
| YRSIC | Yorkshire Regional Spinal Injuries Centre |
Appendix A. Standards Recommendations for System-Wide Change with Table
- Adoption across all providers of a matched collaborative care pathway (see also Supplementary Table S1). The NSIC Stoke Mandeville Psychological Care Pathway (UK Copyright Service 284734611) proposed foundation needs for all PwSCI/D and identified the need for a clinician and peer-facilitated coping effectiveness group intervention to aid self-management, alongside psychoeducation and consideration of psychosexual and family counselling, with four specific interventions depending on needs [63]. The workstream enhanced this by adding screening thresholds for the interventions and renamed it the “psychological health and wellbeing matched collaborative care intervention pathway” to aid system-wide adoption and comparison between SCICs and others in the pathway regarding complexity and workforce need.
- Adoption across all providers of an MDT curriculum, with basic (Level 1) skills needed by all healthcare professionals who have contact with PwSCI/D, with someone trained to advanced (Level 2) skills within each team/clinical area (Supplementary Table S2).
- A preadmission outreach pathway to ensure the parity of admission for people with complex mental health needs (Supplementary Figure S1).
- Implementation of psychological health screening on admission, discharge, readmission and outpatient review across the sector.
- The workstream acknowledged the variety of resourcing across the SCICs and other providers as a limiting factor for the implementation of the standards. Therefore, it was recommended that all services be resourced similarly and to at least the staffing of the current best ratio (London SCIC 1:15) and/or aligned with other SCI providers in the network, such as neurorehabilitation services given the complexity of need [64]. The workstream anticipated that some services would be nonadherent because of staffing variation and recommended yearly audits by SCIPAG/peer review, and where service gaps are identified, an action plan should be implemented.
- The workstream recommended support to consult, finalise and publish the broader evidence-based standards that had been commenced by SCIPAG.
- Three key areas for development were identified across the sector:
- i.
- SCIC Outpatient Services—The workstream referenced the need for psychological support for adjustment to injury to be about 40% (not including those referred to community mental health services) and noted the high prevalence of persistent pain and the current gap in services for PwSCI/D [50,65]. The workstream recommended the development of an MDT clinic and estimated that 60–70% of people presenting with persistent pain would need an associated psychological review.
- ii.
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) provision within SCICs. The workstream acknowledged that whilst SCICs manage the needs of those with co-morbid mild TBIs, those with more severe injuries often fall between neurorehabilitation and SCI/D rehabilitation services. Recommended future development should focus on (a) scoping local services and developing links, providing an integrated pathway for those with moderate TBI and SCI/D by embedding neuro-rehabilitation expertise within SCICs and vice versa, including joint training events and rotational arrangements for therapists and nurses in the first instance, and (b) progress to the employment of staff skilled in managing moderate TBI in SCICs.
- iii.
- Psychiatry provision. The workstream recommended the following: (a) services should foster links with local specialist mental health services, particularly liaison psychiatry services; (b) have service level arrangements with or embed liaison psychiatry services within SCI/D services; (c) improve the training of staff to better manage mental health complexity on SCI/D units through the adoption of the MDT curriculum identified (Supplementary Table S2); (d) arrange collaborative and parallel working practices for people with co-occurring complex mental health and spinal cord injury rehabilitation needs, such as repatriation arrangements; (e) agree on responsible clinician arrangements with local specialist services for people detained under the Mental Health Act [66]; and (f) the development of wheelchair-accessible services across mental health units for PwSCI/D.
| Timing | Quality Standard Summary | References |
|---|---|---|
| Onset of injury/acute care | Psychological health screen (PHQ-5) within 4 weeks of injury. | [14,18,64,67,68] |
| Assessment prior to SCIC/rehabilitation transfer to include screening measures and structured clinical interview with information about known mental health and forensic history, any barriers or additional needs for engagement in rehabilitation, and past and present mental health professional involvement. To be completed where relevant: MOCA, AMTS, 6CIT or another recognised cognitive test if the person has a pre-existing or current cognitive impairment. An assessment of alcohol, tobacco, and recreational drug history and current use. A mental capacity assessment. | [14,18,67,69,70] | |
| Amendment of the NHS England Database to recategorise the current category “mental health” and instead categorise using self-harm/suicide attempt/neglect, severe and enduring mental health/psychosis/schizophrenia, depression/anxiety, substance use, neurodevelopmental diagnosis or dementia. | - | |
| Implement pre-admission outreach flowchart across SCICs and yearly audit of its use by SCIPAG/peer review. | - | |
| Admission to SCIC/rehabilitation | All inpatients to have access to specialist evidence-based psychological treatment intervention and include trauma-based intervention. | [14,15,16,17,18,20,25,26,63,64,67,68,70,71,72,73,74] |
| Implementation of the psychometric screening measures across all parts of the pathway and for all levels and completeness of SCI/D. | [14,17,18,67] | |
| Implementation of the Psychological Health and Wellbeing Matched Collaborative Care Intervention Pathway (Supplementary Table S1) across SCICs and service provision alignment. Yearly audit of implementation and complexity of inpatient needs. | [63,69,71] | |
| Documented pathway for access to liaison psychiatry and other specialist services. | [14,18,20,25,26,63,64,67,69,73,75,76,77] | |
| Outcome comparison by SCIC and other services to track group trajectory profiles by complexity with revision of pathway as required. | - | |
| Initial contact from a psychosocial team member within 5 days of inpatient admission. | [14,18,67,71] | |
| Inpatient access to specialist psychological assessment and therapy within 10 working days of admission and include psychological health screen with psychometrically validated tools. | [14,15,16,18,20,63,67,69,70,73,75,76,77,78] | |
| Where suicidality is present, risk assessment, personal safety plan and treatment plan are to be established. | [14,18,48,67,73,77] | |
| Where motivation/engagement/progress in rehabilitation is limiting progress/change, psychological assessment and intervention should be provided. | [14,15,18,71,75] | |
| Peer support and peer mentoring should be available for all inpatients and the psychosocial care team leading on recruitment and organisation of this model within the SCIC. | [18,20,25,26,63,64,67,70,73] | |
| Provision of support services for the psychological/emotional needs of families/carers, including referrals. | [18,25,26,63,64,69,71,73] | |
| Adoption of the SCI MDT Education Curriculum (Supplementary Table S2) to align healthcare clinicians working in SCICs to be able to identify and support patients’ psychosocial needs, e.g., mood, adjustment issues, risk, substance use, cognition, and behaviours that challenge and know how to escalate for specialist psychological intervention as needed. All staff to have basic (Tier 1) skills and some staff to have advanced (Tier 2) skills. | [14,18,63,67,69,71,73,78] | |
| Inpatients, families and carers are to be offered support on self-management skills and empowered to advocate for their needs and seek support. | [15,18,64,67,71,73,76,78] | |
| Discharge from rehabilitation | Psychological health psychometric screening and psychological assessment are to be repeated prior to discharge. | [14,18,25,26,67,69,73,78] |
| Comprehensive psychological discharge planning, including referrals to relevant services. | [14,18,25,26,67,69,73] | |
| Onward referral made as required to the BackUp Trust peer mentoring or Spinal Injuries Association counselling service. | [18,64] | |
| Follow-up | Psychological health screen (PHQ-4) and substance/alcohol use screen to take place across four time points/ranges: 6–12 weeks post-discharge, 6 months, annually for 5 years, and then every 2 years or as required. | [14,16,18,25,26,64,67,69,70,78] |
| SCIC/ hospital readmission | All secondary rehabilitation admissions of PwSCI/D are to be administered a short form psychological health screen (PHQ-4). A referral is to be made to the SCIC psychological services for full assessment if there is a positive screen. | [14,18,67,71,73,77] |
References
- Wallace, M.; Duff, J.; Grant, L.C. The influence of psychological need on rehabilitation outcomes for people with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2023, 61, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strøm, J.; Bjerrum, M.B.; Nielsen, C.V.; Thisted, C.N.; Nielsen, T.L.; Laursen, M.; Jørgensen, L.B. Anxiety and depression in spine surgery-a systematic integrative review. Spine J. 2018, 18, 1272–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Diemen, T.; Crul, T.; van Nes, I.; SELF-SCI Group; Geertzen, J.H.; Post, M.W. Associations between self-efficacy and secondary health conditions in people living with spinal cord injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 98, 2566–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, A.; Tran, Y.; Guest, R.; Middleton, J. Trajectories of self-efficacy and depressed mood and their relationship in the first 12 months following spinal cord injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 100, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, P.; Kilvert, A.; Hasson, L. A 21-year longitudinal analysis of impact, coping, and appraisals following spinal cord injury. Rehabil. Psychol. 2016, 61, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psychological Professions Network. Maximising the Impact of Psychological Practice in Physical Healthcare: Discussion Paper. 2020. Available online: https://www.ppn.nhs.uk/resources/ppn-publications/34-maximising-the-impact-of-psychological-practice-in-physical-healthcare-discussion-paper/file (accessed on 4 September 2023).
- Nichols, K. Psychological Care for Ill and Injured People—A Clinical Guide; Open University Press: Maidenhead, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Nichols, K. Why is psychology still failing the average patient? Psychologist 2005, 18, 26–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wisely, J.A.; Hoyle, E.; Tarrier, N.; Edwards, J. Where to start? Attempting to meet the psychological needs of burned patients. Burns 2007, 33, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, J.C. Preliminary guidelines for the treatment of distress. Oncology 1997, 11, 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Grassi, L.; Caruso, R.; Sabato, S.; Massarenti, S.; Nanni, M.G.; The UniFe Psychiatry Working Group Coauthors. Psychosocial screening and assessment in oncology and palliative care settings. Front. Psychol. 2015, 5, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute for Clinical Excellence. Improving Supportive and Palliative Care for Adults with Cancer: The Manual; Guidance on Cancer Services; National Institute for Clinical Excellence: London, UK, 2004; ISBN 1-84257-579-1. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/csg4/resources/improving-supportive-and-palliative-care-for-adults-with-cancer-pdf-773375005 (accessed on 10 August 2023).
- Psychological Services for Stroke Survivors and Their Families. In The British Psychological Society, Division of Clinical Psychology and Division of Neuropsychology; Briefing Paper No. 19; British Psychological Society: Leicester, UK, 2002.
- Bombardier, C.H.; Azuero, C.B.; Fann, J.R.; Kautz, D.D.; Richards, J.S.; Sabharwal, S. Management of mental health disorders, substance use disorders, and suicide in adults with spinal cord injury: Clinical practice guideline for healthcare providers. Top. Spinal Cord Inj. Rehabil. 2021, 27, 152–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huston, T.; Gassaway, J.; Wilson, C.; Gordon, S.; Koval, J.; Schwebel, A. Psychology treatment time during inpatient spinal cord injury rehabilitation. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2011, 34, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, H.F.; Richardson, E.J.; Bombardier, C.H.; Dixon, T.M.; Huston, T.A.; Rose, J.; Sheaffer, D.; Smith, S.A.; Ullrich, P.M. Professional standards of practice for psychologists, social workers, and counselors in SCI rehabilitation. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2016, 39, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middleton, J.; Perry, K.N.; Craig, A. A clinical perspective on the need for psychosocial care guidelines in spinal cord injury rehabilitation. Int. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 2, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psychosocial Care of Adults with Spinal Cord Injuries Guide. Available online: https://aci.health.nsw.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0006/891978/ACI-psychosocial-spinal-cord-injury-Recommendations.pdf (accessed on 7 September 2023).
- NSW State Spinal Cord Injury Service. Strategy for the Psychosocial Care of People with Spinal Cord Injury. In The Emotional Wellbeing Toolkit: A Clinician’s Guide to Working with Spinal Cord Injury; NSW State Spinal Cord Injury Service: Agency for Clinical Innovation: New South Wales, Australia, 2016. Available online: https://www.aci.health.nsw.gov.au/resources/spinal-cord-injury/psychosocial_strategy/emotional-wellbeing-toolkit (accessed on 10 August 2023).
- The Asian Spinal Cord Network (ASCoN). Psychosocial Task Force. In Psychosocial Guidelines in Spinal Cord Rehabilitation; Jagadamba Press: Lalitpur, Nepal, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kuiper, H.; van Leeuwen, C.M.C.; Stolwijk-Swüste, J.M.; Mulder, L.; Post, M.W.M. Implementatie van een psychologische screening bij revalidanten met een dwarslaesie. [Implementation of a psychological screening in rehabilitation inpatients with spinal cord injury]. Ned. Tijdschr. Revalidatiegeneeskunde 2020, 42, 21–25. Available online: https://www.kcrutrecht.nl/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/NTR-2020-5-Publicatie-H.-Kuiper-Implementatie-psych-screening-bij-dwarslaesie.pdf (accessed on 14 August 2023).
- International Spinal Cord Injury Psychological Functioning Basic Data Set. Available online: https://www.iscos.org.uk/resource/resmgr/psychological_dataset_/psychological_functioning.pdf (accessed on 14 August 2023).
- Duff, J. Psychological and Mental Health Needs Standards for Adults with Spinal Cord Injury; MASCIP, BSPRM, BASCIS: UK, 2023; Available online: https://spinal.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Psychological-and-Mental-Health-Standards-for-Adults-with-SCI-Final-Jan-2023.pdf (accessed on 7 September 2023).
- Gall, A.; Horne, D.; Kennedy, P.; Turner-Stokes, L.; Tussler, D. No. 9: Chronic Spinal Cord Injury: Management of Patients in Acute Hospital Settings: National Guidelines; Concise Guidance to Good Practice; RCP, BSRM, MASCIP and BASCIS, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- NHS England Spinal Cord Injury Services (Adults and Children); Specification Number 170119S. NHS: London, UK, 2020. Available online: https://www.england.nhs.uk/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/service-spec-spinal-cord-injury-services-all-ages.pdf (accessed on 7 September 2023).
- NHS Standard Contract for Spinal Cord Injuries (All Ages), Specification Number D13/S/a, NHS England. Available online: https://www.england.nhs.uk/commissioning/wp-content/uploads/sites/12/2014/04/d13-spinal-cord-0414.pdf (accessed on 7 September 2023).
- Zigmond, A.S.; Snaith, R.P. The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1983, 67, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitzer, R.L.; Kroenke, K.; Williams, J.B.; Patient Health Questionnaire Primary Care Study Group. Validation and utility of a self-report version of PRIME-MD: The PHQ primary care study. JAMA 1999, 282, 1737–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzer, R.L.; Kroenke, K.; Williams, J.B.; Löwe, B. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: The GAD-7. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NHS England. National Spinal Cord Injury Database Annual Report; NHS: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Spinal Injuries Association (SIA). Available online: www.spinal.co.uk (accessed on 7 September 2023).
- Standards for Specialist Rehabilitation of Spinal Cord Injury; MASCIP, BSPRM, BASCIS: UK, 2022. Available online: https://www.mascip.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/SCIST-FINAL-2022.pdf (accessed on 7 September 2023).
- Dean, R.E.; Kennedy, P. Measuring appraisals following acquired spinal cord injury: A preliminary psychometric analysis of the appraisals of disability. Rehabil. Psychol. 2009, 54, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duff, J.; Grant, L.C. How to identify who needs psychological treatment and when: Addressing the gap through screening (oral). In Proceedings of the 24th Multidisciplinary Association of Spinal Cord Injury Professionals (MASCIP) Conference, Loughborough, UK, 17 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bonanno, G.A.; Kennedy, P.; Galatzer-Levy, I.R.; Lude, P.; Elfström, M.L. Trajectories of resilience, depression, and anxiety following spinal cord injury. Rehabil. Psychol. 2012, 57, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjaj, F.M.; Salek, M.S.; Basra, M.K.; Finlay, A.Y. Non-clinical influences on clinical decision-making: A major challenge to evidence-based practice. J. R. Soc. Med. 2010, 103, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilchrist, H.; Grant, L.C.; Saleh, S.; Sarhan, F.; Duff, J. Identifying and meeting the psychological care training needs of healthcare clinicians and third sector partners (poster). In Proceedings of the 24th Multidisciplinary Association of Spinal Cord Injury Professionals (MASCIP) Conference, Loughborough, UK, 17 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, C.; Kennedy, P. A psychometric analysis of the Needs Assessment Checklist. Spinal Cord 2002, 41, 490–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bombardier, C.; Kalpakjian, C.; Graves, D.; Dyer, J.; Tate, D.; Fann, J. Validity of the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 in assessing major depressive disorder during inpatient spinal cord injury rehabilitation. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 93, 1838–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, M.; Ames, H.; Dunn, C.; Beckwith, S.; Holmes, S.A. Appraisals of disability and psychological adjustment in veterans with spinal cord injuries. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2021, 44, 956–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy-Byrne, P.; Veitengrubet, J.P.; Bystrisky, A.; Edlund, M.J.; Sullivan, G.; Craske, M.G.; Shaw Welch, S.; Rose, R.; Stein, M.B. Brief intervention for anxiety in primary care patients. J. Am. Board Fam. Med. 2009, 22, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coker, J.; Cuthbert, J.; Ketchum, J.M.; Holicky, R.; Huston, R.; Charlifue, S. Re-inventing yourself after spinal cord injury: A site-specific randomized clinical trial. Spinal Cord 2019, 57, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duff, J.; Grant, L.C.; Coker, J.; Monden, K.R. Anxiety in response to sustaining spinal cord injuries and disorders: When should clinicians be concerned? Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2023, 104, 1409–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.; Murray, A. Prevalence of depression after spinal cord injury: A meta-analysis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2015, 96, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, A.; Nicholson Perry, K.; Guest, R.; Tran, Y.; Dezarnaulds, A.; Hales, A.; Ephraums, C.; Middleton, J. Prospective study of the occurrence of psychological disorders and comorbidities after spinal cord injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2015, 96, 1426–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duff, J.; Jackson, K.; Bombardier, C.B.; Zebracki, K. Spinal Cord Injuries and Disorders, Chapter 32. In Oxford Handbook of Rehabilitation Psychology, 2nd ed.; Meade, M., Wegner, S., Bechtold, K., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, in press.
- Guest, R.; Craig, A.; Tran, Y.; Middleton, J. Factors predicting resilience in people with spinal cord injury during transition from inpatient rehabilitation to the community. Spinal Cord 2015, 53, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, P.; Hasson, L. The relationship between pain and mood following spinal cord injury. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2017, 40, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, C.M.; Hoekstra, T.; van Koppenhagen, C.F.; de Groot, S.; Post, M.W. Trajectories and predictors of the course of mental health after spinal cord injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 93, 2170–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, S.; Duff, J.; Wallace, M.; Proudlove, G.; Jones, K. Bridging the gap: Psychological outcomes after discharge (poster). In Proceedings of the 59th International Spinal Cord Injury (ISCoS) Virtual Conference, Tokyo, Japan, 1–5 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Alschuler, K.N.; Jensen, M.P.; Sullivan-Singh, S.J.; Borson, S.; Smith, A.E.; Molton, I.R. The association of age, pain, and fatigue with physical functioning and depressive symptoms in persons with spinal cord injury. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2013, 36, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hirsh, A.T.; Molton, I.R.; Johnson, K.L.; Bombardier, C.H.; Jensen, M.P. The relationship of chronological age, age at injury, and duration of injury to employment status in individuals with spinal cord injury. Psychol. Inj. Law 2009, 2, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, L.E.; Waller, A.; Mitchell, A.J. Screening for distress and unmet needs in patients with cancer: Review and recommendations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1160–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinemann, A.W.; Wilson, C.S.; Huston, T.; Koval, J.; Gordon, S.; Gassaway, J.; Kreider, S.E.; Whiteneck, G. Relationship of psychology inpatient rehabilitation services and patient characteristics to outcomes following spinal cord injury: The SCIRehab project. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2012, 35, 578–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, L.E. Screening alone is not enough: The importance of appropriate triage, referral, and evidence-based treatment of distress and common problems. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3616–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, A.; Negrini, S.; Cieza, A. Toward strengthening rehabilitation in health systems: Methods used to develop a WHO Package of Rehabilitation Interventions. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 100, 2205–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, P.; Kilvert, A.; Hasson, L. Ethnicity and rehabilitation outcomes: The Needs Assessment Checklist. Spinal Cord 2015, 53, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Migilorini, C.E.; New, P.W.; Tonge, B.J. Comparison of depression, anxiety and stress in persons with traumatic and non-traumatic post-acute spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2009, 47, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, A.; Shafer, L.A.; Ethans, K. Does severity of spinal cord injury predict likelihood of suffering chronically from severe depression and anxiety? Spinal Cord Ser. Cases 2022, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cijsouw, A.; Adriaansen, J.J.; Tepper, M.; Dijksta, C.A.; van Linden, S.; ALLRISC; de Groot, S.; Post, M.W. Associations between disability-management self-efficacy, participation and life satisfaction in people with long-standing spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2017, 55, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savic, G.; DeVivo, M.; Frankel, H.; Jamous, M.A.; Soni, B.M.; Charlifue, S. Long-term survival after traumatic spinal cord injury: A 70-year British study. Spinal Cord 2017, 55, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, A.A.; Madrigal-Bauguss, J.A.; Russell, H.F.; Rose, J. Dissemination and use of the professional standards of practice for psychologists, social workers, and counselors in spinal cord injury rehabilitation. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2020, 43, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, A.; Duff, J.; Middleton, J. Spinal cord injuries. In Comprehensive Clinical Psychology, 2nd ed.; Asmundson, G.J.G., Ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2022; Volume 8, pp. 301–328. [Google Scholar]
- British Society of Rehabilitation Medicine. BSRM Standards for Rehabilitation Services, Mapped on to the National Service Framework for Long-Term Conditions; BSRM: London, UK, 2009; Available online: https://www.headway.org.uk/media/3321/bsrm-standards-for-rehabilitation-services.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2023).
- Siddall, P.J.; McClelland, J.M.; Rutkowski, S.B.; Cousins, M.J. A longitudinal study of the prevalence and characteristics of pain in the first 5 years following spinal cord injury. Pain 2003, 103, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mental Health Act 1983. Available online: https://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/1983/20/contents (accessed on 10 August 2023).
- Craig, A.; Perry, K.N. Guide for Health Care Professionals on the Psychosocial Care for Spinal Cord Injury, 2nd ed.; Spinal Cord Injury Service: Sydney, Australia, 2013. Available online: https://www.aci.health.nsw.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0019/155233/Guide-Psychosocial-Care.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2023).
- Department of Health. The National Service Framework for Long-Term Conditions. 2005. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/5a756bede5274a1baf95e73b/National_Service_Framework_for_Long_Term_Conditions.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2023).
- NHS Improvement & NICE—Stroke Psychological Care after Stroke. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/media/default/sharedlearning/531_strokepsychologicalsupportfinal.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2023).
- Dorstyn, D.S.; Mathias, J.L.; Denson, L.A. Psychological intervention during spinal rehabilitation: A preliminary study. Spinal Cord 2010, 48, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royal College of Physicians National Clinical Guidelines for Stroke. Available online: https://www.rcplondon.ac.uk/guidelines-policy/stroke-guidelines-2016 (accessed on 10 August 2023).
- National Institute for Clinical Excellence. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder; NG116; National Institute for Clinical Excellence: London, UK, 2018; Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/NG116 (accessed on 10 August 2023).
- Royal College of Nursing Response to Psychological Best Practice in Inpatient Services of Older People. Available online: https://www.rcn.org.uk/about-us/our-influencing-work/policy-briefings/CONR-0317 (accessed on 10 August 2023).
- Agency for Clinical Innovation Trauma-Informed Care and Practice in Mental Health Services. Available online: https://aci.health.nsw.gov.au/networks/mental-health/trauma-informed-care (accessed on 10 August 2023).
- Distel, D.F.; Amodeo, M.; Joshi, S.; Abramoff, B.A. Cognitive dysfunction in persons with chronic spinal cord injuries. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. 2020, 31, 345–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroke Foundation Australian Clinical Guidelines for Stroke Management. Available online: https://informme.org.au/guidelines/living-clinical-guidelines-for-stroke-management (accessed on 10 August 2023).
- Kennedy, P.; Garmon-Jones, L. Self-harm and suicide before and after spinal cord injury: A systematic review. Spinal Cord 2017, 55, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Faculty of Intensive Care Medicine Guidelines for the Provision of Intensive Care Services. 2019. Available online: https://ficm.ac.uk/sites/ficm/files/documents/2021-10/gpics-v2.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2023).
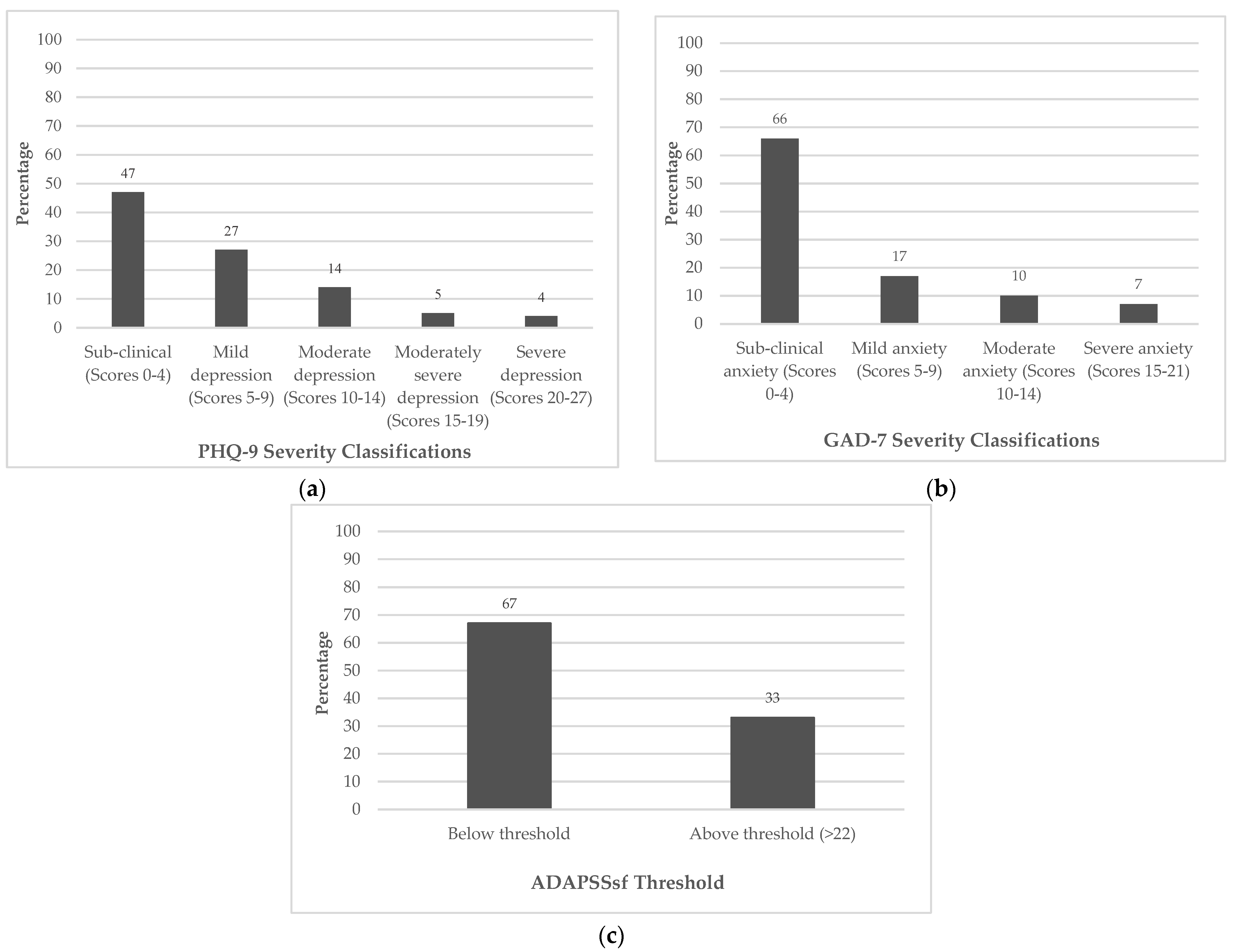

| N (% Total Number) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSIC | MCSI | YRSIC | Combined | ||
| Total | 438 | 87 | 121 | 646 | |
| Sex | Male | 297 (68) | 62 (71) | 76 (63) | 435 (67) |
| Female | 141 (32) | 25 (29) | 45 (37) | 211 (33) | |
| Ethnicity | White | 266 (61) | 54 (63) | 106 (88) * | 426 (66) |
| Black | 30 (7) | 3 (3) | 1 (1) | 34 (5) | |
| Asian | 24 (5) | 1 (1) | 6 (5) | 31 (5) | |
| Mixed | 4 (1) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 6 (1) | |
| Other | 3 (1) | 0 (0) | 3 (2) | 6 (1) | |
| Not stated | 111 (25) | 28 (32) | 4 (3) | 143 (22) | |
| Cause of injury | Traumatic | 221 (51) | 58 (67) | 46 (38) * | 325 (51) |
| Non-traumatic | 217 (49) | 29 (33) | 75 (62) | 321 (49) | |
| Level of injury | Tetraplegia (A/B/C) | 89 (20) | 28 (32) | 37 (31) | 154 (24) |
| Paraplegia (A/B/C) | 168 (39) | 24 (28) | 46 (38) | 238 (37) | |
| All levels D | 181 (41) | 32 (37) | 26 (21) * | 239 (37) | |
| Not stated | 0 (0) | 3 (3) | 12 (10) | 15 (2) | |
| Psychometrics | PHQ-9 | 432 (99) | 85 (98) | 115 (95) | 632 (98) |
| GAD-7 | 432 (99) | 86 (99) | 118 (98) | 636 (98) | |
| ADAPSSsf | 423 (97) | 83 (95) | 110 (91) | 616 (95) | |
| Mean (St. Dev.) | |||||
| NSIC | MCSI | YRSIC | Combined | ||
| Age at injury (years) | 54.64 (17.56) * | 58.36 (19.14) | 60.23 (16.20) | 56.19 (17.66) | |
| Time since injury (years) | 0.41 (0.42) | 0.37 (0.17) | 0.21 (0.30) * | 0.37 (0.38) | |
| PHQ-9 total score | 6.38 (5.86) | 4.95 (4.81) | 7.03 (6.56) | 6.31 (5.88) | |
| GAD-7 total score | 4.44 (5.16) | 2.92 (3.70) | 4.96 (5.67) | 4.33 (5.12) | |
| ADAPSSsf total score | 19.18 (6.60) | 18.78 (6.18) | 19.05 (6.59) | 19.11 (6.59) | |
| Combined Sample N (% Excluding Missing Values) | ||
| Psychometrics | PHQ-9 | 632 |
| GAD-7 | 636 | |
| ADAPSSsf | 616 | |
| Above threshold | PHQ-9 (≥11) | 138 (22) |
| GAD-7 (≥8) | 142 (22) | |
| ADAPSSsf (≥22) | 206 (33) | |
| Combined Sample Mean (St. Dev.) | ||
| PHQ-9 | Above threshold | 15.54 (3.90) |
| Below threshold | 3.72 (3.09) | |
| GAD-7 | Above threshold | 12.60 (3.56) |
| Below threshold | 1.95 (2.18) | |
| ADAPSSsf | Above threshold | 26.50 (3.53) |
| Below threshold | 15.39 (4.20) |
| Mean (St. Dev.) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSIC | MCSI | YRSIC | Combined | |
| PHQ-9 total—admission | 6.26 (5.73) | 5.41 (5.21) | 8.23 (6.95) | 6.33 (5.80) |
| PHQ-9 total—discharge | 5.35 (5.98) | 2.89 (3.41) | 6.30 (5.46) | 5.19 (5.77) |
| GAD-7 total—admission | 4.23 (5.14) | 3.75 (4.67) | 5.22 (6.19) | 4.27 (5.18) |
| GAD-7 total—discharge | 3.84 (5.09) | 2.59 (4.03) | 4.04 (3.07) | 3.74 (4.85) |
| ADAPSSsf total—admission | 19.44 (6.77) | 20.42 (6.31) | 18.55 (7.13) | 19.46 (6.75) |
| ADAPSSsf total—discharge | 19.28 (6.47) | 17.50 (5.83) | 18.14 (6.80) | 19.01 (6.44) |
| Combined Sample N (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Admission | Discharge | ||
| PHQ-9 severity | Total N | 266 | 270 |
| Sub-clinical | 126 (47) | 157 (58) | |
| Mild depression | 71 (27) | 63 (23) | |
| Moderate depression | 41 (15) | 29 (11) | |
| Moderately severe depression | 18 (7) | 11 (4) | |
| Severe depression | 10 (4) | 10 (4) | |
| GAD-7 severity | Total N | 267 | 269 |
| Sub-clinical anxiety | 174 (65) | 181 (67) | |
| Mild anxiety | 44 (17) | 50 (19) | |
| Moderate anxiety | 32 (12) | 26 (10) | |
| Severe anxiety | 17 (6) | 12 (4) | |
| Combined Sample N (% Excluding Missing Values) | |||
| Admission | Discharge | ||
| Psychometrics | PHQ-9 | 266 | 270 |
| GAD-7 | 267 | 269 | |
| ADAPSSsf | 267 | 267 | |
| Above threshold | PHQ-9 | 61 (23) | 38 (14) |
| GAD-7 | 60 (23) | 44 (16) | |
| ADAPSSsf | 98 (37) | 94 (35) | |
| Combined Sample Mean (St. Dev.) | |||
| Admission | Discharge | ||
| PHQ-9 | Above threshold | 15.11 (3.83) | 16.68 (4.65) |
| Below threshold | 3.72 (3.08) | 3.31 (3.17) | |
| GAD-7 | Above threshold | 12.63 (3.63) | 12.89 (4.05) |
| Below threshold | 1.84 (2.15) | 1.95 (2.31) | |
| ADAPSSsf | Above threshold | 26.49 (3.73) | 25.72 (3.63) |
| Below threshold | 15.38 (4.30) | 15.36 (4.37) | |
| 95% CI | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beta | SE | LB | UB | β | p | ||
| PHQ-9 | Admission score | 0.493 | 0.052 | 0.390 | 0.596 | 0.493 | <0.001 * |
| Level of injury | −1.243 | 0.410 | −2.051 | −0.435 | −0.160 | 0.003 * | |
| Age at injury | −0.053 | 0.019 | −0.090 | −0.016 | −0.154 | 0.005 * | |
| Ethnicity | −0.135 | 0.145 | −0.422 | 0.151 | −0.049 | 0.352 | |
| Cause of injury | 0.379 | 0.609 | −0.820 | 1.577 | 0.033 | 0.534 | |
| Time since injury | 0.348 | 0.844 | −1.315 | 2.011 | 0.022 | 0.681 | |
| Sex | −0.090 | 0.662 | −1.393 | 1.213 | 0.007 | 0.892 | |
| GAD-7 | Admission score | 0.473 | 0.048 | 0.379 | 0.567 | 0.504 | <0.001 * |
| Level of injury | −1.172 | 0.330 | −1.822 | −0.522 | −0.181 | <0.001 * | |
| Age at injury | −0.054 | 0.015 | −0.084 | −0.024 | −0.186 | <0.001 * | |
| Ethnicity | −0.072 | 0.118 | −0.304 | 0.160 | −0.031 | 0.541 | |
| Cause of injury | 0.533 | 0.491 | −0.435 | 1.501 | 0.055 | 0.279 | |
| Time since injury | 0.724 | 0.688 | −0.630 | 2.078 | 0.053 | 0.293 | |
| Sex | 0.245 | 0.532 | −0.802 | 1.292 | 0.023 | 0.645 | |
| ADAPPsf | Admission score | 0.574 | 0.047 | 0.481 | 0.667 | 0.604 | <0.001 * |
| Level of injury | −0.768 | 0.434 | −0.89 | −1.622 | 0.086 | 0.078 | |
| Age at injury | 0.004 | 0.020 | −0.035 | 0.043 | 0.010 | 0.839 | |
| Ethnicity | 0.220 | 0.153 | −0.81 | 0.521 | 0.072 | 0.152 | |
| Cause of injury | 0.028 | 0.641 | −1.235 | 1.291 | 0.002 | 0.965 | |
| Time since injury | 0.991 | 0.896 | −0.773 | 2.755 | 0.056 | 0.270 | |
| Sex | 0.012 | 0.687 | −1.341 | 1.366 | 0.001 | 0.986 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duff, J.; Ellis, R.; Kaiser, S.; Grant, L.C. Psychological Screening, Standards and Spinal Cord Injury: Introducing Change in NHS England Commissioned Services. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7667. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12247667
Duff J, Ellis R, Kaiser S, Grant LC. Psychological Screening, Standards and Spinal Cord Injury: Introducing Change in NHS England Commissioned Services. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(24):7667. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12247667
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuff, Jane, Rebecca Ellis, Sally Kaiser, and Lucy C Grant. 2023. "Psychological Screening, Standards and Spinal Cord Injury: Introducing Change in NHS England Commissioned Services" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 24: 7667. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12247667
APA StyleDuff, J., Ellis, R., Kaiser, S., & Grant, L. C. (2023). Psychological Screening, Standards and Spinal Cord Injury: Introducing Change in NHS England Commissioned Services. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(24), 7667. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12247667






