The Uricosuric Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitors Is Maintained in the Long Term in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
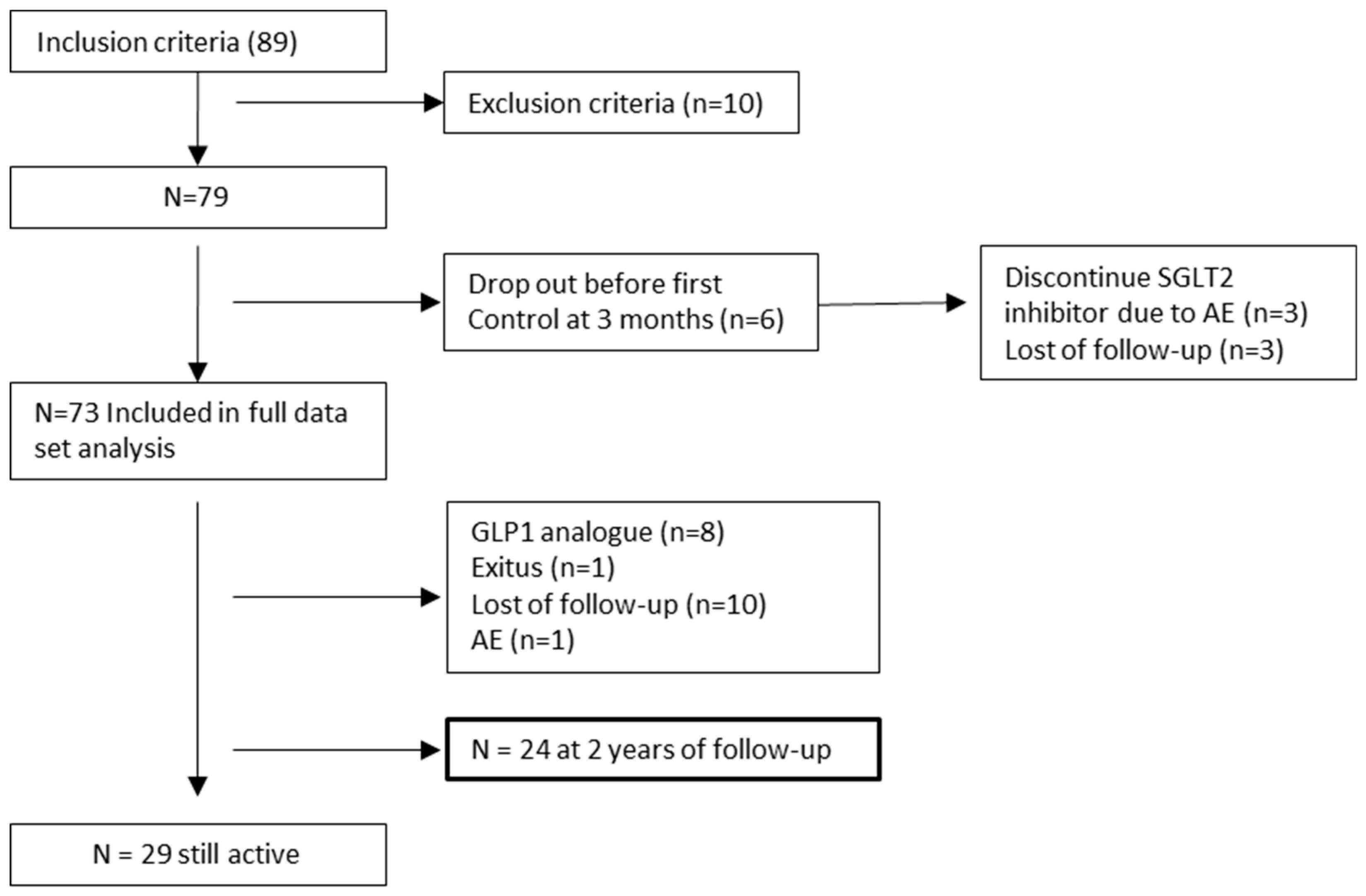
2. Materials and Methods
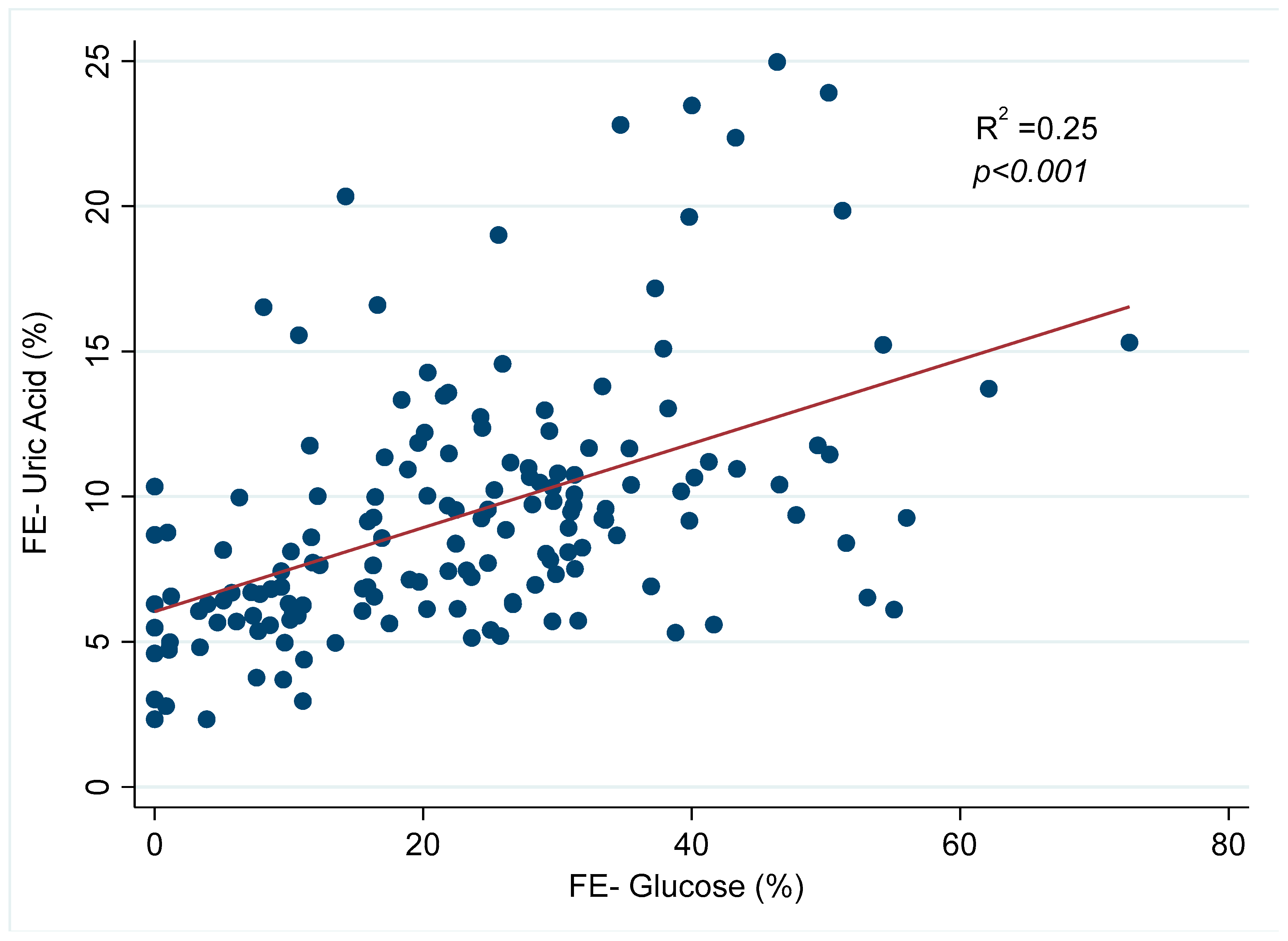
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goicoechea Diezandino, M. Ácido Úrico y Enfermedad Renal Crónica. Nefrol al Día [Internet]. 2021, pp. 1–25. Available online: https://www.nefrologiaaldia.org/200 (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- Takata, T.; Isomoto, H. Pleiotropic effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors: Renoprotective mechanisms beyond glycemic control. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belančić, A.; Klobučar, S. Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors as a Powerful Cardioprotective and Renoprotective Tool: Overview of Clinical Trials and Mechanisms. Diabetology 2023, 4, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chino, Y.; Samukawa, Y.; Sakai, S.; Nakai, Y.; Yamaguchi, J.; Nakanishi, T.; Tamai, I. SGLT2 inhibitor lowers serum uric acid through alteration of uric acid transport activity in renal tubule by increased glycosuria. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2014, 35, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, H.; Dong, P. Empagliflozin reduces blood pressure and uric acid in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2019, 33, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, L.; Tian, D.; Xia, P.; Zheng, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, L. Effects of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors on serum uric acid level: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chino, Y.; Kuwabara, M.; Hisatome, I. Factors Influencing Change in Serum Uric Acid After Administration of the Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor Luseogliflozin in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 62, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, A.S.Y.; Leong, S.; Teo, Y.N.; Syn, N.L.X.; See, R.M.; Wee, C.F.; Chong, E.Y.; Lee, C.-H.; Chan, M.Y.; Yeo, T.-C.; et al. Effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors on serum urate levels in patients with and without diabetes: A systematic review and meta-regression of 43 randomized controlled trials. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2022, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, A.; Rafiee, M.; Sathyapalan, T.; Sahebkar, A. Impacts of Sodium/Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors on Circulating Uric Acid Concentrations: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Diabetes Res. 2022, 2022, 7520632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suijk, D.L.; van Baar, M.J.; van Bommel, E.J.; Iqbal, Z.; Krebber, M.M.; Vallon, V.; Touw, D.; Hoorn, E.J.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Kramer, M.M.; et al. SGLT2 Inhibition and Uric Acid Excretion in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Normal Kidney Function. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 17, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novikov, A.; Fu, Y.; Huang, W.; Freeman, B.; Patel, R.; van Ginkel, C.; Koepsell, H.; Busslinger, M.; Onishi, A.; Nespoux, J.; et al. SGLT2 inhibition and renal urate excretion: Role of luminal glucose, GLUT9, and URAT1. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2019, 316, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannangara, D.R.; Ramasamy, S.N.; Indraratna, P.L.; Stocker, S.L.; Graham, G.G.; Jones, G.; Portek, I.; Williams, K.M.; O Day, R. Fractional clearance of urate: Validation of measurement in spot-urine samples in healthy subjects and gouty patients. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14, R189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F., 3rd; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Xia, X.; Li, B.; Lin, Z.; Yu, X.; Huang, F. Serum uric acid and cardiovascular mortality in chronic kidney disease: A meta-analysis. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gherghina, M.E.; Peride, I.; Tiglis, M.; Neagu, T.P.; Niculae, A.; Checherita, I.A. Uric Acid and Oxidative Stress-Relationship with Cardiovascular, Metabolic, and Renal Impairment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doria, A.; Galecki, A.T.; Spino, C.; Pop-Busui, R.; Cherney, D.Z.; Lingvay, I.; Parsa, A.; Rossing, P.; Sigal, R.J.; Afkarian, M.; et al. Serum Urate Lowering with Allopurinol and Kidney Function in Type 1 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2493–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, K.; Hosoya, T.; Uchida, S.; Inaba, M.; Makino, H.; Ito, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Tomino, Y.; Ohno, I.; Shibagaki, Y.; et al. Febuxostat Therapy for Patients With Stage 3 CKD and Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia: A Randomized Trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 72, 798–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badve, S.V.; Pascoe, E.M.; Tiku, A.; Boudville, N.; Brown, F.G.; Cass, A.; Clarke, P.; Dalbeth, N.; Day, R.O.; de Zoysa, J.R.; et al. Effects of Allopurinol on the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2504–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prezelin-Reydit, M.; Combe, C.; Fouque, D.; Frimat, L.; Jacquelinet, C.; Laville, M.; Massy, Z.A.; Lange, C.; Ayav, C.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; et al. Longitudinal uric acid has nonlinear association with kidney failure and mortality in chronic kidney disease. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KDIGO 2023 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Public Review Draft. July 2023. Available online: https://kdigo.org/guidelines/ckd-evaluation-and-management/ (accessed on 30 June 2023).
- Assimacopoulos-Jeannet, F.; Cusin, I.; Greco-Perotto, R.; Terrettaz, J.; Rohner-Jeanrenaud, F.; Zarjevski, N.; Jeanrenaud, B. Glucose transporters: Structure, function, and regulation. Biochimie 1991, 73, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Patients (n) | 73 |
| Male (%) | 78.1 |
| Age (y; mean, SD) | 72.2 (8.7) |
| Caucasian (%) | 95.0 |
| Comorbidities (%) | |
| High blood pressure | 95.9 |
| Hyperuricemia | 74.0 |
| Heart failure | 26.0 |
| Obesity | 18.5 |
| Dyslipidemia | 68.4 |
| CKD etiology (%) | |
| Diabetes mellitus type 2 | 49.3 |
| Nephroangiosclerosis | 16.0 |
| Glomerulonephritis | 4.1 |
| Interstitial | 9.5 |
| Others | 20.4 |
| Drugs involved in uric acid metabolism (%) | |
| Losartan | 16.4 |
| Insulin | 19.1 |
| Loop diuretics | 27.4 |
| Tiazide | 38.4 |
| Acetylsalicylic acid | 27.4 |
| Alopurinol | 26.0 |
| Febuxostat | 8.2 |
| SGLT2 inhibitor drugs (%) | |
| Canagliflozina | 25.8 |
| Dapagliflozina | 61.3 |
| Empagliflozina | 9.7 |
| Time | Baseline | Month 3 | Month 6 | Month 12 | Month 24 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 73 | 61 | 45 | 45 | 24 |
| Uric acid FE (%) | 5.9 [4.4–8.3] | 8.7 [6.1–11.2] * | 9.1 [6.3–10.8] * | 8.2 [6.7–10.3] * | 9.6 [6.5–12.2] * |
| Glucose FE (%) | 0 | 20.1 [8.6–30.8] * | 25.3 [11.8–31.3] * | 21.9 [11.0–32.3] * | 24.3 [14.2–38.8] * |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 46 [40.0–55.0] | 39 [34.0–52.0] * | 37 [33.0–44.0] * | 38.5 [32.0–47.5] * | 40 [31.0–54.0] * |
| Serum uric acid (mg/dL) | 6.6 [5.6–7.8] | 6.4 [5.0–7.5] | 6.4 [4.8–7.5] | 6.2 [5.2–7.6] | 6.2 [5.2–7.0] |
| Serum glucose (mg/dL) | 131 [111.0–146.0] | 124 [113.0–141.0] | 126 [105.0–152.0] | 133 [115.0–155.0] | 120 [112.0–136.0] |
| Basal eGFR | Baseline | Month 3 | Month 6 | Month 12 | Month 24 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uric acid FE (%) | 30–45 (n30) | 5.6 [4.3–7.9] | 9.3 [6.4–13.7] | 10.0 [6.7–11.4] | 7.6 [7.1–11.7] | 9.2 [5.9–20.3] |
| 45–60 (n32) | 6.8 [4.8–8.9] | 8.6 [6.1–12.2] | 8.8 [5.1–9.6] | 8.4 [6.5–9.6] | 7.8 [6.4–10.9] | |
| >60 (n11) | 5.6 [4.4–5.8] | 8.8 [6.3–10.0] | 7.7 [6.9–10.3] | 8.7 [7.1–11.8] | 11.5 [10.2–12.7] | |
| Glucose FE (%) | 30–45 (n30) | 0 [0.0–0.0] | 19.6 [8.1–31.8] | 28.1 [12.1–46.5] | 18.0 [9.7–32.3] | 12.9 [10.6–16.4] |
| 45–60 (n32) | 0 [0.0–0.0] | 21.2 [12.6–31.1] | 24.6 [16.9–30.0] | 26.2 [22.1–33.5] | 28.1 [20.2–41.1] | |
| >60 (n11) | 0 [0.0–0.0] | 13.2 [7.6–27.9] | 15.9 [11.8–29.6] | 19.3 [8.5–21.9] | 37.0 [24.3–37.3] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sánchez-Briales, P.; Marques Vidas, M.; López-Sánchez, P.; López-Illázquez, M.V.; Martín-Testillano, L.; Vedat-Ali, A.; Portolés, J. The Uricosuric Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitors Is Maintained in the Long Term in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051360
Sánchez-Briales P, Marques Vidas M, López-Sánchez P, López-Illázquez MV, Martín-Testillano L, Vedat-Ali A, Portolés J. The Uricosuric Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitors Is Maintained in the Long Term in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(5):1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051360
Chicago/Turabian StyleSánchez-Briales, Paula, María Marques Vidas, Paula López-Sánchez, María Victoria López-Illázquez, Lucía Martín-Testillano, Aylin Vedat-Ali, and Jose Portolés. 2024. "The Uricosuric Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitors Is Maintained in the Long Term in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 5: 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051360
APA StyleSánchez-Briales, P., Marques Vidas, M., López-Sánchez, P., López-Illázquez, M. V., Martín-Testillano, L., Vedat-Ali, A., & Portolés, J. (2024). The Uricosuric Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitors Is Maintained in the Long Term in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(5), 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051360







