Role of Lung Ultrasonography (LUS) as a Tool for Evaluating Children with Pediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome Temporally Associated with SARS-CoV-2 (PIMS-TS)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
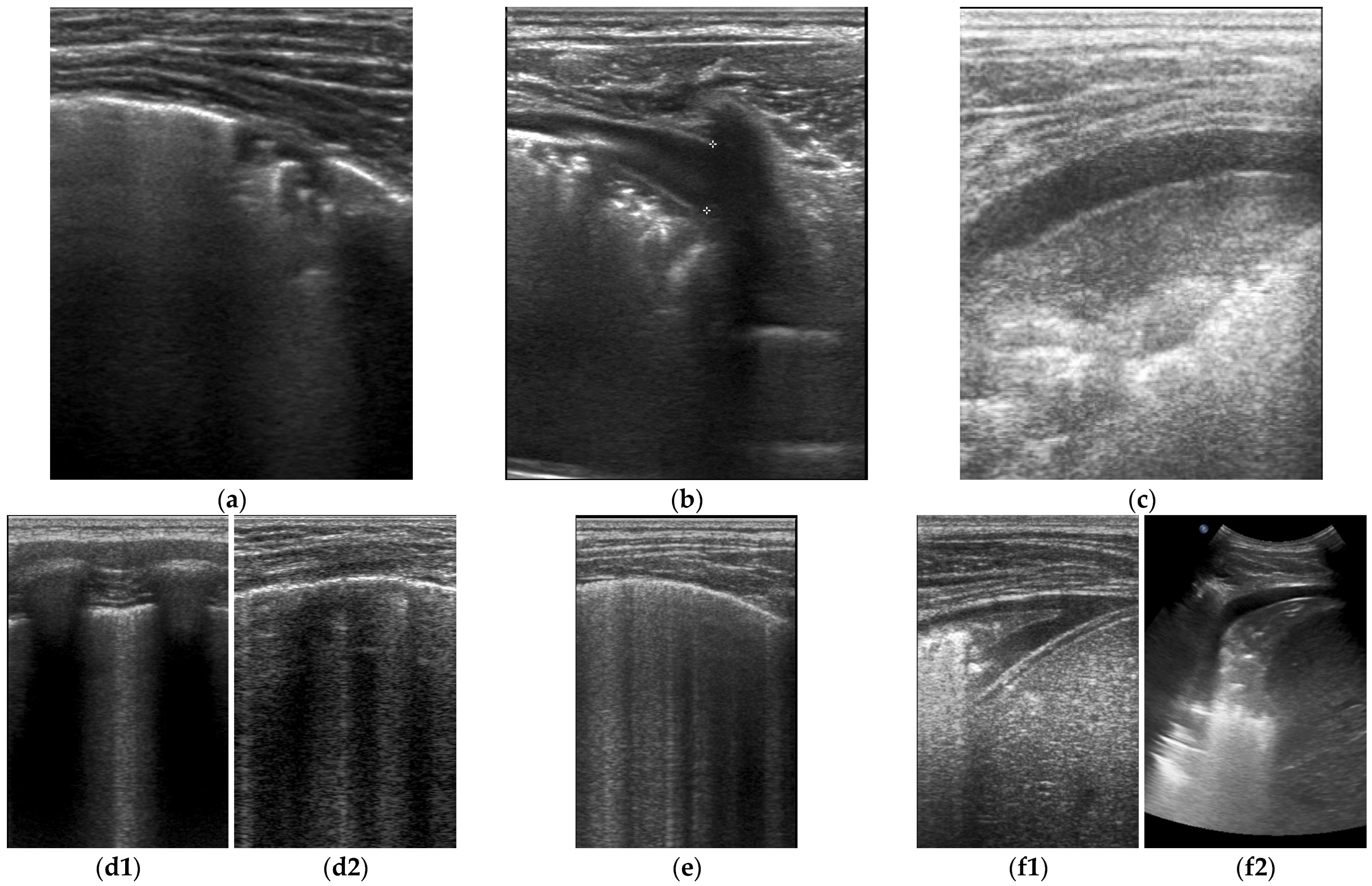
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children and Adolescents with COVID-19. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/multisystem-inflammatory-syndrome-in-children-and-adolescents-with-covid-19 (accessed on 15 May 2020).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Emergency Preparedness and Response: Health Alert Network. 2020. Available online: https://emergency.cdc.gov/han/index.asp (accessed on 14 May 2020).
- Royal College of Pediatrics and Child Health. Guidance: Pediatric Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome Temporally Associated with COVID-19. 2020. Available online: https://www.rcpch.ac.uk/resources/paediatric-multisystem-inflammatory-syndrome-temporally-associated-covid-19-pims-guidance (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Available online: https://icd.who.int/browse10/2019/en#/U00-U49 (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Gupta, A.; Gill, A.; Sharma, M.; Garg, M. Multi-System Inflammatory Syndrome in a Child Mimicking Kawasaki Disease. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2021, 67, fmaa060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, A.; Varisco, T.; Quattrocchi, G.; Amoroso, A.; Beltrami, D.; Venturiello, S.; Ripamonti, A.; Villa, A.; Andreotti, M.; Ciuffreda, M.; et al. Children with Kawasaki disease or Kawasaki-like syndrome (MIS-C/PIMS) at the time of COVID-19: Are they all the same? Case series and literature review. Reumatismo 2021, 73, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opoka-Winiarska, V.; Grywalska, E.; Roliński, J. PIMS-TS, the New Paediatric Systemic Inflammatory Disease Related to Previous Exposure to SARS-CoV-2 Infection-"Rheumatic Fever" of the 21st Century? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lad, S.S.; Kait, S.P.; Suryawanshi, P.B.; Mujawar, J.; Lad, P.; Khetre, R.; Jadhav, L.M.; Bhor, A.; Balte, P.; Kataria, P.; et al. Neurological Manifestations in Pediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome Temporally Associated with SARS-CoV-2 (PIMS-TS). Indian J. Pediatr. 2021, 88, 294–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, E.T.; Humphrey, H.N.; Daniels, I.R.; McDermott, F.D. COVID-19 and the paediatric acute abdomen—The emerging dilemma of PIMS-TS. BJS Open 2022, 6, zrac049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meshaka, R.; Whittam, F.C.; Guessoum, M.; Eleti, S.; Shelmerdine, S.C.; Arthurs, O.J.; McHugh, K.; Hiorns, M.P.; Humphries, P.D.; Calder, A.D.; et al. Abdominal US in Pediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome Associated with SARS-CoV-2 (PIMS-TS). Radiology 2022, 303, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nardo, M.; De Piero, M.E.; Hoskote, A.; Belohlavek, J.; Lorusso, R.; Thiruchelvam, T.; Lillie, J.; Stanley, V.; StJohn, L.; Amodeo, A.; et al. EuroECMO neonatal and paediatric COVID-19 Working Group and EuroELSO Steering Committee. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in children with COVID-19 and PIMS-TS during the second and third wave. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2022, 6, e14–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, M.A.; Villion, A.; Manougian, T.; Salik, I. The Perfect Cytokine Storm: Utilization of Lung Ultrasound During Urgent Surgery in an Infant with Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children and Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Cureus 2021, 13, e15640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okarska-Napierała, M.; Ludwikowska, K.; Szenborn, L.; Dudek, N.; Mania, A.; Buda, P.; Książyk, J.; Mazur-Malewska, K.; Figlerowicz, M.; Szczukocki, M.; et al. Pediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome (PIMS) Did Occur in Poland during Months with Low COVID-19 Prevalence, Preliminary Results of a Nationwide Register. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musolino, A.M.; Tomà, P.; De Rose, C.; Pitaro, E.; Boccuzzi, E.; De Santis, R.; Morello, R.; Supino, M.C.; Villani, A.; Valentini, P.; et al. Ten Years of Pediatric Lung Ultrasound: A Narrative Review. Front. Physiol. 2022, 12, 721951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworska, J.; Buda, N.; Ciuca, I.M.; Dong, Y.; Fang, C.; Feldkamp, A.; Jüngert, J.; Kosiak, W.; Mentzel, H.J.; Pienar, C.; et al. Ultrasound of the pleura in children, WFUMB review paper. Med. Ultrason. 2021, 23, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, C.F.; Buda, N.; Ciuca, I.M.; Dong, Y.; Fang, C.; Feldkamp, A.; Jüngert, J.; Kosiak, W.; Mentzel, H.J.; Pienar, C.; et al. Lung ultrasound in children, WFUMB review paper (part 2). Med. Ultrason. 2021, 23, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, C.F.; Mathis, G.; Blaivas, M.; Volpicelli, G.; Seibel, A.; Atkinson, N.S.; Cui, X.W.; Mei, F.; Schreiber-Dietrich, D.; Yi, D. Lung artefacts and their use. Med. Ultrason. 2016, 18, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpicelli, G.; Elbarbary, M.; Blaivas, M.; Lichtenstein, D.A.; Mathis, G.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Melniker, L.; Gargani, L.; Noble, V.E.; Via, G.; et al. International Liaison Committee on Lung Ultrasound (ILC-LUS) for International Consensus Conference on Lung Ultrasound (ICC-LUS). International evidencebased recommendations for point-of-care lung ultrasound. Intensive Care Med. 2012, 38, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenstein, D.; Goldstein, I.; Mourgeon, E.; Cluzel, P.; Grenier, P.; Rouby, J.-J. Comparative diagnostic performances of auscultation, chest radiography, and lung ultrasonography in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Anesthesiology 2004, 100, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balk, D.S.; Lee, C.; Schafer, J.; Welwarth, J.; Hardin, J.; Novack, V.; Yarza, S.; Hoffmann, B. Lung ultrasound compared to chest X-ray for diagnosis of pediatric pneumonia: A meta-analysis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2018, 53, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoste, L.; Van Paemel, R.; Haerynck, F. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children related to COVID-19: A systematic review. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 180, 2019–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musolino, A.M.; Boccuzzi, E.; Buonsenso, D.; Supino, M.C.; Mesturino, M.A.; Pitaro, E.; Ferro, V.; Nacca, R.; Sinibaldi, S.; Palma, P.; et al. The Role of Lung Ultrasound in Diagnosing COVID-19-Related Multisystemic Inflammatory Disease: A Preliminary Experience. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camporesi, A.; Gemma, M.; Buonsenso, D.; Ferrario, S.; Mandelli, A.; Pessina, M.; Diotto, V.; Rota, E.; Raso, I.; Fiori, L.; et al. Lung Ultrasound Patterns in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C)-Characteristics and Prognostic Value. Children 2022, 9, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, T.M.; Dessie, A.; Kessler, D.O.; Malia, L.; Rabiner, J.E.; Firnberg, M.T.; Ng, L. Point-of-Care Ultrasound Findings in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: A Cross-Sectional Study. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2021, 37, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro-Domínguez, P.; Navallas, M.; Riaza-Martin, L.; Mahani, M.G.; Charcape, C.F.U.; Valverde, I.; D’Arco, F.; Toso, S.; Shelmerdine, S.C.; van Schuppen, J.; et al. Imaging findings of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children associated with COVID-19. Pediatr. Radiol. 2021, 51, 1608–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, S.; Elbaaly, H.; Reid, C.E.L.; Santos, R.M.F.; Shivamurthy, V.; Wong, J.; Jogeesvaran, K.H. Spectrum of Imaging Findings at Chest Radiography, US, CT, and MRI in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Associated with COVID-19. Radiology 2021, 298, E1–E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostad, B.S.; Shah, J.H.; Rostad, C.A.; Jaggi, P.; Richer, E.J.; Linam, L.E.; Alazraki, A.L.; Riedesel, E.L.; Milla, S.S. Chest radiograph features of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) compared to pediatric COVID-19. Pediatr. Radiol. 2021, 51, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostami-Maskopaee, F.; Ladomenou, F.; Razavi-Amoli, S.-K.; Navaeifar, M.R.; Hajialibeig, A.; Shahbaznejad, L.; Hosseinzadeh, F.; Aski, B.H.; Anari, A.M.; Mohammadi, M.; et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of the multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) following COVID-19 infection in Iran: A multicenter study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0274104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| age (years), mean (median) | 6 7/12 (6) |
| sex, n (%) | |
| FEMALE | 13 (30) |
| MALE | 30 (70) |
| respiratory abnormalities signs n (%) | 21 (49) |
| pneumonia criteria n (%) on admission | 39 (91) |
| >1 pathology n (%) | 39 (91) |
| bilateral lesions, n (%) | 28 (65) |
| Normal LUS image, n (%) | 3 (7) |
| by the day of discharge | |
| Total regression, n (%) | 8 (19) |
| Partial regression, n (%) | 35 (81) |
| 1-SIDED (TOT 43; %) | 2-SIDED (TOT 43; %) | TOTAL (TOT 43; %) | AFTER 3 MONTHS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B-Lines Artifacts | 0 (0) | 40 (93) | 40 (93) | 0 (0) |
| Interstitial Syndrome | 0 (0) | 30 (70) | 30 (70) | 0 (0) |
| Interstitial-alveolar syndrome | 0 (0) | 19 (44) | 19 (44) | 0 (0) |
| Consolidations | 7 (16) | 30 (70) | 37 (86) | 0 (0) |
| Atelectasis | 9 (21) | 19 (44) | 28 (65) | 0 (0) |
| Pleural effusion | 0 (0) | 36 (84) | 36 (84) | 0 (0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomczonek-Moruś, J.; Krysiak, N.; Blomberg, A.; Depczyk-Bukała, M.; Tkaczyk, M.; Zeman, K. Role of Lung Ultrasonography (LUS) as a Tool for Evaluating Children with Pediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome Temporally Associated with SARS-CoV-2 (PIMS-TS). J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2850. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082850
Tomczonek-Moruś J, Krysiak N, Blomberg A, Depczyk-Bukała M, Tkaczyk M, Zeman K. Role of Lung Ultrasonography (LUS) as a Tool for Evaluating Children with Pediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome Temporally Associated with SARS-CoV-2 (PIMS-TS). Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(8):2850. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082850
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomczonek-Moruś, Jolanta, Natalia Krysiak, Agnieszka Blomberg, Marta Depczyk-Bukała, Marcin Tkaczyk, and Krzysztof Zeman. 2023. "Role of Lung Ultrasonography (LUS) as a Tool for Evaluating Children with Pediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome Temporally Associated with SARS-CoV-2 (PIMS-TS)" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 8: 2850. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082850
APA StyleTomczonek-Moruś, J., Krysiak, N., Blomberg, A., Depczyk-Bukała, M., Tkaczyk, M., & Zeman, K. (2023). Role of Lung Ultrasonography (LUS) as a Tool for Evaluating Children with Pediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome Temporally Associated with SARS-CoV-2 (PIMS-TS). Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(8), 2850. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082850







