One-Stop Shop: Diagnosis and Treatment of Basal Cell Carcinoma in One Step
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. One-Stop Shop
2.1. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
2.1.1. Technical Details
2.1.2. Experiences with OCT
- In vivo
- Ex vivo
2.2. Reflectance Confocal Microscopy (RCM)
2.2.1. Technical Details
2.2.2. Experiences with RCM
- In vivo
- Ex vivo
2.3. Line-Field Optical Coherence Tomography (LC-OCT)
2.3.1. Technical Details
2.3.2. Experiences with LC-OCT
- In vivo
- Ex vivo
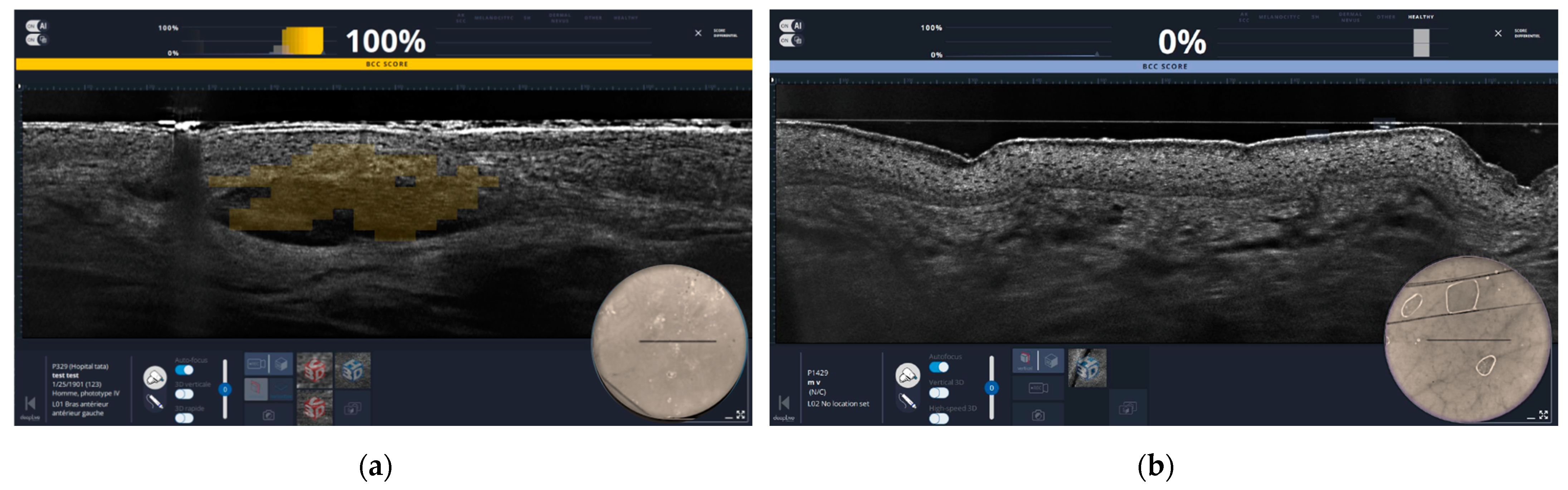
2.4. High Frequency Ultrasound (HFUS)
2.4.1. Technical Details
2.4.2. Experiences with HFUS
- In vivo
- Ex vivo
2.5. Dermoscopy
2.5.1. Technical Details
2.5.2. Experiences with Dermoscopy
- In vivo
- Ex vivo
2.6. Other Tools
2.6.1. Hyperspectral Imaging System (HIS)
2.6.2. Polarization-Enhanced Reflectance and Fluorescence Imaging (PERFI)
2.6.3. Rapid Lump Examination (RLE)
2.6.4. Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy (CLE)
2.6.5. Fluorescence Diagnosis (FD)
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, D.P.; Kus, K.J.B.; Ruiz, E. Basal Cell Carcinoma Review. Hematol. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 33, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Population Ageing, 2019: Highlights. Available online: https://digitallibrary.un.org/record/3846855?v=pdf (accessed on 24 April 2024).
- Peris, K.; Fargnoli, M.C.; Kaufmann, R.; Arenberger, P.; Bastholt, L.; Seguin, N.B.; Bataille, V.; Brochez, L.; Del Marmol, V.; Dummer, R.; et al. European consensus-based interdisciplinary guideline for diagnosis and treatment of basal cell carcinoma-update 2023. Eur. J. Cancer 2023, 192, 113254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzuka, A.G.; Book, S.E. Basal cell carcinoma: Pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, histopathology, and management. Yale J. Boil. Med. 2015, 88, 167–179. [Google Scholar]
- Quazi, S.J.; Aslam, N.; Saleem, H.; Rahman, J.; Khan, S. Surgical Margin of Excision in Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review of Literature. Cureus 2020, 12, e9211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDaniel, B.; Badri, T.; Steele, R.B. Basal Cell Carcinoma. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2024; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, A.M.; Sierra, H.; Rajadhyaksha, M.; Nehal, K. Novel approaches to imaging basal cell carcinoma. Future Oncol. 2015, 11, 3039–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Geer, S.; Frunt, M.; Romero, H.L.; Dellaert, N.P.; Jansen-Vullers, M.H.; Demeyere, T.B.; Neumann, H.A.; Krekels, G.A. One-stop-shop treatment for basal cell carcinoma, part of a new disease management strategy. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2012, 26, 1154–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, J.; Themstrup, L.; Jemec, G.B. Optical coherence tomography in dermatology. G. Ital. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 150, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wan, B.; Ganier, C.; Du-Harpur, X.; Harun, N.; Watt, F.M.; Patalay, R.; Lynch, M.D. Applications and future directions for optical coherence tomography in dermatology. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 184, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschall, S.; Sander, B.; Mogensen, M.; Jørgensen, T.M.; Andersen, P.E. Optical coherence tomography-current technology and applications in clinical and biomedical research. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 2699–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, J.G.; Pitris, C.; Boppart, S.A.; Brezinski, M.E. Optical coherence tomography: An emerging technology for biomedical imaging and optical biopsy. Neoplasia 2000, 2, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivosight dx. Available online: https://de.vivosight.com/products/vivosight-dx/ (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- Vivascope 1500/3000 Data Sheet. Available online: https://vivascope.de/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/VivaScope_Biopsy_InVivo_1500-3000-Datasheet_EN.pdf (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- Vivascope 2500M-G4. Available online: https://www.vivascope.de/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/DS_VS-2500M-G4_287_0219-ohne-Mohs.pdf (accessed on 29 April 2024).
- Ogien, J.; Tavernier, C.; Fischman, S.; Dubois, A. Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography (LC-OCT): Principles and practical use. Ital. J. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 158, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, J.; Barrett, D.L.; Harris, N.; Jeong, J.J.; Yang, X.; Chen, S.C. High-frequency ultrasound in clinical dermatology: A review. Ultrasound J. 2021, 13, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonthalia, S.; Yumeen, S.; Kaliyadan, F. Dermoscopy Overview and Extradiagnostic Applications. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2024; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Eijkenboom, Q.L.; Daxenberger, F.; Gust, C.; Hartmann, D.; Guertler, A.; Steckmeier, S.; Deussing, M.; French, L.E.; Welzel, J.; Schuh, S.; et al. Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography, a novel non-invasive tool for the diagnosis of onychomycosis. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2024, 22, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeltaOne Heine. Available online: https://www.heine.com/de/produkte/dermatoskope-und-digitale-dokumentation/dermatoskope/detail/99957-heine-deltaone-dermatoskop (accessed on 24 April 2024).
- Dermatoskop Illuco. Available online: https://www.dermoscan.de/illuco-ids1100 (accessed on 17 April 2024).
- DUB®Cutis. Available online: https://dermaditum.de/collections/ultraschallsysteme/products/dub-cutis (accessed on 17 April 2024).
- DUB®Cutis Hersteller. Available online: http://www.tpm-online.de/tpm/webneu/index.php/dubcutis.html (accessed on 17 April 2024).
- DermLite DL5. Available online: https://dermlite.com/products/dermlite-dl5 (accessed on 24 April 2024).
- Fuchs, C.S.K.; Ortner, V.K.; Mogensen, M.; Rossi, A.M.; Pellacani, G.; Welzel, J.; Mosterd, K.; Guitera, P.; Nayahangan, L.J.; Johnsson, V.L.; et al. 2021 international consensus statement on optical coherence tomography for basal cell carcinoma: Image characteristics, terminology and educational needs. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomerantz, R.; Zell, D.; McKenzie, G.; Siegel, D.M. Optical Coherence Tomography Used as a Modality to Delineate Basal Cell Carcinoma prior to Mohs Micrographic Surgery. Case Rep. Dermatol. 2011, 3, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akella, S.S.; Lee, J.; May, J.R.; Puyana, C.; Kravets, S.; Dimitropolous, V.; Tsoukas, M.; Manwar, R.; Avanaki, K. Using optical coherence tomography to optimize Mohs micrographic surgery. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, D.; Richardson, T.; Sheth, N.; Orchard, G.; Coleman, A.; Mallipeddi, R. Comparison of ex vivo optical coherence tomography with conventional frozen-section histology for visualizing basal cell carcinoma during Mohs micrographic surgery. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 165, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, S.J.; Osei-Assibey, G.; Patalay, R.; Wakefield, V.; Karner, C. Diagnostic accuracy of reflectance confocal microscopy using VivaScope for detecting and monitoring skin lesions: A systematic review. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 42, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadouch, D.J.; Leeflang, M.M.; Elshot, Y.S.; Longo, C.; Ulrich, M.; van der Wal, A.C.; Wolkerstorfer, A.; Bekkenk, M.W.; de Rie, M.A. Diagnostic accuracy of confocal microscopy imaging vs. punch biopsy for diagnosing and subtyping basal cell carcinoma. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 1641–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.Y.; Lin, J.R.; Cheng, T.T.; Wu, J.Q.; Wu, W.Y. In vivo reflectance confocal microscopy of Basal cell carcinoma: Feasibility of preoperative mapping of cancer margins. Dermatol. Surg. 2012, 38, 1945–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturini, M.; Gualdi, G.; Zanca, A.; Lorenzi, L.; Pellacani, G.; Calzavara-Pinton, P.G. A new approach for presurgical margin assessment by reflectance confocal microscopy of basal cell carcinoma. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 174, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupu, M.; Voiculescu, V.M.; Caruntu, A.; Tebeica, T.; Caruntu, C. Preoperative Evaluation through Dermoscopy and Reflectance Confocal Microscopy of the Lateral Excision Margins for Primary Basal Cell Carcinoma. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richarz, N.A.; Boada, A.; Jaka, A.; Bassas, J.; Ferrándiz, C.; Carrascosa, J.M.; Yélamos, O. Challenges for New Adopters in Pre-Surgical Margin Assessment by Handheld Reflectance Confocal Microscope of Basal Cell Carcinoma; A Prospective Single-center Study. Dermatol. Pr. Concept. 2022, 12, e2022162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleissa, S.; Navarrete-Dechent, C.; Cordova, M.; Sahu, A.; Dusza, S.W.; Phillips, W.; Rossi, A.; Lee, E.; Nehal, K.S. Presurgical evaluation of basal cell carcinoma using combined reflectance confocal microscopy-optical coherence tomography: A prospective study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadouch, D.J.; Elshot, Y.S.; Zupan-Kajcovski, B.; van Haersma de With, A.S.E.; van der Wal, A.C.; Leeflang, M.; Jóźwiak, K.; Wolkerstorfer, A.; Bekkenk, M.W.; Spuls, P.I.; et al. One-stop-shop with confocal microscopy imaging vs. standard care for surgical treatment of basal cell carcinoma: An open-label, noninferiority, randomized controlled multicentre trial. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 177, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scope, A.; Mahmood, U.; Gareau, D.S.; Kenkre, M.; Lieb, J.A.; Nehal, K.S.; Rajadhyaksha, M. In vivo reflectance confocal microscopy of shave biopsy wounds: Feasibility of intraoperative mapping of cancer margins. Br. J. Dermatol. 2010, 163, 1218–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, D.; Krammer, S.; Bachmann, M.R.; Mathemeier, L.; Ruzicka, T.; von Braunmühl, T. Simple 3-criteria-based ex vivo confocal diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma. J. Biophotonics 2018, 11, e201800062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forchhammer, S.; Grunewald, S.; Möhrle, M.; Metzler, G.; Eigentler, T.; Münch, A.K.; Ogrzewalla, H. Diagnosis of Basal Cell Carcinoma with Ex-vivo Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy in a Real-life Setting. Acta Derm.-Venereol. 2023, 103, adv4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Anker, J.; Ribero, S.; Yélamos, O.; García-Herrera, A.; Alos, L.; Alejo, B.; Combalia, M.; Moreno-Ramírez, D.; Malvehy, J.; Puig, S. Basal cell carcinoma characterization using fusion ex vivo confocal microscopy: A promising change in conventional skin histopathology. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 182, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, A.; Levecq, O.; Azimani, H.; Siret, D.; Barut, A.; Suppa, M.; Del Marmol, V.; Malvehy, J.; Cinotti, E.; Rubegni, P.; et al. Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography for high-resolution noninvasive imaging of skin tumors. J. Biomed. Opt. 2018, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gust, C.; Schuh, S.; Welzel, J.; Daxenberger, F.; Hartmann, D.; French, L.E.; Ruini, C.; Sattler, E.C. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography Increases the Diagnostic Accuracy and Confidence for Basal Cell Carcinoma in Equivocal Lesions: A Prospective Study. Cancers 2022, 14, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruini, C.; Schuh, S.; Gust, C.; Kendziora, B.; Frommherz, L.; French, L.E.; Hartmann, D.; Welzel, J.; Sattler, E. Line-field optical coherence tomography: In vivo diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma subtypes compared with histopathology. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 46, 1471–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, K.; Wenande, E.; Ortner, V.K.; Schmidt, G.; Haedersdal, M. Surgical planning with line-field confocal optical coherence tomography for recurrent infiltrative basal cell carcinoma: Visualizing subclinical tumor for margin adjustment. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2024, 22, 462–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradisi, A.; Cornacchia, L.; Cappilli, S.; Abeni, D.; Federico, F.; Di Stefani, A.; Mannino, M.; Peris, K. Preoperative evaluation of high-risk basal cell carcinoma with line-field confocal optical coherence tomography (LC-OCT) reduces Mohs micrographic surgery stage number: A case-control study. EJC Ski. Cancer 2024, 2, 100015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquali, P.; Freites-Martinez, A.; Fortuño-Mar, A. Ex vivo high-frequency ultrasound: A novel proposal for management of surgical margins in patients with non-melanoma skin cancer. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 74, 1278–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozsányi, S.; Boostani, M.; Farkas, K.; Hamilton-Meikle, P.; Varga, N.N.; Szabó, B.; Vasanits, F.; Kuroli, E.; Meznerics, F.A.; Lőrincz, K.; et al. Optically Guided High-Frequency Ultrasound to Differentiate High-Risk Basal Cell Carcinoma Subtypes: A Single-Centre Prospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamas, T.; Dinu, C.; Lenghel, L.M.; Boțan, E.; Tamas, A.; Stoia, S.; Leucuta, D.C.; Bran, S.; Onisor, F.; Băciuț, G.; et al. High-Frequency Ultrasound in Diagnosis and Treatment of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer in the Head and Neck Region. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janowska, A.; Oranges, T.; Granieri, G.; Romanelli, M.; Fidanzi, C.; Iannone, M.; Dini, V. Non-invasive imaging techniques in presurgical margin assessment of basal cell carcinoma: Current evidence. Ski. Res. Technol. 2023, 29, e13271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popadić, M.; Brasanac, D. The use of dermoscopy in distinguishing the histopathological subtypes of basal cell carcinoma: A retrospective, morphological study. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2022, 88, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuki, A.; Takatsuka, S.; Abe, R.; Takenouchi, T. Diagnostic accuracy of dermoscopy for 934 basal cell carcinomas: A single-center retrospective study. J. Dermatol. 2023, 50, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asilian, A.; Momeni, I. Comparison between examination with naked eye, curretage and dermoscopy in determining tumor extension before Mohs micrographic surgery. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2013, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurgen, J.; Gatti, M. Epiluminescence microscopy (dermoscopy) versus visual inspection during Mohs microscopic surgery of infiltrative basal cell carcinoma. Dermatol. Surg. 2012, 38, 1066–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Liu, Z.R.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, M.X.; Wang, X.Q.; Wang, D.G. The effect of dermoscopy in assisting on defining surgical margins of basal cell carcinoma. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caresana, G.; Giardini, R. Dermoscopy-guided surgery in basal cell carcinoma. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2010, 24, 1395–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litaiem, N.; Hayder, F.; Benlagha, I.; Karray, M.; Dziri, C.; Zeglaoui, F. The Use of Dermoscopy in the Delineation of Basal Cell Carcinoma for Mohs Micrographic Surgery: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Dermatol. Pr. Concept. 2022, 12, e2022176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Inatomi, Y.; Nagae, K.; Nakano-Nakamura, M.; Nakahara, T.; Furue, M.; Uchi, H. Narrow-margin excision is a safe, reliable treatment for well-defined, primary pigmented basal cell carcinoma: An analysis of 288 lesions in Japan. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 29, 1828–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruini, C.; Schuh, S.; Sattler, E.; Welzel, J. Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography-Practical applications in dermatology and comparison with established imaging methods. Ski. Res. Technol. 2021, 27, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, C.; Ragazzi, M.; Rajadhyaksha, M.; Nehal, K.; Bennassar, A.; Pellacani, G.; Malvehy Guilera, J. In Vivo and Ex Vivo Confocal Microscopy for Dermatologic and Mohs Surgeons. Dermatol. Clin. 2016, 34, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litaiem, N.; Karray, M.; Jones, M.; Rammeh, S.; Zeglaoui, F. Effectiveness of dermoscopy in the demarcation of surgical margins in slow Mohs surgery. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e14196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete-Dechent, C.; Aleissa, S.; Cordova, M.; Liopyris, K.; Sahu, A.; Rossi, A.M.; Lee, E.H.; Nehal, K.S. Management of complex head-and-neck basal cell carcinomas using a combined reflectance confocal microscopy/optical coherence tomography: A descriptive study. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2021, 313, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftimia, N.; Sahu, A.; Cordova, M.; Maguluri, G.; Gill, M.; Alessi-Fox, C.; Gonzalez, S.; Navarrete-Dechent, C.; Marghoob, A.; Chen, C.J.; et al. The potential utility of integrated reflectance confocal microscopy-optical coherence tomography for guiding triage and therapy of basal cell carcinomas. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 6019–6024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iftimia, N.; Yélamos, O.; Chen, C.J.; Maguluri, G.; Cordova, M.A.; Sahu, A.; Park, J.; Fox, W.; Alessi-Fox, C.; Rajadhyaksha, M. Handheld optical coherence tomography-reflectance confocal microscopy probe for detection of basal cell carcinoma and delineation of margins. J. Biomed. Opt. 2017, 22, 76006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, A.; Yélamos, O.; Iftimia, N.; Cordova, M.; Alessi-Fox, C.; Gill, M.; Maguluri, G.; Dusza, S.W.; Navarrete-Dechent, C.; González, S.; et al. Evaluation of a Combined Reflectance Confocal Microscopy-Optical Coherence Tomography Device for Detection and Depth Assessment of Basal Cell Carcinoma. JAMA Dermatol. 2018, 154, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iftimia, N.; Peterson, G.; Chang, E.W.; Maguluri, G.; Fox, W.; Rajadhyaksha, M. Combined reflectance confocal microscopy-optical coherence tomography for delineation of basal cell carcinoma margins: An ex vivo study. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 16006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, J.; von Braunmühl, T.; Berking, C.; Sattler, E.; Ulrich, M.; Reinhold, U.; Kurzen, H.; Dirschka, T.; Kellner, C.; Schuh, S.; et al. Optical coherence tomography of basal cell carcinoma: Influence of location, subtype, observer variability and image quality on diagnostic performance. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 178, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leemans, G.; Wollenberg, A.; Gutermuth, J. The introduction of bedside ex vivo confocal microscopy during Mohs surgery of basal cell carcinoma: Patient and specialist benefit in an optimized healthcare environment. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 38, e465–e466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, U.; Rajadhyaksha, M.; Jain, M. Combining Reflectance Confocal Microscopy with Optical Coherence Tomography for Noninvasive Diagnosis of Skin Cancers via Image Acquisition. J. Vis. Exp. 2022, 186, e63789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adan, F.; Nelemans, P.J.; Essers, B.A.B.; Brinkhuizen, T.; Dodemont, S.R.P.; Kessels, J.; Quaedvlieg, P.J.F.; Dermont, G.J.; Winnepenninckx, V.J.L.; Abdul Hamid, M.; et al. Optical coherence tomography versus punch biopsy for diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma: A multicentre, randomised, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante di Ruffano, L.; Dinnes, J.; Deeks, J.J.; Chuchu, N.; Bayliss, S.E.; Davenport, C.; Takwoingi, Y.; Godfrey, K.; O’Sullivan, C.; Matin, R.N.; et al. Optical coherence tomography for diagnosing skin cancer in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 12, Cd013189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harst, K.; Welzel, J.; Schuh, S. How efficient is laser therapy for telangiectasias, spider veins, and cherry angiomas?-A study using dynamic optical coherence tomography. Lasers Surg. Med. 2023, 55, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, N.; Schuh, S.; Kindermann, N.; Kästle, R.; Holmes, J.; Welzel, J. Optical coherence tomography for margin definition of basal cell carcinoma before micrographic surgery-recommendations regarding the marking and scanning technique. Ski. Res. Technol. 2018, 24, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinnes, J.; Deeks, J.J.; Saleh, D.; Chuchu, N.; Bayliss, S.E.; Patel, L.; Davenport, C.; Takwoingi, Y.; Godfrey, K.; Matin, R.N.; et al. Reflectance confocal microscopy for diagnosing cutaneous melanoma in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 12, Cd013190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzavara-Pinton, P.; Longo, C.; Venturini, M.; Sala, R.; Pellacani, G. Reflectance confocal microscopy for in vivo skin imaging. Photochem. Photobiol. 2008, 84, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennàssar, A.; Carrera, C.; Puig, S.; Vilalta, A.; Malvehy, J. Fast evaluation of 69 basal cell carcinomas with ex vivo fluorescence confocal microscopy: Criteria description, histopathological correlation, and interobserver agreement. JAMA Dermatol. 2013, 149, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennàssar, A.; Vilata, A.; Puig, S.; Malvehy, J. Ex vivo fluorescence confocal microscopy for fast evaluation of tumour margins during Mohs surgery. Br. J. Dermatol. 2014, 170, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarrete-Dechent, C.; Cordova, M.; Aleissa, S.; Liopyris, K.; Dusza, S.W.; Phillips, W.; Rossi, A.M.; Lee, E.H.; Marghoob, A.A.; Nehal, K.S. Reflectance confocal microscopy confirms residual basal cell carcinoma on clinically negative biopsy sites before Mohs micrographic surgery: A prospective study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 81, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sendín-Martín, M.; Lara-Caro, M.; Harris, U.; Moronta, M.; Rossi, A.; Lee, E.; Chen, C.J.; Nehal, K.; Conejo-Mir Sánchez, J.; Pereyra-Rodríguez, J.J.; et al. Classification of Basal Cell Carcinoma in Ex Vivo Confocal Microscopy Images from Freshly Excised Tissues Using a Deep Learning Algorithm. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 142, 1291–1299.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kose, K.; Fox, C.A.; Rossi, A.; Jain, M.; Cordova, M.; Dusza, S.W.; Ragazzi, M.; Gardini, S.; Moscarella, E.; Diaz, A.; et al. An international 3-center training and reading study to assess basal cell carcinoma surgical margins with ex vivo fluorescence confocal microscopy. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2021, 48, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruini, C.; Vladimirova, G.; Kendziora, B.; Salzer, S.; Ergun, E.; Sattler, E.; French, L.E.; Hartmann, D. Ex-vivo fluorescence confocal microscopy with digital staining for characterizing basal cell carcinoma on frozen sections: A comparison with histology. J. Biophotonics 2021, 14, e202100094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, A.; Levecq, O.; Azimani, H.; Davis, A.; Ogien, J.; Siret, D.; Barut, A. Line-field confocal time-domain optical coherence tomography with dynamic focusing. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 33534–33542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, A.; Xue, W.; Levecq, O.; Bulkin, P.; Coutrot, A.L.; Ogien, J. Mirau-based line-field confocal optical coherence tomography. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 7918–7927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suppa, M.; Fontaine, M.; Dejonckheere, G.; Cinotti, E.; Yélamos, O.; Diet, G.; Tognetti, L.; Miyamoto, M.; Orte Cano, C.; Perez-Anker, J.; et al. Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography of basal cell carcinoma: A descriptive study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suppa, M.; Palmisano, G.; Tognetti, L.; Lenoir, C.; Cappilli, S.; Fontaine, M.; Orte Cano, C.; Diet, G.; Perez-Anker, J.; Schuh, S.; et al. Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography in melanocytic and non-melanocytic skin tumors. Ital. J. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 158, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verzì, A.E.; Micali, G.; Lacarrubba, F. Line-Field Confocal Optical Coherence Tomography May Enhance Monitoring of Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma Treated with Imiquimod 5% Cream: A Pilot Study. Cancers 2021, 13, 4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waszczuk, L.; Ogien, J.; Perrot, J.L.; Dubois, A. Co-localized line-field confocal optical coherence tomography and confocal Raman microspectroscopy for three-dimensional high-resolution morphological and molecular characterization of skin tissues ex vivo. Biomed. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 2467–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid-Wendtner, M.H.; Dill-Müller, D. Ultrasound technology in dermatology. Semin. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2008, 27, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, K.; Okuyama, R.; Uhara, H. Water-based correction fluid is a useful skin marker for determination of the tumor margin of basal cell carcinoma under high-frequency ultrasound. J. Dermatol. 2016, 43, 823–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinnes, J.; Deeks, J.J.; Chuchu, N.; Ferrante di Ruffano, L.; Matin, R.N.; Thomson, D.R.; Wong, K.Y.; Aldridge, R.B.; Abbott, R.; Fawzy, M.; et al. Dermoscopy, with and without visual inspection, for diagnosing melanoma in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 12, Cd011902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinnes, J.; Deeks, J.J.; Chuchu, N.; Matin, R.N.; Wong, K.Y.; Aldridge, R.B.; Durack, A.; Gulati, A.; Chan, S.A.; Johnston, L.; et al. Visual inspection and dermoscopy, alone or in combination, for diagnosing keratinocyte skin cancers in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 12, Cd011901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Salafranca, M.; Ara, M.; Zaballos, P. Dermoscopy in Basal Cell Carcinoma: An Updated Review. Actas Dermo-Sifiliogr. 2021, 112, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, S.; Cecilia, N.; Malvehy, J. Dermoscopic criteria and basal cell carcinoma. G. Ital. Dermatol. Venereol. 2012, 147, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mae, K.; Tsuboi, R.; Irisawa, R.; Sato, T.; Fukushima, N.; Harada, K. Recent reductions in the size of facial pigmented basal cell carcinoma at diagnosis and the surgical margin: A retrospective and comparative study. J. Dermatol. 2021, 48, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, O.; Mimouni, I.; Gdalevich, M.; Marghoob, A.A.; Levi, A.; Hodak, E.; Leshem, Y.A. The diagnostic accuracy of dermoscopy for basal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 1380–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haspeslagh, M.; Hoorens, I.; Degryse, N.; De Wispelaere, I.; Degroote, A.; Van Belle, S.; Verboven, J.; Vossaert, K.; Facchetti, F.; Van Dorpe, J.; et al. Pathologic Evaluation of Skin Tumors with Ex Vivo Dermoscopy with Derm Dotting. JAMA Dermatol. 2017, 153, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno Romero, J.A.; Pérez Muñoz, N.; Campoy Sánchez, A.; Urbano Carrillo, M.; Fernández Figueras, M.T. Derm Dotting: A New Technique That Improves Diagnostic Precision in the Evaluation of Skin Lesions. Actas Dermo-Sifiliogr. 2019, 110, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmivuori, M.; Neittaanmäki, N.; Pölönen, I.; Jeskanen, L.; Snellman, E.; Grönroos, M. Hyperspectral imaging system in the delineation of Ill-defined basal cell carcinomas: A pilot study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aloupogianni, E.; Ichimura, T.; Hamada, M.; Ishikawa, M.; Murakami, T.; Sasaki, A.; Nakamura, K.; Kobayashi, N.; Obi, T. Hyperspectral imaging for tumor segmentation on pigmented skin lesions. J. Biomed. Opt. 2022, 27, 106007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaroslavsky, A.N.; Feng, X.; Neel, V.A. Optical mapping of nonmelanoma skin Cancers-A pilot clinical study. Lasers Surg. Med. 2017, 49, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moehrle, M.; Käflein, L.; Ziefle, S.; Metzler, G. Rapid lump examination (RLE)—A new tool for Mohs surgery? J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2011, 9, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, N.; Schubert, M.; Bauer, J.; Ghoreschi, F.C.; Moehrle, M. Rapid Lump Examination (RLE)—A bedside 3-dimensional microscopy of tumor specimens. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2019, 17, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesslich, R.; Goetz, M.; Vieth, M.; Galle, P.R.; Neurath, M.F. Confocal laser endomicroscopy. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2005, 15, 715–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, A.; Daali, S.; Javed, M.; Fuchs, P.C.; Brockmann, M.; Igressa, A.; Charalampaki, P. Presurgical mapping of basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma by confocal laser endomicroscopy compared to traditional micrographic surgery: A single-centre prospective feasibility study. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2016, 26, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkolyar, E.; Laurie, M.A.; Mach, K.E.; Trivedi, D.R.; Zlatev, D.V.; Chang, T.C.; Metzner, T.J.; Leppert, J.T.; Kao, C.S.; Liao, J.C. Optical biopsy of penile cancer with in vivo confocal laser endomicroscopy. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 37, e801–e809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Song, K.H. Efficacy of fluorescence diagnosis-guided Mohs micrographic surgery for pigmented vs non-pigmented basal cell carcinoma. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2014, 94, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, H.L.; Dellaert, N.P.; van der Geer, S.; Frunt, M.; Jansen-Vullers, M.H.; Krekels, G.A. Admission and capacity planning for the implementation of one-stop-shop in skin cancer treatment using simulation-based optimization. Health Care Manag. Sci. 2013, 16, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takenouchi, T. Key points in dermoscopic diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma and seborrheic keratosis in Japanese. J. Dermatol. 2011, 38, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, T.; Kitoh, M.; Kuriya, N. Characterization of basal cell epithelioma in the Japanese. J. Dermatol. 1982, 9, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogorzelska-Antkowiak, A.; Grzegorczyn, S.; Corneli, P.; Szepietowski, J.C. A Comparative Study of Pigmented and Non-pigmented Basal Cell Carcinoma in Reflectance Confocal Microscopy. In Vivo 2021, 35, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, M.; Sahu, A.; Alessi-Fox, C.; Cordova, M.; Gonzalez, S.; Iftimia, N.; Aleissa, S.; Navarrete-Dechent, C.; Dusza, S.; Rossi, A.; et al. Angulated small nests and cords: Key diagnostic histopathologic features of infiltrative basal cell carcinoma can be identified using integrated reflectance confocal microscopy-optical coherence tomography. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2021, 48, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnier, J.; De Carvalho, N.; Harris, U.; Garfinkel, J.; Saud, A.; Navarrete-Dechent, C.; Liopyris, K.; Reiter, O.; Rubinstien, G.; Iftimia, N.; et al. Combined reflectance confocal microscopy and optical coherence tomography to improve the diagnosis of equivocal lesions for basal cell carcinoma. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 86, 934–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring, H.C.; Israelsen, N.M.; Bang, O.; Haedersdal, M.; Mogensen, M. Potential of contrast agents to enhance in vivo confocal microscopy and optical coherence tomography in dermatology: A review. J. Biophotonics 2019, 12, e201800462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crisan, D.; Wortsman, X.; Alfageme, F.; Catalano, O.; Badea, A.; Scharffetter-Kochanek, K.; Sindrilaru, A.; Crisan, M. Ultrasonography in dermatologic surgery: Revealing the unseen for improved surgical planning. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2022, 20, 913–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widaatalla, Y.; Wolswijk, T.; Adan, F.; Hillen, L.M.; Woodruff, H.C.; Halilaj, I.; Ibrahim, A.; Lambin, P.; Mosterd, K. The application of artificial intelligence in the detection of basal cell carcinoma: A systematic review. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 37, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Device | Method | Image Size/Penetration Depth | Resolution | Medium | Device Costs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VivoSight DxTM (Michelson Diagnostics Ltd., Maidstone, Kent, UK) | OCT | 6 mm × 6 mm/1.5 mm | <10 µm | No medium necessary, plastic spacer | $$ * |
| deepLiveTM (DAMAE Medical, Paris, France) | LC-OCT | Vertical: 1.2 mm × 0.4 mm Horizontal: 1.2 mm × 0.5 mm 3D Block: 1.2 mm × 0.5 mm × 0.5 mm | Up to 1.3 µm | Paraffin oil | $$$ |
| VivaScope® 1500 (VivaScope GmbH, Munich, Germany) | RCM/in vivo | 8 mm × 8 mm/ 0.3 mm | Vertical: <5.0 µm Horizontal: <1.25 µm | Ultrasound gel + paraffin oil | $$–$$$ |
| VivaScope® 3000 (VivaScope GmbH, Munich, Germany) | RCM/in vivo | Unlimited/0.3 mm | Vertical: <5.0 µm Horizontal: <1.25 µm | Ultrasound gel | $$–$$$ |
| VivaScope® 2500M-G4 (VivaScope GmbH, Munich, Germany) | RCM/ex vivo | 25 mm × 25 mm/ 0.2 mm | Vertical: <5.0 µm Horizontal: <1.25 µm (taken picture: 550× magnification possible) | Ultrasound gel on the laser | $$$$ |
| DUB®cutis (tpm taberna pro medicum GmbH, Lüneburg, Germany) | HFUS | 12.8 mm linear/8 mm | Axial: 72 µm with 22 MHz | Ultrasound gel | $$ |
| For example: Illuco IDS-1100 (DermoScan GmbH, Regensburg, Germany), Heine Deltaone Dermatoskop (HEINE Optotechnik GmbH & Co. KG, Gilching, Germany), DermLite® DL5 (DermLite LLC, Aliso Viejo, CA, USA) | Dermatoscope (with or without polarization) | Diameter: 25 mm | Magnification: ×10 | Disinfectant spray, oil or ultrasound gel | $ |
| Method | Role of Experience | Penetration Depth | Resolution | Subtyping | Margin Marking (Lateral Margins) | Margin Marking (Deep Margins) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OCT | +++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | + |
| LC-OCT | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | ++++ | - |
| RCM/in vivo | ++++ | + | ++++ | +++ | +++ | - |
| RCM/ex vivo | ++++ | + | ++++ | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| HFUS | ++ | ++++ | + | + | + | ++++ |
| Dermatoscope | ++ | (+) | (+) | ++ | +–+++ * | - *** |
| RCM-OCT/in vivo ** | +++–++++ | +–+++ | ++++–++ | +++ | +++ | - |
| RCM-OCT/ex vivo ** | +++–++++ | +–+++ | ++++–++ | +++ | +++ | ++ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fünfer, K.; Mozaffari, M.; Mayer, O.; Schlingmann, S.; Welzel, J.; Schuh, S. One-Stop Shop: Diagnosis and Treatment of Basal Cell Carcinoma in One Step. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3830. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133830
Fünfer K, Mozaffari M, Mayer O, Schlingmann S, Welzel J, Schuh S. One-Stop Shop: Diagnosis and Treatment of Basal Cell Carcinoma in One Step. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(13):3830. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133830
Chicago/Turabian StyleFünfer, Kristina, Marco Mozaffari, Oliver Mayer, Sophia Schlingmann, Julia Welzel, and Sandra Schuh. 2024. "One-Stop Shop: Diagnosis and Treatment of Basal Cell Carcinoma in One Step" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 13: 3830. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133830
APA StyleFünfer, K., Mozaffari, M., Mayer, O., Schlingmann, S., Welzel, J., & Schuh, S. (2024). One-Stop Shop: Diagnosis and Treatment of Basal Cell Carcinoma in One Step. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(13), 3830. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133830






