Radiofrequency Lesion in the Atrial Wall: How Variable Is It? 9.4 Tesla MRI Analysis of Radiofrequency Lesion Volume in a Swine Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
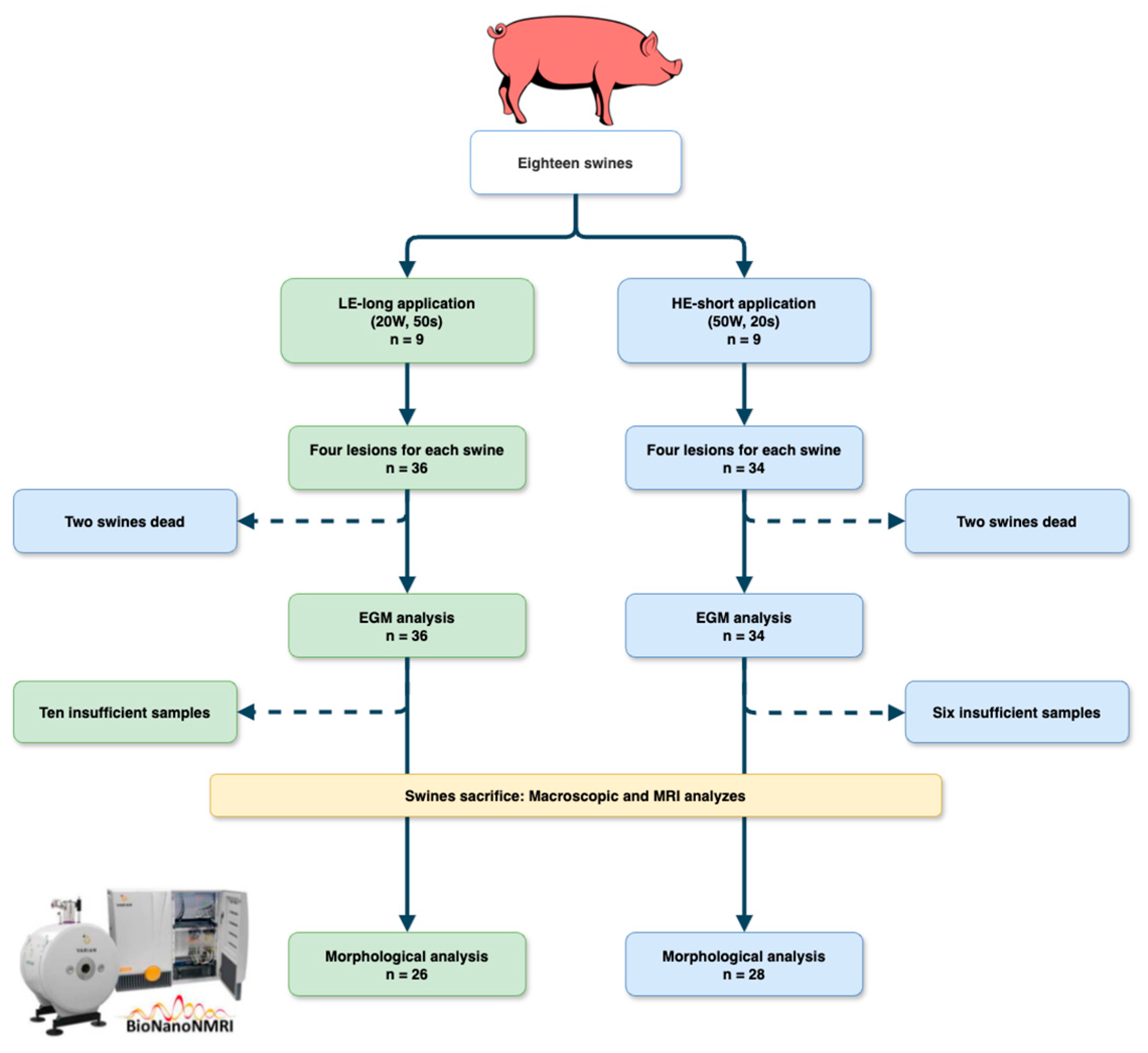
2.1. Study Protocol
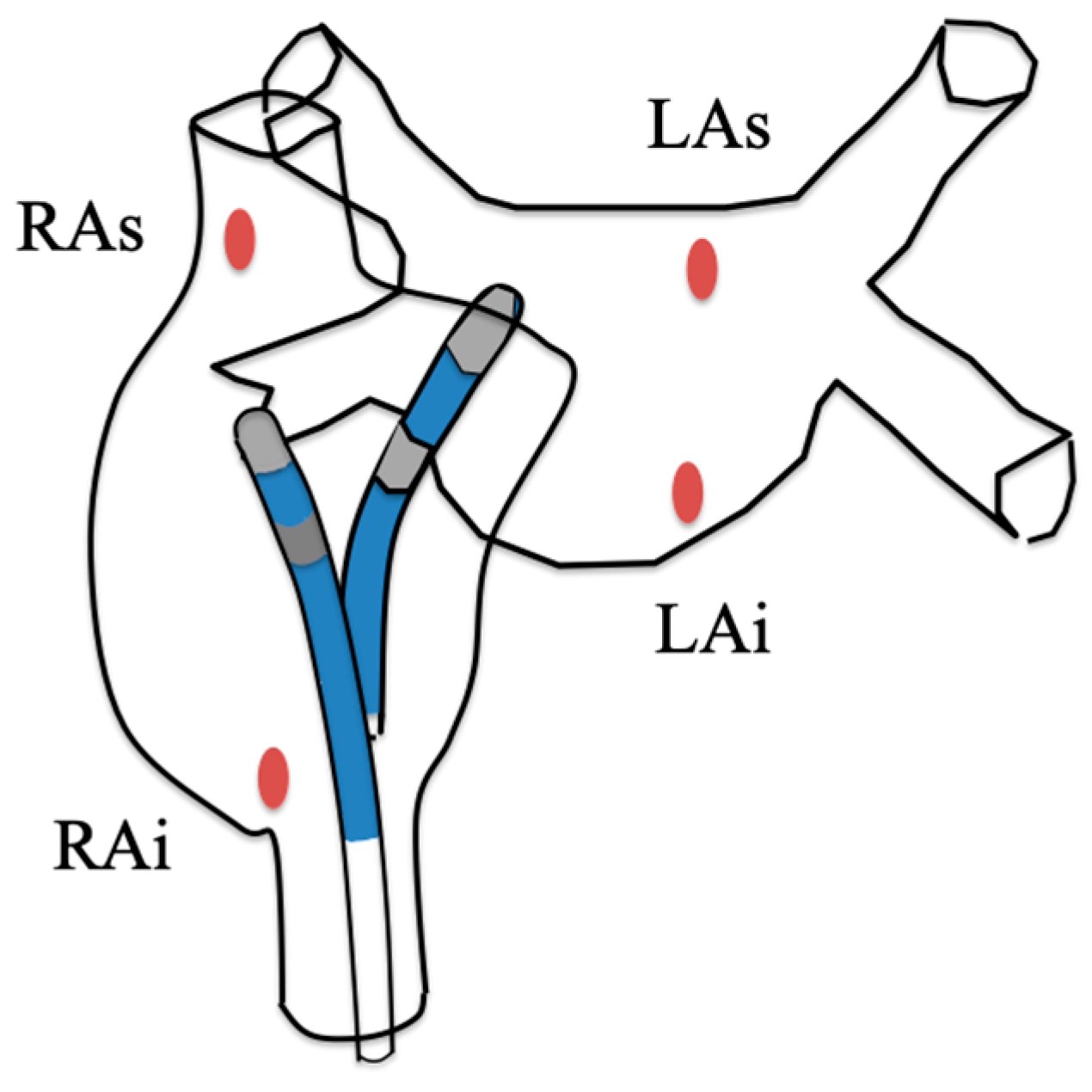
2.2. Ablation Procedure
2.3. Sacrifice and Lesion Volume Measurement
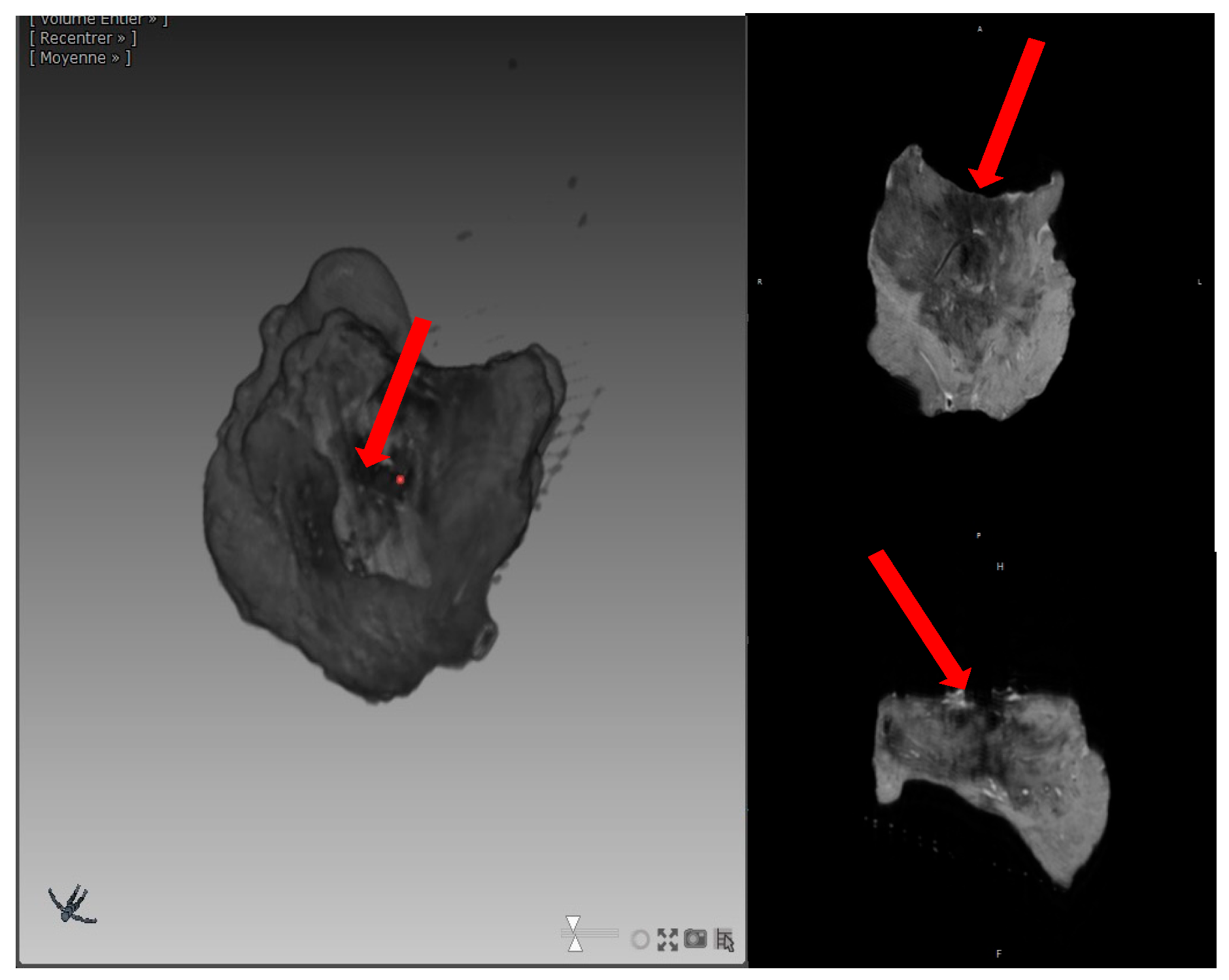
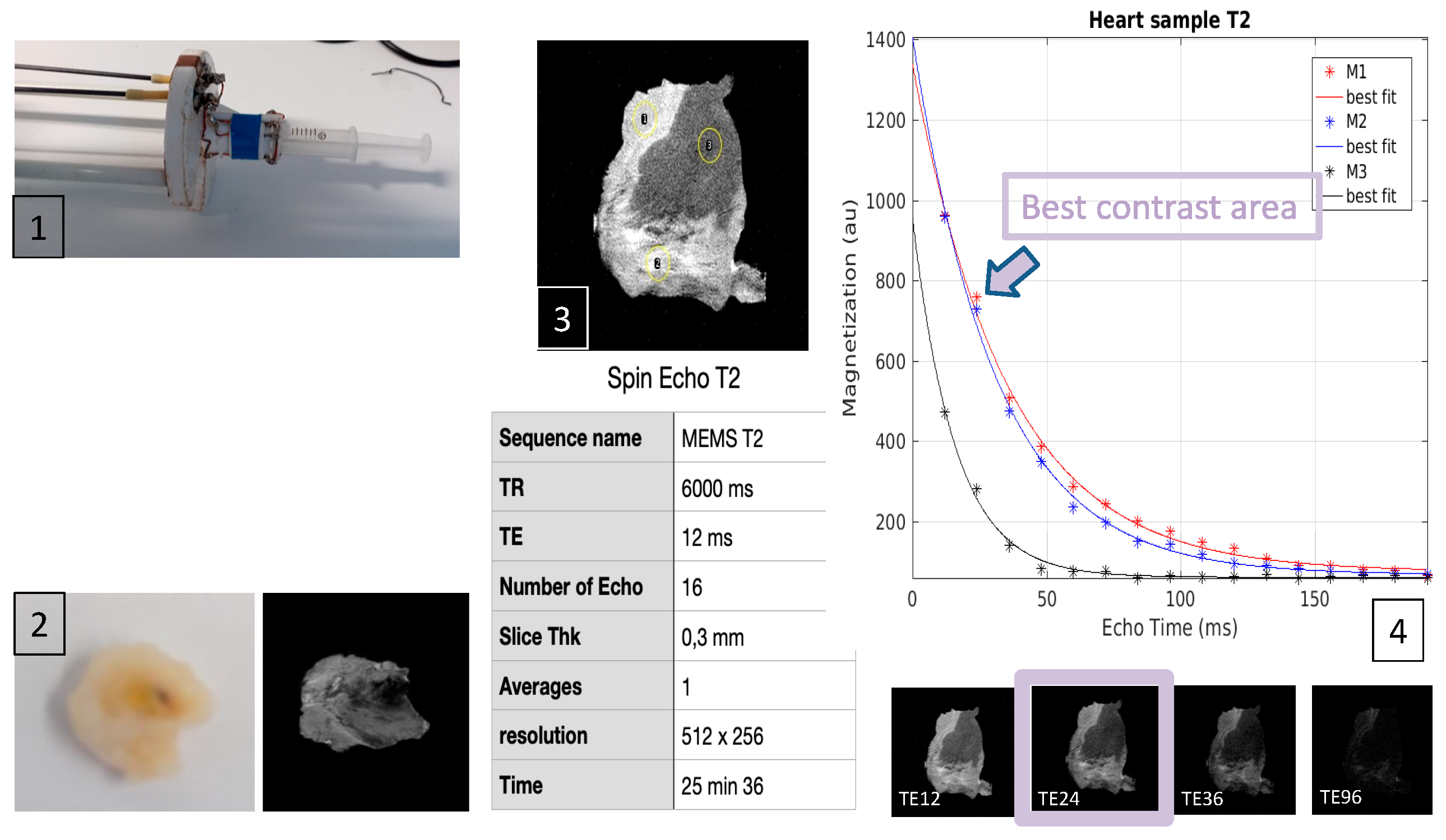
2.4. MRI Processing
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
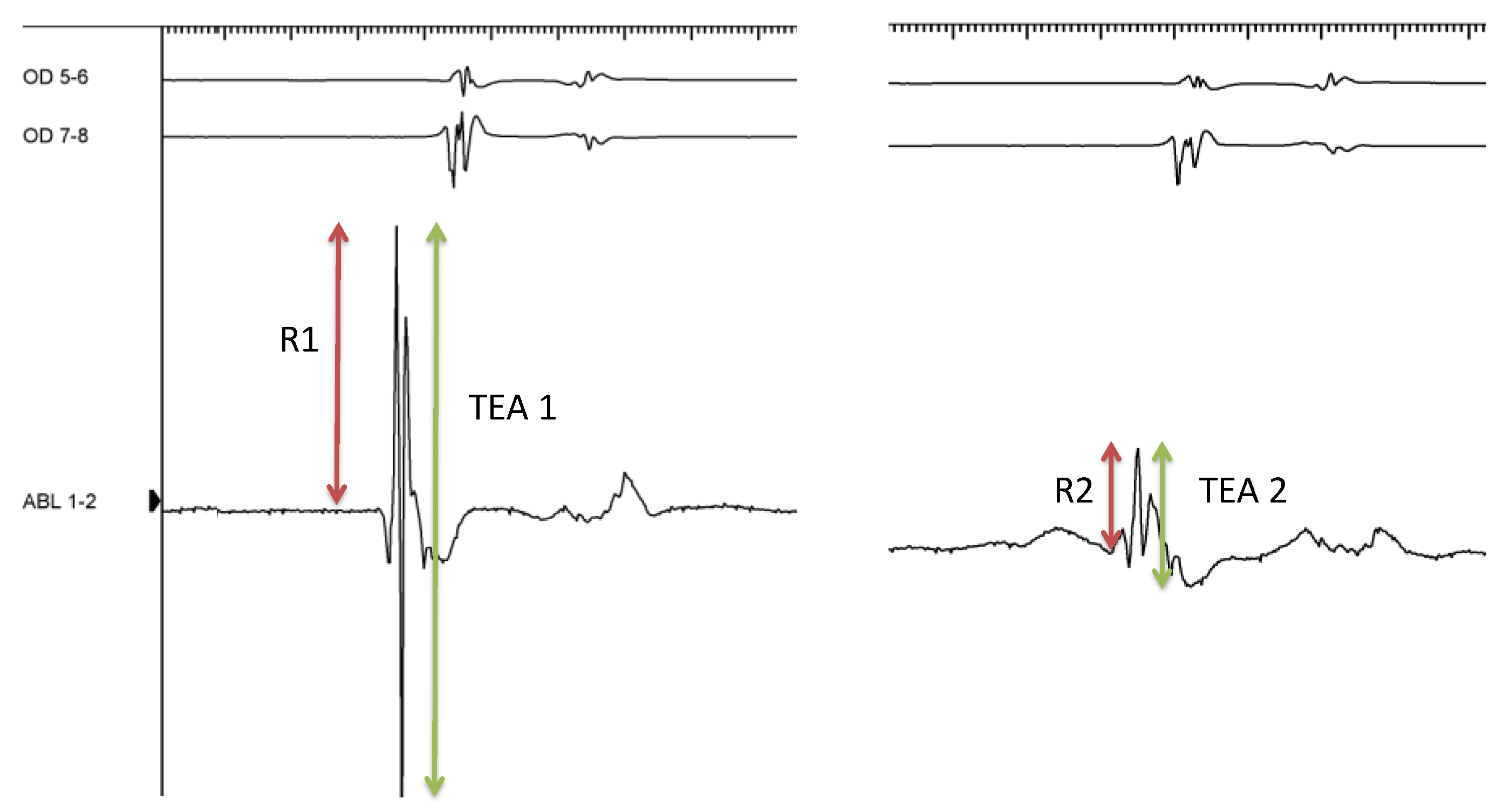
3.1. Ablative Procedure and EGM Analysis
3.2. MRI Volume and Qualitative Analysis
3.3. Complications and Extracardiac Lesions
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.-A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation Developed in Collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the Special Contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- January, C.T.; Wann, L.S.; Calkins, H.; Chen, L.Y.; Cigarroa, J.E.; Cleveland, J.C., Jr.; Ellinor, P.T.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Field, M.E.; Furie, K.L.; et al. 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS Focused Update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society in Collaboration with the Society of Thoracic Surgeons. Circulation 2019, 140, e125–e151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, H. Creation of Continuous and Transmural Radiofrequency Lesions. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2018, 11, e006378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Hajjar, A.H.; Khan, A.A.; Chiu, S.M.; Noujaim, C.; Zhang, Y.; Kholmovski, E.; Ayoub, Y.; Lim, C.H.; Marrouche, N. Predictors of Lesions Contiguity and Transmurality in Canine Ventricular Models After Catheter Ablation. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 920539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Loveday, J.J.; Wynn, G.J.; Gomes, S.; Saeed, Y.; Bonnett, L.J.; Waktare, J.E.; Todd, D.M.; Hall, M.C.; Snowdon, R.L.; et al. Ablation Index, a Novel Marker of Ablation Lesion Quality: Prediction of Pulmonary Vein Reconnection at Repeat Electrophysiology Study and Regional Differences in Target Values. Europace 2017, 19, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, J.; Fish, J.; Harrison, J.; Chubb, H.; Williams, S.E.; Fastl, T.; Corrado, C.; Van Zaen, J.; Gibbs, J.; O’Neill, L.; et al. Lesion Index-Guided Ablation Facilitates Continuous, Transmural, and Durable Lesions in a Porcine Recovery Model. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2018, 11, e005892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzolari, V.; De Mattia, L.; Indiani, S.; Crosato, M.; Furlanetto, A.; Licciardello, C.; Squasi, P.A.M.; Olivari, Z. In Vitro Validation of the Lesion Size Index to Predict Lesion Width and Depth After Irrigated Radiofrequency Ablation in a Porcine Model. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. Clin. Electrophysiol. 2017, 3, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Themistoclakis, S.; Calzolari, V.; De Mattia, L.; China, P.; Russo, A.D.; Fassini, G.; Casella, M.; Caporaso, I.; Indiani, S.; Addis, A.; et al. In Vivo Lesion Index (LSI) Validation in Percutaneous Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2022, 33, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourier, F.; Duchateau, J.; Vlachos, K.; Lam, A.; Martin, C.A.; Takigawa, M.; Kitamura, T.; Frontera, A.; Cheniti, G.; Pambrun, T.; et al. High-Power Short-Duration Versus Standard Radiofrequency Ablation: Insights on Lesion Metrics. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2018, 29, 1570–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemoto, M.; Takami, M.; Fukuzawa, K.; Kiuchi, K.; Kurose, J.; Suehiro, H.; Nagamatsu, Y.; Akita, T.; Nakamura, T.; Sakai, J.; et al. Different Tissue Thermodynamics Between the 40 W and 20 W Radiofrequency Power Settings Under the Same Ablation Index/Lesion Size Index. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2020, 31, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, E.H.; Arpinar, V.E.; Muftuler, L.T.; Stojanovska, J.; Nencka, A.S.; Koch, K.M. Cardiac Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging at 7T: Image Quality Optimization and Ultra-High Field Capabilities. World J. Radiol. 2020, 12, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyerly, S.A.; Bahnson, T.D.; Koontz, J.I.; Bradway, D.P.; Dumont, D.M.; Trahey, G.E.; Wolf, P.D. Intracardiac Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Imaging: A Novel Imaging Method for Intraprocedural Evaluation of Radiofrequency Ablation Lesions. Heart Rhythm 2012, 9, 1855–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dana, N.; Di Biase, L.; Natale, A.; Emelianov, S.; Bouchard, R. In Vitro Photoacoustic Visualization of Myocardial Ablation Lesions. Heart Rhythm 2014, 11, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolandaivelu, A.; Zviman, M.M.; Castro, V.; Lardo, A.C.; Berger, R.D.; Halperin, H.R. Noninvasive Assessment of Tissue Heating During Cardiac Radiofrequency Ablation Using MRI Thermography. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2010, 3, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, M.; Harks, E.; Deladi, S.; Suijver, F.; Barley, M.; van Dusschoten, A.; Fokkenrood, S.; Zuo, F.; Sacher, F.; Hocini, M.; et al. Real-Time Lesion Assessment Using a Novel Combined Ultrasound and Radiofrequency Ablation Catheter. Heart Rhythm 2011, 8, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granier, M.; Winum, P.F.; Granier, M.; Liaud, P.; Cayla, G.; Messner, P.; Pasquie, J.-L.; Schuster, I. Real-Time Atrial Wall Imaging During Radiofrequency Ablation in a Porcine Model. Heart Rhythm 2015, 12, 1827–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttman, M.A.; Tao, S.; Fink, S.; Kolandaivelu, A.; Halperin, H.R.; Herzka, D.A. Non-Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted MRI of Myocardial Radiofrequency Ablation Lesions. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 79, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafoori, E.; Kholmovski, E.G.; Thomas, S.; Silvernagel, J.; Angel, N.; Hu, N.; Dosdall, D.J.; MacLeod, R.; Ranjan, R. Characterization of Gadolinium Contrast Enhancement of Radiofrequency Ablation Lesions in Predicting Edema and Chronic Lesion Size. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2017, 10, e005599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Ishii, R.; Toyoda, Y.; Asami, M.; Takagi, T.; Hashimoto, H.; Hara, H.; Sugi, K.; Moroi, M.; et al. Lesion Size and Adjacent Tissue Damage Assessment with High Power and Short Duration Radiofrequency Ablation: Comparison to Conventional Radiofrequency Ablation Power Setting. Heart Vessel. 2021, 36, 1438–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.Y.; Grimaldi, M.; De Potter, T.; Vijgen, J.M.; Bulava, A.; Duytschaever, M.F.; Martinek, M.; Natale, A.; Knecht, S.; Neuzil, P.; et al. Pulmonary Vein Isolation with Very High Power, Short Duration, Temperature-Controlled Lesions: The QDOT-FAST Trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. Clin. Electrophysiol. 2019, 5, 778–786. [Google Scholar]
- Winkle, R.A.; Mohanty, S.; Patrawala, R.A.; Mead, R.H.; Kong, M.H.; Engel, G.; Salcedo, J.; Trivedi, C.G.; Gianni, C.; Jais, P.; et al. Low Complication Rates Using High Power (45–50 W) for Short Duration for Atrial Fibrillation Ablations. Heart Rhythm 2019, 16, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkle, R.A.; Moskovitz, R.; Mead, R.H.; Engel, G.; Kong, M.H.; Fleming, W.; Salcedo, J.; Patrawala, R.A.; Tranter, J.H.; Shai, I. Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Using Very Short Duration 50 W Ablations and Contact Force Sensing Catheters. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2018, 52, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiagalingam, A.; D’avila, A.; Foley, L.; Guerrero, J.L.; Lambert, H.; Leo, G.; Ruskin, J.N.; Reddy, V.Y. Importance of catheter contact force during irrigated radiofrequency ablation: Evaluation in a porcine ex vivo model using a force-sensing catheter. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2010, 21, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hajjar, A.H.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Mekhael, M.; Noujaim, C.; Dagher, L.; Nedunchezhian, S.; Pottle, C.; Kholmovski, E.; Ayoub, T.; et al. Acute Lesion Imaging in Predicting Chronic Tissue Injury in the Ventricles. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 8, 791217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berte, B.; Cochet, H.; Magat, J.; Naulin, J.; Ghidoli, D.; Pillois, X.; Casassus, F.; Yamashita, S.; Mahida, S.; Derval, N.; et al. Irrigated Needle Ablation Creates Larger and More Transmural Ventricular Lesions Compared with Standard Unipolar Ablation in an Ovine Model. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2015, 8, 1498–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.S.; Schultz, C.; Dang, J.; Alasady, M.; Lau, D.H.; Brooks, A.G.; Wong, C.X.; Roberts-Thomson, K.C.; Young, C.D.; Worthley, M.I.; et al. Time course of inflammation, myocardial injury, and prothrombotic response after radiofrequency catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2014, 7, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kottmaier, M.; Popa, M.; Bourier, F.; Reents, T.; Cifuentes, J.; Semmler, V.; Telishevska, M.; Otgonbayar, U.; Koch-Büttner, K.; Lennerz, C.; et al. Safety and outcome of very high-power short-duration ablation using 70 W for pulmonary vein isolation in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Europace 2020, 22, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavin, H.D.; Leshem, E.; Shapira-Daniels, A.; Sroubek, J.; Barkagan, M.; Haffajee, C.I.; Cooper, J.M.; Anter, E. Impact of High-Power Short-Duration Radiofrequency Ablation on Long-Term Lesion Durability for Atrial Fibrillation Ablation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. Clin. Electrophysiol. 2020, 6, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamatsu, H.; Koyama, J.; Sakai, Y.; Negishi, K.; Hayashi, K.; Tsurugi, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Nakao, K.; Sakamoto, T.; Okumura, K. High-power application is associated with shorter procedure time and higher rate of first-pass pulmonary vein isolation in ablation index-guided atrial fibrillation ablation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2019, 30, 2751–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, L.; El Haddad, M.; Berte, B.; Kobza, R.; Hilfiker, G.; Scherr, D.; Manninger, M.; Wijnmaalen, A.P.; Trines, S.A.; Wielandts, J.-Y.; et al. Very High-Power Ablation for Contiguous Pulmonary Vein Isolation: Results from the Randomized POWER PLUS Trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. Clin. Electrophysiol. 2023, 9, 511–522. [Google Scholar]
- Falasconi, G.; Penela, D.; Soto-Iglesias, D.; Francia, P.; Saglietto, A.; Turturiello, D.; Viveros, D.; Bellido, A.; Alderete, J.; Zaraket, F.; et al. Personalized pulmonary vein isolation with very high-power short-duration lesions guided by left atrial wall thickness: The QDOT-by-LAWT randomized trial. Europace 2024, 26, euae087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciacca, V.; Fink, T.; Körperich, H.; Bergau, L.; Guckel, D.; Nischik, F.; Eckstein, J.; Braun, M.; El Hamriti, M.; Imnadze, G.; et al. Magnetic resonance assessment of left atrial scar formation following a novel very high-power short-duration workflow for atrial fibrillation ablation. Europace 2023, 25, 1392–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskaran, A.; Chik, W.; Pouliopoulos, J.; Nalliah, C.; Qian, P.; Barry, T.; Nadri, F.; Samanta, R.; Tran, Y.; Thomas, S.; et al. Five seconds of 50–60 W radio frequency atrial ablations were transmural and safe: An in vitro mechanistic assessment and force-controlled in vivo validation. Europace 2017, 19, 874–880. [Google Scholar]
- Ravi, V.; Poudyal, A.; Abid, Q.-U.; Larsen, T.; Krishnan, K.; Sharma, P.S.; Trohman, R.G.; Huang, H.D. High-power short duration vs. conventional radiofrequency ablation of atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Europace 2021, 23, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozen, G.; Ptaszek, L.M.; Zilberman, I.; Douglas, V.; Heist, E.K.; Beeckler, C.; Altmann, A.; Ruskin, J.N.; Govari, A.; Mansour, M. Safety and efficacy of delivering high-power short-duration radiofrequency ablation lesions utilizing a novel temperature sensing technology. Europace 2018, 20, f444–f450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parwani, A.S.; Hohendanner, F.; Bode, D.; Kuhlmann, S.; Blaschke, F.; Lacour, P.; Heinzel, F.R.; Pieske, B.; Boldt, L. The force stability of tissue contact and lesion size index during radiofrequency ablation: An ex-vivo study. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2020, 43, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortone, A.; Appetiti, A.; Bouzeman, A.; Maupas, E.; Ciobotaru, V.; Boulenc, J.M.; Pujadas-Berthault, P.; Rioux, P. Unipolar signal modification as a guide for lesion creation during radiofrequency application in the left atrium: Prospective study in humans in the setting of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation catheter ablation. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2013, 6, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badger, T.J.; Oakes, R.S.; Daccarett, M.; Burgon, N.S.; Akoum, N.; Fish, E.N.; Blauer, J.J.; Rao, S.N.; Adjei-Poku, Y.; Kholmovski, E.G.; et al. Temporal left atrial lesion formation after ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 2009, 6, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Low Power (20 W) n = 36 | High Power (50 W) n = 34 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average impedance (ohm) during RF, median (IQR) | 100.5 (96.2–110.7) | 91.5 (89.0–98.5) | <0.001 |
| Temperature (°C), median (IQR) | 34.0 (32.0–35.7) | 37.5 (35.0–40.0) | <0.001 |
| Duration of ablation (seconds), mean (±SD) | 50.0 (±0.17) | 20.0 (±0) | <0.001 |
| FTI, mean (±SD) | 476.28 (±130.20) | 237.0 (±143.11) | <0.001 |
| LSI, mean (±SD) | 4.12 (±0.50) | 5.5 (±1.18) | <0.001 |
| Force (g), median (IQR) | 9.5 (8.0–11) | 10.0 (7.0–13.0) | 0.717 |
| Amplitude bipolar R wave (mV) before ablation, median (IQR) | 0.38 (0.27–0.88) | 0.33 (0.15–0.54) | 0.153 |
| Amplitude bipolar R wave (mV) after ablation, median (IQR) | 0.16 (0.62–0.37) | 0.07 (0.02–0.16) | 0.009 |
| Amplitude unipolar S wave (mV), before ablation, median (IQR) | 0.78 (0.22–1.19) | 0.77 (0.36–1.34) | 0.656 |
| Amplitude unipolar S wave (mV) after ablation, median (IQR) | 0 (0–0.28) | 0 (0–0.40) | 0.811 |
| S-wave disappearance post-RF, n (%) | 19 (61.3) | 16 (55.2) | 0.794 |
| Total EGM amplitude pre-ablation (mV), median (IQR) | 1.38 (0.99–1.92) | 1.03 (0.67–1.43) | 0.052 |
| Total EGM amplitude post-ablation (mV), median (IQR) | 0.72 (0.38–1.18) | 0.42 (0.22–0.62) | <0.001 |
| Low Power (20 W) n = 26 | High Power (50 W) n = 28 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lesion volume (mm3), mean (±SD) | 100.2 (±81.2) | 178.3 (±163.7) | 0.033 |
| Lesion depth (mm), mean (±SD) | 2.78 (±0.85) | 3.17 (±1.60) | 0.290 |
| Beta Standardized Coefficient (95% CI) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|
| High-energy application | 0.403 (8.262; 262.857) | 0.037 |
| Trabeculated surface | −0.072 (−158.591; 108.457) | 0.706 |
| RF application in left atrium | 0.074 (−107.595; 156.891) | 0.708 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cardelli, L.S.; Laumont, T.; Beghian, J.; Achahli, Y.; Cardoso, M.; Bacle, M.; Pasquié, J.-L.; Granier, M. Radiofrequency Lesion in the Atrial Wall: How Variable Is It? 9.4 Tesla MRI Analysis of Radiofrequency Lesion Volume in a Swine Model. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5153. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13175153
Cardelli LS, Laumont T, Beghian J, Achahli Y, Cardoso M, Bacle M, Pasquié J-L, Granier M. Radiofrequency Lesion in the Atrial Wall: How Variable Is It? 9.4 Tesla MRI Analysis of Radiofrequency Lesion Volume in a Swine Model. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(17):5153. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13175153
Chicago/Turabian StyleCardelli, Laura Sofia, Thomas Laumont, July Beghian, Yosra Achahli, Maida Cardoso, Marylène Bacle, Jean-Luc Pasquié, and Mathieu Granier. 2024. "Radiofrequency Lesion in the Atrial Wall: How Variable Is It? 9.4 Tesla MRI Analysis of Radiofrequency Lesion Volume in a Swine Model" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 17: 5153. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13175153
APA StyleCardelli, L. S., Laumont, T., Beghian, J., Achahli, Y., Cardoso, M., Bacle, M., Pasquié, J.-L., & Granier, M. (2024). Radiofrequency Lesion in the Atrial Wall: How Variable Is It? 9.4 Tesla MRI Analysis of Radiofrequency Lesion Volume in a Swine Model. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(17), 5153. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13175153






