Abstract
Background: Perinephric fluid is commonly identified in patients with renal colic and urolithiasis, especially in cases associated with hydronephrosis. However, its clinical relevance, particularly its impact on treatment decisions and prognosis, is not well established. Methods: This retrospective, single-center study included adult patients who presented to the emergency department (ED) with suspected renal colic between January 2021 and October 2023. Patients underwent ultrasound evaluations, which were analyzed for perinephric fluid, hydronephrosis, stone size, and stone location. Data on patient demographics, laboratory results, and clinical outcomes, including the need for urological interventions, were also collected and analyzed. Multivariate logistic regression was used to assess factors associated with perinephric fluid presence. Results: Of the 509 patients included, 200 (39.3%) had perinephric fluid. Hydronephrosis was significantly associated with perinephric fluid (OR: 4.14, p = 0.007), as were stones located in the proximal (OR: 3.06, p = 0.003) and distal ureter (OR: 2.31, p = 0.018). However, sonographic perinephric fluid did not significantly affect the likelihood of urological intervention, in-hospital complications, sepsis, acute kidney injury (AKI), acute kidney disease (AKD), and prolonged hospital stay. Conclusions: Perinephric fluid is a common finding in patients with renal colic and urolithiasis, particularly in cases involving hydronephrosis and ureteral stones. However, despite its prevalence, sonographic perinephric fluid was not significantly associated with the need for urological intervention, longer hospital stays, or worse clinical outcomes. Further prospective studies are required to clarify its clinical implications fully.
1. Introduction
Urolithiasis is a highly common condition, with its prevalence varying from 1 to 20% of the population, depending on geographical regions [1]. Since the early 1990s, the Emergency Department (ED) use by patients presenting with upper tract urolithiasis in the USA has almost doubled to 340 per 100,000 persons despite total ED visits only increasing by 16% [2]. An upper tract stone may completely block the collecting system and compromise adequate urine flow, causing hydronephrosis, which is linked to a variety of complications, including infection, ureteral stricture development, and renal failure [3,4,5]. Such cases are regarded as urologic emergencies and need urgent urinary tract decompression, while definitive removal of the stone should not be completed until the patient’s condition improves [6].
When a diagnosis of nephrolithiasis is clinically suspected, imaging of the kidneys, ureters, and bladder should be performed to support the diagnosis of a stone [1]. Non-contrast computed tomography scan (NCCT) has become the standard of care for diagnosing acute flank pain. However, ultrasound (US) is recommended as the primary diagnostic imaging tool [1], as it is considered an acceptable alternative to NCCT [7,8]. US can directly identify stones located in the kidneys and at the pyelo–ureteral and vesico–ureteric junctions, though it often fails to detect ureteral calculi. Regarding sonographic secondary signs, hydronephrosis is well established in the setting of point of care ultrasound (POCUS) in the ED as an important sign to assess stone size and to predict thirty-day outcomes and the risk of ureteral stricture [3,4,9,10,11]. Perinephric fluid may be an overlooked sonographic finding associated with acute ureteral obstruction, especially when accompanied by hydronephrosis [10], but has also been reported in the setting of procedural complications, pseudoaneurysms, neoplasms, abscess formation, renal laceration with hematoma, and perirenal lymphangiomatosis. There are two main theories in the literature regarding the pathophysiology of perinephric fluid. According to one theory, one of the kidney’s responses to increased pressure in the ureter is the absorption of urine, which then infiltrates the perinephric space along the bridging septa [12]. The other theory suggests that the perinephric fluid collection results from a urinary leak secondary to forniceal rupture. In acute ureteral stone obstruction, a sharp rise in intrapelvic pressure can cause the collecting system to rupture at its weakest point—the fornices [13,14]. To the best of our knowledge, only two studies have shown the correlation between perinephric fluid accumulation and the management of lithiasis [15,16]. The aim of this study is to evaluate the clinical significance of sonographic perinephric fluid collection in patients with renal colic and evidence of urolithiasis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
After the approval of the local Ethics Committee of Fondazione Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli IRCCS, we performed an observational, retrospective, single-center study based on the electronic medical record review of consecutive patients using a prospectively maintained database.
2.2. Patient Recruitment
The recruitment period spanned from January 2021 to October 2023. The inclusion criteria were adult patients (age ≥ 18 years) who presented to the ED with suspected renal colic and underwent US evaluation with a urolithiasis finding. The sonographic evaluation was conducted by experienced radiologists who assessed the presence or the absence of the following parameters: perinephric fluid collection, hydronephrosis, stone size, and stone position. Patients were excluded if they had a final diagnosis other than nephrolithiasis (e.g., pyelonephritis or urinary tract obstruction unrelated to stone disease), if they were pregnant, or if they had a solitary kidney.
2.3. Data Collection
We retrospectively collected data from patient charts, which included baseline demographic and clinical characteristics such as age, sex, body mass index (BMI), comorbidities, previous history of kidney stones or renal colic, initial presentation symptoms, and the presence of fever. Clinical and laboratory data at the time of ED presentation were also recorded, including the diameter of the kidney stones in millimeters, stone location, presence of perinephric fluid, presence of hydronephrosis, and laboratory findings such as creatinine level and leukocytosis, which provided information on renal function and potential infection. Using a curvilinear probe, experienced US radiologists examined the urinary system with a Samsung RS80A US machine. Perinephric fluid was defined as any anechoic stripe within the perirenal space bordered by the renal parenchyma and Gerota’s and Zuckerkandl’s fasciae, not including the anterior or posterior pararenal spaces, or the subcapsular space (Figure 1) [17]. The presence of hydronephrosis was defined as renal pelvic/calyx dilatation. The severity of hydronephrosis was defined according to the renal pelvic diameter (mm): 0–10 mild, 11–20 moderate, and >20 severe. Patients with hydronephrosis upon US without evidence of the cause of obstruction underwent a CT scan to evaluate the presence of a ureteral stone not visible with the US. Additionally, treatment-related data were gathered, including whether patients were discharged home or required hospitalization from the ED, the specific type of intervention performed (such as medical expulsive therapy, ureteral stent placement, nephrostomy tube insertion, or retrograde intrarenal surgery), and the length of hospital stay. For patients with favorable clinical conditions and ureteral stones less than 10 mm, we opted for conservative management and initiated medical expulsive therapy. These patients were discharged from the ED with instructions to return if they experienced recurrent renal colic that did not respond to analgesic therapy or if they developed a fever. Otherwise, they were scheduled for a follow-up urology visit 2 weeks after ED discharge, which included US and bladder exams. Patients with recurrent colic, not responsive to analgesic therapy, or patients with signs and symptoms of infections or compromised renal function were generally treated with immediate surgical intervention, which involved stent or nephrostomy placement, or ureteroscopy when feasible.
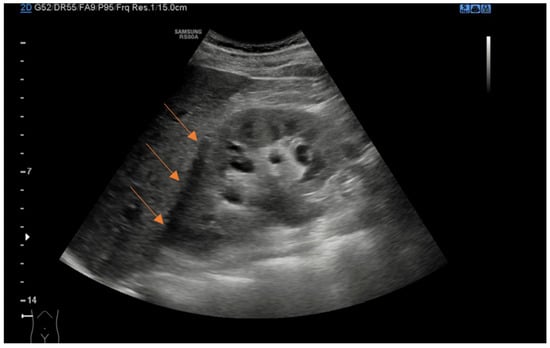
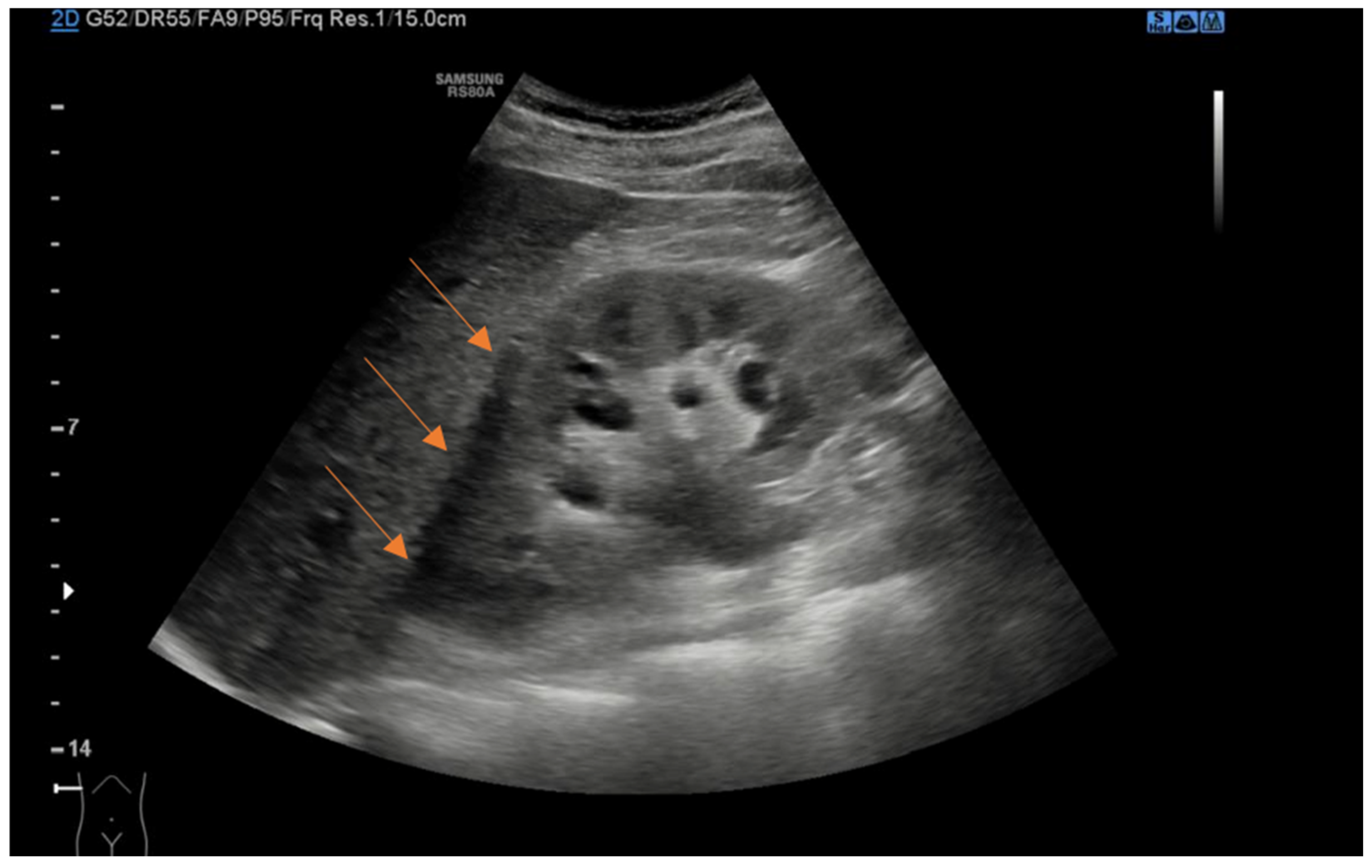
Figure 1.
Coronal ultrasound view of right kidney demonstrating anechoic perinephric fluid (arrows).
2.4. Outcome Measures
The primary outcome of this study was to determine the association between sonographic perinephric fluid collection and clinical outcomes in patients presenting with renal colic and confirmed urolithiasis. This included evaluating the correlation between perinephric fluid collection and the likelihood of requiring urological interventions, such as ureteral stent placement, nephrostomy tube insertion, or retrograde intrarenal surgery. A sub-analysis was conducted within this cohort to assess the association between perinephric fluid presence and clinical outcomes, focusing on in-hospital complications, the incidence of sepsis, and the use of antibiotics, analgesics, and anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as the development of acute kidney injury (AKI) and acute kidney disease (AKD). Additionally, we evaluated whether patients with perinephric fluid collection had longer hospital stays than those without.
AKD was defined according to the 2020 Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) consensus conference criteria as postoperative AKI occurrence, decrease in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) ≥ 35%, or increase in serum creatinine (SCr) level ≥ 50% anytime between postoperative day 1 and day 59 [18]. Postoperative AKI was defined and staged according to the KDIGO criteria [19]. Specifically, AKI was defined as SCr increase ≥0.3 mg/dL or >50%. eGFR was calculated according to the CKD-EPI creatinine equation (2021), and the CKD category was calculated according to the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) classification [20].
The secondary outcome evaluated the association between sonographic perinephric fluid and potential clinical predictors, including hydronephrosis, kidney stone size and location, fever, creatinine levels, and leukocytosis in the ER.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
We analyzed the demographic, clinical, and laboratory characteristics with descriptive statistic techniques. Descriptive statistics were stratified based on the presence or absence of perinephric fluid to assess group differences. We used the Shapiro–Wilk test to evaluate the distribution of the variables. Normally distributed continuous variables were reported as mean ± standard deviation and otherwise as the median and Q1–Q3. We reported categorical variables as absolute and relative frequencies. We performed comparisons using the Chi-square test with Yates correction or Fisher’s exact test for categorical variables and Student’s t-test or the Mann–Whitney’s U test, as appropriate, for continuous variables. We used no imputation techniques for the missing data. Patients with missing values in critical variables such as stone size, laboratory data (creatinine, leukocytosis, etc.), or imaging findings were excluded from relevant analyses. We used multivariate logistic regression models to assess the factors predicting the presence of the perinephric fluid collection. These models were adjusted for potential confounders such as age, sex, kidney stones or renal colic history, and baseline renal function. Effect sizes were communicated as odds ratios (ORs) or Beta coefficients, along with their 95% confidence intervals (CIs). A two-sided p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. We reported this study following the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement [21] and presented the STROBE checklist in the Supplementary Material. We conducted all analyses using statistical software STATA/SE version 18 (StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA).
3. Results
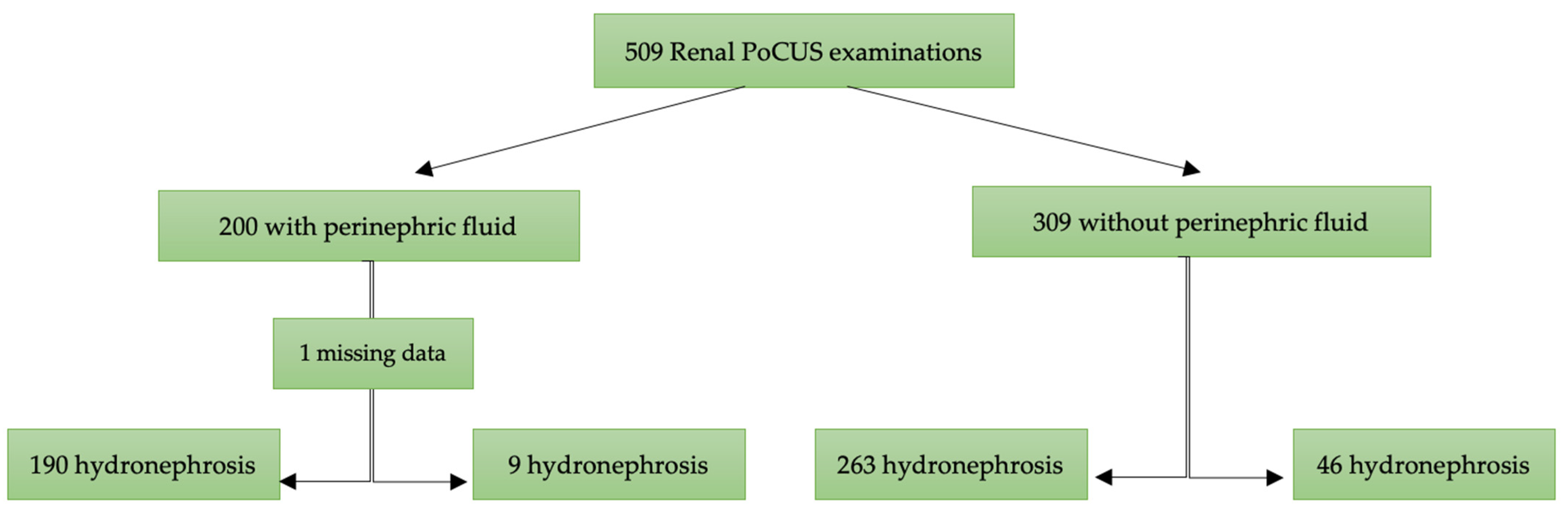
A total of 509 patients were included in this study, with 200 (39.3%) presenting with perinephric fluid and 309 (60.7%) without (Figure 2). The median age was 50 years (IQR: 41–60), with no significant difference between the two groups (p = 0.87). The proportion of males was higher in the group with perinephric fluid (72%) compared to those without (62%) (p = 0.02).
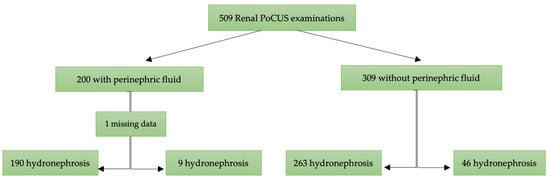
Figure 2.
Flow chart of patients included for analysis. PoCUS: point-of-care ultrasound.
We have summarized the clinical and baseline characteristics of patients in Table 1. The two groups had no significant difference in the history of kidney stones or renal colic (p = 0.91). Hydronephrosis was present in 95% of patients with perinephric fluid compared to 85% of those without (p < 0.001). CT scans were more commonly performed in the perinephric fluid group (72% vs. 38%, p < 0.001). The stone position also varied between the groups, with distal ureter stones more frequent in the perinephric fluid group (64% vs. 55%, p = 0.001). There was no significant difference in stone size between the two groups (p = 0.35). The levels of creatinine and leukocytosis in the ED were also comparable.

Table 1.
Clinical and baseline characteristics of patients with and without perinephric fluid. Values are median (Q1–Q3), means standard deviation, or numbers with percentages.
The rate of urological interventions, including percutaneous nephrostomy and ureteral stent placement, was not significantly different between patients with or without perinephric fluid (p = 0.15 and p = 0.41, respectively).
Patients with hydronephrosis and perinephric fluid had urologic intervention 20.5% of the time, compared to 19.3% of patients with hydronephrosis and no perinephric fluid (p < 0.85).
We performed a sub-analysis of 94 patients with complete medical records requiring urological interventions to evaluate the association between perinephric fluid presence and clinical outcomes (Table 2). We found no statistically significant difference in terms of in-hospital complications, the incidence of sepsis, antibiotic, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory drug use, and the development of AKI and AKD.

Table 2.
Clinical outcomes in patients requiring urological interventions with and without sonographic perinephric fluid.
In the multivariate logistic regression analysis (Table 3), considering the entire population, hydronephrosis and stone location were independently associated with the presence of perinephric fluid. Hydronephrosis significantly increased the odds of perinephric fluid presence (OR: 4.14; p = 0.007). Stone location also emerged as a significant factor, with stones in the proximal ureter (OR: 3.06; p = 0.003) and distal ureter (OR: 2.31; p = 0.018) more likely to be associated with perinephric fluid than kidney stones. Age, sex, fever, history of kidney stones, stone size, creatinine levels, and leukocytosis in the ED were not significantly associated.

Table 3.
Multivariate logistic regression analysis evaluating factors associated with perinephric fluid.
4. Discussion
Perinephric fluid collection is a well-described pathological finding in the setting of acute ureteral stone obstruction. Our study found that perinephric fluid is a common occurrence in patients with renal colic and urolithiasis, with a prevalence of 39%. However, its presence does not significantly impact treatment decisions or clinical outcomes.
The prevalence we found is similar to the 46.5% reported by Nadav et al. [16] in their study on perinephric fluid among patients undergoing radiological US, particularly those with ureteral stones. However, it is higher than the 20% reported by Cannata et al. [15] in patients with ureterolithiasis identified by emergency physicians using POCUS. This discrepancy may be due to the focused nature of POCUS image acquisition with real-time interpretation, compared to more comprehensive US images collected by radiologists on high-resolution monitors.
The existing literature on the significance of perinephric fluid collection in the management of acute ureteral stone obstruction is lacking. Interestingly, despite its association with hydronephrosis (OR: 4.14, p = 0.007) and stones located in the proximal and distal ureters (OR: 3.06, p = 0.003; OR: 2.31, p = 0.018, respectively), perinephric fluid did not correlate with an increased need for urological intervention or prolonged hospitalization. This aligns with previous studies, such as that by Nadav et al., who found no significant relationship between perinephric fluid and the need for interventions [16]. Our sub-analysis of patients requiring urological interventions supports these findings, showing no statistically significant difference in in-hospital complications, sepsis rates, antibiotic use, AKI, or AKD between patients with and without sonographic perinephric fluid.
These results suggest that while perinephric fluid may indicate increased intrarenal pressure due to ureteral obstruction, it does not necessarily predict worse clinical outcomes. This contrasts with findings from Cannata et al., [15] who observed that in the setting of ureterolithiasis, perinephric fluid was associated with a stone size ≥ 5 mm (OR 4.00; p = 0.04) and a higher likelihood of requiring urological intervention (OR 10.38; p < 0.01) [15]. In their study, patients with hydronephrosis and perinephric fluid on POCUS underwent urological intervention 46.7% of the time, compared to just 4.3% of patients with hydronephrosis but no perinephric fluid (p < 0.01) [15]. To our knowledge, this is the first study to establish a relationship between perinephric fluid, stone size, and subsequent urological intervention. One possible explanation for this discrepancy is the difference in imaging modalities and clinical settings. POCUS, often performed by emergency physicians, may not provide the same level of detail as comprehensive US evaluations conducted by radiologists, which could lead to differences in the interpretation of findings.
Our data support the idea that perinephric fluid should not be a determining factor for immediate urological intervention. Even though patients with hydronephrosis and perinephric fluid underwent interventions 20.5% of the time, this rate was not significantly different from those with hydronephrosis alone (19.3%, p = 0.85). Furthermore, the length of hospital stay was comparable between patients with and without perinephric fluid (1.8 vs. 1.6 days, p = 0.40), reinforcing the conclusion that perinephric fluid does not necessitate more aggressive management and does not imply worse clinical outcomes for the patients.
Our results are in line with those of Nadav et al., who found that no patient outcome variables were significantly associated with the presence of perinephric fluid, except for more severe pain (OR 3.8 in the presence of any perinephric fluid, and OR 8.9 in cases of moderate-to-severe perinephric fluid) [16]. Chapman et al. and Setia et al. looked at non-US modalities and found a paradoxical decrease in complications associated with perinephric fluid or no association at all [22,23].
This study has several limitations that should be acknowledged. First, its retrospective and observational nature introduces inherent biases, including potential inaccuracies in data collection and limited control over confounding variables. As a single-center study, the results may not be generalizable to broader populations. Additionally, while we included a substantial number of patients, the relatively small sample size may have resulted in insufficient statistical power for some subgroup analyses, possibly leading to an underestimation of associations between perinephric fluid and certain clinical outcomes. Moreover, the need for standardized, validated, self-administered questionnaires to assess postoperative outcomes, such as pain intensity, limits our ability to evaluate patient-reported outcomes fully. The variability in diagnostic imaging may also have impacted the consistency of perinephric fluid detection, as image quality and operator expertise can vary across different settings. Lastly, while we focused on short-term clinical outcomes, such as the need for urological intervention and hospital length of stay, we did not include long-term follow-up to assess potential delayed complications of urolithiasis like renal abscess, sepsis, or chronic kidney disease. Conflicting reports exist regarding the rate of delayed complications related to perinephric fluid, such as renal abscess or sepsis, particularly in the context of nosocomial infections, and this warrants further investigation [24,25,26].
Further research is crucial to better understand the mechanisms behind perinephric fluid accumulation in acute urinary stone obstruction cases. Large-scale prospective studies are needed to explore the relationship between perinephric fluid collection and various clinical and laboratory parameters and to clarify the significance of this finding in managing acute cases in the ED. This study underscores the importance of collaboration between the radiologist’s US evaluation and the clinician’s assessment in the emergency setting.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our study highlights the presence of perinephric fluid as a common finding in patients with renal colic and urolithiasis, particularly in association with hydronephrosis and stone location in the proximal and distal ureter. However, despite its prevalence, the presence of perinephric fluid did not significantly correlate with the need for urological intervention, longer hospital stays, or worsening clinical outcomes. These findings suggest that while perinephric fluid may reflect increased pressure in the urinary tract, its clinical significance in determining management decisions remains uncertain. Further prospective research is necessary to better understand the implications of perinephric fluid in acute urolithiasis, particularly regarding potential delayed complications and long-term outcomes.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jcm13206118/s1, STROBE Statement—checklist of items that should be included in reports of observational studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.M., U.G. and M.R.; Data curation, U.G., F.M., A.C., G.C.P. and M.M.; Formal analysis, S.M., F.M. and P.R.; Investigation, U.G., G.C.P. and M.M.; Methodology, S.M., F.M., P.R., M.C., N.F., F.P. and M.R.; Resources, U.G. and M.C.; Supervision, F.P. and M.R.; Validation, P.R.; Writing—original draft, S.M.; Writing—review and editing, S.M. and M.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Fondazione Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli IRCCS, Rome, Italy.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in this study.
Data Availability Statement
Data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- EAU Guidelines. Edn. Presented at the EAU Annual Congress Paris 2024; EAU Guidelines Office: Arnhem, The Netherlands, 2024; ISBN 978-94-92671-23-3.
- Fwu, C.-W.; Eggers, P.W.; Kimmel, P.L.; Kusek, J.W.; Kirkali, Z. Emergency Department Visits, Use of Imaging, and Drugs for Urolithiasis Have Increased in the United States. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretto, S.; Saita, A.; Scoffone, C.M.; Talso, M.; Somani, B.K.; Traxer, O.; Angerri, O.; Knoll, T.; Liatsikos, E.; Herrmann, T.R.W.; et al. Ureteral Stricture Rate after Endoscopic Treatments for Urolithiasis and Related Risk Factors: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World J. Urol. 2024, 42, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretto, S.; Saita, A.; Scoffone, C.M.; Talso, M.; Somani, B.K.; Traxer, O.; Angerri, O.; Liatsikos, E.; Ulvik, Y.; Cracco, C.M.; et al. An International Delphi Survey and Consensus Meeting to Define the Risk Factors for Ureteral Stricture after Endoscopic Treatment for Urolithiasis. World J. Urol. 2024, 42, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partin, A.W.; Dmochowski, R.R.; Kavoussi, L.R.; Peters, C.A.; Wein, A. Campbell-Walsh-Wein Urology, 12th ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 2005e9–2084e91. ISBN 9780323546423. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso, A.; Coutinho, A.; Neto, G.; Anacleto, S.; Tinoco, C.L.; Morais, N.; Cerqueira-Alves, M.; Lima, E.; Mota, P. Percutaneous Nephrostomy versus Ureteral Stent in Hydronephrosis Secondary to Obstructive Urolithiasis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Asian J. Urol. 2024, 11, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith-Bindman, R.; Aubin, C.; Bailitz, J.; Bengiamin, R.N.; Camargo, C.A.; Corbo, J.; Dean, A.J.; Goldstein, R.B.; Griffey, R.T.; Jay, G.D.; et al. Ultrasonography versus Computed Tomography for Suspected Nephrolithiasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1100–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmonds, M.L.; Yan, J.W.; Sedran, R.J.; McLeod, S.L.; Theakston, K.D. The Utility of Renal Ultrasonography in the Diagnosis of Renal Colic in Emergency Department Patients. CJEM 2010, 12, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Goertz, J.K.; Lotterman, S. Can the Degree of Hydronephrosis on Ultrasound Predict Kidney Stone Size? Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2010, 28, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moak, J.H.; Lyons, M.S.; Lindsell, C.J. Bedside Renal Ultrasound in the Evaluation of Suspected Ureterolithiasis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2012, 30, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, J.M.; Fischer, J.I.; Anderson, K.L.; Mangili, A.; Panebianco, N.L.; Dean, A.J. The Ability of Renal Ultrasound and Ureteral Jet Evaluation to Predict 30-Day Outcomes in Patients with Suspected Nephrolithiasis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 33, 1402–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boridy, I.C.; Kawashima, A.; Goldman, S.M.; Sandler, C.M. Acute ureterolithiasis: Nonenhanced helical CT findings of perinephric edema for prediction of degree of ureteral obstruction. Radiology 1999, 213, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulidou, M.; Clarke, L.; Donald Napier-Hemy, R. Infected Urinoma Secondary to a Ruptured Renal Calyx from a Partial Staghorn Stone. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2015, 2015, rjv096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Darcy, M. Renal Cysts and Urinomas. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 28, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannata, D.; Boivin, Z.; Xu, C.; Murphy, L.; Herbst, M.K. Prevalence and Implications of Perinephric Fluid on Renal Point-of-Care Ultrasound in the Emergency Department. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2023, 74, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadav, G.; Eyal, K.; Noam, T.; Yeruham, K. Evaluation of the Clinical Significance of Sonographic Perinephric Fluid in Patients with Renal Colic. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2019, 37, 1823–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, T.-F.; Liang, K.-W.; Huang, H.-H.; Tyan, Y.-S.; Chao, Y.-H. Sonography of Perinephric Fluid Collections: A Pictorial Essay. J. Clin. Ultrasound JCU 2019, 47, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lameire, N.H.; Levin, A.; Kellum, J.A.; Cheung, M.; Jadoul, M.; Winkelmayer, W.C.; Stevens, P.E.; Conference Participants. Harmonizing Acute and Chronic Kidney Disease Definition and Classification: Report of a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Consensus Conference. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellum, J.A.; Lameire, N.; Aspelin, P.; Barsoum, R.S.; Burdmann, E.A.; Goldstein, S.L.; Herzog, C.A.; Joannidis, M.; Kribben, A.; Levey, A.S.; et al. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Acute Kidney Injury Work Group. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2012, 2, 1–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Coresh, J.; Balk, E.; Kausz, A.T.; Levin, A.; Steffes, M.W.; Hogg, R.J.; Perrone, R.D.; Lau, J.; Eknoyan, G. National Kidney Foundation Practice Guidelines for Chronic Kidney Disease: Evaluation, Classification, and Stratification. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 139, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; STROBE Initiative. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for Reporting Observational Studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.P.; Gonzalez, J.; Diokno, A.C. Significance of Urinary Extravasation during Renal Colic. Urology 1987, 30, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setia, S.A.; Massie, P.L.; Epsten, M.J.; Sharma, A.; Fogg, L.; Cherullo, E.E.; Chow, A.K. Renal Forniceal Rupture in the Setting of Obstructing Ureteral Stones: An Analysis of Stone Characterization and Urologic Intervention Pattern. J. Endourol. 2020, 34, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, T.N.; Bandari, J.; Shahait, M.; Averch, T. Renal Forniceal Rupture: Is Conservative Management Safe? Urology 2017, 109, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, R.F.; Schneider-Monteiro, E.D.; Mesquita, J.L.B.; Mazzucchi, E.; Marmo Lucon, A.; Srougi, M. Renal and Perinephric Abscesses: Analysis of 65 Consecutive Cases. World J. Surg. 2007, 31, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavi, F.; Fiori, B.; Gandi, C.; Campetella, M.; Bientinesi, R.; Marino, F.; Fettucciari, D.; Rossi, F.; Moretto, S.; Murri, R.; et al. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Hospital Acquired Infections through the COVID-19 Pandemic: Real-Word Data from a Tertiary Urological Centre. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).