Residual Neuromuscular Block Remains a Safety Concern for Perioperative Healthcare Professionals: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Poor Recognition of Residual NMB
2. Monitoring
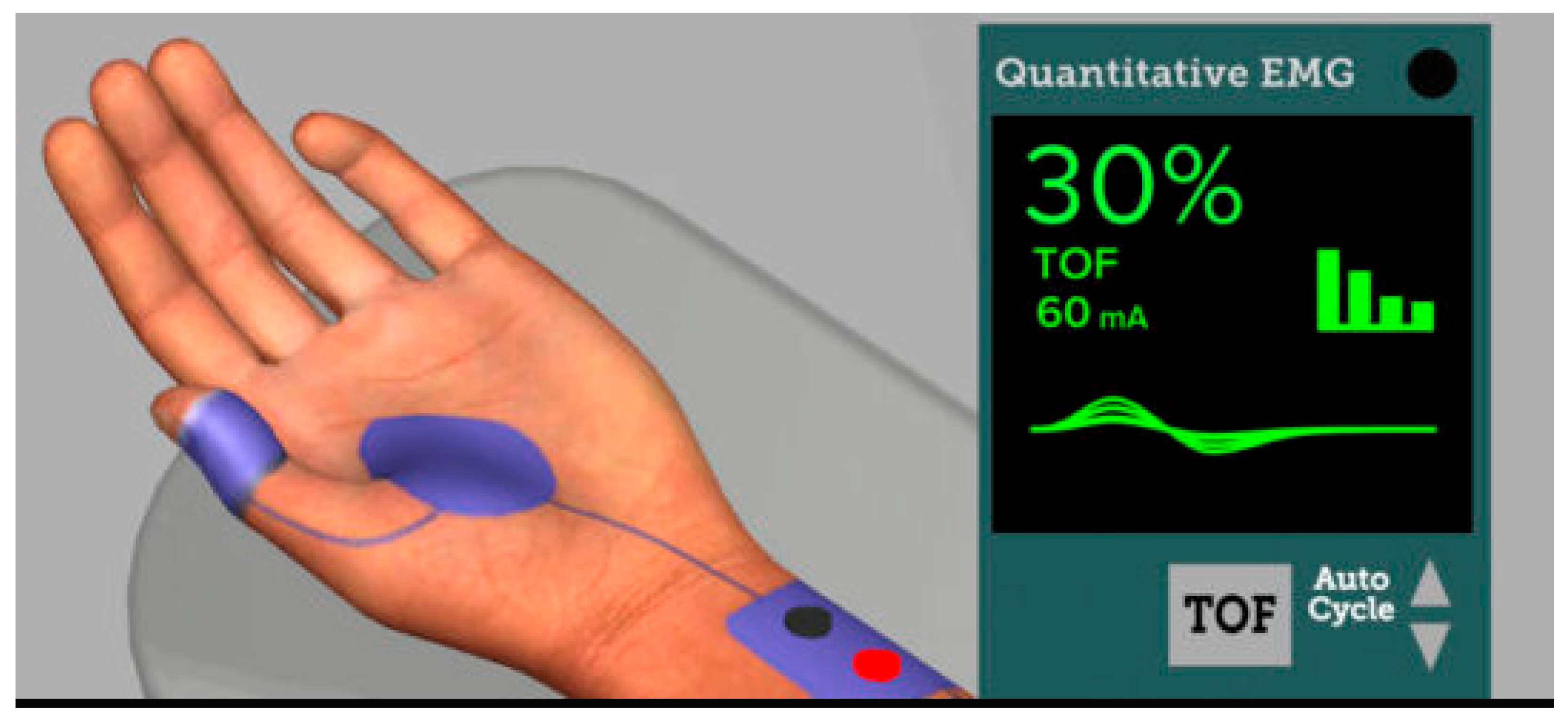
2.1. Quantitative NMB Monitoring
2.2. Qualitative NMB Monitoring
2.3. Clinical Tests
2.4. Obstacles to Quantitative Monitoring Implementation
3. Special Populations
3.1. Cardiac and Thoracic Surgery Population
3.2. Morbidly Obese Population
3.3. End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) Population
3.4. Liver Disease Population
3.5. Neuromuscular Disease Population
3.6. Pediatric Population
3.7. Geriatric Population
4. Prevention of RNMB
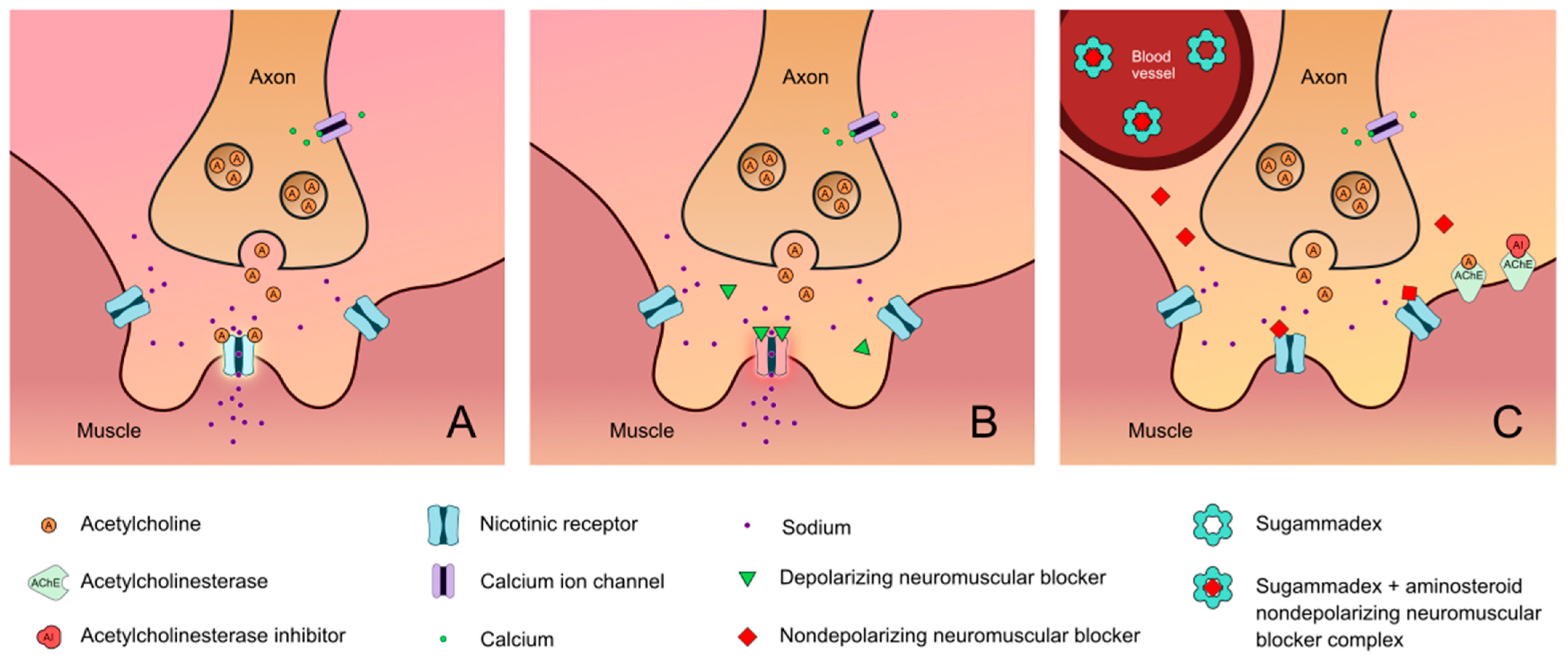
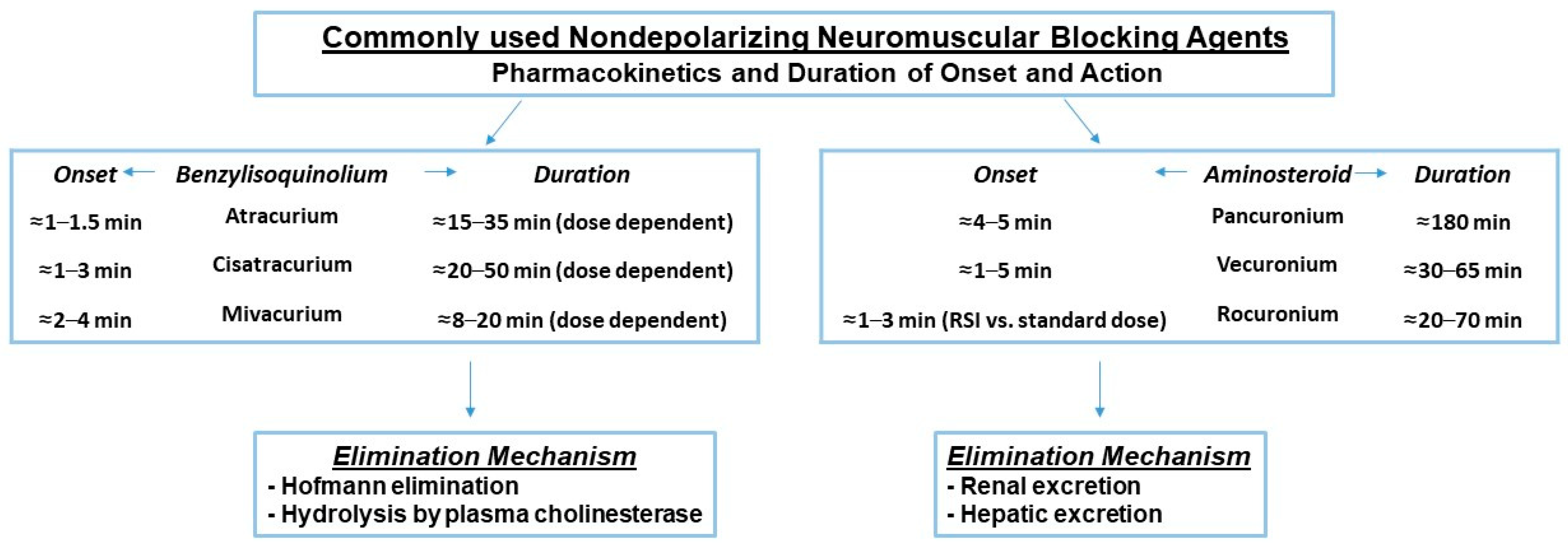
4.1. Reversal of Neuromuscular Block
4.1.1. Neostigmine
4.1.2. Sugammadex
4.1.3. Perioperative Outcomes Associated with Neostigmine vs. Sugammadex
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMG | Acceleromyography |
| APSF | Anesthesia Patient Safety Foundation |
| ARDS | Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome |
| ASA | American Society of Anesthesiologists |
| COPD | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
| DBS | Double burst Suppression |
| ED | Emergency Department |
| EMG | Electromyography |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| FRC | Functional Residual Capacity |
| ICU | Intensive Care Unit |
| KMG | Kinemyography |
| MG | Myasthenia Gravis |
| MMG | Mechanomyography |
| NDMB | Nondepolarizing Neuromuscular Block |
| NMB | Neuromuscular Block |
| NMBA | Neuromuscular Blocking Agent |
| NMJ | Neuromuscular Junction |
| OR | Operating Room |
| PACU | Post Anesthesia Care Unit |
| PPC | Postoperative Pulmonary Complications |
| PTC | Post Tetanic Count |
| qTOFR | Quantitative Train-of-four Ratio |
| RNMB | Residual Neuromuscular Block |
| TOF | Train-of-four |
| TOFC | Train-of-four Count |
| TOFR | Train-of-four Ratio |
References
- Blobner, M.; Frick, C.G.; Stauble, R.B.; Feussner, H.; Schaller, S.J.; Unterbuchner, C.; Lingg, C.; Geisler, M.; Fink, H. Neuromuscular blockade improves surgical conditions (NISCO). Surg. Endosc. 2015, 29, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geller, B.J.; Maciel, C.B.; May, T.L.; Jentzer, J.C. Sedation and shivering management after cardiac arrest. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2023, 12, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tezcan, B.; Turan, S.; Ozgok, A. Current Use of Neuromuscular Blocking Agents in Intensive Care Units. Turk. J. Anaesthesiol. Reanim. 2019, 47, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harlan, S.S.; Philpott, C.D.; Foertsch, M.J.; Takieddine, S.C.; Harger Dykes, N.J. Sugammadex Efficacy and Dosing for Rocuronium Reversal Outside of Perioperative Settings. Hosp. Pharm. 2023, 58, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, G.S.; Szokol, J.W.; Avram, M.J.; Greenberg, S.B.; Shear, T.; Vender, J.S.; Gray, J.; Landry, E. Postoperative residual neuromuscular blockade is associated with impaired clinical recovery. Anesth. Analg. 2013, 117, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brull, S.J.; Murphy, G.S. Residual neuromuscular block: Lessons unlearned. Part II: Methods to reduce the risk of residual weakness. Anesth. Analg. 2010, 111, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkel, R.; Clark, M.A.; Cubeddu, L.X. Pharmacology, 4th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA; London, UK,, 2009; p. 564. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, K.T.; An, T.H. Updated review of resistance to neuromuscular blocking agents. Anesth. Pain Med. 2018, 13, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, M.; Martini, C.; Dahan, A. Recent advances in neuromuscular block during anesthesia. F1000Research 2018, 7, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturgill, E.L.; Campbell, N.F. Neuromuscular Blocking and Reversal Agents. In Basic Clinical Anesthesia; Sikka, P.K., Beaman, S.T., Street, J.A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- D’Souza, R.S.; Porter, B.R.; Johnson, R.L. Nondepolarizing Paralytics. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519510/ (accessed on 5 September 2023).
- Brull, S.J. Neuromuscular blocking agents. In Clinical Anesthesia, 8th ed.; Barash, P.G., Cullen, B.F., Stoelting, R.K., Ortega, R.A., Cahalan, M.K., Holt, N.F., Stock, M.C., Sharar, S.R., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (LWW): Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2017; p. 527. [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi, M.; Takahashi, H.; Iwasaki, H.; Namiki, A. Respiratory acidosis prolongs, while alkalosis shortens, the duration and recovery time of vecuronium in humans. J. Clin. Anesth. 2002, 14, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, B.; Miledi, R. The Effect of Calcium on Acetylcholine Release from Motor Nerve Terminals. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1965, 161, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, V.; Abbott, T.E.F.; Ackland, G.L. Reducing the dose of neuromuscular blocking agents with adjuncts: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Anaesth. 2021, 126, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, G.E.; Wong, K.C.; Shaw, C.L.; Blatnick, R.A. Acute and chronic changes in intra- and extracellular potassium and responses to neuromuscular blocking agents. Anesth. Analg. 1978, 57, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldwell, J.E.; Heier, T.; Wright, P.M.; Lin, S.; McCarthy, G.; Szenohradszky, J.; Sharma, M.L.; Hing, J.P.; Schroeder, M.; Sessler, D.I. Temperature-dependent pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of vecuronium. Anesthesiology 2000, 92, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupp, S.M.; Miller, R.D.; Gencarelli, P.J. Vecuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade during enflurane, isoflurane, and halothane anesthesia in humans. Anesthesiology 1984, 60, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkett, L.; Bikhazi, G.B.; Thomas, K.C., Jr.; Rosenthal, D.A.; Wirta, M.G.; Foldes, F.F. Mutual potentiation of the neuromuscular effects of antibiotics and relaxants. Anesth. Analg. 1979, 58, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, T.C.; Rocha, J.B.; Morsch, V.M.; Neis, R.T.; Schetinger, M.R. Antidepressants inhibit human acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1587, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usubiaga, J.E.; Standaert, F. The effects of local anesthetics on motor nerve terminals. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1968, 159, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bash, L.D.; Turzhitsky, V.; Black, W.; Urman, R.D. Neuromuscular Blockade and Reversal Agent Practice Variability in the US Inpatient Surgical Settings. Adv. Ther. 2021, 38, 4736–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevan, D.R.; Donati, F. Muscle Relaxants. In Clinical Anesthesia, 4th ed.; Barash, P.G., Cullen, B.F., Stoelting, R.K., Eds.; Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2001; pp. 419–447. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, G.S.; Brull, S.J. Residual neuromuscular block: Lessons unlearned. Part I: Definitions, incidence, and adverse physiologic effects of residual neuromuscular block. Anesth. Analg. 2010, 111, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hile, G.B.; Ostinowsky, M.E.; Sandusky, N.P.; Howington, G.T. Evaluation of Sugammadex Dosing for Neurological Examination in the Emergency Department. J. Pharm. Pract. 2023. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.H.; Utting, J.E.; Gray, C. Stimulus frequency in the detection of neuromuscular block in humans. Br. J. Anaesth. 1970, 42, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naguib, M.; Kopman, A.F.; Lien, C.A.; Hunter, J.M.; Lopez, A.; Brull, S.J. A survey of current management of neuromuscular block in the United States and Europe. Anesth. Analg. 2010, 111, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopman, A.F.; Yee, P.S.; Neuman, G.G. Relationship of the train-of-four fade ratio to clinical signs and symptoms of residual paralysis in awake volunteers. Anesthesiology 1997, 86, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heier, T.; Caldwell, J.E.; Feiner, J.R.; Liu, L.; Ward, T.; Wright, P.M. Relationship between normalized adductor pollicis train-of-four ratio and manifestations of residual neuromuscular block: A study using acceleromyography during near steady-state concentrations of mivacurium. Anesthesiology 2010, 113, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, L.I.; Sato, M.; Severinghaus, J.W. Effect of a vecuronium-induced partial neuromuscular block on hypoxic ventilatory response. Anesthesiology 1993, 78, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, L.I.; Sundman, E.; Olsson, R.; Nilsson, L.; Witt, H.; Ekberg, O.; Kuylenstierna, R. Functional assessment of the pharynx at rest and during swallowing in partially paralyzed humans: Simultaneous videomanometry and mechanomyography of awake human volunteers. Anesthesiology 1997, 87, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, G.S.; Szokol, J.W.; Avram, M.J.; Greenberg, S.B.; Marymont, J.H.; Vender, J.S.; Gray, J.; Landry, E.; Gupta, D.K. Intraoperative acceleromyography monitoring reduces symptoms of muscle weakness and improves quality of recovery in the early postoperative period. Anesthesiology 2011, 115, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thilen, S.R.; Weigel, W.A.; Todd, M.M.; Dutton, R.P.; Lien, C.A.; Grant, S.A.; Szokol, J.W.; Eriksson, L.I.; Yaster, M.; Grant, M.D.; et al. 2023 American Society of Anesthesiologists Practice Guidelines for Monitoring and Antagonism of Neuromuscular Blockade: A Report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Neuromuscular Blockade. Anesthesiology 2023, 138, 13–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, M.; Brull, S.J.; Kopman, A.F.; Hunter, J.M.; Fulesdi, B.; Arkes, H.R.; Elstein, A.; Todd, M.M.; Johnson, K.B. Consensus Statement on Perioperative Use of Neuromuscular Monitoring. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 127, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-M.; Yu, H.; Zuo, Y.-D.; Liang, P. Postoperative pulmonary complications after sugammadex reversal of neuromuscular blockade: A systematic review and meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023, 23, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopman, A.F.; Brull, S.J. Is Postoperative Residual Neuromuscular Block Associated with Adverse Clinical Outcomes? What Is the Evidence? Curr. Anesthesiol. Rep. 2013, 3, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, L.; Faulk, D.; Lampotang, S.; Lizdas, D.E.; Gravenstein, N. Quantitative Neuromuscular Blockade. APSF Technology Education Initiative (TEI): Quantitative Neuromuscular Monitoring (QNM); published by the Anesthesia Patient Safety Foundation (APSF) in collaboration with the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA). Online Educational Simulation Environment. 2023. Available online: https://apsf.org/tei/qnm (accessed on 22 November 2023).
- Saager, L.; Maiese, E.M.; Bash, L.D.; Meyer, T.A.; Minkowitz, H.; Groudine, S.; Philip, B.K.; Tanaka, P.; Gan, T.J.; Rodriguez-Blanco, Y.; et al. Incidence, risk factors, and consequences of residual neuromuscular block in the United States: The prospective, observational, multicenter RECITE-US study. J. Clin. Anesth. 2019, 55, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grayling, M.; Sweeney, B.P. Recovery from neuromuscular blockade: A survey of practice. Anaesthesia 2007, 62, 806–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, M.; Kopman, A.F.; Ensor, J.E. Neuromuscular monitoring and postoperative residual curarisation: A meta-analysis. Br. J. Anaesth. 2007, 98, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baillard, C.; Gehan, G.; Reboul-Marty, J.; Larmignat, P.; Samama, C.M.; Cupa, M. Residual curarization in the recovery room after vecuronium. Br. J. Anaesth. 2000, 84, 394–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naguib, M.; Brull, S.J.; Hunter, J.M.; Kopman, A.F.; Fülesdi, B.; Johnson, K.B.; Arkes, H.R. Anesthesiologists’ Overconfidence in Their Perceived Knowledge of Neuromuscular Monitoring and Its Relevance to All Aspects of Medical Practice: An International Survey. Anesth. Analg. 2019, 128, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renew, J.R. UpToDate: Monitoring Neuromuscular Blockade. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/monitoring-neuromuscular-blockade (accessed on 9 May 2023).
- Murphy, G.S.; Brull, S.J. Quantitative Neuromuscular Monitoring and Postoperative Outcomes: A Narrative Review. Anesthesiology 2022, 136, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, G.S.; Szokol, J.W.; Marymont, J.H.; Greenberg, S.B.; Avram, M.J.; Vender, J.S.; Nisman, M. Intraoperative acceleromyographic monitoring reduces the risk of residual neuromuscular blockade and adverse respiratory events in the postanesthesia care unit. Anesthesiology 2008, 109, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, M.; Brull, S.J.; Johnson, K.B. Conceptual and technical insights into the basis of neuromuscular monitoring. Anaesthesia 2017, 72 (Suppl. S1), 16–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemes, R.; Renew, J.R. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Neuromuscular Blockade: What Are the Recommendations in the USA and Other Countries? Curr. Anesthesiol. Rep. 2020, 10, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhananker, S.M.; Treggiari, M.M.; Sellers, B.A.; Cain, K.C.; Ramaiah, R.; Thilen, S.R. Comparison of train-of-four count by anesthesia providers versus TOF-Watch(R) SX: A prospective cohort study. Can. J. Anaesth. 2015, 62, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renew, J.R.; Hernandez-Torres, V.; Chaves-Cardona, H.; Logvinov, I.; Brull, S.J. Comparison of visual and electromyographic assessments with train-of-four stimulation of the ulnar nerve: A prospective cohort study. Can. J. Anaesth. 2023, 70, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundman, E.; Witt, H.; Olsson, R.; Ekberg, O.; Kuylenstierna, R.; Eriksson, L.I. The Incidence and Mechanisms of Pharyngeal and Upper Esophageal Dysfunction in Partially Paralyzed Humans: Pharyngeal Videoradiography and Simultaneous Manometry after Atracurium. Anesthesiology 2000, 92, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eikermann, M.; Vogt, F.M.; Herbstreit, F.; Vahid-Dastgerdi, M.; Zenge, M.O.; Ochterbeck, C.; de Greiff, A.; Peters, J. The predisposition to inspiratory upper airway collapse during partial neuromuscular blockade. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 175, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, H.; Verdonck, M.; Cools, W.; Geerts, L.; Forget, P.; Poelaert, J. Forty years of neuromuscular monitoring and postoperative residual curarisation: A meta-analysis and evaluation of confidence in network meta-analysis. Br. J. Anaesth. 2020, 125, 466–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thilen, S.R.; Bhananker, S.M. Qualitative Neuromuscular Monitoring: How to Optimize the Use of a Peripheral Nerve Stimulator to Reduce the Risk of Residual Neuromuscular Blockade. Curr. Anesthesiol. Rep. 2016, 6, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, L.A.; Ly, N.; Shinefeld, J.; Morewood, G. Universal quantitative neuromuscular blockade monitoring at an academic medical center—A multimodal analysis of the potential impact on clinical outcomes and total cost of care. Perioper. Care Oper. Room Manag. 2021, 24, 100184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.M.; Boland, R.J., Jr.; Aron, D.C. The physician’s experience of changing clinical practice: A struggle to unlearn. Implement. Sci. 2017, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Cambronero, O.; Mazzinari, G.; Errando, C.L.; Garutti, I.; Gurumeta, A.A.; Serrano, A.B.; Esteve, N.; Montanes, M.V.; Neto, A.S.; Hollmann, M.W.; et al. An educational intervention to reduce the incidence of postoperative residual curarisation: A cluster randomised crossover trial in patients undergoing general anaesthesia. Br. J. Anaesth. 2023, 131, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, M.M.; Hindman, B.J.; King, B.J. The implementation of quantitative electromyographic neuromuscular monitoring in an academic anesthesia department. Anesth. Analg. 2014, 119, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, P.; Cieslik, H.; Rathinam, S.; Bishay, E.; Kalkat, M.S.; Rajesh, P.B.; Steyn, R.S.; Singh, S.; Naidu, B. Postoperative pulmonary complications following thoracic surgery: Are there any modifiable risk factors? Thorax 2010, 65, 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.-O.; Brotons, F.; Briant, A.R.; Suehiro, K.; Gozdzik, W.; Sponholz, C.; Kirkeby-Garstad, I.; Joosten, A.; Nigro Neto, C.; Kunstyr, J.; et al. Postoperative Pulmonary Complications After Cardiac Surgery: The VENICE International Cohort Study. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2022, 36, 2344–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, T.J.; Griffiths, T.L.; Mould, H.; Gibson, G.J. Rib cage mechanics after median sternotomy. Thorax 1990, 45, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiefenhövel, F.; Poncette, A.-S.; Boyle, E.M.; Von Heymann, C.; Menk, M.; Vorderwülbecke, G.; Grubitzsch, H.; Treskatsch, S.; Balzer, F. Pleural effusions are associated with adverse outcomes after cardiac surgery: A propensity-matched analysis. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2022, 17, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covarrubias, J.; Grigorian, A.; Schubl, S.; Gambhir, S.; Dolich, M.; Lekawa, M.; Nguyen, N.; Nahmias, J. Obesity associated with increased postoperative pulmonary complications and mortality after trauma laparotomy. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2021, 47, 1561–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, A.E.; Peters, U. The effect of obesity on lung function. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2018, 12, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocak Serin, S.; Isiklar, A.; Karaoren, G.; El-Khatib, M.F.; Caldeira, V.; Esquinas, A. Atelectasis in Bariatric Surgery: Review Analysis and Key Practical Recommendations. Turk. J. Anaesthesiol. Reanim. 2020, 47, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaszynski, T.; Szewczyk, T.; Gaszynski, W. Randomized comparison of sugammadex and neostigmine for reversal of rocuronium-induced muscle relaxation in morbidly obese undergoing general anaesthesia. Br. J. Anaesth. 2012, 108, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, K.R.; Tuteja, A.; Singh, M.; Wong, D.T.; Nagappa, M.; Chung, F.; Wong, J. Postoperative complications with neuromuscular blocking drugs and/or reversal agents in obstructive sleep apnea patients: A systematic review. BMC Anesthesiol. 2018, 18, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocabas, S.; Yedicocuklu, D.; Askar, F.Z. The neuromuscular effects of 0.6 mg kg−1 rocuronium in elderly and young adults with or without renal failure. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2008, 25, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, R.G.; Hunter, J.M. Neuromuscular blocking drugs and their antagonists in patients with organ disease. Anaesthesia 2009, 64 (Suppl. S1), 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BRIDION®. (sugammadex) Injection, for intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval: 2015 2015.
- Staals, L.M.; Snoeck, M.M.; Driessen, J.J.; Flockton, E.A.; Heeringa, M.; Hunter, J.M. Multicentre, parallel-group, comparative trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of sugammadex in patients with end-stage renal failure or normal renal function. Br. J. Anaesth. 2008, 101, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.R.; Tollinche, L.E.; Yeoh, C.B.; Artman, J.; Mehta, M.; Phillips, D.; Fischer, G.W.; Quinlan, J.J.; Sakai, T. Short-term safety and effectiveness of sugammadex for surgical patients with end-stage renal disease: A two-centre retrospective study. Anaesthesia 2020, 75, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, C.M.; Tardelli, M.A.; Tedesco, H.; Garcia, N.N.; Caparros, M.P.; Alvarez-Gomez, J.A.; de Oliveira Junior, I.S. Efficacy and safety of sugammadex in the reversal of deep neuromuscular blockade induced by rocuronium in patients with end-stage renal disease: A comparative prospective clinical trial. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2015, 32, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes, S.; Porter, S.B.; Porter, I.E., 2nd; Renew, J.R. Sugammadex use in patients with end-stage renal disease: A historical cohort study. Can. J. Anaesth. 2020, 67, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Lim, B.-G.; Won, Y.-J.; Oh, S.-K.; Oh, J.-S.; Cho, S.-A. Efficacy and Safety of Sugammadex for the Reversal of Rocuronium-Induced Neuromuscular Blockade in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicina 2021, 57, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Miert, M.M.; Eastwood, N.B.; Boyd, A.H.; Parker, C.J.R.; Hunter, J.M. The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of rocuronium in patients with hepatic cirrhosis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1997, 44, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulatif, M.; Lotfy, M.; Mousa, M.; Afifi, M.H.; Yassen, K. Sugammadex antagonism of rocuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade in patients with liver cirrhosis undergoing liver resection: A randomized controlled study. Minerva Anestesiol. 2018, 84, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, J.A.; Murphy, G.S. Anesthetic consideration for neuromuscular diseases. Curr. Opin. Anesthesiol. 2017, 30, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, M.; Eisenkraft, J.B. Anesthetic implications of myasthenia gravis. Mt. Sinai J. Med. 2002, 69, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Wang, R.; Yan, Y.; Fan, L.; Xue, J.; Wang, T. The efficacy and safety of sugammadex for reversing postoperative residual neuromuscular blockade in pediatric patients: A systematic review. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffenbichler, F.T.; Rudolph, M.I.; Friedrich, S.; Althoff, F.C.; Xu, X.; Spicer, A.C.; Patrocínio, M.; Ng, P.Y.; Deng, H.; Anderson, T.A.; et al. Effects of high neuromuscular blocking agent dose on post-operative respiratory complications in infants and children. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2020, 64, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BRIDION®. (sugammadex) Injection, for intravenous use Initial. U.S. Approval: 2015 2021.
- Murphy, G.S.; Szokol, J.W.; Avram, M.J.; Greenberg, S.B.; Shear, T.D.; Vender, J.S.; Parikh, K.N.; Patel, S.S.; Patel, A. Residual Neuromuscular Block in the Elderly: Incidence and Clinical Implications. Anesthesiology 2015, 123, 1322–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cope, T.M.; Hunter, J.M. Selecting Neuromuscular-Blocking Drugs for Elderly Patients. Drugs Aging 2003, 20, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matteo, R.S.; Ornstein, E.; Schwartz, A.E.; Ostapkovich, N.; Stone, J.G. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Rocuronium (Org 9426) in Elderly Surgical Patients. Anesth. Analg. 1993, 77, 1193–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamus, M.; Hrabalek, L.; Wanek, T.; Gabrhelik, T.; Zapletalova, J. Influence of age and gender on the pharmacodynamic parameters of rocuronium during total intravenous anesthesia. Biomed. Pap. 2011, 155, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brull, S.J.; Kopman, A.F.; Naguib, M. Management Principles to Reduce the Risk of Residual Neuromuscular Blockade. Curr. Anesthesiol. Rep. 2013, 3, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, G.; Wang, X.; Bo, L.; Deng, X. Efficacy and safety of neostigmine for neuromuscular blockade reversal in patients under general anesthesia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, J.M. Reversal of neuromuscular block. Br. J. Anaesth. 2020, 20, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blum, F.E.; Locke, A.R.; Nathan, N.; Katz, J.; Bissing, D.; Minhaj, M.; Greenberg, S.B. Residual Neuromuscular Block Remains a Safety Concern for Perioperative Healthcare Professionals: A Comprehensive Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030861
Blum FE, Locke AR, Nathan N, Katz J, Bissing D, Minhaj M, Greenberg SB. Residual Neuromuscular Block Remains a Safety Concern for Perioperative Healthcare Professionals: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(3):861. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030861
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlum, Franziska Elisabeth, Andrew R. Locke, Naveen Nathan, Jeffrey Katz, David Bissing, Mohammed Minhaj, and Steven B. Greenberg. 2024. "Residual Neuromuscular Block Remains a Safety Concern for Perioperative Healthcare Professionals: A Comprehensive Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 3: 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030861
APA StyleBlum, F. E., Locke, A. R., Nathan, N., Katz, J., Bissing, D., Minhaj, M., & Greenberg, S. B. (2024). Residual Neuromuscular Block Remains a Safety Concern for Perioperative Healthcare Professionals: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(3), 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030861





