Handgrip Strength and Muscle Quality: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Database
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Source and Study Population
2.2. Clinical and Laboratory Evaluations
2.3. Handgrip Strength (kg)
2.4. Body Mass Components Dataset
2.5. Covariates
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Selected Participants
3.1.1. Baseline Characteristics
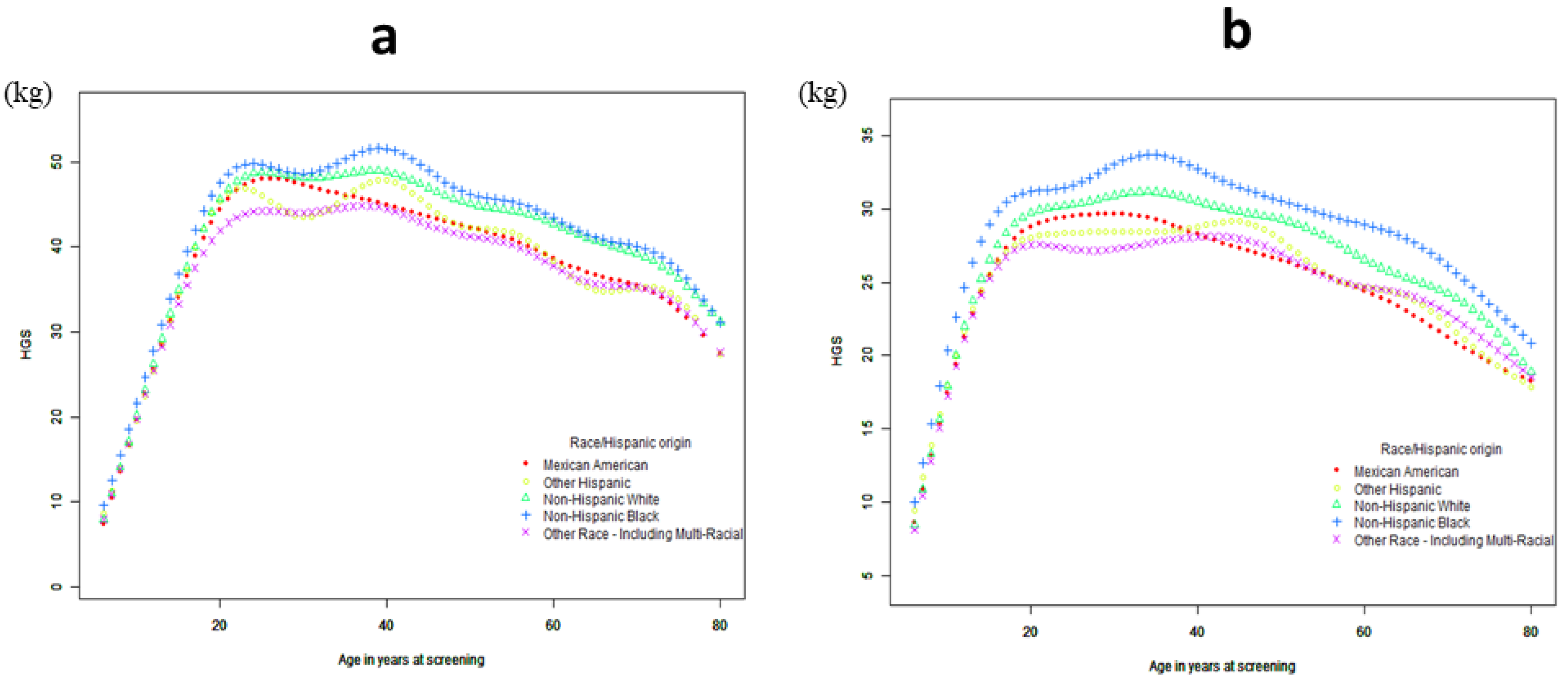
3.1.2. Curve Fitting and Threshold-Effect Analysis
3.1.3. Handgrip Strength and Body Composition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, S.; Umapathysivam, K.; Visvanathan, R. Sarcopenia in older people. JBI Evid. Implement. 2014, 12, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fielding, R.A.; Vellas, B.; Evans, W.J.; Bhasin, S.; Morley, J.E.; Newman, A.B.; van Kan, G.A.; Andrieu, S.; Bauer, J.; Breuille, D.; et al. Sarcopenia: An undiagnosed condition in older adults. Current consensus definition: Prevalence, etiology, and consequences. International working group on sarcopenia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2011, 12, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckinx, F.; Landi, F.; Cesari, M.; Fielding, R.A.; Visser, M.; Engelke, K.; Maggi, S.; Dennison, E.; Al-Daghri, N.M.; Allepaerts, S.; et al. Pitfalls in the measurement of muscle mass: A need for a reference standard. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2018, 9, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guglielmi, G.; Ponti, F.; Agostini, M.; Amadori, M.; Battista, G.; Bazzocchi, A. The role of DXA in sarcopenia. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2016, 28, 1047–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kullberg, J.; Brandberg, J.; Angelhed, J.E.; Frimmel, H.; Bergelin, E.; Strid, L.; Ahlström, H.; Johansson, L.; Lönn, L. Whole-body adipose tissue analysis: Comparison of MRI, CT and dual energy X-ray absorptiometry. Br. J. Radiol. 2009, 82, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Heshka, S.; Gallagher, D.; Kotler, D.P.; Mayer, L.; Albu, J.; Shen, W.; Freda, P.U.; Heymsfield, S.B. Intermuscular adipose tissue-free skeletal muscle mass: Estimation by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry in adults. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 97, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, F.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Liperoti, R.; Russo, A.; Giovannini, S.; Tosato, M.; Capoluongo, E.D.; Bernabei, R.; Onder, G. Sarcopenia and mortality risk in frail older persons aged 80 years and older: Results from ilSIRENTE study. Age Ageing 2013, 42, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawthon, P.M. Assessment of Lean Mass and Physical Performance in Sarcopenia. J. Clin. Densitom. 2015, 18, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, K.; May, C.; Patel, H.P.; Baxter, M.; Sayer, A.A.; Roberts, H. A feasibility study of implementing grip strength measurement into routine hospital practice (GRImP): Study protocol. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2016, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.A.; Syddall, H.; Martin, H.; Patel, H.; Baylis, D.; Cooper, C. The developmental origins of sarcopenia. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2008, 12, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; STROBE Initiative. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/about_nhanes.htm (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- Dietz, P.M.; Homa, D.; England, L.J.; Burley, K.; Tong, V.T.; Dube, S.R.; Bernert, J.T. Estimates of nondisclosure of cigarette smoking among pregnant and nonpregnant women of reproductive age in the United States. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 173, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data the Alcohol Use Questionnaire. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Nhanes/2013-2014/ALQ_H.htm#SEQN (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data. 2021. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Nhanes/2013-2014/MGX_H.htm (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- Bhasin, S.; Travison, T.G.; Manini, T.M.; Patel, S.; Pencina, K.M.; Fielding, R.A.; Magaziner, J.M.; Newman, A.B.; Kiel, D.P.; Cooper, C.; et al. Sarcopenia Definition: The Position Statements of the Sarcopenia Definition and Outcomes Consortium. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2020, 68, 1410–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013–2014. 2020. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Nhanes/2013-2014/DXX_H.htm (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/vitamind/analyticalnote.aspx?h=/Nchs/Nhanes/2013-2014/VID_H.htm&t=VID_H.Doc (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- Blanton, C.A.; Moshfegh, A.J.; Baer, D.J.; Kretsch, M.J. The USDA Automated Multiple-Pass Method accurately estimates group total energy and nutrient intake. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 2594–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshfegh, A.J.; Rhodes, D.G.; Baer, D.J.; Murayi, T.; Clemens, J.C.; Rumpler, W.V.; Paul, D.R.; Sebastian, R.S.; Kuczynski, K.J.; Ingwersen, L.A.; et al. The US Department of Agriculture Automated Multiple-Pass Method reduces bias in the collection of energy intakes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 88, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Nhanes/2013-2014/PAQ_H.htm (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- Kim, J.; Wang, Z.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Gallagher, D. Total-body skeletal muscle mass: Estimation by a new dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry method. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, D.R., Jr. International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Plan and operation of the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–1994. Series 1: Programs and collection procedures. In Vital and Health Statistics: Ser. 1—Programs and Collection Procedures; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; 407p. [Google Scholar]
- Kyle, U.G.; Genton, L.; Hans, D.; Karsegard, L.; O Slosman, D.; Pichard, C. Age-related differences in fat-free mass, skeletal muscle, body cell mass and fat mass between 18 and 94 years. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 55, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, D.; Visser, M.; De Meersman, R.E.; Sepúlveda, D.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Pierson, R.N.; Harris, T.; Heymsfield, S.B. Appendicular skeletal muscle mass: Effects of age, gender, and ethnicity. J. Appl. Physiol. 1997, 83, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, R.M.; Syddall, H.E.; Cooper, R.; Benzeval, M.; Deary, I.J.; Dennison, E.M.; Der, G.; Gale, C.R.; Inskip, H.M.; Jagger, C.; et al. Grip strength across the life course: Normative data from twelve British studies. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, S.X.; Holloway-Kew, K.L.; Hyde, N.; Williams, L.J.; Tembo, M.C.; Mohebbi, M.; Gojanovic, M.; Leach, S.; Pasco, J.A. Handgrip strength and muscle quality in Australian women: Cross-sectional data from the Geelong Osteoporosis Study. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2020, 11, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beenakker, K.G.; Ling, C.H.; Meskers, C.G.; de Craen, A.J.; Stijnen, T.; Westendorp, R.G.; Maier, A.B. Patterns of muscle strength loss with age in the general population and patients with a chronic inflammatory state. Ageing Res. Rev. 2010, 9, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dam, T.V.; Dalgaard, L.B.; Ringgaard, S.; Johansen, F.T.; Bengtsen, M.B.; Mose, M.; Lauritsen, K.M.; Ørtenblad, N.; Gravholt, C.H.; Hansen, M. Transdermal Estrogen Therapy Improves Gains in Skeletal Muscle Mass After 12 Weeks of Resistance Training in Early Postmenopausal Women. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 596130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landi, F.; Calvani, R.; Martone, A.M.; Salini, S.; Zazzara, M.B.; Candeloro, M.; Coelho-Junior, H.J.; Tosato, M.; Picca, A.; Marzetti, E. Normative values of muscle strength across ages in a ‘real world’ population: Results from the longevity check-up 7+ project. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2020, 11, 1562–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijlsma, A.Y.; Meskers, C.; Ling, C.H.Y.; Narici, M.; Kurrle, S.E.; Cameron, I.D.; Westendorp, R.G.J.; Maier, A.B. Defining sarcopenia: The impact of different diagnostic criteria on the prevalence of sarcopenia in a large middle aged cohort. Age 2013, 35, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, B.; Hassan, E.B.; Brennan-Olsen, S.; Vogrin, S.; Bird, S.; Zanker, J.; Phu, S.; Meerkin, J.D.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Duque, G. Body composition reference ranges in community-dwelling adults using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry: The Australian Body Composition (ABC) Study. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2021, 12, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, L.C.C.; Vaz-Gonçalves, L.; Schincaglia, R.M.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Prado, C.M.; de Oliveira, E.P.; Mota, J.P. Sex and population-specific cutoff values of muscle quality index: Results from NHANES 2011–2014. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 1328–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Jiang, J.; Fu, H.; Zhang, W.; Yang, L.; Yang, M. Malnutrition in Relation to Muscle Mass, Muscle Quality, and Muscle Strength in Hospitalized Older Adults. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2022, 23, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Suzuki, T.; Kim, M.; Kojima, N.; Yoshida, Y.; Hirano, H.; Saito, K.; Iwasa, H.; Shimada, H.; Hosoi, E.; et al. Incidence and Predictors of Sarcopenia Onset in Community-Dwelling Elderly Japanese Women: 4-Year Follow-Up Study. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2015, 16, 85.e1–85.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, C.K.; Lapidus, J.A.; Cawthon, P.M.; Dam, T.-T.L.; Sakai, L.Y.; Marshall, L.M.; Osteoporotic Fractures in Men (MrOS) Research Group. Serum albumin in relation to change in muscle mass, muscle strength, and muscle power in older men. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2012, 60, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, J.C.K. Sexual dimorphism of body composition. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 21, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, R.; Tomlinson, D.; Hamer, M.; Pereira, S.M.P. Lifetime body mass index and grip strength at age 46 years: The 1970 British Cohort Study. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 1995–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, R.; Cooper, R.; Sayer, A.A.; Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Cooper, C.; Deary, I.J.; Demakakos, P.; Gallacher, J.; Martin, R.M.; McNeill, G.; et al. Body mass index, muscle strength and physical performance in older adults from eight cohort studies: The HALCyon programme. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceglia, L. Vitamin D and skeletal muscle tissue and function. Mol. Asp. Med. 2008, 29, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.; Blizzard, L.; Fell, J.; Ding, C.; Winzenberg, T.; Jones, G. A prospective study of the associations between 25-hydroxy-vitamin D, sarcopenia progression and physical activity in older adults. Clin. Endocrinol. 2010, 73, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceglia, L.; Morais, M.D.S.; Park, L.K.; Morris, E.; Harris, S.S.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Fielding, R.A.; Dawson-Hughes, B. Multi-step immunofluorescent analysis of vitamin D receptor loci and myosin heavy chain isoforms in human skeletal muscle. J. Mol. Histol. 2010, 41, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceglia, L.; Niramitmahapanya, S.; da Silva Morais, M.; Rivas, D.A.; Harris, S.S.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.; Fielding, R.A.; Dawson-Hughes, B. A randomized study on the effect of vitamin D₃ supplementation on skeletal muscle morphology and vitamin D receptor concentration in older women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E1927–E1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breen, L.; Stokes, K.A.; Churchward-Venne, T.A.; Moore, D.R.; Baker, S.K.; Smith, K.; Atherton, P.J.; Phillips, S.M. Two weeks of reduced activity decreases leg lean mass and induces "anabolic resistance" of myofibrillar protein synthesis in healthy elderly. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 2604–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| HGS | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Male | Female | |
| Anthropometry and demographics | |||
| Age (year) | 39.85 ± 0.43 | 39.04 ± 0.50 | 40.64 ± 0.43 * |
| Race/Hispanic origin (%) | |||
| Mexican American | 9.58 | 8.75 | 7.39 * |
| Other Hispanic | 6.12 | 5.79 | 5.83 |
| Non-Hispanic White | 64.30 | 66.98 | 67.15 |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 12.05 | 10.66 | 12.10 * |
| Other Race—Including Multi-Racial | 7.95 | 7.82 | 7.54 |
| Weight (kg) | 76.42 ± 0.36 | 81.48 ± 0.44 | 71.51 ± 0.52 * |
| Smoking (%) | |||
| Never | 41.9 | 40.35 | 43.82 |
| Yes | 53.44 | 54.16 | 52.56 |
| Ever | 4.66 | 5.49 | 3.62 * |
| Drinking (%) | |||
| Yes | 42.95 | 46.6 | 39.2 * |
| No | 57.05 | 53.4 | 60.8 * |
| Waist Circumference (cm) | 94.03 ± 0.33 | 95.63 ± 0.39 | 92.46 ± 0.43 * |
| Height (cm) | 165.37 ± 0.21 | 171.31 ± 0.28 | 159.60 ± 0.22 * |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.42 ± 0.14 | 27.12 ± 0.13 | 27.71 ± 0.19 * |
| Physical activity (Mets score) | 3299.16 ± 171.23 | 4395.82 ± 252.01 | 2238.04 ± 169.05 * |
| Vitamin D (nmol/L) | 69.51 ± 0.15 | 66.66 ± 1.00 | 72.28 ± 1.22 * |
| Albumin (g/l) | 43.15 ± 0.06 | 44.14 ± 0.08 | 42.20 ± 0.07 * |
| Energy (kcal) | 2166.14 ± 10.72 | 2489.55 ± 14.36 | 1850.86 ± 11.14 * |
| HGS | β(95%CI) | Detail−p |
|---|---|---|
| Mexican American | ||
| <20 | 2.89 (2.74, 3.04) | |
| >20 | −0.24 (−0.28, −0.20) <0.0001 | −3.14 (−3.28, −2.99) <0.0001 |
| Other Hispanic | ||
| <20 | 2.82 (2.66, 2.98) <0.0001 | |
| >20 | −0.22 (−0.26, −0.18) <0.0001 | −3.04 (−3.22, −2.86) <0.0001 |
| Non−Hispanic White | ||
| <20 | 3.11 (3.01, 3.21) <0.0001 | |
| >20 | −0.22 (−0.24, −0.20) <0.0001 | −3.33 (−3.44, −3.22) <0.0001 |
| Non−Hispanic Black | ||
| <20 | 3.01 (2.89, 3.12) <0.0001 | |
| >20 | −0.21 (−0.24, −0.18) <0.0001 | −3.22 (−3.35, −3.09) <0.0001 |
| Other Race—Including Multi-Racial | ||
| <20 | 2.74 (2.61, 2.87) <0.0001 | |
| >20 | −0.21 (−0.24, −0.18) <0.0001 | −2.94 (−3.09, −2.80) <0.0001 |
| Total | ||
| <20 | 3.01 (2.95, 3.06) <0.0001 | |
| >20 | −0.22 (−0.23, −0.21) <0.0001 | −3.22 (−3.29, −3.16) <0.0001 |
| ALMI | β (95%CI) | Detail−p |
|---|---|---|
| Mexican American | ||
| <21 | 0.3 (0.3, 0.3) <0.00 | |
| >21 | −0.0 (−0.0, −0.0) 0.008 | −0.3 (−0.3, −0.3) <0.001 |
| Other Hispanic | ||
| <21 | 0.3 (0.3, 0.3) <0.001 | |
| >21 | −0.0 (−0.0, −0.0) 0.004 | −0.3 (−0.3, −0.3) <0.001 |
| Non−Hispanic White | ||
| <21 | 0.3 (0.3, 0.3) <0.001 | |
| >21 | −0.0 (−0.0, 0.0) 0.146 | −0.3 (−0.3, −0.3) <0.001 |
| Non−Hispanic Black | ||
| <21 | 0.3 (0.3, 0.3) <0.001 | |
| >21 | −0.0 (−0.0, −0.0) <0.001 | −0.3 (−0.4, −0.3) <0.001 |
| Other Race—Including Multi-Racial | ||
| <21 | 0.3 (0.2, 0.3) <0.001 | |
| >21 | −0.0 (−0.0, −0.0) <0.001 | −0.3 (−0.3, −0.2) <0.001 |
| Total | ||
| <21 | 0.3 (0.3, 0.3) <0.001 | |
| >21 | −0.0 (−0.0, −0.0) <0.001 | −0.3 (−0.3, −0.3) <0.001 |
| Category Variables | Model | Coefficient (B) | p Value | R2 Adjusted | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HGS | Male | 1 | −180.7177 | |||
| Age | −0.22 | <0.0001 | ||||
| BMI | 0.28 | <0.0001 | ||||
| Energy | 0.00057 | 0.0004 | ||||
| Vitamin D | 0.0315 | <0.0001 | ||||
| Constant | 42.868 | <0.0001 | ||||
| Female | 1 | age | −0.15855 | <0.0001 | −173.6247 | |
| BMI | 0.13017 | <0.0001 | ||||
| Energy | 0.0003 | 0.0059 | ||||
| Albumin | 0.04352 | <0.0001 | ||||
| Constant | 30.1887 | <0.0001 | ||||
| Male | 2 | Age | −0.06726 | 0.00167 | −112.4302 | |
| Vitamin D | 0.0236 | 0.00916 | ||||
| FMI | −0.593 | <0.0001 | ||||
| ALMI | 3.00662 | <0.0001 | ||||
| Constant | 24.4784 | <0.0001 | ||||
| Female | 2 | Age | −0.01874 | <0.0001 | −99.7666 | |
| Albumin | 0.04517 | 0.0005 | ||||
| FMI | −0.5168 | <0.0001 | ||||
| ALMI | 2.71318 | <0.0001 | ||||
| Constant | <0.0001 |
| Category Variables | Model | Coefficient (B) | p Value | R2 Adjusted | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALMI | Male | 1 | −36.6993 | |||
| Age | −0.01173 | 0.000034 | ||||
| BMI | 0.18884 | <0.000001 | ||||
| Albumin | 0.05302 | <0.000001 | ||||
| Energy | 0.00034 | <0.000001 | ||||
| Vitamin D | 0.00277 | 0.005891 | ||||
| Constant | 0.02210 | 0.956095 | ||||
| Female | 1 | Age | −0.01173 | 0.000034 | −13.9582 | |
| BMI | 0.18675 | <0.0001 | ||||
| Albumin | 0.01003 | 0.023860 | ||||
| Vitamin D | 0.00255 | 0.000473 | ||||
| Energy | 0.00009 | 0.000007 | ||||
| Physical activity | 0.00001 | 0.041227 | ||||
| Constant | 2.02312 | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, Z.; Gu, J.; Chen, R.; Wang, Q.; Ding, N.; Meng, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Sheng, Z.; Zheng, H. Handgrip Strength and Muscle Quality: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Database. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3184. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093184
Wen Z, Gu J, Chen R, Wang Q, Ding N, Meng L, Wang X, Liu H, Sheng Z, Zheng H. Handgrip Strength and Muscle Quality: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Database. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(9):3184. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093184
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Zhangxin, Jiaxuan Gu, Rong Chen, Qinyi Wang, Na Ding, Lingqiong Meng, Xiangbing Wang, Hong Liu, Zhifeng Sheng, and Houfeng Zheng. 2023. "Handgrip Strength and Muscle Quality: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Database" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 9: 3184. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093184
APA StyleWen, Z., Gu, J., Chen, R., Wang, Q., Ding, N., Meng, L., Wang, X., Liu, H., Sheng, Z., & Zheng, H. (2023). Handgrip Strength and Muscle Quality: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Database. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(9), 3184. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093184








