Th2 Cytokines Affect the Innate Immune Barrier without Impairing the Physical Barrier in a 3D Model of Normal Human Skin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. 3D Organotypic Human Skin Culture
2.2. Immunofluorescence Qualitative Analysis
2.3. Immunofluorescence Quantitative Analysis
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy and Morphometric Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
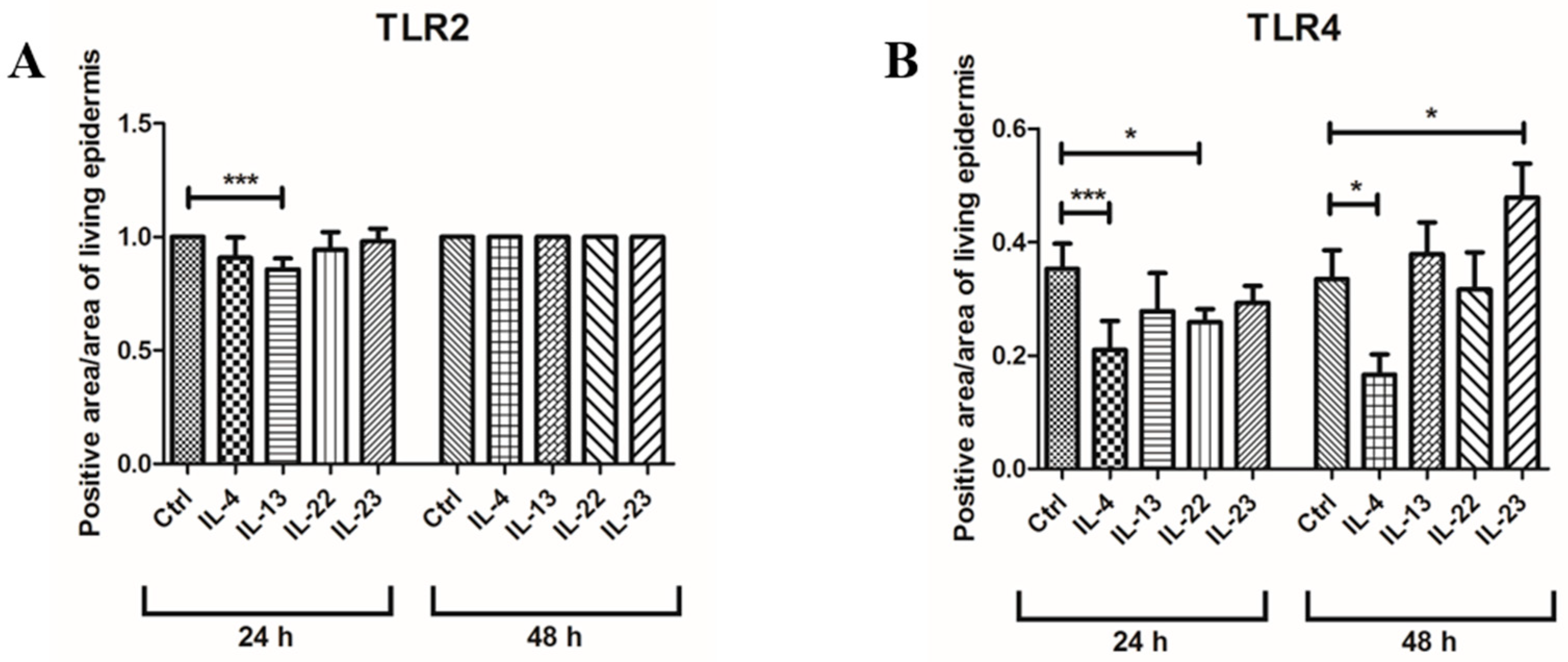
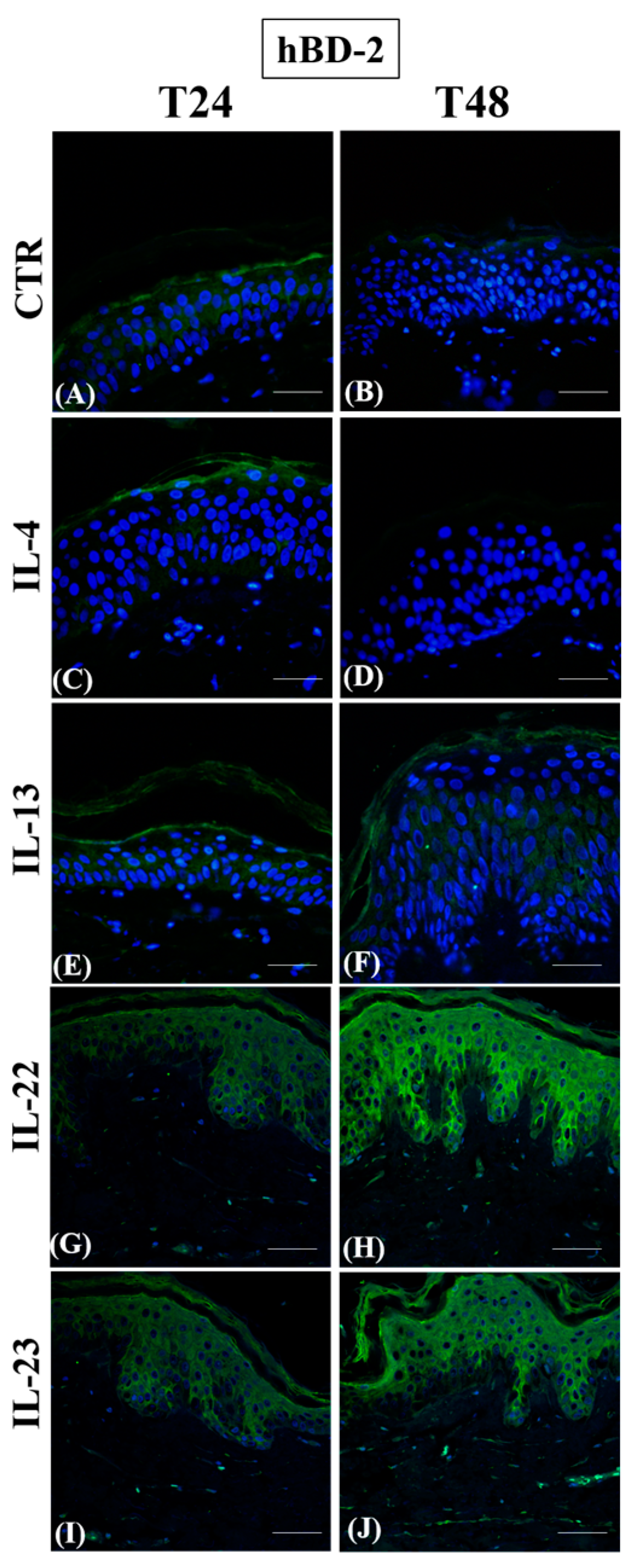
3.1. Th2 Cytokines Affect the Epidermal Innate Immune Barrier without Impairing the TJ Composition
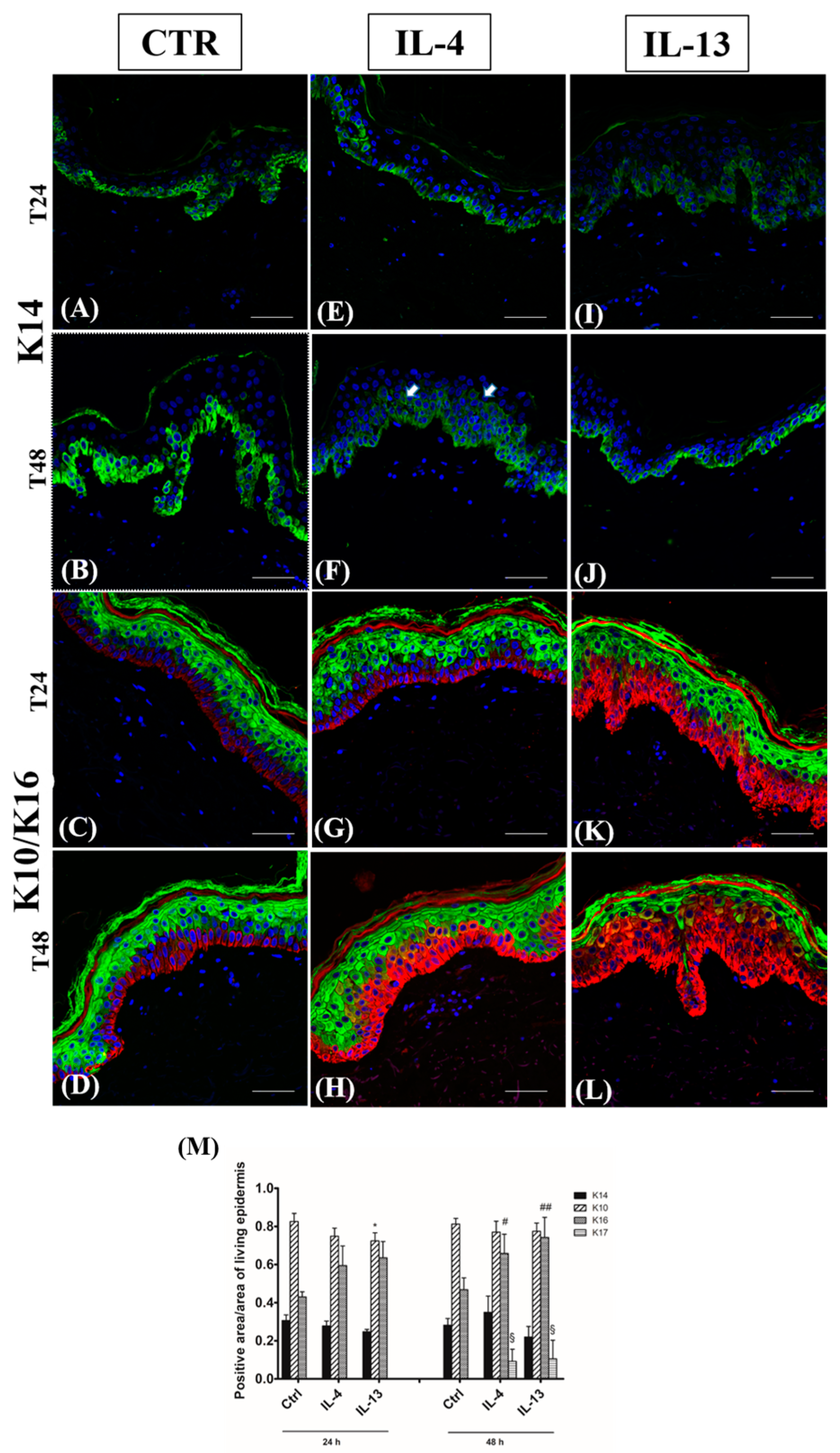
3.2. Epidermal Homeostasis Is Affected Differently by IL-4 and IL-13
3.3. Spongiosis Is an Early AD Event Triggered by Both Th2 Cytokines
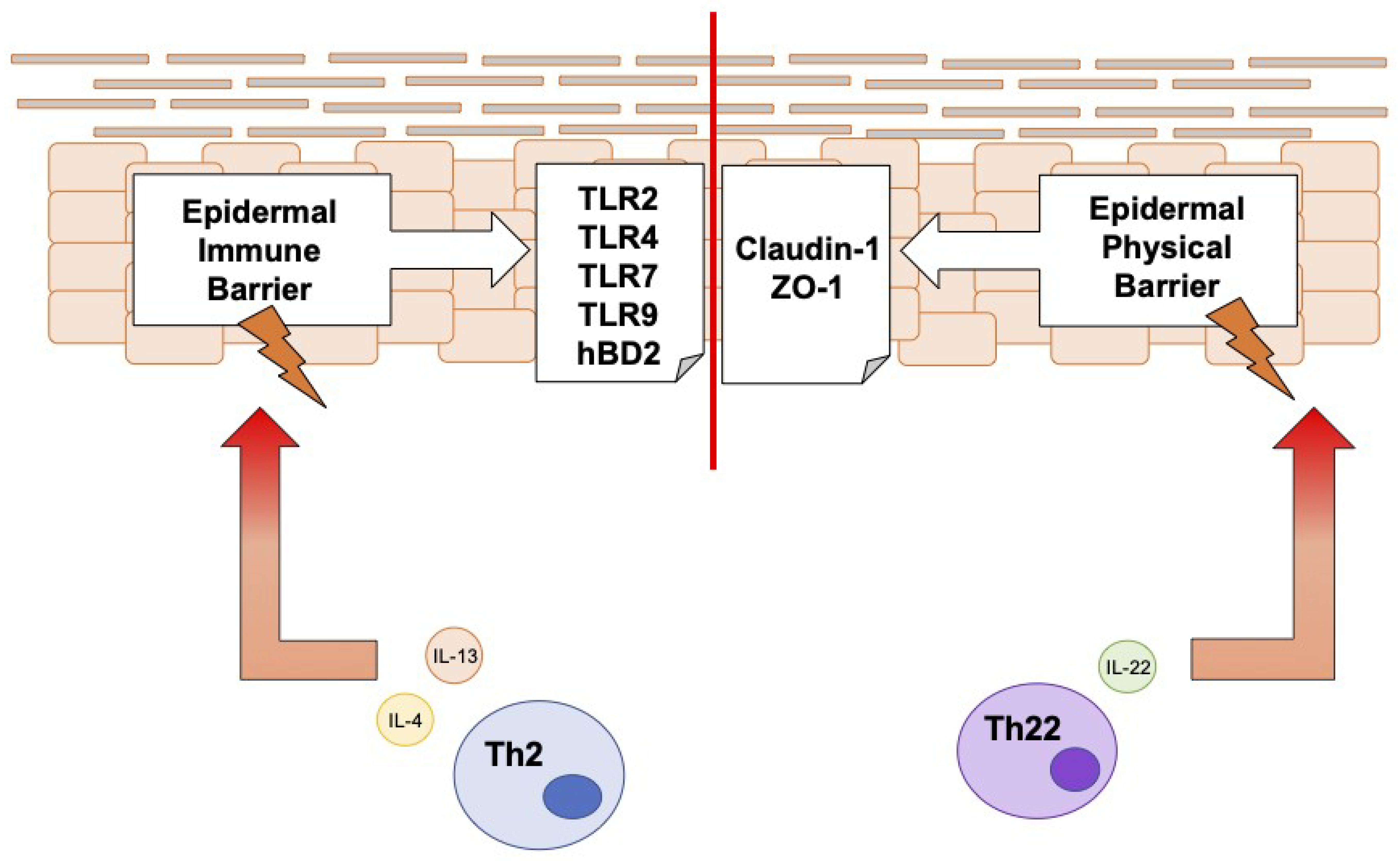
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fölster-Holst, R. Management of Atopic Dermatitis: Are There Differences between Children and Adults? J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2014, 28, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortz, C.G.; Andersen, K.E.; Dellgren, C.; Barington, T.; Bindslev-Jensen, C. Atopic Dermatitis from Adolescence to Adulthood in the TOACS Cohort: Prevalence, Persistence and Comorbidities. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 70, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Ricardo-Gonzalez, R.R.; Moro, K. Skin-Resident Innate Lymphoid Cells—Cutaneous Innate Guardians and Regulators. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gittler, J.K.; Shemer, A.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Gulewicz, K.J.; Wang, C.Q.F.; Mitsui, H.; Cardinale, I.; de Guzman Strong, C.; Krueger, J.G.; et al. Progressive Activation of TH2/TH22 Cytokines and Selective Epidermal Proteins Characterizes Acute and Chronic Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 1344–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teng, M.W.L.; Bowman, E.P.; McElwee, J.J.; Smyth, M.J.; Casanova, J.-L.; Cooper, A.M.; Cua, D.J. IL-12 and IL-23 Cytokines: From Discovery to Targeted Therapies for Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, H.; Hua, S. Regulation of Memory T Cells by Interleukin-23. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 169, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werfel, T.; Allam, J.-P.; Biedermann, T.; Eyerich, K.; Gilles, S.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Hoetzenecker, W.; Knol, E.; Simon, H.-U.; Wollenberg, A.; et al. Cellular and Molecular Immunologic Mechanisms in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coulombe, P.A.; Wong, P. Cytoplasmic Intermediate Filaments Revealed as Dynamic and Multipurpose Scaffolds. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yin, M.; Zhang, L.J. Keratin 6, 16 and 17-Critical Barrier Alarmin Molecules in Skin Wounds and Psoriasis. Cells 2019, 8, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Komine, M.; Freedberg, I.M.; Blumenberg, M. Regulation of Epidermal Expression of Keratin K17 in Inflammatory Skin Diseases. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1996, 107, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Presland, R.B.; Kimball, J.R.; Kautsky, M.B.; Patrick Lewis, S.; Lo, C.Y.; Dale, B.A. Evidence for Specific Proteolytic Cleavage of the N-Terminal Domain of Human Profilaggrin During Epidermal Differentiation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1997, 108, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Furue, M. Regulation of Filaggrin, Loricrin, and Involucrin by IL-4, IL-13, IL-17A, IL-22, AHR, and NRF2: Pathogenic Implications in Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Melecular Sci. 2020, 21, 5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proksch, E.; Brandner, J.M.; Jensen, J.-M. The Skin: An Indispensable Barrier. Exp. Dermatol. 2008, 17, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candi, E.; Schmidt, R.; Melino, G. The Cornified Envelope: A Model of Cell Death in the Skin. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, M.; Dagnino, L. Tissue Barriers Scaffolding Proteins in the Development and Maintenance of the Epidermal Permeability Barrier. Tissue Barriers 2017, 5, e1341969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, L.S. Toll-Like Receptors in Skin. Adv. Dermatol. 2008, 24, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santegoets, K.C.M.; van Bon, L.; van den Berg, W.B.; Wenink, M.H.; Radstake, T.R.D.J. Toll-like Receptors in Rheumatic Diseases: Are We Paying a High Price for Our Defense against Bugs? FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 3660–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. The Role of Pattern-Recognition Receptors in Innate Immunity: Update on Toll-like Receptors. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, N.; Yang, Y.-P.; Li, W.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-W.; Luo, Y.; Fan, Y.-M. Overexpression of NLRP3, NLRC4 and AIM2 Inflammasomes and Their Priming-Associated Molecules (TLR2, TLR4, Dectin-1, Dectin-2 and NFκB) in Malassezia Folliculitis. Mycoses 2018, 61, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donetti, E.; Lombardo, G.; Indino, S.; Cornaghi, L.; Arnaboldi, F.; Pescitelli, L.; Baruffaldi Preis, F.; Prignano, F. The Psoriatic Shift Induced by Interleukin 17 Is Promptly Reverted by a Specific Anti-IL-17A Agent in a Three-Dimensional Organotypic Model of Normal Human Skin Culture. Eur. J. Histochem. 2020, 64, 3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panzer, R.; Blobel, C.; Fölster-Holst, R.; Proksch, E. TLR2 and TLR4 Expression in Atopic Dermatitis, Contact Dermatitis and Psoriasis. Exp. Dermatol. 2014, 23, 364–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donetti, E.; Cornaghi, L.; Arnaboldi, F.; Ricceri, F.; Pescitelli, L.; Maiocchi, M.; Carriero, F.; Baruffaldi Preis, F.; Prignano, F. Epidermal Barrier Reaction to an in Vitro Psoriatic Microenvironment. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 360, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, L.S.; Sørensen, O.E.; Liu, P.T.; Jalian, H.R.; Eshtiaghpour, D.; Behmanesh, B.E.; Chung, W.; Starner, T.D.; Kim, J.; Sieling, P.A.; et al. TGF-α Regulates TLR Expression and Function on Epidermal Keratinocytes. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 6137–6143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ong, P.Y.; Ohtake, T.; Brandt, C.; Strickland, I.; Boguniewicz, M.; Ganz, T.; Gallo, R.L.; Leung, D.Y.M. Endogenous Antimicrobial Peptides and Skin Infections in Atopic Dermatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, B.E.; Leung, D.Y.M. Significance of Skin Barrier Dysfunction in Atopic Dermatitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2018, 10, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bäsler, K.; Bergmann, S.; Heisig, M.; Naegel, A.; Zorn-Kruppa, M.; Brandner, J.M. The Role of Tight Junctions in Skin Barrier Function and Dermal Absorption. J. Control. Release 2016, 242, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, J.D.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Dhingra, N.; Cardinale, I.; Li, X.; Kostic, A.; Ming, J.E.; Radin, A.R.; Krueger, J.G.; Graham, N.; et al. Dupilumab Improves the Molecular Signature in Skin of Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, X.; Shiraishi, K.; Muto, J.; Utsunomiya, R.; Mori, H.; Murakami, M.; Sayama, K. Nuclear IL-33 Plays an Important Role in IL-31-Mediated Downregulation of FLG, Keratin 1, and Keratin 10 by Regulating Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Activation in Human Keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 142, 136–144.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.J.; Mclean, W.H.I. One Remarkable Molecule: Filaggrin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elias, P.M. Primary Role of Barrier Dysfunction in the Pathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, B.E.; Leung, D.Y.M.; Boguniewicz, M.; Howell, M.D. Loricrin and Involucrin Expression Is Down-Regulated by Th2 Cytokines through STAT-6. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 126, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ermertcan, A.T.; Öztürk, F.; Gündüz, K. Toll-like Receptors and Skin. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2011, 25, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäbitz, A.; Eyerich, K.; Garzorz-Stark, N. So Close, and yet so Far Away: The Dichotomy of the Specific Immune Response and Inflammation in Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 290, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttman-Yassky, E.; Krueger, J.G. Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis: Two Different Immune Diseases or One Spectrum? Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2017, 48, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renert-Yuval, Y.; Guttman-Yassky, E. New Treatments for Atopic Dermatitis Targeting beyond IL-4/IL-13 Cytokines. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020, 124, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bedoni, M.; Sforza, C.; Dolci, C.; Donetti, E. Proliferation and Differentiation Biomarkers in Normal Human Breast Skin Organotypic Cultures. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2007, 46, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Donetti, E.; Cornaghi, L.; Gualerzi, A.; Baruffaldi Preis, F.W.; Prignano, F. An Innovative Three-Dimensional Model of Normal Human Skin to Study the Proinflammatory Psoriatic Effects of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha and Interleukin-17. Cytokine 2014, 68, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prignano, F.; Arnaboldi, F.; Cornaghi, L.; Landoni, F.; Tripo, L.; Preis, F.W.B.; Donetti, E. Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha and Interleukin-17 Differently Affects Langerhans Cell Distribution and Activation in an Innovative Three-Dimensional Model of Normal Human Skin. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 94, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiricozzi, A.; Romanelli, M.; Panduri, S.; Donetti, E.; Prignano, F. Relevance of in Vitro 3-D Skin Models in Dissecting Cytokine Contribution to Psoriasis Pathogenesis. Histol. Histopathol. 2017, 32, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornaghi, L.; Gagliano, N.; Preis, F.W.B.; Prignano, F.; Donetti, E. Inside-out and Outside-in Organotypic Normal Human Skin Culture: JAK-STAT Pathway Is Activated after pro-Inflammatory Psoriatic Cytokine Exposure. Tissue Cell 2022, 74, 101675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Benedetto, A. Tight Junctions in the Skin: Still a Lot to Learn. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 184, 388–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donetti, E.; Lombardo, G.; Baruffaldi Preis, F.W.; Cornaghi, L.; Pescitelli, L.; Prignano, F. 3D Skin Model to Investigate the Early Epidermal Morphological Psoriatic Features. J. Transl. Sci. 2020, 6, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuki, T.; Tobiishi, M.; Kusaka-Kikushima, A.; Ota, Y.; Tokura, Y. Impaired Tight Junctions in Atopic Dermatitis Skin and in a Skin-Equivalent Model Treated with Interleukin-17. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cadau, S.; Gault, M.; Berthelemy, N.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Danoux, L.; Pelletier, N.; Goudounèche, D.; Pons, C.; Leprince, C.; André-Frei, V.; et al. An Inflamed and Infected Reconstructed Human Epidermis to Study Atopic Dermatitis and Skin Care Ingredients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Benedetto, A.; Rafaels, N.M.; McGirt, L.Y.; Ivanov, A.I.; Georas, S.N.; Cheadle, C.; Berger, A.E.; Zhang, K.; Vidyasagar, S.; Yoshida, T.; et al. Tight Junction Defects in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 773–786.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hönzke, S.; Wallmeyer, L.; Ostrowski, A.; Radbruch, M.; Mundhenk, L.; Schäfer-Korting, M.; Hedtrich, S. Influence of Th2 Cytokines on the Cornified Envelope, Tight Junction Proteins, and β-Defensins in Filaggrin-Deficient Skin Equivalents. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Itallie, C.M.; Anderson, J.M. Architecture of Tight Junctions and Principles of Molecular Composition. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 36, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakamizo, S.; Dutertre, C.-A.; Khalilnezhad, A.; Zhang, X.M.; Lim, S.; Lum, J.; Koh, G.; Foong, C.; Yong, P.J.A.; Tan, K.J.; et al. Single-Cell Analysis of Human Skin Identifies CD14+ Type 3 Dendritic Cells Co-Producing IL1B and IL23A in Psoriasis. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20202345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, M.D.; Kim, B.E.; Gao, P.; Grant, A.V.; Boguniewicz, M.; DeBenedetto, A.; Schneider, L.; Beck, L.A.; Barnes, K.C.; Leung, D.Y.M. Cytokine Modulation of Atopic Dermatitis Filaggrin Skin Expression. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Danso, M.O.; van Drongelen, V.; Mulder, A.; van Esch, J.; Scott, H.; van Smeden, J.; el Ghalbzouri, A.; Bouwstra, J.A. TNF-α and Th2 Cytokines Induce Atopic Dermatitis-like Features on Epidermal Differentiation Proteins and Stratum Corneum Lipids in Human Skin Equivalents. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1941–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strid, J.; McLean, W.H.I.; Irvine, A.D. Too Much, Too Little or Just Enough: A Goldilocks Effect for IL-13 and Skin Barrier Regulation? J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kezic, S.; O’Regan, G.M.; Yau, N.; Sandilands, A.; Chen, H.; Campbell, L.E.; Kroboth, K.; Watson, R.; Rowland, M.; Irwin McLean, W.H.; et al. Levels of Filaggrin Degradation Products Are Influenced by Both Filaggrin Genotype and Atopic Dermatitis Severity. Allergy 2011, 66, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weidinger, S.; O’Sullivan, M.; Illig, T.; Baurecht, H.; Depner, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Ruether, A.; Klopp, N.; Vogelberg, C.; Weiland, S.K.; et al. Filaggrin Mutations, Atopic Eczema, Hay Fever, and Asthma in Children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 1203–1209.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, V.G.; Orfali, R.L.; de Oliveira Titz, T.; da Silva Duarte, A.J.; Sato, M.N.; Aoki, V. Evidence of Regulatory Myeloid Dendritic Cells and Circulating Inflammatory Epidermal Dendritic Cells-like Modulated by Toll-like Receptors 2 and 7/8 in Adults with Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2017, 56, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kezic, S.; O’Regan, G.M.; Lutter, R.; Jakasa, I.; Koster, E.S.; Saunders, S.; Caspers, P.; Kemperman, P.M.J.H.; Puppels, G.J.; Sandilands, A.; et al. Filaggrin Loss-of-Function Mutations Are Associated with Enhanced Expression of IL-1 Cytokines in the Stratum Corneum of Patients with Atopic Dermatitis and in a Murine Model of Filaggrin Deficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 1031–1039.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moriwaki, M.; Iwamoto, K.; Niitsu, Y.; Matsushima, A.; Yanase, Y.; Hisatsune, J.; Sugai, M.; Hide, M. Staphylococcus Aureus from Atopic Dermatitis Skin Accumulates in the Lysosomes of Keratinocytes with Induction of IL-1α Secretion via TLR9. Allergy 2019, 74, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seung, N.R.; Park, E.J.; Kim, C.W.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, K.J.; Cho, H.J.; Park, H.R. Comparison of Expression of Heat-Shock Protein 60, Toll-like Receptors 2 and 4, and T-Cell Receptor Γδ in Plaque and Guttate Psoriasis. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2007, 34, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, B.S.; Ovigne, J.-M.; Powles, A.V.; Corcoran, S.; Fry, L. Normal Keratinocytes Express Toll-like Receptors (TLRs) 1, 2 and 5: Modulation of TLR Expression in Chronic Plaque Psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2003, 148, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, J.L.; Qin, J.-Z.; Bonish, B.; Carrick, R.; Bacon, P.; Panella, J.; Robinson, J.; Nickoloff, B.J. Innate Immune-Related Receptors in Normal and Psoriatic Skin. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2003, 127, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begon, É.; Michel, L.; Flageul, B.; Beaudoin, I.; Jean-Louis, F.; Bachelez, H.; Dubertret, L.; Musette, P. Expression, Subcellular Localization and Cytokinic Modulation of Toll-like Receptors (TLRs) in Normal Human Keratinocytes: TLR2 up-Regulation in Psoriatic Skin. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2007, 17, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prignano, F.; Lombardo, G.; Indino, S.; Ricceri, F.; Cornaghi, L.; Donetti, E.B.; Donetti, E. Evaluation of Expression of Toll-Like Receptors 7 and 9, Proliferation, and Cytoskeletal Biomarkers in Plaque and Guttate Psoriasis: A Pilot Morphological Study. Eur. J. Histochem. 2021, 65, 3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.C.; Tan, X.-Y.; Luxenberg, D.P.; Karim, R.; Dunussi-Joannopoulos, K.; Collins, M.; Fouser, L.A. Interleukin (IL)-22 and IL-17 Are Coexpressed by Th17 Cells and Cooperatively Enhance Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2271–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Jongh, G.J.; Zeeuwen, P.L.J.M.; Kucharekova, M.; Pfundt, R.; van der Valk, P.G.; Blokx, W.; Dogan, A.; Hiemstra, P.S.; van de Kerkhof, P.C.; Schalkwijk, J. High Expression Levels of Keratinocyte Antimicrobial Proteins in Psoriasis Compared with Atopic Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 125, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omori-Miyake, M.; Yamashita, M.; Tsunemi, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Yagi, J. In Vitro Assessment of IL-4- or IL-13-Mediated Changes in the Structural Components of Keratinocytes in Mice and Humans. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Totsuka, A.; Omori-Miyake, M.; Kawashima, M.; Yagi, J.; Tsunemi, Y. Expression of Keratin 1, Keratin 10, Desmoglein 1 and Desmocollin 1 in the Epidermis: Possible Downregulation by Interleukin-4 and Interleukin-13 in Atopic Dermatitis. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2017, 27, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niehues, H.; Bouwstra, J.A.; El Ghalbzouri, A.; Brandner, J.M.; Zeeuwen, P.L.J.M.; van den Bogaard, E.H. 3D skin models for 3R research: The potential of 3D reconstructed skin models to study skin barrier function. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, A.Y. Molecular Mechanism of Epidermal Barrier Dysfunction as Primary Abnormalities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pescitelli, L.; Rosi, E.; Ricceri, F.; Pimpinelli, N.; Prignano, F. Novel Therapeutic Approaches and Targets for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2021, 22, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmuth, M.; Blunder, S.; Dubrac, S.; Gruber, R.; Moosbrugger-Martinz, V. Epidermal barrier in hereditary ichthyoses, atopic dermatitis, and psoriasis. J. Der Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2015, 13, 1119–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGuckin, M.A.; Eri, R.; Simms, L.A.; Florin, T.H.; Radford-Smith, G. Intestinal barrier dysfunction in inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2009, 15, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
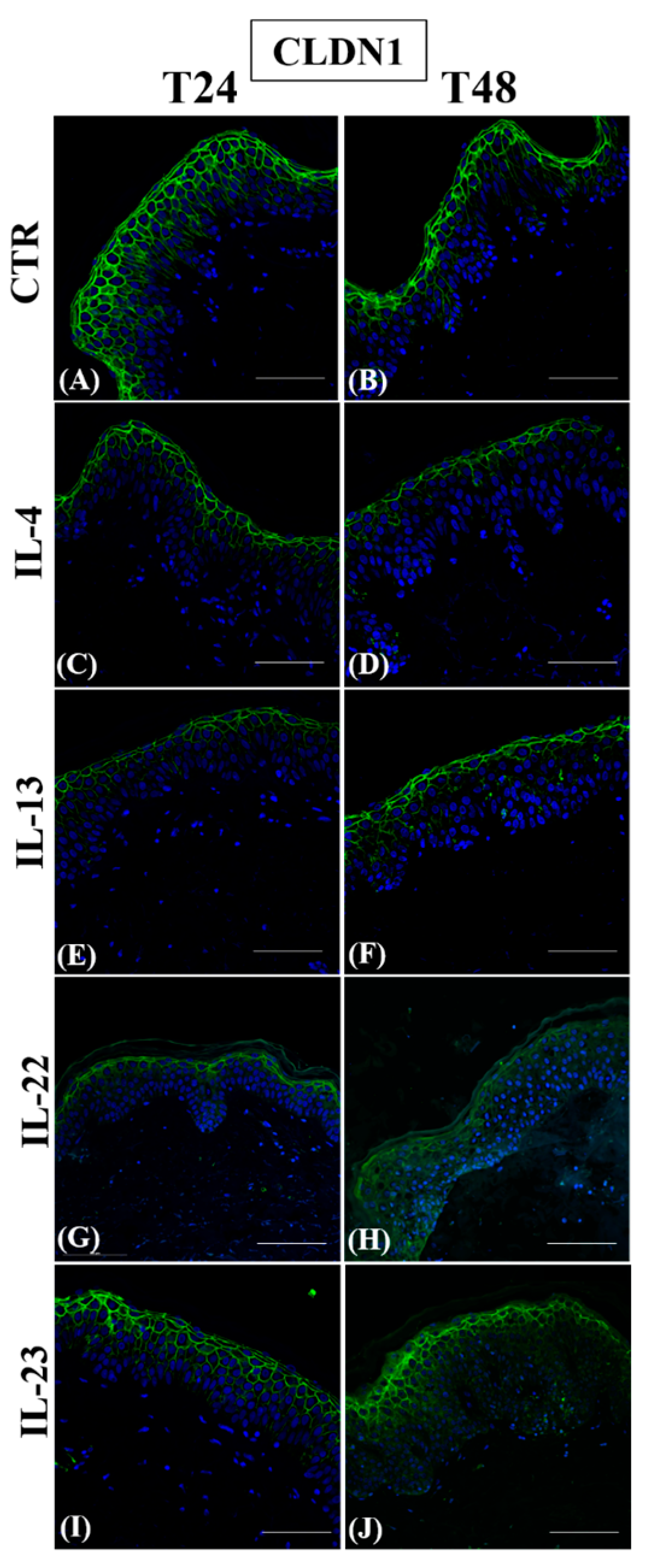
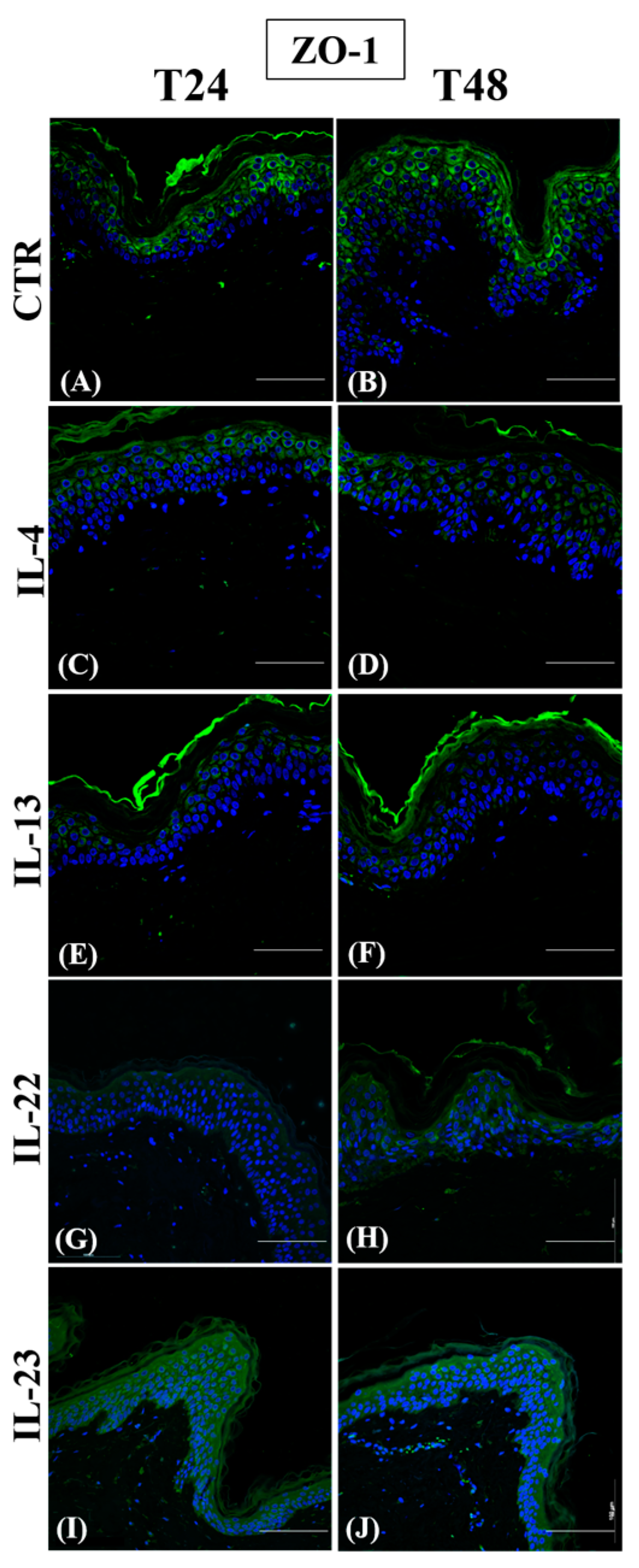

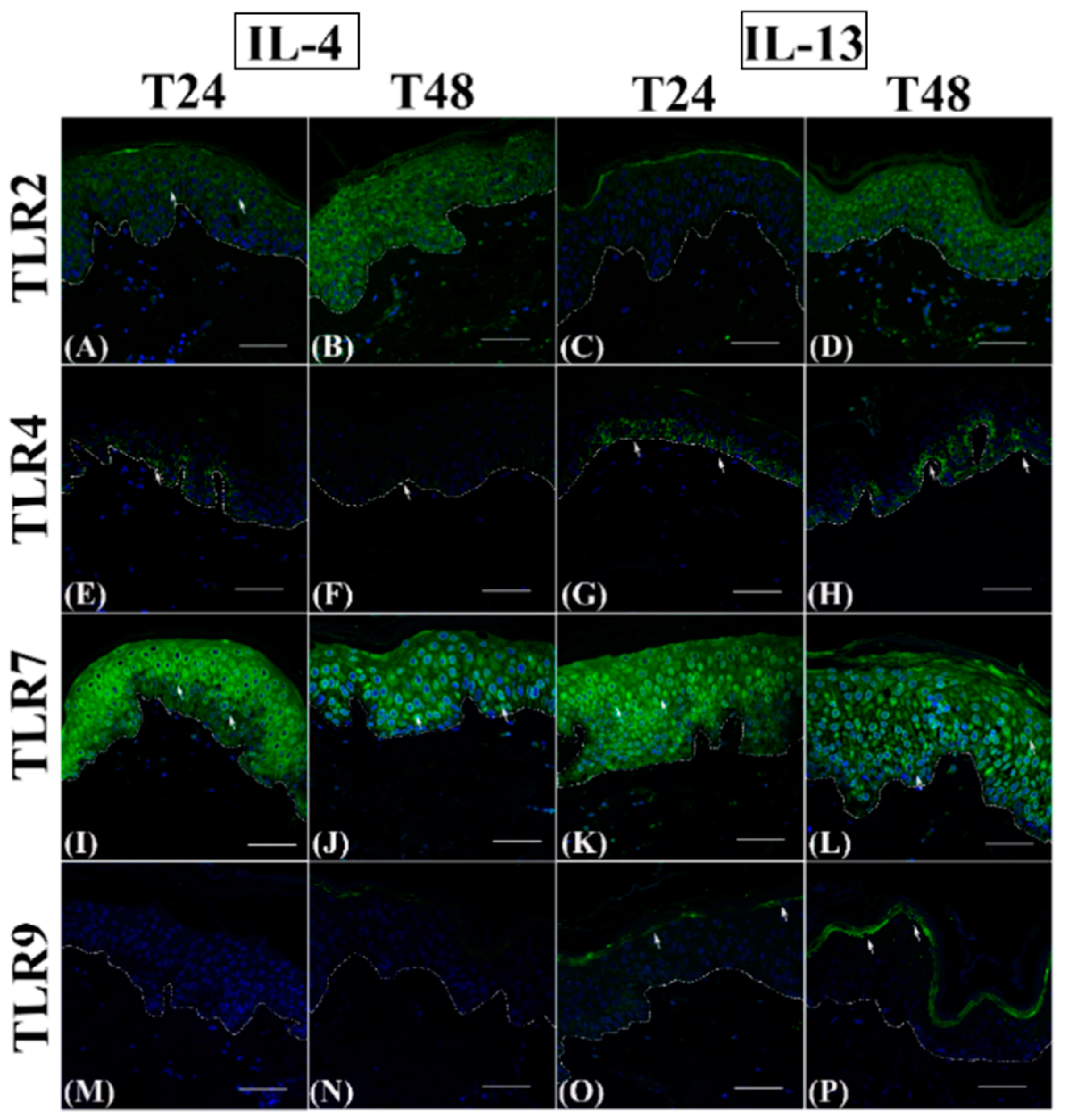
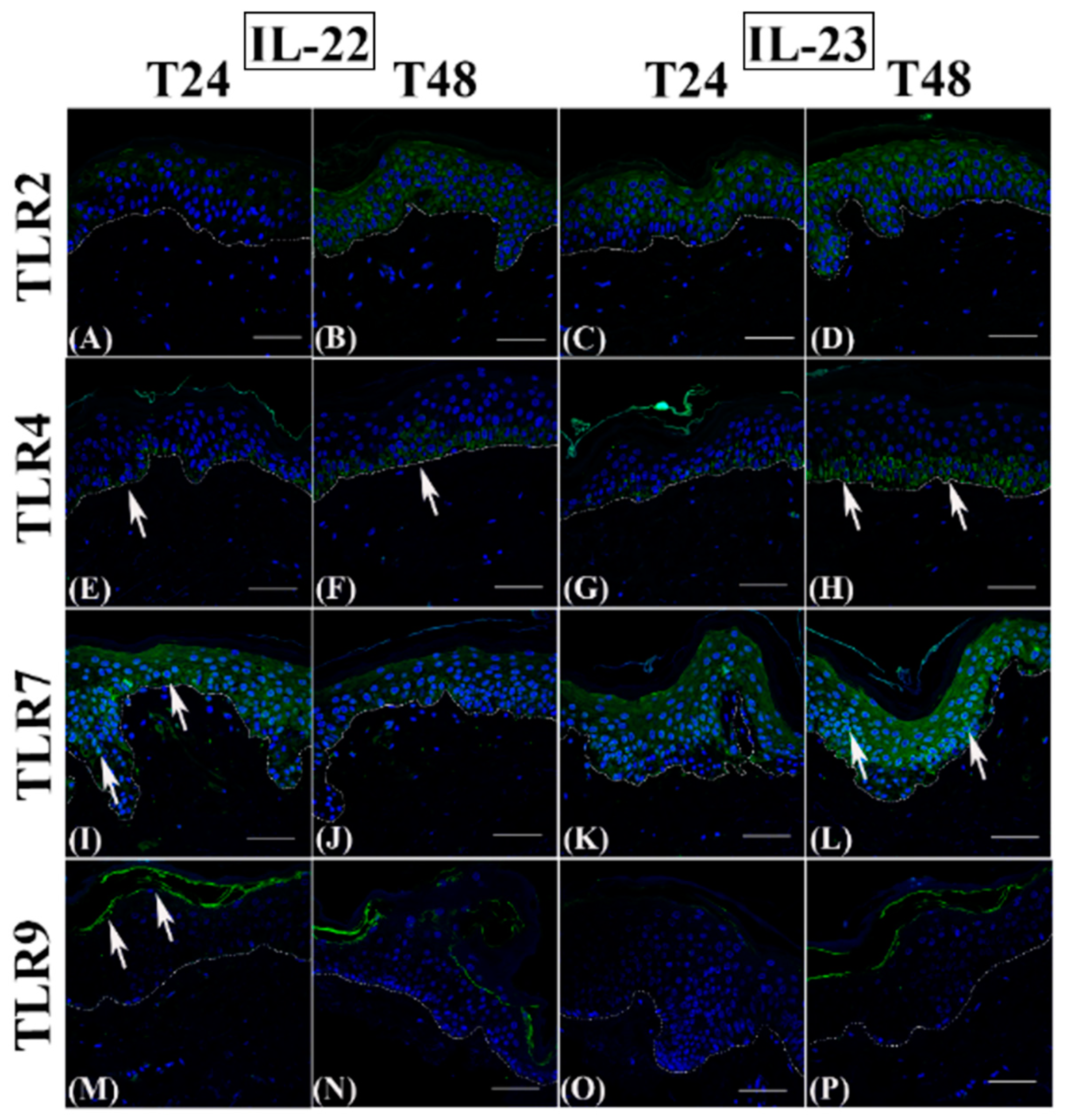


| Antibody | Antigen Retrieval | Incubation (Antibody Diluted in PBS/BSA 2%) |
|---|---|---|
| Polyclonal rabbit anti-human CLDN-1 (ThermoFisher Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA) | 0.01 M citrate buffer pH 6 in MW | dilution 1:100 1 h at 37 °C |
| Polyclonal rabbit anti-human ZO-1 (ThermoFisher Scientific) | Pronase E 10 min at 37°C | dilution 1:100 1 h at 37 °C |
| Monoclonal mouse anti-human TLR2 (Novus Bio, Littleton, CO, USA) | 0.01 M Na citrate buffer pH 6 in MW | 1:100 overnight at 4 °C |
| Monoclonal mouse anti-human TLR4 (Novus Bio) | 1:300 1 h at 37 °C | |
| Monoclonal mouse anti-human TLR9 (Novus Bio) | dilution 1:10 overnight at 4 °C | |
| Polyclonal rabbit anti-human TLR7 (Novus Bio) | 0.05 M Tris HCl pH 8.5 in MW | 1:300 overnight at 4 °C |
| Polyclonal rabbit-anti-human hBD2 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA) | 0.01M Na citrate buffer in autoclave 120 °C 6 min | dilution 1:50 overnight 4 °C |
| Monoclonal mouse anti-human filaggrin (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) | 0.01 M Na citrate buffer pH 6 in MW | dilution 1:250, overnight at 4 °C |
| Monoclonal mouse anti-human involucrin (ThermoFisher Scientific) | dilution 1:1000, overnight at 4 °C | |
| Monoclonal mouse anti-human K10 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) | dilution 1:50 overnight at 4 °C | |
| Monoclonal rabbit anti-human K16 (Bio SB, Santa Barbara, CA, USA) | dilution 1:100, 1 h at 37 °C | |
| Rabbit anti-human K17 (Abcam, Cambridge, UK) | dilution 1:200, overnight at 4 °C | |
| Monoclonal mouse anti-human K14 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) | pepsin 0.05% 15′ RT and 0.01M Na citrate buffer pH 6 in MW | 1:200 overnight at 4 °C |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Donetti, E.; Riva, F.; Indino, S.; Lombardo, G.; Baruffaldi Preis, F.; Rosi, E.; Prignano, F. Th2 Cytokines Affect the Innate Immune Barrier without Impairing the Physical Barrier in a 3D Model of Normal Human Skin. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1941. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051941
Donetti E, Riva F, Indino S, Lombardo G, Baruffaldi Preis F, Rosi E, Prignano F. Th2 Cytokines Affect the Innate Immune Barrier without Impairing the Physical Barrier in a 3D Model of Normal Human Skin. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(5):1941. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051941
Chicago/Turabian StyleDonetti, Elena, Federica Riva, Serena Indino, Giulia Lombardo, Franz Baruffaldi Preis, Elia Rosi, and Francesca Prignano. 2023. "Th2 Cytokines Affect the Innate Immune Barrier without Impairing the Physical Barrier in a 3D Model of Normal Human Skin" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 5: 1941. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051941
APA StyleDonetti, E., Riva, F., Indino, S., Lombardo, G., Baruffaldi Preis, F., Rosi, E., & Prignano, F. (2023). Th2 Cytokines Affect the Innate Immune Barrier without Impairing the Physical Barrier in a 3D Model of Normal Human Skin. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(5), 1941. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051941






