Prescribing Patterns and Outcomes of Edoxaban in Atrial Fibrillation: One-Year Data from the Global ETNA-AF Program
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Those who received the non-recommended 60 mg (once daily; QD) dose vs. those receiving the recommended 30 mg (QD) dose, thus, assessing the effects in the “overdosed” group;
- And those who received the recommended edoxaban 60 mg (QD) dose vs. those receiving the non-recommended 30 mg (QD) dose, thus, assessing the effects in the “underdosed” group.
Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
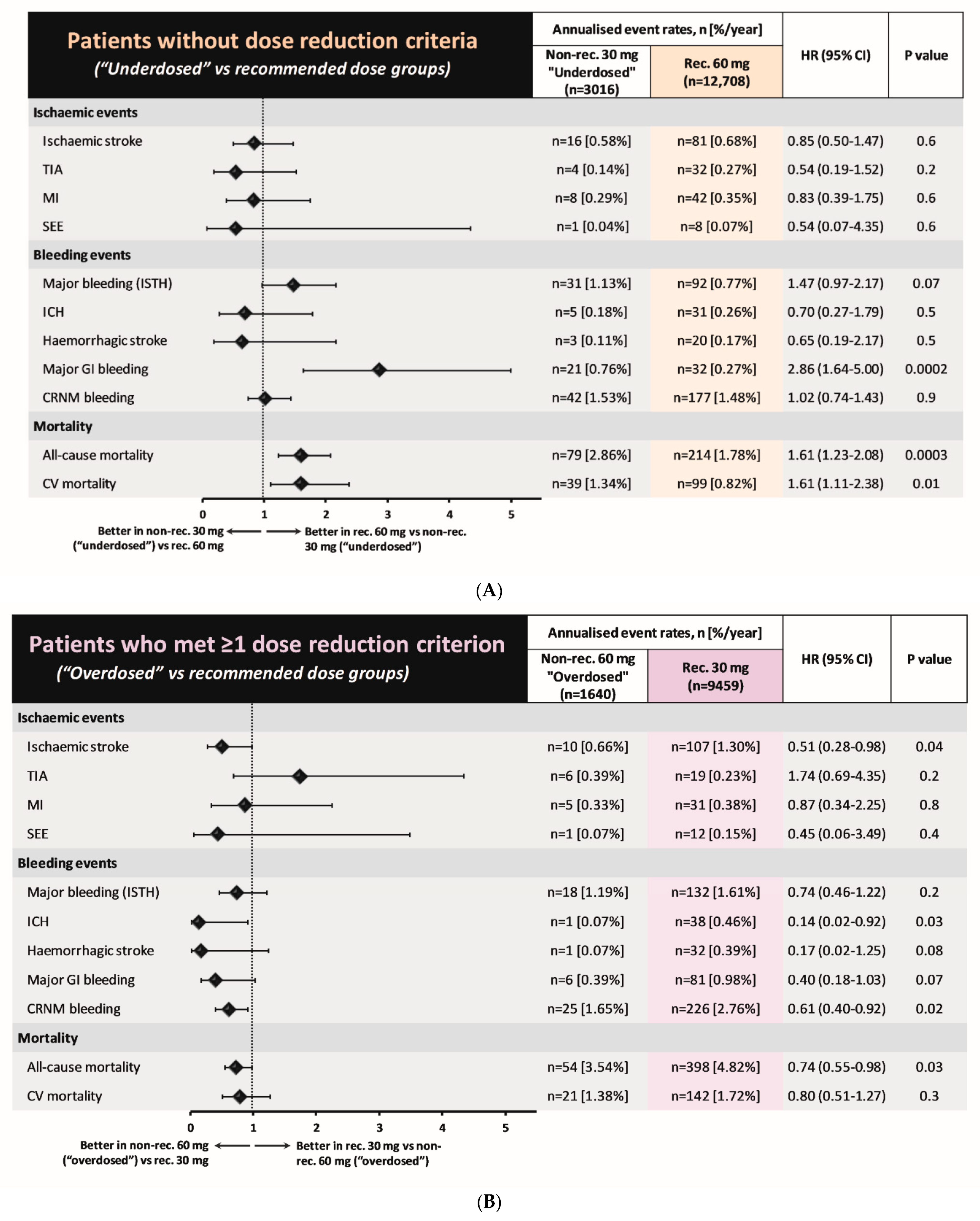
3.2. Patients without Dose Reduction Criteria
3.3. Patients with at Least 1 Dose Reduction Criterion
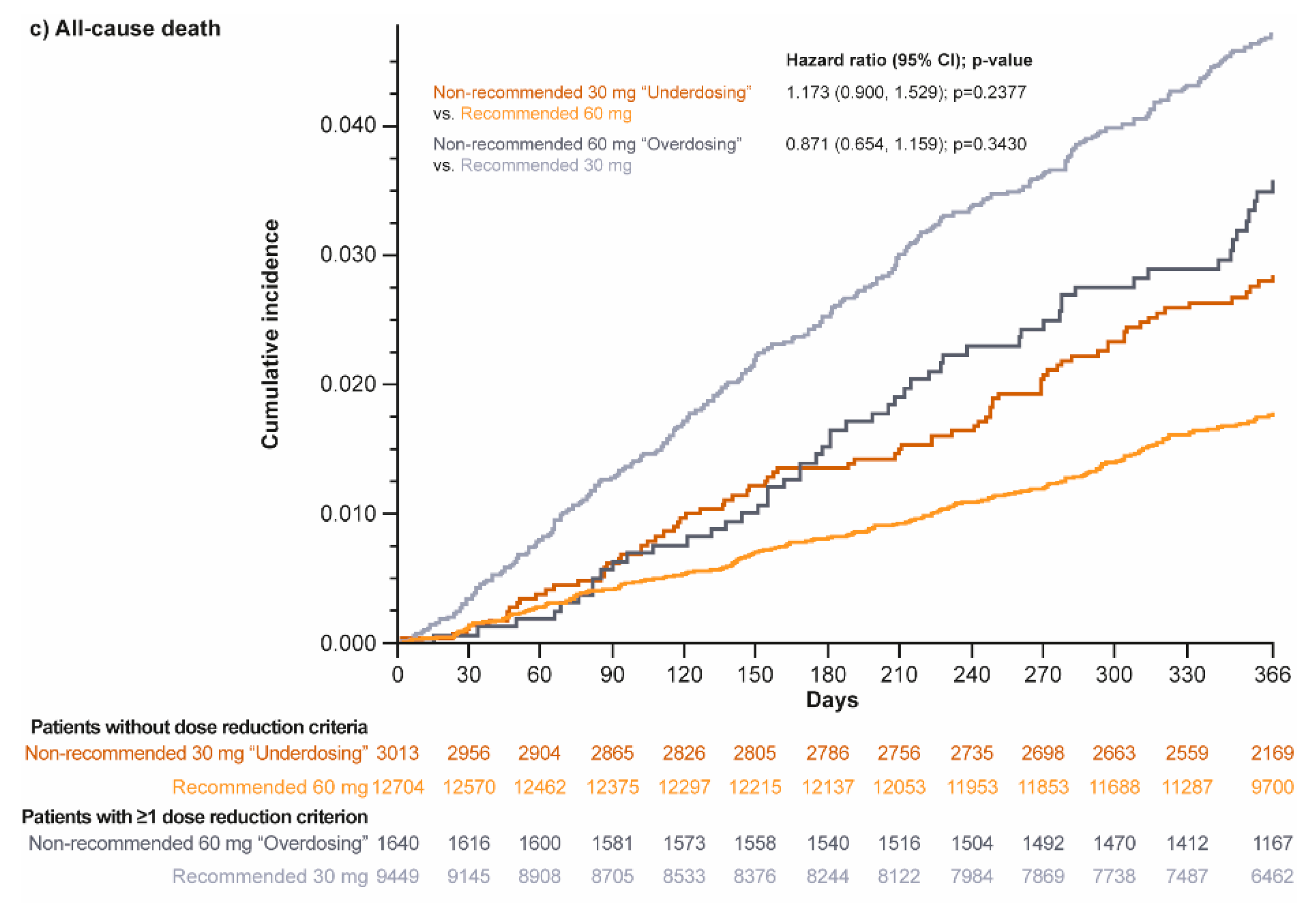
3.4. Clinical Events
4. Discussion
4.1. Prescription Rates of Non-Recommended DOACs
4.2. Clinical Characteristics of Patients Receiving Non-Recommended Dosing DOACs
4.3. Clinical Events Associated with Non-Recommended Dosing
4.4. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomstrom-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivaroxaban–Summary of Product Characteristics. 2008. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/xarelto-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 24 February 2023).
- Dabigatran–Summary of Product Characteristics. 2008. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/pradaxa-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 24 February 2023).
- Apixaban–Summary of Product Characteristics. 2011. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/eliquis-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 24 February 2023).
- Edoxaban–Summary of Product Charactersitics. 2020. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/eliquis-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 24 February 2023).
- Santos, J.; Antonio, N.; Rocha, M.; Fortuna, A. Impact of direct oral anticoagulant off-label doses on clinical outcomes of atrial fibrillation patients: A systematic review. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 86, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.T.; Yang, P.S.; Jang, E.; Kim, T.H.; Uhm, J.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Pak, H.N.; Lee, M.H.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Joung, B. Label adherence of direct oral anticoagulants dosing and clinical outcomes in patients with atrial fibrillation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e014177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, B.A.; Shrader, P.; Thomas, L.; Ansell, J.; Fonarow, G.C.; Gersh, B.J.; Kowey, P.R.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Naccarelli, G.; Reiffel, J.; et al. Off-label dosing of non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants and adverse outcomes: The ORBIT-AF II Registry. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 2597–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.R.; Lee, Y.S.; Park, J.S.; Cha, M.J.; Kim, T.H.; Park, J.; Park, J.K.; Lee, J.M.; Kang, K.W.; Shim, J.; et al. Label adherence for non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants in a prospective cohort of Asian patients with atrial fibrillation. Yonsei Med. J. 2019, 60, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarenco, P.; Haas, S.; Hess, S.; Kirchhof, P.; Lambelet, M.; Bach, M.; Turpie, A.G.G.; Camm, A.J. Outcomes associated with non-recommended dosing of rivaroxaban: Results from the XANTUS study. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2019, 5, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, Y.H.; Chao, T.F.; Chen, S.W.; Lee, H.F.; Yeh, Y.H.; Huang, Y.C.; Chang, S.H.; Kuo, C.T.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Chen, S.A. Off-label dosing of non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants and clinical outcomes in Asian patients with atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2020, 17, 2102–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, S.; Dahlberg, K.W. Physician’s fear of anticoagulant therapy in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 348, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edoxaban-Full Prescribing Information (US). Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2015/206316lbl.pdf (accessed on 24 February 2023).
- De Caterina, R.; Agnelli, G.; Laeis, P.; Unverdorben, M.; Rauer, H.; Wang, C.C.; Nakamura, M.; Chiu, K.M.; Reimitz, P.E.; Koretsune, Y.; et al. The global Edoxaban Treatment in routine cliNical prActice (ETNA) noninterventional study program: Rationale and design. Clin. Cardiol. 2019, 42, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Caterina, R.; Kim, Y.H.; Koretsune, Y.; Wang, C.C.; Yamashita, T.; Chen, C.; Reimitz, P.E.; Unverdorben, M.; Kirchhof, P. Safety and Effectiveness of Edoxaban in Atrial Fibrillation Patients in Routine Clinical Practice: One-Year Follow-Up from the {Global Noninterventional ETNA-AF Program. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Bohm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Celutkiene, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camm, A.J.; Cools, F.; Virdone, S.; Bassand, J.P.; Fitzmaurice, D.A.; Arthur Fox, K.A.; Goldhaber, S.Z.; Goto, S.; Haas, S.; Mantovani, L.G.; et al. Mortality in patients with atrial fibrillation receiving nonrecommended doses of direct oral anticoagulants. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 1425–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeymer, U.; Lober, C.; Wolf, A.; Richard, F.; Schafer, H.; Taggeselle, J.; Kabitz, H.J.; Prondzinsky, R.; Suselbeck, T.; Investigators, A. Use, persistence, efficacy, and safety of apixaban in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation in unselected patients in Germany. Results of the prospective Apixaban in Atrial Fibrillation (APAF) Registry. Cardiol. Ther. 2020, 9, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffel, J.; Ruff, C.T.; Yin, O.; Braunwald, E.; Park, J.G.; Murphy, S.A.; Connolly, S.; Antman, E.M.; Giugliano, R.P. Randomized, Double-Blind Comparison of Half-Dose Versus Full-Dose Edoxaban in 14,014 Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Shah, N.D.; Sangaralingham, L.R.; Gersh, B.J.; Noseworthy, P.A. Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulant Dosing in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation and Renal Dysfunction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 2779–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camm, A.J.; Amarenco, P.; Haas, S.; Hess, S.; Kirchhof, P.; Kuhls, S.; van Eickels, M.; Turpie, A.G.; Investigators, X. XANTUS: A real-world, prospective, observational study of patients treated with rivaroxaban for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Patients without Dose Reduction Criteria | Patients Who Met at Least 1 Dose Reduction Criterion | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recommended 60 mg (n = 12,708) | Non-Recommended 30 mg “Underdosed” (n = 3016) | p Value | Non-Recommended 60 mg “Overdosed” (n = 1640) | Recommended 30 mg (n = 9459) | p-Value | |
| Age (y), mean (SD) | 70 (9.3) | 74 (9.0) | <0.0001 | 75 (9.1) | 78 (8.5) | <0.0001 |
| Age (y), n (%) | ||||||
| <65 | 3024 (23.8) | 395 (13.1) | <0.0001 | 184 (11.2) | 530 (5.6) | <0.0001 |
| 65 to <75 | 5388 (42.4) | 970 (32.2) | 473 (28.8) | 2338 (24.7) | ||
| 75 to <85 | 3919 (30.8) | 1368 (45.4) | 759 (46.3) | 4365 (46.1) | ||
| ≥85 | 376 (3.0) | 282 (9.4) | 224 (13.7) | 2226 (23.5) | ||
| Male, n (%) | 8962 (70.5) | 2080 (69.0) | 0.09 | 653 (39.8) | 3910 (41.3) | 0.2 |
| Weight, kg, mean (SD) | 81.8 (15.5) | 76.0 (13.4) | <0.0001 | 64.1 (11.8) | 56.1 (11.4) | <0.0001 |
| BMI, kg/m2, mean (SD) | 28.3 (4.8) | 27.6 (4.4) | <0.0001 | 24.2 (3.9) | 22.8 (3.7) | <0.0001 |
| CrCl, * mL/min, mean (SD) | 85.8 (26.8) | 72.2 (20.7) | <0.0001 | 54.8 (20.5) | 49.6 (18.1) | <0.0001 |
| Type of AF, % (n) | ||||||
| Paroxysmal | 6573 (53.0) | 1395 (48.3) | <0.0001 | 872 (54.3) | 4465 (50.4) | <0.0001 |
| Persistent | 2860 (23.1) | 497 (17.2) | 329 (20.5) | 1157 (13.1) | ||
| Long-standing persistent | 845 (6.8) | 432 (15.0) | 108 (6.7) | 1476 (16.7) | ||
| Permanent | 1741 (14.0) | 313 (10.8) | 272 (16.9) | 716 (8.1) | ||
| CHA2DS2-VASc score, mean (SD) [median] | 2.8 (1.4) [3.0] | 3.3 (1.5) [3.0] | <0.0001 | 3.5 (1.4) [3.0] | 3.9 (1.5) [4.0] | <0.0001 |
| Modified HAS-BLED score, † mean (SD) [median] | 2.3 (1.1) [2.0] | 2.5 (1.1) [2.0] | <0.0001 | 2.5 (1.1) [2.0] | 2.5 (1.1) [2.0] | 0.4 |
| Medical history, n (%) | ||||||
| Hypertension | 9519 (74.9) | 2319 (76.9) | 0.02 | 1192 (72.7) | 6922 (73.2) | 0.7 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 2903 (22.8) | 858 (28.4) | <0.0001 | 335 (20.4) | 2145 (22.7) | 0.04 |
| Coronary heart disease | 1782 (18.0) | 436 (26.8) | 0.5 | 290 (20.9) | 642 (22.5) | <0.0001 |
| Myocardial infarction | 430 (3.4) | 144 (4.8) | 0.0003 | 49 (3.0) | 396 (4.2) | 0.02 |
| Heart failure ‡ | 1671 (13.2) | 620 (20.6) | <0.0001 | 243 (14.8) | 2638 (27.9) | <0.0001 |
| Peripheral artery disease | 262 (2.1) | 89 (3.0) | 0.003 | 55 (3.4) | 226 (2.4) | 0.02 |
| COPD | 773 (6.1) | 174 (5.8) | 0.5 | 124 (7.6) | 344 (3.6) | <0.0001 |
| Ischemic stroke | 1093 (8.6) | 333 (11.0) | <0.0001 | 167 (10.2) | 1554 (16.4) | <0.0001 |
| TIA | 390 (3.1) | 95 (3.1) | 0.8 | 55 (3.4) | 305 (3.2) | 0.8 |
| Major bleeding (ISTH) | 134 (1.1) | 63 (2.1) | <0.0001 | 20 (1.2) | 247 (2.6) | 0.0007 |
| Intracranial hemorrhage | 103 (0.8) | 45 (1.5) | 0.0005 | 13 (0.8) | 196 (2.1) | 0.0004 |
| Major gastrointestinal bleeding | 14 (0.1) | 11 (0.4) | 0.002 | 4 (0.2) | 35 (0.4) | 0.4 |
| Medication at Baseline, n (%) | Patients without Dose Reduction Criteria | Patients Who Met at Least 1 Dose Reduction Criterion | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recommended 60 mg (n = 12,708) | Non-Recommended 30 mg “Underdosing” (n = 3016) | p Value | Non-Recommended 60 mg “Overdosing” (n = 1640) | Recommended 30 mg (n = 9459) | p-Value | |
| Antiplatelets | 1660 (13.1) | 342 (11.3) | 0.01 | 208 (12.7) | 759 (8.0) | <0.0001 |
| Antiarrhythmic and rate control drugs | 602 (5.4) | 100 (4.6) | 0.1 | 97 (6.5) | 320 (5.8) | 0.4 |
| Heparin/fondaparinux | 905 (9.0) | 96 (5.8) | <0.0001 | 125 (8.8) | 349 (11.3) | 0.01 |
| NSAIDs | 13 (0.1) | 5 (0.3) | 0.1 | 1 (0.1) | 23 (0.7) | 0.004 |
| P-gp inhibitors/inducers for which edoxaban dose adjustment is mandatory | 10 (0.1) | 3 (0.2) | 0.4 | 3 (0.2) | 44 (1.3) | 0.0006 |
| P-gp inhibitors/inducers for which edoxaban dose adjustment is not mandatory | 4 (0) | 3 (0.2) | 0.04 | 3 (0.2) | 13 (0.4) | 0.4 |
| Proton pump inhibitors | 19 (0.2) | 1 (0.1) | 0.2 | 3 (0.2) | 34 (0.8) | 0.01 |
| Hormone therapy | 1 (0) | 1 (0.1) | 0.1 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chao, T.-F.; Unverdorben, M.; Kirchhof, P.; Koretsune, Y.; Yamashita, T.; Crozier, R.A.; Pecen, L.; Chen, C.; Borrow, A.P.; De Caterina, R. Prescribing Patterns and Outcomes of Edoxaban in Atrial Fibrillation: One-Year Data from the Global ETNA-AF Program. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051870
Chao T-F, Unverdorben M, Kirchhof P, Koretsune Y, Yamashita T, Crozier RA, Pecen L, Chen C, Borrow AP, De Caterina R. Prescribing Patterns and Outcomes of Edoxaban in Atrial Fibrillation: One-Year Data from the Global ETNA-AF Program. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(5):1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051870
Chicago/Turabian StyleChao, Tze-Fan, Martin Unverdorben, Paulus Kirchhof, Yukihiro Koretsune, Takeshi Yamashita, Robert A. Crozier, Ladislav Pecen, Cathy Chen, Amanda P. Borrow, and Raffaele De Caterina. 2023. "Prescribing Patterns and Outcomes of Edoxaban in Atrial Fibrillation: One-Year Data from the Global ETNA-AF Program" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 5: 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051870
APA StyleChao, T.-F., Unverdorben, M., Kirchhof, P., Koretsune, Y., Yamashita, T., Crozier, R. A., Pecen, L., Chen, C., Borrow, A. P., & De Caterina, R. (2023). Prescribing Patterns and Outcomes of Edoxaban in Atrial Fibrillation: One-Year Data from the Global ETNA-AF Program. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(5), 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051870







