Aortic Regurgitation in Bicuspid Aortic Valve: The Role of Multimodality Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Normal Aortic Valve Anatomy and Nomenclature
1.2. Classification and Phenotypes of BAV
1.3. BAV Syndromes and Associated Cardiovascular Malformations
1.4. Prognosis of BAV
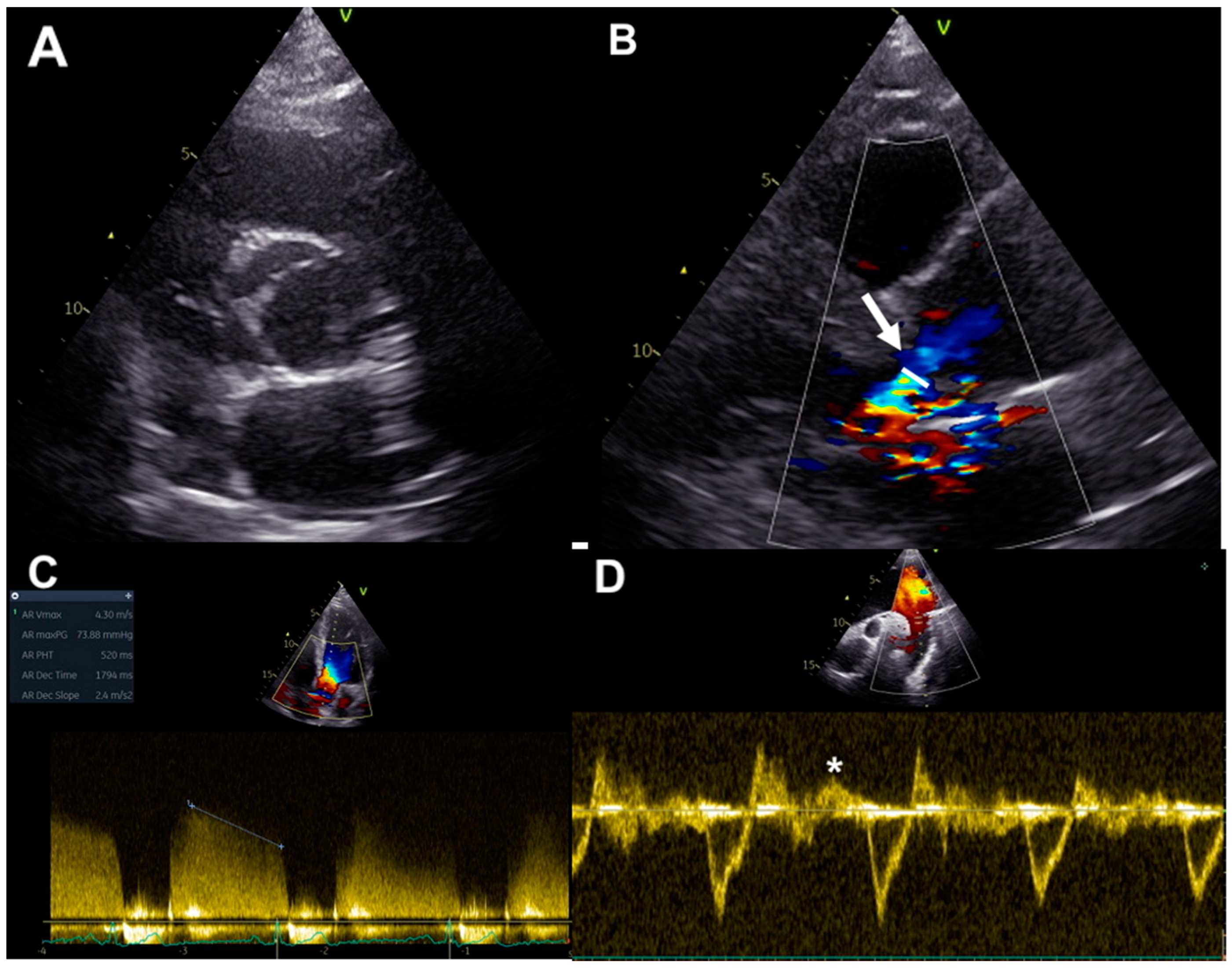
2. Assessment of Chronic AR in BAV: Usefulness and Limitations of Echocardiography
2.1. Qualitative and Quantitative Assessment
2.2. LV and Aortic Size Evaluation
2.3. Strain Imaging
3. Assessment of Chronic AR in BAV: Usefulness and Limitations of CMR
3.1. Quantitative Assessment
3.2. LV Size, Function, and Fibrosis Evaluation
3.3. Myocardial T1 Mapping and Strain Imaging
3.4. Aortic Stiffness
3.5. 4D Flow and Emerging Parameters
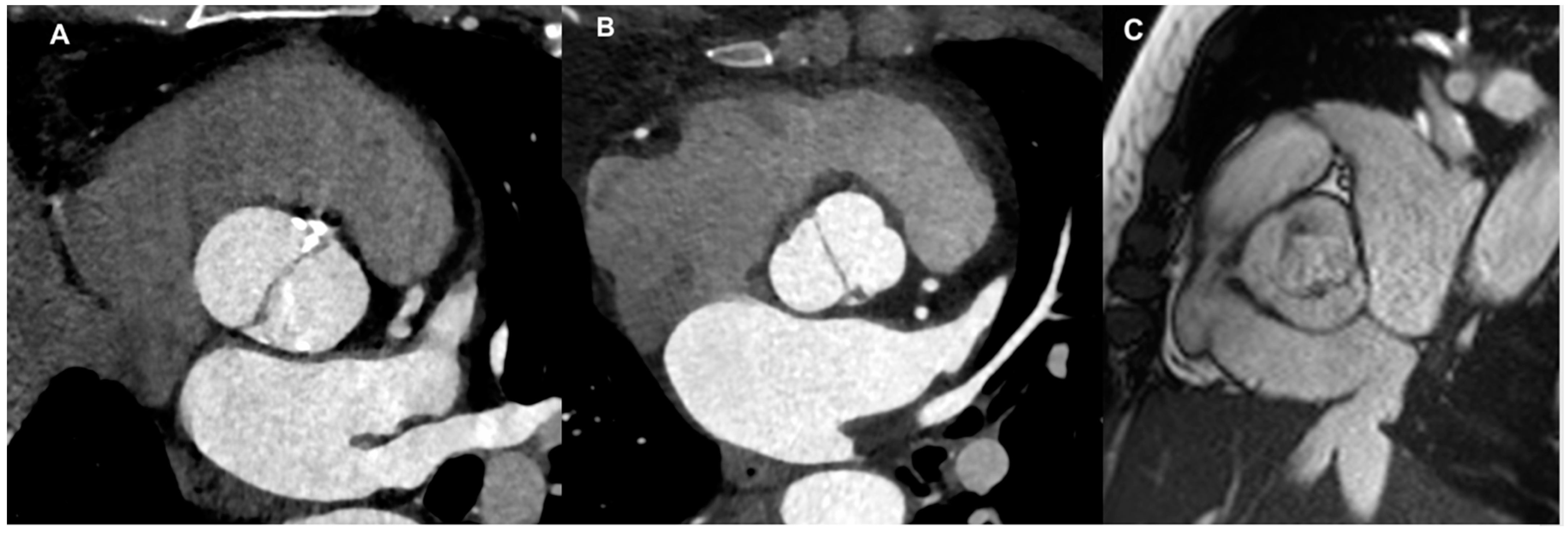
4. Assessment of Chronic Aortic Regurgitation in BAV: Usefulness and Limitations of Cardiac-CT
4.1. Aortic Root and Valve Evaluation
4.2. LV Assessment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BAV | bicuspid aortic valve |
| AR | aortic regurgitation |
| AAo | ascending aorta |
| TTE | transthoracic echocardiography |
| CMR | cardiac MRI |
| LVOT | left ventricle outflow tract |
| L | left |
| R | right |
| N | non coronary |
| CoA | coarctation |
| LV | left ventricular |
| EROA | effective regurgitant orifice area |
| RV | regurgitant volume |
| LVEF | left ventricular ejection fraction |
| PWV | pulse-wave velocity |
| PC-CMR | phase-contrast CMR |
| STE | speckle-tracking echocardiography |
| GLS | global longitudinal strain |
| RF | regurgitant fraction |
| SV | stroke volume |
| LGE | late gadolinium enhancement |
| MDCT | multidetector computed tomography |
| ARO | aortic regurgitant orifice |
References
- Hoffman, J.I.; Kaplan, S. The incidence of congenital heart disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 39, 1890–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilea, I.; Suciu, H.; Tilea, B.; Tatar, C.M.; Ispas, M.; Serban, R.C. Anatomy and function of normal aortic valvular complex. In Calcific Aortic Valve Disease; Aikawa, E., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013; pp. 31–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelena, H.I.; Prakash, S.K.; Della Corte, A.; Bissell, M.M.; Anavekar, N.; Mathieu, P.; Bossé, Y.; Limongelli, G.; Bossone, E.; Benson, D.W.; et al. Bicuspid aortic valve: Identifying knowledge gaps and rising to the challenge from the International Bicuspid Aortic Valve Consortium (BAVCon). Circulation 2014, 129, 2691–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelena, H.I.; Della Corte, A.; Evangelista, A.; Maleszewski, J.J.; Edwards, W.D.; Roman, M.J.; Devereux, R.B.; Fernández, B.; Asch, F.M.; Barker, A.J.; et al. International consensus statement on nomenclature and cassification of congenital bicuspid aortic valve and its aortopathy, for clinical, surgical, interventional and research purposes. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2021, 60, 448–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, H.H.; Schmidtke, C. A classification system for the bicuspid aortic valve from 304 surgical specimens. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2007, 133, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelena, H.I.; Della Corte, A.; Evangelista, A.; Maleszewski, J.J.; Enriquez-Sarano, M.; Bax, J.J.; Otto, C.M.; Schäfers, H.J. Speaking a common language: Introduction to a standard terminology for the bicuspid aortic valve and its aortopathy. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 63, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, S.K.; Bossé, Y.; Muehlschlegel, J.D.; Michelena, H.I.; Limongelli, G.; Della Corte, A.; Pluchinotta, F.R.; Russo, M.G.; Evangelista, A.; Benson, D.W.; et al. A roadmap to investigate the genetic basis of bicuspid aortic valve and its complications: Insights from the International BAVCon (Bicuspid Aortic Valve Consortium). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 64, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Quaegebeur, J.M.; Jonas, R.A.; Weinberg, A.D.; Blackstone, E.H.; Kirklin, J.W. Outcomes in seriouslyill neonates with coarctation of the aorta. A multiinstitutional study. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1994, 108, 841–851, discussion 852-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, J.M.; Gallego, P.; Gonzalez, A.; Aroca, A.; Bret, M.; Mesa, J.M. Risk factors for aortic complications in adults with coarctation of the aorta. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 44, 1641–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doty, D.B. Anomalous origin of the left circumflex coronary artery associated with bicuspid aortic valve. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2001, 122, 842–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.J.; Geffner, M.E.; Lippe, B.M.; Itami, R.M.; Kaplan, S.A.; DiSessa, T.G.; Isabel-Jones, J.B.; Friedman, W.F. Echocardiography reveals a high incidence of bicuspid aortic valve in Turner syndrome. J. Pediatr. 1983, 102, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.D.; Crawford, T.; Magruder, J.T.; Alejo, D.E.; Hibino, N.; Black, J.; Dietz, H.C.; Vricella, L.A.; Cameron, D.E. Cardiovascular operations for Loeys-Dietz syndrome: Intermediate-term results. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2017, 153, 406–412, Erratum in J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2017, 153, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, A.S.; McDonald-McGinn, D.M.; Zackai, E.H.; Goldmuntz, E. Aortic root dilation in patients with 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2009, 149A, 939–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tzemos, N.; Therrien, J.; Yip, J.; Thanassoulis, G.; Tremblay, S.; Jamorski, M.T.; Webb, G.D.; Siu, S.C. Outcomes in adults with bicuspid aortic valves. JAMA 2008, 300, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Corte, A.; Bancone, C.; Buonocore, M.; Dialetto, G.; Covino, F.E.; Manduca, S.; Scognamiglio, G.; D’Oria, V.; De Feo, M. Pattern of ascending aortic dimensions predicts the growth rate of the aorta in patients with bicuspid aortic valve. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 6, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, A.; Dentamaro, I.; Galian, L.; Calvo, F.; Alegret, J.M.; Sanchez, V.; Citro, R.; Moreo, A.; Chirillo, F.; Colonna, P.; et al. Predictors of Ascending Aorta Enlargement and Valvular Dysfunction Progression in Patients with Bicuspid Aortic Valve. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelista Masip, A.; Galian-Gay, L.; Guala, A.; Lopez-Sainz, A.; Teixido-Turà, G.; Ruiz Muñoz, A.; Valente, F.; Gutierrez, L.; Fernandez-Galera, R.; Casas, G.; et al. Unraveling Bicuspid Aortic Valve Enigmas by Multimodality Imaging: Clinical Implications. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahanian, A.; Beyersdorf, F.; Praz, F.; Milojevic, M.; Baldus, S.; Bauersachs, J.; Capodanno, D.; Conradi, L.; De Bonis, M.; De Paulis, R.; et al. 2021 ESC/EACTS Guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 561–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelista, A.; Gallego, P.; Calvo-Iglesias, F.; Bermejo, J.; Robledo-Carmona, J.; Sanchez, V.; Saura, D.; Arnold, R.; Carro, A.; Maldonado, G.; et al. Anatomical and clinical predictors of valve dysfunction and aortic dilation in bicuspid aortic valve disease. Heart 2018, 104, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.-T.; Michelena, H.I.; Maleszewski, J.J.; Schaff, H.V.; Pellikka, P.A. Contemporary Etiologies, Mechanisms, and Surgical Approaches in Pure Native Aortic Regurgitation. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 1158–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelena, H.I.; Katan, O.; Suri, R.M.; Baddour, L.M.; Enriquez-Sarano, M. Incidence of Infective Endocarditis in Patients with Bicuspid Aortic Valves in the Community. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2016, 91, 122–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, C.M.; Nishimura, R.A.; Bonow, R.O.; Carabello, B.A.; Erwin, J.P., III; Gentile, F.; Jneid, H.; Krieger, E.V.; Mack, M.; McLeod, C.; et al. 2020 ACC/AHA Guideline for the Management of Patients with Valvular Heart Disease: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2021, 143, e35–e71, Erratum in Circulation 2021, 143, e228; Erratum in Circulation 2021, 143, e784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, W.K.F.; Delgado, V.; Bax, J.J. Bicuspid Aortic Valve: What to Image in Patients Considered for Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement? Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 10, e005987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancellotti, P.; Tribouilloy, C.; Hagendorff, A.; Popescu, B.A.; Edvardsen, T.; Pierard, L.A.; Badano, L.; Zamorano, J.L. Recommendations for the echocardiographic assessment of native valvular regurgitation: An executive summary from the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 14, 611–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tribouilloy, C.M.; Enriquez-Sarano, M.; Bailey, K.R.; Seward, J.B.; Tajik, A.J. Assessment of severity of aortic regurgitation using the width of the vena contracta: A clinical color Doppler imaging study. Circulation 2000, 102, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewe, S.H.; Delgado, V.; van der Geest, R.; Westenberg, J.J.; Haeck, M.L.; Witkowski, T.G.; Auger, D.; Marsan, N.A.; Holman, E.R.; de Roos, A.; et al. Accuracy of three-dimensional versus two-dimensional echocardiography for quantification of aortic regurgitation and validation by three-dimensional three-directional velocity-encoded magnetic resonance imaging. Am. J. Cardiol. 2013, 112, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mentias, A.; Feng, K.; Alashi, A.; Rodriguez, L.L.; Gillinov, A.M.; Johnston, D.R.; Sabik, J.F.; Svensson, L.G.; Grimm, R.A.; Griffin, B.P.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes in Patients With Aortic Regurgitation and Preserved Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 2144–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, W.K.F.; Vollema, E.M.; Prevedello, F.; Perry, R.; Ng, A.C.T.; Poh, K.K.; Almeida, A.G.; González, A.; Shen, M.; Yeo, T.C.; et al. Prognostic implications of left ventricular global longitudinal strain in patients with bicuspid aortic valve disease and preserved left ventricular ejection fraction. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 21, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, L.; Teixeira, R.; Oliveira-Santos, M.; Barbosa, A.; Martins, R.; Castro, G.; Goncalves, L.; Pego, M. Aortic Valve Disease and Vascular Mechanics: Two-Dimensional Speckle Tracking Echocardiographic Analysis. Echocardiography 2016, 33, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzzarelli, S.; Monney, P.; O’Brien, K.; Faletra, F.; Moccetti, T.; Vogt, P.; Schwitter, J. Quantification of aortic flow by phase-contrast magnetic resonance in patients with bicuspid aortic valve. Eur. Heart J.—Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 15, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longobardo, L.; Carerj, M.L.; Pizzino, G.; Bitto, A.; Piccione, M.C.; Zucco, M.; Oreto, L.; Todaro, M.C.; Calabr, M.P.; Squadrito, F.; et al. Impairment of elastic properties of the aorta in bicuspid aortic valve: Relationship between biomolecular and aortic strain patterns. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 19, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz-Menger, J.; Bluemke, D.A.; Bremerich, J.; Flamm, S.D.; Fogel, M.A.; Friedrich, M.G.; Kim, R.J.; von Knobelsdorff-Brenkenhoff, F.; Kramer, C.M.; Pennell, D.J.; et al. Standardized image interpretation and post-processing in cardiovascular magnetic resonance—2020 update. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reason. 2020, 22, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borer, J.S.; Truter, S.; Herrold, E.M.; Falcone, D.J.; Pena, M.; Carter, J.N.; Dumlao, T.F.; Lee, J.A.; Supino, P.G. Myocardial fibrosis in chronic aortic regurgitation: Molecular and cellular responses to volume overload. Circulation 2002, 105, 1837–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, C.F.; Nigri, M.; Higuchi, M.L.; Pomerantzeff, P.M.; Spina, G.S.; Sampaio, R.O.; Tarasoutchi, F.; Grinberg, M.; Rochitte, C.E. Prognostic significance of myocardial fibrosis quantification by histopathology and magnetic resonance imaging in patients with severe aortic valve disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 56, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomerantz, B.J.; Wollmuth, J.R.; Krock, M.D.; Cupps, B.P.; Moustakidis, P.; Kouchoukos, N.T.; Davila-Roman, V.G.; Pasque, M.K. Myocardial systolic strain is decreased after aortic valve replacement in patients with aortic insufficiency. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2005, 80, 2186–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparrow, P.; Messroghli, D.R.; Reid, S.; Ridgway, J.P.; Bainbridge, G.; Sivananthan, M.U. Myocardial T1 mapping for detection of left ventricular myocardial fibrosis in chronic aortic regurgitation: Pilot study. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2006, 187, W630–W635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Ravenstein, C.D.; Bouzin, C.; Lazam, S.; Boulif, J.; Amzulescu, M.; Melchior, J.; Pasquet, A.; Vancraeynest, D.; Pouleur, A.C.; Vanoverschelde, J.L.; et al. Histological Validation of measurement of diffuse interstitial myocardial fibrosis by myocardial extravascular volume fraction from modified look-locker imaging (MOLLI) T1 mapping at 3 T. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reason. 2015, 17, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungacta, F.F.; Dávila-Román, V.G.; Moulton, M.J.; Moustakidis, P.; Fishman, D.S.; Kouchoukos, N.T.; Pasque, M.K. MRI radiofrequency tissue tagging in patients with aortic insufficiency before and after operation. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1998, 65, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Golfín, C.; Hinojar-Baydes, R.; González-Gómez, A.; Monteagudo, J.M.; Esteban, A.; Alonso-Salinas, G.; Fernández, M.A.; García-Martín, A.; Santoro, C.; Pascual-Izco, M.; et al. Prognostic implications of cardiac magnetic resonance feature tracking derived multidirectional strain in patients with chronic aortic regurgitation. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 5106–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guala, A.; Rodriguez-Palomares, J.; Dux-Santoy, L.; Teixido-Tura, G.; Maldonado, G.; Galian, L.; Huguet, M.; Valente, F.; Gutiérrez, L.; González-Alujas, T.; et al. Influence of Aortic Dilation on the Regional Aortic Stiffness of Bicuspid Aortic Valve Assessed by 4-Dimensional Flow Cardiac Magnetic Resonance. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, 1020–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galian-Gay, L.; Rodríguez-Palomares, J.; Guala, A.; Michelena, H.I.; Evangelista, A. Multimodality imaging in bicuspid aortic valve. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 63, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Palomares, J.F.; Dux-Santoy, L.; Guala, A.; Kale, R.; Maldonado, G.; Teixidó-Turà, G.; Galian, L.; Huguet, M.; Valente, F.; GutiΩrrez, L.; et al. Aortic flow patterns and wall shear stress maps by 4D-flow cardiovascular magnetic resonance in the assessment of aortic dilatation in bicuspid aortic valve disease. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2018, 20, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guala, A.; Evangelista, A.; Teixido-Tura, G.; La Mura, L.; Dux-Santoy, L.; Ruiz-Muñoz, A.; Valente, F.; Galian-Gay, L.; Gutiérrez, L.; González-Alujas, T.; et al. Leaflet fusion length is associated with aortic dilation and flow alterations in non-dysfunctional bicuspid aortic valve. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 9262–9272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzberg, R.W.; Barrett, B.J. Risk of iodinated contrast material-induced nephropathy with intravenous administration. Radiology 2007, 243, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocak, I.; Lacomis, J.M.; Deible, C.R.; Pealer, K.; Parag, Y.; Knollmann, F. The aortic root: Comparison of measurements from ECG-gated CT angiography with transthoracic echocardiography. J. Thorac. Imaging 2009, 24, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, M.J.; Devereux, R.B.; Kramer-Fox, R.; O’Loughlin, J. Two-dimensional echocardiographic aortic root dimensions in normal children and adults. Am. J. Cardiol. 1989, 64, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, C.J.; Maleszewski, J.J.; Araoz, P.A. CT and MR imaging of the aortic valve: Radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics 2012, 32, 1399–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkadhi, H.; Desbiolles, L.; Husmann, L.; Plass, A.; Leschka, S.; Scheffel, H.; Vachenauer, R.; Schepis, T.; Gaemperli, O.; Flohr, T.G.; et al. Aortic regurgitation: Assessment with 64-section CT. Radiology 2007, 245, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jassal, D.S.; Shapiro, M.D.; Neilan, T.G.; Chaithiraphan, V.; Ferencik, M.; Teague, S.D.; Brady, T.J.; Isselbacher, E.M.; Cury, R.C. 64-slice multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) for detection of aortic regurgitation and quantification of severity. Investig. Radiol. 2007, 42, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxt, L.M.; Lipton, M.J.; Kwong, R.Y.; Rybicki, F.; Clouse, M.E. Computed tomography for assessment of cardiac chambers, valves, myocardium and pericardium. Cardiol. Clin. 2003, 21, 561–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Advantages | Limitations | |
|---|---|---|
| Echocardiography | Widely available Cheap No radiation exposure No contrast agents required Information about aortic valve anatomy Visual estimation of AR jet and information about jet eccentricity by color flow Doppler imaging Quantitative assessment and grading of AR Vena contracta evaluation appliable even in eccentric jets Diastolic flow reversal in the descending aorta by pulsed wave Doppler for evaluation of AR severity Information about LV and aortic size Speckle tracking echo provides info about LV deformations in multiple directions and aortic distensibility Three-dimensional echo allows for visualization of the actual shape of the regurgitant aortic orifice | Operator- and window-dependent Irregular shape of the regurgitant orifice and eccentric AR jets in BAV limit quantitative assessment of AR and accuracy in AR grading The ratio between the regurgitant jet width and LV outflow tract diameter is not applicable for irregular-shaped orifices Vena contracta evaluation is not applicable in case of multiple jets The proximal isovelocity surface area method is limited by low feasibility because of difficulty in detection of the flow convergence zone and possible interposition of valve tissue Pressure half time requires adequate Doppler angle and beam alignment; thus, it is hardly applicable in eccentric jets |
| Advantages | Limitations | |
|---|---|---|
| CMR | Acoustic window limitations Multiple imaging planes Accurate and reproducible Visualization of aortic valve anatomy Ventricular volumes/function assessment without geometrical assumptions Qualitative assessment of AR Accurate quantitative assessment of AR (also for eccentric jets) Visualization of aorta in toto Identification of associated abnormalities Detection of myocardial fibrosis | Not widely available Claustrophobia Difficulties in breath-holding Longer time of acquisition Compromised quality in case of arrhythmias Lower temporal resolution Quantitative assessment of aortic regurgitation should be carried out in the LVOT or aortic valve plane when extremely eccentric AR jets are present |
| Advantages | Limitations | |
|---|---|---|
| Cardiac CT | No body habitus/acoustic window limitations Multiple imaging planes Accurate and reproducible High spatial resolution Visualization of aortic valve anatomy Visualization of aorta in toto Identification of associated abnormalities Planimetric measurements of the ARO Ventricular volumes/dimensions assessment Optimal visualization of valve calcification | Use of iodinated contrast (risk of contrast induced nephropathy and allergy) Use of ionizing radiations No qualitative assessment of AR ARO is the only quantitative parameter to be used |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
La Mura, L.; Lembo, M.; Musella, F.; D’Amato, M.; D’Andrea, A.; Izzo, R.; Esposito, G. Aortic Regurgitation in Bicuspid Aortic Valve: The Role of Multimodality Imaging. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3924. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133924
La Mura L, Lembo M, Musella F, D’Amato M, D’Andrea A, Izzo R, Esposito G. Aortic Regurgitation in Bicuspid Aortic Valve: The Role of Multimodality Imaging. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(13):3924. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133924
Chicago/Turabian StyleLa Mura, Lucia, Maria Lembo, Francesca Musella, Marianna D’Amato, Antonello D’Andrea, Raffaele Izzo, and Giovanni Esposito. 2024. "Aortic Regurgitation in Bicuspid Aortic Valve: The Role of Multimodality Imaging" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 13: 3924. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133924
APA StyleLa Mura, L., Lembo, M., Musella, F., D’Amato, M., D’Andrea, A., Izzo, R., & Esposito, G. (2024). Aortic Regurgitation in Bicuspid Aortic Valve: The Role of Multimodality Imaging. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(13), 3924. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133924







