APOE Genotype, ApoE Plasma Levels, Lipid Metabolism, and Cognition in Monozygotic Twins with, at Risk of, and without Affective Disorders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Ethics
2.3. Measures
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
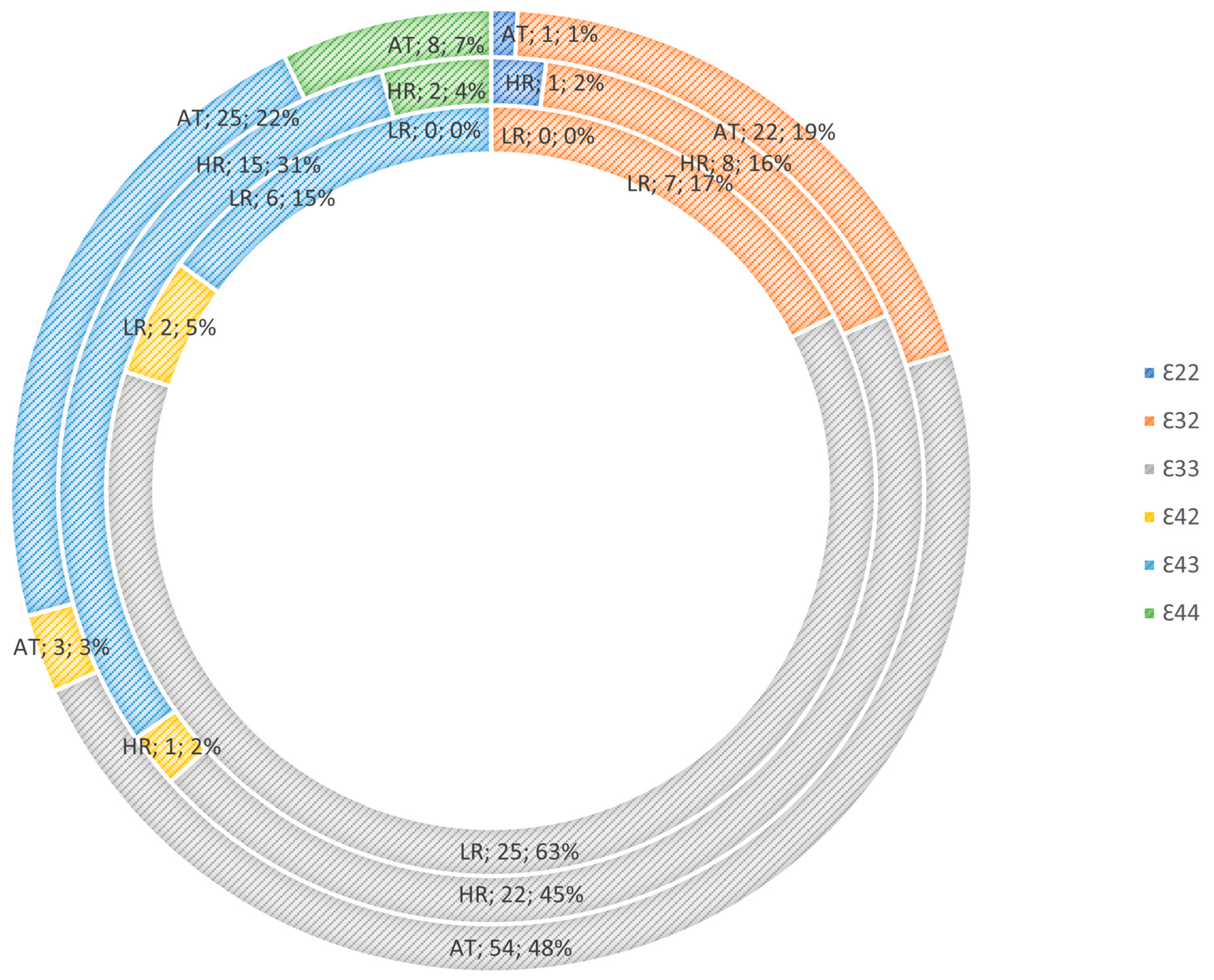
3.1. Apolipoprotein E Genotype Risk Mediation
3.2. Biomarker Risk-Group Analysis
3.3. Apolipoprotein E Levels
3.4. Triglyceride Levels
3.5. High Density Lipoprotein, Low-Density Lipoprotein, and Cholesterol Levels
3.6. Post hoc Correlations between Cognition and ApoE and Lipid Levels
4. Discussion
4.1. APOE Genotype
4.2. Apolipoprotein E Levels
4.3. Triglyceride Levels
4.4. Correlation between Biomarkers and Cognition
4.5. Strengths and Limitations
4.6. Clinical Implications and Treatment Strategies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. WHO Fact Sheet for Depresion. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/depression (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Global Health Data Exchange (GHDx). Available online: http://ghdx.healthdata.org/gbd-results-tool?params=gbd-api-2019-permalink/d780dffbe8a381b25e1416884959e88b (accessed on 4 March 2023).
- Craddock, N.; Sklar, P. Series Bipolar Disorder 1 Genetics of bipolar disorder Search strategy and selection criteria. Lancet 2013, 381, 1654–1662. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johansson, V.; Kuja-Halkola, R.; Cannon, T.D.; Hultman, C.M.; Hedman, A.M. A population-based heritability estimate of bipolar disorder-In a Swedish twin sample. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 278, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Lim, C.C.; Degenhardt, L.; Cannon, D.L.; Bremner, M.; Prentis, F.; Lawrence, Z.; Heffernan, E.; Meurk, C.; Reilly, J.; et al. Comorbidity between mood and substance-related disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2022, 56, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafeman, D.M.; Merranko, J.; Joseph, H.M.; Goldstein, T.R.; Goldstein, B.I.; Levenson, J.; Axelson, D.; Monk, K.; Sakolsky, D.; Iyengar, S.; et al. Early Indicators of Bipolar Risk in Preschool Offspring of Parents with Bipolar Disorder. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2023, 64, 1492–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonker, I.; Rosmalen, J.G.M.; Schoevers, R.A. Childhood Life Events, Immune Activation and the Development of Mood and Anxiety Disorders: The TRAILS Study. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühnel, A.; Czisch, M.; Sämann, P.G.; Binder, E.B.; Kroemer, N.B.; Brückl, T.; Spoormaker, V.I.; Erhardt, A.; Grandi, N.C.; Ziebula, J.; et al. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Stress-Induced Network Reconfigurations Reflect Negative Affectivity. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 92, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantazatos, S.P.; Melhem, N.M.; Brent, D.A.; Zanderigo, F.; Bartlett, E.A.; Lesanpezeshki, M.; Burke, A.; Miller, J.M.; Mann, J.J. Ventral Prefrontal Serotonin 1A Receptor Binding: A Neural Marker of Vulnerability for Mood Disorder and Suicidal Behavior? Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 4136–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceban, F.; Nogo, D.; Carvalho, I.P.; Lee, Y.; Nasri, F.; Xiong, J.; Lui, L.M.W.; Subramaniapillai, M.; Gill, H.; Liu, R.N.; et al. Association between Mood Disorders and Risk of COVID-19 Infection, Hospitalization, and Death. JAMA Psychiatry 2021, 78, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amare, A.T.; Schubert, K.O.; Klingler-Hoffmann, M.; Cohen-Woods, S.; Baune, B.T. The genetic overlap between mood disorders and cardiometabolic diseases: A systematic review of genome wide and candidate gene studies. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, B.I.; Carnethon, M.R.; Matthews, K.A.; Mcintyre, R.S.; Miller, G.E.; Raghuveer, G.; Stoney, C.M.; Wasiak, H.; Mccrindle, B.W. Major Depressive Disorder and Bipolar Disorder Predispose Youth to Accelerated Atherosclerosis and Early Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation 2015, 132, 965–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessing, L.V.; Ziersen, S.C.; Andersen, P.K.; Vinberg, M. A Nation-Wide Population-Based Longitudinal Study Mapping Physical Diseases in Patients with Bipolar Disorder and Their Siblings. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 282, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’rahilly, S. Human genetics illuminates the paths to metabolic disease. Nature 2009, 462, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemsen, G.; Ward, K.J.; Bell, C.G.; Christensen, K.; Bowden, J.; Dalgård, C.; Harris, J.R.; Kaprio, J.; Lyle, R.; Magnusson, P.K.E.; et al. The Concordance and Heritability of Type 2 Diabetes in 34,166 Twin Pairs From International Twin Registers: The Discordant Twin (DISCOTWIN) Consortium. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2015, 18, 762–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golden, S.H. Examining a Bidirectional Association between Depressive Symptoms and Diabetes. JAMA 2008, 299, 2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, D.E.; Gao, K.; Chan, P.K.; Ganocy, S.J.; Findling, R.L.; Calabrese, J.R. Medical Comorbidity in Bipolar Disorder: Relationship between Illnesses of the Endocrine/Metabolic System and Treatment Outcome. Bipolar. Disord. 2010, 12, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Yue, Y.; Jiang, H.; Yuan, Y. Shared genetic risk factors for depression and stroke. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 93, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansur, R.B.; Brietzke, E.; McIntyre, R.S. Is There a “Metabolic-Mood Syndrome”? A Review of the Relationship between Obesity and Mood Disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 52, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atti, A.R.; Valente, S.; Iodice, A.; Caramella, I.; Ferrari, B.; Albert, U.; Mandelli, L.; De Ronchi, D. Metabolic Syndrome, Mild Cognitive Impairment, and Dementia: A Meta-Analysis of Longitudinal Studies. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2019, 27, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, Y.Y.; Verdonschot, M.; Mcevoy, C.T.; Peeters, G. Associations between depression and cognition, mild cognitive impairment and dementia in persons with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 185, 109227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diniz, B.S.; Teixeira, A.L.; Cao, F.; Gildengers, A.; Soares, J.C.; Butters, M.A.; Reynolds, C.F. History of Bipolar Disorder and the Risk of Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2017, 25, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rock, P.L.; Roiser, J.P.; Riedel, W.J.; Blackwell, A.D. Cognitive Impairment in Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Psychol. Med. 2014, 44, 2029–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scult, M.A.; Paulli, A.R.; Mazure, E.S.; Moffitt, T.E.; Hariri, A.R.; Strauman, T.J. The Association between Cognitive Function and Subsequent Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Psychol. Med. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szmulewicz, A.; Valerio, M.P.; Martino, D.J. Longitudinal Analysis of Cognitive Performances in Recent-Onset and Late-Life Bipolar Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Bipolar. Disord. 2020, 22, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varghese, S.; Frey, B.N.; Schneider, M.A.; Kapczinski, F.; de Azevedo Cardoso, T. Functional and Cognitive Impairment in the First Episode of Depression: A Systematic Review. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2022, 145, 156–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Meng, X.; Yao, Y.; Xu, J. The Mechanism and Efficacy of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2022, 13, 2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, D.A.; Weickert, C.S.; Garner, B. Apolipoproteins in the Brain: Implications for Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders. Clin. Lipidol. 2010, 5, 555–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, A.; Lammertse, D.P.; Coll, J.R.; Charlifue, S.; Coughlin, C.T.; Whiteneck, G.G.; Worley, G. Apolipoprotein E S4 Allele and Outcomes of Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury. J. Spinal Cord. Med. 2016, 31, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knöchel, C.; Kniep, J.; Cooper, J.D.; Stäblein, M.; Wenzler, S.; Sarlon, J.; Prvulovic, D.; Linden, D.E.J.; Bahn, S.; Stocki, P.; et al. Altered Apolipoprotein C Expression in Association with Cognition Impairments and Hippocampus Volume in Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 267, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Reedt Dortland, A.K.B.; Giltay, E.J.; van Veen, T.; van Pelt, J.; Zitman, F.G.; Penninx, B.W.J.H. Associations between Serum Lipids and Major Depressive Disorder. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2010, 71, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahim, I.M.; Ghahremani, M.; Camicioli, R.; Smith, E.E.; Ismail, Z. Effects of Race, Baseline Cognition, and APOE on the Association of Affective Dysregulation with Incident Dementia: A Longitudinal Study of Dementia-Free Older Adults. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 332, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessing, L.V.; Jørgensen, O.S. Apolipoprotein E-Ε4 Frequency in Affective Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 1999, 45, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-León, S.; Janssens, A.C.J.W.; González-Zuloeta Ladd, A.M.; Del-Favero, J.; Claes, S.J.; Oostra, B.A.; van Duijn, C.M. Meta-Analyses of Genetic Studies on Major Depressive Disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2008, 13, 772–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatt, J.M.; Burton, K.L.O.; Williams, L.M.; Schofield, P.R. Specific and common genes implicated across major mental disorders: A review of meta-analysis studies. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2014, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, K.L.; Tybjærg-Hansen, A.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Frikke-Schmidt, R. Plasma Levels of Apolipoprotein E, APOE Genotype, and All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality in 105 949 Individuals from a White General Population Cohort. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 2813–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, K.L.; Tybjærg-Hansen, A.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Frikke-Schmidt, R. Plasma Levels of Apolipoprotein E and Risk of Ischemic Heart Disease in the General Population. Atherosclerosis 2016, 246, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, B.; Digney, A.; Sundram, S.; Thomas, E.; Scarr, E. Plasma Apolipoprotein E Is Decreased in Schizophrenia Spectrum and Bipolar Disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2008, 158, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, M.; Roohafza, H.; Afshar, H.; Rajabi, F.; Ramzani, M.; Shemirani, H.; Sarafzadeghan, N. Relationship between Depression and Apolipoproteins A and B: A Case-Control Study. Clinics 2011, 66, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottesen, N.M.; Meluken, I.; Frikke-Schmidt, R.; Plomgaard, P.; Scheike, T.; Fernandes, B.S.; Berk, M.; Poulsen, H.E.; Kessing, L.V.; Miskowiak, K.; et al. Are Remitted Affective Disorders and Familial Risk of Affective Disorders Associated with Metabolic Syndrome, Inflammation and Oxidative Stress?—A Monozygotic Twin Study. Psychol. Med. 2020, 50, 1736–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottesen, N.M.; Meluken, I.; Scheike, T.; Kessing, L.V.; Miskowiak, K.W.; Vinberg, M. Clinical Characteristics, Life Adversities and Personality Traits in Monozygotic Twins with, at Risk of and without Affective Disorders. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wing, J.K.; Babor, T.; Brugha, T.; Burke, J.; Cooper, J.E.; Giel, R.; Jablenski, A.; Regier, D.; Sartorius, N. SCAN. Schedules for Clinical Assessment in Neuropsychiatry. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1990, 47, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, M. Development of a Rating Scale for Primary Depressive Illness. Br. J. Soc. Clin. Psychol. 1967, 6, 278–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, R.C.; Biggs, J.T.; Ziegler, V.E.; Meyer, D.A. A Rating Scale for Mania: Reliability, Validity and Sensitivity. Br. J. Psychiatry 1978, 133, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowie, C.R.; Harvey, P.D. Administration and interpretation of the Trail Making Test. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2277–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, J.H.; Støttrup, M.M.; Nayberg, E.; Knorr, U.; Ullum, H.; Purdon, S.E.; Kessing, L.V.; Miskowiak, K.W. Optimising Screening for Cognitive Dysfunction in Bipolar Disorder: Validation and Evaluation of Objective and Subjective Tools. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 187, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, C.V.; Bjertrup, A.J.; Jensen, J.H.; Ullum, H.; Sjælland, R.; Purdon, S.E.; Vieta, E.; Kessing, L.V.; Miskowiak, K.W. Screening for Cognitive Dysfunction in Unipolar Depression: Validation and Evaluation of Objective and Subjective Tools. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 190, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, B.D. Genetic Influences on Outcome Following Traumatic Brain Injury. Neurochem. Res. 2007, 32, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, F.; Lu, S.S.; Hu, C.Y.; Gong, F.F.; Qian, Z.Z.; Yang, H.Y.; Wu, Y.L.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Bi, P.; Sun, Y.H. Association between Apolipoprotein e Gene Polymorphism and Depression. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 22, 1232–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, M.G.S.; Bio, D.S.; Dias, V.V.; do Prado, C.M.; Campos, R.N.; Costa, L.F.d.O.; Moreno, D.H.; Ojopi, E.B.; Gattaz, W.F.; Moreno, R.A. Short Communication: Apolipoprotein E Genotype and Cognition in Bipolar Disorder. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2010, 16, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meller, M.R.; Patel, S.; Duarte, D. Kapczinski, | Flavio Bipolar Disorder and Frontotemporal Dementia: A Systematic Review. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2021, 144, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, R. Exploring the Relationship between Depression and Dementia. JAMA 2018, 320, 961–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, K.L.; Tybjærg-Hansen, A.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Frikke-Schmidt, R. Plasma Apolipoprotein E Levels and Risk of Dementia: A Mendelian Randomization Study of 106,562 Individuals. Alzheimer’s Dementia 2018, 14, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordestgaard, L.T.; Christoffersen, M.; Afzal, S.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Tybjærg-Hansen, A.; Frikke-Schmidt, R. Triglycerides as a Shared Risk Factor between Dementia and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: A Study of 125 727 Individuals. Clin. Chem. 2021, 67, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rheenen, T.E.; Mcintyre, R.S.; Balanzá-martínez, V.; Berk, M.; Rossell, S.L. Cumulative Cardiovascular Disease Risk and Triglycerides Differentially Relate to Subdomains of Executive Function in Bipolar Disorder; Preliminary Findings. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 278, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Cai, D.; Liu, J.; Liu, R.; Wang, S. Cholesterol and Triglyceride Levels in First-Episode Patients with Major Depressive Disorder: A Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 266, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane-Donovan, C.; Wong, W.M.; Durakoglugil, M.S.; Wasser, C.R.; Jiang, S.; Xian, X.; Herz, J. Genetic Restoration of Plasma Apoe Improves Cognition and Partially Restores Synaptic Defects in ApoE-Deficient Mice. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 10141–10150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooijaart, S.P.; Van Vliet, P.; Van Heemst, D.; Rensen, P.C.N.; Berbéeberb´berbée, J.F.P.; Jolles, J.; De Craen, A.J.M.; Westendorp, R.G.J. Plasma Levels of Apolipoprotein E and Cognitive Function in Old Age. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci 2007, 1100, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Poljak, A.; Crawford, J.; Kochan, N.A.; Wen, W. Plasma Apolipoprotein Levels Are Associated with Cognitive Status and Decline in a Community Cohort of Older Individuals. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 34078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morley, J.E.; Banks, W.A. Lipids and Cognition. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010, 20, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, T.N.; Yin, G.Z.; Yin, X.L.; Wu, J.Q.; Du, X.D.; Zhu, H.L.; Liu, J.H.; Wang, X.Q.; Xu, D.W.; Tang, W.J.; et al. Elevated Triglyceride Levels Are Associated with Cognitive Impairments among Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. Compr. Psychiatry 2017, 75, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicent Sánchez-Ortí, J.; Balanzá-Martínez, V.; Correa-Ghisays, P.; Selva-Vera, G.; Vila-Francés, J.; Magdalena-Benedito, R.; Escribano-Lopez, I.; Crespo-Facorro, B.; Tabarés-Seisdedos, R. Specific Metabolic Syndrome Components Predict Cognition and Social Functioning in People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Severe Mental Disorders. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2022, 146, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anstey, K.J.; Lipnicki, D.M.; Low, L.F. Cholesterol as a risk factor for dementia and cognitive decline: A systematic review of prospective studies with meta-analysis. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2008, 16, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, R.; Ma, Y.; Li, C.; Zhong, B.; Xie, W. Low Levels of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and Cognitive Decline. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 1684–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Lange, S.M.M. Metabolic Syndrome in Psychiatric Patients: Overview, Mechanisms, and Implications. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 20, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, K.; Petersen, I.; Skytthe, A.; Herskind, A.M.; McGue, M.; Bingley, P. Comparison of academic performance of twins and singletons in adolescence: Follow-up study. Br. Med. J. 2006, 333, 1095–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kläning, U.; Laursen, T.M.; Licht, R.W.; Kyvik, K.O.; Skytthe, A.; Mortensen, P.B. Is the Risk of Bipolar Disorder in Twins Equal to the Risk in Singletons? A Nationwide Register-Based Study. J. Affect. Disord. 2004, 81, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öberg, S.; Cnattingius, S.; Sandin, S.; Lichtenstein, P.; Morley, R.; Iliadou, A.N. Twinship Influence on Morbidity and Mortality across the Lifespan. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 41, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, I.; Nielsen, M.M.F.; Beck-Nielsen, H.; Christensen, K. No Evidence of a Higher 10 Year Period Prevalence of Diabetes among 77,885 Twins Compared with 215,264 Singletons from the Danish Birth Cohorts 1910–1989. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 2016–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bora, E. Neurocognitive Features in Clinical Subgroups of Bipolar Disorder: A Meta-Analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 229, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.K.N.; Tong, C.H.Y.; Wong, C.S.M.; Chen, E.Y.H.; Chang, W.C. Life Expectancy and Years of Potential Life Lost in Bipolar Disorder: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Psychiatry 2022, 221, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erlangsen, A.; Andersen, P.K.; Toender, A.; Laursen, T.M.; Nordentoft, M.; Canudas-Romo, V. Cause-Specific Life-Years Lost in People with Mental Disorders: A Nationwide, Register-Based Cohort Study. Lancet Psychiatry 2017, 4, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessing, L.V.; Vradi, E.; Andersen, P.K. Life Expectancy in Bipolar Disorder. Bipolar. Disord. 2015, 17, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldfarb, M.; De Hert, M.; Detraux, J.; Di Palo, K.; Munir, H.; Music, S.; Piña, I.; Ringen, P.A. Severe Mental Illness and Cardiovascular Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 80, 918–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momen, N.C.; Plana-Ripoll, O.; Agerbo, E.; Christensen, M.K.; Iburg, K.M.; Laursen, T.M.; Mortensen, P.B.; Pedersen, C.B.; Prior, A.; Weye, N.; et al. Mortality Associated with Mental Disorders and Comorbid General Medical Conditions. JAMA Psychiatry 2022, 79, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.K.; Ling, S.; Lui, L.M.W.; Ceban, F.; Vinberg, M.; Kessing, L.V.; Ho, R.C.; Rhee, T.G.; Gill, H.; Cao, B.; et al. Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Impaired Fasting Glucose, General Obesity, and Abdominal Obesity in Patients with Bipolar Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 300, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Risk Status | Affected | High Risk | Low Risk | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number, n | 115 | 49 | 40 | |
| Demographics | ||||
| Age, years (SD) | 36.1 (8.8) | 36.9 (9.6) | 37.1 (9.2) | 0.868 |
| Sex female, n (%) | 75 (65.2) | 34 (69.4) | 24 (60.0) | 0.652 |
| Years of education, (SD) | 14.5 (3.3) | 15.7 (3.1) | 15.3 (2.6) | 0.123 |
| In occupation, n (employment + education, %): | 65 (57.0) | 40 (81.6) | 32 (80.0) | 0.001 |
| Smoking and alcohol | ||||
| Currently smoking, n (%) | 35 (30.4) | 13 (26.5) | 4 (10.0) | 0.038 |
| Alcohol consumption (units/week, SD) | 2.5 (4.0) | 3.8 (5.3) | 3.6 (3.1) | 0.563 |
| Affective symptoms | ||||
| HDRS-17 (SD) | 4.4 (3.7) | 4.1 (3.6) | 2.2 (2.3) | 0.008 |
| YMRS (SD) | 1.8 (2.1) | 1.5 (1.3) | 1.2 (1.5) | 0.217 |
| Cognition | ||||
| SCIP total, (SD) | 73.6 (12.5) | 77.1 (12.1) | 78.2 (12.9) | |
| TMT-A, (SD) | 30.5 (11.5) | 29.2 (11.2) | 28.8 (8.3) | |
| TMT-B, (SD) | 79.9 (37.6) | 78.4 (35.4) | 72.3 (22.9) | |
| Diagnoses | ||||
| Bipolar disorder, n (%) | 31 (27) | NA | NA | |
| Unipolar disorder, n (%) | 84 (73) | NA | NA | |
| Age of onset, years (SD) | 23.4 (7.7) | NA | NA | |
| Duration of affective disorder, years (SD) | 12.6 (7.6) | NA | NA | |
| Affective episodes, n (SD) | 3.4 (4.8) | NA | NA | |
| Admissions, n (SD) | 2.3 (10.3) | NA | NA | |
| Months in remission, (SD) | 42.7 (50.4) | NA | NA | |
| Medication | ||||
| Current medication, n (%) | 73 (63.5) | 9 (18.4) | 6 (15) | |
| Antidepressants, n (%) | 45 (39.0) | 1 (2.0) | 0 | |
| Antipsychotics, n (%) | 18 (15.7) | 0 | 0 | |
| Mood stabilizers, n (%) | 22 (19.1) | 0 | 0 | |
| Concordance Groups | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Risk Twins | Discordant Twins | Concordant Affected Twins | ||
| APOE Genotype | E22 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 0.0% | 2.2% | 0,0% | ||
| E32 | 6 | 13 | 11 | |
| 15.8% | 14.4% | 20.8% | ||
| E33 | 24 | 43 | 26 | |
| 63.2% | 47.8% | 49.1% | ||
| E42 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| 5.3% | 2.2% | 3.8% | ||
| E43 | 6 | 26 | 8 | |
| 15.8% | 28.9% | 15.1% | ||
| E44 | 0 | 4 | 6 | |
| 0.0% | 4.4% | 11.3% | ||
| 3.A: Primary Analyses | Post hoc Group-Wise Comparison, p | Post hoc Group-Wise Comparison, Adjusted p | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk Status | Affected (n = 105) | High Risk (n = 48) | Low Risk (n = 38) | p | AF vs. LR | AF vs. HR | HR vs. LR | AF vs. LR | AF vs. HR | HR vs. LR |
| ApoE Titer (mg/L, CI) | 41.9 (39.5–44.4) | 38.9 (35.9–41.9) | 42.1 (37.3–46.9) | 0.097 | 0.951 | 0.035 | 0.261 | 0.906 | 0.045 | 0.345 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L, CI) | 1.1 (1.0–1.2) | 0.9 (0.8–1.1) | 0.8 (0.5–1.0) | 0.052 | 0.026 | 0.176 | 0.189 | 0.962 | 0.012 | 0.048 |
| HDL (nmol/L, CI) | 1.6 (1.5–1.7) | 1.6 (1.5–1.7) | 1.7 (1.5–1.9) | 0.289 | 0.118 | 0.946 | 0.148 | 0.095 | 0.994 | 0.116 |
| LDL (nmol/L, CI) | 2.9 (2.7–3.1) | 2.9 (2.7–3.1) | 2.7 (2.4–3.1) | 0.731 | 0.524 | 0.696 | 0.440 | 0.390 | 0.621 | 0.300 |
| Cholesterol (nmol/L, CI) | 4.8 (4.5–5.0) | 4.8 (4.5–5.0) | 4.7 (4.2–5.1) | 0.888 | 0.698 | 0.811 | 0.630 | 0.565 | 0.759 | 0.487 |
| 3.B: Secondary concordance analyses | Post hoc pairwise comparison, p | Post hoc adjusted pairwise comparison, p | ||||||||
| Risk Status | Concordant affected (25 twin pairs) | Discordant (45 twin pairs) | Low risk (19 twin pairs) | p | CA vs. LR | CA vs. Di | Di vs. LR | CA vs. LR | CA vs. Di | Di vs. LR |
| ApoE Titer (mg/L, CI) | 44.0 (39.7–48.2) | 38.6 (35.4–41.8) | 42.1 (37.2–47.0) | 0.260 | 0.568 | 0.046 | 0.231 | 0.549 | 0.054 | 0.282 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L, CI) | 1.3 (1.1–1.5) | 0.9 (0.7–1.1) | 0.7 (0.5–1.0) | 0.025 | 0.003 | 0.008 | 0.362 | 0.002 | 0.008 | 0.264 |
| HDL (nmol/L, CI) | 1.7 (1.5–1.7) | 1.5 (1.4–1.7) | 1.7 (1.5–1.9) | 0.439 | 0.595 | 0.260 | 0.107 | 0.505 | 0.253 | 0.086 |
| LDL (nmol/L, CI) | 2.7 (2.4–3.1) | 2.9 (2.7–3.2) | 2.7 (2.4–3.2) | 0.764 | 0.836 | 0.310 | 0.485 | 0.940 | 0.333 | 0.353 |
| Cholesterol (nmol/L, CI) | 4.6 (4.3–5.0) | 4.7 (4.5–5.0) | 4.6 (4.3–5.1) | 0.876 | 0.849 | 0.595 | 0.785 | 0.944 | 0.659 | 0.644 |
| 3.C: Tertiary discordance analyses | ||||||||||
| Risk Status | Affected twin (n = 45) | Unaffected twin (n = 45) | p | |||||||
| ApoE Titer (mg/L) | 39.4 | 36.8 | 0.037 | |||||||
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.542 | |||||||
| HDL (nmol/L) | 1.5 | 1.5 | 0.826 | |||||||
| LDL (nmol/L) | 2.8 | 2.9 | 0.590 | |||||||
| Cholesterol (nmol/L) | 4.6 | 4.7 | 0.594 | |||||||
| SCIP-VFT | SCIP-VLT-1 | SCIP-VLT-D | SCIP-WMT | SCIP-PST | SCIP-total | TMT-A | TMT-B | [ApoE] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [ApoE] | |||||||||
| p | 0.625 | 0.604 | 0.909 | 0.974 | 0.696 | 0.808 | 0.890 | 0.642 | - |
| r | −0.04 | −0.04 | −0.01 | 0.00 | −0.03 | −0.02 | −0.01 | 0.03 | - |
| [Triglycerides] | |||||||||
| p | 0.727 | 0.641 | 0.499 | 0.799 | 0.295 | 0.342 | 0.223 | 0.871 | 0.000 |
| r | −0.02 | −0.03 | −0.05 | −0.02 | −0.07 | −0.07 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.44 |
| [Cholesterol] | |||||||||
| p | 0.487 | 0.546 | 0.601 | 0.050 | 0.026 | 0.114 | 0.003 | 0.010 | 0.000 |
| r | −0.05 | −0.04 | −0.04 | −0.14 | −0.16 | −0.11 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.41 |
| [HDL] | |||||||||
| p | 0.112 | 0.001 | 0.018 | 0.864 | 0.360 | 0.022 | 0.453 | 0.989 | 0.996 |
| r | 0.11 | 0.24 | 0.17 | −0.01 | 0.06 | 0.16 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| [LDL] | |||||||||
| p | 0.514 | 0.099 | 0.268 | 0.079 | 0.044 | 0.066 | 0.009 | 0.016 | 0.000 |
| r | −0.05 | −0.12 | −0.08 | −0.12 | −0.14 | −0.13 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sperling, J.D.; Frikke-Schmidt, R.; Scheike, T.; Kessing, L.V.; Miskowiak, K.; Vinberg, M. APOE Genotype, ApoE Plasma Levels, Lipid Metabolism, and Cognition in Monozygotic Twins with, at Risk of, and without Affective Disorders. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13082361
Sperling JD, Frikke-Schmidt R, Scheike T, Kessing LV, Miskowiak K, Vinberg M. APOE Genotype, ApoE Plasma Levels, Lipid Metabolism, and Cognition in Monozygotic Twins with, at Risk of, and without Affective Disorders. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(8):2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13082361
Chicago/Turabian StyleSperling, Jon Dyg, Ruth Frikke-Schmidt, Thomas Scheike, Lars Vedel Kessing, Kamilla Miskowiak, and Maj Vinberg. 2024. "APOE Genotype, ApoE Plasma Levels, Lipid Metabolism, and Cognition in Monozygotic Twins with, at Risk of, and without Affective Disorders" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 8: 2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13082361
APA StyleSperling, J. D., Frikke-Schmidt, R., Scheike, T., Kessing, L. V., Miskowiak, K., & Vinberg, M. (2024). APOE Genotype, ApoE Plasma Levels, Lipid Metabolism, and Cognition in Monozygotic Twins with, at Risk of, and without Affective Disorders. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(8), 2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13082361






