All You Need to Know About TACE: A Comprehensive Review of Indications, Techniques, Efficacy, Limits, and Technical Advancement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Indications
3. Procedural Equipment and Preparation
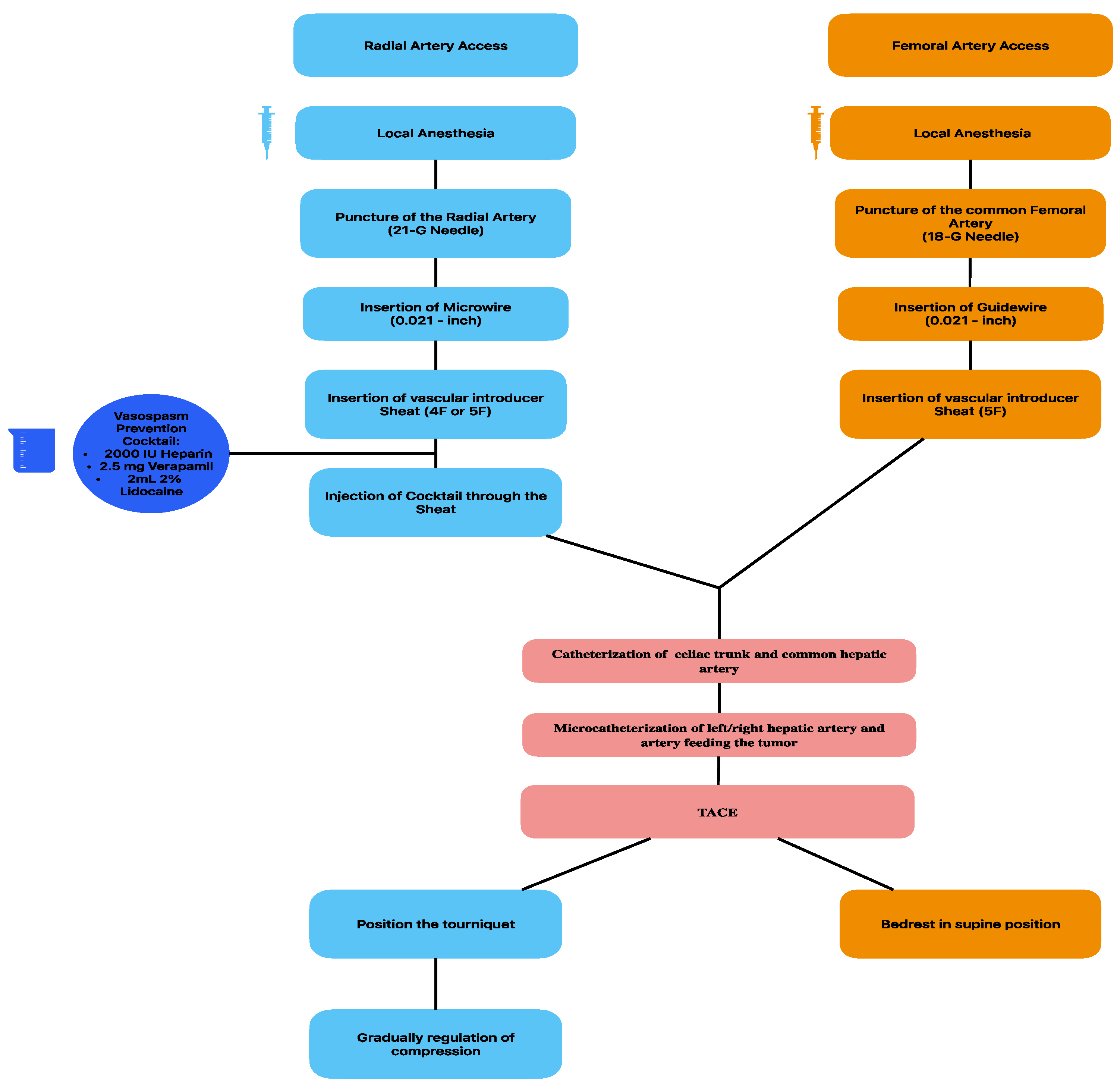
3.1. Vascular Access
3.2. Guidance Systems
3.3. Chemodrugs
4. Types of TACE
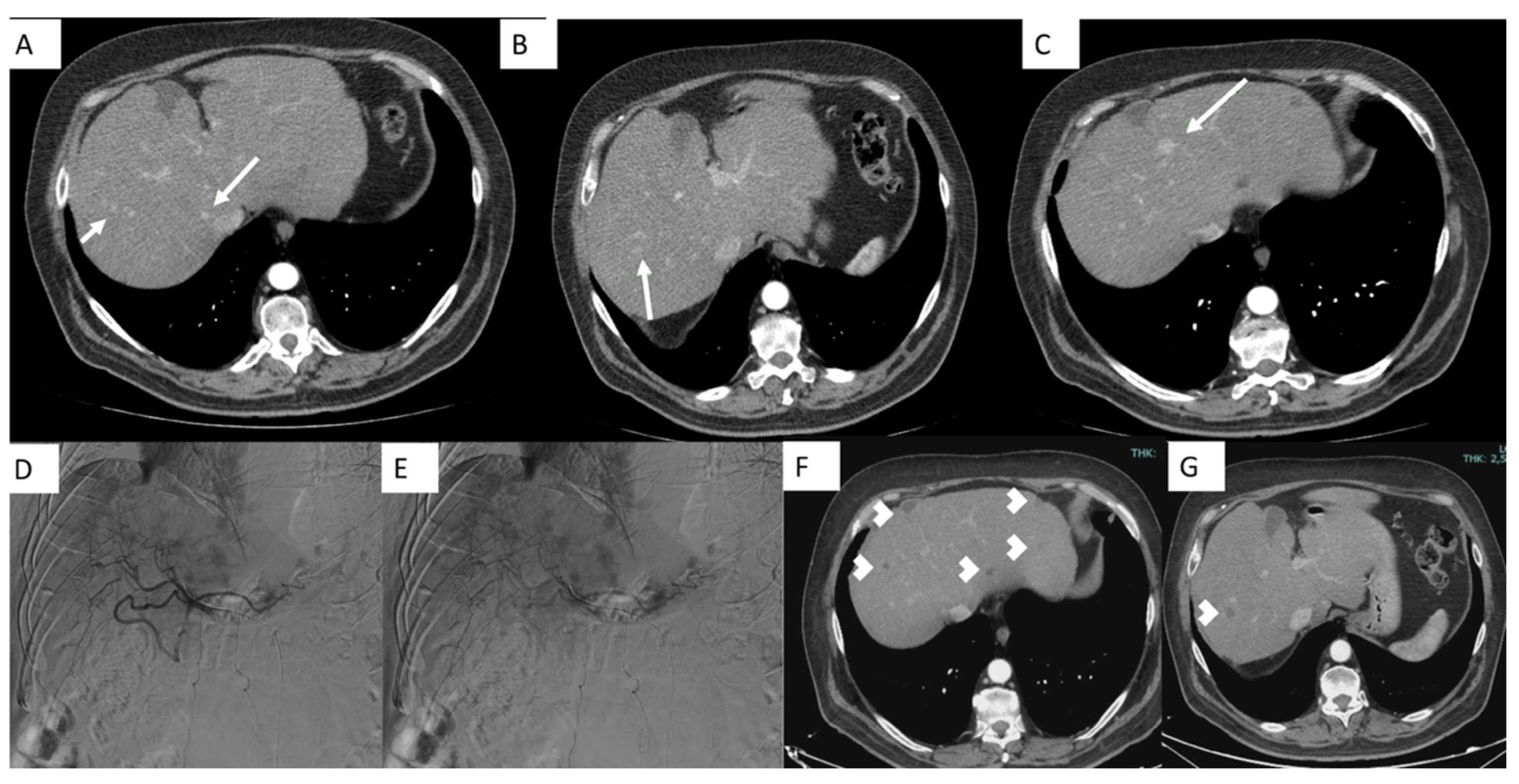
4.1. Conventional TACE (c-TACE)
4.2. Balloon-Occluded Transarterial Chemoembolization (b-TACE)
4.3. Degradable Starch Microsphere (DSM) Transarterial Chemoembolization (DSM-TACE)
4.4. Drug Eluting Microspheres Transarterial Chemoembolization (DEM-TACE)
- DC Beads
- DC Bead LUMI
- HepaSphere
- TANDEM Microspheres
4.5. Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy (HAIC)
5. Complications
5.1. Early Complications
5.1.1. Intraprocedural Complications
5.1.2. Post-Procedural Complications
5.1.3. Acute Pancreatitis
5.1.4. Skin Injury
5.2. Late Complications
5.2.1. Liver Failure
5.2.2. Renal Failure
5.2.3. Liver Infarction
5.2.4. Liver Abscess
5.2.5. Tumor Rupture
5.2.6. Biliary Complications
5.2.7. Post Embolization Syndrome (PES)
6. Follow-Up and Response to Treatment
7. Future Perspectives
8. Artificial Intelligence
9. Discussion
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Renzulli, M.; Brandi, N.; Argalia, G.; Brocchi, S.; Farolfi, A.; Fanti, S.; Golfieri, R. Morphological, dynamic and functional characteristics of liver pseudolesions and benign lesions. Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Bruix, J. Novel advancements in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma in 2008. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, S20–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolondi, L. Screening for hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2003, 39, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, S.-M.; Huang, H.; Cheng, M.-Q.; Lin, M.-X.; Hu, H.-T.; Huang, Y.; Lu, M.-D.; Wang, W. Shear-wave elastography combined with contrast-enhanced ultrasound algorithm for noninvasive characterization of focal liver lesions. Radiol. Med. 2022, 128, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şendur, A.B.; Cerit, M.N.; Şendur, H.N. Clinical applicability of US-based hepatic fat quantification tools may be expedited by adherence to guidelines. Radiol. Med. 2023, 128, 1589–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmo, F.F.; Barr, R.G.; Yokoo, T.; Ferraioli, G.; Lee, J.T.; Dillman, J.R.; Horowitz, J.M.; Jhaveri, K.S.; Miller, F.H.; Modi, R.Y.; et al. Liver Fibrosis, Fat, and Iron Evaluation with MRI and Fibrosis and Fat Evaluation with US: A Practical Guide for Radiologists. RadioGraphics 2023, 43, e220181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondetti, P.; Lanza, C.; Carriero, S.; Arrigoni, F.; Bevilacqua, M.; Ruffino, A.; Triggiani, S.; Sorce, A.; Coppola, A.; Ierardi, A.M.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Transarterial Chemoembolization with DC Beads LUMI in the Treatment of HCC: Experience from a Tertiary Centre. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 22, 15330338231184840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galle, P.R.; Forner, A.; Llovet, J.M.; Mazzaferro, V.; Piscaglia, F.; Raoul, J.-L.; Schirmacher, P.; Vilgrain, V. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reig, M.; Forner, A.; Rimola, J.; Ferrer-Fàbrega, J.; Burrel, M.; Garcia-Criado, Á.; Kelley, R.K.; Galle, P.R.; Mazzaferro, V.; Salem, R.; et al. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J. Hepatol. 2021, 76, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.G.; Llovet, J.M.; Yarchoan, M.; Mehta, N.; Heimbach, J.K.; Dawson, L.A.; Jou, J.H.; Kulik, L.M.; Agopian, V.G.; Marrero, J.A.; et al. AASLD Practice Guidance on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2023, 78, 1922–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Wu, J.; Wei, H.; Jiang, Z.; Wan, M.; Wu, C.; Xue, W.; Ma, R.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, H. Combining serum AFP and CEUS LI-RADS for better diagnostic performance in Chinese high-risk patients. Radiol. Med. 2023, 128, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korean Liver Cancer Association. 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea Practice Guidelines for the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Korean J. Radiol. 2022, 23, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, A.; Martinelli, E.; Cervantes, A.; Chau, I.; Daniele, B.; Llovet, J.; Meyer, T.; Nault, J.-C.; Neumann, U.; Ricke, J.; et al. Updated treatment recommendations for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) from the ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horikawa, M.; Miyayama, S.; Irie, T.; Kaji, T.; Arai, Y. Development of Conventional Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinomas in Japan: Historical, Strategic, and Technical Review. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 205, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, J.M.; Iezzi, R.; Theysohn, J.M.; Albrecht, T.; Posa, A.; Gross, A. European Multicenter Study on Degradable Starch Microsphere TACE: The Digestible Way to Conquer HCC in Patients with High Tumor Burden. Cancers 2021, 13, 5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, P.; Kaldewey, D.; Rennebaum, F.; Trebicka, J.; Pascher, A.; Wildgruber, M.; Köhler, M.; Masthoff, M. Safety, efficacy, and survival of different transarterial chemoembolization techniques in the management of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A comparative single-center analysis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 150, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.D.; Hainaut, P.; Gores, G.J.; Amadou, A.; Plymoth, A.; Roberts, L.R. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: Trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Choi, J.W.; Kwon, H.; Kim, K.Y.; Lee, B.C.; Chu, H.H.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, H.A.; Kim, G.M.; Oh, J.S.; et al. Transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: 2023 expert consensus-based practical recommendations of the Korean Liver Cancer Association. J. Liver Cancer 2023, 23, 241–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association For The Study Of The Liver. European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer. EASL–EORTC clinical practice guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 908–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhao, M.; Arai, Y.; Zhong, B.-Y.; Zhu, H.-D.; Qi, X.-L.; de Baere, T.; Pua, U.; Yoon, H.K.; Madoff, D.C.; et al. Clinical practice of transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: Consensus statement from an international expert panel of International Society of Multidisciplinary Interventional Oncology (ISMIO). HepatoBiliary Surg. Nutr. 2021, 10, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forner, A.; Gilabert, M.; Bruix, J.; Raoul, J.-L. Treatment of intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoul, J.-L.; Sangro, B.; Forner, A.; Mazzaferro, V.; Piscaglia, F.; Bolondi, L.; Lencioni, R. Evolving strategies for the management of intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: Available evidence and expert opinion on the use of transarterial chemoembolization. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2011, 37, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieghart, W.; Hucke, F.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M. Transarterial chemoembolization: Modalities, indication, and patient selection. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.M.; Kim, J.H.; Park, I.S.; Ko, G.; Yoon, H.; Sung, K.; Lim, Y.; Lee, H.C.; Chung, Y.H.; Lee, Y.S.; et al. Reappraisal of repeated transarterial chemoembolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein invasion. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 24, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M.; Han, K.-H.; Ye, S.-L.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Y.-H.; Lin, S.-M.; Wang, C.-K.; Ikeda, M.; Chan, S.L.; Choo, S.P.; et al. A Changing Paradigm for the Treatment of Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Asia-Pacific Primary Liver Cancer Expert Consensus Statements. Liver Cancer 2020, 9, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, C.; Sheng, R.; Dai, Y.; Zeng, M. Predicting the recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma (≤5 cm) after resection surgery with promising risk factors: Habitat fraction of tumor and its peritumoral micro-environment. Radiol. Med. 2023, 128, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Fanelli, F.; Haage, P.; Hausegger, K.; Van Lienden, K.P. Patient Safety in Interventional Radiology: A CIRSE IR Checklist. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 35, 244–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-Y.; Liu, P.; Wu, Y.-S.; Lin, H.; Chen, X. Transradial vs transfemoral access in patients with hepatic malignancy and undergoing hepatic interventions. Medicine 2018, 97, e13926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, K.; Guo, T.; Sun, D.; Song, H.; Liu, Z. Transradial versus transfemoral approach for TACE: A retrospective study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023, 23, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Gupta, V.; Al Khalifah, A.; Akhter, N.M. Transradial versus transfemoral arterial access in DEB-TACE for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Imaging Sci. 2022, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iezzi, R.; Pompili, M.; Posa, A.; Annicchiarico, E.; Garcovich, M.; Merlino, B.; Rodolfino, E.; Di Noia, V.; Basso, M.; Cassano, A.; et al. Transradial versus Transfemoral Access for Hepatic Chemoembolization: Intrapatient Prospective Single-Center Study. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 28, 1234–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; He, J.; Wu, T.; Sun, R.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yin, X.; Zhu, Z. Transradial arterial chemoembolization reduces complications and costs in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Indian J. Cancer 2015, 52, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedjoudje, M.; Barat, M.; Dohan, A.; Lucas, A.; Dautry, R.; Coriat, R.; Marchese, U.; Pol, S.; Parlati, L.; Soyer, P. Comparison Between Radial and Femoral Artery Access for Transarterial Chemoembolisation in Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2024, 75, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, R.; Bracewell, S.; Bassaco, B.; Camacho, J.; Anderson, M.B.; Conrad, A.; Lynn, C.; Burns, P.; Collins, H.; Guimaraes, M. Transradial Versus Transfemoral Arterial Access in Liver Cancer Embolization: Randomized Trial to Assess Patient Satisfaction. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 29, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virmani, S.; Ryu, R.K.; Sato, K.T.; Lewandowski, R.J.; Kulik, L.; Mulcahy, M.F.; Larson, A.C.; Salem, R.; Omary, R.A. Effect of C-arm Angiographic CT on Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization of Liver Tumors. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2007, 18, 1305–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floridi, C.; Radaelli, A.; Abi-Jaoudeh, N.; Grass, M.; De Lin, M.; Chiaradia, M.; Geschwind, J.-F.; Kobeiter, H.; Squillaci, E.; Maleux, G.; et al. C-arm cone-beam computed tomography in interventional oncology: Technical aspects and clinical applications. Radiol. Med. 2014, 119, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucatelli, P.; Burrel, M.; Guiu, B.; de Rubeis, G.; van Delden, O.; Helmberger, T. CIRSE Standards of Practice on Hepatic Transarterial Chemoembolisation. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2021, 44, 1851–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothary, N.; Abdelmaksoud, M.H.; Tognolini, A.; Fahrig, R.; Rosenberg, J.; Hovsepian, D.M.; Ganguly, A.; Louie, J.D.; Kuo, W.T.; Hwang, G.L.; et al. Imaging Guidance with C-arm CT: Prospective Evaluation of Its Impact on Patient Radiation Exposure during Transhepatic Arterial Chemoembolization. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2011, 22, 1535–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacher, V.; Radaelli, A.; Lin, M.; Geschwind, J.-F. How I Do It: Cone-Beam CT during Transarterial Chemoembolization for Liver Cancer. Radiology 2015, 274, 320–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baere, T.; Arai, Y.; Lencioni, R.; Geschwind, J.-F.; Rilling, W.; Salem, R.; Matsui, O.; Soulen, M.C. Treatment of Liver Tumors with Lipiodol TACE: Technical Recommendations from Experts Opinion. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 39, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucatelli, P.; Argirò, R.; Bascetta, S.; Saba, L.; Catalano, C.; Bezzi, M.; Sandri, G.B.L. Single injection dual phase CBCT technique ameliorates results of trans-arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular cancer. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyayama, S.; Yamashiro, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Hashimoto, N.; Ikuno, M.; Okumura, K.; Yoshida, M.; Matsui, O. Comparison of Local Control in Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma ≤6 cm With or Without Intraprocedural Monitoring of the Embolized Area Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 37, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogl, T.J.; Gruber-Rouh, T. HCC: Transarterial Therapies—What the Interventional Radiologist Can Offer. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 64, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahara, S.; Kawai, N.; Sato, M.; Tanaka, T.; Ikoma, A.; Nakata, K.; Sanda, H.; Minamiguchi, H.; Nakai, M.; Shirai, S.; et al. Prospective Evaluation of Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization (TACE) with Multiple Anti-Cancer Drugs (Epirubicin, Cisplatin, Mitomycin C, 5-Fluorouracil) Compared with TACE with Epirubicin for Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 35, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yodono, H.; Matsuo, K.; Shinohara, A. A retrospective comparative study of epirubicin–lipiodol emulsion and cisplatin–lipiodol suspension for use with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2011, 22, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabe, N.; Hashimoto, S.; Nakano, T.; Nakaoka, K.; Fukui, A.; Yoshioka, K. Transcatheter arterial infusion chemotherapy with cisplatin in combination with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization decreases intrahepatic distant recurrence of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. JGH Open 2021, 5, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, M.; Kudo, M.; Aikata, H.; Nagamatsu, H.; Ishii, H.; Yokosuka, O.; Torimura, T.; Morimoto, M.; Ikeda, K.; Kumada, H.; et al. Transarterial chemoembolization with miriplatin vs. epirubicin for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase III randomized trial. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyayama, S. Treatment Strategy of Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozzanigo, U.; Gatti, F.; Luppi, G.; Costa, L.; Petralia, B.; Pravadelli, C.; Maioli, I.; Frisinghelli, M.; Fersino, S.; Berletti, R.; et al. Chemoembolization with Degradable Starch Microspheres (DSM-TACE): Expanding indications in HCC multidisciplinary tumor board. Hepatoma Res. 2023, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Geng, H.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yang, K.; Yang, L.; Hui, F.; Zhang, Y. Which is the best TACE agent for patients with different NLR hepatocellular carcinomas? A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoul, J.-L.; Forner, A.; Bolondi, L.; Cheung, T.T.; Kloeckner, R.; de Baere, T. Updated use of TACE for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: How and when to use it based on clinical evidence. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2019, 72, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Bruix, J. Systematic review of randomized trials for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Chemoembolization improves survival. Hepatology 2003, 37, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Cao, C.; Wei, X.; Shen, K.; Shu, Y.; Wan, X.; Sun, J.; Ren, X.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. A comparison between drug-eluting bead-transarterial chemoembolization and conventional transarterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2020, 16, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyayama, S.; Yamashiro, M.; Okuda, M.; Aburano, H.; Shigenari, N.; Morinaga, K.; Matsui, O. Anastomosis between the hepatic artery and the extrahepatic collateral or between extrahepatic collaterals: Observation on angiography. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2009, 53, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyayama, S.; Matsui, O. Superselective Conventional Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Rationale, Technique, and Outcome. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 27, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Matsui, O.; Miyayama, S.; Ibukuro, K.; Yoneda, N.; Inoue, D.; Kozaka, K.; Minami, T.; Koda, W.; Gabata, T. Isolated Arteries Originating from the Intrahepatic Arteries: Anatomy, Function, and Importance in Intervention. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 29, 531–537.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Hongo, O.; Iwamoto, H.; Sanefuji, H. Excellent outcomes with angiographic subsegmentectomy in the treatment of typical hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 2010, 116, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Hashimoto, T.; Oi, H.; Sawada, S. Transcatheter oily chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology 1989, 170, 783–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, W.-S.; Wu, R.-H.; Chang, S.-C.; Chou, C.-K.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chen, J.-J.; Yang, S.-C.; Lin, C.-H. Ionic Versus Nonionic Contrast Media Solvents Used with an Epirubicin-based Agent for Transarterial Chemoembolization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2008, 19, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.-M.; Ngan, H.; Tso, W.-K.; Liu, C.-L.; Lam, C.-M.; Poon, R.T.-P.; Fan, S.-T.; Wong, J. Randomized controlled trial of transarterial lipiodol chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2002, 35, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Real, M.I.; Montaña, X.; Planas, R.; Coll, S.; Aponte, J.; Ayuso, C.; Sala, M.; Muchart, J.; Solà, R.; et al. Arterial embolisation or chemoembolisation versus symptomatic treatment in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2002, 359, 1734–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucatelli, P.; Corradini, L.G.; De Rubeis, G.; Rocco, B.; Basilico, F.; Cannavale, A.; Nardis, P.G.; Corona, M.; Saba, L.; Catalano, C.; et al. Balloon-Occluded Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization (b-TACE) for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Performed with Polyethylene-Glycol Epirubicin-Loaded Drug-Eluting Embolics: Safety and Preliminary Results. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 42, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golfieri, R.; Bezzi, M.; Verset, G.; Fucilli, F.; Mosconi, C.; Cappelli, A.; Paccapelo, A.; Lucatelli, P.; Magand, N.; Rode, A.; et al. Balloon-Occluded Transarterial Chemoembolization: In Which Size Range Does It Perform Best? A Comparison of Its Efficacy versus Conventional Transarterial Chemoembolization, Using Propensity Score Matching. Liver Cancer 2021, 10, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irie, T.; Kuramochi, M.; Takahashi, N. Dense Accumulation of Lipiodol Emulsion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Nodule during Selective Balloon-occluded Transarterial Chemoembolization: Measurement of Balloon-occluded Arterial Stump Pressure. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 36, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, S.C.; Narsinh, K.H.; Isaacson, A.J.; Fischman, A.M.; Golzarian, J. The Beauty and Bane of Pressure-Directed Embolotherapy: Hemodynamic Principles and Preliminary Clinical Evidence. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 212, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, T.; Endo, J.; Hashida, K.; Ichikawa, H.; Kojima, S.; Takashimizu, S.; Watanabe, N.; Yamagami, T.; Hasebe, T. Balloon-occluded transarterial chemoembolization using a 1.8-French tip Coaxial microballoon catheter for hepatocellular carcinoma: Technical and safety considerations. Minim. Invasive Ther. Allied Technol. 2015, 24, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ierardi, A.M.; Stellato, E.; Pellegrino, G.; Bonelli, C.; Cellina, M.; Renzulli, M.; Biondetti, P.; Carrafiello, G. Fluid-dynamic control microcatheter used with glue: Preliminary experience on its feasibility and safety. Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, M.; Takayasu, K.; Hirayama, M.; Miura, T.; Shiozawa, K.; Abe, M.; Matsumoto, N.; Nakagawara, H.; Ohshiro, S.; Yamamoto, T.; et al. Efficacy of a microballoon catheter in transarterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma using miriplatin, a lipophilic anticancer drug: Short-term results. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, E60–E69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, H.; Abe, T.; Takayama, H.; Toyoda, M.; Ueno, T.; Kakizaki, S.; Sato, K. Safety and efficacy of balloon-occluded transcatheter arterial chemoembolization using miriplatin for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2014, 45, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.H.; Gwon, D.I.; Kim, G.H.; Kim, J.H.; Ko, G.-Y.; Shin, J.H.; Ko, H.-K.; Yoon, H.-K. Balloon-occluded transarterial chemoembolization versus conventional transarterial chemoembolization for the treatment of single hepatocellular carcinoma: A propensity score matching analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 33, 2655–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucatelli, P.; Rocco, B.; Ciaglia, S.; Damato, E.; Mosconi, C.; Argirò, R.; Catalano, C. Microballoon Interventions for Liver Tumors: Review of Literature and Future Perspectives. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucatelli, P.; De Rubeis, G.; Rocco, B.; Basilico, F.; Cannavale, A.; Abbatecola, A.; Nardis, P.G.; Corona, M.; Brozzetti, S.; Catalano, C.; et al. Balloon occluded TACE (B-TACE) vs DEM-TACE for HCC: A single center retrospective case control study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucatelli, P.; De Rubeis, G.; Trobiani, C.; Ungania, S.; Rocco, B.; De Gyurgyokai, S.Z.; Masi, M.; Pecorella, I.; Cappelli, F.; Lai, Q.; et al. In Vivo Comparison of Micro-Balloon Interventions (MBI) Advantage: A Retrospective Cohort Study of DEB-TACE Versus b-TACE and of SIRT Versus b-SIRT. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2022, 45, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irie, T.; Kuramochi, M.; Kamoshida, T.; Takahashi, N. Selective balloon-occluded transarterial chemoembolization for patients with one or two hepatocellular carcinoma nodules: Retrospective comparison with conventional super-selective TACE. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lote, K.; Følling, M.; Rosengren, B.; Svanes, K.; Lekven, J. Transient Intestinal Ischaemia Induced by Degradable Starch Microspheres: Experiments in the cat. Acta Radiol. Oncol. 1980, 19, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsberg, J.O.; Jung, B.; Larsson, B. Mucosal Protection During Irradiation of Exteriorized Rat Ileum: Effect of Hypoxia Induced by Starch Microspheres. Acta Radiol. Oncol. Radiation, Physics, Biol. 1978, 17, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wiggermann, P.; Heibl, M.; Niessen, C.; Müller-Wille, R.; Gössmann, H.; Uller, W.; Poschenrieder, F.; Schreyer, A.; Wohlgemuth, W.; Stroszczynski, C.; et al. Degradable starch microspheres transarterial chemoembolisation (DSM-TACE) of HCC: Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasonography (DCE-US) based evaluation of therapeutic efficacy using a novel perfusion software. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2012, 52, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schicho, A.; Hellerbrand, C.; Krüger, K.; Beyer, L.P.; Wohlgemuth, W.; Niessen, C.; Hohenstein, E.; Stroszczynski, C.; Pereira, P.L.; Wiggermann, P. Impact of Different Embolic Agents for Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Procedures on Systemic Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Levels. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2016, 4, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubold, J.; Reinboldt, M.P.; Wetter, A.; Li, Y.; Ludwig, J.M.; Lange, C.; Wedemeyer, H.; Schotten, C.; Umutlu, L.; Theysohn, J. DSM-TACE of HCC: Evaluation of Tumor Response in Patients Ineligible for Other Systemic or Loco-Regional Therapies. Rofo-Fortschritte Auf Dem Geb. Der Rontgenstrahlen Und Der Bild. Verfahr. 2020, 192, 862–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, I.; Yildiz, I.; Deniz, S.; Deniz, S.; Ozer, A.; Ozer, A.; Caliskan, K.; Caliskan, K. Trans-Arterial Chemoembolization with 50 μm Degradable Starch Microspheres Versus 300–500 μm Drug Eluting Beads in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Comparative Analysis of Initial Treatment Outcomes. J. Belg. Soc. Radiol. 2022, 106, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlacchio, A.; Chegai, F.; Merolla, S.; Francioso, S.; Del Giudice, C.; Angelico, M.; Tisone, G.; Simonetti, G. Downstaging disease in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma outside up-to-seven criteria: Strategies using degradable starch microspheres transcatheter arterial chemo-embolization. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 1694–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlacchio, A.; Chegai, F.; Roma, S.; Merolla, S.; Bosa, A.; Francioso, S. Degradable starch microspheres transarterial chemoembolization (DSMs-TACE) in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): Long-term results from a single-center 137-patient cohort prospective study. Radiol. Med. 2020, 125, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlacchio, A.; Chegai, F.; Francioso, S.; Merolla, S.; Monti, S.; Angelico, M.; Tisone, G.; Mannelli, L. Repeated Transarterial Chemoembolization with Degradable Starch Microspheres (DSMs-TACE) of Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Prospective Pilot Study. Curr. Med. Imaging Rev. 2018, 14, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, K.; Khwaja, A.; Liapi, E.; Torbenson, M.S.; Georgiades, C.S.; Geschwind, J.-F.H. New Intra-arterial Drug Delivery System for the Treatment of Liver Cancer: Preclinical Assessment in a Rabbit Model of Liver Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 2563–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchiorre, F.; Patella, F.; Pescatori, L.; Pesapane, F.; Fumarola, E.; Biondetti, P.; Brambillasca, P.; Monaco, C.; Ierardi, A.M.; Franceschelli, G.; et al. DEB-TACE: A Standard Review. Futur. Oncol. 2018, 14, 2969–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.T.; Do, R.K.; Gonen, M.; Covey, A.M.; Getrajdman, G.I.; Sofocleous, C.T.; Jarnagin, W.R.; D’angelica, M.I.; Allen, P.J.; Erinjeri, J.P.; et al. Randomized Trial of Hepatic Artery Embolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Doxorubicin-Eluting Microspheres Compared With Embolization With Microspheres Alone. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2046–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloeckner, R.; Weinmann, A.; Prinz, F.; dos Santos, D.P.; Ruckes, C.; Dueber, C.; Pitton, M.B. Conventional transarterial chemoembolization versus drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucatelli, P.; Argirò, R.; De Rubeis, G.; Rocco, B.; Corradini, S.G.; Corona, M.; Nardis, P.G.; Saba, L.; Mennini, G.; Fiorentino, F.; et al. Polyethylene Glycol Epirubicin-Loaded Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization Procedures Utilizing a Combined Approach with 100 and 200 μm Microspheres: A Promising Alternative to Current Standards. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 30, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, K.; Tang, Y.; Britton, H.; Domenge, O.; Blino, D.; Bushby, A.J.; Shuturminska, K.; Hartog, M.D.; Radaelli, A.; Negussie, A.H.; et al. Characterization of a novel intrinsically radiopaque Drug-eluting Bead for image-guided therapy: DC Bead LUMI™. J. Control. Release 2017, 250, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luis, E.; Bilbao, J.I.; De Ciércoles, J.A.G.J.; Martínez-Cuesta, A.; Rodríguez, A.D.M.; Lozano, M.D. In Vivo Evaluation of a New Embolic Spherical Particle (HepaSphere) in a Kidney Animal Model. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2008, 31, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, G.; Radeleff, B.; Stroszczynski, C.; Pereira, P.; Helmberger, T.; Barakat, M.; Huppert, P. Safety and Feasibility of Chemoembolization with Doxorubicin-Loaded Small Calibrated Microspheres in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Results of the MIRACLE I Prospective Multicenter Study. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 41, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lencioni, R.; De Baere, T.; Burrel, M.; Caridi, J.G.; Lammer, J.; Malagari, K.; Martin, R.C.G.; O’Grady, E.; Real, M.I.; Vogl, T.J.; et al. Transcatheter Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Doxorubicin-loaded DC Bead (DEBDOX): Technical Recommendations. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 35, 980–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malagari, K.; Chatzimichael, K.; Alexopoulou, E.; Kelekis, A.; Hall, B.; Dourakis, S.; Delis, S.; Gouliamos, A.; Kelekis, D. Transarterial Chemoembolization of Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Drug Eluting Beads: Results of an Open-Label Study of 62 Patients. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2008, 31, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammer, J.; Malagari, K.; Vogl, T.; Pilleul, F.; Denys, A.; Watkinson, A.; Pitton, M.; Sergent, G.; Pfammatter, T.; Terraz, S.; et al. Prospective Randomized Study of Doxorubicin-Eluting-Bead Embolization in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Results of the PRECISION V Study. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 33, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golfieri, R.; Giampalma, E.; Renzulli, M.; Cioni, R.; Bargellini, I.; Bartolozzi, C.; Breatta, A.D.; Gandini, G.; Nani, R.; Gasparini, D.; et al. Randomised controlled trial of doxorubicin-eluting beads vs conventional chemoembolisation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Liang, J.; Qu, Z.; Yang, F.; Liao, Z.; Gou, H. Transarterial strategies for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zheng, X.; Lu, D.; Tan, Y.; Hou, C.; Dai, J.; Shi, W.; Jiang, B.; Yao, Y.; Lu, Y.; et al. A multi-institutional study to predict the benefits of DEB-TACE and molecular targeted agent sequential therapy in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma using a radiological-clinical nomogram. Radiol. Med. 2023, 129, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, N.; Wang, H.; He, C.; Wang, X.; Huang, J.; Yang, Y. Optimal interventional treatment for liver cancer: HAIC, TACE or iTACE? J. Interv. Med. 2023, 6, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Cai, H.; He, B.; Guan, R.; Lee, C.; Guo, R. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy versus transarterial chemoembolization, potential conversion therapies for single huge hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective comparison study. Int. J. Surg. 2023, 109, 3303–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, M.; Morizane, C.; Ueno, M.; Okusaka, T.; Ishii, H.; Furuse, J. Chemotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Current status and future perspectives. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 48, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueshima, K.; Komemushi, A.; Aramaki, T.; Iwamoto, H.; Obi, S.; Sato, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Matsueda, K.; Moriguchi, M.; Saito, H.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy with a Port System Proposed by the Japanese Society of Interventional Radiology and Japanese Society of Implantable Port Assisted Treatment. Liver Cancer 2022, 11, 407–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, E.; Ooka, Y.; Chiba, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Kanogawa, N.; Motoyama, T.; Saito, T.; Ogasawara, S.; Tawada, A.; Yokosuka, O. Incidental tumor necrosis caused by the interventional alteration of hepatic arterial flow in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. . Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 8, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Ono, N.; Yodono, H.; Ichida, T.; Nakamura, H. Phase II study of hepatic arterial infusion of a fine-powder formulation of cisplatin for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2008, 38, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, H.; Fukuchi, H.; Tanaka, C. Toxicity and efficacy of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2012, 3, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck-Radosavljevic, M.; Bota, S.; Hucke, F. Time to stop using hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma?—The SCOOP-2 trial experience. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.H.; Song, I.H.; Song, B.C.; Lee, G.C.; Koh, M.S.; Yoon, H.K.; Lee, Y.S.; Sung, K.B.; Suh, D.J. Combined therapy consisting of intraarterial cisplatin infusion and systemic interferon-alpha for hepatocellular carcinoma patients with major portal vein thrombosis or distant metastasis. Cancer 2000, 88, 1986–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouso, K.; Miyahara, K.; Uchida, D.; Kuwaki, K.; Izumi, N.; Omata, M.; Ichida, T.; Kudo, M.; Ku, Y.; Kokudo, N.; et al. Effect of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy of 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in the Nationwide Survey of Primary Liver Cancer in Japan. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 1904–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monden, M.; Sakon, M.; Sakata, Y.; Ueda, Y.; Hashimura, E. 5-fluorouracil arterial infusion + interferon therapy for highly advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A multicenter, randomized, phase II study. Hepatol. Res. 2012, 42, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucatelli, P.; De Rubeis, G.; Corradini, L.G.; Basilico, F.; Di Martino, M.; Lai, Q.; Corradini, S.G.; Cannavale, A.; Nardis, P.G.; Corona, M.; et al. Intra-procedural dual phase cone beam computed tomography has a better diagnostic accuracy over pre-procedural MRI and MDCT in detection and characterization of HCC in cirrhotic patients undergoing TACE procedure. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 124, 108806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, M.; Shimizu, S.; Sato, T.; Morimoto, M.; Kojima, Y.; Inaba, Y.; Hagihara, A.; Kudo, M.; Nakamori, S.; Kaneko, S.; et al. Sorafenib plus hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy with cisplatin versus sorafenib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Randomized phase II trial. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 2090–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M.; Ueshima, K.; Yokosuka, O.; Obi, S.; Izumi, N.; Aikata, H.; Nagano, H.; Hatano, E.; Sasaki, Y.; Hino, K.; et al. Prospective Randomized Controlled Phase III Trial Comparing the Efficacy of Sorafenib versus Sorafenib in Combination with Low-Dose Cisplatin/Fluorouracil Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy in Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S209–S210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, E.; Tanaka, M.; Yamashita, F.; Kuromatsu, R.; Yutani, S.; Fukumori, K.; Sumie, S.; Yano, Y.; Okuda, K.; Sata, M. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. Cancer 2002, 95, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.-J.; He, M.-K.; Chen, H.-W.; Fang, W.-Q.; Zhou, Y.-M.; Xu, L.; Wei, W.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Guo, Y.; Guo, R.-P.; et al. Hepatic Arterial Infusion of Oxaliplatin, Fluorouracil, and Leucovorin Versus Transarterial Chemoembolization for Large Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Randomized Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.-S.; Hong, T.-C.; Wu, H.-T.; Lin, Y.-J.; Chang, T.-T.; Wang, C.-T.; Liu, W.-C.; Hsieh, M.-T.; Wu, I.-C.; Chen, P.-J.; et al. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors, alone or in combination, in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with macrovascular invasion: A single-centre experience in Taiwan. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2023, 14, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beran, A.; Abuhelwa, Z.; Abdulsattar, W.; Alloghbi, A.; Alqahtani, A.; Hamouda, D.M. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy versus trans-arterial chemoembolization in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, e16141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, T.W.I. Complications of Hepatic Chemoembolization. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2006, 23, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, H.; Yasuda, S.; Shiota, S.; Chatani, S.; Tsukii, R.; Kitagawa, H.; Fukushima, T.; Urasaki, S.; Kumada, T. Safety, feasibility, and comfort of hepatic angiography and transarterial intervention with radial access for hepatocellular carcinoma. JGH Open 2021, 5, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muglia, R.; Marra, P.; Dulcetta, L.; Carbone, F.S.; Bonaffini, P.A.; Sironi, S. US-guided percutaneous thrombin injection to treat non-femoral artery pseudoaneurysms: Preliminary experience and review of the literature. Radiol. Med. 2022, 128, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, E.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, J.-H.; Yoon, H.-K.; Ko, G.-Y.; Sung, K.-B. Arterial dissections during transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: A 19-year clinical experience at a single medical institution. Acta Radiol. 2017, 58, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belli, L.; Magistretti, G.; Puricelli, G.P.; Damiani, G.; Colombo, E.; Cornalba, G.P. Arteritis following intra-arterial chemotherapy for liver tumors. Eur. Radiol. 1997, 7, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naymagon, S.; Warner, R.R.P.; Patel, K.; Harpaz, N.; Machac, J.; Weintraub, J.L.; Kim, M.K. Gastroduodenal Ulceration Associated with Radioembolization for the Treatment of Hepatic Tumors: An Institutional Experience and Review of the Literature. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 2450–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, I.; Aso, N.; Nagaoki, K.; Matsuoka, Y.; Uetani, M.; Ashizawa, K.; Iwanaga, S.; Mori, M.; Morikawa, M.; Fukuda, T.; et al. Complications associated with transcatheter arterial embolization for hepatic tumors. RadioGraphics 1998, 18, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-G.; Cho, S.M.; Whang, K.; Jang, Y.G.; Kim, J.; Choi, J. Spinal Cord Infarction After Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Korean J. Neurotrauma 2022, 18, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Oh, J.S.; Chun, H.J.; Kim, S.H. Incidence and Risk Factors of Acute Ischemic Cholecystitis after Transarterial Chemoembolization: Correlation with Cone Beam CT Findings. J. Korean Soc. Radiol. 2024, 85, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolbrink, D.; Kolwijck, E.; Oever, J.T.; Horvath, K.; Bouwense, S.; Schouten, J. Management of infected pancreatic necrosis in the intensive care unit: A narrative review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagpal, P.; Bhalala, M.; Vidholia, A.; Sao, R.; Sharma, N.; Mehta, D.; McCabe, S.; Bodin, R. Abdominal Skin Rash After TACE Due to Non-Target Embolization of Hepatic Falciform Artery. ACG Case Rep. J. 2016, 3, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsin, I.-F.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Huang, H.-C.; Huang, Y.-H.; Lin, H.-C.; Lee, R.-C.; Chiang, J.-H.; Lee, F.-Y.; Huo, T.-I.; Lee, S.-D. Liver Failure After Transarterial Chemoembolization for Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Ascites. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 45, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, R.; Ding, Y.; Du, L.; Hou, C.; Lu, D.; Hao, L.; Lv, W. Prognostic factors for acute kidney injury following transarterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 2579–2586. [Google Scholar]
- Orlacchio, A.; Guastoni, C.; Beretta, G.D.; Cosmai, L.; Galluzzo, M.; Gori, S.; Grassedonio, E.; Incorvaia, L.; Marcantoni, C.; Netti, G.S.; et al. SIRM-SIN-AIOM: Appropriateness criteria for evaluation and prevention of renal damage in the patient undergoing contrast medium examinations—Consensus statements from Italian College of Radiology (SIRM), Italian College of Nephrology (SIN) and Italian Association of Medical Oncology (AIOM). Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.N.; Hyun, D. Complications Related to Transarterial Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review. Korean J. Radiol. 2023, 24, 204–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, C.M.; Lee, Y.Y.; Kim, S.K.; Jeong, Y.Y.; Heo, S.H.; Shin, S.S. Four-dimensional flow MR imaging for evaluating treatment response after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in cirrhotic patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiol. Med. 2023, 128, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, M.; Degirmencioglu, S. Liver abscesses after transcatheter arterial embolization. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 47, 1124–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, T.; Zhu, P.; Liu, Z.; Ren, Q.; Zheng, C.; Xia, X. Liver abscess after drug-eluting bead chemoembolization in patients with metastatic hepatic tumors. Br. J. Radiol. 2022, 95, 20211056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Hodavance, M.; Ronald, J.; Suhocki, P.V.; Kim, C.Y. Minimal Risk of Biliary Tract Complications, Including Hepatic Abscess, After Transarterial Embolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Concentrated Antibiotics Mixed with Particles. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 41, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh Bhinder, N.; Zangan, S. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Rupture Following Transarterial Chemoembolization. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 32, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sun, J.-H.; Wang, L.-G.; Bao, H.-W.; Lou, J.-L.; Cai, L.-X.; Wu, C.; Chen, L.-M.; Zheng, S.-S. Emergency embolization in the treatment of ruptured hepatocellular carcinoma following transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Hepatogastroenterology 2010, 57, 616–619. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.-L.; Fan, S.-T.; Lo, C.-M.; Tso, W.-K.; Poon, R.T.-P.; Lam, C.-M.; Wong, J. Management of Spontaneous Rupture of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Single-Center Experience. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 3725–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier, A.; Guiu, B.; Duran, R.; Aho, S.; Bize, P.; Deltenre, P.; Dunet, V.; Denys, A. Liver and biliary damages following transarterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison between drug-eluting beads and lipiodol emulsion. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 1431–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, R. Identifying predictors and evaluating the role of steroids in the prevention of post-embolization syndrome after transarterial chemoembolization and bland embolization. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2020, 34, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehlen, N.; Stoehr, F.; Müller, L.; Luxenburger, H.; Gairing, S.J.; Reincke, M.; Schultheiss, M.; Berisha, F.; Weinmann, A.; Foerster, F.; et al. Prediction of postembolization syndrome after transarterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma and its impact on prognosis. Hepatol. Commun. 2023, 7, e0252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, D.A.; Goin, J.E.; Sickles, C.; Raskay, B.J.; Soulen, M.C. Determinants of Postembolization Syndrome after Hepatic Chemoembolization. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2001, 12, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Rmilah, A.; Qrareya, M.N.; Fleming, C.; Alkurashi, A.K.; Nyberg, S.; Leise, M.; Andrews, J.C. Association of Cirrhosis and Other Patient and Procedural Characteristics With Postembolization Syndrome After Bland Hepatic Artery Embolization for Hepatic Malignancy. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2022, 218, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, M.C.; Massarweh, N.N.; Salami, A.; Sultenfuss, M.A.; Anaya, D.A. Post-embolization syndrome as an early predictor of overall survival after transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. HPB 2015, 17, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Seon, J.; Sung, P.S.; Oh, J.S.; Lee, H.L.; Jang, B.; Chun, H.J.; Jang, J.W.; Bae, S.H.; Choi, J.Y.; et al. Dexamethasone Prophylaxis to Alleviate Postembolization Syndrome after Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Study. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 28, 1503–1511.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therasse, P.; Arbuck, S.G.; Eisenhauer, E.A.; Wanders, J.; Kaplan, R.S.; Rubinstein, L.; Verweij, J.; Van Glabbeke, M.; van Oosterom, A.T.; Christian, M.C.; et al. New Guidelines to Evaluate the Response to Treatment in Solid Tumors. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.-T.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Xu, L.; Qu, Q.; Lu, M.-T.; Jiang, J.-F.; Zhao, X.-C.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Zhang, T. A multivariate model based on gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI using Li-RADS v2018 and other imaging features for preoperative prediction of dual-phenotype hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiol. Med. 2023, 128, 1333–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, R.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zheng, B.; Han, J.; Sun, W.; Zeng, M. The significance of the predominant component in combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma: MRI manifestation and prognostic value. Radiol. Med. 2023, 128, 1047–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.K.; Kim, S.U.; Kim, K.A.; Chung, Y.E.; Kim, M.-J.; Park, M.-S.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, M.D.; et al. Complete response at first chemoembolization is still the most robust predictor for favorable outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 1304–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Gu, X.-T.; Huang, X.-L.; Wei, Y.-C.; Chen, L.; Luo, N.-B.; Lin, H.-S.; Jin-Yuan, L. Nomogram based on clinical and preoperative CT features for predicting the early recurrence of combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma: A multicenter study. Radiol. Med. 2023, 128, 1460–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Z.-Y.; Chen, P.-Y.; Lin, J.; Liao, J.-Y. Pre-operative MRI features predict early post-operative recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma with different degrees of pathological differentiation. Radiol. Med. 2023, 128, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Fan, W.; Zhu, B.; Wang, G.; Sun, J.; Xiao, C.; Huang, F.; Tang, R.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, Z.; et al. Lenvatinib Combined With Transarterial Chemoembolization as First-Line Treatment for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Phase III, Randomized Clinical Trial (LAUNCH). J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-X.; Chen, P.; Liu, S.; Zu, Q.-Q.; Shi, H.-B.; Zhou, C.-G. Safety and Efficacy of Transarterial Chemoembolization and Immune Checkpoint Inhibition with Camrelizumab for Treatment of Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2022, ume 9, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Merle, P.; Kudo, M.; Bouattour, M.; Lim, H.Y.; Breder, V.; Edeline, J.; Chao, Y.; Ogasawara, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab As Second-Line Therapy in Patients With Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma in KEYNOTE-240: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Sangro, B.; Yau, T.; Crocenzi, T.S.; Kudo, M.; Hsu, C.; Kim, T.-Y.; Choo, S.-P.; Trojan, J.; Welling, T.H., 3rd; et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): An open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 2492–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lencioni, R.; Kudo, M.; Erinjeri, J.; Qin, S.; Ren, Z.; Chan, S.; Arai, Y.; Heo, J.; Mai, A.; Escobar, J.; et al. EMERALD-1: A phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled study of transarterial chemoembolization combined with durvalumab with or without bevacizumab in participants with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma eligible for embolization. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, LBA432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.-W.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Liang, H.-H.; Lin, X.-J.; Guo, R.-P.; Chen, M.-S. Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Sequential Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization and RF Ablation versus RF Ablation Alone: A Prospective Randomized Trial. Radiology 2012, 262, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iezzi, R. Combined locoregional treatment of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: State of the art. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 1935–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iezzi, R.; Posa, A.; Tanzilli, A.; Carchesio, F.; Pompili, M.; Manfredi, R. Balloon-Occluded MWA (b-MWA) Followed by Balloon-Occluded TACE (b-TACE): Technical Note on a New Combined Single-Step Therapy for Single Large HCC. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 43, 1702–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minici, R.; Siciliano, M.A.; Ammendola, M.; Santoro, R.C.; Barbieri, V.; Ranieri, G.; Laganà, D. Prognostic Role of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR), Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio (LMR), Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR) and Lymphocyte-to-C Reactive Protein Ratio (LCR) in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) undergoing Chemoembolizations (TACE) of the Liver: The Unexplored Corner Linking Tumor Microenvironment, Biomarkers and Interventional Radiology. Cancers 2022, 15, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.-S.; Lin, K.-T. A meta-analysis of the diagnostic test accuracy of CT-based radiomics for the prediction of COVID-19 severity. Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagawa, M.; Ito, R.; Nozaki, T.; Fujioka, T.; Yamada, A.; Fujita, S.; Kamagata, K.; Fushimi, Y.; Tsuboyama, T.; Matsui, Y.; et al. New trend in artificial intelligence-based assistive technology for thoracic imaging. Radiol. Med. 2023, 128, 1236–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.; Laguna, A.; Ikeda, I.; Maxwell, A.W.P.; Chapiro, J.; Nadolski, G.; Jiao, Z.; Bai, H.X. Using Machine Learning to Predict Response to Image-guided Therapies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Radiology 2023, 309, e222891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakaura, T.; Higaki, T.; Awai, K.; Ikeda, O.; Yamashita, Y. A primer for understanding radiology articles about machine learning and deep learning. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2020, 101, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorontsov, E.; Cerny, M.; Régnier, P.; Di Jorio, L.; Pal, C.J.; Lapointe, R.; Vandenbroucke-Menu, F.; Turcotte, S.; Kadoury, S.; Tang, A. Deep Learning for Automated Segmentation of Liver Lesions at CT in Patients with Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2019, 1, 180014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, K.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, M. Radiomics model based on multi-sequence MR images for predicting preoperative immunoscore in rectal cancer. Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartrand, G.; Cheng, P.M.; Vorontsov, E.; Drozdzal, M.; Turcotte, S.; Pal, C.J.; Kadoury, S.; Tang, A. Deep Learning: A Primer for Radiologists. RadioGraphics 2017, 37, 2113–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masci, G.M.; Ciccarelli, F.; Mattei, F.I.; Grasso, D.; Accarpio, F.; Catalano, C.; Laghi, A.; Sammartino, P.; Iafrate, F. Role of CT texture analysis for predicting peritoneal metastases in patients with gastric cancer. Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waller, J.; O’connor, A.; Raafat, E.; Amireh, A.; Dempsey, J.; Martin, C.; Umair, M. Applications and challenges of artificial intelligence in diagnostic and interventional radiology. Pol. J. Radiol. 2022, 87, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Robertis, R.; Geraci, L.; Tomaiuolo, L.; Bortoli, L.; Beleù, A.; Malleo, G.; D’onofrio, M. Liver metastases in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A predictive model based on CT texture analysis. Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 1079–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’amore, B.; Smolinski-Zhao, S.; Daye, D.; Uppot, R.N. Role of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in Interventional Oncology. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 23, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letzen, B.; Wang, C.J.; Chapiro, J. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Interventional Oncology: A Primer. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 30, 38–41.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiti, G.; Grazzini, G.; Flammia, F.; Matteuzzi, B.; Tortoli, P.; Bettarini, S.; Pasqualini, E.; Granata, V.; Busoni, S.; Messserini, L.; et al. Gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms (GEP-NENs): A radiomic model to predict tumor grade. Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 928–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autorino, R.; Gui, B.; Panza, G.; Boldrini, L.; Cusumano, D.; Russo, L.; Nardangeli, A.; Persiani, S.; Campitelli, M.; Ferrandina, G.; et al. Radiomics-based prediction of two-year clinical outcome in locally advanced cervical cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Zhang, P.; Ma, X.; He, B.; Fang, C.; Jia, F. Radiomic Feature-Based Predictive Model for Microvascular Invasion in Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda Magalhaes Santos, J.M.; Clemente Oliveira, B.; Araujo-Filho, J.d.A.B.; Assuncao, A.N., Jr.; de MMachado, F.A.; Carlos Tavares Rocha, C.; Horvat, J.V.; Menezes, M.R.; Horvat, N. State-of-the-art in radiomics of hepatocellular carcinoma: A review of basic principles, applications, and limitations. Abdom. Imaging 2019, 45, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, S.; Botta, F.; Raimondi, S.; Origgi, D.; Fanciullo, C.; Morganti, A.G.; Bellomi, M. Radiomics: The facts and the challenges of image analysis. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2018, 2, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, D.; Bicci, E.; Cavigli, E.; Danti, G.; Bettarini, S.; Tortoli, P.; Mazzoni, L.N.; Busoni, S.; Pradella, S.; Miele, V. Radiomics in pulmonary neuroendocrine tumours (NETs). Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, B.; Durmaz, E.S.; Ates, E.; Kilickesmez, O. Radiomics with artificial intelligence: A practical guide for beginners. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 25, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, V.; Fusco, R.; De Muzio, F.; Cutolo, C.; Setola, S.V.; Dell’aversana, F.; Grassi, F.; Belli, A.; Silvestro, L.; Ottaiano, A.; et al. Radiomics and machine learning analysis based on magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of liver mucinous colorectal metastases. Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spieler, B.; Sabottke, C.; Moawad, A.W.; Gabr, A.M.; Bashir, M.R.; Do, R.K.G.; Yaghmai, V.; Rozenberg, R.; Gerena, M.; Yacoub, J.; et al. Artificial intelligence in assessment of hepatocellular carcinoma treatment response. Abdom. Imaging 2021, 46, 3660–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palatresi, D.; Fedeli, F.; Danti, G.; Pasqualini, E.; Castiglione, F.; Messerini, L.; Massi, D.; Bettarini, S.; Tortoli, P.; Busoni, S.; et al. Correlation of CT radiomic features for GISTs with pathological classification and molecular subtypes: Preliminary and monocentric experience. Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Bian, S.; Zhu, D.; Yuan, Y.; Pan, K.; Pan, Z.; Feng, X.; Tang, K.; Yang, Y. Machine learning-based radiomics for multiple primary prostate cancer biological characteristics prediction with 18F-PSMA-1007 PET: Comparison among different volume segmentation thresholds. Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 1170–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Griethuysen, J.J.M.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Fillion-Robin, J.-C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Mamidipalli, A.; Retson, T.; Bahrami, N.; Hasenstab, K.; Blansit, K.; Bass, E.; Delgado, T.; Cunha, G.; Middleton, M.S.; et al. Automated CT and MRI Liver Segmentation and Biometry Using a Generalized Convolutional Neural Network. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2019, 1, 180022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Sohaib, S.; Turner, B.; A Hanson, J.; Farquharson, M.; Oliver, R.T.; Reznek, R.H. CT assessment of tumour response to treatment: Comparison of linear, cross-sectional and volumetric measures of tumour size. Br. J. Radiol. 2000, 73, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, D.; Polici, M.; Rinzivillo, M.; Zerunian, M.; Nacci, I.; Marasco, M.; Magi, L.; Tarallo, M.; Gargiulo, S.; Iannicelli, E.; et al. CT-based radiomics for prediction of therapeutic response to Everolimus in metastatic neuroendocrine tumors. Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, S.; Song, K.D.; Chung, J.W. Basics of Deep Learning: A Radiologist’s Guide to Understanding Published Radiology Articles on Deep Learning. Korean J. Radiol. 2020, 21, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Yu, N.; Yu, Y.; He, T.; Duan, X. Performance of CT radiomics in predicting the overall survival of patients with stage III clear cell renal carcinoma after radical nephrectomy. Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.J.; Kim, H.; Min, H.; Sohn, A.; Cho, Y.Y.; Yoo, J.-J.; Lee, D.H.; Cho, E.J.; Lee, J.-H.; Gim, J.; et al. Targeted Proteomics Predicts a Sustained Complete-Response after Transarterial Chemoembolization and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 1239–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshid, A.; Elsayes, K.M.; Khalaf, A.M.; Elmohr, M.M.; Yu, J.; Kaseb, A.O.; Hassan, M.; Mahvash, A.; Wang, Z.; Hazle, J.D.; et al. A Machine Learning Model to Predict Hepatocellular Carcinoma Response to Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2019, 1, e180021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Kang, S.; Ning, Z.; Deng, H.; Shen, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, W.; Li, X.; Gong, W.; et al. Residual convolutional neural network for predicting response of transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma from CT imaging. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 30, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Jiang, H.; Feng, S.-T.; Xia, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, S.; Wang, D.; Zeng, X.; Chen, Y.; Xin, Y.; et al. Noninvasive Imaging Evaluation Based on Computed Tomography of the Efficacy of Initial Transarterial Chemoembolization to Predict Outcome in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2022, ume 9, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Chen, Q.; Guo, D.; Jiang, C. Preoperative estimation of the survival of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma achieving complete response after conventional transcatheter arterial chemoembolization: Assessments of clinical and LI-RADS MR features. Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacher, V.; Lin, M.; Duran, R.; Yarmohammadi, H.; Lee, H.; Chapiro, J.; Chao, M.; Wang, Z.; Frangakis, C.; Sohn, J.H.; et al. Comparison of Existing Response Criteria in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Transarterial Chemoembolization Using a 3D Quantitative Approach. Radiology 2016, 278, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Chen, J.; Wei, Y.; Cao, L.; Ye, Z.; Li, X.; Ma, L.; Song, B. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Radiomics nomogram on gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging for early postoperative recurrence prediction. Cancer Imaging 2019, 19, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, S.; Yamana, H.; Akahane, M.; Kishimoto, M.; Nishioka, Y.; Noda, T.; Matsui, H.; Fushimi, K.; Yasunaga, H.; Kasahara, K.; et al. Association between prophylactic antibiotic use for transarterial chemoembolization and occurrence of liver abscess: A retrospective cohort study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 1514.e5–1514.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fobbe, F.; Boese-Landgraf, J. TACE for HCC: A critical review of the 2021 CIRSE recommendations with presentation of a technique for a degradable starch microsphere—TACE. Liver Cancer Int. 2023, 4, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, P.; Young, S.; Golzarian, J. Current Trends in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Transarterial Embolization: Variability in Technical Aspects. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 42, 1322–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsey, E.; Lee, H.M. Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in 2024: The Multidisciplinary Paradigm in an Evolving Treatment Landscape. Cancers 2024, 16, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, T.; Kirkwood, A.; Roughton, M.; Beare, S.; Tsochatzis, E.; Yu, D.; Davies, N.; Williams, E.; Pereira, S.P.; Hochhauser, D.; et al. A randomised phase II/III trial of 3-weekly cisplatin-based sequential transarterial chemoembolisation vs embolisation alone for hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Gao, J.; Zhuang, W.; Wu, Z.; Li, B.; Chen, S. Efficacy and safety of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy combined with transarterial embolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A propensity score-matching cohort study. JGH Open 2020, 4, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Zheng, Q.; Sun, P. Embolization alone is as effective as TACE for unresectable HCC: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trails. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024, 24, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsanos, K.; Kitrou, P.; Spiliopoulos, S.; Maroulis, I.; Petsas, T.; Karnabatidis, D. Comparative effectiveness of different transarterial embolization therapies alone or in combination with local ablative or adjuvant systemic treatments for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| TACE | Type of Particles | Chemotherapeutic Dosage | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cTACE | Chemotherapeutic agent mixed with iodized oil (Lipiodol) | 50–75 mg of Doxorubicin Max 150 mg per single treatment | -Embolization of small occult tumor feeders -Cheap -Intra- and post-procedural visualization of Lipiodol particles | -Variable response rate -Systemic symptoms usually require pre-medications |
| DSM-TACE | Degradable starch microsphere (Embocept) | Doxorubicin at a dose of 50 mg/m2 adjusted for body surface | -Administration in lobar fashion -Feasible in patients with PVT, Child–Pugh score 8–9, ineligible for other locoregional or systemic treatments -Lower liver toxicity -Temporary embolic effect | Requires at least two procedures |
| DEM-TACE | DC Bead, HepaSphere, TANDEM, DC Bead LUMI, etc. | 50–75 mg of Doxorubicin Max 150 mg per single treatment | -Wide choice of particle types and sizes -Chemotherapeutic release sustained for a longer period -Stronger embolizing effect | -Not feasible in patient with PVT or high Child–Pugh score -Requires microsphere preparation (>40 min) |
| b-TACE | Could be combined with different types of particles | 50–75 mg of Doxorubicin Max 150 mg per single treatment | -Anti-reflux system -Increased chemotherapeutic dosage accumulation in the nodule -Could be combined with different particles and techniques | -Arterial vessel diameter ≤ 4 mm Longer procedural time -Higher risk of vessel wall damage -High cost of the micro-balloon catheter |
| HAIC | No use of particles | Depends on chosen chemotherapy protocol | -PVT not a contraindication -Better outcome for HCC nodules > 5 cm | Requires multiple procedures or arterial port-a-cath implantation |
| c-TACE | Doxorubicin dose: 30–75 mg/m2, up to 150 mg. Mixed with 5–20 mL Lipiodol. |
| DEM-TACE | -Limited Disease: 50–75 mg Doxorubicin loaded into 2 mL DC Beads (1 vial). -Advanced Disease: Up to 150 mg Doxorubicin loaded into 2 vials. |
| DSM-TACE | -Slow injection of the first 4 mL of EmboCept (450 mg/7.5 mL) mixed with 6 mL of non-ionic contrast medium and 50 mg/m2 of Doxorubicin diluted in 5–10 mL of saline solution -Residual 3.5 mL of EmboCept, added with an equivalent volume of contrast medium until flow stasis is reached. |
| Reference | Type of Study | Key Results |
|---|---|---|
| Irie T, Kuramochi M, Takahashi N (2013) [67] | Observational study | Balloon-occluded transarterial chemoembolization (b-TACE) improved Lipiodol accumulation, enhancing tumor targeting efficacy. |
| Chu HH, Gwon D IL, Kim GH, et al. (2022) [72] | Observational study (propensity score) | b-TACE showed better local tumor control and fewer complications compared to conventional TACE for single hepatocellular carcinoma. |
| Lucatelli P, De Rubeis G, Trobiani C, et al. (2022) [75] | Retrospective cohort study | b-TACE demonstrated improved response rates compared to DEB-TACE, particularly in patients undergoing micro-balloon interventions. |
| Irie T, Kuramochi M, Kamoshida T, Takahashi N (2016) [77] | Observational study | b-TACE showed improved outcomes for small hepatocellular carcinoma compared to conventional TACE, with higher overall response rates. |
| Wiggermann P, Heibl M, Niessen C, et al. (2012) [80] | Observational study | DSM-TACE evaluated using DCE-US demonstrated good tumor response and promising efficacy for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment. |
| Schicho A, Hellerbrand C, Krüger K, et al. (2016) [81] | Observational study | Different embolic agents used in TACE procedures were associated with varied systemic VEGF level changes, influencing tumor angiogenesis. |
| Brown KT, Do RK, Gonen M, et al. (2016) [89] | Randomized controlled trial | Doxorubicin-eluting microspheres showed similar efficacy but better safety compared to bland embolization in hepatocellular carcinoma. |
| Kloeckner R, Weinmann A, Prinz F, et al. (2015) [90] | Observational study | Drug-eluting bead TACE (DEB-TACE) showed better local disease control compared to conventional TACE in hepatocellular carcinoma. |
| Lammer J, Malagari K, Vogl T, et al. (2010) [97] | Randomized controlled trial | DEB-TACE was effective in treating hepatocellular carcinoma with reduced systemic toxicity compared to conventional TACE. |
| Golfieri R, Giampalma E, Renzulli M, et al. (2014) [98] | Randomized controlled trial | DEB-TACE achieved comparable tumor response to conventional TACE but offered better tolerability and fewer adverse events. |
| Yang B, Liang J, Qu ZY, et al. (2020) [99] | Systematic review | Reviewed various transarterial strategies, concluding that DEB-TACE was safer and more effective than conventional TACE in many cases. |
| Liu K, Zheng X, Lu D, et al. (2023) [100] | Observational study | DEB-TACE combined with molecular targeted agents improved survival rates and treatment efficacy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. |
| Ikeda M, Shimizu S, Sato T, et al. (2016) [103] | Randomized phase II trial | Sorafenib combined with Cisplatin infusion improved progression-free survival compared to Sorafenib alone in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. |
| Kudo M, Ueshima K, Yokosuka O, et al. (2016) [113] | Randomized controlled trial | Sorafenib combined with low-dose Cisplatin infusion showed no significant survival benefit compared to Sorafenib alone but had higher treatment-related adverse events. |
| Wang et al., 2020 [55] | Observational Study | DEB-TACE showed advantages over conventional TACE in terms of efficacy and patient outcomes. |
| Orlacchio et al., 2020 [85] | Prospective Cohort Study | DSM-TACE demonstrated promising long-term results for unresectable HCC patients. |
| Orlacchio et al., 2018 [86] | Prospective Pilot Study | Repeated DSM-TACE was safe and effective for unresectable HCC patients. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lanza, C.; Ascenti, V.; Amato, G.V.; Pellegrino, G.; Triggiani, S.; Tintori, J.; Intrieri, C.; Angileri, S.A.; Biondetti, P.; Carriero, S.; et al. All You Need to Know About TACE: A Comprehensive Review of Indications, Techniques, Efficacy, Limits, and Technical Advancement. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020314
Lanza C, Ascenti V, Amato GV, Pellegrino G, Triggiani S, Tintori J, Intrieri C, Angileri SA, Biondetti P, Carriero S, et al. All You Need to Know About TACE: A Comprehensive Review of Indications, Techniques, Efficacy, Limits, and Technical Advancement. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(2):314. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020314
Chicago/Turabian StyleLanza, Carolina, Velio Ascenti, Gaetano Valerio Amato, Giuseppe Pellegrino, Sonia Triggiani, Jacopo Tintori, Cristina Intrieri, Salvatore Alessio Angileri, Pierpaolo Biondetti, Serena Carriero, and et al. 2025. "All You Need to Know About TACE: A Comprehensive Review of Indications, Techniques, Efficacy, Limits, and Technical Advancement" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 2: 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020314
APA StyleLanza, C., Ascenti, V., Amato, G. V., Pellegrino, G., Triggiani, S., Tintori, J., Intrieri, C., Angileri, S. A., Biondetti, P., Carriero, S., Torcia, P., Ierardi, A. M., & Carrafiello, G. (2025). All You Need to Know About TACE: A Comprehensive Review of Indications, Techniques, Efficacy, Limits, and Technical Advancement. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(2), 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020314






