Unraveling the Link of Altered TGFβ Signaling with Scoliotic Vertebral Malformations in Osteogenesis Imperfecta: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Clinical and Bone Metabolic Characteristics
3. TGFβ Signaling in OI
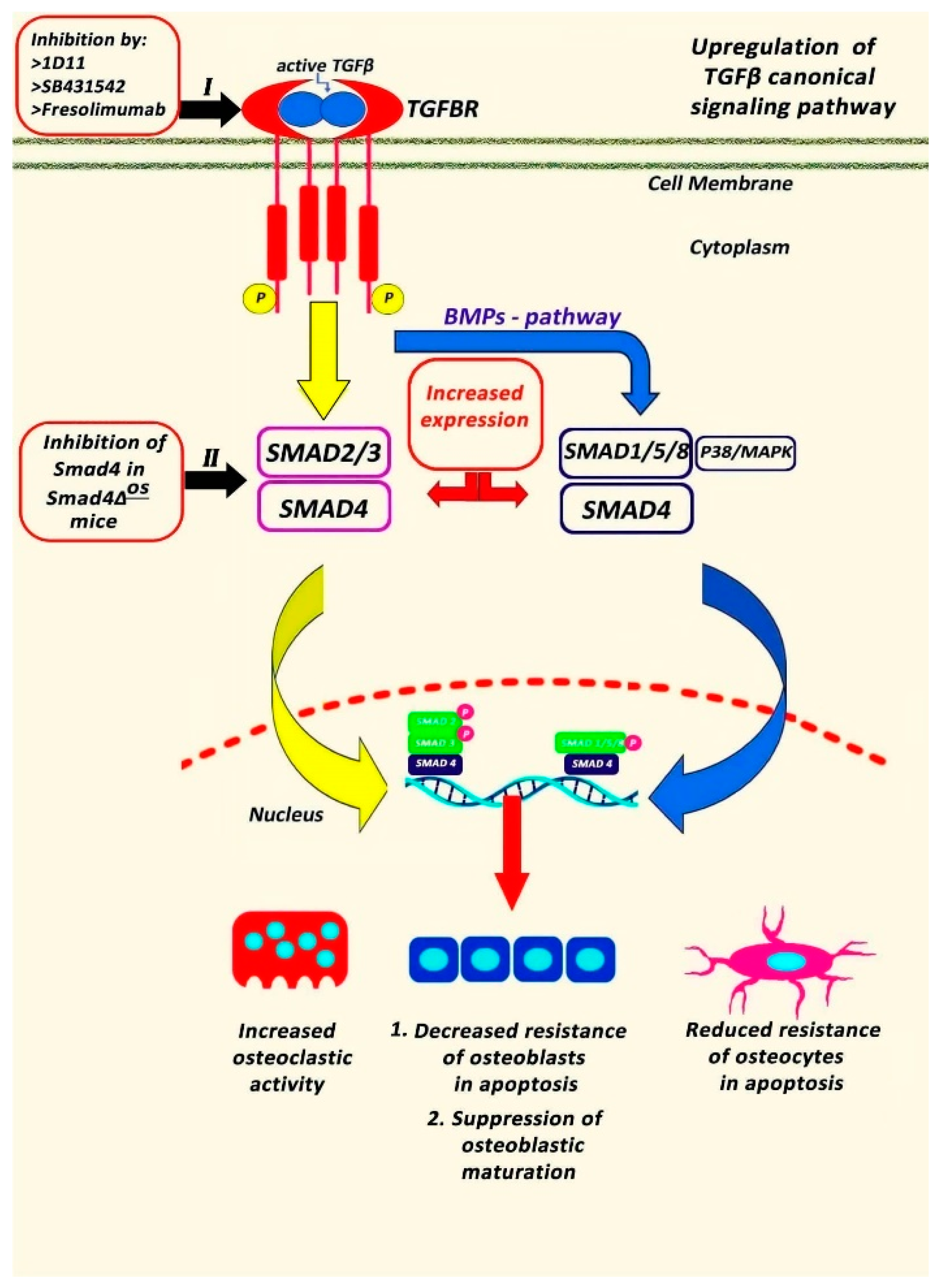
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arponen, H.; Mäkitie, O.; Waltimo-Sirén, J. Association between joint hypermobility, scoliosis, and cranial base anomalies in paediatric Osteogenesis imperfecta patients: A retrospective cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2014, 15, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, J.C.; Forlino, A.; Bächinger, H.P.; Bishop, N.J.; Byers, P.H.; Paepe, A.; Fassier, F.; Fratzl-Zelman, N.; Kozloff, K.M.; Krakow, D.; et al. Osteogenesis imperfecta. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2017, 3, 17052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.E.; Rauch, D.; Glorieux, F.H.; Rauch, F. Pubertal growth in osteogenesis imperfecta caused by pathogenic variants in COL1A1/COL1A2. Genet Med. 2022, 24, 1920–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, W.; Wu, Z.; Wu, N. The genetic implication of scoliosis in osteogenesis imperfecta: A review. J. Spine Surg. 2017, 3, 666–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillence, D.O.; Rimoin, D.L.; Danks, D.M. Clinical variability in osteogenesis imperfecta-variable expressivity or genetic heterogeneity. Birth Defects Orig. Artic. Ser. 1979, 15, 113–129. [Google Scholar]
- Tyurin, A.; Merkuryeva, E.; Zaripova, A.; Markova, T.; Nagornova, T.; Dantsev, I.; Nadyrshina, D.; Zakharova, E.; Khusainova, R. Does the c.-14C>T Mutation in the IFITM5 Gene Provide Identical Phenotypes for Osteogenesis Imperfecta Type V? Data from Russia and a Literature Review. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Shek, H.T.; Dong, Z.; Feng, L.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, S.; Qiu, A.; Dong, L.; Gao, B.; Chen, P.; et al. Retrospective analyses of clinical features in 28 Chinese patients with type V osteogenesis imperfecta: New perspectives in an old issue. Osteoporos. Int. 2023, 34, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldridge, D.; Schwarze, U.; Morello, R.; Lennington, J.; Bertin, T.K.; Pace, J.M.; Pepin, M.G.; Weis, M.; Eyre, D.R.; Walsh, J.; et al. CRTAP and LEPRE1 mutations in recessive osteogenesis imperfecta. Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, A.; Hussain, S.; Bilal, M.; Kausar, M.; Almuzzaini, B.; Abbas, S.; Tanveer, A.; Khan, A.; Siddiqi, S.; Foo, J.N.; et al. Biallelic variants in four genes underlying recessive osteogenesis imperfecta. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2020, 63, 103954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadares, E.R.; Carneiro, T.B.; Santos, P.M.; Oliveira, A.C.; Zabel, B. What is new in genetics and osteogenesis imperfecta classification? J. Pediatr. 2014, 90, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, D.R.; Donaldson, D.H.; Millar, E.A. The spine in osteogenesis imperfecta. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1978, 60, 925–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorefield, W.G., Jr.; Miller, G.R. Aftermath of osteogenesis imperfecta: The disease in adulthood. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1980, 62, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albright, J.A.; Grunt, J.A. Studies of patients with osteogenesis imperfecta. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1971, 53, 1415–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Amor, I.M.; Roughley, P.; Glorieux, F.H.; Rauch, F. Skeletal clinical characteristics of osteogenesis imperfecta caused by haploinsufficiency mutations in COL1A1. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2013, 28, 2001–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, F.; Moffatt, P.; Cheung, M.; Roughley, P.; Lalic, L.; Lund, A.M.; Ramirez, N.; Fahiminiya, S.; Majewski, J.; Glorieux, F.H. Osteogenesis imperfecta type V: Marked phenotypic variability despite the presence of the IFITM5 c.-14C>T mutation in all patients. J. Med. Genet. 2013, 50, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbowski, A.; Schwitalle, M.; Eckardt, A. Scoliosis in patients with osteogenesis imperfecta: A federal nation-wide cross-sectional study. Zentralbl Chir. 1998, 123, 1252–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dijk, F.S.; Sillence, D.O. Osteogenesis imperfecta: Clinical diagnosis, nomenclature and severity assessment. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2014, 164A, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhou, Y.; Tan, Z.; Lin, Y.; Lin, D.L.; Wu, J.; Li, Z.; Shek, H.T.; Wu, J.; Hu, Y.; et al. Scoliosis in osteogenesis imperfecta: Identifying the genetic and non-genetic factors affecting severity and progression from longitudinal data of 290 patients. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2023, 18, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonewald, L.F.; Mundy, G.R. Role of transforming growth factor-beta in bone remodeling. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1990, 250, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, R.; Eto, Y. Involvement of activin in the regulation of bone metabolism. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2001, 180, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, I.W.; Nagamani, S.C.; Nguyen, D.; Grafe, I.; Sutton, V.R.; Gannon, F.H.; Munivez, E.; Jiang, M.M.; Tran, A.; Wallace, M.; et al. Targeting TGF-β for treatment of osteogenesis imperfecta. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e152571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolova, S.; Dikova, M.; Dikov, D.; Djerov, A.; Savov, A.; Kremensky, I.; Loukanov, A. Positive Association between TGFB1 Gene and Susceptibility to Idiopathic Scoliosis in Bulgarian Population. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2018, 2018, 6836092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zieba, J.; Zhang, W.; Chong, J.X.; Forlenza, K.N.; Martin, J.H.; Heard, K.; Grange, D.K.; Butler, M.G.; Kleefstra, T.; Lachman, R.S.; et al. A postnatal role for embryonic myosin revealed by MYH3 mutations that alter TGFβ signaling and cause autosomal dominant spondylocarpotarsal synostosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieba, J.; Forlenza, K.N.; Khatra, J.S.; Sarukhanov, A.; Duran, I.; Rigueur, D.; Lyons, K.M.; Cohn, D.H.; Merrill, A.E.; Krakow, D. TGFβ and BMP Dependent Cell Fate Changes Due to Loss of Filamin B Produces Disc Degeneration and Progressive Vertebral Fusions. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1005936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Sun, W.; Qin, X.; Qiu, Y.; Zhu, Z. The TGFB1 gene is associated with curve severity but not with the development of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A replication study in the Chinese population. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2016, 17, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.Y.; Qin, L.; Simons, M. TGFβ signaling pathways in human health and disease. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1113061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, B.; Russo, R.J.; Dwyer, S.; Malley, K.; Roberts, E.; Serrielo, J.; Piepenhagen, P.; Cummings, S.; Ryan, S.; Zarazinski, C.; et al. Inhibition of TGF-β Increases Bone Volume and Strength in a Mouse Model of Osteogenesis Imperfecta. JBMR Plus. 2021, 5, e10530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.M.; Nagamani, S.C.; Cuthbertson, D.; Campeau, P.M.; Krischer, J.P.; Shapiro, J.R.; Steiner, R.D.; Smith, P.A.; Bober, M.B.; Byers, P.H.; et al. A cross-sectional multicenter study of osteogenesis imperfecta in North America—Results from the linked clinical research centers. Clin. Genet. 2015, 87, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anissipour, A.K.; Hammerberg, K.W.; Caudill, A.; Kostiuk, T.; Tarima, S.; Zhao, H.S.; Krzak, J.J.; Smith, P.A. Behavior of scoliosis during growth in children with osteogenesis imperfecta. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2014, 96, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelbert, R.H.; Uiterwaal, C.S.; van der Hulst, A.; Witjes, B.; Helders, P.J.; Pruijs, H.E. Scoliosis in children with osteogenesis imperfecta: Influence of severity of disease and age of reaching motor milestones. Eur. Spine J. 2003, 12, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wekre, L.L.; Kjensli, A.; Aasand, K.; Falch, J.A.; Eriksen, E.F. Spinal deformities and lung function in adults with osteogenesis imperfecta. Clin. Respir. J. 2014, 8, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, J.R.; Lietman, C.; Grover, M.; Lu, J.T.; Nagamani, S.C.; Dawson, B.C.; Baldridge, D.M.; Bainbridge, M.N.; Cohn, D.H.; Blazo, M.; et al. Phenotypic variability of osteogenesis imperfecta type V caused by an IFITM5 mutation. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2013, 28, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarze, U.; Cundy, T.; Pyott, S.M.; Christiansen, H.E.; Hegde, M.R.; Bank, R.A.; Pals, G.; Ankala, A.; Conneely, K.; Seaver, L.; et al. Mutations in FKBP10, which result in Bruck syndrome and recessive forms of osteogenesis imperfecta, inhibit the hydroxylation of telopeptide lysines in bone collagen. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norimatsu, H.; Mayuzumi, T.; Takahashi, H. The development of the spinal deformities in osteogenesis imperfecta. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1982, 162, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, G.; Kawaguchi, S.; Matsuyama, T.; Yamashita, T. Correlation of scoliotic curvature with Z-score bone mineral density and body mass index in patients with osteogenesis imperfecta. Spine 2007, 32, E488–E494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, M.J.; Kruse, R.W.; Shah, S.A. The Spine in Patients With Osteogenesis Imperfecta. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2017, 25, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verra, W.C.; Pruijs, H.J.; Beek, E.J.; Castelein, R.M. Prevalence of vertebral pars defects (spondylolysis) in a population with osteogenesis imperfecta. Spine 2009, 34, 1399–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatz, D.; Esposito, P.W.; Schroeder, B.; Burke, B.; Lutz, R.; Hasley, B.P. The incidence of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis in children with osteogenesis imperfecta. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2011, 31, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, S.; Kumar, S.J.; Takahashi, H.E.; Homma, M. Vertebral body shape as a predictor of spinal deformity in osteogenesis imperfecta. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1996, 78, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashii, M.; Kanayama, S.; Kitaoka, T.; Makino, T.; Kaito, T.; Iwasaki, M.; Kubota, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Ozono, K.; Yoshikawa, H. Development of scoliosis in young children with osteogenesis imperfecta undergoing intravenous bisphosphonate therapy. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2019, 37, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo, T.; Fassier, F.; Ouellet, J.; Sato, A.; Montpetit, K.; Glorieux, F.H.; Rauch, F. Intravenous Bisphosphonate Therapy of Young Children With Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Skeletal Findings During Follow Up Throughout the Growing Years. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2015, 30, 2150–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, A.; Ouellet, J.; Muneta, T.; Glorieux, F.H.; Rauch, F. Scoliosis in osteogenesis imperfecta caused by COL1A1/COL1A2 mutations—Genotype-phenotype correlations and effect of bisphosphonate treatment. Bone 2016, 86, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, C.; Rauch, F.; Munns, C.F.; Sahebjam, S.; Glorieux, F.H. Vertebral morphometry in children and adolescents with osteogenesis imperfecta: Effect of intravenous pamidronate treatment. Bone 2006, 39, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindahl, K.; Kindmark, A.; Rubin, C.J.; Malmgren, B.; Grigelioniene, G.; Söderhäll, S.; Ljunggren, Ö.; Åström, E. Decreased fracture rate, pharmacogenetics and BMD response in 79 Swedish children with osteogenesis imperfecta types, I.; III and IV treated with Pamidronate. Bone 2016, 87, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Guo, R.; Itoh, S.; Moreno, L.; Rosenthal, E.; Zappitelli, T.; Zirngibl, R.A.; Flenniken, A.; Cole, W.; Grynpas, M.; et al. First mouse model for combined osteogenesis imperfecta and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2014, 29, 1412–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.H.; Ma, S.C.; Wu, C.T.; Chen, P.Q. All pedicle screw fixation technique in correcting severe kyphoscoliosis in an osteogenesis imperfecta patient: A case report. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2006, 19, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelbert, R.H.; Gerver, W.J.; Breslau-Siderius, L.J.; van der Graaf, Y.; Pruijs, H.E.; van Doorne, J.M.; Beemer, F.A.; Helders, P.J. Spinal complications in osteogenesis imperfecta: 47 patients 1-16 years of age. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1998, 69, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton Ede, M.M.; Jones, S.W. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: Evidence for intrinsic factors driving aetiology and progression. Int. Orthop. 2016, 40, 2075–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assoian, R.K.; Komoriya, A.; Meyers, C.A.; Miller, D.M.; Sporn, M.B. Transforming growth factor-beta in human platelets. Identification of a major storage site, purification, and characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 1983, 258, 7155–7160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentry, L.E.; Lioubin, M.N.; Purchio, A.F.; Marquardt, H. Molecular events in the processing of recombinant type 1 pre-pro-transforming growth factor beta to the mature polypeptide. Mol. Cell Biol. 1988, 8, 4162–4168. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, I.B.; Rifkin, D.B. Regulation of the Bioavailability of TGF-β and TGF-β-Related Proteins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a021907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annes, J.P.; Munger, J.S.; Rifkin, D.B. Making sense of latent TGFbeta activation. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116 Pt 2, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.L.; Lee, Y.J.; Shin, J.; Lee, E.; Park, S.O.; McCarty, J.H.; Oh, S.P. TGF-β signaling in endothelial cells, but not neuroepithelial cells, is essential for cerebral vascular development. Lab. Investig. 2011, 91, 1554–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massagué, J. Receptors for the TGF-beta family. Cell 1992, 69, 1067–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.E. Non-Smad pathways in TGF-beta signaling. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grafe, I.; Yang, T.; Alexander, S.; Homan, E.P.; Lietman, C.; Jiang, M.M.; Bertin, T.; Munivez, E.; Chen, Y.; Dawson, B.; et al. Excessive transforming growth factor-β signaling is a common mechanism in osteogenesis imperfecta. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Song, W.; Boulanger, J.H.; Tang, W.; Sabbagh, Y.; Kelley, B.; Gotschall, R.; Ryan, S.; Phillips, L.; Malley, K.; et al. Role of TGF-β in a mouse model of high turnover renal osteodystrophy. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2014, 29, 1141–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balooch, G.; Balooch, M.; Nalla, R.K.; Schilling, S.; Filvaroff, E.H.; Marshall, G.W.; Marshall, S.J.; Ritchie, R.O.; Derynck, R.; Alliston, T. TGF-beta regulates the mechanical properties and composition of bone matrix. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 18813–18818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrand, A.; Romarís, M.; Rasmussen, L.M.; Heinegård, D.; Twardzik, D.R.; Border, W.A.; Ruoslahti, E. Interaction of the small interstitial proteoglycans biglycan, decorin and fibromodulin with transforming growth factor beta. Biochem. J. 1994, 302 Pt 2, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markmann, A.; Hausser, H.; Schönherr, E.; Kresse, H. Influence of decorin expression on transforming growth factor-beta-mediated collagen gel retraction and biglycan induction. Matrix Biol. 2000, 19, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, S.M.; Dimori, M.; Heard-Lipsmeyer, M.E.; Morello, R. The Osteocyte Transcriptome Is Extensively Dysregulated in Mouse Models of Osteogenesis Imperfecta. JBMR Plus. 2019, 3, e10171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forlino, A.; Porter, F.D.; Lee, E.J.; Westphal, H.; Marini, J.C. Use of the Cre/lox recombination system to develop a non-lethal knock-in murine model for osteogenesis imperfecta with an alpha1(I) G349C substitution. Variability in phenotype in BrtlIV mice. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 37923–37931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, Y.J.; Yun, C.Y.; Choi, H.; Ka, S.O.; Kim, J.R.; Park, B.H.; Cho, E.S. Smad4 controls bone homeostasis through regulation of osteoblast/osteocyte viability. Exp. Mol. Med. 2016, 48, e256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Reed, L.A.; Davies, M.V.; Girgenrath, S.; Goad, M.E.; Tomkinson, K.N.; Wright, J.F.; Barker, C.; Ehrmantraut, G.; Holmstrom, J.; et al. Regulation of muscle growth by multiple ligands signaling through activin type II receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 18117–18122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latres, E.; Mastaitis, J.; Fury, W.; Miloscio, L.; Trejos, J.; Pangilinan, J.; Okamoto, H.; Cavino, K.; Na, E.; Papatheodorou, A.; et al. Activin A more prominently regulates muscle mass in primates than does GDF8. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, S.; Hayashi, M.; Komiya, S.; Imamura, T.; Miyazono, K. Endogenous TGF-beta signaling suppresses maturation of osteoblastic mesenchymal cells. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, B.C.; Singhal, V.; Herrera, A.J.; Tomlinson, R.E.; Kim, S.; Faugere, M.C.; Germain-Lee, E.L.; Clemens, T.L.; Lee, S.J.; DiGirolamo, D.J. Activin receptor type 2A (ACVR2A) functions directly in osteoblasts as a negative regulator of bone mass. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 13809–13822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luu, H.H.; Song, W.X.; Luo, X.; Manning, D.; Luo, J.; Deng, Z.L.; Sharff, K.A.; Montag, A.G.; Haydon, R.C.; He, T.C. Distinct roles of bone morphogenetic proteins in osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J. Orthop. Res. 2007, 25, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.L.; Cantrill, L.C.; Schindeler, A.; Little, D.G. Induction of periosteal bone formation by intraosseous BMP-2 injection in a mouse model of osteogenesis imperfecta. J. Child. Orthop. 2019, 13, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donohue, A.K.; Dao, A.; Bobyn, J.D.; Munns, C.F.; Little, D.G.; Schindeler, A. Modeling anabolic and antiresorptive therapies for fracture healing in a mouse model of osteogenesis imperfecta. Orthop. Res. 2023, 41, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchta, K.; Muszewska, A.; Knizewski, L.; Steczkiewicz, K.; Wyrwicz, L.S.; Pawlowski, K.; Rychlewski, L.; Ginalski, K. FAM46 proteins are novel eukaryotic non-canonical poly(A) polymerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 3534–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Tsukano, K.; Hirano, S.; Horikawa, A.; Michiue, T. Fam46a regulates BMP-dependent pre-placodal ectoderm differentiation in Xenopus. Development 2018, 145, dev166710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaspiris, A.; Vasiliadis, E.S.; Tsalimas, G.; Melissaridou, D.; Lianou, I.; Panagopoulos, F.; Katzouraki, G.; Vavourakis, M.; Kolovos, I.; Savvidou, O.D.; et al. Unraveling the Link of Altered TGFβ Signaling with Scoliotic Vertebral Malformations in Osteogenesis Imperfecta: A Comprehensive Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3484. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123484
Kaspiris A, Vasiliadis ES, Tsalimas G, Melissaridou D, Lianou I, Panagopoulos F, Katzouraki G, Vavourakis M, Kolovos I, Savvidou OD, et al. Unraveling the Link of Altered TGFβ Signaling with Scoliotic Vertebral Malformations in Osteogenesis Imperfecta: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(12):3484. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123484
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaspiris, Angelos, Elias S. Vasiliadis, Georgios Tsalimas, Dimitra Melissaridou, Ioanna Lianou, Fotios Panagopoulos, Galateia Katzouraki, Michail Vavourakis, Ioannis Kolovos, Olga D. Savvidou, and et al. 2024. "Unraveling the Link of Altered TGFβ Signaling with Scoliotic Vertebral Malformations in Osteogenesis Imperfecta: A Comprehensive Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 12: 3484. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123484
APA StyleKaspiris, A., Vasiliadis, E. S., Tsalimas, G., Melissaridou, D., Lianou, I., Panagopoulos, F., Katzouraki, G., Vavourakis, M., Kolovos, I., Savvidou, O. D., Papadimitriou, E., & Pneumaticos, S. G. (2024). Unraveling the Link of Altered TGFβ Signaling with Scoliotic Vertebral Malformations in Osteogenesis Imperfecta: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(12), 3484. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123484





