Diagnostic Role of mNGS in Polymicrobial Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
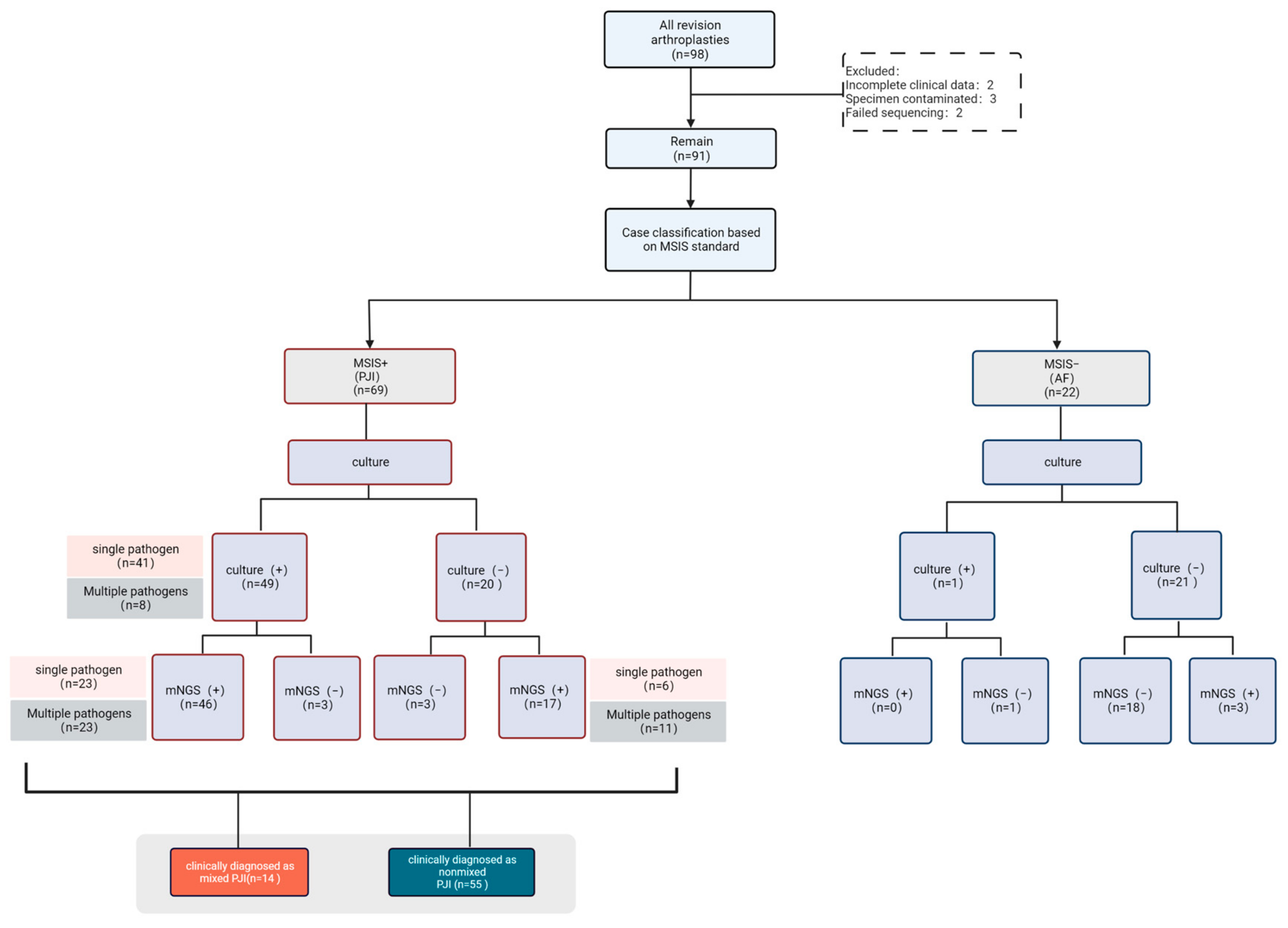
2.1. Study Population Selection
2.2. Specimen Collection and Processing
2.3. mNGS
2.4. Interpretation of mNGS Results
2.5. Clinical Diagnostic Criteria for Polymicrobial PJI
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
3.2. Comparison of mNGS and Conventional Microbial Culture in Pathogens Detection
3.2.1. Culture Results
3.2.2. mNGS Results
3.3. Comparison of Diagnostic Efficacy of Conventional Microbial Culture and mNGS
3.4. Diagnostic Efficacy of Culture and mNGS for Polymicrobial PJI Diagnosis
3.5. Case Analysis of Clinically Diagnosed Polymicrobial Infection
3.6. Cases with Negative Culture Result but Diagnosed as Polymicrobial Infection after Supplemental Pathogen Information by mNGS
3.7. Cases with Single Pathogens Cultured but Diagnosed as Polymicrobial Infection after Supplemental Pathogen Information by mNGS
3.8. Cases with Multiple Pathogens Detected by Both Culture and mNGS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akgün, D.; Perka, C.; Trampuz, A.; Renz, N. Outcome of Hip and Knee Periprosthetic Joint Infections Caused by Pathogens Resistant to Biofilm-Active Antibiotics: Results from a Prospective Cohort Study. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2018, 138, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavolus, J.J.; Cunningham, D.J.; Rao, S.R.; Wellman, S.S.; Seyler, T.M. Polymicrobial Infections in Hip Arthroplasty: Lower Treatment Success Rate, Increased Surgery, and Longer Hospitalization. J. Arthroplast. 2019, 34, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lora-Tamayo, J.; Murillo, O.; Iribarren, J.A.; Soriano, A.; Sánchez-Somolinos, M.; Baraia-Etxaburu, J.M.; Rico, A.; Palomino, J.; Rodríguez-Pardo, D.; Horcajada, J.P.; et al. A Large Multicenter Study of Methicillin-Susceptible and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Prosthetic Joint Infections Managed with Implant Retention. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, T.L.; Kheir, M.M.; Tan, D.D.; Parvizi, J. Polymicrobial Periprosthetic Joint Infections: Outcome of Treatment and Identification of Risk Factors. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2016, 98, 2082–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, A.; Patrick, S. Evaluation of Nonculture Methods for the Detection of Prosthetic Hip Biofilms. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2005, 437, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawietz, L.; Classen, R.-A.; Schröder, J.H.; Dynybil, C.; Perka, C.; Skwara, A.; Neidel, J.; Gehrke, T.; Frommelt, L.; Hansen, T.; et al. Proposal for a Histopathological Consensus Classification of the Periprosthetic Interface Membrane. J. Clin. Pathol. 2006, 59, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peel, T.N.; Cheng, A.C.; Buising, K.L.; Choong, P.F.M. Microbiological Aetiology, Epidemiology, and Clinical Profile of Prosthetic Joint Infections: Are Current Antibiotic Prophylaxis Guidelines Effective? Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 2386–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kheir, M.M.; Tan, T.L.; Higuera, C.; George, J.; Della Valle, C.J.; Shen, M.; Parvizi, J. Periprosthetic Joint Infections Caused by Enterococci Have Poor Outcomes. J. Arthroplast. 2017, 32, 933–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tande, A.J.; Patel, R. Prosthetic Joint Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 302–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceroni, D.; Dayer, R.; Steiger, C. Are We Approaching the End of Pediatric Culture-Negative Osteoarticular Infections? Future Microbiol. 2019, 14, 917–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolcott, R.; Costerton, J.W.; Raoult, D.; Cutler, S.J. The Polymicrobial Nature of Biofilm Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gude, S.; Pinçe, E.; Taute, K.M.; Seinen, A.-B.; Shimizu, T.S.; Tans, S.J. Bacterial Coexistence Driven by Motility and Spatial Competition. Nature 2020, 578, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, Z.; Fang, X.; Li, W.; Yang, B.; Zhang, W. Diagnosis and Treatment of Mycoplasmal Septic Arthritis: A Systematic Review. Int. Orthop. 2020, 44, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, B. The Value of Cultures to Modern Microbiology. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2017, 110, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbari, E.F.; Marculescu, C.; Sia, I.; Lahr, B.D.; Hanssen, A.D.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Gullerud, R.; Osmon, D.R. Culture-Negative Prosthetic Joint Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvizi, J.; Erkocak, O.F.; Della Valle, C.J. Culture-Negative Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2014, 96, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bejon, P.; Berendt, A.; Atkins, B.L.; Green, N.; Parry, H.; Masters, S.; McLardy-Smith, P.; Gundle, R.; Byren, I. Two-Stage Revision for Prosthetic Joint Infection: Predictors of Outcome and the Role of Reimplantation Microbiology. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levy, P.-Y.; Fournier, P.-E.; Fenollar, F.; Raoult, D. Systematic PCR Detection in Culture-Negative Osteoarticular Infections. Am. J. Med. 2013, 126, 1143.e25–1143.e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Fang, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, H.; Wang, Q.; Lin, J.; Zhang, W. Comparison of Culture and Broad-Range Polymerase Chain Reaction Methods for Diagnosing Periprosthetic Joint Infection: Analysis of Joint Fluid, Periprosthetic Tissue, and Sonicated Fluid. Int. Orthop. 2018, 42, 2035–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malandain, D.; Bémer, P.; Leroy, A.G.; Léger, J.; Plouzeau, C.; Valentin, A.S.; Jolivet-Gougeon, A.; Tandé, D.; Héry-Arnaud, G.; Lemarié, C.; et al. Assessment of the Automated Multiplex-PCR Unyvero I60 ITI® Cartridge System to Diagnose Prosthetic Joint Infection: A Multicentre Study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 83.e1–83.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.-F.; Shi, X.-P.; Chen, Y.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, B. Rapid Diagnosis of Sepsis with TaqMan-Based Multiplex Real-Time PCR. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2018, 32, e22256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peel, T.N.; Cole, N.C.; Dylla, B.L.; Patel, R. Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry and Diagnostic Testing for Prosthetic Joint Infection in the Clinical Microbiology Laboratory. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 81, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, Z.; Han, D.; Zhang, R.; Li, J. Metagenomics Next-Generation Sequencing Tests Take the Stage in the Diagnosis of Lower Respiratory Tract Infections. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 38, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Miller, S.; Chiu, C.Y. Clinical Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing for Pathogen Detection. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2019, 14, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Q.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Q.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, W.; Yao, Y.; Su, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, M.; et al. Microbiological Diagnostic Performance of Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing When Applied to Clinical Practice. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, S231–S240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Tang, J.; Shen, H.; Zhang, X. Better Choice of the Type of Specimen Used for Untargeted Metagenomic Sequencing in the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infections. Bone Jt. J. 2021, 103, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Li, W.; Lee, G.-C.; Fang, X.; Xing, L.; Yang, B.; Lin, J.; Zhang, W. Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing of Synovial Fluid Demonstrates High Accuracy in Prosthetic Joint Infection Diagnostics: MNGS for Diagnosing PJI. Bone Jt. Res. 2020, 9, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Han, Y.; Feng, J. Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing for Mixed Pulmonary Infection Diagnosis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shohat, N.; Bauer, T.; Buttaro, M.; Budhiparama, N.; Cashman, J.; Della Valle, C.J.; Drago, L.; Gehrke, T.; Marcelino Gomes, L.S.; Goswami, K.; et al. Hip and Knee Section, What Is the Definition of a Periprosthetic Joint Infection (PJI) of the Knee and the Hip? Can the Same Criteria Be Used for Both Joints?: Proceedings of International Consensus on Orthopedic Infections. J. Arthroplast. 2019, 34, S325–S327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Fang, X.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Yang, B.; Zhang, W. Metagenomic next Generation Sequencing Improves Diagnosis of Prosthetic Joint Infection by Detecting the Presence of Bacteria in Periprosthetic Tissues. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 96, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Fang, X.; Huang, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.-F.; Yang, B.; Zhang, W. Value of MNGS in Sonication Fluid for the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Arthroplasty 2019, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, X.; Cai, Y.; Mei, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yang, B.; Li, W.; Zhang, W. Optimizing Culture Methods According to Preoperative MNGS Results Can Improve Joint Infection Diagnosis. Bone Jt. J. 2021, 103, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Yang, B.; Li, W.-B.; Zhang, C.-J.; Fang, X.-Y.; Zhang, C.-F.; Zhang, W.-M.; Lin, J.-H. Pathogenic Detection by Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing in Osteoarticular Infections. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Gao, H.; Meng, H.; Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, H. Detection of Pulmonary Infectious Pathogens from Lung Biopsy Tissues by Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Street, T.L.; Sanderson, N.D.; Atkins, B.L.; Brent, A.J.; Cole, K.; Foster, D.; McNally, M.A.; Oakley, S.; Peto, L.; Taylor, A.; et al. Molecular Diagnosis of Orthopedic-Device-Related Infection Directly from Sonication Fluid by Metagenomic Sequencing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2334–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, X.; Cai, Y.; Chen, X.; Huang, C.; Lin, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, W. The Role of Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing in the Pathogen Detection of Invasive Osteoarticular Infection. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 122, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Cai, Y.; Shi, T.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Yang, B.; Zhang, W.; Guan, Z. Detecting the Presence of Bacteria in Low-Volume Preoperative Aspirated Synovial Fluid by Metagenomic next-Generation Sequencing. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 99, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-X.; Huang, Z.; Fang, X.; Li, W.; Yang, B.; Zhang, W. Comparison of Broad-Range Polymerase Chain Reaction and Metagenomic next-Generation Sequencing for the Diagnosis of Prosthetic Joint Infection. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 95, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indelli, P.F.; Ghirardelli, S.; Violante, B.; Amanatullah, D.F. Next Generation Sequencing for Pathogen Detection in Periprosthetic Joint Infections. EFORT Open Rev. 2021, 6, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, S.; Yi, Q.; Xia, Y.; Geng, B. Diagnostic Value of Next-Generation Sequencing in Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Systematic Review. Orthop. Surg. 2022, 14, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marculescu, C.E.; Cantey, J.R. Polymicrobial Prosthetic Joint Infections: Risk Factors and Outcome. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2008, 466, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qu, X.; Zhai, Z.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Dai, K. PCR-Based Diagnosis of Prosthetic Joint Infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2742–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgenstern, C.; Cabric, S.; Perka, C.; Trampuz, A.; Renz, N. Synovial Fluid Multiplex PCR Is Superior to Culture for Detection of Low-Virulent Pathogens Causing Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 90, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calanna, F.; Chen, F.; Risitano, S.; Vorhies, J.S.; Franceschini, M.; Giori, N.J.; Indelli, P.F. Debridement, Antibiotic Pearls, and Retention of the Implant (DAPRI): A Modified Technique for Implant Retention in Total Knee Arthroplasty PJI Treatment. J. Orthop. Surg. 2019, 27, 4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carijo, J.H.; Courtney, P.M.; Goswami, K.; Groff, H.; Kendoff, D.; Matos, J.; Sandiford, N.A.; Scheper, H.; Schmaltz, C.A.S.; Shubnyakov, I.; et al. Hip and Knee Section, Pathogen Factors: Proceedings of International Consensus on Orthopedic Infections. J. Arthroplast. 2019, 34, S381–S386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triffault-Fillit, C.; Valour, F.; Guillo, R.; Tod, M.; Goutelle, S.; Lustig, S.; Fessy, M.-H.; Chidiac, C.; Ferry, T.; Lyon, B.J.I. Study Group Prospective Cohort Study of the Tolerability of Prosthetic Joint Infection Empirical Antimicrobial Therapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00163-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M.; Benito, N.; Soriano, A. The Effect of Preoperative Antimicrobial Prophylaxis on Intraoperative Culture Results in Patients with a Suspected or Confirmed Prosthetic Joint Infection: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2765–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Cui, P.; Zhang, H.-C.; Wu, H.-L.; Ye, M.-Z.; Zhu, Y.-M.; Ai, J.-W.; Zhang, W.-H. Clinical Application and Evaluation of Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing in Suspected Adult Central Nervous System Infection. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvizi, J.; Tan, T.L.; Goswami, K.; Higuera, C.; Della Valle, C.; Chen, A.F.; Shohat, N. The 2018 Definition of Periprosthetic Hip and Knee Infection: An Evidence-Based and Validated Criteria. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 1309–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, M.; Sousa, R.; Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M.; Chen, A.F.; Soriano, A.; Vogely, H.C.; Clauss, M.; Higuera, C.A.; Trebše, R. The EBJIS Definition of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Bone Jt. J. 2021, 103, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | All Patients (n = 91) | PJI (n = 69) | AF (n =22) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years, median (range) | 64.6 ± 13.5 | 65.3 ± 13.5 | 62.7 ± 13.6 | 0.448 |
| Gender, female, n (%) | 53 (58.2%) | 42 (60.9%) | 11 (50.0%) | 0.368 |
| Location, n (%) | 0.099 | |||
| Hip | 46 (50.5%) | 30 (43.5%) | 14 (63.6%) | |
| Knee | 45 (49.5%) | 39 (56.5%) | 8 (36.4%) | |
| Sinus tract, n (%) | 15 (16.5%) | 15 (21.7%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.017 |
| Antibiotics prior to surgery, n | 23 | 23 | 0 | 0.002 |
| ESR, mm/h | 53.3 ± 37.4 | 65.6 ± 33.8 | 14.5 ± 14.6 | <0.001 |
| CRP, mg/L | 44.2 ± 43.6 | 51.8 ± 46.4 | 20.2 ± 19.4 | 0.002 |
| SF-WBC × 106/L | 21,976.9 ± 44,518.9 | 28,471.2 ± 49,456.3 | 1608.4 ± 797.9 | <0.001 |
| SF-PMN, % | 73.8 ± 47.4 | 75.4 ± 16.0 | 68.9 ± 93.7 | <0.001 |
| Methods | No. of Patients (n =) | PJI Group | AF Group | Sensitivity % (95% CI) | Specifificity % (95% CI) | PPV % (95% CI) | NPV % (95% CI) | Accuracy (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intraoperative sample culture | 91 | 49/20 | 1/21 | 71.0 (58.8–81.3) | 95.4 (77.1–99.8) | 98.0 (89.3–99.9) | 51.2 (35.1–67.1) | 76.9 (66.9–85.1) |
| Intraoperative sample mNGS | 91 | 63/6 | 3/19 | 91.3 (82.0–96.7) | 86.3 (65.0–97.0) | 95.4 (87.2–99.0) | 76.0 (54.8–90.6) | 90.1 (82.0–95.3) |
| Methods | No. of Patients (n =) | Polymicrobial PJI Group | Mono-Microorganism PJI Group | Sensitivity % (95% CI) | Specifificity % (95% CI) | PPV % (95% CI) | NPV % (95% CI) | Accuracy (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intraoperative sample culture | 69 | 8/6 | 0/55 | 57.1 (28.9–82.3) | 100 (93.5–100) | 100 (63.0–100) | 90.2 (79.8–96.3) | 91.3 (82.0–96.7) |
| Intraoperative sample mNGS | 69 | 12/2 | 22/33 | 85.7 (57.2–98.2) | 60.0 (45.9–73.0) | 35.3 (19.8–53.5) | 94.3 (80.8–99.3) | 65.2 (52.8–76.3) |
| Patient No. | Administration of Antibiotic Pre-Operatively (Yes, Y/No, N) | Underlying Joint Disorder | Sinus Tract OR Incision Reputure | Co-Morbidity | Infection Type | mNGS Results | Culture Results | Antibiotic Regimen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. 1 | Y | Osteoarthritis | none | Hypertension; Diabetes mellitus | chronic | Cutibacterium acnes; Candida parapsilosis | Staphylococcus haemolyticus; Staphylococcus epidermidis; Candida parapsilosis | Vancomycin; Moxifloxacin; Fluconazole |
| No. 2 | Y | femoral-head necrosis | none | Hypertension; urinary tract infection | acute | Mycoplasma hominis | Candida tropicalis | Fluconazole; Erythromycin |
| No. 3 | Y | Osteoarthritis | none | None | chronic | Mycoplasma hominis; Acinetobacter_baumannii | Negative | Vancomycin; Ceftazidime; Levofloxacin; Doxycycline |
| No. 4 | Y | Septic Arthritis | Sinus tract | None | chronic | Enterococcus faecalis; Staphylococcus epidermidis; Acinetobacter nosocomialis; Acinetobacter baumannii; Mycobacterium tuberculosis | Enterococcus faecalis; Staphylococcus epidermidis; Acinetobacter nosocomialis; Acinetobacter baumannii | Vancomycin; Imipenem; Levofloxacin; Rifampicin; isoniazid |
| No. 5 | Y | Osteoarthritis | none | Diabetes mellitus; urinary tract infection | acute | Mycoplasma hominis | Staphylococcus aureus | Vancomycin; Cefuroxime; Erythromycin |
| No. 6 | Y | Osteoarthritis | incision reputure | None | chronic | Finegoldia magna; Anaerococcus tetradius; Peptoniphilus_lacrimalis | Finegoldia magna; Staphylococcus epidermidis | Vancomycin; Meropenem; Piperacillin; Linezolid; Amoxicillin; Metronidazole |
| No. 7 | N | Osteoarthritis | Sinus tract | Hypertension; gout | acute | Enterobacter cloacae; Acinetobacter pittii | Enterococcus faecalis | Meropenem; Vancomycin; Piperacillin; Penicillin; Teicoplanin |
| No. 8 | N | Osteoarthritis | none | none | chronic | Enterococcus faecalis; Staphylococcus epidermidis | Enterococcus faecalis; Staphylococcus epidermidis | Vancomycin; levofloxacin; |
| No. 9 | Y | femoral-head necrosis | none | Hypertension; Diabetes mellitus; Hypoproteinemia | chronic | Klebsiella pneumoniae; Bacteroides fragilis; Clostridium clostridioforme | Klebsiella pneumoniae; Bacteroides fragilis | Vancomycin; Meropenem; Colapitol |
| No. 10 | Y | Fracture | none | Diabetes mellitus | chronic | Staphylococcus epidermidis; Escherichia coli; Shigella boydii | Staphylococcus epidermidis; Escherichia coli | Vancomycin; Meropenem |
| No. 11 | Y | Fracture | none | Diabetes mellitus | chronic | Prevotella bivia; Streptococcus constellatus; Dialister invisus | Klebsiella pneumoniae; Escherichia coli; Clostridium ramosum | Vancomycin; Meropenem; Ceftazidime; Metronidazole |
| No. 12 | N | Osteoarthritis | Sinus tract | Hyperthyroidism; Diabetes mellitus | chronic | Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Klebsiella oxytoca; Mycoplasma hominis | Negative | Vancomycin; Meropenem; Ceftazidime; Doxycycline |
| No. 13 | N | Osteoarthritis | none | None | chronic | Staphylococcus epidermidis; Cutibacterium acnes | Ralstonia pickettii; Staphylococcus epidermidis | Vancomycin; Linezolid |
| No. 14 | Y | Osteoarthritis | Sinus tract | Diabetes mellitus; Rheumatoid arthritis | chronic | Streptococcus oralis; Klebsiella oxytoca | Streptococcus oralis | Vancomycin; Meropenem; Ceftriaxone |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mei, J.; Hu, H.; Zhu, S.; Ding, H.; Huang, Z.; Li, W.; Yang, B.; Zhang, W.; Fang, X. Diagnostic Role of mNGS in Polymicrobial Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051838
Mei J, Hu H, Zhu S, Ding H, Huang Z, Li W, Yang B, Zhang W, Fang X. Diagnostic Role of mNGS in Polymicrobial Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(5):1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051838
Chicago/Turabian StyleMei, Jian, Hongxin Hu, Si Zhu, Haiqi Ding, Zida Huang, Wenbo Li, Bin Yang, Wenming Zhang, and Xinyu Fang. 2023. "Diagnostic Role of mNGS in Polymicrobial Periprosthetic Joint Infection" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 5: 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051838
APA StyleMei, J., Hu, H., Zhu, S., Ding, H., Huang, Z., Li, W., Yang, B., Zhang, W., & Fang, X. (2023). Diagnostic Role of mNGS in Polymicrobial Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(5), 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051838





