Posterior Correction and Fusion Using a 4D Anatomical Spinal Reconstruction Technique Improves Postural Stability Under the Eye-Closed Condition in Patients with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Postural Stability Evaluation
2.4. Radiographic Evaluation
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
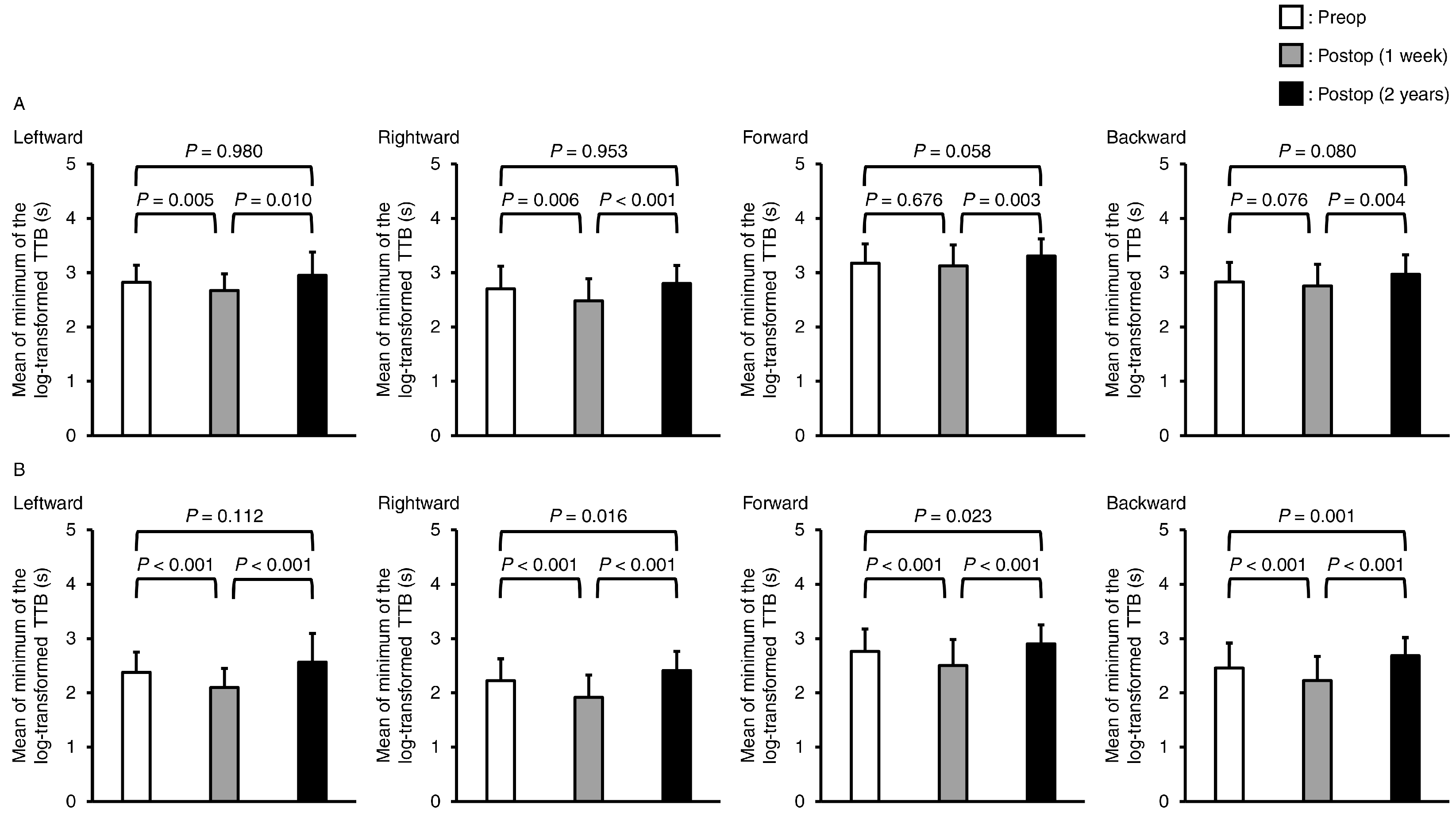
3.1. Postural Stability Parameters
3.2. Radiographic Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, J.C.; Castelein, R.M.; Chu, W.C.; Danielsson, A.J.; Dobbs, M.B.; Grivas, T.B.; Gurnett, C.A.; Luk, K.D.; Moreau, A.; Newton, P.O.; et al. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufvenberg, M.; Adeyemi, F.; Rajendran, I.; Öberg, B.; Abbott, A. Does postural stability differ between adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis and typically developed? A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2018, 13, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.Q.; Wang, J.L.; Tsuang, Y.H.; Liao, T.L.; Huang, P.I.; Hang, Y.S. The postural stability control and gait pattern of idiopathic scoliosis adolescents. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 1998, 13, S52–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nault, M.L.; Allard, P.; Hinse, S.; Le Blanc, R.; Caron, O.; Labelle, H.; Sadeghi, H. Relations between standing stability and body posture parameters in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 2002, 27, 1911–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Abreu, D.C.; Gomes, M.M.; de Santiago, H.A.; Herrero, C.F.; Porto, M.A.; Defino, H.L. What is the influence of surgical treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis on postural control? Gait Posture 2012, 36, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, T.; Yoo, H.; Lee, D.; Suh, S.W.; Yang, J.H.; Kim, H.; Mun, J.H. Analysis of sensory system aspects of postural stability during quiet standing in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2018, 15, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, J.L.; Chau, E.; Kimkpe, C.; Vallade, M.J. Restoration of thoracic kyphosis by posterior instrumentation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: Comparative radiographic analysis of two methods of reduction. Spine 2008, 33, 1579–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, J.M.; Bridwell, K.H.; Won, D.S.; Lenke, L.G.; Chotigavanichaya, C.; Hanson, D.S. Sagittal plane analysis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: The effect of anterior versus posterior instrumentation. Spine 2002, 27, 2350–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudo, H. Four-Dimensional Anatomical Spinal Reconstruction in Thoracic Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. JBJS Essent. Surg. Tech. 2022, 12, e21.00038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudo, H.; Abe, Y.; Kokabu, T.; Kuroki, K.; Iwata, A.; Iwasaki, N. Impact of Multilevel Facetectomy and Rod Curvature on Anatomical Spinal Reconstruction in Thoracic Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Spine 2018, 43, E1135–E1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokabu, T.; Kanai, S.; Abe, Y.; Iwasaki, N.; Sudo, H. Identification of optimized rod shapes to guide anatomical spinal reconstruction for adolescent thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. J. Orthop. Res. 2018, 36, 3219–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachi, H.; Kato, K.; Abe, Y.; Kokabu, T.; Yamada, K. Surgical Outcome Prediction Using a Four-Dimensional Planning Simulation System with Finite Element Analysis Incorporating Pre-bent Rods in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: Simulation for Spatiotemporal Anatomical Correction Technique. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 746902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudo, H.; Tachi, H.; Kokabu, T.; Yamada, K.; Iwata, A.; Endo, T.; Takahata, M.; Abe, Y.; Iwasaki, N. In vivo deformation of anatomically pre-bent rods in thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osuka, S.; Sudo, H.; Yamada, K.; Tachi, H.; Watanabe, K.; Sentoku, F.; Chiba, T.; Iwasaki, N.; Mukaino, M.; Tohyama, H. Effects of Posterior Spinal Correction and Fusion on Postural Stability in Patients with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 12, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeka, J.; Oie, K.S.; Kiemel, T. Multisensory information for human postural control: Integrating touch and vision. Exp. Brain Res. 2000, 134, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboobin, A.; Loughlin, P.J.; Redfern, M.S.; Sparto, P.J. Sensory re-weighting in human postural control during moving-scene perturbations. Exp. Brain Res. 2005, 167, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, R.S.; Lemos, A.; Wiesiolek, C.C.; Soares, L.G.M.; Raposo, M.C.F.; Lambertz, D.; Belian, R.B.; Ferraz, K.M. Postural Sway Velocity of Deaf Children with and without Vestibular Dysfunction. Sensors 2024, 24, 3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashner, L.M.; Black, F.O.; Wall, C., 3rd. Adaptation to altered support and visual conditions during stance: Patients with vestibular deficits. J. Neurosci. 1982, 2, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasma, J.H.; Engelhart, D.; Maier, A.B.; Schouten, A.C.; van der Kooij, H.; Meskers, C.G. Changes in sensory reweighting of proprioceptive information during standing balance with age and disease. J. Neurophysiol. 2015, 114, 3220–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertel, J.; Olmsted-Kramer, L.C.; Challis, J.H. Time-to-boundary measures of postural control during single leg quiet standing. J. Appl. Biomech. 2006, 22, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertel, J.; Olmsted-Kramer, L.C. Deficits in time-to-boundary measures of postural control with chronic ankle instability. Gait Posture 2007, 25, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, D.S.; Phan, V.; Richmond, S.B.; Lee, H. Effects of dual-tasking on time-to-boundary during stance in people with PD: A preliminary study. Clin. Biomech. 2021, 88, 105420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richmond, S.B.; Whittier, T.T.; Peterson, D.S.; Fling, B.W. Advanced characterization of static postural control dysfunction in persons with multiple sclerosis and associated neural mechanisms. Gait Posture 2021, 83, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riemann, B.L.; Lininger, M.; Kirkland, M.K.; Petrizzo, J. Age related changes in balance performance during self-selected and narrow stance testing. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2018, 75, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, MI, USA, 1988; pp. 19–51. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.M.; Kim, J.S.; Oh, J.; Lee, S.Y. Time-to-boundary analysis of postural control following acute lateral ankle sprain. Gait Posture 2019, 67, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante Valles, K.D.; Long, J.T.; Riedel, S.A.; Graf, A.; Krzak, J.; Hassani, S.; Riordan, M.; Zaharski, K.; Sturm, P.F.; Harris, G.F. Analysis of postural stability following posterior spinal fusion in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2010, 158, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oie, K.S.; Kiemel, T.; Jeka, J.J. Multisensory fusion: Simultaneous re-weighting of vision and touch for the control of human posture. Cogn. Brain Res. 2002, 14, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterka, R.J.; Loughlin, P.J. Dynamic regulation of sensorimotor integration in human postural control. J. Neurophysiol. 2004, 91, 410–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashner, L.; Berthoz, A. Visual contribution to rapid motor responses during postural control. Brain Res. 1978, 150, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahpour, N.; Ghasemi, S.; Allard, P.; Saba, M.S. Electromyographic responses of erector spinae and lower limb’s muscles to dynamic postural perturbations in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2014, 24, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Ko, J.Y.; Jang, J.Y.; Lee, S.; Beom, J.; Ryu, J.S. Asymmetrical activation and asymmetrical weakness as two different mechanisms of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrack, R.L.; Whitecloud, T.S., 3rd; Burke, S.W.; Cook, S.D.; Harding, A.F. Proprioception in idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 1984, 9, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, K.K.L.; Law, K.K.P.; Kwan, K.Y.H.; Cheung, J.P.Y.; Cheung, K.M.C.; Wong, A.Y.L. Timely Revisit of Proprioceptive Deficits in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Global Spine J. 2022, 12, 1852–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St-Georges, M.; Teles, A.R.; Rabau, O.; Saran, N.; Ouellet, J.A.; Ferland, C.E. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: Evaluating perioperative back pain through a simultaneous morphological and biomechanical approach. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2020, 21, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, P.O.; Yaszay, B.; Upasani, V.V.; Pawelek, J.B.; Bastrom, T.P.; Lenke, L.G.; Lowe, T.; Crawford, A.; Betz, R.; Lonner, B.; et al. Preservation of thoracic kyphosis is critical to maintain lumbar lordosis in the surgical treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 2010, 35, 1365–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowenstein, J.E.; Matsumoto, H.; Vitale, M.G.; Weidenbaum, M.; Gomez, J.A.; Lee, F.Y.; Hyman, J.E.; Roye, D.P., Jr. Coronal and sagittal plane correction in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A comparison between all pedicle screw versus hybrid thoracic hook lumbar screw constructs. Spine 2007, 32, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Lenke, L.G.; Kim, J.; Bridwell, K.H.; Cho, S.K.; Cheh, G.; Sides, B. Comparative analysis of pedicle screw versus hybrid instrumentation in posterior spinal fusion of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 2006, 31, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucato, D.J.; Agrawal, S.; O’Brien, M.F.; Lowe, T.G.; Richards, S.B.; Lenke, L. Restoration of thoracic kyphosis after operative treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A multicenter comparison of three surgical approaches. Spine 2008, 33, 2630–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clément, J.L.; Pesenti, S.; Ilharreborde, B.; Morin, C.; Charles, Y.P.; Parent, H.F.; Violas, P.; Szadkowski, M.; Boissière, L.; Solla, F. Proximal junctional kyphosis is a rebalancing spinal phenomenon due to insufficient postoperative thoracic kyphosis after adolescent idiopathic scoliosis surgery. Eur. Spine J. 2021, 30, 1988–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

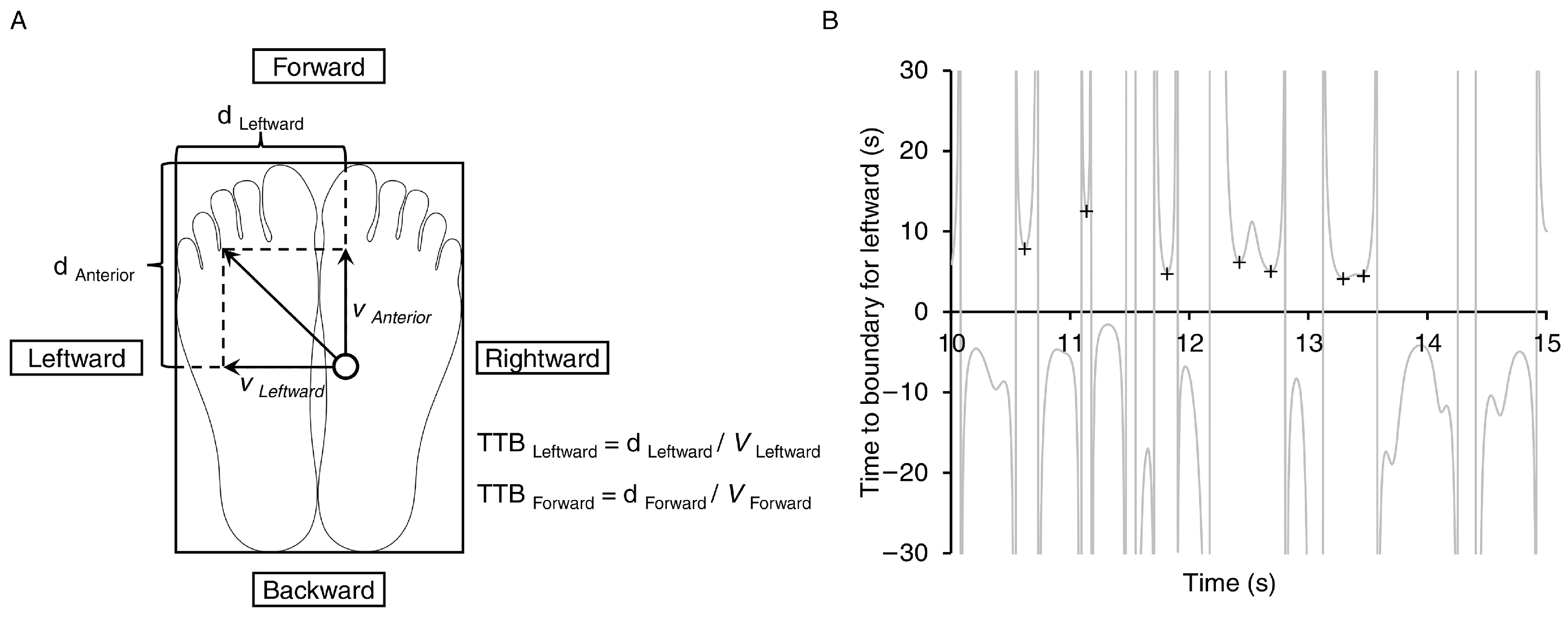

| Mean (Standard Deviation) | Range | |
|---|---|---|
| Age at surgery, yrs | 14.4 (2.2) | 11–18 |
| Height at surgery, cm | 156.7 (7.6) | 140.0–171.0 |
| Weight at surgery, kg | 47.3 (8.1) | 29.5–62.5 |
| Risser sign | 3.6 (1.5) | 0–5 |
| Cobb length (upper end to lower end vertebra) | 7.7 (0.8) | 6–10 |
| Instrumentation length (segments) | 10.9 (1.6) | 8–14 |
| Operation time, min | 251.4 (58.7) | 126–402 |
| Eye-Open Condition | Eye-Closed Condition | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preop to Postop (1 week) | Preop to Postop (2 years) | Postop (1 week) to Postop (2 years) | Preop to Postop (1 week) | Preop to Postop (2 years) | Postop (1 week) to Postop (2 years) | |
| Mean of minimum time-to-boundary | ||||||
| Leftward direction | 0.608 | 0.200 | 0.681 | 0.771 | 0.397 | 1.002 |
| Rightward direction | 0.556 | 0.190 | 0.802 | 0.759 | 0.483 | 1.276 |
| Forward direction | 0.178 | 0.334 | 0.519 | 0.587 | 0.361 | 0.932 |
| Backward direction | 0.285 | 0.305 | 0.587 | 0.512 | 0.546 | 1.135 |
| Standard deviation of minimum time-to-boundary | ||||||
| Leftward direction | 0.454 | 0.037 | 0.409 | 0.639 | 0.399 | 0.970 |
| Rightward direction | 0.420 | 0.056 | 0.517 | 0.612 | 0.496 | 1.172 |
| Forward direction | 0.073 | 0.287 | 0.346 | 0.517 | 0.458 | 0.910 |
| Backward direction | 0.237 | 0.228 | 0.444 | 0.447 | 0.584 | 1.190 |
| Eye-Open Condition | Eye-Closed Condition | Time-Condition Interaction p | Time Main Effect p | Condition Main Effect p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preop | Postop (1 week) | Postop (2 years) | Preop | Postop (1 week) | Postop (2 years) | ||||
| Maximum velocity, cm/s | |||||||||
| Leftward direction *,**,*** | 1.395 (0.298) | 1.539 (0.316) a | 1.249 (0.353) b | 1.788 (0.344) | 2.088 (0.383) a | 1.584 (0.409) a,b | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Rightward direction *,**,*** | 1.431 (0.330) | 1.553 (0.342) | 1.238 (0.291) | 1.783 (0.345) | 2.056 (0.411) | 1.600 (0.415) | 0.078 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Forward direction *,**,*** | 1.254 (0.382) | 1.363 (0.309) | 1.115 (0.273) | 1.658 (0.433) | 1.853 (0.471) | 1.531 (0.334) | 0.387 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Backward direction *,*** | 1.241 (0.411) | 1.301 (0.325) | 1.156 (0.346) b | 1.638 (0.415) | 1.909 (0.462) a | 1.502 (0.350) a,b | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Range, cm | |||||||||
| Lateral direction **,*** | 0.828 (0.236) | 0.877 (0.284) | 0.701 (0.370) | 1.144 (0.309) | 1.242 (0.340) | 0.961 (0.391) | 0.083 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Anteroposterior direction * | 0.815 (0.329) | 0.904 (0.293) | 0.797 (0.377) | 1.001 (0.317) | 1.174 (0.384) | 1.018 (0.381) | 0.184 | 0.021 | <0.001 |
| 95% confidence ellipse area, cm2 | 1.352 (0.541) | 1.403 (0.537) | 1.214 (0.709) | 1.765 (0.627) | 1.999 (0.703) a | 1.614 (0.697) b | 0.007 | 0.019 | <0.001 |
| Preop | Postop (1 week) | Postop (2 years) | Overall p | Post Hoc Test p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preop to Postop (1 week) | Preop to Postop (2 years) | Postop (1 week) to Postop (2 years) | |||||
| Coronal-plane data | |||||||
| Proximal thoracic curve, degree | 26.7 (8.1) | 12.2 (5.6) | 12.2 (6.7) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 1.000 |
| Main thoracic curve, degree | 57.1 (9.4) | 12.4 (7.3) | 14.5 (6.1) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.329 |
| Thoracolumbar/Lumbar curve, degree | 35.9 (13.7) | 9.7 (7.2) | 9.2 (6.0) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 1.000 |
| Sagittal-plane data | |||||||
| Thoracic kyphosis (T5 to T12), degree | 16.0 (8.4) | 25.8 (6.5) | 26.4 (6.7) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 1.000 |
| Lumbar lordosis (L1 to S1), degree | 44.3 (13.3) | 45.2 (9.4) | 51.4 (12.8) | 0.003 | 1.000 | 0.024 | 0.009 |
| Balance parameters and translational data | |||||||
| C7 translation from central sacral vertical line, mm | 16.6 (11.3) | 15.8 (11.2) | 10.0 (9.3) | 0.047 | 1.000 | 0.058 | 0.255 |
| Sagittal vertical axis, mm | −13.0 (18.9) | −6.6 (21.8) | −21.8 (24.2) | 0.009 | 0.483 | 0.257 | 0.011 |
| Thoracic apical vertebral translation, mm | 47.3 (18.1) | 11.2 (10.2) | 13.1 (8.6) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 1.000 |
| Thoracolumbar/Lumbar apical vertebral translation, mm | 18.4 (16.7) | 12.2 (9.6) | 12.5 (8.8) | 0.216 | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osuka, S.; Sudo, H.; Yamada, K.; Tachi, H.; Fukushima, A.; Mani, H.; Watanabe, K.; Sentoku, F.; Chiba, T.; Hori, H.; et al. Posterior Correction and Fusion Using a 4D Anatomical Spinal Reconstruction Technique Improves Postural Stability Under the Eye-Closed Condition in Patients with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6366. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13216366
Osuka S, Sudo H, Yamada K, Tachi H, Fukushima A, Mani H, Watanabe K, Sentoku F, Chiba T, Hori H, et al. Posterior Correction and Fusion Using a 4D Anatomical Spinal Reconstruction Technique Improves Postural Stability Under the Eye-Closed Condition in Patients with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(21):6366. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13216366
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsuka, Satoshi, Hideki Sudo, Katsuhisa Yamada, Hiroyuki Tachi, Akira Fukushima, Hiroki Mani, Kentaro Watanabe, Fuma Sentoku, Takeshi Chiba, Hiroaki Hori, and et al. 2024. "Posterior Correction and Fusion Using a 4D Anatomical Spinal Reconstruction Technique Improves Postural Stability Under the Eye-Closed Condition in Patients with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 21: 6366. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13216366
APA StyleOsuka, S., Sudo, H., Yamada, K., Tachi, H., Fukushima, A., Mani, H., Watanabe, K., Sentoku, F., Chiba, T., Hori, H., Iwasaki, N., Mukaino, M., & Tohyama, H. (2024). Posterior Correction and Fusion Using a 4D Anatomical Spinal Reconstruction Technique Improves Postural Stability Under the Eye-Closed Condition in Patients with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(21), 6366. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13216366







