Patent Foramen Ovale and Cryptogenic Stroke: Integrated Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology and Classification
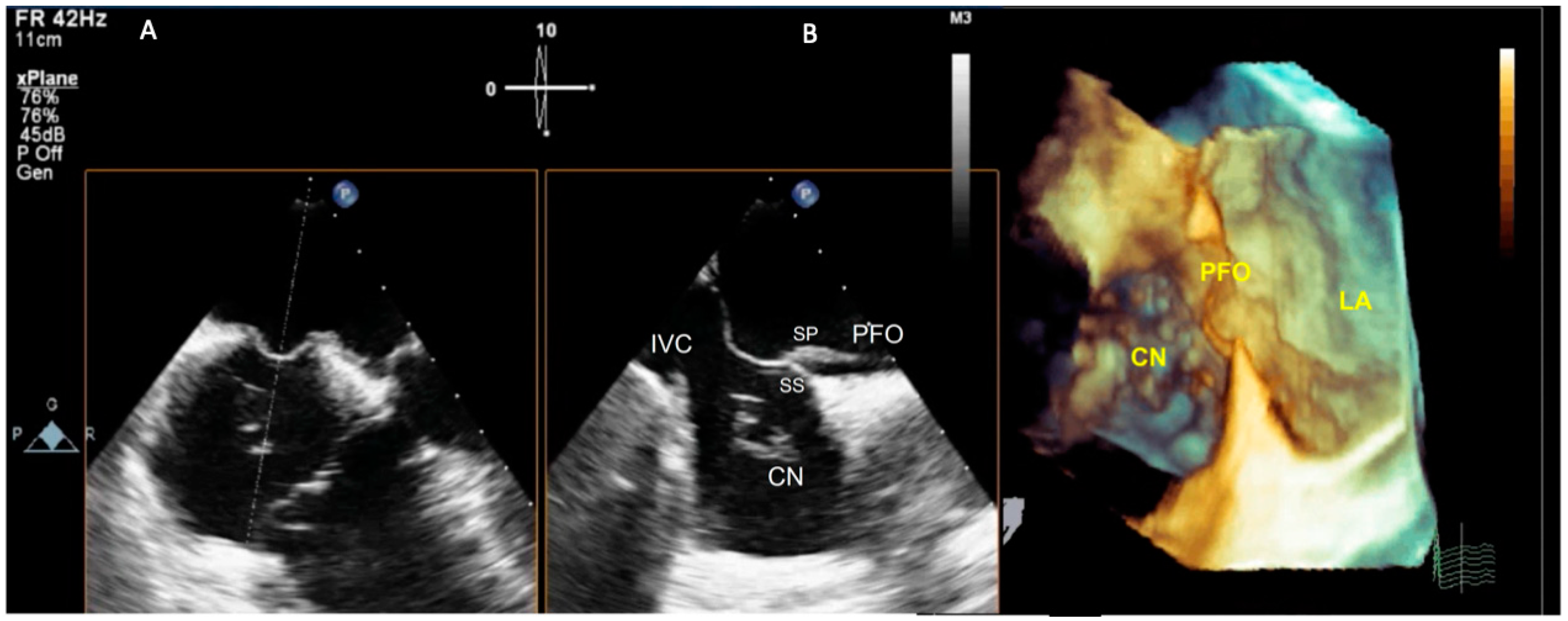
3. Imaging Assessment of Suspected Paradoxical Embolism
4. Thrombophilia Screening in Cryptogenic Stroke
5. Medical and Interventional Treatment
6. Assessment of Hidden Atrial Fibrillation and Rhythm Evaluation
7. Antiplatelet Strategy after PFO Closure
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zoghbi, W.A. Patent foramen ovale: Going beyond the bubbles. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 7, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechat, P.; Mas, J.L.; Lascault, G.; Loron, P.; Theard, M.; Klimczac, M.; Drobinski, G.; Thomas, D.; Grosgogeat, Y. Prevalence of patent foramen ovale in patients with stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 318, 1148–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orsinelli, D.A.; Rajpal, S. Doing a Deep Dive on Patent Foramen Ovale: Stay Tuned in the PFO World. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 15, 190–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trabattoni, D.; Brambilla, M.; Canzano, P.; Becchetti, A.; Teruzzi, G.; Porro, B.; Fiorelli, S.; Muratori, M.; Tedesco, C.C.; Veglia, F.; et al. Migraine in Patients Undergoing PFO Closure: Characterization of a Platelet-Associated Pathophysiological Mechanism: The LEARNER Study. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2022, 7, 525–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othman, F.; Bailey, B.; Collins, N.; Lau, E.; Tanous, D.; Rao, K.; Celermajer, D.; Cordina, R. Platypnea-Orthodeoxia Syndrome in the Setting of Patent Foramen Ovale Without Pulmonary Hypertension or Major Lung Disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, e024609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dia, A.; Cifu, A.S.; Shah, A.P. Management of Patients With a Patent Foramen Ovale With History of Stroke or TIA. JAMA 2021, 325, 81–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeger, J.; Hildick-Smith, D. Patent Foramen Ovale: Closing the Gap of Indications for Closure-Time for a Patient-Tailored Therapy. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2020, 13, 2753–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsheikh-Ali, A.A.; Thaler, D.E.; Kent, D.M. Patent foramen ovale in cryptogenic stroke: Incidental or pathogenic? Stroke 2009, 40, 2349–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saver, J.L.; Carroll, J.D.; Thaler, D.E.; Smalling, R.W.; MacDonald, L.A.; Marks, D.S.; Tirschwell, D.L. Long-Term Outcomes of Patent Foramen Ovale Closure or Medical Therapy after Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornung, M.; Bertog, S.C.; Franke, J.; Id, D.; Taaffe, M.; Wunderlich, N.; Vaskelyte, L.; Hofmann, I.; Sievert, H. Long-term results of a randomized trial comparing three different devices for percutaneous closure of a patent foramen ovale. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 3362–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stortecky, S.; da Costa, B.R.; Mattle, H.P.; Carroll, J.; Hornung, M.; Sievert, H.; Trelle, S.; Windecker, S.; Meier, B.; Jüni, P. Percutaneous closure of patent foramen ovale in patients with cryptogenic embolism: A network meta-analysis. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kent, D.M.; Dahabreh, I.J.; Ruthazer, R.; Furlan, A.J.; Reisman, M.; Carroll, J.D.; Saver, J.L.; Smalling, R.W.; Jüni, P.; Mattle, H.P.; et al. Device Closure of Patent Foramen Ovale After Stroke: Pooled Analysis of Completed Randomized Trials. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mas, J.L.; Derumeaux, G.; Guillon, B.; Massardier, E.; Hosseini, H.; Mechtouff, L.; Arquizan, C.; Béjot, Y.; Vuillier, F.; Detante, O.; et al. Patent Foramen Ovale Closure or Anticoagulation vs. Antiplatelets after Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pristipino, C.; Sievert, H.; D’Ascenzo, F.; Louis Mas, J.; Meier, B.; Scacciatella, P.; Hildick-Smith, D.; Gaita, F.; Toni, D.; Kyrle, P.; et al. European position paper on the management of patients with patent foramen ovale. General approach and left circulation thromboembolism. Eur. Heart. J. 2019, 40, 3182–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleindorfer, D.O.; Towfighi, A.; Chaturvedi, S.; Cockroft, K.M.; Gutierrez, J.; Lombardi-Hill, D.; Kamel, H.; Kernan, W.N.; Kittner, S.J.; Leira, E.C.; et al. 2021 Guideline for the Prevention of Stroke in Patients With Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack: A Guideline From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2021, 52, e364–e467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wein, T.; Lindsay, M.P.; Côté, R.; Foley, N.; Berlingieri, J.; Bhogal, S.; Bourgoin, A.; Buck, B.H.; Cox, J.; Davidson, D.; et al. Canadian stroke best practice recommendations: Secondary prevention of stroke, sixth edition practice guidelines, update 2017. Int. J. Stroke 2018, 13, 420–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolominsky-Rabas, P.L.; Weber, M.; Gefeller, O.; Neundoerfer, B.; Heuschmann, P.U. Epidemiology of ischemic stroke subtypes according to TOAST criteria: Incidence, recurrence, and long-term survival in ischemic stroke subtypes: A population-based study. Stroke 2001, 32, 2735–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leys, D.; Bandu, L.; Hénon, H.; Lucas, C.; Mounier-Vehier, F.; Rondepierre, P.; Godefroy, O. Clinical outcome in 287 consecutive young adults (15 to 45 years) with ischemic stroke. Neurology 2002, 59, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kent, D.M.; Ruthazer, R.; Weimar, C.; Mas, J.L.; Serena, J.; Homma, S.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Di Tullio, M.R.; Lutz, J.S.; Elkind, M.S.; et al. An index to identify stroke-related vs incidental patent foramen ovale in cryptogenic stroke. Neurology 2013, 81, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saver, J.L. Cryptogenic Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, H.P., Jr.; Bendixen, B.H.; Kappelle, L.J.; Biller, J.; Love, B.B.; Gordon, D.L.; Marsh, E.E., 3rd. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke 1993, 24, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amarenco, P.; Bogousslavsky, J.; Caplan, L.R.; Donnan, G.A.; Wolf, M.E.; Hennerici, M.G. The ASCOD phenotyping of ischemic stroke (Updated ASCO Phenotyping). Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2013, 36, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ay, H.; Benner, T.; Arsava, E.M.; Furie, K.L.; Singhal, A.B.; Jensen, M.B.; Ayata, C.; Towfighi, A.; Smith, E.E.; Chong, J.Y.; et al. A computerized algorithm for etiologic classification of ischemic stroke: The Causative Classification of Stroke System. Stroke 2007, 38, 2979–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Nassif, M.; Khairy, P.; de Groot, J.R.; Roos, Y.; de Winter, R.J.; Mulder, B.J.M.; Bouma, B.J. Cardiac diagnostic work-up of ischaemic stroke. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 1851–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, A.C.; Ferro, J.M. Cryptogenic stroke. Eur. J. Neurol. 2015, 22, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.J.; Sohn, H.; Sun, B.J.; Song, J.K.; Kang, D.W.; Kim, J.S.; Kwon, S.U. Imaging characteristics of ischemic strokes related to patent foramen ovale. Stroke 2013, 44, 3350–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elgendy, A.Y.; Saver, J.L.; Amin, Z.; Boudoulas, K.D.; Carroll, J.D.; Elgendy, I.Y.; Grunwald, I.Q.; Gertz, Z.M.; Hijazi, Z.M.; Horlick, E.M.; et al. Proposal for Updated Nomenclature and Classification of Potential Causative Mechanism in Patent Foramen Ovale-Associated Stroke. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Li, K.; Lu, X.; Xie, M. Diagnostic value of transthoracic echocardiography for patent foramen ovale: A meta-analysis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2013, 39, 1743–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojadidi, M.K.; Winoker, J.S.; Roberts, S.C.; Msaouel, P.; Zaman, M.O.; Gevorgyan, R.; Tobis, J.M. Accuracy of conventional transthoracic echocardiography for the diagnosis of intracardiac right-to-left shunt: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Echocardiography 2014, 31, 1036–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madala, D.; Zaroff, J.G.; Hourigan, L.; Foster, E. Harmonic imaging improves sensitivity at the expense of specificity in the detection of patent foramen ovale. Echocardiography 2004, 21, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojadidi, M.K.; Winoker, J.S.; Roberts, S.C.; Msaouel, P.; Gevorgyan, R.; Zolty, R. Two-dimensional echocardiography using second harmonic imaging for the diagnosis of intracardiac right-to-left shunt: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 30, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falanga, G.; Carerj, S.; Oreto, G.; Khandheria, B.K.; Zito, C. How to Understand Patent Foramen Ovale Clinical Significance: Part I. J. Cardiovasc. Echogr. 2014, 24, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yared, K.; Baggish, A.L.; Solis, J.; Durst, R.; Passeri, J.J.; Palacios, I.F.; Picard, M.H. Echocardiographic assessment of percutaneous patent foramen ovale and atrial septal defect closure complications. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2009, 2, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vigna, C.; Marchese, N.; Zanchetta, M.; Chessa, M.; Inchingolo, V.; Pacilli, M.A.; Amico, C.; Fanelli, M.; Fanelli, R.; Loperfido, F. Echocardiographic guidance of percutaneous patent foramen ovale closure: Head-to-head comparison of transesophageal versus rotational intracardiac echocardiography. Echocardiography 2012, 29, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojadidi, M.K.; Mahmoud, A.N.; Elgendy, I.Y.; Agarwal, N.; Tobis, J.M. Transesophageal Echocardiography for the Detection of Patent Foramen Ovale. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2017, 30, 933–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mojadidi, M.K.; Roberts, S.C.; Winoker, J.S.; Romero, J.; Goodman-Meza, D.; Gevorgyan, R.; Tobis, J.M. Accuracy of transcranial Doppler for the diagnosis of intracardiac right-to-left shunt: A bivariate meta-analysis of prospective studies. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 7, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spencer, M.P.; Thomas, G.I.; Nicholls, S.C.; Sauvage, L.R. Detection of middle cerebral artery emboli during carotid endarterectomy using transcranial Doppler ultrasonography. Stroke 1990, 21, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorensen, S.G.; Aguilar, H.; McKnight, W.K.; Thomas, H.; Muhlestein, J.B. Transcranial Doppler quantification of residual shunt after percutaneous patent foramen ovale closure. Comparison of two devices. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2010, 23, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.N.; Elgendy, I.Y.; Agarwal, N.; Tobis, J.M.; Mojadidi, M.K. Identification and Quantification of Patent Foramen Ovale-Mediated Shunts: Echocardiography and Transcranial Doppler. Interv. Cardiol. Clin. 2017, 6, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushparajah, K.; Miller, O.I.; Simpson, J.M. 3D echocardiography of the atrial septum: Anatomical features and landmarks for the echocardiographer. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2010, 3, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frankfurter, C.; Muthuppalaniappan, A.M.; Gorocica-Romero, R.; Abrahamyan, L.; Olesovsky, C.; Ma, J.; Benson, L.; Osten, M.; Horlick, E.M. Coronary Artery Disease in Adults Undergoing Percutaneous Patent Foramen Ovale Closure Following Cryptogenic Stroke. J. Invasive Cardiol. 2021, 33, E870–E876. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bushnell, C.D.; Goldstein, L.B. Diagnostic testing for coagulopathies in patients with ischemic stroke. Stroke 2000, 31, 3067–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morris, J.G.; Singh, S.; Fisher, M. Testing for inherited thrombophilias in arterial stroke: Can it cause more harm than good? Stroke 2010, 41, 2985–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.; Cox, N.; Witt, D.M. Stroke diagnosis associated with thrombophilia testing overutilization. Thromb Res. 2017, 157, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kernan, W.N.; Ovbiagele, B.; Black, H.R.; Bravata, D.M.; Chimowitz, M.I.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Fang, M.C.; Fisher, M.; Furie, K.L.; Heck, D.V.; et al. Guidelines for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2014, 45, 2160–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedani, A.G.; Cole, J.W.; Mitchell, B.D.; Kittner, S.J. Meta-analysis of factor V Leiden and ischemic stroke in young adults: The importance of case ascertainment. Stroke 2010, 41, 1599–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holmes, M.V.; Newcombe, P.; Hubacek, J.A.; Sofat, R.; Ricketts, S.L.; Cooper, J.; Breteler, M.M.; Bautista, L.E.; Sharma, P.; Whittaker, J.C.; et al. Effect modification by population dietary folate on the association between MTHFR genotype, homocysteine, and stroke risk: A meta-analysis of genetic studies and randomised trials. Lancet 2011, 378, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dharmasaroja, P.A.; Muengtaweepongsa, S.; Lechawanich, C.; Pattaraarchachai, J. Causes of ischemic stroke in young adults in Thailand: A pilot study. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2011, 20, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, A.J.; Reisman, M.; Massaro, J.; Mauri, L.; Adams, H.; Albers, G.W.; Felberg, R.; Herrmann, H.; Kar, S.; Landzberg, M.; et al. Closure or medical therapy for cryptogenic stroke with patent foramen ovale. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meier, B.; Kalesan, B.; Mattle, H.P.; Khattab, A.A.; Hildick-Smith, D.; Dudek, D.; Andersen, G.; Ibrahim, R.; Schuler, G.; Walton, A.S.; et al. Percutaneous closure of patent foramen ovale in cryptogenic embolism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carroll, J.D.; Saver, J.L.; Thaler, D.E.; Smalling, R.W.; Berry, S.; MacDonald, L.A.; Marks, D.S.; Tirschwell, D.L. Closure of patent foramen ovale versus medical therapy after cryptogenic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, Y.; Howard, J.P.; Arnold, A.; Shin, M.S.; Cook, C.; Petraco, R.; Demir, O.; Williams, L.; Iglesias, J.F.; Sutaria, N.; et al. Patent foramen ovale closure vs. medical therapy for cryptogenic stroke: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 1638–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Staubach, S.; Steinberg, D.H.; Zimmermann, W.; Wawra, N.; Wilson, N.; Wunderlich, N.; Sievert, H. New onset atrial fibrillation after patent foramen ovale closure. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2009, 74, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darmoch, F.; Al-Khadra, Y.; Soud, M.; Fanari, Z.; Alraies, M.C. Transcatheter Closure of Patent Foramen Ovale versus Medical Therapy after Cryptogenic Stroke: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 45, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kheiri, B.; Abdalla, A.; Osman, M.; Ahmed, S.; Hassan, M.; Bachuwa, G. Patent foramen ovale closure versus medical therapy after cryptogenic stroke: An updated meta-analysis of all randomized clinical trials. Cardiol. J. 2019, 26, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.L.; Kang, L.N.; Wang, L.; Xu, B. Percutaneous closure versus medical therapy for stroke with patent foramen Ovale: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2018, 18, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akobeng, A.K.; Abdelgadir, I.; Boudjemline, Y.; Hijazi, Z.M. Patent foramen ovale (PFO) closure versus medical therapy for prevention of recurrent stroke in patients with prior cryptogenic stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2018, 92, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasner, S.E.; Lavados, P.; Sharma, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dávalos, A.; Shamalov, N.; Cunha, L.; Lindgren, A.; Mikulik, R.; et al. Characterization of Patients with Embolic Strokes of Undetermined Source in the NAVIGATE ESUS Randomized Trial. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 27, 1673–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, Y.; Nijjer, S.; Cook, C.M.; El-Harasis, M.; Graby, J.; Petraco, R.; Kotecha, T.; Baker, C.S.; Malik, I.S.; Bellamy, M.F.; et al. A new method of applying randomised control study data to the individual patient: A novel quantitative patient-centred approach to interpreting composite end points. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 195, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, S.J. Atrial Fibrillation After Percutaneous PFO Closure: Not So Rare After All. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2022, 15, 2323–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Bajaj, N.S.; Kumbhani, D.J.; Tuzcu, E.M.; Kapadia, S.R. Meta-analysis of transcatheter closure versus medical therapy for patent foramen ovale in prevention of recurrent neurological events after presumed paradoxical embolism. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2012, 5, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verma, S.K.; Tobis, J.M. Explantation of patent foramen ovale closure devices: A multicenter survey. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2011, 4, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kent, D.M.; Saver, J.L.; Kasner, S.E.; Nelson, J.; Carroll, J.D.; Chatellier, G.; Derumeaux, G.; Furlan, A.J.; Herrmann, H.C.; Jüni, P.; et al. Heterogeneity of Treatment Effects in an Analysis of Pooled Individual Patient Data From Randomized Trials of Device Closure of Patent Foramen Ovale After Stroke. JAMA 2021, 326, 2277–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homma, S.; Sacco, R.L. Patent foramen ovale and stroke. Circulation 2005, 112, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaler, D.E.; Ruthazer, R.; Weimar, C.; Mas, J.L.; Serena, J.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Papetti, F.; Homma, S.; Mattle, H.P.; Nedeltchev, K.; et al. Recurrent stroke predictors differ in medically treated patients with pathogenic vs. other PFOs. Neurology 2014, 83, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Messé, S.R.; Kent, D.M. Still no closure on the question of PFO closure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1152–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, B.K.; Lessler, J.; Stuart, E.A. Improving propensity score weighting using machine learning. Stat. Med. 2010, 29, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anzola, G.P.; Zavarize, P.; Morandi, E.; Rozzini, L.; Parrinello, G. Transcranial Doppler and risk of recurrence in patients with stroke and patent foramen ovale. Eur. J. Neurol. 2003, 10, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.H.; Song, J.K.; Kim, J.S.; Heo, R.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.H.; Song, J.M.; Kang, D.H.; Kwon, S.U.; Kang, D.W.; et al. Cryptogenic Stroke and High-Risk Patent Foramen Ovale: The DEFENSE-PFO Trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 2335–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzucco, S.; Li, L.; Binney, L.; Rothwell, P.M. Prevalence of patent foramen ovale in cryptogenic transient ischaemic attack and non-disabling stroke at older ages: A population-based study, systematic review, and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaler, D. Patent foramen ovale in older patients with cryptogenic stroke or transient ischaemic attack. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 573–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alperi, A.; Guedeney, P.; Horlick, E.; Nombela-Franco, L.; Freixa, X.; Pascual, I.; Mesnier, J.; Houde, C.; Abrahamyan, L.; Montalescot, G.; et al. Transcatheter Closure of Patent Foramen Ovale in Older Patients With Cryptogenic Thromboembolic Events. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2022, 15, e011652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homma, S.; DiTullio, M.R.; Sacco, R.L.; Sciacca, R.R.; Mohr, J.P. Age as a determinant of adverse events in medically treated cryptogenic stroke patients with patent foramen ovale. Stroke 2004, 35, 2145–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scacciatella, P.; Meynet, I.; Presbitero, P.; Giorgi, M.; Lucarelli, C.; Zavalloni Parenti, D.; Biava, L.M.; Marra, S. Recurrent cerebral ischemia after patent foramen ovale percutaneous closure in older patients: A two-center registry study. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2016, 87, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahl, A.; Tai, T.; Praz, F.; Schwerzmann, M.; Seiler, C.; Nedeltchev, K.; Windecker, S.; Mattle, H.P.; Meier, B. Late results after percutaneous closure of patent foramen ovale for secondary prevention of paradoxical embolism using the amplatzer PFO occluder without intraprocedural echocardiography: Effect of device size. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2009, 2, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merkler, A.E.; Gialdini, G.; Yaghi, S.; Okin, P.M.; Iadecola, C.; Navi, B.B.; Kamel, H. Safety Outcomes After Percutaneous Transcatheter Closure of Patent Foramen Ovale. Stroke 2017, 48, 3073–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzucco, S.; Li, L.; Rothwell, P.M. Prognosis of Cryptogenic Stroke With Patent Foramen Ovale at Older Ages and Implications for Trials: A Population-Based Study and Systematic Review. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardt, S.E.; Eicken, A.; Berger, F.; Schubert, S.; Carminati, M.; Butera, G.; Grohmann, J.; Höhn, R.; Nielsen-Kudsk, J.E.; Hildick-Smith, D. Closure of patent foramen ovale defects using GORE® CARDIOFORM septal occluder: Results from a prospective European multicenter study. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2017, 90, 824–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, M.J.; Javois, A.J.; Moore, P.; Forbes, T.; Paolillo, J.A.; Group, G.I. Use of the GORE® CARDIOFORM Septal Occluder for percutaneous closure of secundum atrial septal defects: Results of the multicenter US IDE trial. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2020, 95, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amplatzer, P. Occluder: Instructions for Use; St. Jude Medical: Plymouth, MN, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gaetti, G.; Beneduce, A.; La Fauci, D.; Scardoni, A.; Chiappa, F.; Bellini, L.; Franzin, M.; Natale, A.M.; Marras, P.; Ranieri, P. Suture-Mediated Patent Foramen Ovale Closure Using the NobleStitch EL: Results from a Hospital-Based HTA. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaer, B.A.; Zellweger, M.J.; Cron, T.A.; Kaiser, C.A.; Osswald, S. Value of routine holter monitoring for the detection of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in patients with cerebral ischemic events. Stroke 2004, 35, e68–e70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jabaudon, D.; Sztajzel, J.; Sievert, K.; Landis, T.; Sztajzel, R. Usefulness of ambulatory 7-day ECG monitoring for the detection of atrial fibrillation and flutter after acute stroke and transient ischemic attack. Stroke 2004, 35, 1647–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gaillard, N.; Deltour, S.; Vilotijevic, B.; Hornych, A.; Crozier, S.; Leger, A.; Frank, R.; Samson, Y. Detection of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation with transtelephonic EKG in TIA or stroke patients. Neurology 2010, 74, 1666–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacco, R.L.; Kasner, S.E.; Broderick, J.P.; Caplan, L.R.; Connors, J.; Culebras, A.; Elkind, M.S.; George, M.G.; Hamdan, A.D.; Higashida, R.T. An updated definition of stroke for the 21st century: A statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2013, 44, 2064–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cotter, P.E.; Martin, P.J.; Ring, L.; Warburton, E.A.; Belham, M.; Pugh, P.J. Incidence of atrial fibrillation detected by implantable loop recorders in unexplained stroke. Neurology 2013, 80, 1546–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ziegler, P.D.; Glotzer, T.V.; Daoud, E.G.; Wyse, D.G.; Singer, D.E.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Koehler, J.L.; Hilker, C.E. Incidence of newly detected atrial arrhythmias via implantable devices in patients with a history of thromboembolic events. Stroke 2010, 41, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ritter, M.A.; Kochhäuser, S.; Duning, T.; Reinke, F.; Pott, C.; Dechering, D.G.; Eckardt, L.; Ringelstein, E.B. Occult atrial fibrillation in cryptogenic stroke: Detection by 7-day electrocardiogram versus implantable cardiac monitors. Stroke 2013, 44, 1449–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svendsen, J.H.; Diederichsen, S.Z.; Højberg, S.; Krieger, D.W.; Graff, C.; Kronborg, C.; Olesen, M.S.; Nielsen, J.B.; Holst, A.G.; Brandes, A.; et al. Implantable loop recorder detection of atrial fibrillation to prevent stroke (The LOOP Study): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 1507–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidenreich, P.A.; Bozkurt, B.; Aguilar, D.; Allen, L.A.; Byun, J.J.; Colvin, M.M.; Deswal, A.; Drazner, M.H.; Dunlay, S.M.; Evers, L.R.; et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2022, 145, e895–e1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavinsky, C.J.; Szerlip, M.; Goldsweig, A.M.; Amin, Z.; Boudoulas, K.D.; Carroll, J.D.; Coylewright, M.; Elmariah, S.; MacDonald, L.A.; Shah, A.P. SCAI guidelines for the management of patent foramen ovale. J. Soc. Cardiovasc. Angiogr. Interv. 2022, 1, 100039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boriani, G.; Laroche, C.; Diemberger, I.; Fantecchi, E.; Popescu, M.I.; Rasmussen, L.H.; Sinagra, G.; Petrescu, L.; Tavazzi, L.; Maggioni, A.P.; et al. Asymptomatic atrial fibrillation: Clinical correlates, management, and outcomes in the EORP-AF Pilot General Registry. Am. J. Med. 2015, 128, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horlick, E.; Kavinsky, C.J.; Amin, Z.; Boudoulas, K.D.; Carroll, J.D.; Hijazi, Z.M.; Leifer, D.; Lutsep, H.L.; Rhodes, J.F.; Tobis, J.M. SCAI expert consensus statement on operator and institutional requirements for PFO closure for secondary prevention of paradoxical embolic stroke: The American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this statement as an educational tool for neurologists. Catheter Cardiovasc. Interv. 2019, 93, 859–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rubiera, M.; Aires, A.; Antonenko, K.; Lémeret, S.; Nolte, C.H.; Putaala, J.; Schnabel, R.B.; Tuladhar, A.M.; Werring, D.J.; Zeraatkar, D.; et al. European Stroke Organisation (ESO) guideline on screening for subclinical atrial fibrillation after stroke or transient ischaemic attack of undetermined origin. Eur. Stroke J. 2022, 7, Vi. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messé, S.R.; Gronseth, G.S.; Kent, D.M.; Kizer, J.R.; Homma, S.; Rosterman, L.; Carroll, J.D.; Ishida, K.; Sangha, N.; Kasner, S.E. Practice advisory update summary: Patent foramen ovale and secondary stroke prevention: Report of the Guideline Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2020, 94, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Andrea, A.; Dweck, M.R.; Holte, E.; Fontes-Carvalho, R.; Cameli, M.; Aboumarie, H.S.; Diener, H.C.; Haugaa, K.H. EACVI survey on the management of patients with patent foramen ovale and cryptogenic stroke. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2021, 22, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sposato, L.A.; Cipriano, L.E.; Saposnik, G.; Ruíz Vargas, E.; Riccio, P.M.; Hachinski, V. Diagnosis of atrial fibrillation after stroke and transient ischaemic attack: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladstone, D.J.; Spring, M.; Dorian, P.; Panzov, V.; Thorpe, K.E.; Hall, J.; Vaid, H.; O’Donnell, M.; Laupacis, A.; Côté, R.; et al. Atrial fibrillation in patients with cryptogenic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2467–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanna, T.; Diener, H.-C.; Passman, R.S.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Bernstein, R.A.; Morillo, C.A.; Rymer, M.M.; Thijs, V.; Rogers, T.; Beckers, F. Cryptogenic stroke and underlying atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2478–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noubiap, J.J.; Agbaedeng, T.A.; Kamtchum-Tatuene, J.; Fitzgerald, J.L.; Middeldorp, M.E.; Kleinig, T.; Sanders, P. Rhythm monitoring strategies for atrial fibrillation detection in patients with cryptogenic stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 2021, 34, 100780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, B.H.; Hill, M.D.; Quinn, F.R.; Butcher, K.S.; Menon, B.K.; Gulamhusein, S.; Siddiqui, M.; Coutts, S.B.; Jeerakathil, T.; Smith, E.E.; et al. Effect of Implantable vs Prolonged External Electrocardiographic Monitoring on Atrial Fibrillation Detection in Patients With Ischemic Stroke: The PER DIEM Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 325, 2160–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachter, R.; Gröschel, K.; Gelbrich, G.; Hamann, G.F.; Kermer, P.; Liman, J.; Seegers, J.; Wasser, K.; Schulte, A.; Jürries, F.; et al. Holter-electrocardiogram-monitoring in patients with acute ischaemic stroke (Find-AF(RANDOMISED)): An open-label randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, R.A.; Kamel, H.; Granger, C.B.; Piccini, J.P.; Sethi, P.P.; Katz, J.M.; Vives, C.A.; Ziegler, P.D.; Franco, N.C.; Schwamm, L.H. Effect of Long-term Continuous Cardiac Monitoring vs Usual Care on Detection of Atrial Fibrillation in Patients With Stroke Attributed to Large- or Small-Vessel Disease: The STROKE-AF Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 325, 2169–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Søndergaard, L.; Kasner, S.E.; Rhodes, J.F.; Andersen, G.; Iversen, H.K.; Nielsen-Kudsk, J.E.; Settergren, M.; Sjöstrand, C.; Roine, R.O.; Hildick-Smith, D.; et al. Patent Foramen Ovale Closure or Antiplatelet Therapy for Cryptogenic Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Z.; Thijs, V.N. Atrial Fibrillation Following Patent Foramen Ovale Closure: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies and Clinical Trials. Stroke 2021, 52, 1653–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukadinović, D.; Scheller, B.; Ukena, C.; Ewen, S.; Mahfoud, F.; Böhm, M. Device-related risk of atrial fibrillation after closure of patent foramen ovale: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2022, 111, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedeney, P.; Laredo, M.; Zeitouni, M.; Hauguel-Moreau, M.; Wallet, T.; Elegamandji, B.; Alamowitch, S.; Crozier, S.; Sabben, C.; Deltour, S.; et al. Supraventricular Arrhythmia Following Patent Foramen Ovale Percutaneous Closure. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2022, 15, 2315–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiblawi, F.M.; Sommer, R.J.; Levchuck, S.G. Transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale in older adults. Catheter Cardiovasc. Interv. 2006, 68, 136–142, discussion 143-134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanczak, L.J.; Bertog, S.C.; Wunderlich, N.; Franke, J.; Sievert, H. PFO closure with the Premere PFO closure device: Acute results and follow-up of 263 patients. EuroIntervention 2012, 8, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagdi, P. Incidence and predictors of atrial fibrillation following transcatheter closure of interatrial septal communications using contemporary devices. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2010, 99, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knerr, M.; Bertog, S.; Vaskelyte, L.; Hofmann, I.; Sievert, H. Results of percutaneous closure of patent foramen ovale with the GORE(®) septal occluder. Catheter Cardiovasc. Interv. 2014, 83, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turc, G.; Calvet, D.; Guérin, P.; Sroussi, M.; Chatellier, G.; Mas, J.L. Closure, Anticoagulation, or Antiplatelet Therapy for Cryptogenic Stroke With Patent Foramen Ovale: Systematic Review of Randomized Trials, Sequential Meta-Analysis, and New Insights From the CLOSE Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartolucci, A.A.; Tendera, M.; Howard, G. Meta-analysis of multiple primary prevention trials of cardiovascular events using aspirin. Am. J. Cardiol. 2011, 107, 1796–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Berardis, G.; Lucisano, G.; D’Ettorre, A.; Pellegrini, F.; Lepore, V.; Tognoni, G.; Nicolucci, A. Association of aspirin use with major bleeding in patients with and without diabetes. JAMA 2012, 307, 2286–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García Rodríguez, L.A.; Martín-Pérez, M.; Hennekens, C.H.; Rothwell, P.M.; Lanas, A. Bleeding Risk with Long-Term Low-Dose Aspirin: A Systematic Review of Observational Studies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, A.; Ekmejian, A.; Collins, N.; Bhagwandeen, R. Multidisciplinary Assessment in Optimising Results of Percutaneous Patent Foramen Ovale Closure. Heart Lung Circ. 2017, 26, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheli, M.; Canepa, M.; Brunelli, C.; Bezante, G.P.; Favorini, S.; Rollando, D.; Sivori, G.; Viani, E.; Finocchi, C.; Balbi, M. Recurrent and Residual Shunts After Patent Foramen Ovale Closure: Results From a Long-Term Transcranial Doppler Study. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2015, 28, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaman, R.; Faganello, G.; Gimeno, J.R.; Szantho, G.V.; Nelson, M.; Curtis, S.; Martin, R.P.; Turner, M.S. Efficacy of percutaneous closure of patent foramen ovale: Comparison among three commonly used occluders. Heart 2011, 97, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaci, A.; Unlu, S.; Alsancak, Y.; Kaya, U.; Sezenoz, B. Short and long term complications of device closure of atrial septal defect and patent foramen ovale: Meta-analysis of 28,142 patients from 203 studies. Catheter Cardiovasc. Interv. 2013, 82, 1123–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzai, H.; Child, J.; Natterson, B.; Krivokapich, J.; Fishbein, M.C.; Chan, V.K.; Tobis, J.M. Incidence of thrombus formation on the CardioSEAL and the Amplatzer interatrial closure devices. Am. J. Cardiol. 2004, 93, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chessa, M.; Carminati, M.; Butera, G.; Bini, R.M.; Drago, M.; Rosti, L.; Giamberti, A.; Pomè, G.; Bossone, E.; Frigiola, A. Early and late complications associated with transcatheter occlusion of secundum atrial septal defect. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 39, 1061–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodés-Cabau, J.; Palacios, A.; Palacio, C.; Girona, J.; Galve, E.; Evangelista, A.; Casaldáliga, J.; Albert, D.; Picó, M.; Soler-Soler, J. Assessment of the markers of platelet and coagulation activation following transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects. Int. J. Cardiol. 2005, 98, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bédard, E.; Rodés-Cabau, J.; Houde, C.; Mackey, A.; Rivest, D.; Cloutier, S.; Noël, M.; Marrero, A.; Côté, J.M.; Chetaille, P.; et al. Enhanced thrombogenesis but not platelet activation is associated with transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale in patients with cryptogenic stroke. Stroke 2007, 38, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seeger, J.; Uber, A.; Wöhrle, J. Long-Term Outcome After Percutaneous Closure of Patent Foramen Ovale for Cryptogenic Ischemic Events. J. Invasive Cardiol. 2019, 31, E242–E248. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wintzer-Wehekind, J.; Alperi, A.; Houde, C.; Côté, J.M.; Asmarats, L.; Côté, M.; Rodés-Cabau, J. Long-Term Follow-Up After Closure of Patent Foramen Ovale in Patients With Cryptogenic Embolism. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wintzer-Wehekind, J.; Alperi, A.; Houde, C.; Côté, J.M.; Guimaraes, L.F.C.; Côté, M.; Rodés-Cabau, J. Impact of Discontinuation of Antithrombotic Therapy Following Closure of Patent Foramen Ovale in Patients With Cryptogenic Embolism. Am. J. Cardiol. 2019, 123, 1538–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| RoPE Score Calculator | |
|---|---|
| Absence of hypertension | +1 |
| Absence of diabetes | +1 |
| Absence of stroke/TIA | +1 |
| Nonsmoker | +1 |
| Cortical infarct, on imaging | +1 |
| Age | |
| 18–29 | +5 |
| 30–39 | +4 |
| 40–49 | +3 |
| 50–59 | +2 |
| 60–69 | +1 |
| >70 | 0 |
| Risk Source | Features |
|---|---|
| Very high | A PFO and a straddling thrombus |
| High | Concomitant pulmonary embolism or deep venous thrombosis preceding an index infarct, combined with either a PFO and ASA or a large-shunt PFO |
| Medium | A PFO and an ASA or a large-shunt PFO |
| Low | A small-shunt PFO without an atrial septal aneurysm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lucà, F.; Pino, P.G.; Parrini, I.; Di Fusco, S.A.; Ceravolo, R.; Madeo, A.; Leone, A.; La Mair, M.; Benedetto, F.A.; Riccio, C.; et al. Patent Foramen Ovale and Cryptogenic Stroke: Integrated Management. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1952. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051952
Lucà F, Pino PG, Parrini I, Di Fusco SA, Ceravolo R, Madeo A, Leone A, La Mair M, Benedetto FA, Riccio C, et al. Patent Foramen Ovale and Cryptogenic Stroke: Integrated Management. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(5):1952. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051952
Chicago/Turabian StyleLucà, Fabiana, Paolo G. Pino, Iris Parrini, Stefania Angela Di Fusco, Roberto Ceravolo, Andrea Madeo, Angelo Leone, Mark La Mair, Francesco Antonio Benedetto, Carmine Riccio, and et al. 2023. "Patent Foramen Ovale and Cryptogenic Stroke: Integrated Management" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 5: 1952. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051952
APA StyleLucà, F., Pino, P. G., Parrini, I., Di Fusco, S. A., Ceravolo, R., Madeo, A., Leone, A., La Mair, M., Benedetto, F. A., Riccio, C., Oliva, F., Colivicchi, F., Gulizia, M. M., & Gelsomino, S. (2023). Patent Foramen Ovale and Cryptogenic Stroke: Integrated Management. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(5), 1952. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051952







