Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment in Musculocontractural Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome Caused by Biallelic Loss-of-Function Variants of Gene for Dermatan Sulfate Epimerase
Abstract
1. Introduction
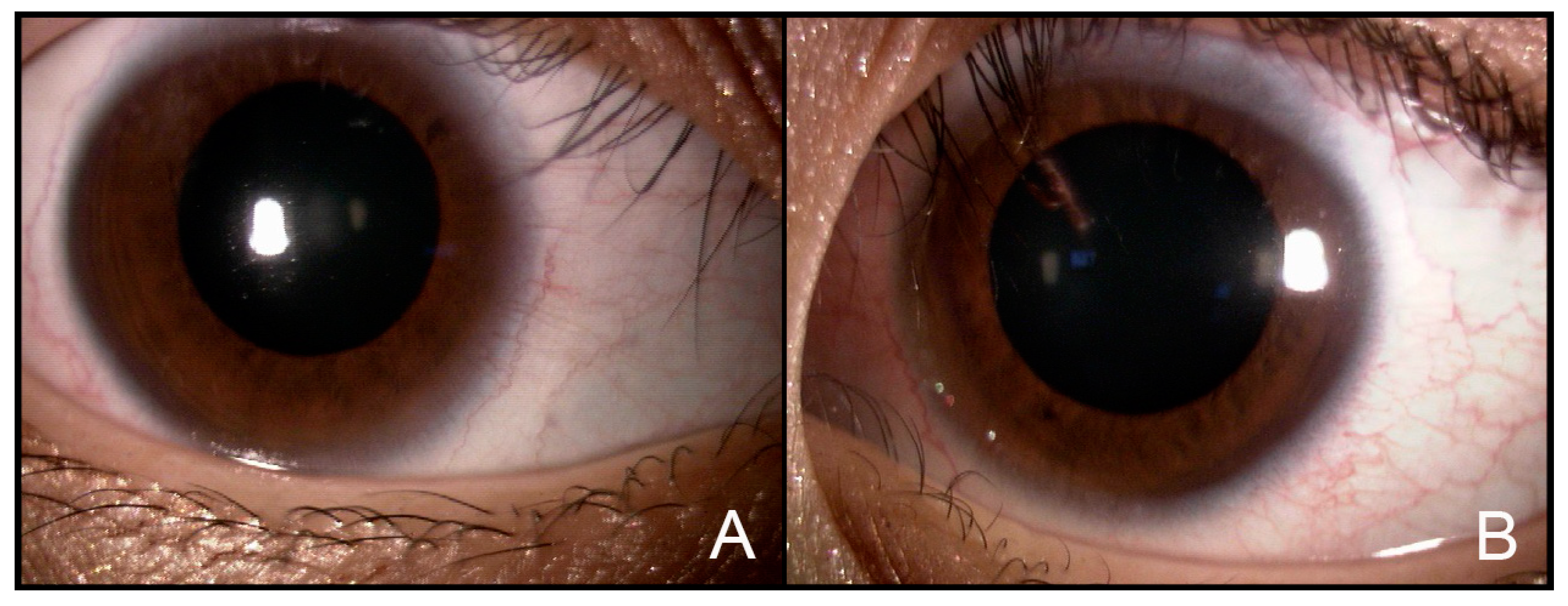
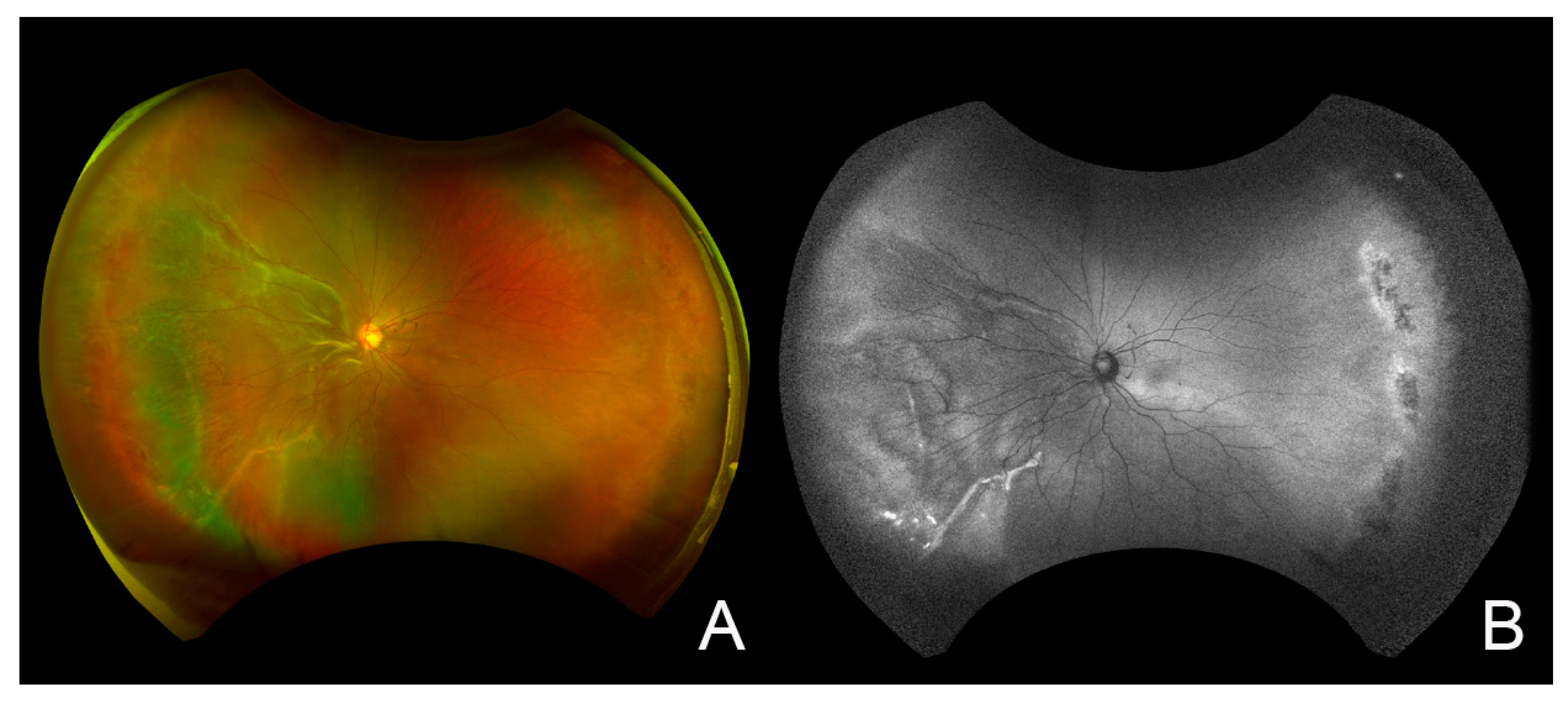
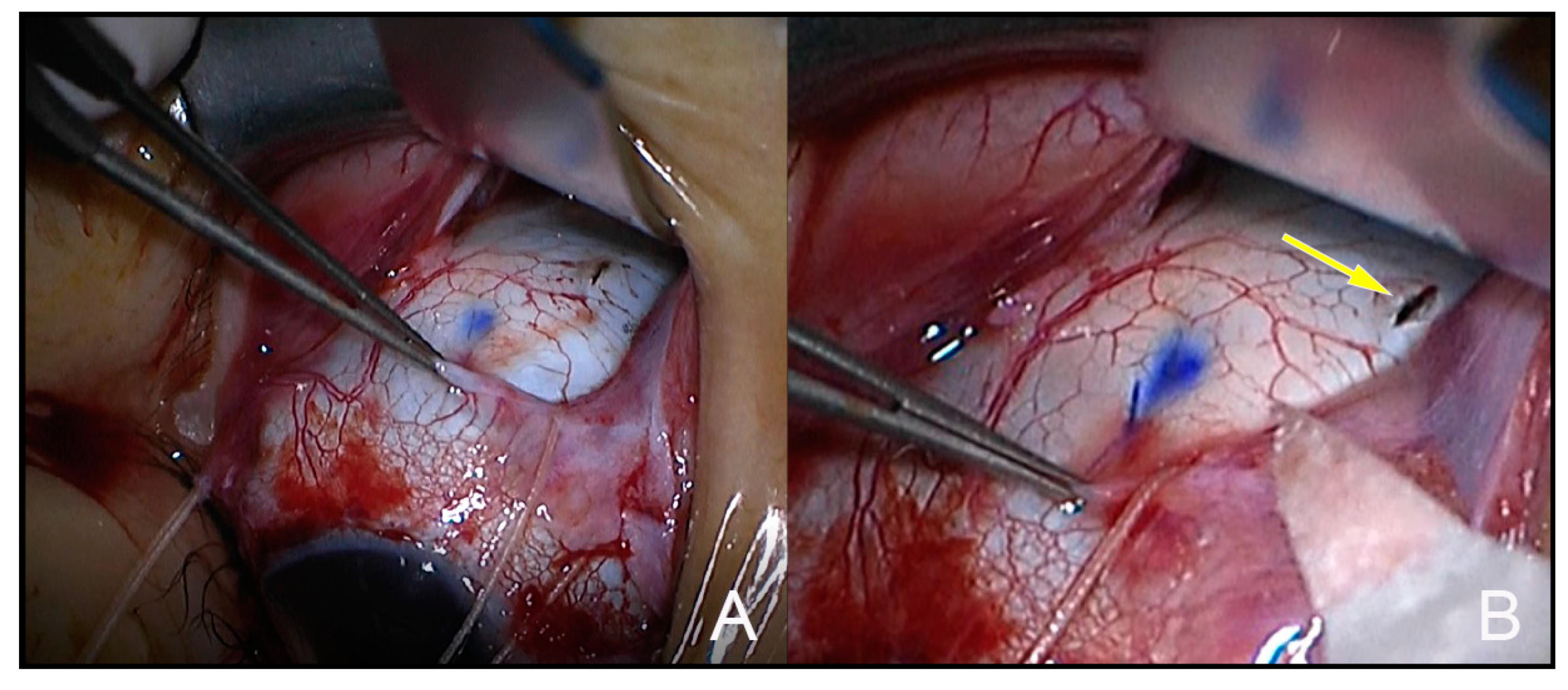
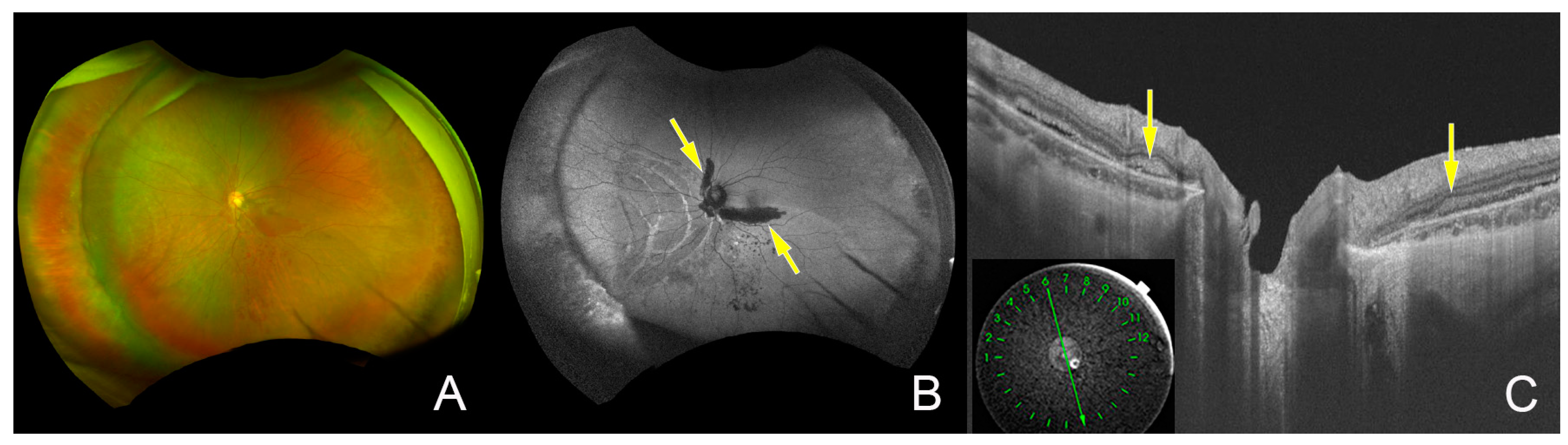
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malfait, F.; Francomano, C.; Byers, P.; Belmont, J.; Berglund, B.; Black, J.; Bloom, L.; Bowen, J.M.; Brady, A.F.; Burrows, N.P.; et al. The 2017 international classification of the Ehlers-Danlos syndromes. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2017, 175, 8–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosho, T.; Mizumoto, S.; Watanabe, T.; Yoshizawa, T.; Miyake, N.; Yamada, S. Recent Advances in the Pathophysiology of Musculocontractural Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. Genes 2019, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lautrup, C.K.; Teik, K.W.; Unzaki, A.; Mizumoto, S.; Syx, D.; Sin, H.H.; Nielsen, I.K.; Markholt, S.; Yamada, S.; Malfait, F.; et al. Delineation of musculocontractural Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome caused by dermatan sulfate epimerase deficiency. Mol. Genet. Genomic. Med. 2020, 8, e1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, T.; Mizumoto, S.; Suresh, I.; Komatsu, Y.; Vodopiutz, J.; Dundar, M.; Straub, V.; Lingenhel, A.; Melmer, A.; Lechner, S.; et al. Loss of dermatan sulfate epimerase (DSE) function results in musculocontractural Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 3761–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirwani, S.; Metcalfe, K.; Wagner, B.; Berry, I.; Sobey, G.; Jewell, R. DSE associated musculocontractural EDS, a milder phenotype or phenotypic variability. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2020, 63, 103798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebag, J. Anomalous posterior vitreous detachment: A unifying concept in vitreo-retinal disease. Graefes Arch Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2004, 242, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechrakis, N.E.; Dimmer, A. [Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment: Epidemiology and risk factors]. Ophthalmologe 2018, 115, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beighton, P. Serious ophthalmological complications in the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1970, 54, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodanowitz, S.; Hesse, L.; Pöstgens, H.; Kroll, P. [Retinal detachment in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome Treatment by pars plana vitrectomy]. Ophthalmologe 1997, 94, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, H.; Adachi, Y.; Minami, T.; Ishida, T.; Kato, Y.; Imai, K. Combination therapy of DDAVP and conjugated estrogens for a recurrent large subcutaneous hematoma in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Am. J. Hematol. 2003, 72, 71–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfait, F.; Syx, D.; Vlummens, P.; Symoens, S.; Nampoothiri, S.; Hermanns-Le, T.; Van Laer, L.; De Paepe, A. Musculocontractural Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (former EDS type VIB) and adducted thumb clubfoot syndrome (ATCS) represent a single clinical entity caused by mutations in the dermatan-4-sulfotransferase 1 encoding CHST14 gene. Hum. Mutat. 2010, 31, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janecke, A.R.; Li, B.; Boehm, M.; Krabichler, B.; Rohrbach, M.; Muller, T.; Fuchs, I.; Golas, G.; Katagiri, Y.; Ziegler, S.G.; et al. The phenotype of the musculocontractural type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome due to CHST14 mutations. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2016, 170A, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitlow, S.; Idrees, Z. RD repair using 360-degree scleral graft for extensive scleral ectasia in a patient with Ehlers Danlos syndrome. Am. J. Ophthalmol. Case Rep. 2020, 17, 100554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumi, X.; Bergant, G.; Lumi, A.; Mahnic, M. Outcomes of vitrectomy for retinal detachment in a patient with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2021, 15, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minatogawa, M.; Unzaki, A.; Morisaki, H.; Syx, D.; Sonoda, T.; Janecke, A.R.; Slavotinek, A.; Voermans, N.C.; Lacassie, Y.; Mendoza-Londono, R.; et al. Clinical and molecular features of 66 patients with musculocontractural Ehlers-Danlos syndrome caused by pathogenic variants in. J. Med. Genet. 2022, 59, 865–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dündar, M.; Müller, T.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, J.; Steinmann, B.; Vodopiutz, J.; Gruber, R.; Sonoda, T.; Krabichler, B.; Utermann, G.; et al. Loss of dermatan-4-sulfotransferase 1 function results in adducted thumb-clubfoot syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 85, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syx, D.; Van Damme, T.; Symoens, S.; Maiburg, M.C.; van de Laar, I.; Morton, J.; Suri, M.; Del Campo, M.; Hausser, I.; Hermanns-Lê, T.; et al. Genetic heterogeneity and clinical variability in musculocontractural Ehlers-Danlos syndrome caused by impaired dermatan sulfate biosynthesis. Hum. Mutat. 2015, 36, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfait, F.; De Paepe, A. Bleeding in the heritable connective tissue disorders: Mechanisms, diagnosis and treatment. Blood. Rev. 2009, 23, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paepe, A.; Malfait, F. Bleeding and bruising in patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and other collagen vascular disorders. Br. J. Haematol. 2004, 127, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wen, F.; Wu, D.Z.; Luo, G.; Huang, S.; Guan, T.; Liu, C. Fundus analysis and visual prognosis of macular hemorrhage in pathological myopia without choroidal neovasculopathy. Yan Ke Xue Bao 2004, 20, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- De Wandele, I.; Rombaut, L.; Leybaert, L.; Van de Borne, P.; De Backer, T.; Malfait, F.; De Paepe, A.; Calders, P. Dysautonomia and its underlying mechanisms in the hypermobility type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2014, 44, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Authors, Year | Age | Sex | Subtype | Gene Mutation | Surgery | Ocular Complications | Systemic Complications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beighton P 1970 [8] | 36 | woman | unknown | unknown | unknown | high myopia, strabismus, congenital glaucoma, microcornea, blue sclera | bilateral talipes equinovarus deformities of the feet, thoracolumbar kyphoscoliosis, frequent dislocations of both shoulders and subluxations, hiatus hernia, breast cystic masses |
| Bodanowitz S 1997 [9] | 47 | man | type VI | unknown | vitrectomy | blue sclera, keratoconus | hyperpigmentation and scarring of the skin, hyperextensibility of the thumb end links |
| Yasui H et al., 2003 [10] | 23 | man | musculocontractural type | CHST14 | unknown | none | hyperextensible skin and hypermobile joint, anemia, hematoma |
| Malfait F et al., 2010 [11] | 14 * | woman | musculocontractural type | CHST14 | unknown | high myopia, glaucoma | large fontanel, flexion–adduction contractures of the thumb, kyphoscoliosis, skin fragility, hiatal hernia, craniofacial abnormalities |
| Malfait F et al., 2010 [11] | 14 * | woman | musculocontractural type | CHST14 | unknown | high myopia, glaucoma | muscular hypotonia, dislocations of the patellae, lumbar scoliosis, skin fragility |
| Janecke A et al., 2016 [12] | 45 | woman | musculocontractural type | CHST14 | unknown | down slanting palpebral fissures, blue sclerae, microcornea, myopia, circumscribed retinal degenerations at the periphery | laxity of joints, frequent bruising, delayed wound healing, skin fragility with prolonged bleeding, dermal hyperelasticity |
| Whitlow S et al. 2020 [13] | 33 | woman | type VI | unknown | pneumatic retinopexy → vitrectomy and 360-degree scleral graft | high myopia | unknown |
| Lumi X et al., 2021 [14] | 40 | man | type IV | COL3A1 | vitrectomy | high myopia | colon perforation, muscle and arterial rupture in both lower limbs, recurrent shoulder joint luxation |
| Current case | 21 | woman | musculocontractural type | dermatan sulfate epimerase | scleral buckling | high myopia, thin sclera | hyperextensible skin and hypermobile joint, prolonged bleeding, bradycardia |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoshikawa, Y.; Koto, T.; Ishida, T.; Uehara, T.; Yamada, M.; Kosaki, K.; Inoue, M. Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment in Musculocontractural Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome Caused by Biallelic Loss-of-Function Variants of Gene for Dermatan Sulfate Epimerase. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051728
Yoshikawa Y, Koto T, Ishida T, Uehara T, Yamada M, Kosaki K, Inoue M. Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment in Musculocontractural Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome Caused by Biallelic Loss-of-Function Variants of Gene for Dermatan Sulfate Epimerase. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(5):1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051728
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoshikawa, Yuji, Takashi Koto, Tomoka Ishida, Tomoko Uehara, Mamiko Yamada, Kenjiro Kosaki, and Makoto Inoue. 2023. "Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment in Musculocontractural Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome Caused by Biallelic Loss-of-Function Variants of Gene for Dermatan Sulfate Epimerase" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 5: 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051728
APA StyleYoshikawa, Y., Koto, T., Ishida, T., Uehara, T., Yamada, M., Kosaki, K., & Inoue, M. (2023). Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment in Musculocontractural Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome Caused by Biallelic Loss-of-Function Variants of Gene for Dermatan Sulfate Epimerase. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(5), 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051728







