Stromal Vascular Fraction Cells from Individuals Who Have Previously Undergone Radiotherapy Retain Their Pro-Wound Healing Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Tissue Collection
2.2. SVF Isolation
2.3. Dermal Fibroblast (DF) Isolation
2.4. Preadipocyte Cell Culture
2.5. Immunocytochemistry
2.6. Collection of Conditioned Media
2.7. Quantification of Paracrine Factors
2.8. Scratch Wound Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
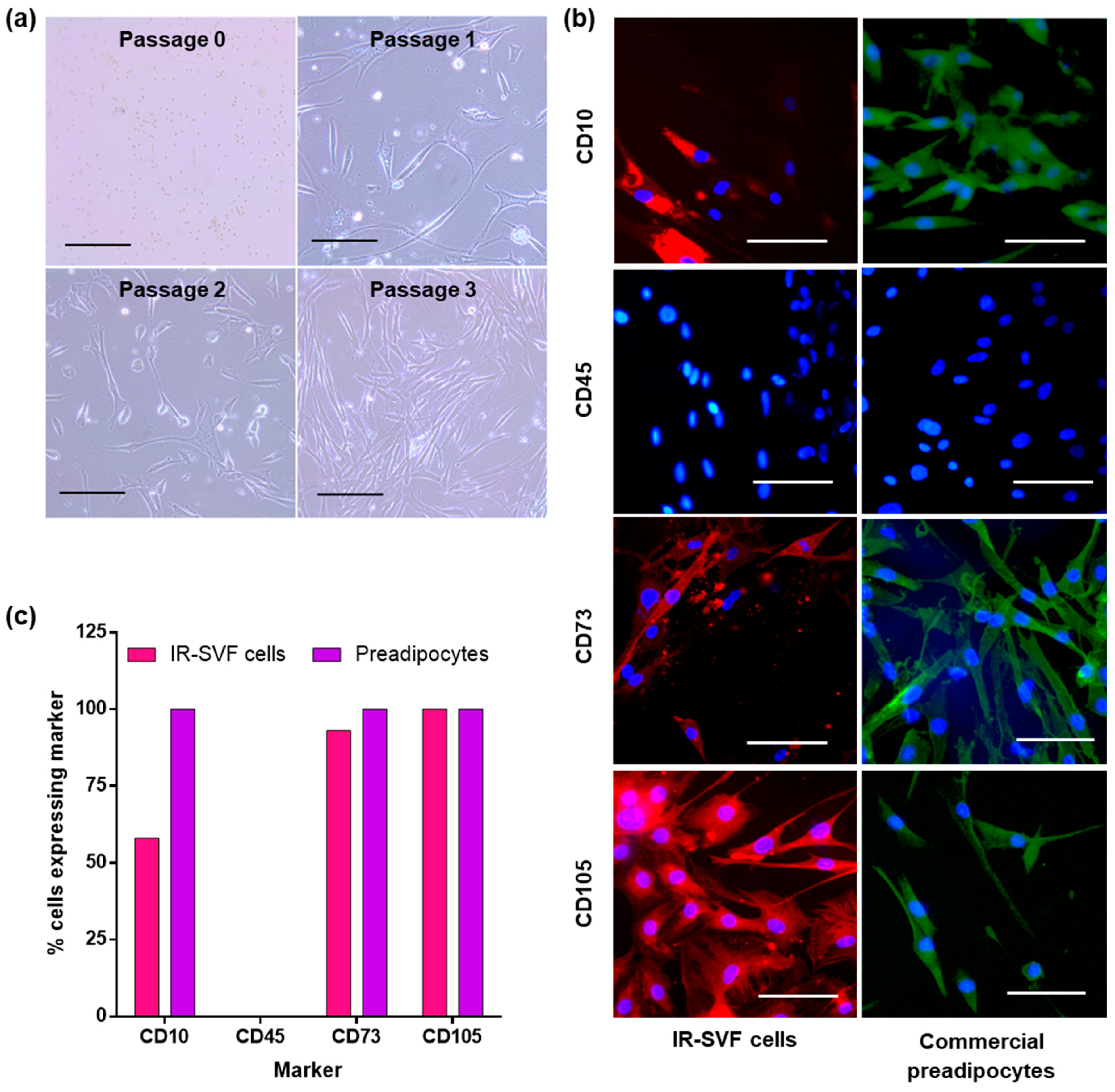
3.1. Isolation of SVF
3.2. Characterisation of Adherent Cells from SVF as Preadipocytes
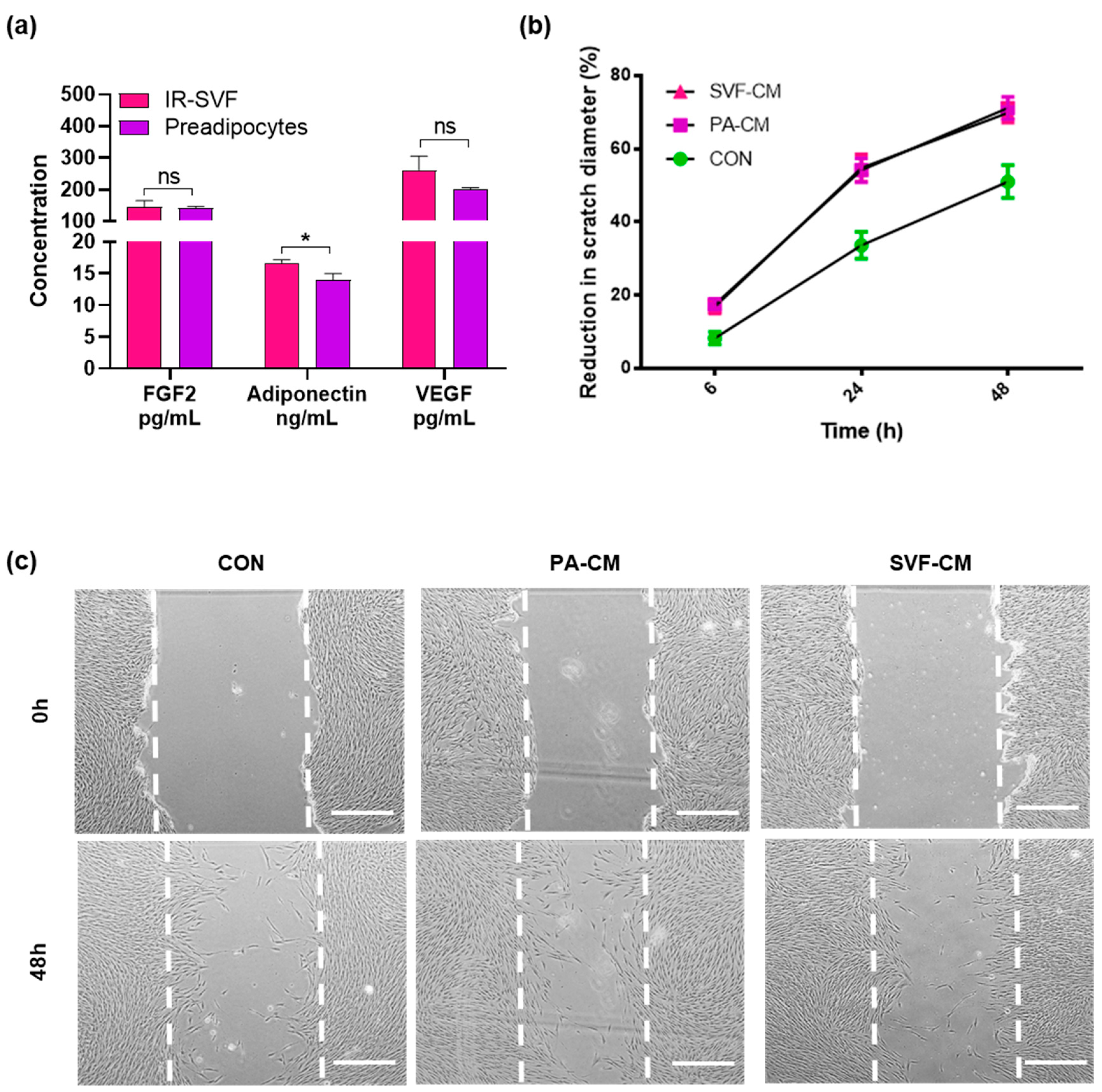
3.3. Conditioned Media from IR-SVF Promotes Wound Healing In Vitro
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeong, W.; Yang, X.; Lee, J.; Ryoo, Y.; Kim, J.; Oh, Y.; Kwon, S.; Liu, D.; Son, D. Serial changes in the proliferation and differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells after ionizing radiation. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2016, 7, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gieringer, M.; Gosepath, J.; Naim, R. Radiotherapy and wound healing: Principles, management and prospects (review). Oncol. Rep. 2011, 26, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, L.K.; Johnson, M.B.; Dedhia, R.D.; Niknam-Bienia, S.; Wong, A.K. Impaired wound healing after radiation therapy: A systematic review of pathogenesis and treatment. JPRAS Open 2017, 13, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronowitz, S.J. Current status of implant-based breast reconstruction in patients receiving postmastectomy radiation therapy. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2012, 130, 513e–523e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parsa, A.A.; Jackowe, D.J.; Johnson, E.W.; Lye, K.D.; Iwahira, Y.; Huynh, T.V.; Pedro, P.; Pang, J.; Parsa, F.D. Selection criteria for expander/implant breast reconstruction following radiation therapy. Hawaii Med. J. 2009, 68, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yun, J.H.; Diaz, R.; Orman, A.G. Breast Reconstruction and Radiation Therapy. Cancer Control 2018, 25, 1073274818795489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevor, L.V.; Riches-Suman, K.; Mahajan, A.L.; Thornton, M.J. Adipose Tissue: A Source of Stem Cells with Potential for Regenerative Therapies for Wound Healing. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, S.R.; Johnstone, B.H.; Phinney, D.G.; March, K.L. Adipose stromal/stem cells: Basic and translational advances: The IFATS collection. Stem Cells 2008, 26, 2664–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuk, P.A.; Zhu, M.; Mizuno, H.; Huang, J.; Futrell, J.W.; Katz, A.J.; Benhaim, P.; Lorenz, H.P.; Hedrick, M.H. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: Implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001, 7, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsuji, W.; Rubin, J.P.; Marra, K.G. Adipose-derived stem cells: Implications in tissue regeneration. World J. Stem Cells 2014, 6, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, M.; Windsor, J.; Dunbar, P.R. Human adipose-derived stem cells: Isolation, characterization and applications in surgery. ANZ J. Surg. 2009, 79, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubner, F.; Muschter, D.; Pohl, F.; Schreml, S.; Prantl, L.; Gassner, H.G. A Co-Culture Model of Fibroblasts and Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells Reveals New Insights into Impaired Wound Healing After Radiotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 25947–25958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrison, M.A.A.; Al-Ghadban, S.I.; O’Donnell, B.T.; Mohiuddin, O.A.; Wise, R.M.; Sullivan, B.N.; Bunnell, B.A. Establishing the Adipose Stem Cell Identity: Characterization Assays and Functional Properties. Sci. Princ. Adipose Stem Cells 2022, 23–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mildmay-White, A.; Khan, W. Cell Surface Markers on Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: A Systematic Review. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 12, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Broadbent, J.A.; Huan, J.; Yang, H. The Effects of Adipose Stem Cell-Conditioned Media on Fibrogenesis of Dermal Fibroblasts Stimulated by Transforming Growth Factor-β1. J. Burn Care Res. 2018, 39, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.R.; Wang, C.; Patel, R.; Trujillo, A.; Patel, N.A.; Prather, J.; Gould, L.J.; Wu, M.H. Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Conditioned Media and Exosomes Containing MALAT1 Promote Human Dermal Fibroblast Migration and Ischemic Wound Healing. Adv. Wound Care (New Rochelle) 2018, 7, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubey, N.K.; Mishra, V.K.; Dubey, R.; Deng, Y.H.; Tsai, F.C.; Deng, W.P. Revisiting the Advances in Isolation, Characterization and Secretome of Adipose-Derived Stromal/Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hassan, W.U.; Greiser, U.; Wang, W. Role of adipose-derived stem cells in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2014, 22, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trzyna, A.; Banaś-Ząbczyk, A. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Secretome and its Potential Application in “Stem Cell-Free Therapy”. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunnell, B.A.; Flaat, M.; Gagliardi, C.; Patel, B.; Ripoll, C. Adipose-derived stem cells: Isolation, expansion and differentiation. Methods 2008, 45, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.J.; Liu, H.Y.; Chang, Y.T.; Cheng, Y.H.; Mersmann, H.J.; Kuo, W.H.; Ding, S.T. Isolation and Differentiation of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells from Porcine Subcutaneous Adipose Tissues. J Vis. Exp. 2016, 109, e53886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Rikabi, A.H.A.; Tobin, D.J.; Riches-Suman, K.; Thornton, M.J. Dermal fibroblasts cultured from donors with type 2 diabetes mellitus retain an epigenetic memory associated with poor wound healing responses. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, S.R. Facial recontouring with lipostructure. Clin. Plast. Surg. 1997, 24, 347–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoareau, L.; Bencharif, K.; Girard, A.C.; Gence, L.; Delarue, P.; Hulard, O.; Festy, F.; Roche, R. Effect of centrifugation and washing on adipose graft viability: A new method to improve graft efficiency. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2013, 66, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, C.; Mao, Y.; Nie, F.; Xing, Y.; Sha, W.; Wang, X.; Irwin, D.M.; Tan, H. Stromal vascular fraction promotes migration of fibroblasts and angiogenesis through regulation of extracellular matrix in the skin wound healing process. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, K.R.; Côrtes, I.; Liechocki, S.; Carneiro, J.R.; Souza, A.A.; Borojevic, R.; Maya-Monteiro, C.M.; Baptista, L.S. Characterization of stromal vascular fraction and adipose stem cells from subcutaneous, preperitoneal and visceral morbidly obese human adipose tissue depots. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Pei, M. Significance of Cellular Cross-Talk in Stromal Vascular Fraction of Adipose Tissue in Neovascularization. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 1034–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, W.; Wein, F.; Seckinger, A.; Frankhauser, M.; Wirkner, U.; Krause, U.; Blake, J.; Schwager, C.; Eckstein, V.; Ansorge, W.; et al. Comparative characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells from human bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord blood. Exp. Hematol. 2005, 33, 1402–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brem, H.; Kodra, A.; Golinko, M.S.; Entero, H.; Stojadinovic, O.; Wang, V.M.; Sheahan, C.M.; Weinberg, A.D.; Woo, S.L.; Ehrlich, H.P.; et al. Mechanism of sustained release of vascular endothelial growth factor in accelerating experimental diabetic healing. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 2275–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, H.; Cheng, Y.; Ye, J.; Cai, P.; Zhang, J.; Li, R.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lin, C.; et al. bFGF Promotes the Migration of Human Dermal Fibroblasts under Diabetic Conditions through Reactive Oxygen Species Production via the PI3K/Akt-Rac1- JNK Pathways. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 11, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, S.; Tada, Y.; Asano, Y.; Hau, C.S.; Kato, T.; Saeki, H.; Yamauchi, T.; Kubota, N.; Kadowaki, T.; Sato, S. Adiponectin regulates cutaneous wound healing by promoting keratinocyte proliferation and migration via the ERK signaling pathway. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 3231–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- da Silva Rosa, S.C.; Liu, M.; Sweeney, G. Adiponectin Synthesis, Secretion and Extravasation from Circulation to Interstitial Space. Physiology (Bethesda) 2021, 36, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranovskii, D.S.; Klabukov, I.D.; Arguchinskaya, N.V.; Yakimova, A.O.; Kisel, A.A.; Yatsenko, E.M.; Ivanov, S.A.; Shegay, P.V.; Kaprin, A.D. Adverse events, side effects and complications in mesenchymal stromal cell-based therapies. Stem Cell Investig. 2022, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasilnikova, O.A.; Baranovskii, D.S.; Lyundup, A.V.; Shegay, P.V.; Kaprin, A.D.; Klabukov, I.D. Stem and Somatic Cell Monotherapy for the Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcers: Review of Clinical Studies and Mechanisms of Action. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2022, 18, 1974–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, P.; Garcovich, S. Systematic Review: Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Platelet-Rich Plasma and Biomaterials as New Regenerative Strategies in Chronic Skin Wounds and Soft Tissue Defects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trevor, L.V.; Riches-Suman, K.; Mahajan, A.L.; Thornton, M.J. Stromal Vascular Fraction Cells from Individuals Who Have Previously Undergone Radiotherapy Retain Their Pro-Wound Healing Properties. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2052. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12052052
Trevor LV, Riches-Suman K, Mahajan AL, Thornton MJ. Stromal Vascular Fraction Cells from Individuals Who Have Previously Undergone Radiotherapy Retain Their Pro-Wound Healing Properties. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(5):2052. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12052052
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrevor, Lucy V., Kirsten Riches-Suman, Ajay L. Mahajan, and M. Julie Thornton. 2023. "Stromal Vascular Fraction Cells from Individuals Who Have Previously Undergone Radiotherapy Retain Their Pro-Wound Healing Properties" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 5: 2052. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12052052
APA StyleTrevor, L. V., Riches-Suman, K., Mahajan, A. L., & Thornton, M. J. (2023). Stromal Vascular Fraction Cells from Individuals Who Have Previously Undergone Radiotherapy Retain Their Pro-Wound Healing Properties. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(5), 2052. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12052052





