Accuracy Validation of the New Barrett True Axial Length Formula and the Optimized Lens Factor Using Sum-of-Segment Biometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Device Protocol
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Setting
2.4. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.5. Primary Outcome Measures
2.6. Retrospective Analysis Methods
3. Results
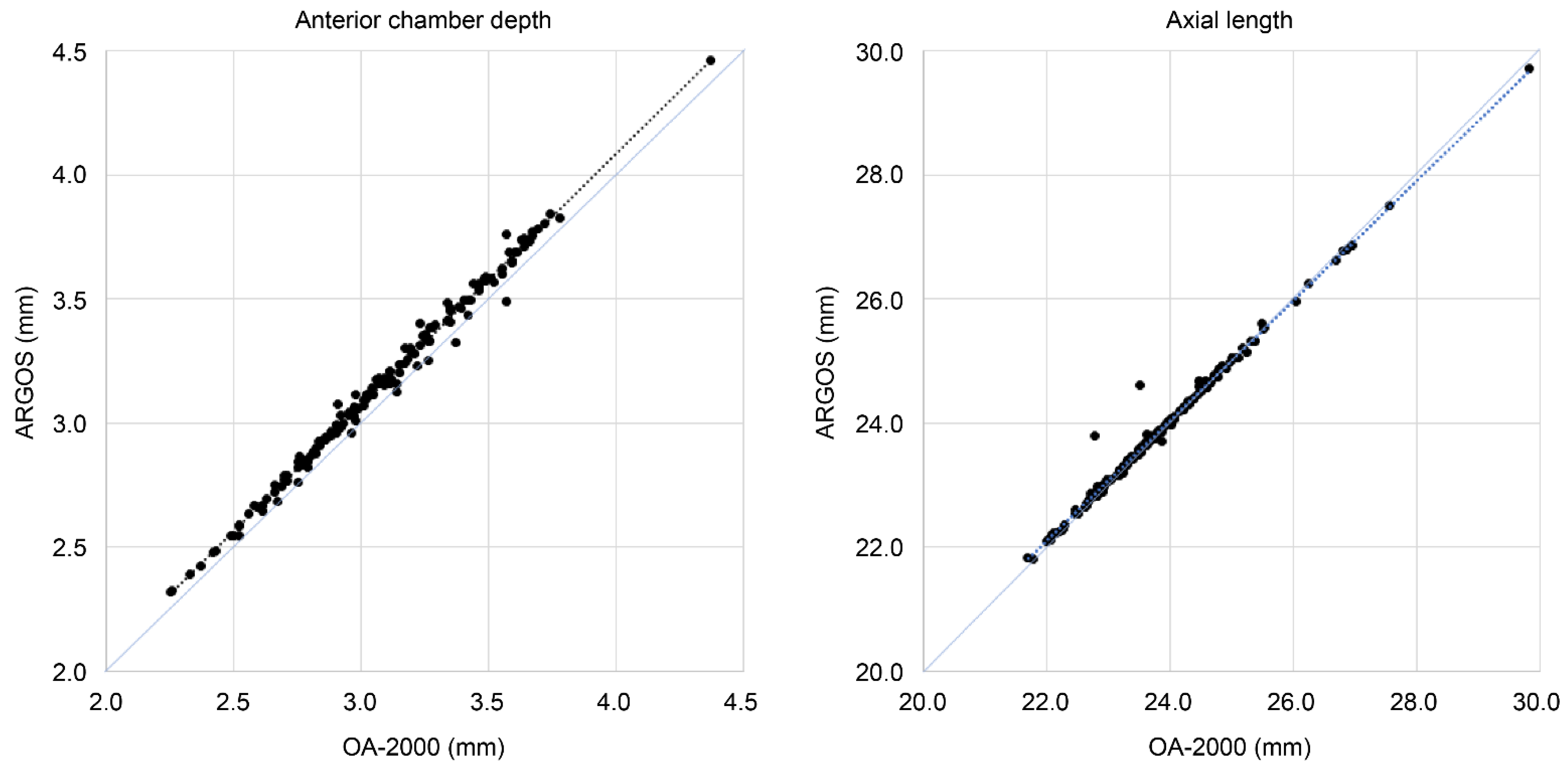
3.1. Participant Characteristics and Measurements
3.2. Analysis of LFs and A Constants
3.3. Comparison of Formula Accuracy
3.4. Additional Measurements
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shammas, H.J.; Taroni, L.; Pellegrini, M.; Shammas, M.C.; Jivrajka, R.V. Accuracy of newer intraocular lens power formulas in short and long eyes using sum-of-segments biometry. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2022, 48, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, Y.; Ayaki, M.; Tamaoki, A.; Tanaka, Y.; Ichikawa, K.; Ichikawa, K. Accuracy of new intraocular lens power calculation formula for short and long eyes using segmental refractive indices. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2024, 50, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blehm, C.; Hall, B. Refractive predictability of a swept source optical coherence tomography biometer in long and short eyes implanted with extended depth of focus intraocular lenses. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2023, 17, 3525–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjerdrum, B.; Gundersen, K.G.; Nilsen, C.; Gundersen, M.; Jensen, P. Refractive predictability and biometry agreement of a combined swept source optical coherence and reflectometry biometer compared to an optical low coherence reflectometry biometer and an SS-OCT Biometer. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2023, 17, 1439–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamaoki, A.; Kojima, T.; Hasegawa, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Kaga, T.; Tanaka, K.; Ichikawa, K. Clinical evaluation of a new swept-source optical coherence biometer that uses individual refractive indices to measure axial length in cataract patients. Ophthalmic Res. 2019, 62, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashiyama, T.; Mori, H.; Nakajima, F.; Ohji, M. Comparison of a new biometer using swept-source optical coherence tomography and a conventional biometer using partial coherence interferometry. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omoto, M.K.; Torii, H.; Masui, S.; Ayaki, M.; Tsubota, K.; Negishi, K. Ocular biometry and refractive outcomes using two swept-source optical coherence tomography-based biometers with segmental or equivalent refractive indices. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.M.; Lim, D.H.; Kim, H.J.; Chung, T.Y. Comparison of two swept-source optical coherence tomography biometers and a partial coherence interferometer. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blehm, C.; Hall, B. Comparing predictive accuracy of a swept source optical coherence tomography biometer and an optical low coherence reflectometry biometer. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2023, 17, 2125–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, G.D. An improved universal theoretical formula for intraocular lens power prediction. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 1993, 19, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montés-Micó, R.; Pastor-Pascual, F.; Ruiz-Mesa, R.; Tañá-Rivero, P. Ocular biometry with swept-source optical coherence tomography. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2021, 47, 802–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Gao, R.; Yu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, W.; McAlinden, C.; Wang, Q. Comprehensive Comparison of Axial Length Measurement With Three Swept-Source OCT-Based Biometers and Partial Coherence Interferometry. J. Refract. Surg. 2019, 35, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retzlaff, J.A.; Sanders, D.R.; Kraff, M.C. Development of the SRK/T intraocular lens implant power calculation formula. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 1990, 16, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffer, K.J.; Aramberri, J.; Haigis, W.; Olsen, T.; Savini, G.; Shammas, H.J.; Bentow, S. Protocols for studies of intraocular lens formula accuracy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 160, 403–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, L.; Mo, E.; Zhu, K.; Zhu, Y.; Feng, K.; Wu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, F.; Gong, X.; et al. The effect of corneal power on the accuracy of 14 IOL power formulas. BMC Ophthalmol. 2024, 24, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stopyra, W.; Langenbucher, A.; Grzybowski, A. Intraocular lens power calculation formulas—A systematic review. Ophthalmol. Ther. 2023, 12, 2881–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshirfar, M.; Sulit, C.A.; Brown, A.H.; Irwin, C.; Ronquillo, Y.C.; Hoopes, P.C. Comparing the accuracy of the Kane, Barrett universal II, hill-radial basis function, emmetropia verifying optical, and Ladas super formula intraocular lens power calculation formulas. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2023, 17, 2643–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K. Evaluation of refractive accuracy of ORA and the factors impacting residual astigmatism in patients implanted with trifocal IOLs during cataract surgery: A retrospective observational study. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2022, 16, 2491–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaylock, J.F.; Hall, B.J. Clinical outcomes of monofocal toric IOLs using digital tracking and intraoperative aberrometry. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2021, 15, 3593–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bernardo, M.; Cione, F.; Capasso, L.; Coppola, A.; Rosa, N. A formula to improve the reliability of optical axial length measurement in IOL power calculation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shammas, H.J.; Shammas, M.C.; Jivrajka, R.V.; Cooke, D.L.; Potvin, R. Effects on IOL power calculation and expected clinical outcomes of axial length measurements based on multiple vs single refractive indices. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2020, 14, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spekreijse, L.S.; Bauer, N.J.C.; van den Biggelaar, F.J.H.M.; Simons, R.W.P.; Veldhuizen, C.A.; Berendschot, T.T.J.M.; Nuijts, R.M.M.A. Predictive accuracy of an intraoperative aberrometry device for a new monofocal intraocular lens. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2022, 48, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Y.; Kang, E.-K.; Kim, H.; Kang, M.-J.; Byun, Y.-S.; Joo, C.-K. Accuracy of swept-source optical coherence tomography based biometry for intraocular lens power calculation: A retrospective cross-sectional study. BMC Ophthalmol. 2019, 19, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Characteristic | Total (n = 156) | CNA0T0 (n = 80) | CNX0Tx (n = 76) | p-Value (Subgroup) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 74.7 ± 7.2 | 73.4 ± 8.2 | 76.1 ± 5.7 | <0.05 |
| Sex (male) | 86 (55.1) | 35 (43.7) | 51 (67.16) | <0.01 |
| ARGOS measurements | ||||
| Average K (D) | 44.22 ± 1.34 | 44.43 ± 1.26 | 44.01 ± 1.39 | 0.051 |
| Cylinder (D) | 1.04 ± 0.65 | 0.68 ± 0.30 | 1.43 ± 0.70 | <0.001 |
| ACD (mm) | 3.17 ± 0.37 | 3.19 ± 0.37 | 3.14 ± 0.38 | 0.394 |
| AL (mm) | 23.84 ± 1.16 | 23.85 ± 1.32 | 23.83 ± 0.98 | 0.449 |
| OA-2000 measurements | ||||
| Average K (D) | 44.10 ± 1.35 | 44.31 ± 1.29 | 43.89 ± 1.37 | 0.068 |
| Cylinder (D) | 1.07 ± 0.69 | 0.66 ± 0.29 | 1.51 ± 0.72 | <0.001 |
| ACD (mm) | 3.09 ± 0.36 | 3.12 ± 0.36 | 3.06 ± 0.37 | 0.375 |
| AL (mm) | 23.79 ± 1.19 | 23.81 ± 1.35 | 23.77 ± 1.01 | 0.605 |
| Postoperative subjective measures | ||||
| Cylinder (D) | 0.48 ± 0.42 | 0.55 ± 0.44 | 0.42 ± 0.39 | <0.05 |
| CVA | –0.046 ± 0.070 | –0.055 ± 0.059 | –0.036 ± 0.078 | <0.001 |
| Parameter | T-AL | AR-B | OA-B | p-Value | P Post Hoc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All cases | |||||
| MAE ± SD (D) | 0.225 ± 0.179 | 0.219 ± 0.168 | 0.242 ± 0.207 | 0.663 | |
| Standard error | 0.0144 | 0.0135 | 0.0166 | ||
| MedAE (D) | 0.189 | 0.185 | 0.196 | ||
| 95% CI (MAE) (D) | 0.197–0.253 | 0.193–0.246 | 0.209–0.274 | ||
| Rate (%) | |||||
| <0.25 D | 60.3 | 62.8 | 59.0 | 0.622 | |
| <0.5 D | 92.9 | 95.5 | 90.4 | 0.08 | |
| CNA0T0 subgroup | |||||
| Lens factor | |||||
| Device Opt | 2.248 | 2.236 | 2.08 | ||
| Zero Opt | 2.262 | 2.287 | 2.160 | ||
| A constant | |||||
| Device Opt | 119.52 | 119.52 | 119.38 | ||
| Zero Opt | 119.55 | 119.55 | 119.34 | ||
| MAE ± SD (D) | 0.243 ± 0.186 | 0.238 ± 0.168 | 0.209 ± 0.187 | <0.05 | <0.05 (A vs. O) |
| Standard error | 0.0208 | 0.0188 | 0.0209 | ||
| MedAE (D) | 0.202 | 0.203 | 0.167 | ||
| 95% CI (MAE) (D) | 0.202–0.285 | 0.200–0.275 | 0.167–0.251 | ||
| Rate (%) | |||||
| <0.25 D | 56.3 | 56.3 | 67.5 | 0.067 | |
| <0.5 D | 90.0 | 95.0 | 92.5 | 0.336 | |
| CNW0Tx subgroup | |||||
| Lens factor | |||||
| Device Opt | 2.289 | 2.246 | 2.07 | ||
| Zero Opt | 2.287 | 2.303 | 2.171 | ||
| A constant | |||||
| Device Opt | 119.57 | 119.57 | 119.37 | ||
| Zero Opt | 119.61 | 119.61 | 119.40 | ||
| MAE ± SD (D) | 0.206 ± 0.171 | 0.200 ± 0.167 | 0.276 ± 0.221 | 0.174 | |
| Standard error | 0.0197 | 0.0192 | 0.0254 | ||
| MedAE (D) | 0.170 | 0.171 | 0.247 | ||
| 95% CI (MAE) (D) | 0.166–0.245 | 0.162–0.238 | 0.225–0.327 | ||
| Rate (%) | |||||
| <0.25 D | 64.5 | 73.7 | 50.0 | <0.001 | <0.001 (A vs. O) |
| <0.5 D | 96.1 | 96.1 | 88.2 | <0.05 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miyamoto, S.; Kamiya, K. Accuracy Validation of the New Barrett True Axial Length Formula and the Optimized Lens Factor Using Sum-of-Segment Biometry. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4639. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164639
Miyamoto S, Kamiya K. Accuracy Validation of the New Barrett True Axial Length Formula and the Optimized Lens Factor Using Sum-of-Segment Biometry. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(16):4639. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164639
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiyamoto, Sumitaka, and Kazutaka Kamiya. 2024. "Accuracy Validation of the New Barrett True Axial Length Formula and the Optimized Lens Factor Using Sum-of-Segment Biometry" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 16: 4639. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164639
APA StyleMiyamoto, S., & Kamiya, K. (2024). Accuracy Validation of the New Barrett True Axial Length Formula and the Optimized Lens Factor Using Sum-of-Segment Biometry. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(16), 4639. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164639







